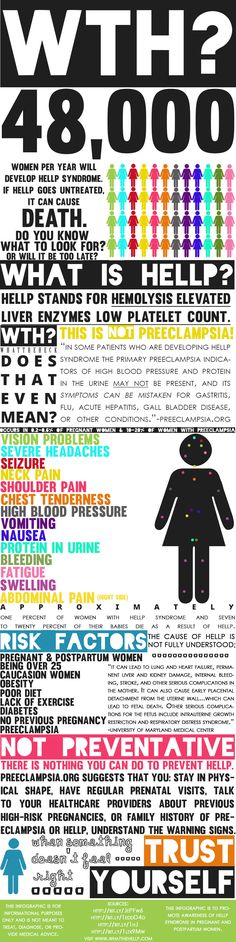
How long after a missed miscarriage do you bleed
Miscarriage - What happens - NHS
If there's no pregnancy tissue left in your womb, no treatment is required.
However, if there's still some pregnancy tissue in your womb, your options are:
- expectant management – wait for the tissue to pass out of your womb naturally
- medical management – take medicine that causes the tissue to pass out of your womb
- surgical management – have the tissue surgically removed
The risk of complications is very small for all these options. It's important to discuss them all with the doctor in charge of your care.
Expectant management
If you have a miscarriage in your first trimester, you may choose to wait 7 to 14 days after a miscarriage for the tissue to pass out naturally. This is called expectant management.
If the pain and bleeding have lessened or stopped completely during this time, this usually means the miscarriage has finished. You should be advised to take a home pregnancy test after 3 weeks.
If the test shows you're still pregnant, you may need to have further tests.
If the pain and bleeding have not started within 7 to 14 days or are continuing or getting worse, this could mean the miscarriage has not begun or has not finished. In this case, you should be offered another scan.
After this scan, you may decide to either continue waiting for the miscarriage to occur naturally, or have drug treatment or surgery. If you choose to continue to wait, your healthcare professional should check your condition again up to 14 days later.
Contact your hospital immediately if the bleeding becomes particularly heavy, you develop a high temperature (fever) or you experience severe pain.
Medicine
You may choose to have medicine to remove the tissue if you do not want to wait, or if it does not pass out naturally within 2 weeks. This involves taking tablets that cause the cervix to open, allowing the tissue to pass out.
In most cases, you'll be offered tablets called pessaries that are inserted directly into your vagina, where they dissolve.
The tablets usually begin to work within a few hours. You'll experience symptoms similar to a heavy period, such as cramping and heavy vaginal bleeding. You may also experience vaginal bleeding for up to 3 weeks.
In most units, you'll be sent home for the miscarriage to complete. This is safe, but ring your hospital if the bleeding becomes very heavy.
You should be advised to take a home pregnancy test 3 weeks after taking this medicine. If the pregnancy test shows you're still pregnant, you may need to have further tests.
If the pregnancy test shows you're still pregnant, you may need to have further tests.
You may be advised to contact your healthcare professional to discuss your options if bleeding has not started within 24 hours of taking the medicine.
Surgery
In some cases, surgery is used to remove any remaining pregnancy tissue. You may be advised to have immediate surgery if:
- you experience continuous heavy bleeding
- there's evidence the pregnancy tissue has become infected
- medicine or waiting for the tissue to pass out naturally has been unsuccessful
Surgery involves removing any remaining tissue in your womb with a suction device. You should be offered a choice of general anaesthetic or local anaesthetic if both are suitable.
After a miscarriage
A miscarriage can be very upsetting, and you and your partner may need counselling or support. You may also have questions about trying for another baby and what happens to the miscarried foetus.
You may also have questions about trying for another baby and what happens to the miscarried foetus.
For more information, read what happens after a miscarriage.
Page last reviewed: 09 March 2022
Next review due: 09 March 2025
What Does a Miscarriage Look Like? Bleeding, Duration, and More
A miscarriage is a spontaneous pregnancy loss before 20 weeks of gestation. Some 8 to 20 percent known pregnancies end in miscarriage, with the majority happening before the 12th week.
The signs and symptoms of miscarriage vary from person to person. Symptoms may also vary depending on how far along you are. For example, a fetus at 14 weeks will be much larger than a fetus at 5 weeks of gestation, so there may be more bleeding and tissue loss with a later miscarriage.
Miscarriage symptoms may include:
- spotting or bleeding from the vagina
- abdominal cramping or pain in the lower back
- passage of tissue, fluid, or other products from the vagina
Read on to learn more about identifying a miscarriage and what to do if you suspect you’re experiencing one.
Bleeding may start as light spotting, or it could be heavier and appear as a gush of blood. As the cervix dilates to empty, the bleeding becomes heavier.
The heaviest bleeding is generally over within three to five hours from the time heavy bleeding begins. Lighter bleeding may stop and start over one to two weeks before it completely ends.
The color of the blood can range from pink to red to brown. Red blood is fresh blood that leaves the body quickly. Brown blood, on the other hand, is blood that’s been in the uterus a while. You may see discharge the color of coffee grounds, or near black, during a miscarriage.
Exactly how much bleeding you’ll experience depends on a variety of circumstances, including how far along you are and whether or not your miscarriage is progressing naturally.
While you may see a lot of blood, let your doctor know if you fill more than two sanitary pads an hour for two or more hours in a row.
What does a missed miscarriage look like?
You may not experience bleeding or other symptoms with a miscarriage, at least at first.
A missed miscarriage, also referred to as a missed abortion, happens when the fetus has died but the products of conception remain in the uterus. This type of miscarriage is usually diagnosed via ultrasound.
Just as with the amount of blood you’ll see, the duration of a miscarriage will vary from person to person and even from pregnancy to pregnancy.
In many cases, a miscarriage will take around two weeks to pass naturally. Your doctor may prescribe the medication misoprostol (Cytotec) to help a miscarriage pass more quickly. Bleeding may start within two days of beginning the medication. For others, it may take up to two weeks.
Once the miscarriage has started, the tissue and heaviest bleeding should be passed in about three to five hours. After the fetus has passed, you may still experience spotting and mild tissue loss for one to two weeks.
It may be difficult to tell a very early miscarriage from a late period. In fact, many miscarriages happen before a person even knows they’re pregnant.
In general, a miscarriage will cause more intense symptoms than a menstrual period. For example:
- Your menstrual flow may be relatively similar from month to month with heavy days and light days. A miscarriage can also have heavy and light days, but bleeding may be especially heavy at times and last longer than you’re used to.
- Bleeding from a miscarriage may also contain large clots and tissue you don’t normally see during your period.
- Cramps can be a part of your normal monthly cycle, but with a miscarriage, they may be particularly painful as the cervix dilates.
- The color of blood during your period can range from pink to red to brown. If you see a color you’re not used to seeing, it may be a sign of miscarriage.
Always contact your doctor if you’re pregnant and experience bleeding. While a miscarriage can’t be stopped once it starts, you doctor can run tests to help determine if you’re experiencing the loss of your pregnancy or something else.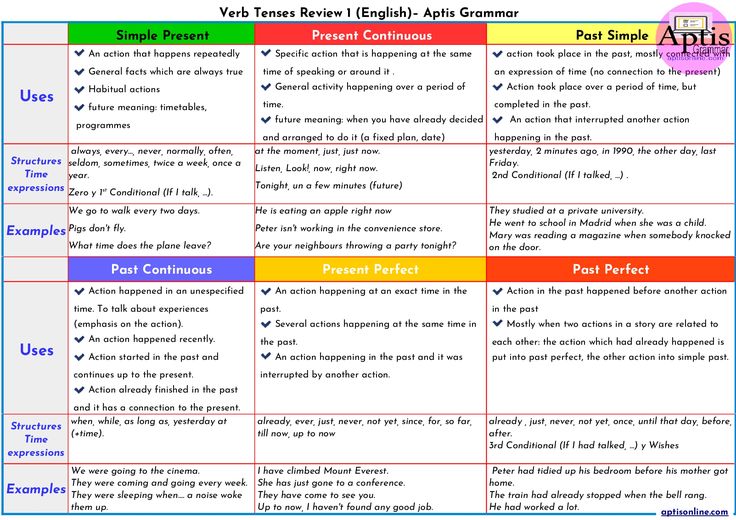
To diagnose a miscarriage, your doctor will likely perform an ultrasound to look for the baby’s heartbeat, if you’re far enough along to see a heartbeat. Your doctor may also order a blood test to check human chorionic gonadotropin (hcG) levels to see if they’re rising or falling.
If a miscarriage is confirmed, your doctor may suggest “expectant management” or waiting for the miscarriage to pass naturally. This generally happens within two weeks.
Incomplete miscarriage
The miscarriage may be incomplete if:
- your bleeding is particularly heavy
- you have a fever
- an ultrasound reveals there’s still tissue in your uterus
If this is the case, your doctor may suggest a dilation and curettage (D and C), which is a surgical procedure done to remove remaining tissue. The procedure is done under general or regional anesthesia, and is considered safe. D and C doesn’t usually lead to long-term complications.
Threatened miscarriage
It’s important to report any bleeding or pain you experience in your pregnancy to your doctor. In some cases, you may have what’s called a threatened miscarriage, and there may be certain treatments that can help. These include:
In some cases, you may have what’s called a threatened miscarriage, and there may be certain treatments that can help. These include:
- hormone supplements if the bleeding is caused by low progesterone
- a cerclage (stitch in the cervix) if the issue is with the cervix opening prematurely
Speak with your healthcare provider if you’re looking to get pregnant again after a miscarriage. While it may be safe to start trying after your first normal period, you may want to schedule a checkup depending on the cause or the number of miscarriages you’ve had.
The reason for loss isn’t always known, but around half of miscarriages are caused by issues with the baby’s chromosomes.
Other possible causes include:
- uterine issues
- hormonal imbalances
- other health conditions, such as diabetes, autoimmune disorders, or polycystic ovary syndrome
After a miscarriage, you may have hcG in your blood for one to two months, which could lead to a false positive pregnancy test. In most cases, your period will return within four to six weeks, though you may start ovulating almost immediately following a miscarriage.
In most cases, your period will return within four to six weeks, though you may start ovulating almost immediately following a miscarriage.
Speak with your doctor about birth control options if you don’t wish to become pregnant after a miscarriage.
Will I miscarry again?
Having one miscarriage doesn’t necessarily increases your chances of having another. The risk remains around 20 percent.
Two or more miscarriages is referred to as recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL). The risk of miscarriage after two losses is 28 percent. After three consecutive losses, it increases to 43 percent.
Only 1 percent of people experience three or more miscarriages. About 65 percent of those with unexplained RPL go on to have successful pregnancies.
Activities like exercise, work, morning sickness, and sex don’t cause miscarriages. Even things like smoking or drinking alcohol or caffeine, which can lead to other complications, are also unlikely to lead to early pregnancy loss.
A miscarriage can be physically painful, and it may also cause a variety of emotions. While your body may recover in a few weeks, be sure to take time to process your feelings, grieve, and reach out for help when you need it.
Miscarriage: causes, symptoms, diagnosis, prevention
Article content
- Symptoms and signs of miscarriage
- Causes of development
- Risk factors
- Complications
- When to see a doctor
- Preparing for a visit to a gynecologist
- Diagnosis of missed pregnancy
- Treatment
- Home remedies
- Prophylaxis
- How to make an appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist?
A frozen pregnancy at an early stage is the death of the fetus in the womb. It stops its development and dies for up to 28 weeks. Symptoms may be mild, which increases the risk of maternal toxicity. If during pregnancy the fetus froze and stopped its development, an urgent visit to an obstetrician-gynecologist is necessary.
It stops its development and dies for up to 28 weeks. Symptoms may be mild, which increases the risk of maternal toxicity. If during pregnancy the fetus froze and stopped its development, an urgent visit to an obstetrician-gynecologist is necessary.
Symptoms and signs of missed pregnancy
A frozen pregnancy at an early stage proceeds absolutely imperceptibly, it can last for 1-2 weeks. This is the danger of the situation.
After 10-12 days, a woman has the first symptoms of a missed pregnancy:
- discharge with blood;
- severe pain in lower abdomen;
- after 18 weeks, you can track the cessation of fetal movement.
There are no symptoms of a missed pregnancy in the first trimester. Sometimes there are spotting spotting, there is a pulling feeling below the navel.
The second frozen pregnancy indicates the presence of a pathology that requires careful study.
Causes of development
Unfortunately, the first missed pregnancy is more common. This is due to the lack of preparation of one's own body. This can happen to any woman.
This is due to the lack of preparation of one's own body. This can happen to any woman.
Main reasons:
- genetic and chromosomal abnormalities cause the development of anomalies that are incompatible with the life of the fetus;
- the fetus was infected with sexually transmitted infections and viruses - even before pregnancy, the risk of the presence or development of such diseases must be excluded;
- hormonal failure increases the risk of miscarriage, progesterone levels should be monitored during gestation;
- a clotting problem causes blood clots to form, preventing them from delivering enough oxygen to the baby;
- Rh conflict causes the production of antibodies that provoke oxygen starvation of the fetus.
Risk factors
Accurately answer the question "Why does pregnancy freeze?" pretty hard.
Consider the most common factors:
- viral diseases can affect the development of the fetus;
- the main reason is hormonal imbalance;
- non-compliance with doctor's recommendations;
- severe stress;
- overheating or severe freezing is prohibited during childbearing;
- smoking and alcohol;
- very tight clothing may harm pregnancy;
- should abandon self-medication and taking drugs not prescribed by a doctor, the body's chemical processes are closely interconnected with each other, the effect can be unpredictable.

Complications
Signs of a missed pregnancy cause the following complications:
- depression. Requires medical treatment, visits to a psychiatrist;
- mummification of the fetus occurs with prolonged missed pregnancy, mummification occurs due to calcium salts, requires surgical intervention;
- infection of the mother's body. Toxins, which are formed due to the decomposition of the fetus, quickly enter the woman's blood. There is sepsis, intoxication, the correct blood clotting is disturbed;
- Lithopedion is a fossilized fetus that has undergone calcification in the body. A woman may not feel any painful symptoms.
When to see a doctor
The gynecologist should observe his patients throughout the entire period of pregnancy. If there is a risk of a missed pregnancy, the terms of which do not exceed 12 weeks, you should immediately consult a doctor. He will determine the condition of the fetus and prescribe further examinations and treatment.
He will determine the condition of the fetus and prescribe further examinations and treatment.
Preparing for a Gynecological Visit
- Shower before visiting a doctor.
- It is better to visit a doctor with an empty bladder, so as not to interfere with palpation.
- Do not take drugs that can affect the microflora or the general condition of the body, this will prevent the doctor from taking an accurate anamnesis.
Symptoms of a missed pregnancy may not appear at all. To avoid intoxication of the body, you should regularly visit a gynecologist.
Diagnosis of missed pregnancy
Diagnosis is carried out in 2 ways: a blood test and ultrasound. If fetal cardiac arrest is detected on ultrasound, the patient is referred to a gynecologist for further procedures.
The patient can make an appointment and get a consultation at a convenient time for him. The pregnancy management program fully complies with clinical guidelines and the latest standards.
JSC "Medicine" (clinic of Academician Roitberg) is located in the Central Administrative District of Moscow, not far from Mayakovskaya, Belorusskaya, Novoslobodskaya, Tverskaya, Chekhovskaya metro stations. Address: 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskoy lane, building 10.
Treatment
Treatment occurs in 3 ways:
- curettage;
- aspiration;
- artificial childbirth.
Curettage - curettage of the uterine cavity. Cleaning after a frozen pregnancy is carried out for a period of 5 weeks.
Aspiration - pumping out the remains of the fetal egg. Carried out in the early stages up to 5 weeks.
Curettage and aspiration are performed under anesthesia. The procedure takes about 30 minutes. After the operation, a course of antibiotics is prescribed. The patient then visits the doctor every week. If complications do not appear, and the causes of a missed pregnancy are eliminated, a woman can continue life in her usual rhythm.
After the loss of an embryo, many women are depressed, they begin to blame themselves for doing something wrong. This is an absolute mistake that can lead to depression. To alleviate your condition, you should contact a psychologist, as well as a gynecologist and other specialists who will help prepare the body for pregnancy.
After treatment, a woman can plan a pregnancy after a missed pregnancy in six months.
Home remedies
Treatment of a missed pregnancy, the terms of which exceeded 12 weeks, involves surgery. At home, the restoration of the body is impossible. Successful recovery requires a large number of tests and a long recovery, associated with the use of antibiotics. At home, it is possible to raise the overall tone of the body.
Important! During gestation, any drugs should be taken as prescribed by a doctor. Many decoctions and herbs have a negative effect on the fetus and can even provoke early labor or miscarriage.
To raise your progesterone levels, you need to:
- include fermented milk products, cheeses, cottage cheese, milk, cream in the diet;
- eat fatty fish;
- do not forget about nuts, berries, fruits and vegetables;
- drink a decoction of plantain seeds, hogweed, raspberry leaves.
It is better to use decoctions in the second half of the cycle. Drink a drink in a volume of 200 ml, no more than 2 times a day.
Important! Decoctions that increase progesterone should not be drunk simultaneously with hormonal drugs.
To prepare for pregnancy, you need:
- replace coffee with tea with chamomile, mint, rosehip and oregano;
- replace sugar and sweeteners with natural honey;
- drink more pure water;
- be treated for sexual infections and maintain health with a decoction of the red brush, hog uterus, coltsfoot.
Prevention
Prevention is a thorough preparation for a new bearing of the fetus. To do this, it is necessary to study the problem of a previous stop in the development of the embryo.
To do this, it is necessary to study the problem of a previous stop in the development of the embryo.
To exclude signs of a frozen pregnancy, you need:
- visit a geneticist who will consult a man and a woman. He will calculate the probability of a missed pregnancy;
- Both partners should be screened for sexually transmitted infections. If they are present, do not start conception until the body is fully restored;
- before conception, you need to find out the Rh factor and blood type. If the Rh is negative, the woman should be observed by a doctor who will control the dynamic observation and will control the antibody titer;
- control of the hormone progesterone will reduce the risk of miscarriage and developmental arrest. If its level is too low, a woman is prescribed special drugs.
It also makes sense to stop smoking and drinking pleasure drinks. It is necessary to do this not only for a woman, but also for a man.
How to make an appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist?
You can make an appointment with a doctor by filling out a simple form on the website or by calling +7 (495) 775-73-60. You can call around the clock. The causes of a missed pregnancy cannot be detected on their own, consultation of several specialists is required.
We are located near Mayakovskaya metro station and Belorusskaya metro station.
Miscarriage due to miscarriage | Articles by EMC doctors about diseases, diagnosis and treatment
What is a miscarriage?
According to medical statistics, miscarriage is the most common complication during pregnancy. About 10-20% of all recorded pregnancies end in miscarriage. Miscarriage is a sporadic, sudden, termination of pregnancy, which is accompanied by complete or partial emptying of the uterus.
Missed pregnancy loss (MP) can be seen on ultrasound. It consists in confirming the non-viability of the fetus without bleeding. The ST can end in a miscarriage, when the body gets rid of the dead fetus on its own, or in a medical abortion, when medical or surgical manipulations are used to clean the uterine cavity.
The ST can end in a miscarriage, when the body gets rid of the dead fetus on its own, or in a medical abortion, when medical or surgical manipulations are used to clean the uterine cavity.
Causes of miscarriage and miscarriage
80% of miscarriages occur in the first trimester before 12 weeks. In 50% of cases, this occurs due to genetic defects in the fetus. The threat of miscarriage due to chromosomal abnormalities decreases with the course of pregnancy: by 20 weeks it is 10-20% versus 41-50% in the first trimester. The main cause of genetically determined early miscarriages are autonomous trisomies - when three homologous chromosomes are present in the cells instead of two. Such defects occur at the time of conception and are not subject to correction. They lead to miscarriage or to the development of severe genetic diseases. In addition to genetics, immunological, endocrine and infectious causes are distinguished.
In the second trimester, various diseases and disorders in the mother's body become the main cause of miscarriage.
There is a list of factors that can trigger early pregnancy loss:
-
woman's age. At the age of 20-30 years, the risk of spontaneous miscarriage is 9-17%, at 35-40 years old - 20%, at 40-45 - 40%;
-
alcohol abuse;
-
abuse of caffeine;
-
smoking;
-
drug use;
-
chronic diseases of the mother;
-
maternal infections;
-
use of medications incompatible with pregnancy;
-
history of spontaneous abortion. The risk of subsequent pregnancy loss in women with one miscarriage in history is 18-20%, with two - 30%, with three - 43%.
Symptoms and signs of miscarriage
You can suspect a miscarriage by sudden spotting and sharp pain in the lower abdomen. If these symptoms appear, seek immediate medical attention. The doctor must conduct an ultrasound diagnosis. Transvaginal scanning (TVS) is considered the gold standard for diagnostics - when the sensor is inserted into the uterus through the vagina. If TVS is not available, a transabdominal scan can be applied - through the anterior abdominal wall.
If TVS is not available, a transabdominal scan can be applied - through the anterior abdominal wall.
Missed pregnancy may be asymptomatic and not manifest until the next scheduled ultrasound.
How does a miscarriage happen?
The miscarriage process has four stages. This does not happen overnight and lasts from several hours to several days.
The first stage - the threat of miscarriage. Among the symptoms: pulling pains in the lower abdomen, scanty blood discharge, increased uterine tone. The process of detachment of the placenta from the place of attachment in the uterus begins. The internal os is closed. The main thing is to seek help in time, then with proper therapy if there is a chance to stop the miscarriage and save the pregnancy.
The second stage - the beginning of a miscarriage. Strong discharge, the cervical canal is ajar, the doctor diagnoses the final detachment of the placenta.
Third stage - miscarriage in progress. You can feel the regular contractions of the uterus, the outcome of the fetus, placenta and uterine contents, profuse blood discharge has begun.
You can feel the regular contractions of the uterus, the outcome of the fetus, placenta and uterine contents, profuse blood discharge has begun.
The last fourth stage is a complete miscarriage. The pregnancy is interrupted, the uterine cavity does not contain the fetus and products of conception.
How to determine ST?
It should be remembered that a miscarriage can be diagnosed only during an ultrasound examination. Home tests will not give reliable results. Ultrasound will show the presence or absence of a heartbeat in the fetus.
Treatment of miscarriage and miscarriage
Due to the fact that the vast majority of spontaneously terminated pregnancies are due to genetic abnormalities (non-viability) of the fetus, then, speaking about the treatment of miscarriage, it is worth talking about ensuring complete and safe cleansing of the uterus, preventing infection and preventing bruising. With the help of an ultrasound examination, the doctor will check whether the uterus has completely cleared.