Can urinating frequently be a sign of pregnancy
Causes and what to do
Urinating more frequently than normal is common during pregnancy. As a standalone symptom, it is not a cause for concern, but a pregnant person should consult their doctor if they experience pain while urinating or other symptoms of a urinary tract infection (UTI).
Frequent urination is a common early sign of pregnancy. Urinary frequency initially occurs due to increased levels of the hormones progesterone and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
While some pregnant people may experience mild changes, others may feel the need to continuously run to the bathroom throughout the day and night.
Frequency can also reappear later in the pregnancy as the uterus and baby continue to grow, creating pressure on the bladder.
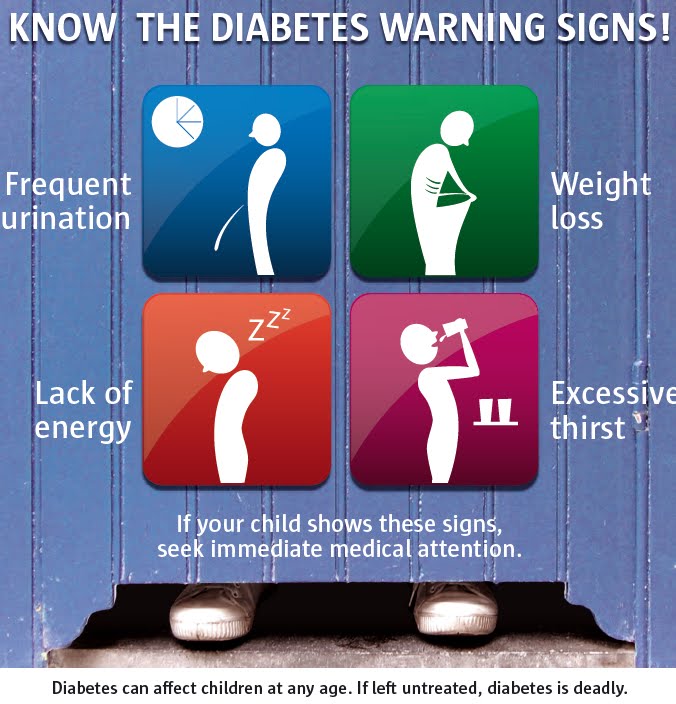
Pregnant people who have a fever or chills, or notice a burning sensation while urinating, should seek immediate medical attention as it could be a urinary tract infection (UTI). Other symptoms may include back pain or a sharp increase in the need to urinate in a small period of time.
In this article, we discuss the causes and symptoms of frequent urination during pregnancy, how to manage and prevent frequent urination, how long it lasts, and outlook.
Although symptoms may vary from person to person, many pregnant people notice they begin to need to urinate more frequently during their first trimester (week 1 to week 12). Some people may also experience leakage or stress urinary incontinence (SUI) while pregnant as the fetus grows and presses down on the bladder, urethra, and pelvic floor muscles.
The Office on Women’s Health notes that leakage may occur when:
- sneezing
- coughing
- laughing
- exercising
- lifting something
- walking
Sometimes urinary frequency symptoms indicate an underlying condition, such as a UTI — an infection of the urinary system.
In addition to urgency, other symptoms of a UTI include:
- blood in the urine
- cloudy or foul-smelling urine
- lower abdominal pain
- nausea
- pain or burning when urinating
- loss of bladder control
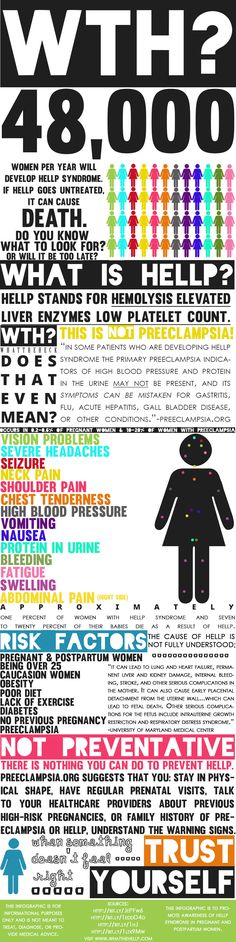
Pregnant people are at increased risk for UTIs.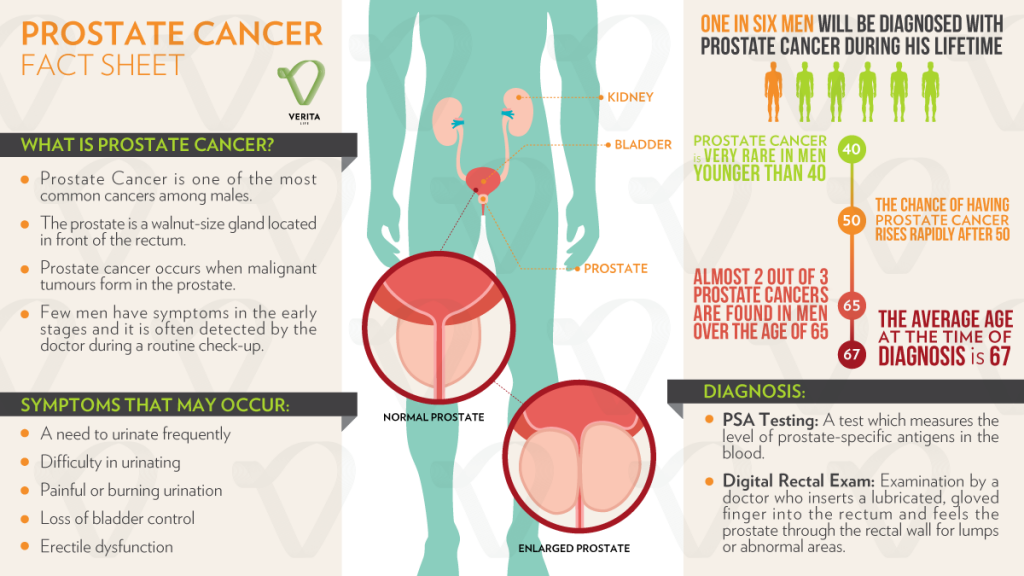 According to one study from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately 8% of pregnant people develop a UTI.
According to one study from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately 8% of pregnant people develop a UTI.
If left untreated, a UTI can pose a serious health risk to a pregnant person and their developing fetus.
Doctors can often diagnose urinary frequency based on a person’s symptoms. In addition to doing a physical examination, they may ask a series of questions about how often the person is going to the restroom and how much they are urinating with each trip.
They may also ask about:
- changes in the smell, color, or consistency of the urine
- daily fluid consumption
- the pattern of frequency (i.e. when it started and what time of day symptoms occur)
If a doctor suspects that the symptoms are not pregnancy-related, they may order one or more diagnostic tests.
Tests may include:
- urinalysis
- ultrasound
- cystoscopy
- bladder stress test
- sexually transmitted infection (STI) tests
Frequent urination is an early sign of pregnancy and can begin as early as the first couple of weeks following conception.
Most people, however, may begin to experience urgency in weeks 10 to 13, as this is when the uterus begins to push on the bladder.
After an embryo implants in the uterus, the body produces progesterone and hCG, both of which are pregnancy hormones that can lead to urgency.
During pregnancy, the body’s blood supply increases to support the fetus. Approximately 20–25% of a person’s blood filters through the kidneys and leaves the body as waste or urine. The more blood a person’s body produces, the harder their kidneys have to work to flush the extra fluid.
Pressure is another contributing factor. As the uterus expands, it pushes down on the bladder, urethra, and pelvic floor muscles, increasing the urge to urinate.
Pelvic floor exercises, also known as Kegel exercises, can strengthen the muscles of the pelvis and urethra and support the bladder. Performing Kegel exercises during pregnancy may help some people regain control over their urine flow.
Kegel exercises are safe to perform during pregnancy and after childbirth.
To perform Kegel exercises, empty the bladder and then follow these steps:
- Relax the abdomen, chest, thighs, and buttocks.
- Tighten the pelvic floor muscles and hold for 5 to 10 seconds.
- Relax the muscles for 5 to 10 seconds.
- Repeat 10 times.
The National Association for Continence (NAFC) recommends doing 10 repetitions three times per day.
Staying hydrated by drinking eight to 12 cups of water per day is vital during pregnancy. However, there are a few things a pregnant person can do to ease the flow, including:
- cutting down on fluids before bed
- avoiding caffeinated drinks
- leaning forward when urinating
- keeping a bladder journal or recording bathroom breaks
The average person goes to the bathroom between 6 and 7 times per day, though this number can vary depending on what the person drinks and how often.
Urinating between four and 10 times per day can also be “normal” as long as the person is healthy and comfortable with how often they visit the restroom.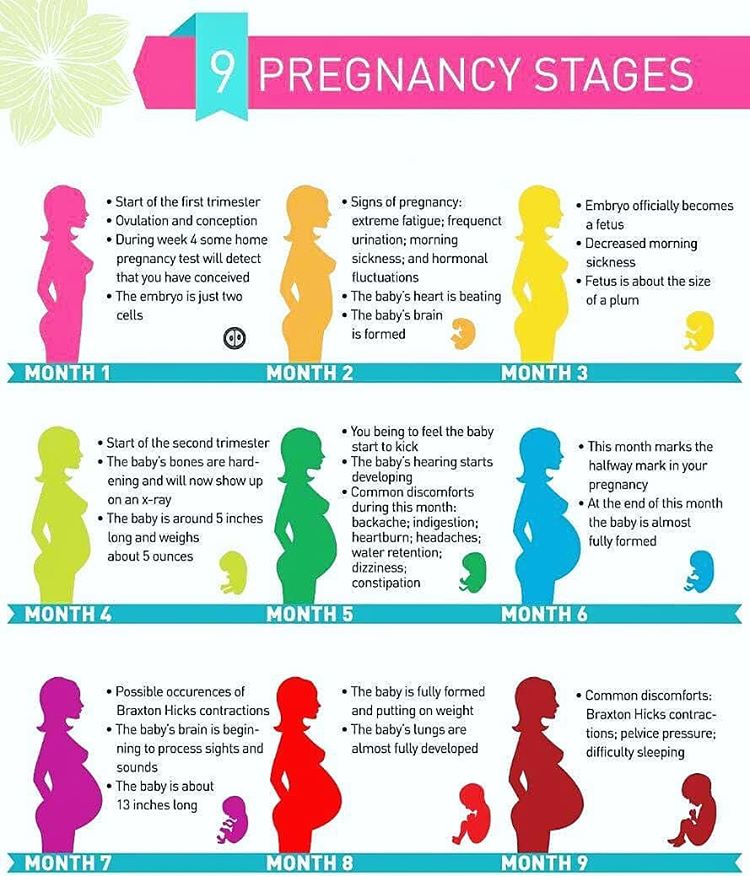
For pregnant people, this number will depend on the individual’s “normal.” For example, if a person typically uses the restroom eight times per day, becoming pregnant may increase their visits to 10 times per day.
Pregnancy-related urinary frequency may ease up in the second trimester but usually returns in the final weeks of the pregnancy. Once the baby is born, a more frequent than usual urge to go to the bathroom should go away.
Frequent urination is a normal pregnancy symptom. However, it also can be a sign of an underlying condition that may require medical treatment.
Pregnant people who show additional symptoms of a UTI, including painful urination, should contact their doctor as soon as possible.
Frequent urination is a part of being pregnant and should resolve after childbirth.
However, some pregnant people may experience symptoms up to six weeks after giving birth.
Pregnant people who experience pain with urination or who are still having bladder problems following birth should make an appointment to see their doctor.
Many people experience urinary frequency during pregnancy, especially in the first and third trimesters.
Unless the frequency is accompanied by burning or painful urination, or other potential signs of a UTI, there is usually no need for concern.
Urinary frequency generally will subside once the baby is born.
Frequent Urination During Pregnancy | Pampers
You may be wondering whether peeing a lot is a sign of pregnancy or whether this urge to pee so often will ever go away. Frequent urination is a common early pregnancy symptom, but it can also reappear later on during pregnancy as your uterus and baby grow, putting pressure on your bladder. Although it can definitely be annoying, in most cases, it's nothing to worry about. Read on to find out what causes frequent urination during pregnancy, get some tips to help you manage it, and learn the signs that indicate it may be linked to another condition, like a urinary tract infection.
What Causes Frequent Urination During Pregnancy?
What makes you need to pee more is often the increased amount of blood in your body. To process this blood flow, your kidneys need to produce extra fluids, which then end up in your bladder. Although peeing often during pregnancy is annoying, it's also a normal and common pregnancy symptom. Here are some frequently asked questions about this symptom:
To process this blood flow, your kidneys need to produce extra fluids, which then end up in your bladder. Although peeing often during pregnancy is annoying, it's also a normal and common pregnancy symptom. Here are some frequently asked questions about this symptom:
What is considered frequent urination in pregnancy? There's no set number of visits to the bathroom – it's simply needing to go more often than you usually would.
When does frequent urination start during pregnancy? How soon it may start differs for each woman, but you may find yourself needing to pee more often from around six to eight weeks of pregnancy.
Will I need to pee this often the whole pregnancy? It may ease up for a while after you enter the second trimester, but you may find the increased urge to pee returns later on, as your growing baby places more pressure on your bladder. Toward the end of the third trimester, when your baby “drops," the extra pressure on your pelvis and bladder might have you rushing to pee even more frequently.
How often should you pee? Whenever you have to! It's better not to hold it in.
Tips to Manage Peeing Often While Pregnant
You can't really avoid more frequent urination, and you really wouldn't want to, as it's a natural consequence of drinking lots of fluids to stay well hydrated and healthy during pregnancy. Here are some tips that might help make your life easier:
Lean forward when you pee so that you properly empty your bladder
To prevent increased urination at night, try not to drink too much water just before going to bed
Avoid beverages and foods containing caffeine, which can make you need to pee more often. (Read our article to find out more about what not to eat or drink while you're pregnant.)
Practice Kegel exercises to strengthen your pelvic floor muscles, as this can help prevent leaking when you cough, sneeze, or laugh, both before and after giving birth.
 (If you do find yourself peeing when you sneeze, consider wearing a panty liner.)
(If you do find yourself peeing when you sneeze, consider wearing a panty liner.)If your urine is dark yellow or orange, this may be a sign of dehydration − try to increase your fluid intake until your urine is back to a normal pale yellow
If you're heading out the door, or you know you're going into a long meeting, consider one more dash to the toilet beforehand. You can also try to scout out where the nearest bathroom so you're not caught off guard.
Can Pregnancy Peeing Be a Sign of a Problem?
More frequent urination is usually a normal pregnancy symptom. However, sometimes it can be a sign of a medical condition that may require treatment by your healthcare provider. These conditions include:
Urinary tract infection (UTI). Many women wonder whether frequent urination is part of pregnancy or a UTI. If it's a UTI, you may notice a painful, burning sensation while peeing, have a fever, notice cloudy urine, or see blood in the toilet.
 You may also feel the strong urge to pee, but then only a few drops will come out. Pregnant women face an increased risk of UTI from week 6 to week 24, because the growing uterus can place pressure on the urinary tract, increasing the chance of bacterial infections. If you suspect you have a UTI, consult your healthcare provider, as this infection requires treatment – often antibiotics.
You may also feel the strong urge to pee, but then only a few drops will come out. Pregnant women face an increased risk of UTI from week 6 to week 24, because the growing uterus can place pressure on the urinary tract, increasing the chance of bacterial infections. If you suspect you have a UTI, consult your healthcare provider, as this infection requires treatment – often antibiotics.Gestational diabetes. Frequent urination can sometimes be a sign of gestational diabetes, generally a temporary form of diabetes that affects a small percentage of moms-to-be. Healthcare providers usually test for gestational diabetes between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. If gestational diabetes is treated, then the baby's health isn't adversely impacted, and the diabetes will usually go away after you give birth. If you notice symptoms like frequent urination combined with persistent thirst, nausea, or fatigue, consult your healthcare provider.
Frequent urination during early pregnancy is common and usually nothing to worry about. Although it may feel as if you are peeing all the time, keep in mind that it may ease up for a time, before returning later on. Once your baby is born, your urge to pee more often should go away, and you'll only have your newborn's pee to worry about!
Although it may feel as if you are peeing all the time, keep in mind that it may ease up for a time, before returning later on. Once your baby is born, your urge to pee more often should go away, and you'll only have your newborn's pee to worry about!
Are you pregnant? Early signs of pregnancy.
Finally! Your period is delayed. If you want a baby, there is great hope that you will get pregnant this time. A pregnancy test will soon show you more. At the same time, you can observe yourself - perhaps you have already noticed any changes. Your body usually clearly shows you that fertilization has taken place. Most of the symptoms are associated with an increase in hormone levels.
Of course, not every sign means you are pregnant. But the more typical symptoms you notice, the more likely it is. However, in the end, only a doctor can make the final decision: "You're pregnant - congratulations!"
Share this information
Uncertain early signs of pregnancy
The first signs of pregnancy are as varied as they are vague. Often the early signs of pregnancy appear even before the missed period. These Could Be Early Pregnancy Symptoms:
Often the early signs of pregnancy appear even before the missed period. These Could Be Early Pregnancy Symptoms:
- nausea and vomiting
- “lead” fatigue and fatigue
- frequent urination
- increased traction for food and unusual food addictions
- sensitive breasts and darkened nipples
- change in the oscillatory and taste
- spasms - cramps - cramps in the abdomen, slight bleeding and discharge
- Growth of hair and nails
- Skin changes
- Forgetfulness
- Mood swings
- Bloating or constipation
- Bad sleep
Nausea and vomiting
You've seen the most famous first sign of pregnancy a thousand times in the movies: the heroine runs away in a hurry, she suddenly feels sick. She doesn't know she's having a baby yet, but everyone in the movie theater has already taken the hint.
In fact, nausea is not so typical. Some women feel very ill, others tend to feel a little sick.
"Lead" tiredness and fatigue
Are you as tired during the day as if you had sat up all night? The sofa is calling you at noon, and your eyes start to close as if by magic? A huge need for sleep is one of the most common signs of pregnancy. If you notice unusual tiredness or fatigue, you may be pregnant.
Frequent urination
You constantly have to run to the toilet, even if you do not drink more than usual. This can be another early sign of pregnancy: once the embryo is implanted, the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is released, which makes you go to the toilet more often.
Food cravings and unusual eating habits
Is your body just screaming for chocolate or would you get up at night to buy greasy chips at the gas station? Or do you have other unusual eating habits ? Bingo! It is possible that you are pregnant. Many women report strange eating habits as early signs of pregnancy : for example, they pour hot salsa straight out of a can or, being vegans, feel an irresistible craving to bite straight from a stick of hearty salami.
Sensitive breasts and darkened nipples
Your breasts may also show early signs of pregnancy. Pay attention to the following symptoms: the breast begins to thicken and fill up, as before menstruation. To the touch, the mammary glands are more plump and large and very sensitive to touch. Your areola often looks darker than usual. The opposite symptom - discoloration - can also be caused by a hormonal imbalance or a previous pregnancy.
Changes in smell and taste
Every day you find that detergent smells unbearably . Or you complain to your husband that he has been bathing in cologne lately. Are you familiar with this? Hypersensitivity to odors is commonly observed in early pregnancy. Some women get a strange metallic taste in their mouths . Another early sign of pregnancy can also be a sudden aversion to alcohol or tobacco.
Abdominal cramps, slight bleeding and discharge
Pulling in the abdomen, as if menstruation is about to begin. You think disappointedly: "It didn't work out with the child again!". Or you even notice a small spot or highlights. But day after day passes, and there are still no periods. Then these symptoms may be early signs of pregnancy. These symptoms are usually harmless and are caused by the implantation of a fertilized egg in the uterus. If you want to be on the safe side, try not to strain yourself and avoid exercise. If you notice anything unusual, see your doctor.
You think disappointedly: "It didn't work out with the child again!". Or you even notice a small spot or highlights. But day after day passes, and there are still no periods. Then these symptoms may be early signs of pregnancy. These symptoms are usually harmless and are caused by the implantation of a fertilized egg in the uterus. If you want to be on the safe side, try not to strain yourself and avoid exercise. If you notice anything unusual, see your doctor.
Elevated basal body temperature
You can find out if you are pregnant by regularly measuring your basal body temperature: if in the morning after waking up for eighteen days your temperature is higher than usual , then most likely you are pregnant.
When do the early signs of pregnancy appear?
It is impossible to say exactly in which week of pregnancy certain symptoms of pregnancy appear. When the first signs of pregnancy appear and whether they appear at all depends on the individual woman. However, the early symptoms of pregnancy can be roughly attributed to the following weeks.
However, the early symptoms of pregnancy can be roughly attributed to the following weeks.
4th week: implantation pain and slight bleeding, breast tenderness.
5th and 6th week: mood swings, fatigue, hunger, nausea and vomiting
7th and 8th week: nausea, circulation problems, dizziness, low blood pressure, insomnia , frequent urination,
9th and 10th weeks: breast changes, nausea, shortness of breath
11th and 12th weeks: bloating, constipation
The three surest signs of pregnancy
There are many early symptoms of pregnancy, but the surest signs of how to understand that you are still pregnant:
1. Cessation of menstruation.
This is the surest sign of pregnancy. Sometimes stress, hormonal fluctuations or an organic disease are to blame, but it is better to take a pregnancy test.
2. You suffer from nausea.
You suffer from nausea.
A few days after conception, you may feel slightly unwell. Some women experience nausea only in the morning (morning sickness), others more frequently during the day. This is caused by the pregnancy hormone, human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
3. Your pregnancy test is positive.
Congratulations! - then rather contact your gynecologist and start looking for an obstetrician-gynecologist for childbirth.
Remember: If anything seems unusual, see a doctor as soon as possible. Even if the pregnancy test is positive, make an appointment with your doctor.
First signs of pregnancy | Kotex®
Although pregnancy tests and ultrasound are the only ways to accurately determine pregnancy, there are a number of signs and symptoms to watch out for. The first signs of pregnancy include not only the absence of a period, but may also include fatigue, sensitivity to smells, and morning sickness. It is worth remembering that these are POSSIBLE signs of pregnancy, they can appear in both pregnant and non-pregnant women and are associated with ovulation and menstruation.
It is worth remembering that these are POSSIBLE signs of pregnancy, they can appear in both pregnant and non-pregnant women and are associated with ovulation and menstruation.
When do symptoms appear?
Oddly enough, the first week of pregnancy is determined by the date of the last menstruation.
Your last period counts as the first week of pregnancy, even if you haven't actually been pregnant yet. The estimated due date is calculated from the first day of your last period.
Taking a home pregnancy test is the cheapest and easiest way to find out if you're pregnant. Remember that home pregnancy tests measure the level of a hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in the urine, and there is usually less of it in urine than in blood.
The test gives the most accurate results from the moment of missed menstruation.
The menstrual cycle is considered delayed if the menstruation did not begin within 5 or more days after the day of their expected start.
However, it is worth remembering that even the day after the expected delay, more than a third of women will give a negative result from such home tests, and if you test too early, the result can be negative, even if you are already pregnant. You can do another test at home after a couple of days to get a more accurate result.
Signs and symptoms of pregnancy
If you are pregnant for the first time, then you may not notice these first signs of pregnancy or confuse them with symptoms of impending menstruation.
It is not worth spending long hours looking for answers on the forums in experiences, in any case, your research will not change what has already happened or has not happened, but mood and sleep can thoroughly spoil.
Slight lower abdominal pain and spotting
Absence of menstruation
Fatigue
Nausea
Breast swelling
Frequent urination
Constipation
Vertigo on motion
Mood swings
Temperature changes
High blood pressure
Pain and slight bleeding
From weeks 1 to 4, changes in a woman's body are still happening at the cellular level. A fertilized egg creates a group of cells filled with fluid, which is called a blastocyst, which, after pregnancy, will have to turn into organs and body parts of the fetus.
A fertilized egg creates a group of cells filled with fluid, which is called a blastocyst, which, after pregnancy, will have to turn into organs and body parts of the fetus.
Approximately 10-14 days after conception (4 weeks), the blastocyst attaches itself to the endometrium lining the uterine wall. This process can cause some bleeding, which can be confused with light menstruation.
Here are some signs of such bleeding:
-
color can be red, pink or brown
-
bleeding: usually comparable to normal menstruation, usually lighter
-
painful sensations
-
usually lasts about three days
No period
After the blastocyst attaches to the walls of the uterus, the body begins to produce a hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin, which tells the body that it is time to stop releasing eggs from the ovaries every month.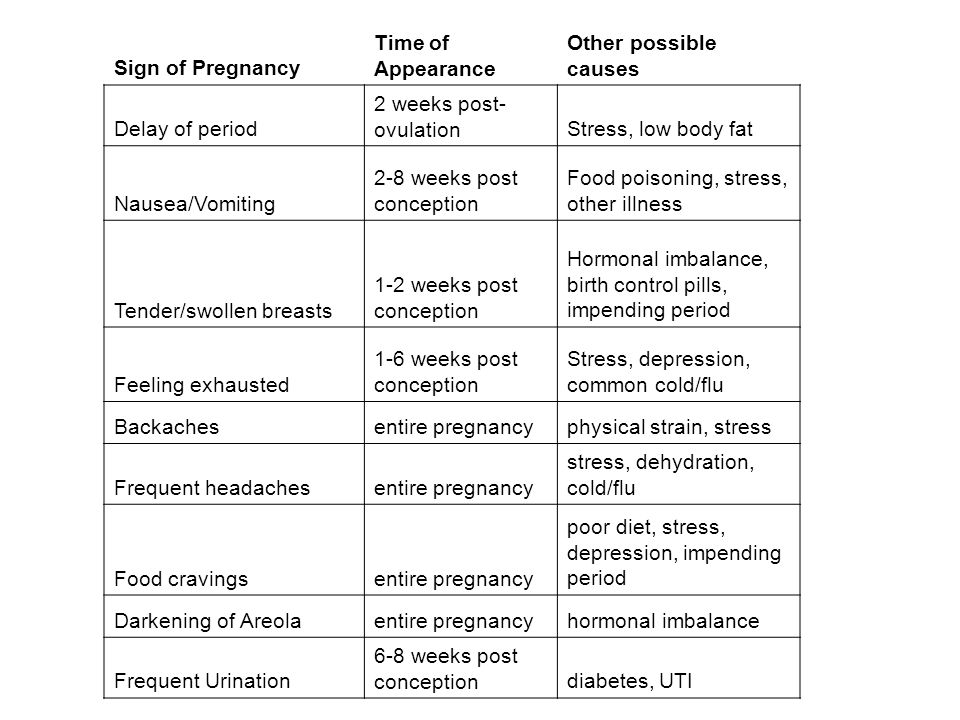 Most often, after conception, menstruation disappears at 4 weeks of pregnancy.
Most often, after conception, menstruation disappears at 4 weeks of pregnancy.
If you're late, it's worth taking a home pregnancy test, especially if you have irregular periods.
Fatigue
Fatigue may appear at any time during pregnancy. During pregnancy, progesterone levels rise, and this hormone can make you feel sleepy. If you feel tired, then make sure you get enough sleep.
Morning sickness and vomiting
Nausea and morning vomiting usually develop between 4 and 6 weeks of gestation. In fact, such symptoms can occur not only in the morning, but in general at any time of the day. This symptom is typical for the first 12 weeks of pregnancy. If you often feel sick, then you need to make sure that you drink enough water to avoid dehydration.
Breast swelling and tenderness
Breast changes may begin at 4-6 weeks of gestation. They are also associated with changes in hormone levels. Most often, the breast swells somewhat and becomes more sensitive than usual. Usually these symptoms disappear in the future, when the body gets used to the changed hormonal background.
They are also associated with changes in hormone levels. Most often, the breast swells somewhat and becomes more sensitive than usual. Usually these symptoms disappear in the future, when the body gets used to the changed hormonal background.
Frequent urination
During pregnancy, blood flow increases and this causes the kidneys to process more fluid than usual, which can cause frequent urination even in the early stages of pregnancy.
Constipation and bloating
This symptom is similar to the typical menstrual symptom and is also caused by hormonal changes, which can slow down the digestive processes, which causes bloating and constipation.
High blood pressure and dizziness during pregnancy
Most often in the early stages of pregnancy in women, blood pressure drops, which can cause a feeling of dizziness due to vasodilation of the brain. High blood pressure in the first 20 weeks of pregnancy usually means that there are some health problems that occur along with pregnancy. Such a symptom may have been present unnoticed prior to pregnancy, or it may have developed during the process. In such cases, it is especially important to monitor your blood pressure and consult your doctor.
High blood pressure in the first 20 weeks of pregnancy usually means that there are some health problems that occur along with pregnancy. Such a symptom may have been present unnoticed prior to pregnancy, or it may have developed during the process. In such cases, it is especially important to monitor your blood pressure and consult your doctor.
Mood swings
Since estrogen and progesterone levels are elevated during pregnancy, this can cause changes in your emotional background and you may become more sensitive than usual. They can cause such strong feelings as depression, irritability, euphoria and anxiety.
Increase in basal body temperature
Basal body temperature is the lowest body temperature it reaches during rest or sleep. It is determined by measuring the temperature in the early morning by inserting a thermometer into the rectum. Normal body temperature may also rise, especially during heat or physical activity.