How do you estimate your due date
Calculate your due date: How to find your baby's due date
Choose a calculation method Last periodConception dateI know my due date
First day of my last period
BabyCenter's Due Date Calculator
Use our pregnancy due date calculator by plugging in either the date of your last menstrual cycle or the date you know you conceived. The calculator will do the rest.
How is my due date calculated?
There are several ways your due date is determined. If you happen to know the day you conceived, you can count 38 weeks from that day to find your due date. (Human gestation takes about 38 weeks.)
But very few expectant moms know exactly when they conceived. Even if you only had sex once during your fertile period, you wouldn't conceive on that day unless you happen to be ovulating. Sperm can live for up to five days inside your fallopian tubes. So, it could be up to five days after you have sex that you release an egg (ovulate) and it gets fertilized by a waiting sperm. That's the day you conceive.
So, without knowing the day of conception, how does anyone determine a due date?
First day of your last period
The most common way to calculate your pregnancy due date is by counting 40 weeks from the first day of your last menstrual period (LMP). And that's how most healthcare providers do it.
If your menstrual cycle length is the average length (28-day cycle), your menstrual cycle probably started about two weeks before you conceived. This explains why pregnancies are said to last 40 weeks instead of 38 weeks.
This method doesn't take into account how long your menstrual cycle actually is or when you think you might have conceived. But generally speaking, women typically ovulate about two weeks after their menstrual cycle starts. And women are more likely to know when their last period started than the day they ovulated.
Conception date
If you do happen to know precisely when you conceived – say, if you were using an ovulation predictor kit or tracking your ovulation symptoms – you can calculate your pregnancy due date based on your conception date. Just choose that calculation method from the pulldown above and put in your date.
Just choose that calculation method from the pulldown above and put in your date.
Note: Again, you don't necessarily conceive on the day you have sex.
IVF transfer date
If you conceived through IVF, you can calculate your due date using your IVF transfer date. If you had a Day 5 embryo transfer, count 261 days from your transfer date. If you had a Day 3 embryo transfer, count 263 days.
Can my due date change?
Your healthcare provider might revise your due date if your baby is measured during a first trimester ultrasound scan and found to be much bigger or smaller than expected for gestational age. This is more likely to happen if you have an irregular menstrual cycle length that makes it hard to pinpoint the date of conception.
Your healthcare provider will measure your baby during that ultrasound exam to figure out how far along your baby is and then provide you with a new due date.
What if I already know my due date?
If you already know your due date, you can use this calculator to see your pregnancy timeline. It will tell you when you'll hit various milestones, and when you may be due for prenatal tests and prenatal visits. You'll also find what your baby's sign and birthstone will probably be and which famous people were born on your due date.
It will tell you when you'll hit various milestones, and when you may be due for prenatal tests and prenatal visits. You'll also find what your baby's sign and birthstone will probably be and which famous people were born on your due date.
How likely am I to give birth on my due date?
Of course, a due date calculation is always approximate, whether it's from our tool or from your doctor or midwife. Only 1 in 20 women delivers on their due date. You're just as likely to go into labor any day during the two weeks before or after.
Want more information about how the weeks, months, and trimesters of pregnancy are counted? See our pregnancy timing chart.
How soon can I take a pregnancy test?
With all this talk about pregnancy due dates, you may be wondering when you can take a pregnancy test. To ensure you get the most accurate reading, it's best to wait a few days after your missed period to take a pregnancy test.
At-home urine tests measure the amount of hCG (human Chorionic Gonadotropin) present in your body. If you take a pregnancy test before you miss your period, you may not get an accurate result, despite what some tests advertise.
If you take a pregnancy test before you miss your period, you may not get an accurate result, despite what some tests advertise.
If you're getting a blood test in your provider's office, you may get results sooner. These tests also measure the amount of hCG in your bloodstream, but they're more sensitive than at-home urine tests. Blood tests may be able to detect pregnancy six to eight days after ovulation.
Read more
- Your pregnancy, week by week
- Your first trimester pregnancy checklist
- Pregnancy Weight Gain Calculator
- Ovulation Calculator
- See all tools
How do periods work? Facts about the menstrual cycle phases
Your reproductive organs are responsible for the menstrual cycle, which includes both your period and ovulation. Your cycle is made up of four phases, including menstruation, the follicular phase, the ovulation phase, and the luteal phase. All together, these phases will take around 28 days. But every woman is different, and anywhere from 21 to 35 days is considered normal. Around the middle of your cycle, one ovary will release a mature egg into the fallopian tubes. This is ovulation, and if a your egg is fertilized by sperm, you may be pregnant.
But every woman is different, and anywhere from 21 to 35 days is considered normal. Around the middle of your cycle, one ovary will release a mature egg into the fallopian tubes. This is ovulation, and if a your egg is fertilized by sperm, you may be pregnant.
What is a menstrual cycle?
You probably have a good idea about how your menstrual cycle works. But if you're hoping to get pregnant (or if you aren't), it's a great idea to make sure you understand the finer details of your cycle.
The menstrual cycle begins in puberty, when hormones help prepare the uterus for carrying a pregnancy each month. Over the course of roughly 28 days, the menstrual cycle includes a period, the maturing of eggs, and ovulation. The female reproductive systems include the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, cervix, vagina, and breasts.
When you're born, your ovaries contain all your eggs – about 1 million of them. These small, oval shaped organs on each side of the uterus will release roughly 400 eggs during your fertile years, and your body will reabsorb those that aren't released.
At ovulation, ovaries release a mature egg into the fallopian tubes. Typically, this is where fertilization will occur if a sperm meets the egg at the right time. Then, the egg travels through the fallopian tubes to the uterus.
During pregnancy, your uterus holds your baby. As part of your menstrual cycle, the lining of your uterus thickens each month so it's hospitable if an egg is fertilized during ovulation. If sperm doesn't fertilize the egg, your body will release the egg and shed your uterine lining during your period.
What is a period?
Your period begins your menstrual cycle. This is when your body releases unfertilized eggs and sheds the lining of your uterus. Day 1 of your period is considered day 1 of your menstrual cycle.
Everyone's body is different, so a period can vary greatly from person to person. Typically, women begin having their period during puberty and continue this monthly cycle until they experience menopause in their late 40s to mid-50s.
Menstrual bleeding can last between 2 and 7 days, and is usually light to moderate, but can be heavy for some women.
Menstrual cycle phases
The average length of a menstrual cycle is 28 days, but anywhere from 21 days to 35 days is considered normal. This cycle is divided into phases based on how your hormones change over the course of a month:
Menstruation
Menstruation is the first phase of your cycle and typically lasts from day 1 to 5. When you get your period, your estrogen and progesterone levels are low. The first day of your menstrual period (when you begin to bleed) is called "cycle day one" – or "CD1."
Some women have regular periods, meaning their cycle always lasts the same number of days each month. Others find their cycle length varies – and that can be normal, too. But if your cycle length varies by more than a week for months at a time or if you're missing periods, it's a good idea to talk to your healthcare provider.
Follicular phase: around days 1 to 13
The first day of your period also marks the beginning of the follicular phase.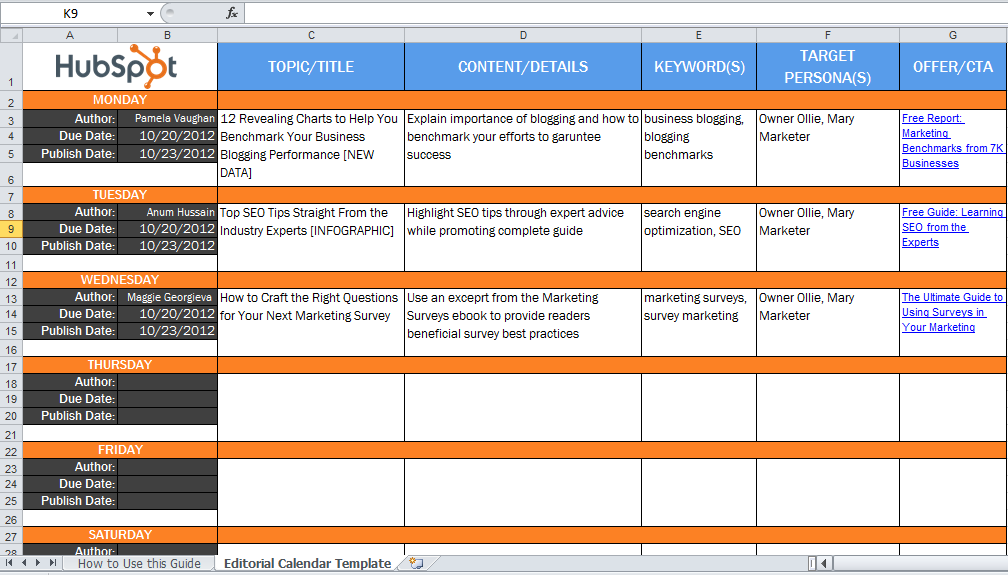 During this phase, your body is preparing your uterus and your eggs for a possible pregnancy. Thanks to the Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), which is produced in the hypothalamus region in your brain, levels of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) slowly rise.
During this phase, your body is preparing your uterus and your eggs for a possible pregnancy. Thanks to the Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), which is produced in the hypothalamus region in your brain, levels of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) slowly rise.
FSH is produced in the pituitary gland, a small area near the hypothalamus. It tells the eggs in your ovaries to start "ripening" and controls the release of estrogen from the ovaries. Each egg is inside a sac called a follicle.
One follicle grows quicker than all the others. This dominant follicle is the one that will release an egg this cycle. In a 28-day cycle, the follicular phase typically lasts until about day 13. This phase accounts for most of the variation in women's cycle lengths: In a shorter cycle, the follicular phase is shorter; in a longer cycle, the follicular phase is longer.
FSH also stimulates the ovaries to produce estrogen. Estrogen encourages cells in the endometrium to grow. As a result, your uterine lining thickens and becomes spongier. Blood vessels also swell, increasing blood flow to the lining. These changes prepare your uterus to support a pregnancy. (If you don't get pregnant, this uterine lining is shed during your period.)
Blood vessels also swell, increasing blood flow to the lining. These changes prepare your uterus to support a pregnancy. (If you don't get pregnant, this uterine lining is shed during your period.)
Estrogen also causes your cervical mucus to become thinner and more slippery. This type of mucus helps sperm cells slip more easily through the cervix and into the uterus.
Ovulation: around day 14
Ovulation – when an egg is released from the ovary – typically happens about 14 days before the first day of a woman's next period. So, in a 28-day cycle, ovulation may happen on cycle day 14. A rise in estrogen causes a surge of the luteinizing hormone (LH), which stimulates your ovaries to release eggs.
About 36 hours after an LH surge, the egg breaks out of the follicle. Almost immediately, the egg is swept into the fallopian tube by the finger-like projections that surround the tube's opening. There, the egg is in position to meet up with a sperm cell.
The egg survives in the fallopian tube for only about 12 to 24 hours. Sperm, however, can survive up to five days in your reproductive tract. So, if you ovulate on cycle day 15, for example, it's possible that sperm entering your body between cycle days 10 and 15 may reach your egg.
Sperm, however, can survive up to five days in your reproductive tract. So, if you ovulate on cycle day 15, for example, it's possible that sperm entering your body between cycle days 10 and 15 may reach your egg.
If you want to get pregnant, a good approach is to have sex two days before ovulation, so sperm are waiting in the fallopian tubes when the egg is released, and again on the day you ovulate. To improve your chances, experts often suggest having sex every other day around the time you expect to ovulate.
Luteal phase: around days 15 to 28
The luteal phase begins after you ovulate. In a 28-day cycle, it may start on day 15. Once this phase starts, levels of FSH and LH drop. The time for conception has passed, and your body is preparing for pregnancy – or your period.
In your ovary, the now-empty follicle collapses and becomes a small yellow mass of cells called the corpus luteum. The corpus luteum produces progesterone, which changes the mucus in the cervix. You may notice that your vaginal discharge becomes thicker and stickier during this stage of your cycle.
You may notice that your vaginal discharge becomes thicker and stickier during this stage of your cycle.
Progesterone also affects the lining of your uterus, which continues to thicken as a result of an increased blood supply. The lining secretes special substances that will nourish a fertilized egg.
If a sperm cell has successfully fertilized your egg, the developing ball of cells (called a zygote at first and then an embryo) makes its way down your fallopian tube toward your uterus. In about a week, it will likely implant in your uterine lining. At that point, you'll be pregnant!
Within a week or so of implantation, you may see a positive result on a home pregnancy test. And within another week or more you're likely to feel pregnancy symptoms. Often, one early clue that you're expecting is breast tenderness, which is caused by increased progesterone and estrogen. During pregnancy, levels of both hormones will skyrocket.
If the egg isn't fertilized or isn't viable, it degenerates as it travels along the fallopian tube to your uterus, and its microscopic remnants will leave your body along with your menstrual flow.
During the last few days of your cycle, if you're not pregnant, the levels of both progesterone and estrogen drop. This hormonal shift causes the blood vessels in the uterine lining to constrict, and without a steady blood supply, the uterine lining starts to break down.
Meanwhile, chemicals with hormone-like effects called prostaglandins– which are produced in the disintegrating uterine lining – make your uterine muscles contract and bring on menstrual cramps. Eventually, the blood vessels in the lining rupture, and the blood and tissue from your uterus flow out of your body through your vagina. In other words, you get your period.
Then the cycle starts again. Except during pregnancies, your body will likely continue this incredible process until menopause.
What things affect my menstrual cycle?
Some variation in your menstrual cycle is normal. Your cycle could be anywhere from 21 days to 35 days, and the individual phases of your cycle could vary by a few days, too. However, if your cycle is markedly irregular, health or environmental factors could be affecting your menstrual cycle. Examples of an irregular cycle include going 45 days or more between periods, missing periods, having increased pain during periods, or having heavy bleeding lasting more than 7 days.
However, if your cycle is markedly irregular, health or environmental factors could be affecting your menstrual cycle. Examples of an irregular cycle include going 45 days or more between periods, missing periods, having increased pain during periods, or having heavy bleeding lasting more than 7 days.
Some of the most common things that can affect your cycle include:
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding
- Significant weight loss along with over-exercising or disordered eating.
- Excessive cortisol, the hormone produced by the body when under stress
- Medical conditions including polycystic ovary syndrome, premature ovarian failure, pelvic inflammatory disease, and uterine fibroids.
Should I be concerned about missing periods?
If you missed a period, and confirmed you're not pregnant, there might not be any reason to worry. The occasional missed period typically isn't reason for concern. However, it's a good idea to take note of missed periods and other period irregularities. If these symptoms continue, there may be something going on with your hormones.
If these symptoms continue, there may be something going on with your hormones.
If you miss more than one period, talk with your doctor. They can help you figure out what's going on and how to get your cycle back on track.
Instructions: what to do after a pregnancy test showed two lines
We use cookies,
to be better!
Good
Author: Maria Ozol
June 2, 2021
8908 views
. Here's a guide so you don't miss anything.
The test can sometimes give a false result. To make sure that a woman is pregnant, she needs to contact an obstetrician-gynecologist and take tests. You can undergo an examination at the antenatal clinic at the place of residence or at a private clinic.
The doctor will perform a gynecological examination and refer the woman for an ultrasound of the pelvic organs. In addition, a woman must take a blood and urine test for human chorionic gonadotropin.
If the pregnancy is confirmed, the woman must be registered before the 12th week of pregnancy. This, again, can be done in a municipal or private clinic. To process the documents, you will need a passport, a medical policy and SNILS.
At the first visit, the obstetrician-gynecologist conducts a general examination, asks about chronic diseases, operations, allergies, how previous pregnancies went, if any. Then the nurse measures the weight and height of the woman: according to the height-weight indicator, the doctor will determine how many kilograms the woman should gain in all nine months.
After the obstetrician-gynecologist conducts a gynecological examination, evaluates the size of the uterus, sets the expected date of delivery, takes a swab for the vaginal microflora. The doctor draws up a pregnancy management plan and determines the risk group if the woman has pathologies.
Also, at the appointment, an “Individual card of a pregnant woman and a puerperal woman” and an exchange card are drawn up, in which the dynamics of the state and the results of the tests will be noted. The exchange card is handed over to the patient - it must be brought with you at each visit to the doctor. And it will also be needed when registering at the maternity hospital.
The exchange card is handed over to the patient - it must be brought with you at each visit to the doctor. And it will also be needed when registering at the maternity hospital.
After filling out the cards, the pregnant woman is given referrals for consultations of narrow specialists and tests in accordance with the Order of the Ministry of Health.
In the first trimester of pregnancy, the expectant mother should have:
- complete blood count;
- biochemical blood test;
- coagulogram - blood clotting test;
- blood test for antibodies of classes M and G to rubella virus and toxoplasma;
- urinalysis;
- blood group and Rh test;
- blood test for syphilis - determination of antibodies to pale treponema in the blood, HIV and antibodies to hepatitis B and C viruses;
- smear for microscopic examination of gonococcus and fungi of the genus Candida:
- blood test for glucose.

The woman also needs to have a pelvic ultrasound and electrocardiography, if indicated. When registering, you can tell the doctor if something is bothering you and ask questions.
Folic acid may prevent birth defects of the neural tube in the baby, such as spina bifida. Therefore, pregnant women need to drink 400 micrograms of folic acid every day until the 12th week of pregnancy.
Vitamin D is also important: it regulates the amount of calcium and phosphate needed to keep bones, teeth and muscles healthy. A pregnant woman should take 1000-1200 IU of vitamin D every day from September to March.
During pregnancy, it is important for a woman to monitor her physical health and take care of her emotional state.
Here's what you need to do to maintain the health of the expectant mother and child:
- eat a balanced diet and sleep at least 7 hours a day;
- know which foods to avoid during pregnancy to prevent food poisoning or infectious disease.
 It is better to avoid unpasteurized milk and milk products, raw or undercooked meat, liver, all types of pate, raw or partially cooked eggs. It is better for pregnant women not to eat swordfish, shark and king mackerel, bigeye tuna, since these types of fish contain a large amount of mercury - this is harmful to the baby;
It is better to avoid unpasteurized milk and milk products, raw or undercooked meat, liver, all types of pate, raw or partially cooked eggs. It is better for pregnant women not to eat swordfish, shark and king mackerel, bigeye tuna, since these types of fish contain a large amount of mercury - this is harmful to the baby; - do not drink alcohol or smoke;
- monitor medication. It is necessary to consult a doctor before taking any drugs during pregnancy: not all of them are safe during this period. If a woman is already taking prescribed medications, do not stop taking them without a doctor's recommendation;
- keep physically active during the day, do safe exercises to strengthen the muscles of the abdomen and pelvic floor. Which ones, it is better to check with an obstetrician-gynecologist;
- avoid infections that could harm the baby. In order not to get toxoplasmosis from a cat - do not clean the cat tray yourself, you can ask your partner to do it.
 And if this is not possible, then after cleaning thoroughly wash your hands with soap and treat with an antiseptic. It is better not to contact sick people and wash your hands more often;
And if this is not possible, then after cleaning thoroughly wash your hands with soap and treat with an antiseptic. It is better not to contact sick people and wash your hands more often; - learn to deal with feelings and emotions. When a pregnant woman is sad and it starts to affect her life, you can talk to a friend, family member, doctor, or try calming breathing exercises. If this does not help, it is better to get additional support from a psychotherapist.
In order for the pregnancy to proceed well and the baby be born healthy, it is necessary to take tests as prescribed by an obstetrician-gynecologist and be examined by narrow specialists from the early stages of pregnancy. This will help to eliminate problems in time and, if necessary, undergo treatment.
Mandatory minimum number of doctors and examinations during pregnancy:
- obstetrician-gynecologist - at least seven times;
- therapist and dentist - twice;
- otorhinolaryngologist, ophthalmologist — at least once;
- other specialist doctors - according to indications, taking into account the pathology;
- Ultrasound three times at 11-14 weeks, 18-21 weeks and 30-34 weeks;
- screening for the amount of hCG hormone - three times;
- complete laboratory examination - two times.

Lectures on the peculiarities of pregnancy and childbirth are given at courses in the antenatal clinic, and group classes are held.
Prenatal classes cover the following topics:
- health during pregnancy, including healthy nutrition;
- exercises to keep you active during pregnancy;
- how to help yourself during labor and childbirth;
- what are the types of anesthesia;
- relaxation techniques;
- baby care and feeding;
- woman's health after childbirth;
- emotions and feelings during pregnancy, childbirth and after.
Prenatal classes are a good way to make friends with other parents-to-be. Perhaps this will become additional psychological support in anticipation of the child and in the first few months after the birth of the baby.
How do you rate the article?
Understandable
Unclear
Topics
Women's Health
Editor's Choice
Parsing
→
How and where to undergo ultrasound screensing during pregnancy
170 views
Pregnancy
October 4, 2022
Hearing Check
→
Pregnant women?
4218 views
Pregnancy
June 11, 2021
Hearing test
→
Why store the umbilical cord after delivery
5004 Pregnancy 40 9028 views0002 April 16, 2021
Checking hearing
→
Is it true that the mother’s mood during pregnancy affects the child
4217 Views
Pregnancy
March 15, 2021
90,000 answers of Vladimir Putin to questions during a meeting with executed persons • President of Russia T. Karyakina: Tamara Karyakina, Employment Service.
Karyakina: Tamara Karyakina, Employment Service.
Vladimir Vladimirovich, Greetings from the Tver region.
Vladimir Putin: Thank you.
T. Karyakina: We are right next to Moscow and we even say: "Tver is the door to Moscow." And it so happened that young people long ago learned how this door opens. And the area is getting old. Our demography is such that the region is a retired grandmother. Therefore, we can especially see how important and timely the efforts to increase pensions are, how important any positive is in improving the medical care for the elderly. You have to make it, that's understandable.
Therefore, in connection with this, I have a question for you: how do you personally assess the human potential of the generation that is already leaving us, the older generation, in comparison with the potential of the current one? Don't you think that the current leaven is not the same?
Vladimir Putin: First, regarding the preservation of villages and small towns. I think that we will not solve this problem only by increasing pensions and benefits. It is necessary to develop agricultural production, develop the social sphere of the village, which we recently spoke about at one of the outreach events. It is necessary to increase the incomes of the rural population. And this is a separate issue. I think it has received quite a bit of attention lately. We will pay no less attention in the future.
I think that we will not solve this problem only by increasing pensions and benefits. It is necessary to develop agricultural production, develop the social sphere of the village, which we recently spoke about at one of the outreach events. It is necessary to increase the incomes of the rural population. And this is a separate issue. I think it has received quite a bit of attention lately. We will pay no less attention in the future.
As for the comparison of generations, I can say, you know, this is such a philosophical question: someone considers the previous generation to be the best, someone the worst. In my opinion, change is happening very slowly. Man has changed little in a millennium. Living conditions are changing. And in the new conditions, people manifest themselves differently, since the older generations could not show themselves, because they lived in completely different circumstances. But I am absolutely convinced that the main thing we have is the national character. I am absolutely convinced that in this sense the younger generation does not lag behind the older one.
I am absolutely convinced that in this sense the younger generation does not lag behind the older one.
But in order to prove this, we must do everything to make the older generation feel comfortable in our country. Therefore, we will continue to step up efforts to improve the pension system and create conditions that improve the well-being of those people who gave the country the best years of their lives and did everything to ensure that it got back on its feet after various periods of its difficult history. I see this as one of the priority tasks of all levels of government, including the task of the President.
L. Vasilyeva: Vladimir Vladimirovich, I am Lidia Mikhailovna Vasilyeva from the city of Astrakhan, I head the research and production center for sturgeon breeding.
We, fish workers, are very worried about the extremely difficult situation in the industry. For 10 years, the headquarters of the industry has been reorganized four times. The chairmen of our committee changed ten times. During your presidency, we expected that order would be restored in the committee. But even during this period of time, the chairman of our committee has changed four times. Non-professionals come to the leadership of the industry, people who do not know the industry, and illiterately manage this industry. We, the fishermen, are simply driven, we will say, to despair.
During your presidency, we expected that order would be restored in the committee. But even during this period of time, the chairman of our committee has changed four times. Non-professionals come to the leadership of the industry, people who do not know the industry, and illiterately manage this industry. We, the fishermen, are simply driven, we will say, to despair.
The last step that worries us the most is the question of privatization of research and scientific centers in the fishing industry. Transferring to private ownership those functions that the state should decide - I think this is the final collapse of the fishing industry.
I hear little from your speeches about the fishing industry. I would very much like you to pay attention to this industry, especially in this difficult time.
Thank you.
Vladimir Putin: Thank you for your question.
Naturally, the fishing industry primarily concerns those who work there, so there is such a reaction in the hall. Meanwhile, I would like to draw the attention of all the colleagues who have gathered here today: the issue is very serious. It has a nationwide sound, because the funds there are huge, and the results, when they are, they are reflected in the realities of our life, in the lives of ordinary citizens. If they are not, it is also very noticeable. And Lydia Mikhailovna put the question absolutely correctly. This is one of the problems that has not yet been solved. And personnel reshuffling takes place, and fundamentally the Government failed to regulate issues in the way that could and should have been done from the very beginning. I hope that the latest decision related to the distribution of quotas and so on will somehow correct the situation and increase the role of the regions in resolving these issues. And here is the case when it is impossible to approach scholastically with bare formulas. We need to look at the realities of our lives, at the realities of the lives of those people whose existence depends on the functioning of the industry.
Meanwhile, I would like to draw the attention of all the colleagues who have gathered here today: the issue is very serious. It has a nationwide sound, because the funds there are huge, and the results, when they are, they are reflected in the realities of our life, in the lives of ordinary citizens. If they are not, it is also very noticeable. And Lydia Mikhailovna put the question absolutely correctly. This is one of the problems that has not yet been solved. And personnel reshuffling takes place, and fundamentally the Government failed to regulate issues in the way that could and should have been done from the very beginning. I hope that the latest decision related to the distribution of quotas and so on will somehow correct the situation and increase the role of the regions in resolving these issues. And here is the case when it is impossible to approach scholastically with bare formulas. We need to look at the realities of our lives, at the realities of the lives of those people whose existence depends on the functioning of the industry. But as for the privatization of scientific institutions, I must say frankly that I have not heard anything about it yet. I will pay attention to this.
But as for the privatization of scientific institutions, I must say frankly that I have not heard anything about it yet. I will pay attention to this.
But, probably, you also know that the so-called scientific fishing quotas actually turned into commercial ones a long time ago. And if this scientism consists only in the fact that those people who sit at the same time fill their pockets, then such state institutions are not needed.
But if they are engaged in real scientific activity, then this is a different matter. But in any case, the Government must put things in order here. With this I absolutely agree.
A. Aksenova: Vladimir Vladimirovich, Vladimir and Suzdal, you have visited us many times.
Vladimir Putin: Hello. I remember.
A. Aksenova: Vladimir Vladimirovich, please, at least a few words about your view on the problems of culture. A lot of them.
Vladimir Putin: Culture is just like air: it is the basis of our life, it is what the entire building of our statehood is built on. We have, as I have said many times, a multinational and multi-confessional state, we have a unique richness of culture. I can hardly find another country with such cultural richness as ours. Therefore, the first thing we need to do here is to preserve everything that we have, to preserve this wealth, this linguistic and cultural heritage and, of course, increase it. Here you need to be very careful about all the processes that take place in this area. There are profitable areas, and there, of course, we need to develop market relations, help develop market relations. But, as a rule, the sphere of culture requires especially careful attention from the state and support from the state. The funds needed to solve these problems will be provided in the state budget and will be increased.
We have, as I have said many times, a multinational and multi-confessional state, we have a unique richness of culture. I can hardly find another country with such cultural richness as ours. Therefore, the first thing we need to do here is to preserve everything that we have, to preserve this wealth, this linguistic and cultural heritage and, of course, increase it. Here you need to be very careful about all the processes that take place in this area. There are profitable areas, and there, of course, we need to develop market relations, help develop market relations. But, as a rule, the sphere of culture requires especially careful attention from the state and support from the state. The funds needed to solve these problems will be provided in the state budget and will be increased.
N. Belyaev: Vladimir Vladimirovich, in your speech you dwelled on the collapse, the disintegration of the Soviet Union. What is your personal attitude towards this issue? And is it possible, in your opinion, in the future to create such a state?
Thank you.
Vladimir Putin: Nikolai Aleksandrovich, I am deeply convinced that the collapse of the Soviet Union is a national tragedy of enormous proportions.
I think that ordinary citizens of the former Soviet Union and citizens of the post-Soviet space, the CIS countries, ordinary citizens did not gain anything from this - on the contrary, people faced a huge number of problems.
As for cultural identity, questions of language, history, this is what our colleague was actually asking about now, they could have been solved on a new basis and within the framework of a single state, but things turned out differently. Today is what we have at the moment.
By the way, in that period of time there were different opinions, different points of view, including those of various leaders of the Union republics. For example, Nursultan Abishevich Nazarbayev was a categorical opponent of the dissolution of the Soviet Union and spoke about it directly, offering various forms of preserving the state within common borders. But, I repeat, this is in the past. Today we need to look at the realities in which we live. You can’t just look back and swear on this issue - you need to look forward.
But, I repeat, this is in the past. Today we need to look at the realities in which we live. You can’t just look back and swear on this issue - you need to look forward.
There are certain advantages to the state we are in. I think that mainly the so-called elites and a part, such a nationalist-minded part in these republics, benefited from such a delimitation. But it happened, it is accepted by the peoples of these countries, recognized by the international community and the Russian Federation itself. These are independent, full-fledged independent states, and they must be treated with respect. Respectfully means recognizing their legitimate interests. And on this basis, there are pluses for us as well. The pluses are that Russia should stop being a cash cow for everyone and everyone. And, fulfilling the requirement to treat all our partners, taking into account their interests, we have the right to demand the same attitude towards ourselves, so that everyone takes into account our interests, and build new relationships on this basis. Can we do it effectively or not? I'm just convinced that we can. We have everything for this: we have something that is not available in other regions of the world, where integration processes are also very active. After all, they are going in the most active way in almost all regions of the world. We have Europe at our side here, we see what is happening there, but the same thing is happening in Latin America, and in Asia, everywhere. We, unlike other regions of the world, if we take the post-Soviet space, have clear advantages: we have the language of interethnic communication, Russian, which everyone speaks. We have a similar mentality, we have a common history, we have an interpenetration of economies, industries and personal ties just at the genetic level, a lot of mixed marriages, and so on. This is an excellent basis for building new relations of an integration nature, which, of course, will benefit both Russia and our CIS partners. Our partners have an understanding of this process, the importance of this process.
Can we do it effectively or not? I'm just convinced that we can. We have everything for this: we have something that is not available in other regions of the world, where integration processes are also very active. After all, they are going in the most active way in almost all regions of the world. We have Europe at our side here, we see what is happening there, but the same thing is happening in Latin America, and in Asia, everywhere. We, unlike other regions of the world, if we take the post-Soviet space, have clear advantages: we have the language of interethnic communication, Russian, which everyone speaks. We have a similar mentality, we have a common history, we have an interpenetration of economies, industries and personal ties just at the genetic level, a lot of mixed marriages, and so on. This is an excellent basis for building new relations of an integration nature, which, of course, will benefit both Russia and our CIS partners. Our partners have an understanding of this process, the importance of this process. I hope that we will implement these plans.
I hope that we will implement these plans.
V.KALASHNIKOV, Tyumen region: Vladimir Vladimirovich, in four years you will not have time to do everything that you have planned.
Vladimir Putin: You help, we will do it.
V.Kalashnikov: It is necessary to increase the term to seven years.
Thank you.
Vladimir Putin: I have already answered these questions and I would like to reiterate my position. Of course, this is a desire for a certain stability, but such stability can also develop into stagnation. You can always find arguments, referring to which you can indefinitely increase the term of stay in power of one or another boss, one or another leader. Of course, maybe even five years would be nothing, somehow the figure is more rounded. I think seven is a lot.
If today we perform the duties that the head of the Russian state should perform, then, bearing in mind the huge number of accumulated problems, we need to work with full dedication. If you work like this for seven years with full dedication, you can go crazy, you understand?
There is another component to this problem. You know, I myself thought about this too, and it turns out that we want to achieve stability by undermining the Basic Law of the state - the Constitution. As soon as we start amending the Constitution, this is already the path to some kind of unstable situation. You just have to start - then you won't stop. Therefore, it is better not to touch the Basic Law of the State and work within the framework that those people who worked on this law laid down. Four years is not a long time, but not a short one either. Twice in four years, if a person has worked normally, people will still understand and appreciate it. It will be eight years. And then the task of any leader, especially of such a rank, is to offer the society a person whom he considers worthy of working in this place further. If people agree, then they will support. And it will be a continuation of what is being done now. But in this case, even if this is a worthy, experienced person, it is still a different person, fresh people, fresh ideas, fresh approaches to solving the problems facing the country come with him.
You know, I myself thought about this too, and it turns out that we want to achieve stability by undermining the Basic Law of the state - the Constitution. As soon as we start amending the Constitution, this is already the path to some kind of unstable situation. You just have to start - then you won't stop. Therefore, it is better not to touch the Basic Law of the State and work within the framework that those people who worked on this law laid down. Four years is not a long time, but not a short one either. Twice in four years, if a person has worked normally, people will still understand and appreciate it. It will be eight years. And then the task of any leader, especially of such a rank, is to offer the society a person whom he considers worthy of working in this place further. If people agree, then they will support. And it will be a continuation of what is being done now. But in this case, even if this is a worthy, experienced person, it is still a different person, fresh people, fresh ideas, fresh approaches to solving the problems facing the country come with him. It's always a plus.
It's always a plus.
A. MAGOMETOV, Rector of the North Ossetian State University: Vladimir Vladimirovich, you were at our university, you liked it - God willing, you will be again.
Vladimir Putin: Thank you.
A. Magometov: I have a question that probably worries a lot of rectors - this is the question of branches of central universities and all sorts of other departments on the periphery. At present, there are small towns in the North Caucasus, where there are up to 25–50 branches of central higher educational institutions. We are not afraid of competition. We have a consistently high passing score, a normal competitive situation. But the fact is that these branches interfere with our work, interfere with the work of professors, teachers, whom they tear to pieces, that is, a teacher working at a university, for example, does not have time for educational work, there is no time for scientific work, and sometimes even for a normal family life.
Is it possible to change something in the legislation or give some opportunities to the Ministry on this issue. Let's say the council of rectors, me, the chairman of the council of rectors - we do not give our consent. Reasonably, objectively, at a meeting of the council, we make a decision that we do not need such a branch here, because these specialties are in one university, in another, third, fourth - and nevertheless, some time passes, and a new sign appears: branch one or another central university.
Let's say the council of rectors, me, the chairman of the council of rectors - we do not give our consent. Reasonably, objectively, at a meeting of the council, we make a decision that we do not need such a branch here, because these specialties are in one university, in another, third, fourth - and nevertheless, some time passes, and a new sign appears: branch one or another central university.
Thank you.
From the audience: Have you tried to raise wages?
Vladimir Putin: As for wage increases and competition in this labor market, this is a question, of course, related to this problem as well. But in general, I talked about this in my speech, we have all sorts of universities and colleges growing like mushrooms; the quality of training is low. That's what you said, branches - somewhere they are justified, somewhere they are not. Graduates too - I also said about this: the vast majority do not work in their specialty, it is generally not clear what people do afterwards.
This area requires special attention from the state, but this attention should not lead to exclusive suppression of everything and everyone. But a certain order must be established here. We recently met at one of the academic institutes with members of the Council for Science under the President, we also talked about this there. There are certain ideas, developments on how we can develop the education system in general. This is basically the problem of the development of the education system. And I agree with you that the attention of the state and the Government should be increased. In general, the geography of distribution, the number of higher educational institutions, the number of people who are trained in certain specialties, it should be clear to the Government. Here I absolutely agree with you.
A. KLEBESHEV, Rector of Kaliningrad State University: I would like to ask a question that probably would not concern education.
Among the citizens of Russia, Kaliningraders probably most acutely feel that the solution of internal problems is sometimes very closely connected with foreign policy processes - including, as we see, with the positions of the most developed Western powers. In this regard, I have a question: in your opinion, do our current allies or partners: America, England, France - do they generally help us today to follow the path you spoke about, or hinder us? It seems that many do not trust us or they do not have such a desire.
In this regard, I have a question: in your opinion, do our current allies or partners: America, England, France - do they generally help us today to follow the path you spoke about, or hinder us? It seems that many do not trust us or they do not have such a desire.
Thank you.
Vladimir Putin: Why should they help us? Are we invalids or what? You know, I have also already spoken about this: in the world, of course, there are forces that still live by the stereotypes of the Cold War. I must say that I feel it, and, apparently, you have the same feeling; The question arose not by chance, I feel it in my practical work.
Indeed, there are quite powerful forces that simply cannot get out of this "freezer" and still perceive us as some kind of their geopolitical counterparties. But we must admit - you know, after all, among our people, as they say: "We see a speck in someone else's eye, but we don't notice a log in our own", - after all, we also have different people and different political forces, and extremist-minded, and moreover, on at a high level, they publicly express certain thoughts, including on international issues, so I would not brush everyone with the same brush: there are different people, different approaches. We must look for allies in civilized countries. We must melt this ice of distrust, which, of course, has developed over 80 years of confrontation between the Soviet Union and the rest of the world. We must be patient. We must act carefully, in no case allow those who want to quarrel us with the rest of the world (and there are such people, they act on purpose), in no case allow themselves to be provoked into something, into some action. But healthy forces all over the world and in developed countries, in Europe, in North America, in the United States - in the majority, after all, and they are our partners. We will focus on working with these political forces in these countries. And our goal is for Russia to become a full-fledged, full-fledged member of the international community today.
We must look for allies in civilized countries. We must melt this ice of distrust, which, of course, has developed over 80 years of confrontation between the Soviet Union and the rest of the world. We must be patient. We must act carefully, in no case allow those who want to quarrel us with the rest of the world (and there are such people, they act on purpose), in no case allow themselves to be provoked into something, into some action. But healthy forces all over the world and in developed countries, in Europe, in North America, in the United States - in the majority, after all, and they are our partners. We will focus on working with these political forces in these countries. And our goal is for Russia to become a full-fledged, full-fledged member of the international community today.
We have taken quite a few steps in this direction, but, of course, on this path we must in no case lose our own interests. This does not mean that we should scatter everything and turn out all our pockets - of course not. We will act consistently, persistently, but very carefully in this regard. And I am sure that such a restrained position will eventually develop positively, and we will achieve our goals in this sense.
We will act consistently, persistently, but very carefully in this regard. And I am sure that such a restrained position will eventually develop positively, and we will achieve our goals in this sense.
D. Kozak: Any more questions? Please.
K.ACHMIZ, Republic of Adygea: We really liked the economic part of your platform. Russia is a federal state. There are budget-forming regions, and there are also subsidized regions. What is the prospect of building interbudgetary relations, how do you see it? Will the subsidized regions also be subsidized in your new period of presidency?
Thank you.
Vladimir Putin: Interbudgetary relations should be aimed at stimulating subsidized regions to develop their own economy. How successful this will be, we will see in the coming years. But at the same time, we proceed from the fact that as long as these regions need the support of the federal center, this should happen. And you know what I will say: many times during previous years, in conversation with our colleagues, leaders of the regions of the Russian Federation, I returned to this topic. The so-called donor regions keep saying: what are we going to pay, what are we all going to deduct? Here the golden mean must be found.
The so-called donor regions keep saying: what are we going to pay, what are we all going to deduct? Here the golden mean must be found.
Of course, if you only deduct from donors and do not create conditions and incentives for the development of territories, then this is bad. But we must also admit something else: the so-called donor regions nevertheless accumulated their wealth or production capacities at the expense of the whole country, including at the expense of citizens who live in those territories that today need support. And therefore, there is only one way to redistribute these resources - through the federal budget.
In recent years, we have encountered the fact that the rights and obligations of various levels of government are unregulated: municipal, regional and federal. A lot of obligations were dumped on the municipalities, without providing real financial resources. That huge package of laws, some of which were adopted in the Duma and some are still being finalized (other laws confirming the financial powers of various levels of government should be adopted), is aimed at making municipalities, regions and the federal center self-sufficient.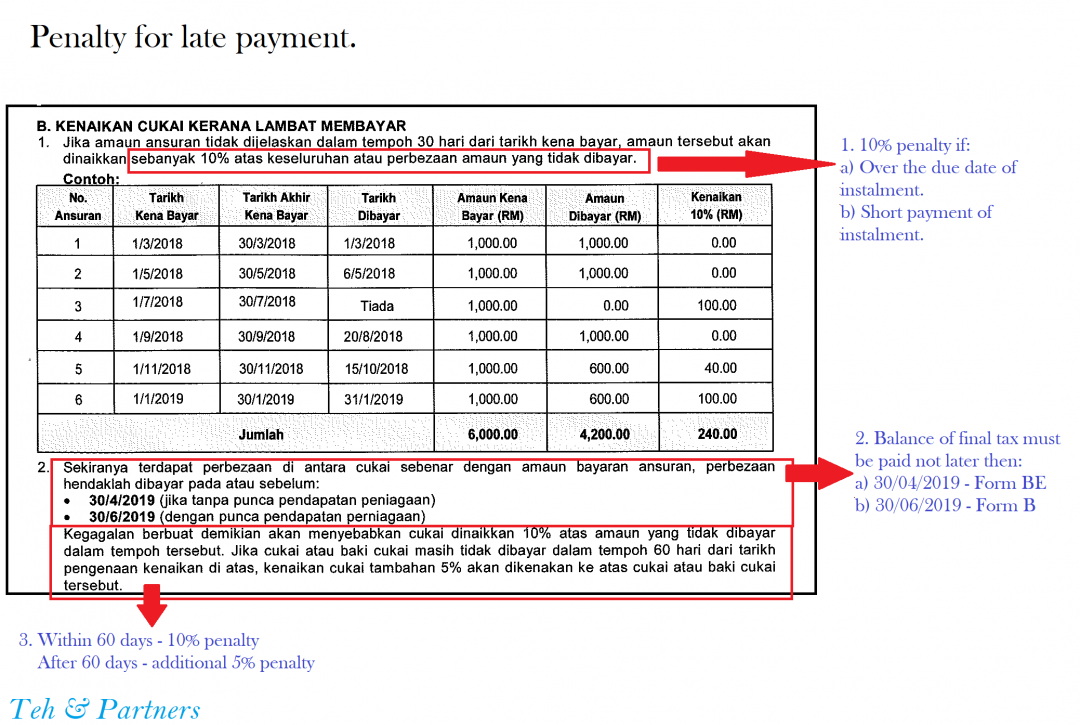 This is one of the key issues that we must resolve in the very near future.
This is one of the key issues that we must resolve in the very near future.
D. Kozak: Colleagues, do you have any more questions? Last two questions. Unfortunately, time is relentless.
S. KHORKINA, two-time Olympic champion in artistic gymnastics: Hello. At the upcoming Olympic Games in Athens, what do you think, what should the Russian Olympic team do to be the first in the overall medal standings?
Vladimir Putin: Win the way you know how to do it. I watched the last competitions, I saw how brilliantly you performed. I want to congratulate you on these brilliant performances and I hope that our other athletes will also show character, show what they are capable of, and the Sports Committee, the Government and I, if necessary, are ready to do everything to ensure the preparation of the national team. We wish you success.
Question: Vladimir Vladimirovich, what is your vision of the national idea, the national mission of Russia in the 21st century?
Vladimir Putin: I have already spoken about this.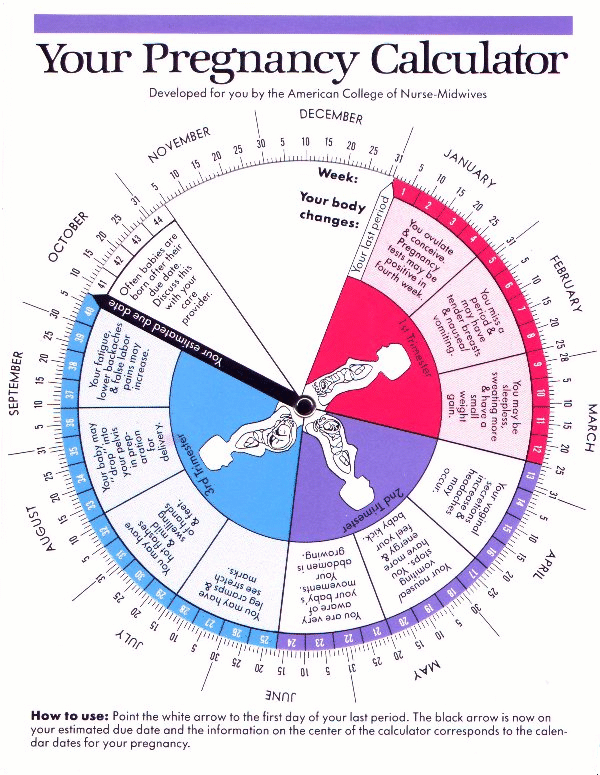 You can gather and discuss this topic as much as you like. You know, I am deeply convinced that we are facing a very serious challenge of the times: various countries and regions of the world are developing very actively - if we keep referring to our thousand-year history and talking about how rich in natural resources we are and how smart we are and rest on these laurels, we will finally fall into decay. We need to be competitive in everything: a person must be competitive, a city, a village, a branch of production and the whole country. This is our main national idea today.
You can gather and discuss this topic as much as you like. You know, I am deeply convinced that we are facing a very serious challenge of the times: various countries and regions of the world are developing very actively - if we keep referring to our thousand-year history and talking about how rich in natural resources we are and how smart we are and rest on these laurels, we will finally fall into decay. We need to be competitive in everything: a person must be competitive, a city, a village, a branch of production and the whole country. This is our main national idea today.
Please.
N.Korolchenko: I am a village teacher, director of a school, near Moscow. Vladimir Vladimirovich, you were in our school, and it was obvious to all of us, most importantly, you love children very much, you have two daughters in your family.
Vladimir Vladimirovich, when will we be able to create conditions in our country so that our families will not be afraid to give birth to three or four children, because this is probably, first of all, the future of our Motherland?
Vladimir Putin: Of course. This is also one of the problems - the decline, the natural decline of the population. There are many factors here: this is the factor of the Great Patriotic War, it still influences accordingly negatively; it's also a start factor of 90-s. There is such a concept as "planning horizon" - for a person, for a country, for a region, for a city. And this planning horizon expands as a person feels himself in a more or less stable environment. He can plan for some more or less long-term perspective, calculate something for himself and for his family. This is not the only, but rather important factor. We, of course, cannot act as they do in other countries. For example, in some countries (I will not name them) there is a very high birth rate. It is believed that this is due to the lack of a pension system: in some countries there is no pension system at all, and having a large number of children is a way to secure a more or less decent, dignified old age; and there was no pension system historically.
This is also one of the problems - the decline, the natural decline of the population. There are many factors here: this is the factor of the Great Patriotic War, it still influences accordingly negatively; it's also a start factor of 90-s. There is such a concept as "planning horizon" - for a person, for a country, for a region, for a city. And this planning horizon expands as a person feels himself in a more or less stable environment. He can plan for some more or less long-term perspective, calculate something for himself and for his family. This is not the only, but rather important factor. We, of course, cannot act as they do in other countries. For example, in some countries (I will not name them) there is a very high birth rate. It is believed that this is due to the lack of a pension system: in some countries there is no pension system at all, and having a large number of children is a way to secure a more or less decent, dignified old age; and there was no pension system historically. But we cannot return to such a state, we will never do this. We have a different society, a different country, and we must look for other modern ways to increase the birth rate. But I must say that the most important of them is political and economic stability and well-considered decisions in the development of the state's economy.
But we cannot return to such a state, we will never do this. We have a different society, a different country, and we must look for other modern ways to increase the birth rate. But I must say that the most important of them is political and economic stability and well-considered decisions in the development of the state's economy.
It was no coincidence that I said that we need a frank dialogue between society and government, because in order to be effective and competitive, certain decisions must be made. You need to understand and honestly tell people: this is ineffective, so you need to get rid of it; you need to replace it with this one, because the consequences, we expect, will be such and such.
We need to move away from the habitual stereotypes in which we lived under the planned system. At first glance, they are beautiful, but in fact they are absolutely inefficient in the modern economy and in the modern world. And this is what you need to understand, explain, make the right decision and have the will to bring them to the end. And then people will feel that the shaking has stopped, that even if it is difficult and difficult, it is clear why and it is clear when it will end and how. Now, if there will be such a clear, understandable forecast and there will be such a progressive development that we have had at least over the previous four years (and still we agree that the growth of gross domestic product, the growth of the economy has been very significant during this time), if only so it will be - we still need a little more - I am sure that the trends in the birth rate will be positive.
And then people will feel that the shaking has stopped, that even if it is difficult and difficult, it is clear why and it is clear when it will end and how. Now, if there will be such a clear, understandable forecast and there will be such a progressive development that we have had at least over the previous four years (and still we agree that the growth of gross domestic product, the growth of the economy has been very significant during this time), if only so it will be - we still need a little more - I am sure that the trends in the birth rate will be positive.
Let's do it again, there are those who wish. Please.
S. ZAYTSEV, MPO Mashinostroenie, Director of the United Spacecraft Directorate: Vladimir Vladimirovich, today Russia's security largely depends on the existence of a nuclear shield. We all know how much effort, knowledge and skills were put into its creation. Today, chaos is happening in the world, regional conflicts are flaring up. Tell me, do you pay enough attention to ensuring that no one will ever dare to raise a hand against us?
Vladimir Putin: This is one of the key issues, the issue of our security. And I must say that it excites - first of all, of course, it should excite us - but, strange as it may seem, it excites not only us.
And I must say that it excites - first of all, of course, it should excite us - but, strange as it may seem, it excites not only us.
In the days of the Soviet Union, the very factor of the Soviet Union, its might, above all the might of its nuclear forces, was a serious stabilizing element: it was an element of the balance of power in the world. Today the situation has changed dramatically. But in the military-strategic sphere, the balance is still maintained to a certain extent, and it is maintained thanks to the sufficiently developed, powerful nuclear deterrence forces of the Russian Federation.
We, I am absolutely convinced of this, should in no case behave in such a way that we are feared in the world. That is why our actions within the country and in the international arena must be understandable and predictable. We must become, as I said in answering the previous questions, part of the modern world, part of the civilized world, so that this world perceives our military power as an element of security on the planet. But it also means that we must maintain this power, and we will definitely do it.
But it also means that we must maintain this power, and we will definitely do it.
We have plans for the development of the Armed Forces for the next decade. Each year, the decisions taken within the framework of these ten-year plans are seriously tested in determining the main parameters and making decisions on the budget, the current budget and the budget for the next year, but these issues have been, are and will be in the focus of the political leadership of the country.
This is also confirmed by the exercises of the nuclear deterrence forces scheduled for the very near future with the participation of other branches and types of troops of the Russian Federation, which should take place in the near future and which have not been conducted for a long time due to the lack of financial resources and readiness for such large-scale activities in the military sphere. We will conduct them in the near future and will continue to conduct them based on the development of all types and branches of the Armed Forces, including the nuclear deterrence forces.
Please.
D. Kozak: Colleagues, the last two questions. There is another concept, a very strict one – the schedule of the President. Please.
L. Roshal: And maybe, Vladimir Vladimirovich, if you still have time, sit with us for a bit - perhaps more questions, because this conversation is very interesting, I have repeatedly said: I personally enjoy such conversations when eye to eye, it's true.
Vladimir Putin: Thank you very much, me too.
L. Roshal: I understand that there is special attention to today's meeting, people are waiting for it. This is actually the first performance of its kind. And if we don’t say anything about Russian healthcare, it will be wrong. I would like your vision of the further development of Russian healthcare, how do you see it all? But everyone knows that today it is “lowered” like never before: they also know that in our village only 30 percent of doctors work; they also know that 50 percent of polyclinics lack doctors; the fact that we are experiencing not only a colossal shortage of personnel, but we are experiencing a financial hunger for development both in the countryside and in areas of Russian healthcare. And when we conduct some surveys, the people first of all complain about the form in which they receive healthcare today.
And when we conduct some surveys, the people first of all complain about the form in which they receive healthcare today.
Doctors, they work, go to commercial structures, there is such an outflow, but the main backbone continues to work. And, of course, I would like to ask you one more question in connection with this. What is your vision of transferring teachers and doctors to the ranks of employees?
Thank you.
Vladimir Putin: Leonid Mikhailovich, this is one of the most important questions, I touched on it, but in a very general way. I think that the health care system that was created in Soviet times - I closely followed, among other things, those discussions in which you took part, and here I agree with you - was one of the best in the world, this is a fact. And we must do everything to preserve certain key elements of this system, bearing in mind that all citizens use it. It's an affordable system. And if we remember that almost 30 million more people live below the poverty line, then paid medical services for many more people will be inaccessible for a long time. And therefore, the state must do everything to, I repeat, preserve the key elements of the old system.
And therefore, the state must do everything to, I repeat, preserve the key elements of the old system.
At the same time - and this is what I also already spoke about - if all this is in market conditions, then it cannot function as before. In order for everything to function as before, we need to return the country back. But it's impossible. Therefore, we need to adapt the health care system, as well as the education system, in those elements where it collides with the market - and it collides almost everywhere - to new conditions. And here different options are possible: this is a medical practice organized in a certain way, as you know, and so on and so forth. We need to develop a system of paid services, but do it carefully, of course. And, of course, at this stage, we just need to increase direct budget financing of this type of activity. Although I would like our medical institutions, as I have said repeatedly, to receive money not for the very fact of their existence in nature, in a city or in a village, but for the quality and quantity of services provided - this, it seems to me, is the solution to the problem .
As for teachers, this year we have just made a decision - from January 1, it came into force - in order to raise a number of issues in this area at the state level, at the level of the region of the Russian Federation, on salaries and on technical equipping schools. Here is the first step. We will see how this will function, and based on this we will draw conclusions for making further decisions.
D. Kozak: One more question, colleagues. One question please.
Vladimir Putin: Please take the microphone.
Question: Over the past four years, a system has been created in the country that allows solving issues in the agricultural sector that have not been resolved for decades. In our region alone, a thousand combines were received under federal leasing, and the fleet has been renovated by a quarter.
My question to you: will financial support for agriculture continue to increase in proportion to how rich our state is? Once.
And the second. What is your attitude to the idea of creating a package of laws allowing the state to regulate prices, to participate in the event of a threat, like with the price of bread, that is, this entire package of laws was destroyed, the state was eliminated. Should I return to this topic today and create such a package?
Should I return to this topic today and create such a package?
Vladimir Putin: I can say right away that I think it is necessary. The state can use market mechanisms to prevent an economically unjustified, speculative rise in prices, it can do this by market means, it is not necessary to grab and not let go. It is possible to carry out interventions in the market, it is necessary to create appropriate exchanges, and so on, all this is possible, the Government knows this, it is delaying the adoption of a decision, but I hope that this will be implemented. First.
Second, with regard to supporting some sectors of the economy. In general, it is wrong to support one sector at the expense of another. But we must keep in mind that almost 40 million people live in our countryside, and in general these are people who not only work, but their life is all in the countryside. By the way, all countries of the world are showing increased attention to the village. Let's see what development plans are currently in the European Union, there are three main areas: infrastructure, rural areas and science. We are also carefully watching what is happening in the world - maybe with a certain overkill, I think they are doing there in some areas.
We are also carefully watching what is happening in the world - maybe with a certain overkill, I think they are doing there in some areas.
We support the village. This is also expressed in gentle taxation, in the development of leasing, which you mentioned, and further this item of expenditure will continue to exist and increase. Leasing will also be used. We will try to support the development of our own agricultural machinery industry. And, of course, the Government should pursue a more flexible and more sensitive policy in terms of allowing agricultural products from other countries to the domestic market - so that we help our producer with these tools, but would not allow an increase in prices for basic food products.
Question: A big hello to you, of course, from all the people of Pskov. We remember you very much and always invite and wait.
There was a question about medicine. I must tell everyone present that 4 years ago, when Vladimir Vladimirovich was in the Pskov region, he looked after our regional children's hospital and helped us a lot. The second stage is handed over at the beginning of March, we invite you officially to the opening of the second stage.
The second stage is handed over at the beginning of March, we invite you officially to the opening of the second stage.
But that's not what I wanted to say. In your speech, you paid attention to small towns, and I represent a small territory, but not on a territorial basis, not on the basis of the number of people, although, of course, we can talk about this: a small territory is about a small economic contribution to the common treasury of Russia. This is how it happened in the Pskov region: no gas, no oil, no coal, no big factories that would have been built under Soviet rule - there is none of this. But we are rich and we contribute a lot spiritually. The Pskov region can be proud of this, like a number of other territories. We celebrated the 1100th anniversary literally last year.
I have a question. In your opinion, is Russia today, its economy mature enough to pay special attention to these small territories - not cities, but the territories I mentioned? There are first steps - and in electricity tariffs, we notice it, it's great, but it's not enough. We were in 96th place seven years ago in the overall economic rank, today we are in 64th place. But then it will be harder and harder for us to do it on our own.
We were in 96th place seven years ago in the overall economic rank, today we are in 64th place. But then it will be harder and harder for us to do it on our own.
Thank you.
Vladimir Putin: What do you mean: “It will be harder on our own in the future”?
Question (not from the microphone): If this is the bar under which all regions of Russia are practically... budgetary assistance to the regions, if it is the same for all... (Inaudible.)
Vladimir Putin: I understand. I want to inform you that there is no such approach, averaging everyone, today. After all, when answering a colleague from Adygea, I said that the Ministry of Finance, the Government of Russia developed a system in which there is a redistribution of resources - partially, of course - a redistribution from donors to subsidized regions, so as to support their development. This is how it is done. The only question is not to overdo it, because constant replenishment, pumping of subsidized territories from the federal budget kills the incentive for their own development.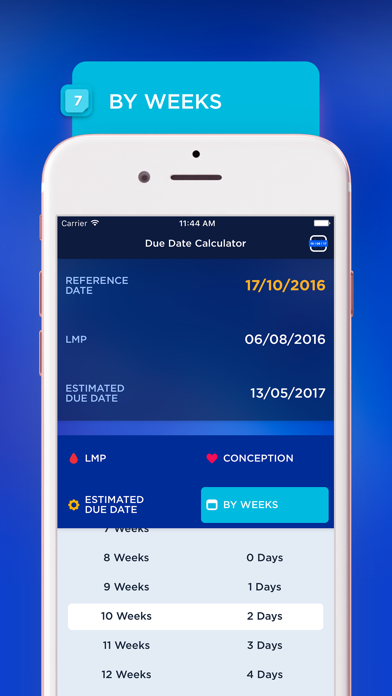 And in order to have this incentive, it is necessary to create certain framework conditions for the functioning of the economy. We have a very different country. You mentioned Pskov. Here, a colleague raised his hand and said that you intercepted a question from him, he was from the “norths” and probably wanted to ask a question about the “norths”. In our country, 70 percent of the territories are classified as northern territories and remote territories, and they also require special attention, and this is 70 percent. And the Far East? Go to the Far East, listen there. Many people there believe that they need to pay only for the fact that they live there.
And in order to have this incentive, it is necessary to create certain framework conditions for the functioning of the economy. We have a very different country. You mentioned Pskov. Here, a colleague raised his hand and said that you intercepted a question from him, he was from the “norths” and probably wanted to ask a question about the “norths”. In our country, 70 percent of the territories are classified as northern territories and remote territories, and they also require special attention, and this is 70 percent. And the Far East? Go to the Far East, listen there. Many people there believe that they need to pay only for the fact that they live there.
You know, we still need to come to an understanding that the Far East, and Siberia, and remote territories, and the center of the country, and the Non-Black Earth Region are still a single country that should live according to uniform laws, but in such that would allow the efficient development of the economy. But, of course, we must try to do it in such a way that local authorities adapt certain economic regimes for the effective development of their territories.