Blood umbilical cord after falls off
What is normal and what to do
A newborn’s belly button may bleed while the cord is falling off or shortly after it does. Most often, newborn belly button bleeding is not a cause for concern but a regular part of the healing process. Occasionally though, it can signal a problem.
The umbilical cord supplies a fetus with nutrients from the mother. Once the baby is born, it no longer needs the umbilical cord to provide its nutrients, and so doctors cut the cord. Eventually, the cord dries out and falls off, leaving behind a belly button in its place.
Read on to find out why a newborn’s belly button may bleed, how to take care of the area, and when bleeding from a newborn’s belly button may need medical attention.
Share on PinterestIt is not uncommon for a newborn’s belly button to bleed.Most cases of belly button bleeding are natural.
Many parents and caregivers may notice a small area of bleeding at the point where the newborn’s umbilical cord begins to separate from the body.
Sometimes a newborn’s diaper or even a piece of clothing may rub against the umbilical cord. This can irritate the area and cause bleeding as well.
To stop a newborn baby’s belly button bleeding, hold a piece of clean gauze gently but firmly over the belly button area. A doctor should evaluate any bleeding that does not stop with gentle pressure.
Caring for the umbilical cord stump properly can help prevent or reduce belly button bleeding. A new parent or caregiver can care for a newborn’s umbilical cord stump by:
- Keeping the area dry. Keeping the umbilical cord stump dry can help the remaining cord dry out and fall off.
- Giving the baby a sponge bath while the cord stump is still attached. Instead of submerging the baby’s body in water, use sponge baths to wash the newborn to keep the area dry.
- Exposing the area to air. Keeping the stump uncovered for a little time each day can help it dry out.
- Changing the baby’s diapers regularly. A clean, dry diaper should prevent urine or stool from reaching the umbilical area and can help prevent infection.
- Letting the cord fall off on its own. Pulling at the stump or trying to remove the stump before it is ready to fall off can cause pain and bleeding and may lead to an infection.
Share on PinterestDiapers can irritate the belly button.
While the stump is healing, avoid:
- Covering the area with a diaper. A diaper can rub and irritate the area. Many diapers for newborns are cut lower at the front, so do not cover the belly button area. However, where this is not the case, fold the diaper down in the front so that it does not touch the stump or surrounding area.
- Rubbing alcohol on the stump. Rubbing alcohol may delay the cord from drying out. Most doctors do not recommend applying alcohol to a baby’s umbilical stump unless there is a specific reason for doing so.
- Tying anything around the cord. This can prevent the area from drying or cause injury to the baby.
According to the American Academy of Pediatrics, most babies will lose their cord stumps in 10 to 14 days.
However, it is not unusual for a baby’s umbilical cord to fall off as early as 1 week after birth or as late as 3 weeks after birth.
It is typical for a baby’s umbilical cord to fall off before or after this time frame as well.
Share on PinterestA doctor can assess a newborn for signs of infection.
Most of the time, newborn belly button bleeding is normal. However, if the bleeding is hard to stop or if there is more than just a few drops of blood, take the baby to see a pediatrician.
Also, a doctor needs to examine a newborn’s belly button if there are any signs of infection, including:
- pus or cloudy, foul-smelling drainage from the belly button area
- red, warm skin surrounding the umbilical cord stump area
- a fever of over 100.
 4°F
4°F - the belly button area seems painful to the touch
While a bleeding belly button can cause alarm to new parents, some newborn belly button bleeding is nothing to worry about.
Slight bleeding from the umbilical cord stump is generally not serious and usually resolves within the first few weeks after birth.
In rare cases, newborn belly button bleeding can indicate the baby has an infection at the site of the umbilical cord stump. If a newborn shows any signs of infection, take the baby to the pediatrician immediately.
What is normal and what to do
A newborn’s belly button may bleed while the cord is falling off or shortly after it does. Most often, newborn belly button bleeding is not a cause for concern but a regular part of the healing process. Occasionally though, it can signal a problem.
The umbilical cord supplies a fetus with nutrients from the mother. Once the baby is born, it no longer needs the umbilical cord to provide its nutrients, and so doctors cut the cord.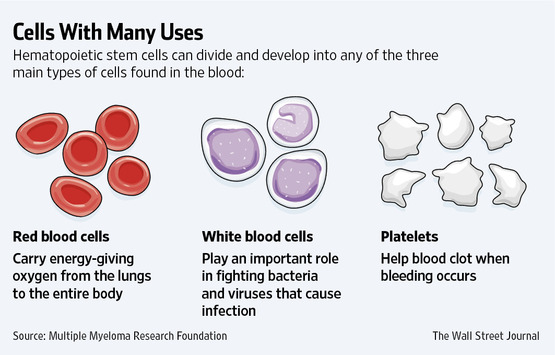 Eventually, the cord dries out and falls off, leaving behind a belly button in its place.
Eventually, the cord dries out and falls off, leaving behind a belly button in its place.
Read on to find out why a newborn’s belly button may bleed, how to take care of the area, and when bleeding from a newborn’s belly button may need medical attention.
Share on PinterestIt is not uncommon for a newborn’s belly button to bleed.Most cases of belly button bleeding are natural.
Many parents and caregivers may notice a small area of bleeding at the point where the newborn’s umbilical cord begins to separate from the body.
Sometimes a newborn’s diaper or even a piece of clothing may rub against the umbilical cord. This can irritate the area and cause bleeding as well.
To stop a newborn baby’s belly button bleeding, hold a piece of clean gauze gently but firmly over the belly button area. A doctor should evaluate any bleeding that does not stop with gentle pressure.
Caring for the umbilical cord stump properly can help prevent or reduce belly button bleeding.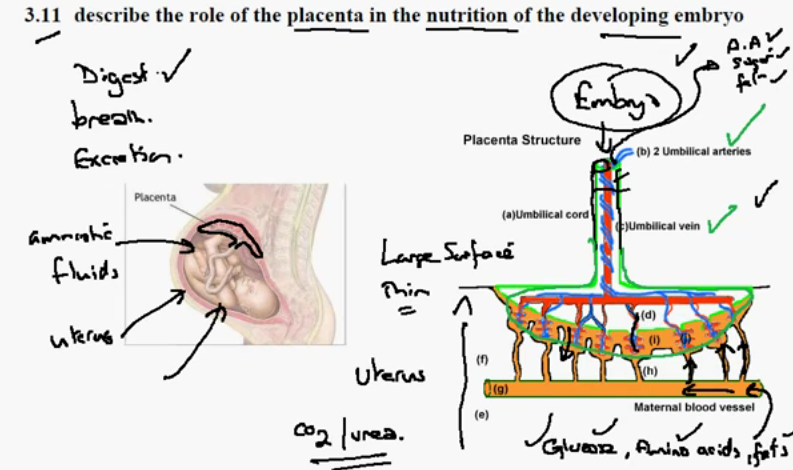 A new parent or caregiver can care for a newborn’s umbilical cord stump by:
A new parent or caregiver can care for a newborn’s umbilical cord stump by:
- Keeping the area dry. Keeping the umbilical cord stump dry can help the remaining cord dry out and fall off.
- Giving the baby a sponge bath while the cord stump is still attached. Instead of submerging the baby’s body in water, use sponge baths to wash the newborn to keep the area dry.
- Exposing the area to air. Keeping the stump uncovered for a little time each day can help it dry out.
- Changing the baby’s diapers regularly. A clean, dry diaper should prevent urine or stool from reaching the umbilical area and can help prevent infection.
- Letting the cord fall off on its own. Pulling at the stump or trying to remove the stump before it is ready to fall off can cause pain and bleeding and may lead to an infection.
Share on PinterestDiapers can irritate the belly button.
While the stump is healing, avoid:
- Covering the area with a diaper.
 A diaper can rub and irritate the area. Many diapers for newborns are cut lower at the front, so do not cover the belly button area. However, where this is not the case, fold the diaper down in the front so that it does not touch the stump or surrounding area.
A diaper can rub and irritate the area. Many diapers for newborns are cut lower at the front, so do not cover the belly button area. However, where this is not the case, fold the diaper down in the front so that it does not touch the stump or surrounding area. - Rubbing alcohol on the stump. Rubbing alcohol may delay the cord from drying out. Most doctors do not recommend applying alcohol to a baby’s umbilical stump unless there is a specific reason for doing so.
- Tying anything around the cord. This can prevent the area from drying or cause injury to the baby.
According to the American Academy of Pediatrics, most babies will lose their cord stumps in 10 to 14 days.
However, it is not unusual for a baby’s umbilical cord to fall off as early as 1 week after birth or as late as 3 weeks after birth.
It is typical for a baby’s umbilical cord to fall off before or after this time frame as well.
Share on PinterestA doctor can assess a newborn for signs of infection.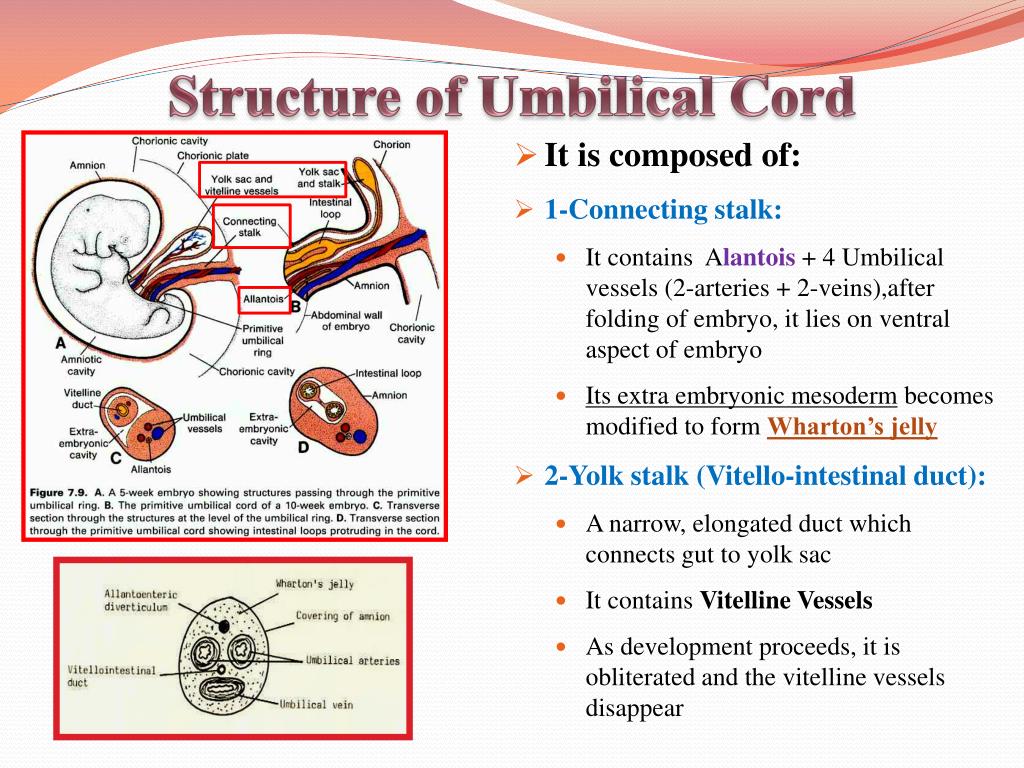
Most of the time, newborn belly button bleeding is normal. However, if the bleeding is hard to stop or if there is more than just a few drops of blood, take the baby to see a pediatrician.
Also, a doctor needs to examine a newborn’s belly button if there are any signs of infection, including:
- pus or cloudy, foul-smelling drainage from the belly button area
- red, warm skin surrounding the umbilical cord stump area
- a fever of over 100.4°F
- the belly button area seems painful to the touch
While a bleeding belly button can cause alarm to new parents, some newborn belly button bleeding is nothing to worry about.
Slight bleeding from the umbilical cord stump is generally not serious and usually resolves within the first few weeks after birth.
In rare cases, newborn belly button bleeding can indicate the baby has an infection at the site of the umbilical cord stump. If a newborn shows any signs of infection, take the baby to the pediatrician immediately.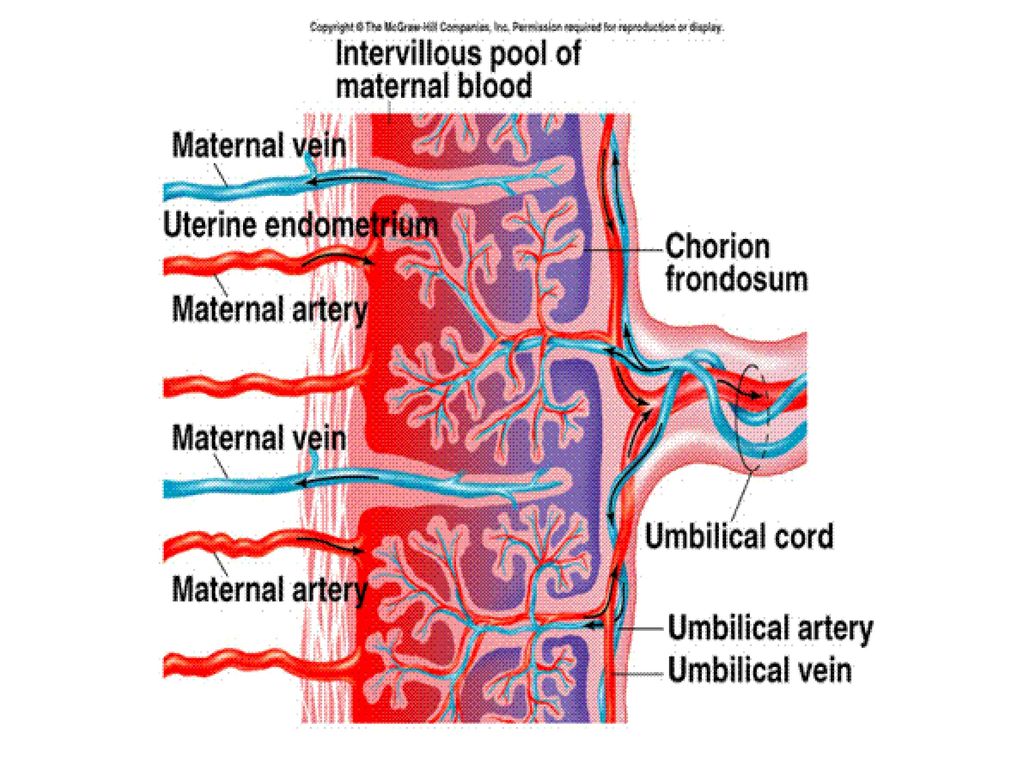
What is cord blood - Leleka Maternity Hospital
What is cord blood
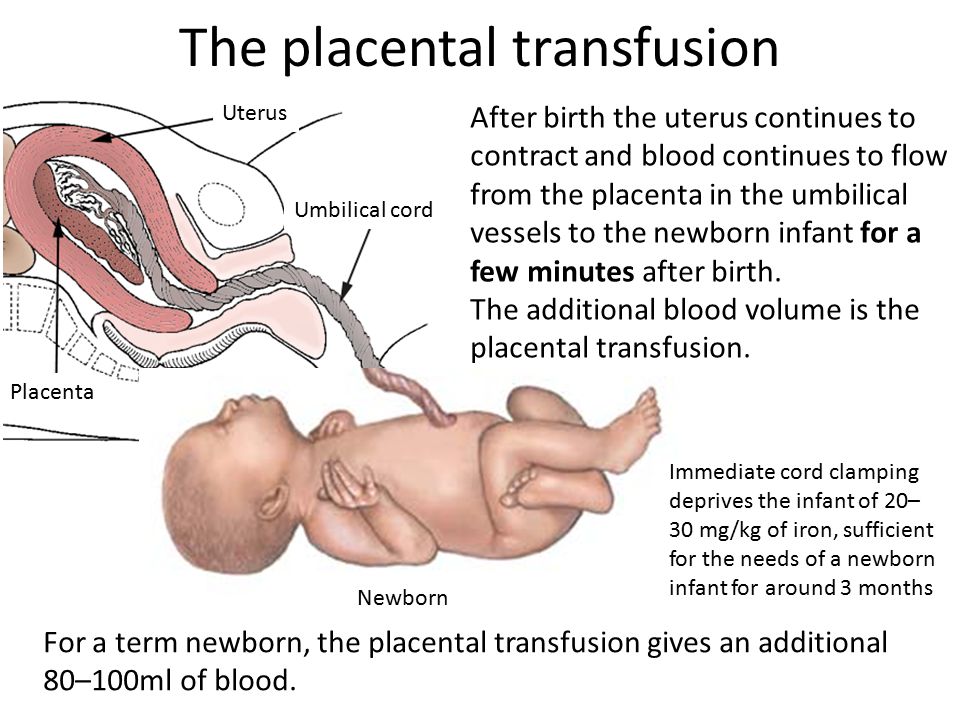
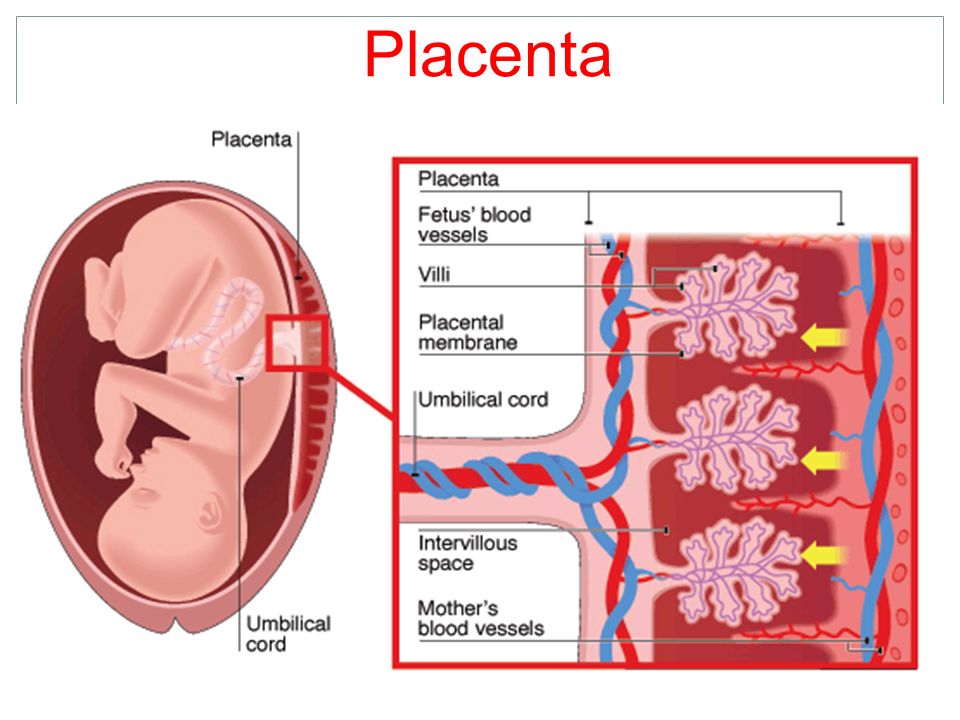
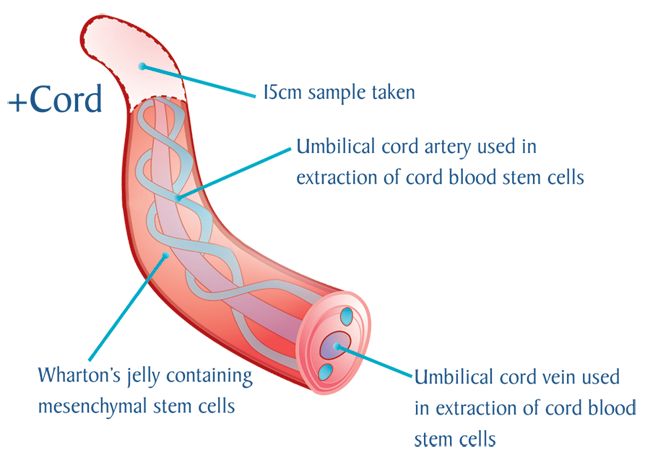
The birth of a child occurs in several stages. First, the baby himself is born, and a few minutes later, with the help of obstetricians, the placenta, the placenta, is removed from the uterus. The placenta is connected to the baby's body by the umbilical cord - a dense cord of connective tissue through which the baby is supplied with blood. A few minutes after birth, the umbilical cord pumps blood from the placenta into the baby's body. It is this blood that is called placental.
After the baby has begun to breathe, doctors clamp the umbilical cord and cut it. There are no nerve endings in the umbilical cord, so the baby does not feel pain. The wound is treated: then there will be a navel in this place. Meanwhile, up to 80 grams of blood can leak from the placenta through the umbilical cord vein. If the baby is born premature, premature clamping of the umbilical cord is not recommended: every gram of maternal blood is critical.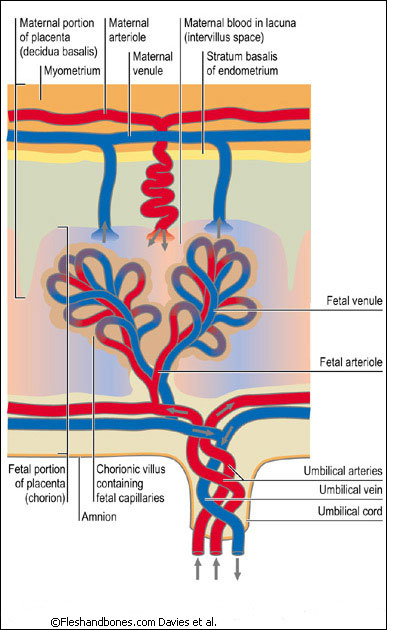 But for a healthy child, these grams are insignificant. So cord blood can be collected and stored. Previously, this blood was disposed of along with the placenta, but now scientists have found a way to use it to treat dangerous diseases.
But for a healthy child, these grams are insignificant. So cord blood can be collected and stored. Previously, this blood was disposed of along with the placenta, but now scientists have found a way to use it to treat dangerous diseases.
Why cord blood is collected
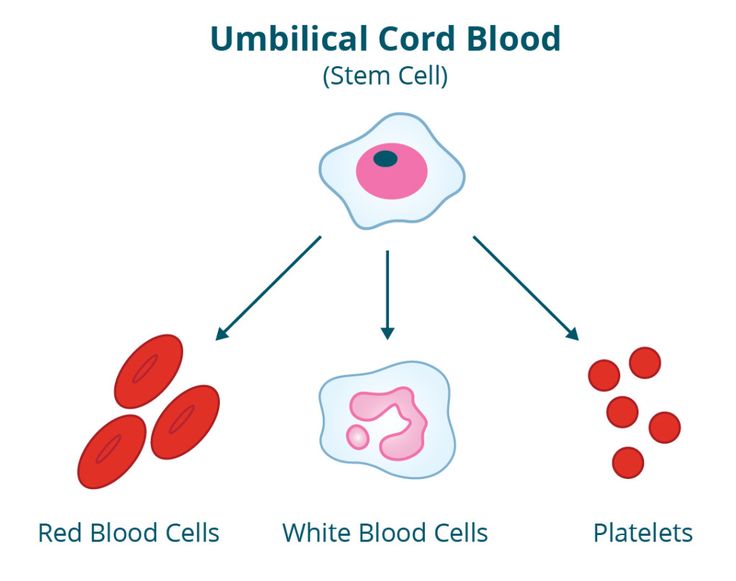
Cord blood contains stem cells. They are used to treat more than 70 different diseases, mainly leukemia and other diseases of the hematopoietic organs. One common use of cord blood is for newborns undergoing heart surgery in the first hours of life.
Direct indications for the use of cord blood:
- Leukemias, lymphoblastic and non-lymphoblastic, in the acute stage;
- Remissions after leukemia;
- Resistant lymphomas;
- Neuroblastomas and other brain tumors;
- Some types of sarcomas;
- Other malignant diseases of the hematopoietic system.
The potential of stem cells has not yet been fully explored, and trials are ongoing to use stem cells to treat heart disease, liver disease, muscular dystrophy, Parkinson's disease, and so on.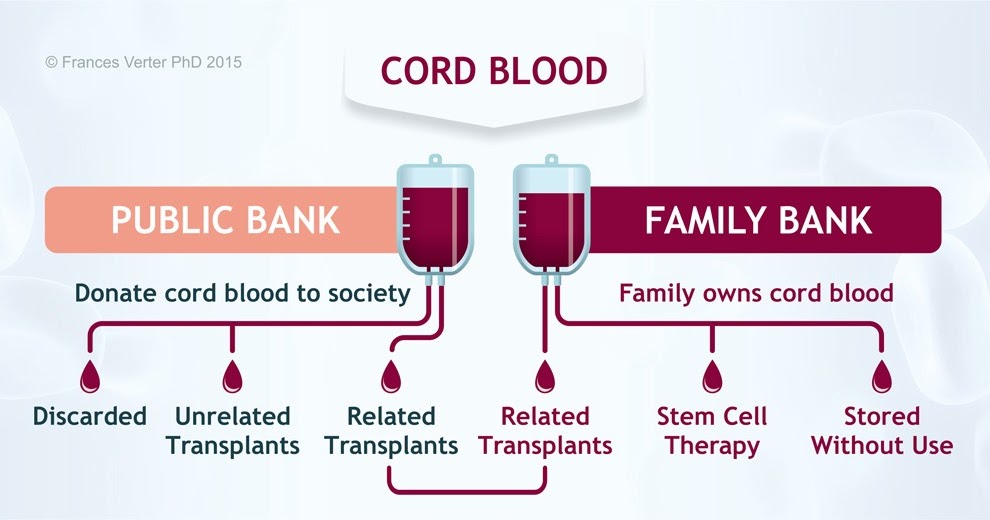 Therefore, private and public storage facilities for cord blood, biobanks are developing more and more - as a rule, in the same institutions where bone marrow, eggs and other biomaterial are stored.
Therefore, private and public storage facilities for cord blood, biobanks are developing more and more - as a rule, in the same institutions where bone marrow, eggs and other biomaterial are stored.
What is the role of parents in cord blood collection
Parents of a child can collect and freeze cord blood in a special blood bank in case something happens to the baby. In developed countries, there are state biobanks, and every woman in labor is informed that cord blood can be saved. Storage in state biobanks is free. The blood can be used to treat other patients, not just the donor.
There is no state blood bank in Ukraine, but there are private ones. Storage of blood in private banks is paid, but the material will be used only for the donor's family, or at their order. Fortunately, the probability that the baby himself will need his blood does not exceed 1\1400 cases. In about a quarter of cases, this blood will be suitable for the treatment of brothers and sisters.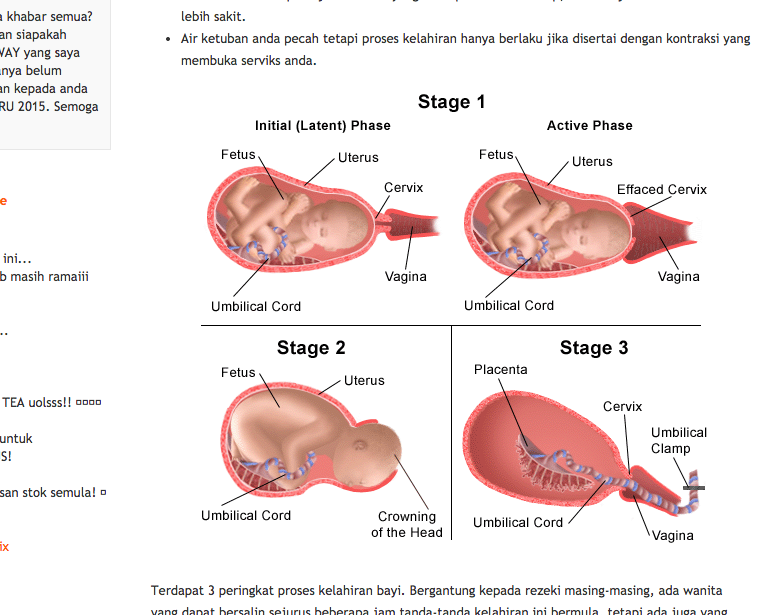 In some cases, they are even used to treat parents, although experiments on the use of material with incomplete compatibility are still ongoing.
In some cases, they are even used to treat parents, although experiments on the use of material with incomplete compatibility are still ongoing.
Pros and cons of using cord blood
The technology of transplanting your own stem cells is quite new. There are no well-established protocols for the use of this material yet. This means that every operation with stem cells is, to some extent, an experiment. In Ukraine, such operations are regulated by the relevant orders of the Ministry of Health, but this does not remove the general problems.
In addition, cord blood and the stem cells it contains are not a panacea. Yes, the use of stem cells increases the prognosis of the survival of patients with diseases of the hematopoietic organs up to 63%. But, unfortunately, a 100% cure is not guaranteed.
On the other hand, the use of cord blood has already saved the lives of several hundred children in Ukraine alone. In addition, the blood in the biobank is stored for years, and technology does not stand still.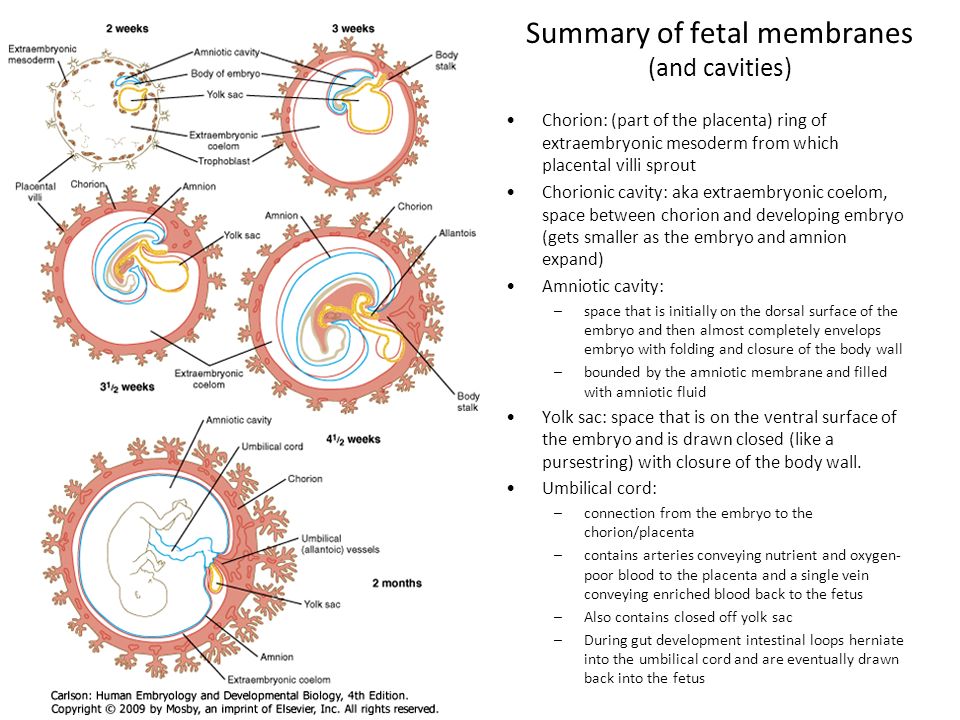 As research continues, new possibilities are being discovered for the use of stem cells in the treatment of various diseases. Therefore, the preservation of cord blood has its own meaning.
As research continues, new possibilities are being discovered for the use of stem cells in the treatment of various diseases. Therefore, the preservation of cord blood has its own meaning.
Top 10 questions about newborns
The birth of a child for many parents is a period of stress and uncertainty. Many questions arise: how to deal with him, how to understand his needs, how to reassure him, but everything is fine with him?
Many books and articles have been written on this topic that sometimes there is not enough time to read all the literature. Therefore, we highlight the special facts about newborns that everyone needs to know:
1. How to care for the navel?
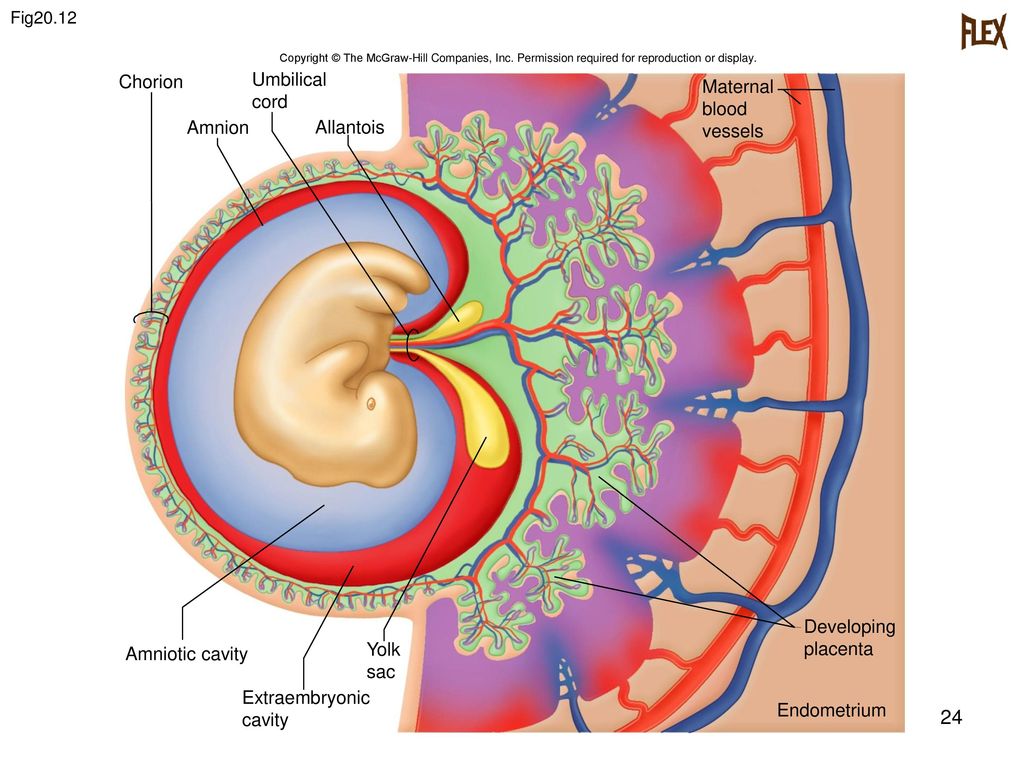
After discharge from the hospital, the umbilical cord residue is kept clean and dry, disappears naturally. It does not need to be twirled, let alone torn off - in a week or two after discharge, it will fall off on its own. The fall off of the umbilical cord occurs on the 10-15th day after the birth of the child, sometimes later.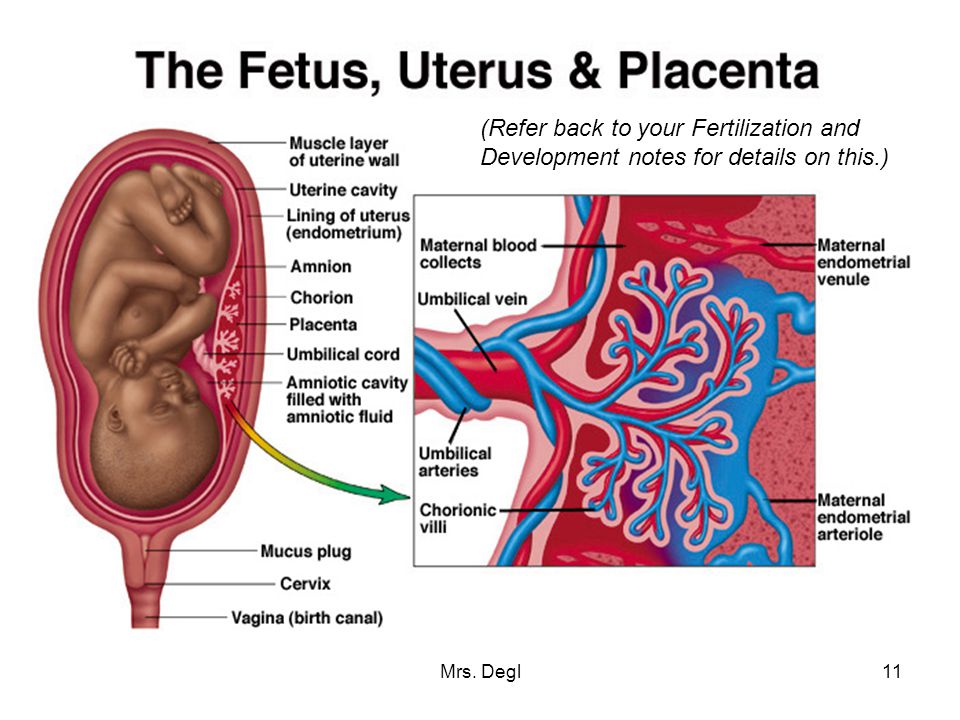 During this normal process, a small amount of cloudy mucus may accumulate at the site of separation, which may be mistaken for pus. The umbilical cord may be wet or sticky, but this is all part of a normal physiological process. The umbilical cord should be left open to air or covered with clean, loose clothing. The diaper should not cover the rest of the umbilical cord until it falls off. It has been proven that the local use of antiseptics not only does not reduce the frequency of infections, but also contributes to the delay of spontaneous falling off of the umbilical cord. Avoid contact with urine or cosmetics. If urine or feces get on the umbilical cord or umbilical wound, it is necessary to rinse with water, incl. the area adjacent to it; blot dry with a clean towel or diaper. It is important to use only water for washing, as the use of other substances can interfere with the natural healing process. Do not use dry cotton to care for the umbilical cord, as it may leave villi on it, which can cause infection.
During this normal process, a small amount of cloudy mucus may accumulate at the site of separation, which may be mistaken for pus. The umbilical cord may be wet or sticky, but this is all part of a normal physiological process. The umbilical cord should be left open to air or covered with clean, loose clothing. The diaper should not cover the rest of the umbilical cord until it falls off. It has been proven that the local use of antiseptics not only does not reduce the frequency of infections, but also contributes to the delay of spontaneous falling off of the umbilical cord. Avoid contact with urine or cosmetics. If urine or feces get on the umbilical cord or umbilical wound, it is necessary to rinse with water, incl. the area adjacent to it; blot dry with a clean towel or diaper. It is important to use only water for washing, as the use of other substances can interfere with the natural healing process. Do not use dry cotton to care for the umbilical cord, as it may leave villi on it, which can cause infection. After the umbilical cord falls off, an umbilical wound is formed, which is treated in the same way until complete healing (about 2 weeks). Give your child more air baths to provide oxygen to the wound, so it will heal faster.
After the umbilical cord falls off, an umbilical wound is formed, which is treated in the same way until complete healing (about 2 weeks). Give your child more air baths to provide oxygen to the wound, so it will heal faster.
2. How to bathe a newborn?
Until the umbilical cord residue falls off, rubbing with a sponge to maintain cleanliness is quite enough.
It is most convenient to bathe a baby in a special bath, especially with a slide. The duration of the hygienic bath is 5-10 minutes. Gently submerge the baby in the water, first the legs and then the whole body. Pay attention to every skin fold. Clean the perineum last. You can not leave the child alone in the water, one hand should always support him. The temperature in the bathing room is 24-26 degrees. Ordinary tap water is used, there is no need to boil water, the water temperature is up to 37-38 0C (according to a water thermometer). Up to 1 month, the child is bathed with soap once a week, after a month - 1-2 times a week. Daily hygienic baths without the use of detergents - up to 1 year. After bathing, the child's skin is dried (but not wiped!) with a towel or diaper made of soft cotton fabric with blotting movements
Daily hygienic baths without the use of detergents - up to 1 year. After bathing, the child's skin is dried (but not wiped!) with a towel or diaper made of soft cotton fabric with blotting movements
3. How to take care of your skin?
The skin of a newborn baby is very thin, soft and sensitive. Sometimes rubbing emollients (creams, oils) into the skin can cause redness, a rash, so skin care products must be selected individually.
In general, the fewer additional interventions in establishing the process of life outside the womb, the better. The skin of the baby must adapt to the external environment and its irritants. You don’t need to smear the folds of a healthy baby with normal skin with boiled oil, sprinkle powder on the ass (if you really want to smear his ass with something, then choose special diaper creams with zinc) and coat the baby with lotions and creams.
If irritation occurs, it is recommended to start changing the diaper more often and regularly arrange air baths.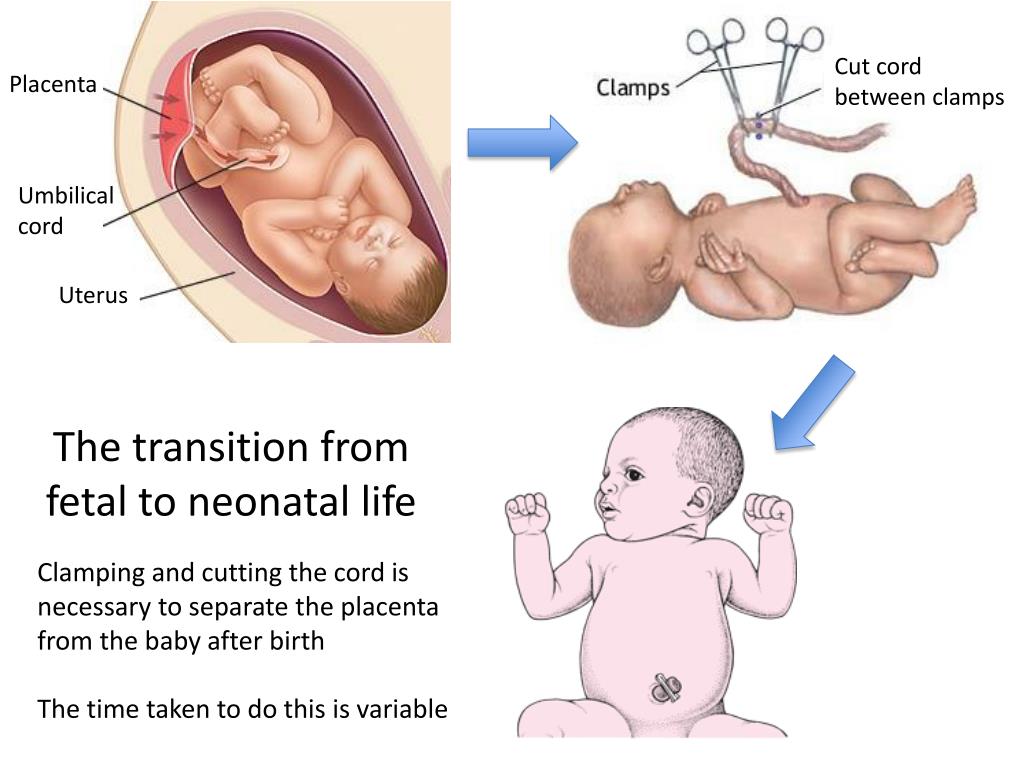
Often small pimples appear on the skin of newborns. But it’s not always worth panicking, it can be newborn acne (infant acne, neonatal pustulosis) - caused by stimulation of the baby’s sebaceous glands with androgens. It is localized more often on the face, sometimes spreads to the scalp, less often to the collar zone. Acne is red pimples, with a whitish head, and possible redness around. Doesn't give the baby any worries. Does not cause itching and discomfort. As a rule, acne symptoms appear closer to the second week of a child's life, and this process can last up to four months. They resolve spontaneously, without scarring. The skin needs to be cleansed and moisturized.
An allergic reaction, unlike acne, spreads throughout the baby's body. It usually appears on the cheeks, forehead, chest, pope, less often on the legs and arms. If an allergic reaction occurs, the child becomes restless, because the rash gives him great discomfort, itching. This condition requires a visit to the pediatrician.
Sweating, unlike acne, occurs in the skin folds of the baby. Often found on the neck, elbows and knees, gluteal region, genitals, in the armpits of the baby. Sweating is most often the result of non-compliance with the hygiene of the child. Less commonly occurs during overheating of the baby. It is also red pimples, without signs of a whitish core.
4. How to correctly carry out the morning toilet of a newborn?
It is necessary to create comfortable conditions for the newborn: the humidity in the room is 40-60%, and the temperature in the room is 22-23 degrees.
The child is placed on the changing table and completely undressed, and then the skin, skin folds (cervical, axillary, inguinal), mouth, nose, eyes, nails are carefully examined.
The eyes are washed with cotton wool (cotton pad) soaked in boiled water from the outer corner to the inner. A separate swab (disk) is used for each eye. It is necessary to ensure that water does not get from one eye to the other, therefore, when washing the eyes, we lay the child alternately on the right and left sides.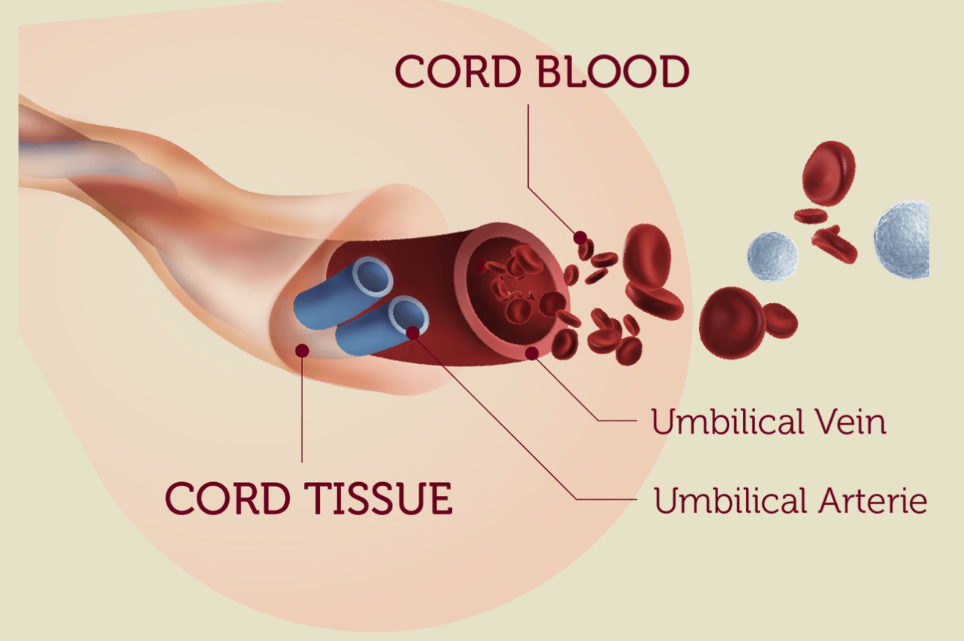
The mouth of a newborn child is not processed, but must be examined daily. The appearance of white plaques on the oral mucosa (thrush) requires the consultation of a local doctor.
Normally, the nose clears when a child sneezes. In case of difficulty in breathing due to the formation of "crusts" or with a physiological runny nose, it can be cleaned manually. It is best to do this before feeding or during the morning toilet. To do this, twist the flagellum out of cotton wool, wet it with boiled water (physiological saline, sea water or preparations based on them), gently turn it in the child’s nose, removing the crusts. Each nasal passage is cleaned in turn. Use a separate flagellum for each nostril.
Another way to toilet the nose of a newborn - a few minutes before the procedure, 2-3 drops of a sterile isotonic solution are instilled into the nose, preferably based on sea water, for example, Aqualor baby drops. This helps thin the mucus and dissolve the crusts and clots and remove them with a nasal aspirator.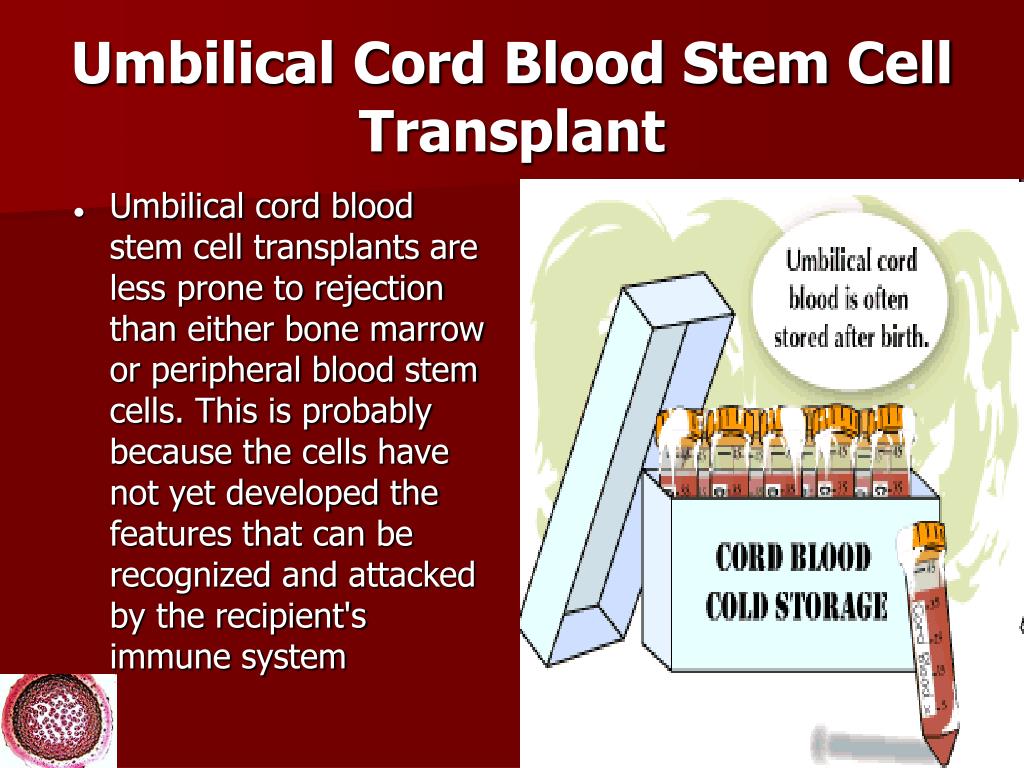 In no case should cotton swabs or cotton wool wound around a match be used to clean the nose.
In no case should cotton swabs or cotton wool wound around a match be used to clean the nose.
Symptoms of a physiological runny nose: clear and liquid consistency of mucus, no hyperthermia and signs of intoxication, no hyperemia of the pharynx, "grunting" breathing and partly open mouth during sleep, morning and night nasal congestion. Breathing problems in the morning often signal excessively dry indoor air. If moisturizing measures normalize the patency of the nasal canals in infants, then the reason was precisely the lack of air humidity. Physiological rhinitis can last no more than 3 months.
An increase in body temperature, copious opaque discharge from the nose, conjunctivitis, swelling and hyperemia of the nasopharynx are signs that require a pediatrician's consultation.
The ear canal of a newborn is not cleaned, only the auricles are treated. But you need to pay attention to the skin behind the ears. In newborns, the ears are pressed tightly to the head, so they need to be carefully folded back and the skin cleaned with cotton pads dipped in warm water. After the bath, it is necessary to remove the remaining water from the folds of the auricles with dry cotton wool. At the same time, turn the child's head to the side.
After the bath, it is necessary to remove the remaining water from the folds of the auricles with dry cotton wool. At the same time, turn the child's head to the side.
5. How to wash a newborn?
Boys are washed under the tap, both from front to back and vice versa, with ordinary water, without the use of antiseptics and soap, daily in the morning and before bedtime, and also after each bowel movement. It is necessary to thoroughly wash off the particles of feces in the folds between the anus and the scrotum. We do not touch the skin of the foreskin.
The girl is washed with plain water without the addition of antiseptics and without the use of soap daily (in the morning, before going to bed, and also after each bowel movement). Direct the water jet from front to back. If particles of feces are found in the genital slit, be sure to remove them with cotton wool (cotton pad) soaked in plain water. Separate the child's legs, open the labia and with a moistened cotton ball (disk) gently wipe between them in the direction from front to back to avoid getting microbes from the anus to the perineum.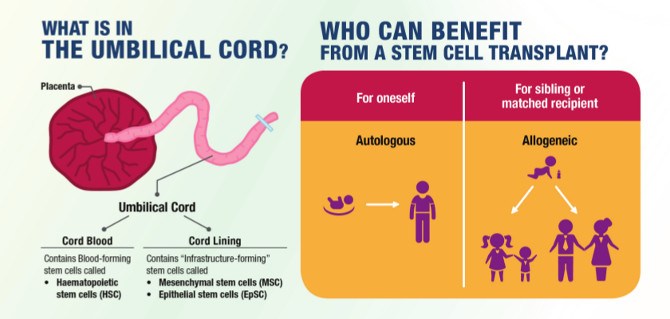 The discharge collects between the vulva and the outer lips, this place must be washed especially carefully.
The discharge collects between the vulva and the outer lips, this place must be washed especially carefully.
6. How to feed a newborn?
The newborn can be breastfed (breastfeeding), an adapted formula (formula feeding), or both (mixed feeding). In the last two cases, you should contact your pediatrician for recommendations on the feeding regimen.
If you are breastfeeding, WHO (World Health Organization) recommends feeding your baby on demand day and night, the more often the baby is breastfed, the more lactation is stimulated.
7. How to dress for a walk?
When dressing a child, you need to remember that newborns easily freeze and overheat (and overheating is no less harmful than hypothermia). The basic rule goes like this: the baby should have as many layers of clothes as you have, plus one.
They walk with a healthy child at any time of the year. With a small child, they begin to walk when they reach a weight of 2000 grams. If the baby was born in winter, walk at a street temperature of at least -15 0C. It is necessary to accustom the newborn to lower temperatures gradually. In winter, on the street, a child aged 1.5-2 months is better to sleep in the arms of an adult, only after 2 months of life - in a stroller. For the first time, they walk with the baby for no more than 10 minutes, gradually the stay in the fresh air is brought up to 1.5-2 hours. By the age of 2 months and in good weather, you can walk daily 2-3 times a day.
If the baby was born in winter, walk at a street temperature of at least -15 0C. It is necessary to accustom the newborn to lower temperatures gradually. In winter, on the street, a child aged 1.5-2 months is better to sleep in the arms of an adult, only after 2 months of life - in a stroller. For the first time, they walk with the baby for no more than 10 minutes, gradually the stay in the fresh air is brought up to 1.5-2 hours. By the age of 2 months and in good weather, you can walk daily 2-3 times a day.
8. How to swaddle?
Tight swaddling "column" is harmful to infant joints. But soft swaddling - for example, with the help of knitted Velcro diapers that do not restrict the movement of the legs, can help the child calm down and sleep better, because in the womb he was constrained in his movements in the last stages, which is why many babies like free swaddling. Many children wave their arms in their sleep and wake up from this - in such cases, a diaper is indispensable.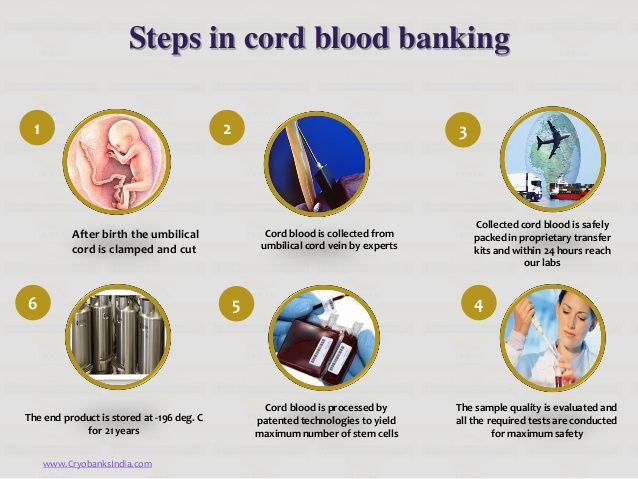
9. How to wash and iron children's clothes?
Many people buy special baby powders for babies, but it makes sense to use them only if you are ready to wash all other things with this powder. It makes no sense to wash children's things separately: the newborn will still come into contact with "adult" textiles - whether it be a sheet on your bed or your sweater, to which he will press his cheek.
Ironing children's clothes is also not necessary - unless you really want to.
10. How much sleep should a newborn baby have?
If you're lucky, your newborn can sleep up to 20 hours a night, and the first few weeks of life are definitely not the best time to try to get him to sleep.
The safest sleep for babies is sleeping in the supine position, in a separate hard surface sleeping area, without any soft bedding, and in the same room as the baby's caregivers. Read more: CHILDREN'S DREAM. ABOUT SAFETY AND RISK FACTORS (https://medspecial.