Amnio testing pregnancy
Amniocentesis - Results - NHS
After amniocentesis has been carried out, the sample of amniotic fluid will be sent to a laboratory for testing.
Getting the results
The first results should be available within 3 working days, and this will tell you whether a chromosomal condition, such as Down's syndrome, Edwards' syndrome or Patau's syndrome, has been found.
If rarer conditions are also being tested for, it can take 3 weeks or more for the results to come back.
You can usually choose whether to get the results over the phone, or during a face-to-face meeting at the hospital or at home.
You'll also receive written confirmation of the results.
What the results mean
Amniocentesis is estimated to give a definitive result in 98 to 99 out of every 100 women having the test.
But it cannot test for every condition and, in a small number of cases, it's not possible to get a conclusive result.
Many women who have amniocentesis will have a "normal" result. This means that none of the conditions that were tested for were found in the baby.
But a normal result does not guarantee that your baby will be completely healthy, as the test only checks for conditions caused by certain genes and it cannot exclude every condition.
If your test result is positive, your baby has 1 of the conditions they were tested for.
In this instance, the implications will be fully discussed with you and you'll need to decide what to do next.
What happens if a condition is found
If the test finds that your baby will be born with a condition, you can speak to a number of specialists about what this means.
These could include a midwife, a doctor who specialises in childrens' health (consultant paediatrician), a geneticist and a genetic counsellor.
They'll be able to give you detailed information about the condition to help you decide what to do, including the possible symptoms your child may have, the treatment and support they might need, and whether their life expectancy will be affected.
A baby born with 1 of these conditions will always have the condition, so you'll need to consider your options carefully.
Your options are to:
- continue with your pregnancy – it can help to find out as much as you can about the condition your baby will have
- end your pregnancy (have a termination)
This can be a very difficult decision, but you do not have to make it on your own.
As well as discussing it with specialist healthcare professionals, it can help to talk things over with your partner and speak to close friends and family.
You can also get support and more information from charities like:
- Antenatal Results and Choices (ARC)
- Down's Syndrome Association
- Sickle Cell Society
- SOFT (Support Organisation for Trisomy 13 and 18)
Page last reviewed: 12 October 2022
Next review due: 12 October 2025
Pregnancy tests amniocentesis - Better Health Channel
Actions for this page
Summary
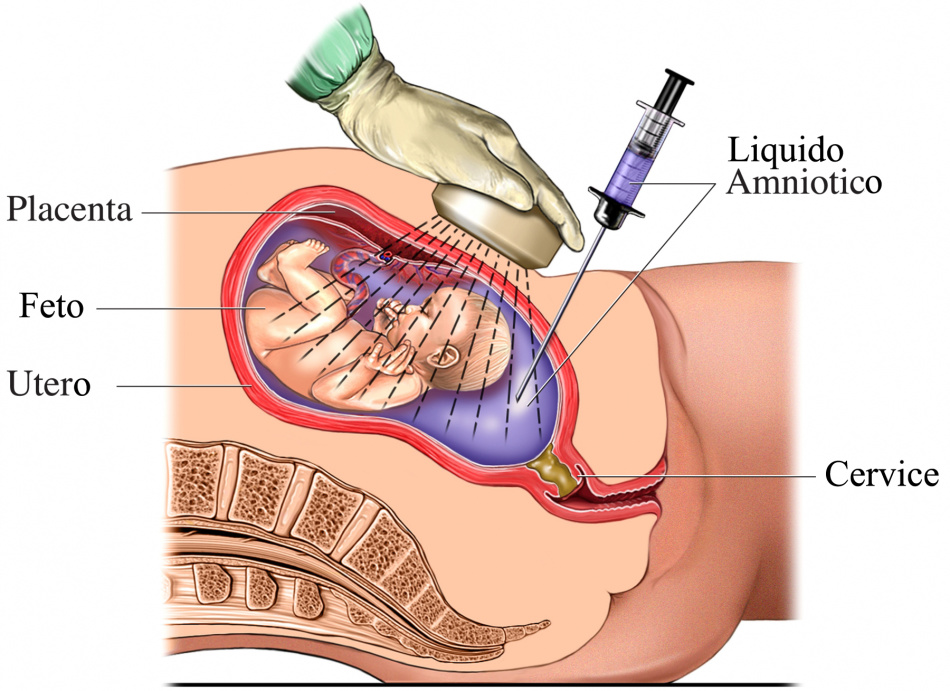
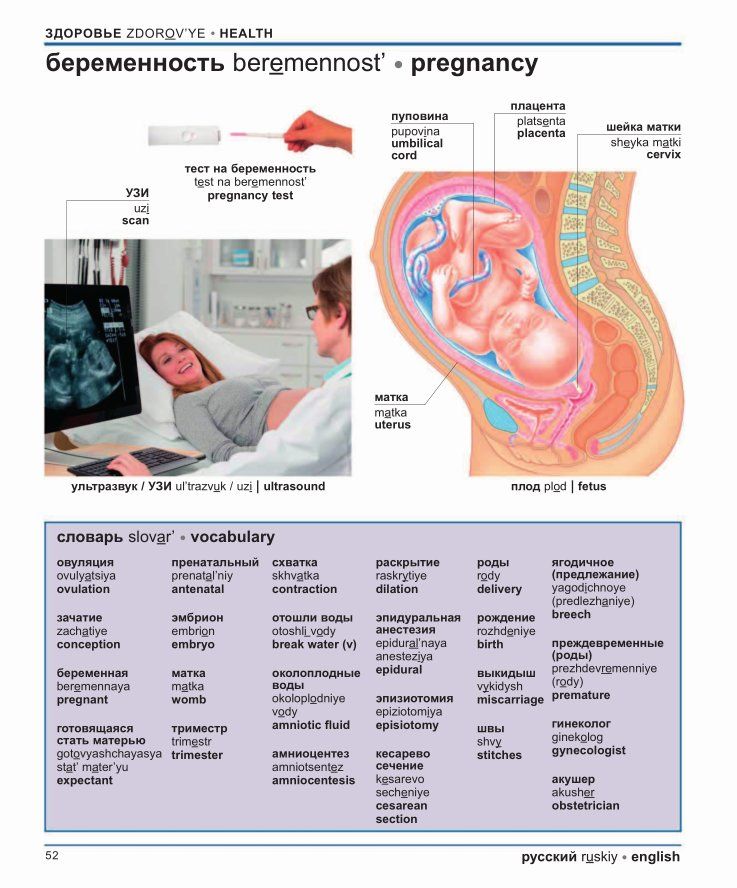
Read the full fact sheet- Amniocentesis is a prenatal procedure performed on a pregnant woman to withdraw a small amount of amniotic fluid from the sac surrounding the fetus.
- The goal of amniocentesis is to examine a small amount of this fluid to obtain information about the baby, including its sex, and to detect physical abnormalities such as Down syndrome or spina bifida.
- Amniocentesis is only performed on women thought to be at higher risk of delivering a child with a birth defect.
Amniocentesis is a prenatal procedure that your doctor may recommend you have during pregnancy. The test checks for fetal abnormalities (birth defects) such as Down syndrome, cystic fibrosis or spina bifida. In most cases, the results are normal.
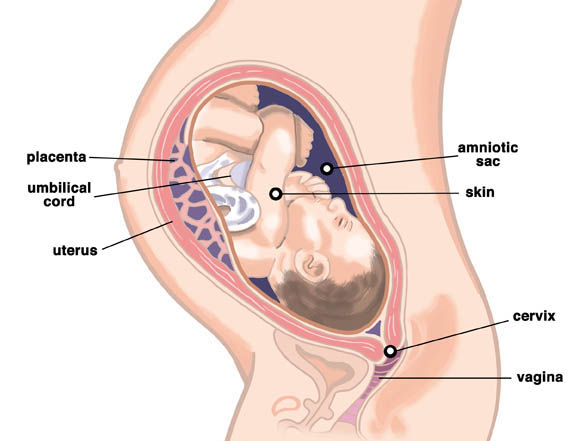
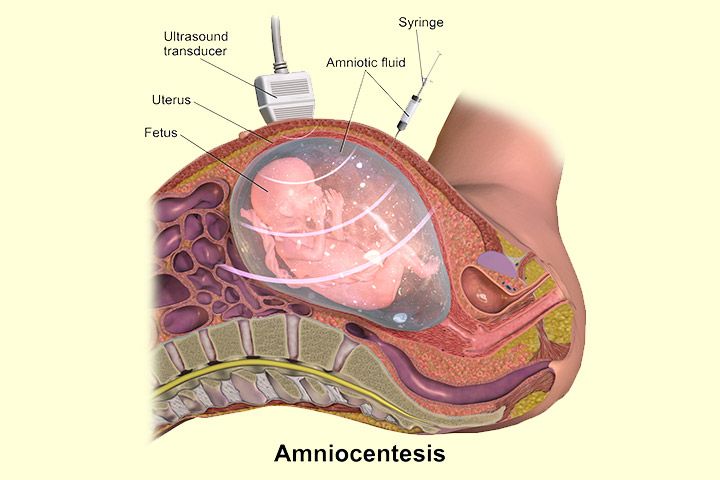
Amniocentesis is performed between 16 and 20 weeks into the pregnancy. By around this time, the developing baby is suspended in about 130ml of amniotic fluid, which the baby constantly swallows and excretes. A thin needle is used to withdraw a small amount of this fluid from the sac surrounding the fetus.
The fluid is examined to obtain information about the baby – including its sex – and to detect physical abnormalities such as Down syndrome or spina bifida. Amniotic fluid samples can also be DNA tested to identify a range of genetic disorders, such as cystic fibrosis and fragile X syndrome.
Amniotic fluid samples can also be DNA tested to identify a range of genetic disorders, such as cystic fibrosis and fragile X syndrome.
Amniocentesis is only performed on women thought to be at higher risk of delivering a child with a birth defect. Discuss with your doctor or obstetrician whether amniocentesis is right for you.
Problems detected by amniocentesis
Amniocentesis can detect a number of chromosomal and other birth abnormalities in a developing fetus. These include:
- Down syndrome
- Neural tube defects, such as spina bifida
- Genetic disorders – amniotic fluid samples can be DNA tested to identify a range of genetic disorders, such as cystic fibrosis and fragile X syndrome.
Women who may benefit from amniocentesis
As a woman grows older, the risk of having a child with Down syndrome begins to increase significantly – from about one in 2,000 (at age 20 years) to one in 100 (at 40 years).
Pregnant women who may be candidates for amniocentesis include:
- Women over the age of 40 years (Victorian women aged 37 years and over are routinely offered this test)
- Women with a family history of chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome
- Women who have already had children with chromosomal abnormalities
- Women known to be carriers of genetic disorders
- Women with partners who have a family history of a genetic disorder or chromosomal abnormality
- Women who return an abnormal 'serum screen' blood test or ultrasound examination result.

The amniocentesis procedure
Before having amniocentesis, it is usual for the woman and her partner to be counselled on the risks of the procedure. The entire procedure takes about 90 minutes.
Steps involved in amniocentesis:
- The woman lies down and the position of the fetus and the placenta are determined by an ultrasound scan.
- When the doctor is sure of a safe spot, they swab the woman's belly with antiseptic and inject a local anaesthetic into the skin.
- Using a long, thin needle, the doctor extracts about 15 to 20ml (approximately three teaspoons) of amniotic fluid. This takes about 30 seconds.
- The fetus is checked afterwards to make sure all is well.
The doctor will advise when the results are expected. In some cases, the results may take up to three weeks.
Immediately after amniocentesis
You may need to wait in the surgery for around 20 minutes before leaving for home. Most women find amniocentesis to be painless, although it is recommended to continue resting for an hour or so afterwards.
Side effects of the procedure may include:
- Mild discomfort
- Slight bruising at the injection site.
Complications of amniocentesis
While amniocentesis is generally considered a safe procedure, possible complications may include:
- Infection – symptoms include fever. Contact your doctor immediately.
- Vaginal leakage – amniotic fluid may leak from the vagina (in about one per cent of cases). Contact your doctor for reassurance. In most cases, the leakage slows and stops within two days.
- Spontaneous abortion – can occur in less than one per cent of women undergoing this test. Exact figures are hard to calculate, since some miscarriages would have happened anyway, with or without the amniocentesis.
- Rh sensitisation – rarely, the baby’s blood cells may enter the mother’s bloodstream. If the mother is Rh negative, she may form antibodies that attack the baby’s red blood cells.
 To prevent this, an Rh negative mother will be given Rh(D) immunoglobulin (anti-D). Injury to the baby – very rarely, the needle used during the procedure may accidentally touch some part of the baby's body.
To prevent this, an Rh negative mother will be given Rh(D) immunoglobulin (anti-D). Injury to the baby – very rarely, the needle used during the procedure may accidentally touch some part of the baby's body.
Taking care of yourself at home
Most women feel fine after the procedure and no alteration to normal routine is necessary. However, it is generally advised that you take it easy for the next couple of days.
Long-term outlook after amniocentesis
Amniocentesis rarely causes harm to either the mother or her baby in the long term. Complications following amniocentesis are very rare. However, if you experience unusual symptoms, such as bleeding from your vagina, seek medical attention promptly.
Where to get help
- Your doctor
- Obstetrician
- Gynaecologist
Things to remember
- Amniocentesis is a prenatal procedure performed on a pregnant woman to withdraw a small amount of amniotic fluid from the sac surrounding the fetus.

- The goal of amniocentesis is to examine a small amount of this fluid to obtain information about the baby, including its sex, and to detect physical abnormalities such as Down syndrome or spina bifida.
- Amniocentesis is only performed on women thought to be at higher risk of delivering a child with a birth defect.
Give feedback about this page
Was this page helpful?
More information
Content disclaimer
Content on this website is provided for information purposes only. Information about a therapy, service, product or treatment does not in any way endorse or support such therapy, service, product or treatment and is not intended to replace advice from your doctor or other registered health professional. The information and materials contained on this website are not intended to constitute a comprehensive guide concerning all aspects of the therapy, product or treatment described on the website.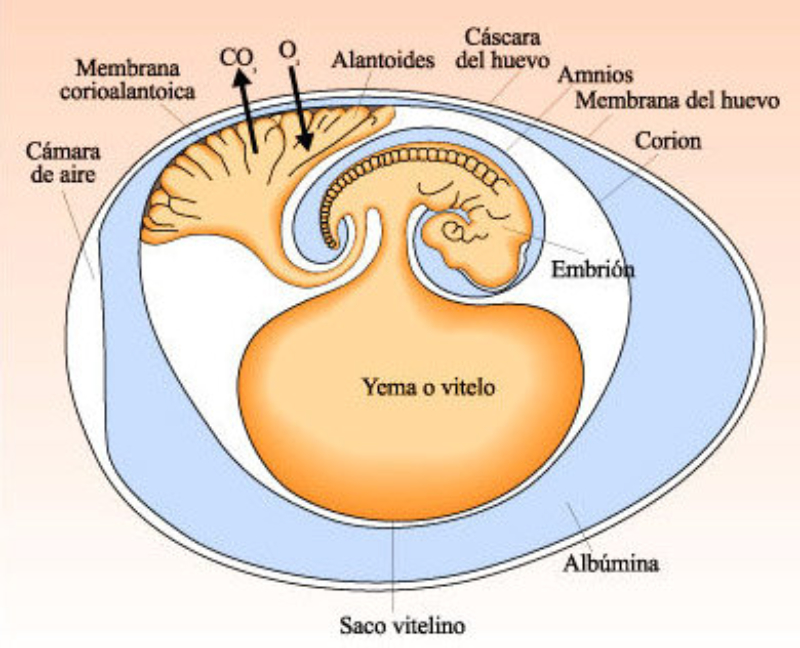 All users are urged to always seek advice from a registered health care professional for diagnosis and answers to their medical questions and to ascertain whether the particular therapy, service, product or treatment described on the website is suitable in their circumstances. The State of Victoria and the Department of Health shall not bear any liability for reliance by any user on the materials contained on this website.
All users are urged to always seek advice from a registered health care professional for diagnosis and answers to their medical questions and to ascertain whether the particular therapy, service, product or treatment described on the website is suitable in their circumstances. The State of Victoria and the Department of Health shall not bear any liability for reliance by any user on the materials contained on this website.
Reviewed on: 20-06-2016
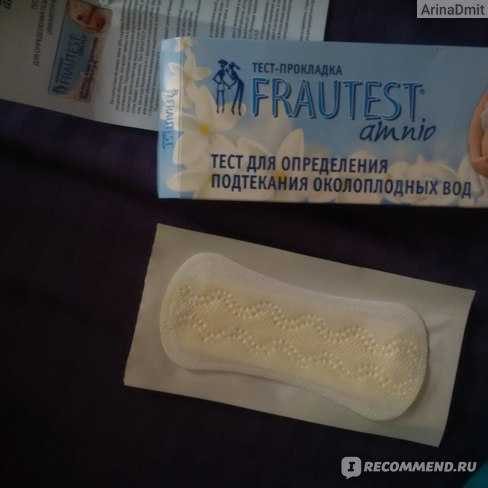
AmnioQuick amniotest (determination of amniotic fluid leakage)
← Back to catalog
The AmnioQuick amniotest is a rapid amniotic fluid leak test used to detect ruptured membranes in pregnant women.
The amniotic fluid that surrounds the fetus in the amniotic sac of the uterus can leak, which is a potential threat to the continuation of the pregnancy and infection. Rupture of membranes can occur at any stage of pregnancy, especially in the third trimester when the fetus is large enough to press on the cervix.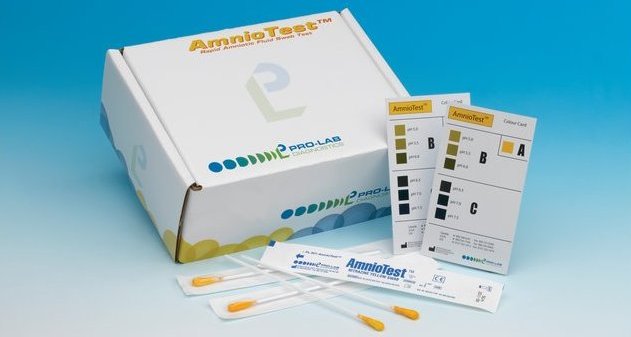 The amniotic fluid has no color or smell, so the pregnant woman herself cannot accurately recognize the leak. For this, a rapid test is used.
The amniotic fluid has no color or smell, so the pregnant woman herself cannot accurately recognize the leak. For this, a rapid test is used.
Benefits of using AmnioQuick
Laboratory express test for amniotic fluid leakage allows you to determine the presence of amniotic fluid in the vaginal discharge even with a small amount in a few minutes, diagnose the rupture of the membranes and take measures to preserve the pregnancy.
The principle of the test can be compared to a pregnancy test - two lines mean a positive result.
The AmnioQuick test has the following advantages over other methods:
- the result is ready in 10 minutes;
- easy to use - does not require insertion of a speculum into the vagina to collect a sample of secretions;
- exact result;
- detects subclinical ruptures of membranes even without symptoms of leakage;
- high sensitivity to reagents;
- does not require decryption.

Performing the procedure
The AmnioQuick test is performed on a gynecological chair or on a couch. A tampon is gently and shallowly inserted into the vagina, which absorbs the secretions. A swab with a sample of secretions is placed in a container with a reagent. The secretions dissolve in the reagent within 1 minute, after which the swab is removed and discarded. The resulting solution is used to conduct a rapid test.
Interpretation of results
The presence of amniotic fluid in the solution is determined by the presence of IGFBP-1 protein in it. Its high concentration in the liquid indicates the release of amniotic fluid into the vagina.
A positive result is transmitted in the form of two strips: one strip is responsible for the test result, the second is the control.
The maximum response time is 15 minutes.
Indications for testing
AmnioQuick is recommended at any stage of pregnancy.
A gynecologist prescribes an examination if there are such complaints:
- feeling of leakage of fluid from the vagina when changing the position of the body sitting or lying down, when lifting weights;
- watery discharge when moving;
- Sensation of fluid leakage that cannot be stopped by contraction of the pelvic floor muscles.
The pregnant woman does not experience other symptoms, so she should pay attention to wet underwear with a liquid similar to water and consult a doctor in a timely manner. Rupture of the amniotic membrane leads to the penetration of infections to the fetus.
Examination preparation
No preparation required.
No contraindications.
- Code:
-
9
- Price:
-
2500 R.
Offices providing this service
field servicefield service
-
Belomorskaya
st.
 Petrozavodskaya, 24, bldg. 2
Petrozavodskaya, 24, bldg. 2 -
Dmitry Donskoy Boulevard
st. Grina, 30
-
Buninskaya alley
Residential complex Buninsky meadows, st.
 Alexandra Monakhova, d. 88, bldg. 3
Alexandra Monakhova, d. 88, bldg. 3 -
Water Stadium
Golovinskoye shosse, 7
-
Kaluga
st.
 Khersonskaya, 17
Khersonskaya, 17 -
Lermontovsky Avenue
Zhulebinsky Boulevard, 10/6
-
Lefortovo
st.
 Soldatskaya, 3, room. 1
Soldatskaya, 3, room. 1 -
Lomonosovsky prospect
st. Mosfilmovskaya, 17/25
-
Nakhimovsky prospect
Nakhimovsky prospect, 22
-
New Cheryomushki
Leninsky Avenue, 89/2
-
Ryazansky prospect
Ryazansky prospect, 38
-
Sevastopolskaya
st.
 Malaya Yushunskaya, 3
Malaya Yushunskaya, 3 -
Stakhanovskaya
2nd Grayvoronovsky passage, 44, bldg. 1
-
Textile workers
st.
 Lyublinskaya, d. 9, bldg. 1
Lyublinskaya, d. 9, bldg. 1 -
Skobelevskaya Street
st. Polyany, d. 5A, bldg. 1
-
University
Lomonosovsky prospect, 23
-
Frunzenskaya
Komsomolsky prospect, 28
-
Cherkizovskaya
st.
 Amurskaya, d. 1a, bldg. 3
Amurskaya, d. 1a, bldg. 3
Consult a specialist for possible contraindications
Amniotic fluid leakage test (AMNIOTEST™)
The AmnioTest™, also referred to as the amniotic fluid leakage test, is a one-time amniotic fluid leakage test.
Determination of rupture of the amniotic sac is carried out by determining the pH level in the posterior third of the vagina. Test na podtekanie okoloplodnyh vod - AmniTest_upakovka Amniotic fluid (amniotic fluid) has an acidity above 6.5. The pH level in the posterior third of the vagina, equal to or higher than pH = 6. 5, indicates the penetration of amniotic fluid.
5, indicates the penetration of amniotic fluid.
The AmnioTest is to detect a protein that is found in water and is absent from all other secretions. A cytological study makes it possible to detect fern-like crystals in the secretions, which are also found in the amniotic fluid and are absent in other fluids.
Amniotic fluid leakage test The AmnioTest is used most often in late pregnancy. As the fetus develops and enlarges, the bladder may become compressed and forced to empty more frequently. In addition, a pregnant woman may have various vaginal discharges that are not a pathology and a threat to pregnancy. Or maybe premature leakage of amniotic fluid, which is a serious threat to the life and health of the child. Testing of the fluid secreted from the vagina is necessary to establish its nature and determine the presence or absence of amniotic fluid in it. With the timely Test na podtekanie okoloplodnyh vod - AmniTest foto detection of amniotic fluid leakage and contacting a specialist, a number of measures are taken to identify the cause of leakage: analysis of amniotic fluid and urine, ultrasound of pregnancy and visual examination, and then measures are taken to save the life and health of the child.
AmnioTest is a quick and informative method for diagnosing ruptured bladder membranes in pregnant women.
AmnioTest consists of disposable swabs impregnated with nitrazine yellow, each test in a separate package.
Amniotic fluid test sterile, sterilized by gamma irradiation.
AmnioTest instructions for use:
To perform the test, the cervix is exposed using a vaginal speculum. Under visual control, a test with nitrazine - yellow is carefully injected into the posterior fornix or the external cervical os is touched for at least 15 seconds. Carefully remove the test and immediately determine its staining. To do this, use the standard color palette on the color card attached to the test.
To be used only under specialist supervision.
Storage at 15 to 30 C
Shelf life: 3 years in a cardboard box.
Amniotest (diagnosis of fetal water leakage) No. 20
Amniotest (diagnosis of fetal water leakage) No. 25
Amniotest (diagnosis of fetal water leakage) No.