How do i qualify for additional child tax credit
Additional Child Tax Credit Definition
What Is the Additional Child Tax Credit?
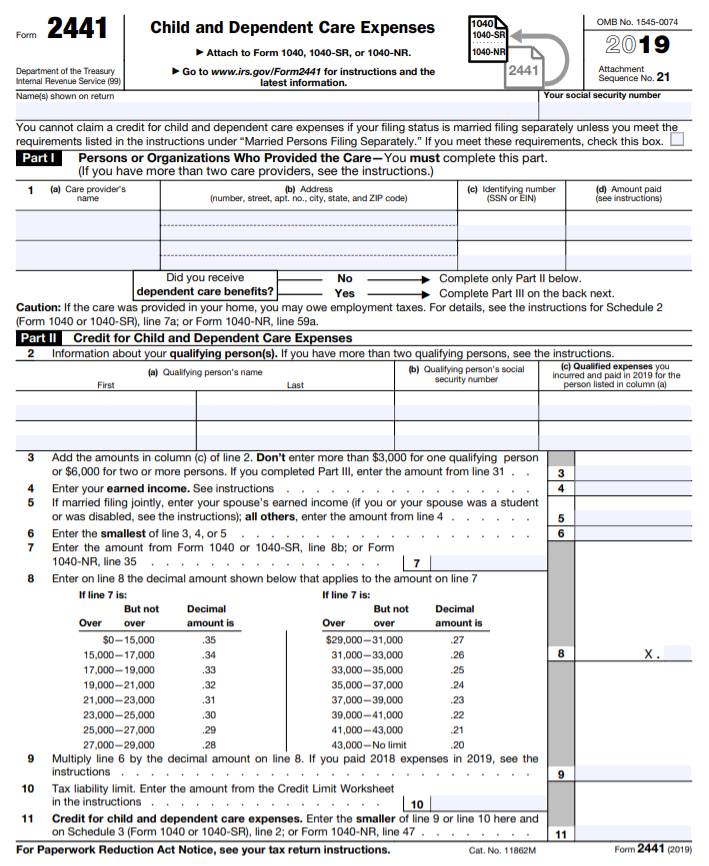
The additional child tax credit was the refundable portion of the child tax credit. It could be claimed by families who owed the IRS less than their qualified child tax credit amount. Since the child tax credit was non-refundable, the additional child tax credit refunded the unused portion of the child tax credit to the taxpayer. This provision was eliminated from 2018 to 2025 by the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA).
However, under the TCJA, the child tax credit includes some provisions for refundable credits. In addition, on March 11, 2021, President Biden’s American Rescue Plan was voted into law and made child tax credits fully refundable in 2021.
Key Takeaways
- The additional child tax credit was the refundable portion of the child tax credit.
- It could be claimed by families who owed the IRS less than their qualified child tax credit amount.
- The additional child tax credit was eliminated for 2018 to 2025 by the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act,
- Child tax credits for 2021, however, were made fully refundable as part of the American Rescue Plan.
- For 2021, advance child tax credits could be claimed via monthly payments in the amount of half of their total child tax credit. The second half can be claimed by those eligible on their 2021 tax returns.
Tax Deductions Vs. Tax Credits
Understanding the Additional Child Tax Credit
A tax credit is a benefit given to eligible taxpayers to help reduce their tax liabilities. If Susan's tax bill is $5,550 but she qualifies for a $2,500 tax credit, she will only have to pay $3,050. Some tax credits are refundable, meaning that if the tax credit amounts to more than what is owed as tax, the individual will receive a refund. If Susan's tax credit is actually $6,050 and is refundable, she will be given a check for $6,050 – $5,550 = $500.
Depending on what tax group a taxpayer falls in, they may be eligible to claim a tax credit. For example, taxpayers with children may qualify for the child tax credit which helps to offset the costs of raising kids.
For the 2022 through 2025 tax year, the child tax credit allows eligible tax filers to reduce their tax liability by up to $2,000 per child. To be eligible for the child tax credit, the child or dependent must:
- Be 16 years or younger by the end of the tax year
- Be a U.S. citizen, national, or resident alien
- Have lived with the taxpayer for more than half of the tax year
- Be claimed as a dependent on the federal tax return
- Not have provided more than half of their own financial support
- Have a Social Security number
Child Tax Credit vs. Additional Child Tax Credit
Previously, the child tax credit was non-refundable, which means the credit could reduce a taxpayer’s bill to zero, but any excess from the credit would not be refunded. Families who wanted to keep the unused portion of the child tax credit could go the route of another available tax credit called the additional child tax credit.
This credit was a refundable tax credit that families could qualify for if they already qualified for the non-refundable child tax credit. The additional child tax credit was ideal for families who owed less than the child tax credit and wanted to receive a refund for the surplus credit.
The additional child tax credit was ideal for families who owed less than the child tax credit and wanted to receive a refund for the surplus credit.
While the additional child tax credit was eliminated in 2018 under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), up to $1,400 of the $2,000 child tax credit can be refundable for each qualifying child if certain conditions are met. For example, a taxpayer needs to earn more than $2,500 for the tax year to qualify for any refund. To claim a refund, filers must complete Schedule 8812.
The American Rescue Plan created major changes to the child tax credit for 2021. The maximum credit rose to $3,000 (children up to 17) or $3,600 (children younger than six). Qualifying families started receiving monthly checks (half of the full credit) in July 2021. The credit also became fully refundable in 2021, and families may claim the second half of the credit on their 2021 tax return. This child-related tax benefit begins to phase out for individual filers with children who earn more than $75,000 and joint filers earning more than $150,000.
The additional child tax credit in its previous form was eliminated from 2018 to 2025 by the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA).
Example of the Additional Child Tax Credit
Before the TCJA, the IRS allowed families with an annual income of more than $3,000 to claim a refund using the additional child tax credit. The tax credit depended on how much the taxpayer earned and was calculated by taking 15% of the taxpayer's taxable earned income over $3,000 up to the maximum amount of the credit, which was then $1,000 per child. The total amount above $3,000 (subject to annual adjustments for inflation) was refundable.
For example, a taxpayer with two dependents qualifies for the child tax credit. Their earned income is $28,000, which means income over $3,000 is $25,000. Since 15% x $25,000 = $3,750 is greater than the maximum credit of $2,000 for two kids, they would have received the full portion of any unused credit.
So if the taxpayer received an $800 child tax credit, they would be refunded a $1,200 Additional child tax credit. However, if the taxable earned income was $12,000 instead, 15% of this amount over $3,000 is 15% x $9,000 = $1,350. Because the refundable portion of the credit cannot exceed 15% of earned income above $3,000, the taxpayer would receive a maximum refund of $1,350, not $2,000.
However, if the taxable earned income was $12,000 instead, 15% of this amount over $3,000 is 15% x $9,000 = $1,350. Because the refundable portion of the credit cannot exceed 15% of earned income above $3,000, the taxpayer would receive a maximum refund of $1,350, not $2,000.
Taxpayers who were residents of Puerto Rico with income below $3,000 were eligible if they had at least three qualifying dependents and paid Social Security tax in excess of the amount of their earned-income credit for the year.
What Is the Difference Between Child Tax Credit and Additional Child Tax Credit?
Under President Biden's 2021 American Rescue Plan, the child tax credit offers a maximum credit of $3,600 (younger than six years of age) and $3,000 (over age six and up to age 17) to those families who meet eligibility requirements. The additional child tax credit (up to $2,000 per child) was eliminated in 2018 under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA).
Is the New Child Tax Credit for 2020 or 2021?
President Biden's new child tax credit is based on 2020 tax returns and will be used when you file 2021 taxes in April 2022. The changes to the child tax credit apply (as of July 2021) for the tax year 2021 only, unless they are extended.
The changes to the child tax credit apply (as of July 2021) for the tax year 2021 only, unless they are extended.
Who Qualifies for the Additional Child Tax Credit?
The additional child tax credit was eliminated in 2018, so no one at present qualifies for the additional child tax credit. However, the full new child tax credit is offered to parents (who file jointly) who make up to $150,000 a year.
Are There Additional Requirements for the 2021 Child Tax Credit?
To qualify for advanced payments for the 2021 tax year to receive the Economic Impact Payment, had a main home in the U.S. for more than half the year (or file a joint return with a spouse who has a main home in the United States for more than half the year), have a qualifying child who is under age 18 at the end of 2021 and who has a valid Social Security number, and made less than certain income limits.
What is the Child Tax Credit & Additional Child Tax Credit?
As a parent, you might be eligible to claim the Child Tax Credit (CTC).
The Child Tax Credit is a credit for parents of children ages 16 and under. The Child Tax Credit is $2,000 per child. The amount of credit a taxpayer can claim is based on Modified Adjusted Gross Income (MAGI) and earned income.
How much is the Child Tax Credit?You may be able to claim a credit of up to $2,000 for each qualifying child. This credit reduces your tax bill dollar for dollar. Once your taxes are reduced to zero, any remaining credit up to $1,400 per eligible child may be claimed as the Additional Child Tax Credit.
How to calculate the Child Tax CreditThe Child Tax Credit is worth up to $2,000 for each qualifying child, but that amount is based on the MAGI of the taxpayer, and phases out when the MAGI exceeds the following thresholds:
- $400,000 for jointly filed returns
- $200,000 for all other returns
Use IRS Publication 972 as a worksheet to help you calculate the Child Tax Credit.
To be eligible, the child must be your qualifying child dependent for federal tax purposes. A child must:
- Be your biological child, stepchild, adopted child, foster child, sibling, or descendent such as a grandchild, niece, or nephew.
- Not have provided more than half of their own financial support during the tax year.
- Be a US citizen or a US national or resident alien.
- Have lived with you for more than half of the year.
- Be your dependent for federal tax purposes.
For purposes of the credit, the child must be under 17 as of December 31 of the tax year.
Make sure that your child meets all criteria as a Qualifying Child before claiming the Child Tax Credit.
Is there an income limit?You can claim the full Child Tax Credit if your Modified Adjusted Gross Income (MAGI) is under $200,000 – or under $400,000 if you and your spouse file a joint return. If your MAGI is greater than $200,000 ($400,000) the credit is reduced by $50 for each $1,000 over the threshold amount.
If your MAGI is greater than $200,000 ($400,000) the credit is reduced by $50 for each $1,000 over the threshold amount.
The Child Tax Credit is nonrefundable and reduces the amount of income tax you owe, up to the total amount. It is also refundable up to $1,400 per child on any remaining credit. If you owe $5,000 in taxes and are eligible for a $2,000 Child Tax Credit, your tax bill would be $3,000. If you owe $2,000 and your Child Tax Credit is $3,000, your tax bill would be zero and you may receive a refund of the remaining $1,000 credit by claiming the Additional Child Tax Credit.
How to claim the Child Tax CreditIf you are eligible for the credit, you can do so by claiming it on Form 1040 or Form 1040NR.
If a child’s parents are separated or divorced, who claims the Child Tax Credit?It’s most common for the custodial parent to claim the Child Tax Credit. However, the parent the child lives with for more than half the year, can allow the other parent to claim the credit by completing Form 8332 for the year and giving it to the other parent for their tax return.
However, the parent the child lives with for more than half the year, can allow the other parent to claim the credit by completing Form 8332 for the year and giving it to the other parent for their tax return.
Use Schedule 8812 to determine the amount of Additional Child Tax Credit you may claim.
What is the Additional Child Tax Credit (ACTC)?The Additional Child Tax Credit is a refundable credit that you may receive if your Child Tax Credit is greater than the total amount of income taxes you owe. For instance, if you’re eligible for a $2,000 Child Tax Credit and your taxes are only $1,000, you may add the remaining $1,000 credit to your refund.
What is the maximum amount of Additional Child Tax Credit?The maximum Additional Child Tax Credit is $1,400 per child. If you don't need any of your Child Tax Credit, the $600 between the $2,000 Child Tax Credit, and the $1,400 Additional Child Tax Credit per child is lost.
You must have an earned income of at least $2,500 to qualify. If your income is low, your credit may be limited to 15% of the amount of earned income over $2,500. Unemployment compensation and retirement or IRA distributions are not considered earned income.
{{metadata.tags.og.title}}
{{metadata.tags.og.description}}
Start now
{{/content}}One-time allowance for the birth of a child
The applicant has the right to file a complaint against the decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, its officials in the provision of public services (complaint), including in the pre-trial (out of court) procedure in the following cases:
- violation of the application registration deadline;
- violation of the term for the provision of public services;
- requirement from the applicant of documents, information or actions not provided for by the regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation for the provision of public services;
- refusal to provide a public service, if the grounds for refusal are not provided for by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation adopted in accordance with them;
- refusal to accept documents, the submission of which is provided for by regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation for the provision of public services;
- requesting from the applicant, when providing a public service, a fee not provided for by the regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation;
- refusal of the authorized body, its officials to correct the misprints and errors made by them in the documents issued as a result of the provision of public services or violation of the deadline for such corrections;
- violation of the term or procedure for issuing documents based on the results of the provision of public services;
- suspension of the provision of public services, if the grounds for suspension are not provided for by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation adopted in accordance with them, laws and other regulatory legal acts of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, municipal legal acts.

Subject of complaint
The subject of the complaint is a violation of the rights and legitimate interests of the applicant, unlawful decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, its officials in the provision of public services, violation of the provisions of the administrative regulations and other regulatory legal acts that establish requirements for the provision of public services.
Ways to make a complaint
A citizen has the right to file a complaint in writing on paper by mail or in person to any PFR Client Service, as well as in electronic form:
- on the official website pfr.gov.ru;
- portal vashkontrol.ru;
- portal do.gosuslugi.ru.
The reason for the appeal may be dissatisfaction with the quality of the provision of public services by the PFR, violation of the terms for the provision of services, violation of the terms for registering a request for a service, refusal to correct errors or typos, refusal to provide a public service, refusal to accept documents, demand for an additional fee.
Procedure for filing and handling a complaint
The complaint must contain:
- name of the authorized body, last name, first name, patronymic (if any) of its officials providing the public service and (or) their leaders, decisions and actions (inaction) of which are being appealed;
- last name, first name, patronymic (if any) of the applicant, information about the place of residence, as well as contact phone number (numbers), e-mail address (s) (if any) and postal address to which the answer should be sent to the applicant;
- information about the appealed decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, an official of the authorized body, its head;
- arguments on the basis of which the applicant does not agree with the decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, an official of the authorized body, its head.
The applicant shall submit documents (if any) confirming his arguments or copies thereof.
When filing a complaint in electronic form, the documents specified in paragraph 106 of the administrative regulations may be submitted in the form of an electronic document signed with an electronic signature, the form of which is provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation. In this case, an identity document of the applicant is not required.
In the authorized body, officials authorized to consider complaints are determined, who ensure:
- receiving and handling complaints;
- sending complaints to the body authorized to consider them.
Complaints against decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of an official of the authorized body are considered by the head of the authorized body or an official of the authorized body authorized to consider complaints. Complaints against decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the head of the authorized body are considered by an official of the executive authority of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation authorized to consider complaints.
If the complaint is filed by the applicant with a body whose competence does not include making a decision on the complaint, within 3 working days from the date of its registration, the said body sends the complaint to the body authorized to consider it and informs the complainant in writing about the redirection of the complaint.
The authorized body ensures:
- equipment for receiving complaints;
- informing applicants about the procedure for appealing against decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, officials of the authorized body by posting information on information boards in places where public services are provided, on the website of the authorized body, on the Single portal, service portal;
- advising applicants on the procedure for appealing against decisions and (or) actions (inaction) of the authorized body, officials of the authorized body at a personal appointment, by phone, using the website of the authorized body;
- conclusion of agreements on interaction between the multifunctional center and the authorized body in terms of the implementation by the multifunctional center of receiving complaints and issuing the results of consideration of complaints to the applicant;
- formation and quarterly submission to the Federal Service for Labor and Employment of reports on received and considered complaints (including the number of satisfied and unsatisfied complaints).

Deadlines for considering a complaint
A complaint received by the authorized body shall be subject to registration no later than the working day following the day of its receipt.
The complaint is subject to consideration within 15 working days from the date of its registration, and in the event of an appeal against the refusal of the authorized body to accept documents from the applicant or to correct misprints and errors, or in the event of an appeal against a violation of the established deadline for such corrections - within 5 working days from the date of its registration.
Result of consideration of the complaint
The result of the consideration of the complaint is the adoption of one of the following decisions:
- satisfy the complaint, including in the form of cancellation of the decision made by the authorized body, correction of typos and errors in documents issued as a result of the provision of public services, return to the applicant of funds, the collection of which is not provided for by the regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, regulatory legal acts of the subjects Russian Federation, municipal legal acts;
- refuse to satisfy the complaint.

When satisfying the complaint, the authorized body takes comprehensive measures to eliminate the identified violations, including the issuance of the result of the public service to the applicant no later than 5 working days from the date of the relevant decision, unless otherwise provided by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
A complaint may be denied in the following cases:
- availability of a court decision that has entered into legal force on a complaint about the same subject and on the same grounds;
- filing a complaint by a person whose powers have not been confirmed in the manner prescribed by the legislation of the Russian Federation;
- the presence of a decision on a complaint made earlier in accordance with the requirements of the Rules for filing and considering complaints against decisions and actions (inaction) of federal executive bodies and their officials, federal civil servants, officials of state non-budgetary funds of the Russian Federation, state corporations endowed with in accordance with federal laws, the powers to provide public services in the established field of activity, and their officials, organizations provided for by Part 1.
 1 of Article 16 of the Federal Law "On the organization of the provision of state and municipal services", and their employees, as well as multifunctional centers for the provision of state and municipal services and their employees, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 840 dated August 16, 2012, in respect of the same applicant and on the same subject of the complaint.
1 of Article 16 of the Federal Law "On the organization of the provision of state and municipal services", and their employees, as well as multifunctional centers for the provision of state and municipal services and their employees, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 840 dated August 16, 2012, in respect of the same applicant and on the same subject of the complaint.
A complaint may be left unanswered in the following cases:
- presence in the complaint of obscene or offensive expressions, threats to life, health and property of an official of the authorized body, as well as members of his family;
- the inability to read any part of the text of the complaint, the last name, first name, patronymic (if any) and (or) the postal address of the applicant indicated in the complaint.
In response to the results of the consideration of the complaint, the following shall be indicated:
- name of the public service provider that considered the complaint, position, last name, first name, patronymic (if any) of the official who made the decision on the complaint;
- number, date, place of the decision, including information about the official of the authorized body, the decision and (or) action (omission) of which is being appealed;
- last name, first name, patronymic (if any) of the applicant;
- grounds for making a decision on the complaint;
- decision made on the complaint;
- if the complaint is found to be justified, the terms for eliminating the identified violations, including the term for providing the result of the public service;
- information on the procedure for appealing against the decision taken on the complaint.
In the event that, during or following the consideration of a complaint, signs of an administrative offense or crime are established, an official of the authorized body authorized to consider complaints shall send the available materials to the prosecution authorities.
The procedure for informing the applicant about the results of the consideration of the complaint
A reasoned response based on the results of consideration of the complaint is signed by the official authorized to consider the complaint and sent to the applicant in writing or, at the request of the applicant, in the form of an electronic document signed by the electronic signature of the official authorized to consider the complaint, the type of which is established by the legislation of the Russian Federation, no later than the day following the day the decision is made on the results of the consideration of the complaint.
Procedure for appealing a decision on a complaint
The applicant has the right to appeal the decision taken on the complaint by sending it to the Federal Service for Labor and Employment.
If the applicant is not satisfied with the decision made during the consideration of the complaint or the absence of a decision on it, then he has the right to appeal the decision in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
The applicant's right to receive information and documents necessary to substantiate and consider the complaint
The applicant has the right to receive comprehensive information and documents necessary to substantiate and consider the complaint.
Ways to inform complainants about the procedure for filing and considering a complaint
Information on the procedure for filing and considering a complaint is posted on information stands at the places of provision of public services, on the website of the authorized body, on the Single Portal, Services Portal, and can also be communicated to the applicant orally and (or) in writing.
List of normative legal acts regulating the procedure for pre-trial (out-of-court) appeal against decisions and actions (inaction) of the authorized body, as well as its officials
The procedure for pre-judicial (out-of-court) appeals against decisions and actions (inaction) of the body providing public services, as well as its officials, is regulated by Federal Law No. 210-FZ of July 27, 2010 “On the organization of the provision of state and municipal services” and a decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of August 16 .2012 No. 840 “On the procedure for filing and considering complaints against decisions and actions (inaction) of federal executive bodies and their officials, federal civil servants, officials of state non-budgetary funds of the Russian Federation, state corporations vested in accordance with federal laws with powers to provision of public services in the established field of activity, and their officials, organizations provided for by Part 1.1 of Article 16 of the Federal Law "On the organization of the provision of state and municipal services", and their employees, as well as multifunctional centers for the provision I am state and municipal services and their employees”.
210-FZ of July 27, 2010 “On the organization of the provision of state and municipal services” and a decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of August 16 .2012 No. 840 “On the procedure for filing and considering complaints against decisions and actions (inaction) of federal executive bodies and their officials, federal civil servants, officials of state non-budgetary funds of the Russian Federation, state corporations vested in accordance with federal laws with powers to provision of public services in the established field of activity, and their officials, organizations provided for by Part 1.1 of Article 16 of the Federal Law "On the organization of the provision of state and municipal services", and their employees, as well as multifunctional centers for the provision I am state and municipal services and their employees”.
Large family allowance - frequently asked questions
1. Which families will receive the large family allowance?
The right to receive the allowance for a large family is one of the parents, guardian or trustee who brings up three or more children in the family who meet the conditions for receiving child allowance. Children under the age of 16 are entitled to receive child allowance, and in the case of a child studying - until he reaches 19years. If the child turns 19 in the current school year, the child allowance is paid until the end of the school year.
Children under the age of 16 are entitled to receive child allowance, and in the case of a child studying - until he reaches 19years. If the child turns 19 in the current school year, the child allowance is paid until the end of the school year.
2. Is the allowance for a large family paid monthly or only once?
The allowance for a large family is paid monthly.
3. If our family already has three children, will our family receive this benefit?
Yes, one of the parents, guardian or caregiver who is raising three or more children in the family receiving child allowance as of 07/01/2017 has the right to receive allowance for a large family.
4. Is this benefit exclusively for families who are just expecting a third child?
No, one of the parents, guardian or caregiver who is already raising three or more children in the family receiving child allowance as of 07/01/2017 has the right to receive allowance for a large family. Is the allowance for a large family paid automatically, or will it be necessary to apply?
Is the allowance for a large family paid automatically, or will it be necessary to apply?
If before 01.07.2017 there are three or more children in the family for whom one person receives child allowance, no application is required.
If the third child is born in the family after 01.07.2017, in this case, it is required to submit an application for family benefit for the newborn and at the same time indicate the desire to receive the allowance for a large family.
The application can be submitted on the self-service portal of the Social Insurance Board. Application for parental benefit, family benefits and supplementary contributions to the mandatory funded pension.
6. To whose current account and on what date is the money transferred?
The money is paid automatically on the 8th day of each month to the person to whose current account child allowances have been transferred so far.
If you want to change the beneficiary of benefits, another person submits an application for granting benefits. The person who has received benefits so far gives his or her consent to withdraw from receiving benefits.
The person who has received benefits so far gives his or her consent to withdraw from receiving benefits.
7. Are beneficiaries of parental benefit also entitled to family allowance?
Yes, receiving parental benefit does not limit the right to receive benefits for a large family.
8. If my spouse and I have 2 children from a joint marriage, and at the same time the spouse has one child from a previous life together, are we entitled to receive benefits for a large family?
The purpose of family allowances is to partially cover the costs associated with raising a child, so the allowance is paid to the parent who takes care of the child on a daily basis. Thus, it is important here that these parents bring up all three children on a daily basis. If there is a situation in which the same parent receives child allowance for a child from a previous marriage and for two children born in a new marriage, that parent will automatically receive the allowance for a large family.
It is important that the child allowances for all three children are issued to the same person.
9. Mother and father have 2 children in common. In addition, the mother / father has a child from a previous life together, who lives half the time in one family and half in another, while his hobby groups / clothes, etc. paid equally by parents. At the same time, the mother's/father's previous life partner(s) has two more children. What will happen in such a situation?
When determining family allowances, all children brought up in a family who are entitled to receive child allowance are taken into account. The family does not include children who live separately from this particular family with the other parent.
An exception is the situation in which, when the parents separate, the child lives equally in two families. In this case, the parents agree on which family the child is included in.
The Social Insurance Board does not have the authority to decide which family a child should be included in.
The right to receive the allowance for a large family is one of the parents who brings up three or more children in the family who meet the conditions for receiving child allowance. Children under the age of 16 are entitled to receive child allowance, and in the case of a child studying, up to the age of 19. If the child turns 19 in the current school year, the child allowance is paid until the end of the school year.
10. Is it possible to share the child allowance and the allowance for a large family between parents?
No, the recipient of the child allowance and the family allowance must be the same person. The payment of child allowances and allowances for a large family is made to one current account chosen by the person.
11. Is it possible for one parent to receive child benefits for three or more children, while the other parent receives child benefits for a large family?
No, a parent, guardian or custodian, or other person who is eligible for child benefits for three or more children is eligible for Large Family Allowance.
12. If the third child is born, for example, on July 15, 2017, from what time does the right to receive benefits for a large family arise?
The right to receive benefits for a large family will arise from the moment of the birth of the third child, i.e. from 07/15/2017
13. Will the large family allowance affect the living allowance paid by the social welfare department of the place of residence?
Yes, it will. The allowance for a large family is included in the family income when calculating the subsistence allowance. Therefore, in the future, this family may not qualify as a recipient of a subsistence allowance, or the amount of the assigned subsistence allowance may decrease.
14. If my spouse and I have 3 children for two, while the spouse has 2 children from a previous life together, and I have 1 child. We do not have common children. All three children live with us, which means daily expenses on our part.
 Are we eligible for family allowance?
Are we eligible for family allowance?
If the parents are legally married, then one of the spouses will be entitled to receive the large family allowance, despite the fact that there are no common children in the family.
15. If there are three children in a family and one of them, aged sixteen, has graduated from basic school and is going to study at a gymnasium in autumn, will the payment of benefits for a large family begin in July or in autumn? If the child is studying at a gymnasium, is there information about this or is special confirmation required?
In this case, the payment of the allowance for a large family will begin in July. Children under the age of 16 are entitled to receive child allowance, and in the case of a child studying, up to the age of 19. If the child turns 19 in the current academic year, the child allowance is paid until the end of the academic year. The beginning of the academic year is considered September 1st, and the end is August 31st, in case of graduation from the gymnasium - June 30th.
If the child is studying in Estonia, a study certificate is not required. We obtain information about studies from the Estonian Education Information System (EHIS). If the child is studying abroad, a certificate of study must be submitted annually to the Social Insurance Board.
16. My husband works in Finland and receives child benefits there for our children. I am a housewife, I live with children in Estonia. When will the allowance for a large family begin to be paid, how will our family allowances be paid in the future?
If the total amount of family benefits in Finland is less than the total family benefits in Estonia, Estonia will have to pay an additional benefit equal to the difference between the family benefits in Estonia and Finland. The allowance for a large family is distributed equally among the children.
Example 1: There are three children in the family: 15 years old, 12 years old and 9 years old. The compensation payable by Estonia is formed as follows:
15-year-old child (50+100) – 133.