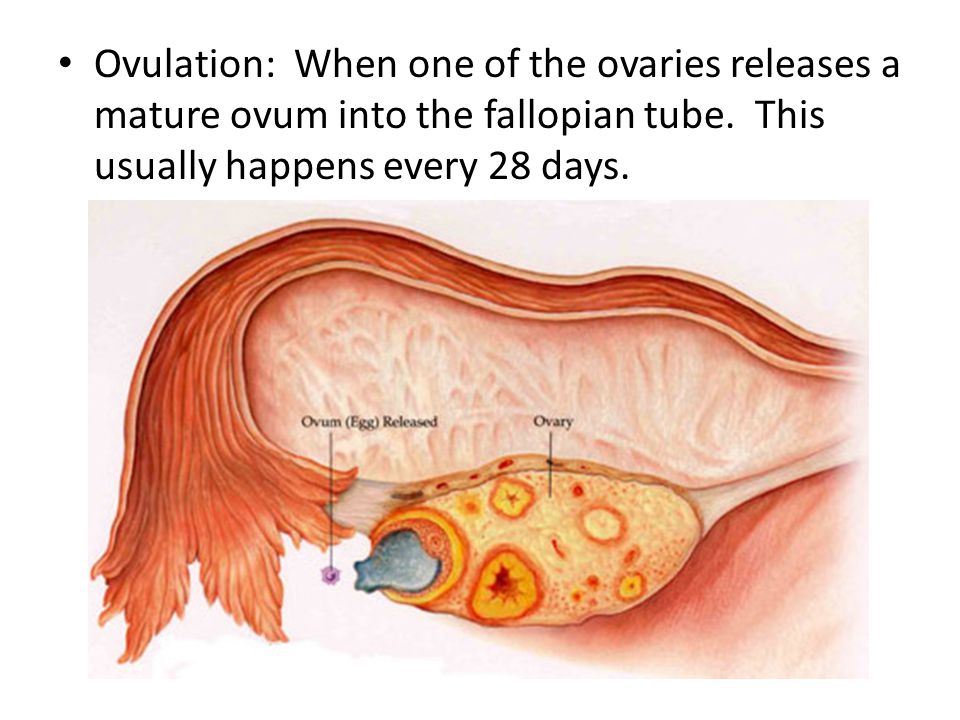
How long can an egg be fertilized after ovulation
Conception: How It Works | Patient Education
To become pregnant, the following steps must occur:
- Sperm transport — The sperm must be deposited and transported to the site of fertilization.
- Egg transport — Ovulation must occur and the egg must be "picked up" by the tube.
- Fertilization and embryo development — Union between the sperm and egg must result.
- Implantation — The embryo must implant and begin to grow in the uterus.
These steps are described below.
Sperm Transport
The transport of sperm depends on several factors:
- The sperm must be capable of propelling themselves through the environment of the female vagina and cervix.
- This environment, which is under cyclic hormonal control, must be favorable to admit the sperm without destroying them.
- The sperm must possess the capability of converting to a form that can penetrate the cell membrane of the egg (capacitation).
Following ejaculation, the semen forms a gel that protects it from the acidic environment of the vagina. The gel is liquefied within 20 to 30 minutes by enzymes from the prostate gland. This liquefaction is important for freeing the sperm so transportation may occur. The seminal plasma is left in the vagina.
The protected sperm with the greatest motility travel through the layers of cervical mucus that guard the entrance to the uterus. During ovulation, this barrier becomes thinner and changes its acidity, creating a friendlier environment for the sperm. The cervical mucus acts as a reservoir for extended sperm survival.
Once the sperm have entered the uterus, contractions propel the sperm upward into the fallopian tubes. The first sperm enter the tubes minutes after ejaculation. The first sperm, however, are likely not the fertilizing sperm. Motile sperm can survive in the female reproductive tract for up to five days.
Egg Transport
Egg transport begins at ovulation and ends once the egg reaches the uterus. Following ovulation, the fimbriated, or finger-like, end of the fallopian tube sweeps over the ovary. Adhesive sites on the cilia, which are located on the surface of the fimbriae, are responsible for egg pickup and movement into the tube. The cilia within the tube, and muscular contractions resulting from the movement of the egg, create a forward motion. Transport through the tube takes about 30 hours.
Following ovulation, the fimbriated, or finger-like, end of the fallopian tube sweeps over the ovary. Adhesive sites on the cilia, which are located on the surface of the fimbriae, are responsible for egg pickup and movement into the tube. The cilia within the tube, and muscular contractions resulting from the movement of the egg, create a forward motion. Transport through the tube takes about 30 hours.
Conditions such as pelvic infections and endometriosis can permanently impair the function of the fallopian tubes, due to scarring or damage to the fimbriae.
Fertilization and Embryo Development
Following ovulation, the egg is capable of fertilization for only 12 to 24 hours. Contact between the egg and sperm is random.
Once the egg arrives at a specific portion of the tube, called the ampullar-isthmic junction, it rests for another 30 hours. Fertilization — sperm union with the egg — occurs in this portion of the tube. The fertilized egg then begins a rapid descent to the uterus.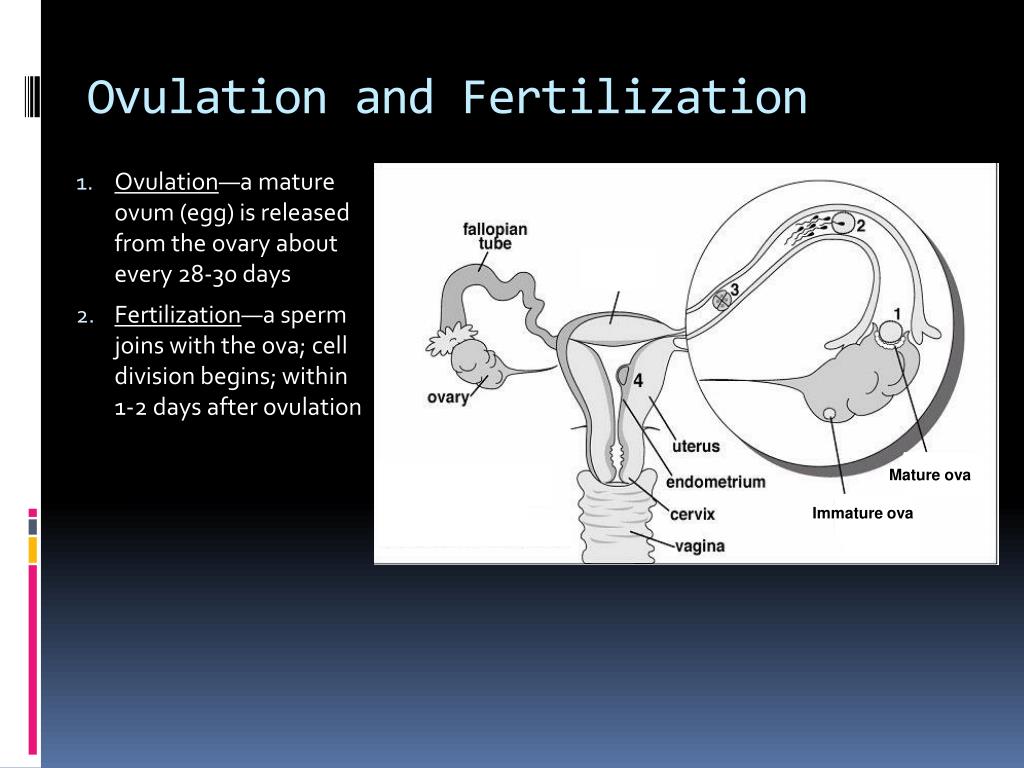 The period of rest in the tube appears to be necessary for full development of the fertilized egg and for the uterus to prepare to receive the egg.
The period of rest in the tube appears to be necessary for full development of the fertilized egg and for the uterus to prepare to receive the egg.
Defects in the fallopian tube may impair transport and increase the risk of a tubal pregnancy, also called ectopic pregnancy.
A membrane surrounding the egg, called the zona pellucida, has two major functions in fertilization. First, the zona pellucida contains sperm receptors that are specific for human sperm. Second, once penetrated by the sperm, the membrane becomes impermeable to penetration by other sperm.
Following penetration, a series of events set the stage for the first cell division. The single-cell embryo is called a zygote. Over the course of the next seven days, the human embryo undergoes multiple cell divisions in a process called mitosis. At the end of this transition period, the embryo becomes a mass of very organized cells, called a blastocyst. It's now believed that as women get older, this process of early embryo development is increasingly impaired due to diminishing egg quality.
Implantation
Once the embryo reaches the blastocyst stage, approximately five to six days after fertilization, it hatches out of its zona pellucida and begins the process of implantation in the uterus.
In nature, 50 percent of all fertilized eggs are lost before a woman's missed menses. In the in vitro fertilization (IVF) process as well, an embryo may begin to develop but not make it to the blastocyst stage — the first stage at which those cells destined to become the fetus separate from those that will become the placenta. The blastocyst may implant but not grow, or the blastocyst may grow but stop developing before the two week time at which a pregnancy can be detected. The receptivity of the uterus and the health of the embryo are important for the implantation process.
How many days after ovulation can you get pregnant?
It is possible to become pregnant after ovulation. When a person has sex within 12–24 hours after the release of a mature egg, there is a high chance of conceiving.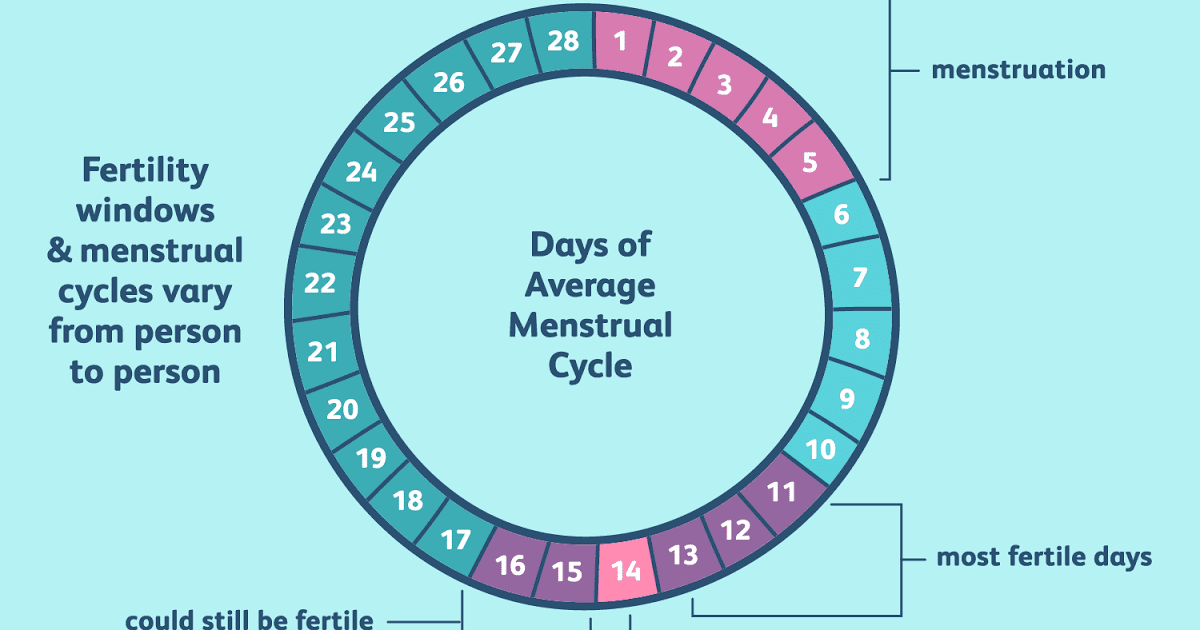
Ovulation occurs when one of the ovaries releases a mature egg. This is the time when the body is ready to receive sperm for fertilization.
If fertilization does not occur, the egg disintegrates into the uterine lining. The body will then shed the remains during a person’s monthly period.
Ovulation lasts anywhere from 12–24 hours. After the ovary releases an egg, it survives for about 24 hours before it dies, unless a sperm fertilizes it.
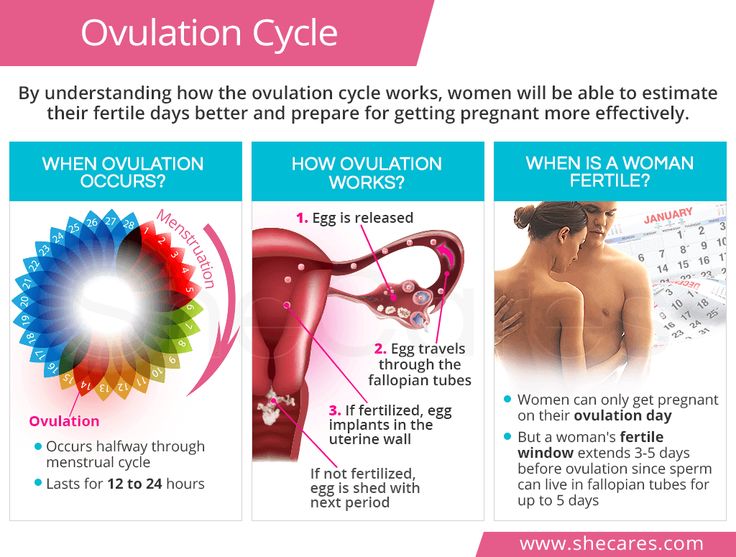
If a person has sex days before or during the ovulation period, there is a high chance of conceiving. This is because sperm can survive up to 5 days in the cervix. Therefore, it is important to understand the fertile window.
The fertile window is the period of time during which it is possible to become pregnant from sex. This is the day of ovulation plus the amount of time that sperm can live inside the cervix before it fertilizes the egg.
According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), a person can become pregnant if they have sex anywhere from 5 days before until 1 day after ovulation.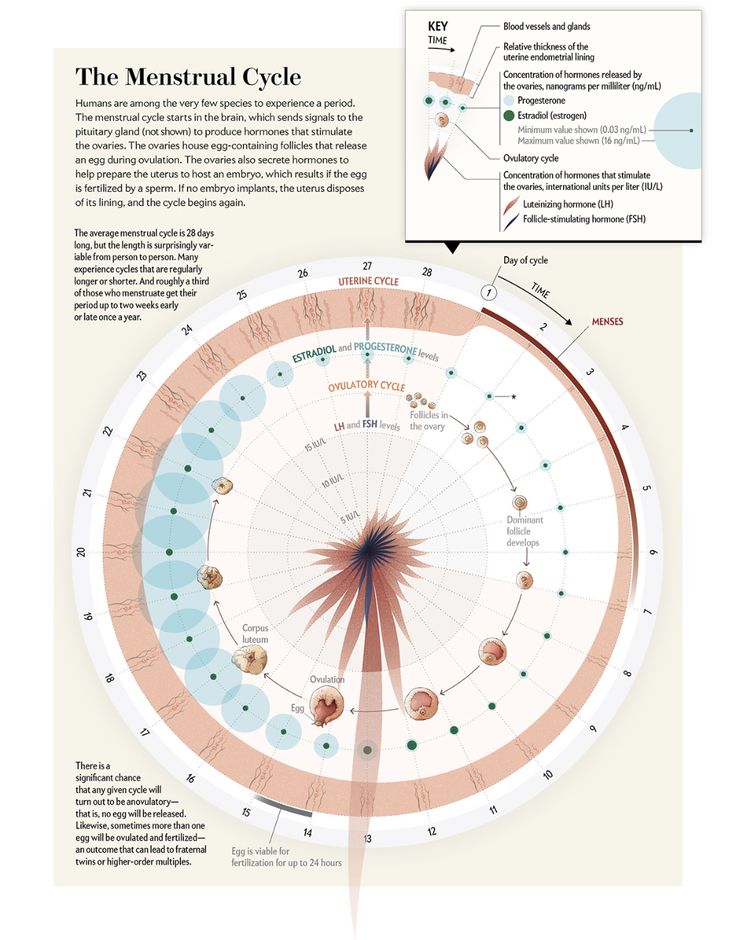
Depending on the menstrual cycle, the fertile window may vary from one person to another.
To calculate the fertility window, a person should note the first day of a period until the next period occurs. This timeframe is the menstrual cycle. On average, most people who menstruate have a 28-day cycle.
However, according to the Office on Women’s Health, for some, it may last 21–35 days.
According to the ACOG, ovulation occurs around day 14 of the menstrual cycle.
A person with a 28-day cycle, for example, will have their fertile window 5 days before the ovulation date.
Pregnancy is possible 12–24 hours after ovulation. This is because the released egg can only survive 24 hours before the sperm can no longer fertilize it.
The likelihood of getting pregnant on the days before and after ovulation varies from one person to another.
An older study from 1995 looked at the timing of sexual intercourse in relation to ovulation and the likelihood of conception.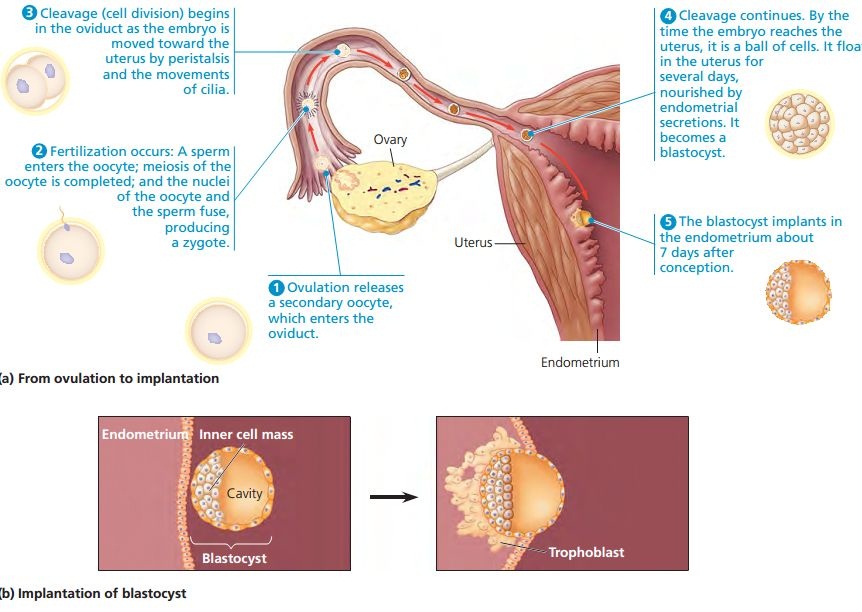
Out of 221 healthy women, there were 192 pregnancies. Researchers concluded they could estimate the odds of becoming pregnant on each day of the fertile window as between 10–33%, depending on the day.
| 5 days before ovulation | 10% |
| 4 days before ovulation | 16% |
| 3 days before ovulation | 14% |
| 2 days before ovulation | 27% |
| 1 day before ovulation | 31% |
| Ovulation day | 33% |
The same study authors also note there could be a 12% chance of conceiving on either day 7 before ovulation and the day after ovulation.
However, the chances of becoming pregnant before or after ovulation depend on several factors, including:
- age
- frequency of sexual intercourse
- menstrual cycle
For those trying to conceive, tracking ovulation is crucial to ensure they identify the most fertile days in the menstrual cycle.
Here are some of the methods a person can use to track or predict ovulation.
Basal body temperature charting
Basal body temperature (BBT) is the temperature when the body is at rest.
Charting BBT for a series of months by measuring every morning after waking up will help predict ovulation.
During or when ovulation approaches, there is a slight increase in BBT. A person can use a digital thermometer to track these small changes in temperature.
Monitoring BBT can help tell when ovulation occurs and therefore predict the days in the cycle when pregnancy is possible.
Ovulation predictor kits
Using ovulation predictor kits, such as test strips and digital tests, will help measure the level of luteinizing hormone (LH), which usually rises during ovulation.
A person needs to take tests for consecutive days to detect the rise in LH.
Once they notice a consistent rise, experts recommend having sex daily for the next couple of days to increase the chances of pregnancy.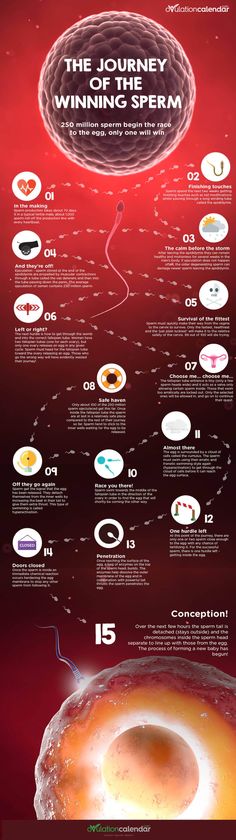
Cycle charting apps
Several cycle apps, such as the Clue period tracker and Flo period ovulation tracker, can help calculate the ovulation period and fertile window.
Charting ovulation using these apps will indicate the ovulation date and days when a person’s body is most fertile.
Fertility monitors
For people trying to conceive or wishing to avoid pregnancy, using fertility monitors to track ovulation can help people plan intercourse.
Fertility monitors work by measuring significant body changes, such as BBT, heart rate, and breathing.
By compiling this data, the fertility monitor can predict the fertile window.
Cervical mucus method
Observing cervical mucus can give an idea of when a person may be ovulating.
When ovulation approaches, the cervical mucus changes to a thin, clear, stringy, slippery consistency. It may look similar to raw egg whites.
The mucus allows the sperm to swim to the released egg during intercourse.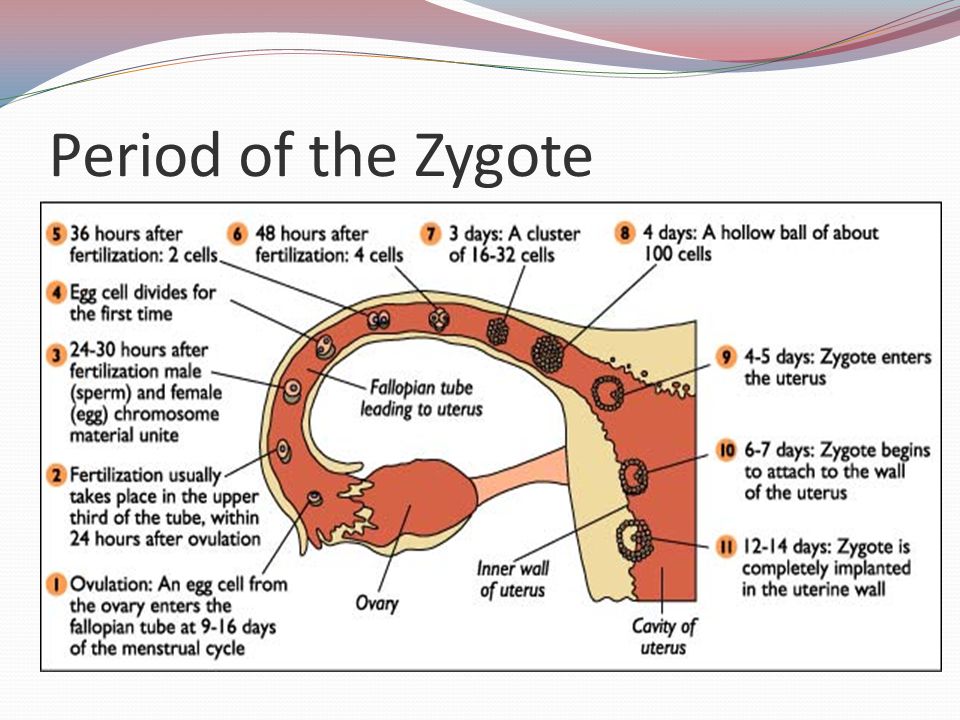
Ideally, this is the ideal time to have sex due to the high chances of becoming pregnant.
Watching ovulation signs, such as a slight increase in BBT, changes in cervical mucus, and increased sex drive, can help determine the best time to have sex to boost chances of becoming pregnant.
In addition, having sex during the fertile window increases the chances of conception. During this timeframe, the body is ready to receive sperm for fertilization.
On average, a menstrual cycle lasts between 21–35 days.
An irregular cycle or absent cycle that lasts fewer than 21 days or more than 35 days, can mean that a person is not ovulating.
A person should speak with a doctor if they do not become pregnant after 1 year of trying to conceive.
Age may also determine when to seek help. People between 35–40 years of age should speak with a doctor after 6 months of trying to get pregnant. For those above 40 years of age, a healthcare professional may run some fertility tests.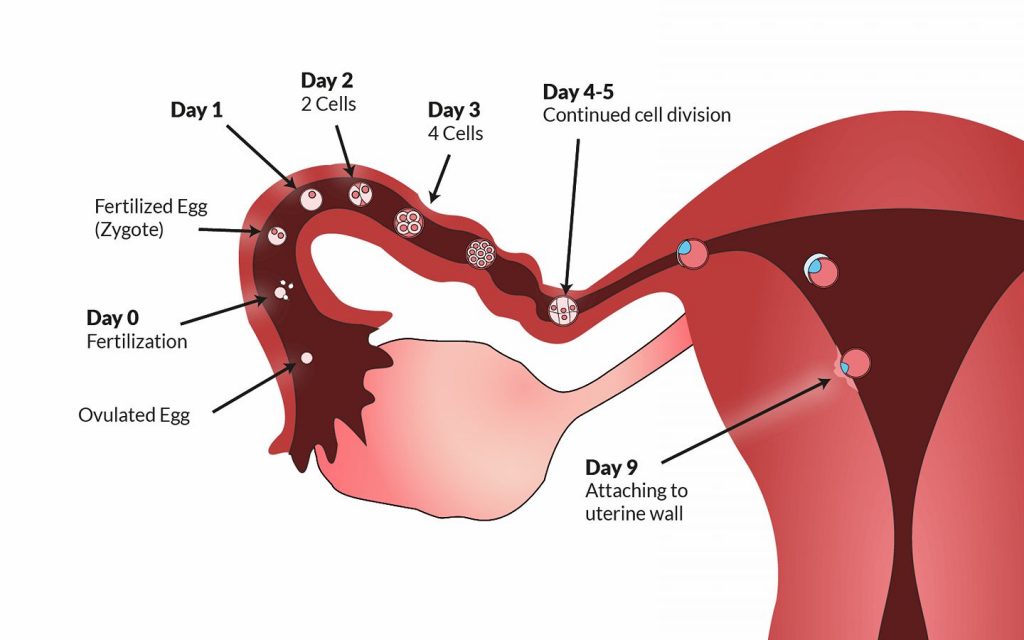
A doctor may also test for possible signs of infertility or if a person has ever had repeated miscarriages, pelvic inflammatory disease, endometriosis, prior cancer treatment, or a history of irregular periods.
A person can get pregnant 12–24 hours after ovulation, as a released egg can survive up to 24 hours within the cervix.
For those trying to conceive, it is crucial to understand the menstrual cycle.
Beyond this, a person can use methods, such as BBT charting, cycle charting apps, fertility monitors, changes in cervical mucus, and ovulation predictor kits to boost the chances of pregnancy.
Ovulation and pregnancy | Huggies® Official Website
PreviousNext
- How does ovulation and fertilization occur?
- When does pregnancy occur? Right after ovulation?
- So how do you calculate ovulation?
- What should be the sensations after ovulation?
- When will signs of pregnancy appear after ovulation and conception?
- Why did not conception occur after ovulation?
Contents:
Ovulation is a special event. It means that a woman has begun a period in which she can give a new life. How to calculate the date of ovulation? What are the best days for getting pregnant? How long after ovulation does conception occur? We answer the questions of expectant mothers.
It means that a woman has begun a period in which she can give a new life. How to calculate the date of ovulation? What are the best days for getting pregnant? How long after ovulation does conception occur? We answer the questions of expectant mothers.
How does ovulation and fertilization occur?
In the first phase of the menstrual cycle, follicle maturation begins in one of the ovaries. This small vesicle consists of an ovum enclosed in a "shell" of connective tissue. The follicle grows from 1 mm to 12–16 mm 1 and then bursts, releasing the egg into the fallopian tube. This moment is called ovulation.
What happens after ovulation? The egg becomes available for fertilization. For this to happen, there must be enough sperm in the fallopian tube. Contrary to popular belief, the winner will not be the most agile of them all. The ovum is surrounded by a special membrane called the "radiant crown" 2 (sounds very nice, doesn't it?).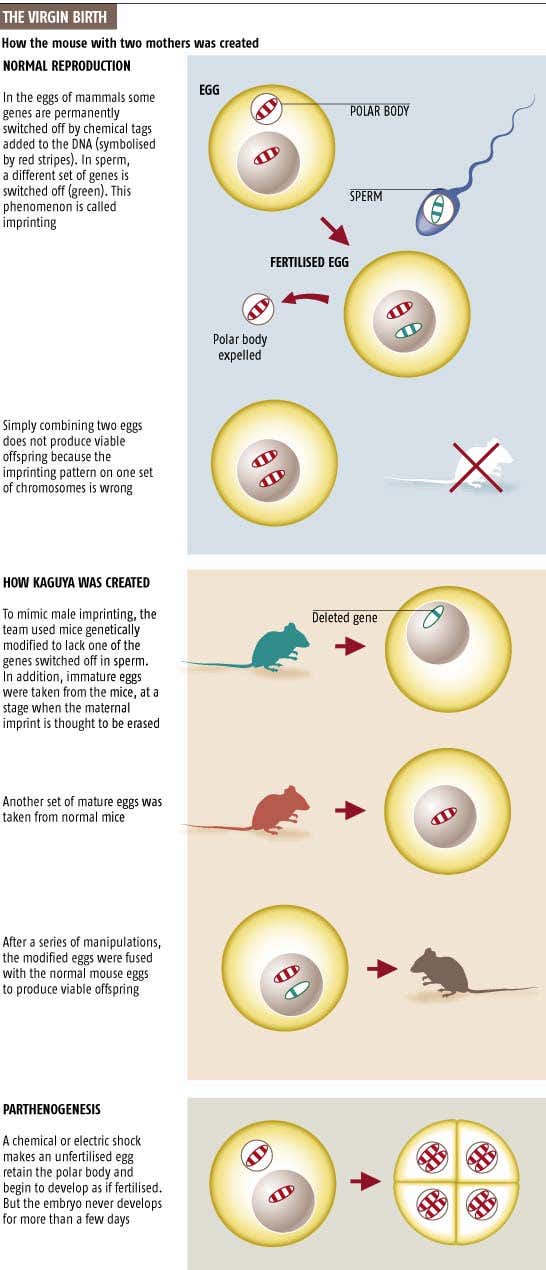 First, many fighters will die trying to destroy the protective shell, and only then one lucky one will get inside and fertilize the egg.
First, many fighters will die trying to destroy the protective shell, and only then one lucky one will get inside and fertilize the egg.
When does pregnancy occur? Right after ovulation?
The period in which a woman can become pregnant does not last very long: the egg cell lives only about 24 hours 3 . This gives us the answer to the question of how long after ovulation conception occurs - at any point in this short period. In particular, fertilization can happen almost immediately if the spermatozoa made their way into the fallopian tube even before the egg is released from the follicle.
Some women report that they did not become pregnant on the day of ovulation, but earlier or later. This is impossible in principle, and they are wrong - it's just that the actual date of this event may not coincide with the calculated one. It is normal if ovulation happened a day or two earlier or later than the plan, and under certain conditions (hormonal changes, stress, and others), it can go beyond this. More details in this article.
More details in this article.
So how do you calculate ovulation?
Pregnancy begins after ovulation and fertilization of the egg by sperm. It's up to the small thing - to understand when this important event will happen. Take a calendar and look at our drawing. With it, you can calculate the approximate date of ovulation. But remember, this is just a prediction, and that's why we've drawn high, medium, and low pregnancy probability areas around the central day.
Do not try to get pregnant exactly at ovulation. It is better to cover the entire period of high probability with a “queue”. Start having sex for pregnancy 4 days before the planned date and do it every other day: 4th day before, 2nd day before, day of ovulation, 2nd day after, 4th day after. This will greatly increase your chances of success.
Approximate menstrual cycle schedule. Calculations are given for cycles with a duration of 25 to 31 days.
The ideal menstrual cycle is 28 days.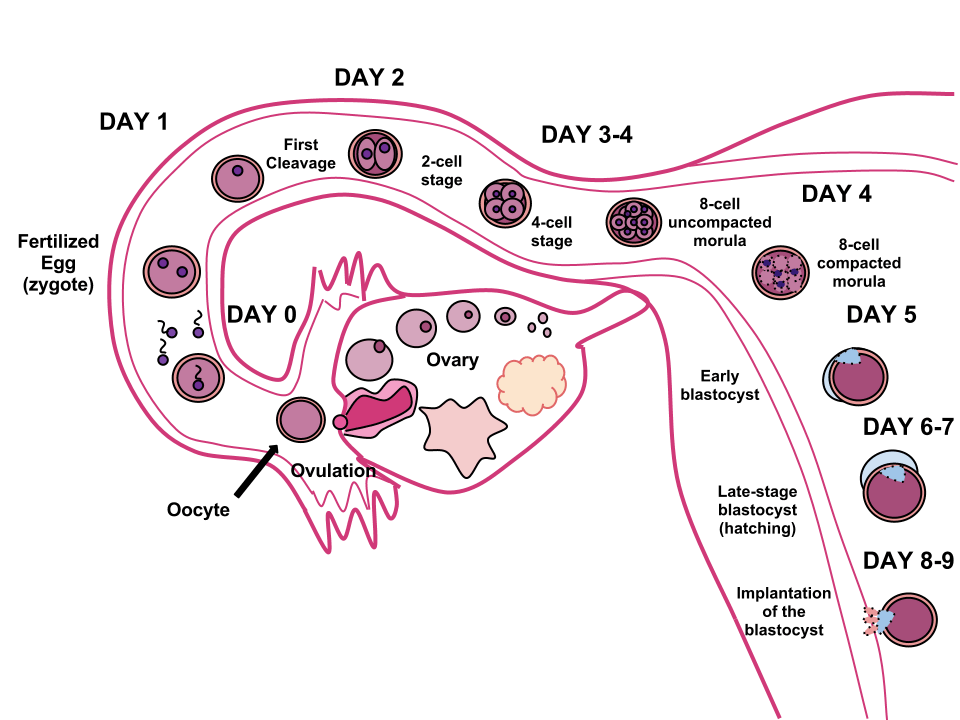 In many articles on conception and ovulation, all the reasoning is built around this textbook case. Indeed, it is very convenient - ovulation in it occurs on the 14th day, dividing the cycle into two equal halves. Life is different from the ideal: the duration of the cycle for different women varies, but usually ranges from 25 to 31 days 4 .
In many articles on conception and ovulation, all the reasoning is built around this textbook case. Indeed, it is very convenient - ovulation in it occurs on the 14th day, dividing the cycle into two equal halves. Life is different from the ideal: the duration of the cycle for different women varies, but usually ranges from 25 to 31 days 4 .
Most likely, you will find your case in this figure, but if your cycle is shorter or longer, there is nothing strange in this - the duration is from 21 to 35 days 5 . The following knowledge will help calculate the day of ovulation: with a change in the length of the cycle, its first part usually decreases or grows, while the second remains unchanged and is always about two weeks. Set aside 14 days back from the planned first day of menstruation - get the approximate day of ovulation.
There are many more signs of ovulation that you can check out in this article.
In terms of conception, the menstrual cycle can be divided into the following phases (shown in the figure):
-
Menstruation.
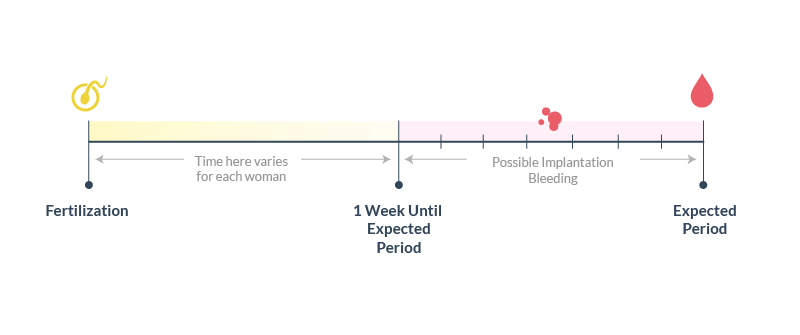 Sex during this period can only lead to conception under very unusual circumstances. For now, relax - auspicious days ahead.
Sex during this period can only lead to conception under very unusual circumstances. For now, relax - auspicious days ahead. -
From the end of menstruation to the 6th day to the planned ovulation. The probability of conception at this time is minimal. Most likely, the egg has not only not left the ovary, but has not even matured yet.
-
5 to 3 days before estimated ovulation date. The chance of getting pregnant increases, and there are two reasons for this. Firstly, the real day of ovulation does not always coincide with the calculated one. Secondly, spermatozoa know how to wait. Most of them will die in the vagina within a couple of hours - its acidic environment fights well not only with bacteria. However, those that can penetrate the uterus are able to live up to three, sometimes up to five days 6 .
-
Planned day of ovulation plus or minus two days. During this period, a woman is most fertile. Given the lifespan of the egg and sperm, sex these days is highly likely to lead to pregnancy.
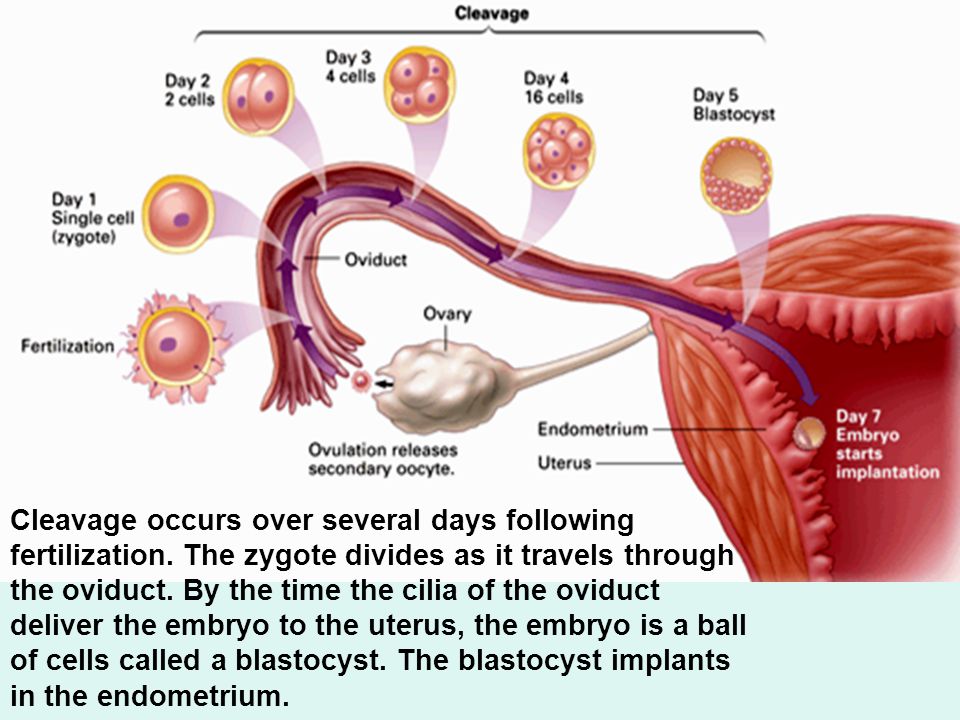 Of course, if there are no factors that can interfere with this.
Of course, if there are no factors that can interfere with this. -
3 to 4 days after estimated ovulation date. The chance of getting pregnant is decreasing, but still remains. Do you remember that calculating the day of ovulation is not a very exact science? So anything is possible.
-
From the 5th day after the planned ovulation until the end of the cycle. Do not seriously expect that you will be able to conceive these days, have sex just for fun. If you have tried to get pregnant on your fertile days, you may have already conceived!
What should be the feeling after ovulation?
During the menstrual cycle, there is only one period in which a woman feels the changes taking place in her body. This is menstruation itself, and the sensations from it are very familiar to you. All other phases of the cycle are "asymptomatic".
The answer to the question of how to understand that ovulation was successful is prosaic: no way. The woman's body simply does not have a mechanism that would tell the brain about it. So, if you woke up with the certainty that today is that very day, these are just mind games that frolicked in a dream with the thought you desired about the joy of motherhood. Although, coincidences also happen :)
The woman's body simply does not have a mechanism that would tell the brain about it. So, if you woke up with the certainty that today is that very day, these are just mind games that frolicked in a dream with the thought you desired about the joy of motherhood. Although, coincidences also happen :)
When will signs of pregnancy appear after ovulation and conception?
Reliable - not soon. A regular pregnancy test will show two cherished strips only after a delay, a test with increased sensitivity or laboratory analysis - 3-4 days earlier. The final confirmation with the help of ultrasound will have to wait another couple of weeks.
Do not expect pregnancy symptoms immediately after ovulation. While the fertilized egg slowly gets from the fallopian tube to its destination, almost no changes occur in the body. The first signs of pregnancy will appear only 6-10 days after ovulation, when the embryo attaches to the wall of the uterus 7 . And they will be almost invisible:
-
Change in basal body temperature.
 If you have been measuring your basal temperature all this time, you will notice a slight drop on the chart, and then a rise to a new, higher level.
If you have been measuring your basal temperature all this time, you will notice a slight drop on the chart, and then a rise to a new, higher level. -
Implantation bleeding. In the process of attaching the embryo to the wall of the uterus, the endometrium is damaged - its inner mucosa. In this case, the expectant mother may notice slight spotting.
-
Pain or cramps in the lower abdomen. Along with bleeding, mild pain may come. Therefore, women often attribute these first signs of pregnancy to early menstruation.
Why did not conception occur after ovulation?
You tried to get pregnant, but your next period started right on time. Why did it happen? Only your doctor can accurately answer this question, but we will list some likely causes.
-
Anovulatory cycle. Some menstrual cycles do not ovulate and this is perfectly normal 8 . They are called anovulatory and are needed by the body so that it can take a little break from the constant preparation for pregnancy.
 During the year, a woman experiences 1-2 anovulatory cycles.
During the year, a woman experiences 1-2 anovulatory cycles. -
Gynecological diseases. Sometimes conception after ovulation does not occur because the woman has gynecological diseases. Inflammation of the ovaries, blockage of the fallopian tubes, and some other conditions can significantly reduce the likelihood of pregnancy, and under certain conditions, even make conception impossible. A gynecologist can identify such diseases and prescribe treatment.
-
Immune or autoimmune reactions. Spermatozoa are very unusual cells. They contain only half of the chromosome set, and from the point of view of the immune system, they look like mutants. Everything is so bad that nature even had to collect them in special refrigerated bags and hang them outside the man's body. In some cases, the immune mechanisms of a woman can deal with spermatozoa at the time of passage of the cervix 9 . Autoimmune reactions also occur when a man's body destroys them.
 If the doctor considers that this may be the reason for unsuccessful attempts at conception, he will prescribe tests for both the expectant mother and the future dad.
If the doctor considers that this may be the reason for unsuccessful attempts at conception, he will prescribe tests for both the expectant mother and the future dad. -
Poor semen quality. After intercourse, spermatozoa will have to overcome the champion's obstacle course - survive in the aggressive environment of the vagina, break through the cervical mucus in the cervix, get to the right fallopian tube, destroy the protection of the egg. If the spermatozoa of the future dad are not very active, they can go the distance before conception. To exclude this cause, it is necessary to make a spermogram.
When conception occurs after ovulation, future parents take it for granted. If pregnancy does not occur, they often begin to panic and think with horror that they will never hear ringing children's laughter and light steps of tiny legs in their house. Drive unconstructive thoughts away - many couples were able to conceive far from the first time. Try again next month. We believe you will definitely succeed!
We believe you will definitely succeed!
Links to sources:
-
Ovaries: follicles, growth and development disorders.
-
Pansky, Ben (1982), "Chapter 12: Fertilization", Review of MEDICAL EMBRYOLOGY.
-
Depares J, Ryder RE, Walker SM, Scanlon MF, Norman CM (1986). Ovarian ultrasonography highlights precision of symptoms of ovulation as markers of ovulation. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 292 (6535): 1562.
-
Chiazze L, Brayer FT, Macisco JJ, Parker MP, Duffy BJ (February 1968). "The length and variability of the human menstrual cycle". JAMA. 203(6): 377–80.
-
"Menstruation and the menstrual cycle fact sheet". Office of Women's Health, USA. December 23, 2014.
-
Clubb E.
 Natural methods of family planning. JR Soc Health. 1986 Aug;106(4):121-6.
Natural methods of family planning. JR Soc Health. 1986 Aug;106(4):121-6. -
Wilcox AJ, Baird DD, Weinberg CR (1999). "Time of implantation of the Conceptus and loss of pregnancy". New England Journal of Medicine. 340(23): 1796–1799.
-
Anovulatory Cycle: Symptoms and Detection.
-
What Are Antisperm Antibodies?
Follow us on Yandex Zen
1-4 weeks of pregnancy
From a tiny fetus to a small person, a child's body develops in just 9 months. What changes are happening to the expectant mother and what changes are observed inside her during this difficult and joyful period of life?
Each new life begins with the union of the egg and sperm. Conception is the process by which a sperm enters an egg and fertilizes it.
It should be noted that the fetal and obstetric periods are different.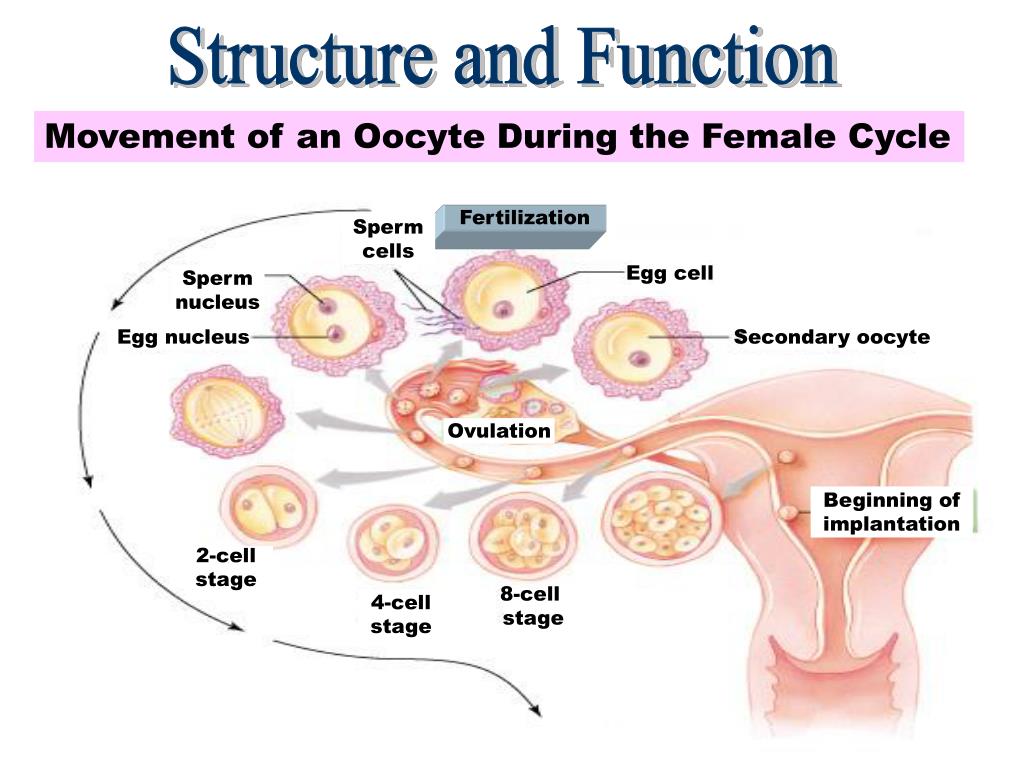 The thing is that among specialists it is customary to consider the period from the first day of the last menstruation, that is, the obstetric period includes the period of preparation for pregnancy. So it turns out that the embryo has just appeared, and the gestation period is already two weeks. It is the obstetric period that is indicated in all the documents of a woman and is the only reporting period for specialists.
The thing is that among specialists it is customary to consider the period from the first day of the last menstruation, that is, the obstetric period includes the period of preparation for pregnancy. So it turns out that the embryo has just appeared, and the gestation period is already two weeks. It is the obstetric period that is indicated in all the documents of a woman and is the only reporting period for specialists.
Before the meeting, the spermatozoon and the ovum lived for a certain time, being in the stage of development and maturation. The development of the future fetus significantly depends on the quality of these processes.
First week
Growth and maturation of the egg starts from the first day of the cycle. A mature egg contains 23 chromosomes as the genetic material for the future embryo, and also contains all the nutrients necessary to start its development. It contains reserves of carbohydrates, proteins and fats, designed to support the embryo during the first days after its occurrence.
A certain number of eggs are laid in each ovary of a girl before she is born. During the childbearing period, they only grow and develop, the process of their formation does not occur. By the time a girl is born, the number of cells from which eggs can develop in the future reaches a million, but this number decreases significantly over the course of life. So, by the time of puberty, there are several hundred thousand of them, and by maturity - about 500.
The ovary each month gives the opportunity to develop most often one egg, the maturation of which occurs inside a fluid-filled vesicle called a follicle. From the first day of the cycle, the uterine mucosa begins to prepare for a possible pregnancy. For implantation, i.e., the introduction of the resulting embryo into the wall of the uterus, an optimal environment is created. To do this, due to the influence of hormones, the endometrium thickens, it becomes covered with a network of vessels and accumulates the nutrients necessary for the future embryo.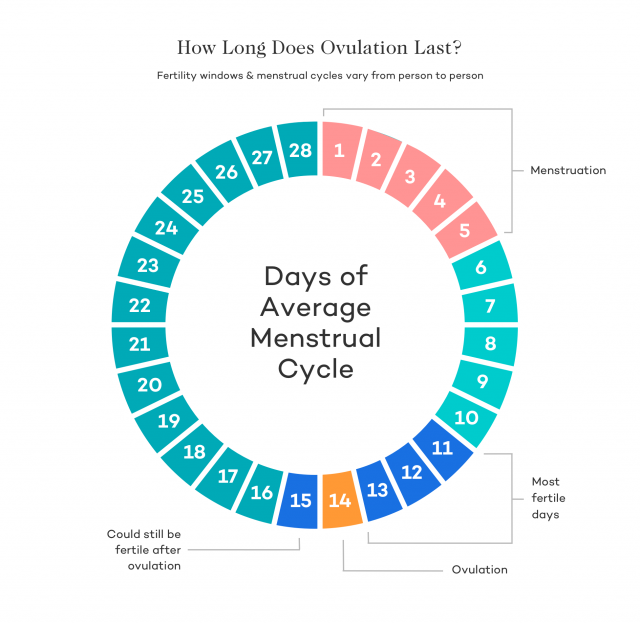
Male reproductive cells are formed in the gonads - in the testicles or testes. The maturation of spermatozoa occurs in the epididymis, into which they move after formation. The liquid structure of semen is formed due to the secretion of the seminal vesicles and the prostate gland. A liquid medium is necessary for storing mature spermatozoa and creating favorable conditions for their life.
The number of spermatozoa is quite large: tens of millions in one milliliter. Despite such a significant number, only one of them will be able to fertilize the egg. In spermatozoa, there is exclusively genetic material - 23 chromosomes, which are necessary for the appearance of the embryo.
Spermatozoa are characterized by high motility. Once in the female genital tract, they begin their movement towards the egg. Only half an hour or an hour passes from the moment of ejaculation, when sperm enter the uterine cavity. It takes one and a half to two hours for spermatozoa to penetrate into the widest part, which is called the ampulla. Most spermatozoa die on the way to the egg, meeting the folds of the endometrium, getting into the vaginal environment, cervical mucus.
Most spermatozoa die on the way to the egg, meeting the folds of the endometrium, getting into the vaginal environment, cervical mucus.
Second week
In the middle of the cycle, the egg fully matures and leaves the ovary. It enters the abdominal cavity. This process is called ovulation. With a regular cycle of 30 days, ovulation occurs on the fifteenth. The egg is unable to move on its own. When she leaves the follicle, the fimbriae of the fallopian tube ensure her penetration inside. The fallopian tubes are characterized by longitudinal folding, they are filled with mucus. The muscular movements of the tubes have a wave-like character, which, with a significant number of cilia, creates optimal conditions for transporting the egg.
Through the tubes, the egg enters the widest part of them, which is called the ampulla. This is where fertilization takes place. If there is no meeting with the sperm, the egg dies, and the female body receives the appropriate signal to start a new cycle. There is a rejection of the mucous membrane, which was created by the uterus. The manifestation of such rejection is bloody discharge, which is called menstruation.
There is a rejection of the mucous membrane, which was created by the uterus. The manifestation of such rejection is bloody discharge, which is called menstruation.
The waiting time for fertilization by the egg is short. On average, it takes no more than a day. Fertilization is likely on the day of ovulation and maximum on the next. Sperm have a longer lifespan, averaging three to five days, in some cases seven. Accordingly, if a spermatozoon enters the female genital tract before ovulation, there is a possibility that it will be able to wait for the appearance of an egg.
When an egg is in a state of waiting for fertilization, certain substances are released that are designed to detect it. If spermatozoa find an egg, they begin to secrete special enzymes that can loosen its shell. As soon as one of the spermatozoa penetrates the egg, the others can no longer do this due to the restoration of the density of its shell. Thus, one egg can only be fertilized by one sperm.
After fertilization, the chromosome sets of the parents merge - 23 chromosomes from each.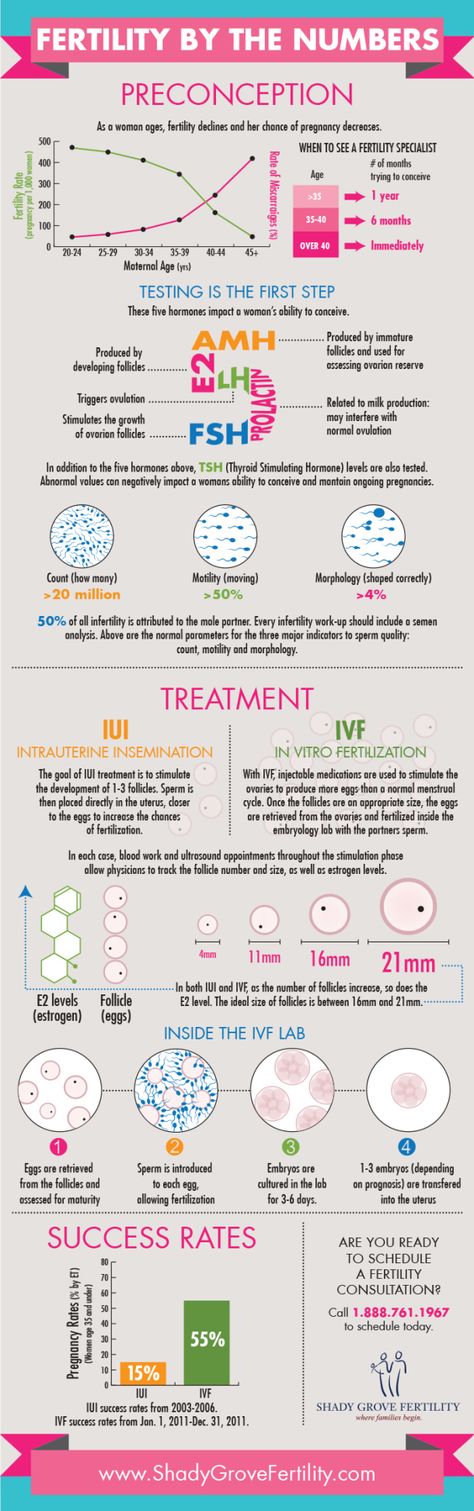 As a result, one cell is formed from two different cells, which is called a zygote. The sex of the unborn child depends on which of the chromosomes, X or Y, was in the sperm. Eggs contain only X chromosomes. When XX is combined, girls are born. If the spermatozoon contains a Y chromosome, that is, with a combination of XY, boys are born. As soon as a zygote is formed in the body, a mechanism is launched in it aimed at maintaining pregnancy. There are changes in the hormonal background, biochemical reactions, immune mechanisms, and the receipt of nerve signals. The female body creates all the necessary conditions for the safe development of the fetus.
As a result, one cell is formed from two different cells, which is called a zygote. The sex of the unborn child depends on which of the chromosomes, X or Y, was in the sperm. Eggs contain only X chromosomes. When XX is combined, girls are born. If the spermatozoon contains a Y chromosome, that is, with a combination of XY, boys are born. As soon as a zygote is formed in the body, a mechanism is launched in it aimed at maintaining pregnancy. There are changes in the hormonal background, biochemical reactions, immune mechanisms, and the receipt of nerve signals. The female body creates all the necessary conditions for the safe development of the fetus.
Third week
As soon as a day has passed after the formation of the embryo, he will need to make his first journey. The movements of the cilia and the contraction of the muscles of the tube direct it into the uterine cavity. During this process, inside the egg, fragmentation into identical cells occurs.
After four days, the appearance of the egg changes: it loses its round shape and becomes vine-shaped.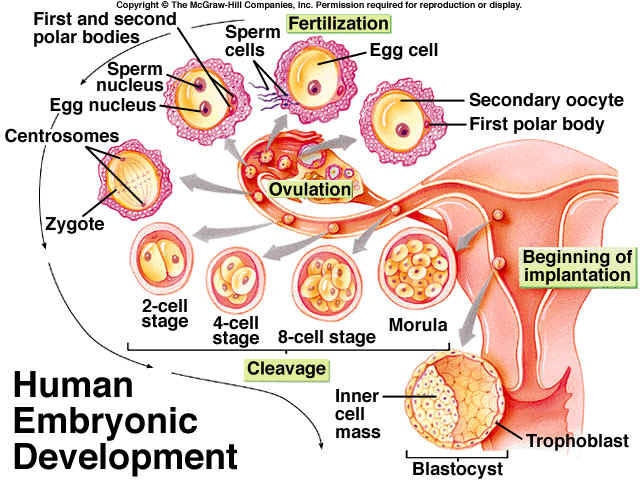 This stage is called morula, embryogenesis begins - an important stage in the development of the embryo, during which the formation of the rudiments of organs and tissues occurs. Cleavage of cells continues for several days, on the fifth day their complexes are formed, which have different functions. The central cluster forms directly the embryo, the outer one, called the trophoblast, is designed to melt the endometrium - the inner layer of the uterus.
This stage is called morula, embryogenesis begins - an important stage in the development of the embryo, during which the formation of the rudiments of organs and tissues occurs. Cleavage of cells continues for several days, on the fifth day their complexes are formed, which have different functions. The central cluster forms directly the embryo, the outer one, called the trophoblast, is designed to melt the endometrium - the inner layer of the uterus.
It takes 5-7 days for the embryo to reach the uterus. When implantation occurs in its mucous membrane, the number of cells reaches one hundred. The term implantation refers to the process of implantation of the embryo into the endometrial layer.
Implantation takes place on the seventh or eighth day after fertilization. The first critical period of pregnancy is this stage, since the embryo will have to demonstrate its viability for the first time.
During implantation, the outer cells of the embryo actively divide, and the process itself takes about forty hours. The number of cells outside the embryo increases dramatically, they stretch, they penetrate into the uterine mucosa, and the thinnest blood vessels are formed inside, which are necessary for the supply of nutrients to the embryo. Time will pass, and these vessels will be transformed first into the chorion, and subsequently into the placenta, which will be able to supply the fetus with everything necessary until the baby is born.
The number of cells outside the embryo increases dramatically, they stretch, they penetrate into the uterine mucosa, and the thinnest blood vessels are formed inside, which are necessary for the supply of nutrients to the embryo. Time will pass, and these vessels will be transformed first into the chorion, and subsequently into the placenta, which will be able to supply the fetus with everything necessary until the baby is born.
The embryo at this stage of life is called a blastocyst. It contacts with the endometrium, melts the cells of the endometrium with its activity, creates a path for itself to the deeper layers. The blood vessels of the embryo intertwine with the mother's body, which allows it to immediately begin to extract useful and necessary substances for development. This is vital, because by this time the stock that the mature egg carried in itself is exhausted.
Next, the production of the trophoblast cells, i.e., the outer cells of human chorionic gonadotropin, the hCG hormone, begins. The distribution of this hormone throughout the body notifies it of the onset of pregnancy, which causes the launch of active hormonal changes and the beginning of corresponding changes in the body.
The distribution of this hormone throughout the body notifies it of the onset of pregnancy, which causes the launch of active hormonal changes and the beginning of corresponding changes in the body.
After fertilization and before the start of hCG, it usually takes eight or nine days. Therefore, already from the tenth day after fertilization, it becomes possible to determine this hormone in the mother's blood. Such an analysis is the most reliable confirmation of the onset of pregnancy. The tests that are offered today to determine pregnancy are based on the detection of this hormone in the urine of a woman. After the first day of delayed menstruation with its regular cycle, it is already possible to determine pregnancy using a test on your own.
What happens to a woman in the third week of pregnancy
If a woman is planning a pregnancy, 21-24 days, subject to a regular cycle, should become important for her. This is a period of possible implantation, when you should pay special attention to your own lifestyle. During this period, thermal effects and excessive physical exertion are undesirable, and the influence of various kinds of radiation should also be prevented.
During this period, thermal effects and excessive physical exertion are undesirable, and the influence of various kinds of radiation should also be prevented.
The woman does not feel anything at this stage, because implantation has no external signs. If you adjust your lifestyle in accordance with the simple rules listed above, you will be able to create optimal conditions for successful implantation.
Fourth week
In the fourth obstetric week or the second week of the fetus's life, its body consists of two layers. Endoblast - cells of the inner layer - will become the beginning of the digestive and respiratory systems, ectoblast - cells of the outer layer - will start the development of the nervous system and skin.
The size of the embryo at this stage is 1.5 mm. The flat arrangement of the cells determined the name of the embryo of this age - the disc.
The fourth week is characterized by intensive development of extra-embryonic organs. Such organs should surround the embryo and create the most favorable conditions for its development.