Pregnant with triplets symptoms
Pregnant With Triplets? What You Should Know
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
Reviewed by Dan Brennan, MD on March 11, 2021
In this Article
- What Causes Triplet Pregnancies?
- Risks Associated With Triplet Pregnancies
- What Triplet Pregnancies Are Like for the Mother
Many women look forward to becoming pregnant and starting or growing their family. Most of the time, you don’t expect to see three tiny fetuses on your ultrasound. But if you do, here’s what you need to know about triplet pregnancy.
What Causes Triplet Pregnancies?
If you’re pregnant with more than one baby, it is often referred to as multiples. Pregnancies of more than one child represent approximately three in 100 births. If more than one egg is fertilized and implants in the uterus, your multiples are fraternal. If one egg is fertilized and splits before implanting in the uterine lining, you have identical multiples. In triplets — or any multiples more than two — the siblings can be all fraternal, all identical, or a combination of both.
There are several factors that increase your chances of being pregnant with more than one baby:
- Heredity. If you have a family history of multiple babies during pregnancy, it’s more likely that you will have twins or triplets.
- Age. If you’re older than 30, there’s a greater chance you’ll have multiples.
- Previous pregnancies. If you’ve been pregnant at least once before, you’re more likely to have a multiple pregnancy your second or third time. This is especially true if you previously gave birth to twins or triplets.
- Race. African American women are more likely than any other race to have a multiple pregnancy. Asian and Native American women are the least likely. White women who are older than 35 have the highest rate of multiple births that are more than twins (triplets, quadruplets, etc.).
- Ovulation-stimulation medicine. Medications like clomiphene citrate and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) help your body produce eggs.
 These are often used for low fertility but can lead to a triplet pregnancy if multiple eggs are released and fertilized.
These are often used for low fertility but can lead to a triplet pregnancy if multiple eggs are released and fertilized. - In vitro fertilization (IVF). This and other similar treatments help parents get pregnant by fertilizing eggs in a lab and then returning them to the uterus to grow. IVF pregnancies are more likely to produce multiples than natural pregnancies.
Risks Associated With Triplet Pregnancies
Premature birth. The greatest risk in carrying triplets is your babies being born prematurely. In fact, 60% of all multiple pregnancies occur before 37 weeks of gestation. The average gestation for a triplet pregnancy is even lower, at 32 weeks.
Delivery. Many triplet pregnancies end in a cesarean section for the safety of the babies and the mother. The probability of a vaginal delivery depends on:
- Size of each baby
- Positions of the babies
- Health of the babies
- Size and shape of the mother’s pelvis
During pregnancy, it is important to be aware of the signs of premature labor:
- Pelvic pressure
- Lower back pain
- Significant vaginal discharge
- Change in frequency or intensity of contractions
If you suspect you are experiencing premature labor, contact your doctor immediately. If caught early enough, the labor can be stopped so your babies have longer to grow.
If caught early enough, the labor can be stopped so your babies have longer to grow.
Placenta. The placenta is an organ that attaches to the wall of the uterus and transfers blood, oxygen, and nutrition from mother to baby through the umbilical cord. When a placenta supports more than one baby, it ages faster, limiting your babies’ growth potential.
The placenta may also provide imbalanced nutrients to each baby, causing one to grow larger while another remains smaller.
Preeclampsia.Preeclampsia is a dangerous condition when your blood pressure gets too high during pregnancy, putting you at risk for seizures. You’re at a much higher risk for preeclampsia with triplets. Symptoms of preeclampsia include:
- High blood pressure
- Protein in urine
- Swelling in the legs, hands, face, and sometimes the entire body
- Headaches
- Changes in vision
- Nausea and abdominal pain
- Trouble breathing
Diabetes. Gestational diabetes is very common in women with triplet pregnancies. However, it is also common in pregnancies of only one baby, so it is well known and easy to manage.
Gestational diabetes is very common in women with triplet pregnancies. However, it is also common in pregnancies of only one baby, so it is well known and easy to manage.
Newborn complications. The average weight at birth for triplets is just under 4 pounds. Approximately 20% of triplet pregnancies result in one child having a life-long handicap of some sort. Preterm delivery means an increased risk that your baby’s lungs, eyes, brain, circulatory system, and intestinal system are not fully developed yet.
It is likely that your babies will require a stay in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) where any complications will be treated, and they can thrive and grow.
What Triplet Pregnancies Are Like for the Mother
Due to the greater risks associated with pregnancy with triplets, you will need more medical care during your pregnancy. Even if everything goes well, you should still be seeing your doctor more often to check for issues with your babies.
You are more likely to experience common pregnancy symptoms like reflux, hemorrhoids, constipation, back pain, and varicose veins. You will also grow bigger more quickly, which may mean you need supplements or a specific nutrition plan. Talk to your doctor to create a plan for your triplet pregnancy.
Twins, Triplets, Complications & Symptoms
What is a multiple pregnancy?
A multiple pregnancy is a pregnancy where you’re carrying more than one baby at a time. If you’re carrying two babies, they are called twins. Three babies that are carried during one pregnancy are called triplets. You can also carry more than three babies at one time (high-order multiples). There are typically more risks linked to a multiple pregnancy than a singleton (carrying only one baby) pregnancy.
How do multiple pregnancies happen?
There are two main ways that a multiple pregnancy can happen:
- One fertilized egg (ovum) splits before it implants in the uterine lining.
- Two or more separate eggs are fertilized by different sperm at the same time.
These two different types of multiple pregnancy result in either identical or fraternal siblings. The difference between identical and fraternal babies goes back to how the multiple pregnancy happens.
Identical twins or triplets happen when a single egg is fertilized and then later splits. These newly divided embryos are identical. Children that are identical multiples will look like each other and be the same sex.
Fraternal multiples develop from separate eggs that are fertilized by a different sperm. Because these are different eggs and different sperm, the genetic material is varied. These children won’t look identical and can be different sexes from each other.
In a pregnancy with triplets or more, your babies could be all identical, all fraternal or a mixture of both. This can happen if your body releases multiple eggs and more than one is fertilized. In a case where you have both identical and fraternal multiples, more than one egg was fertilized and then at least one of those eggs also split after fertilization.
Are identical twins or triplets always the same sex?
Because identical twins or triplets share genetic material, they are always the same sex. The sex of a baby is determined by the particular sperm cell that fertilizes the egg at conception. There are two kinds of sperm cells — those carrying an X chromosome or Y chromosome. The mother’s egg carries an X chromosome. If a sperm cell carrying an X chromosome fertilizes the egg, it will make a XX combination (female). If the sperm cell is carrying a Y chromosome, you end up with an XY pairing (male).
Identical multiples start as one egg and then split, so whatever chromosome combination is present at fertilization is the sex of all multiples.
What increases the chance of a multiple pregnancy?
There are several factors that can increase the risk of a multiple birth. You might be at a higher risk of getting pregnant with more than one baby at a time if you:
- Are older (women in their 30s are at a higher risk of multiples because the body starts to release multiple eggs at one time when you get older).

- Are a twin yourself or have twins in your family.
- Are using fertility drugs.
You might also be at a higher risk of a multiple pregnancy if you are taller than average or have a higher body weight.
Another risk factor for a multiple pregnancy is genetic. There is an increased possibility of a multiple pregnancy if you are a multiple yourself, or if multiples run in your family. This heredity trait is generally passed down through the maternal (mother’s) side of the family.
The use of fertility drugs can be another reason you might have a multiple birth. Treatments for infertility can increase your risk of a multiple pregnancy because procedures, like in vitro fertilization (IVF), often involve transferring more than one fertilized egg into your uterus. Your provider usually transfers more than one egg at a time to increase the odds of a successful pregnancy.
How common are multiple births?
Multiple births have become more common in recent years because more people are using fertility drugs and procedures, such as IVF, to help conceive a baby.
What are the signs of a multiple pregnancy?
The only way to know if you’re pregnant with more than one baby during your pregnancy is through an ultrasound exam with your healthcare provider. During this test, your provider can look at images of the inside of your uterus and confirm how many babies are in there.
You might experience more intense symptoms during a multiple pregnancy than with a single pregnancy. These can include:
- Severe nausea and vomiting (morning sickness).
- Rapid weight gain in the first trimester of pregnancy.
- Sore or very tender breasts.
- High human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) levels — this hormone is made during pregnancy and is what a pregnancy test picks up.
- High amounts of the protein alpha-fetoprotein in your blood.
Apart from an ultrasound, your provider might suspect multiples if there’s more than one heartbeat detected during a fetal Doppler scan.
What complications are linked to multiple births?
Anyone can experience complications during pregnancy — regardless of how many babies you’re carrying. However, most healthcare providers consider multiple pregnancies higher risk than single pregnancies. This doesn’t mean that every woman who carries more than one baby during a pregnancy is going to have problems. If you’re pregnant with multiples, your provider will want to watch you for possible complications that can happen when you carry more than one baby at once. Your provider will talk to you about each risk factor and frequently check with you to make sure you aren’t experiencing anything concerning.
However, most healthcare providers consider multiple pregnancies higher risk than single pregnancies. This doesn’t mean that every woman who carries more than one baby during a pregnancy is going to have problems. If you’re pregnant with multiples, your provider will want to watch you for possible complications that can happen when you carry more than one baby at once. Your provider will talk to you about each risk factor and frequently check with you to make sure you aren’t experiencing anything concerning.
Possible complications include:
- Premature labor and birth: The most common complication of multiple births is premature labor. If you’re pregnant for multiples, you are more likely to go into premature labor (before 37 weeks) than a woman carrying only one baby. The goal for many moms of multiples is to complete 37 weeks. This is considered term in a twin pregnancy and reaching this week of gestation increases the chance the babies will be born healthy and at a good weight.
 Babies that are born prematurely are at risk of another complication of multiple births — low birth weight.
Babies that are born prematurely are at risk of another complication of multiple births — low birth weight. - Preeclampsia or gestational hypertension (high blood pressure): High blood pressure is called hypertension. During pregnancy, your healthcare provider will watch your blood pressure carefully to make sure you don’t develop gestational hypertension (high blood pressure during pregnancy). This can lead to a dangerous condition called preeclampsia. Complications related to high blood pressure happen at twice the rate in women carrying multiples compared to women pregnant with only one baby. This complication also tends to happen earlier in pregnancy and be more severe in multiple pregnancies than single pregnancies.
- Gestational diabetes: You can develop diabetes during pregnancy. This happens because of the increased amount of hormones from the placenta. The size of the placenta can also be a factor in this condition.
 If you have two placentas, there’s an increased resistance to insulin.
If you have two placentas, there’s an increased resistance to insulin. - Placenta abruption: This condition happens when the placenta detaches (separates) from the wall of your uterus before delivery. This is an emergency situation. Placenta abruption is more common in women who are carrying multiples.
- Fetal growth restriction: This condition can also be called intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) or small for gestational age (SGA). This condition happens when one or more of your babies is not growing at the proper rate. This condition might cause the babies to be born prematurely or at a low birth-weight. Nearly half of pregnancies with more than one baby have this problem.
Fraternal twins always have two placentas. The risks of pregnancies with fraternal twins are similar to those of pregnancies with only one baby. However, the number of possible risks are increased when compared to pregnancies with one baby.
Identical twins may have one placenta (70% of the cases) or two placentas (30% of the cases). The risks of identical twins with two placentas are similar to those listed above for fraternal twins. Identical twins with one placenta (called monochorionic) have risks that are unique to them. In 5 to 15% of the cases, they may develop a condition called twin-twin-transfusion-syndrome (TTTS). This is the consequence of vascular communications at the placenta level between the twins. Due to these communications, the twins may share their blood. When this happens — if nothing is done — there is a 90% risk that the twins will die in-utero. In-utero procedures are performed to decrease the fetal death risk for the twins.
The risks of identical twins with two placentas are similar to those listed above for fraternal twins. Identical twins with one placenta (called monochorionic) have risks that are unique to them. In 5 to 15% of the cases, they may develop a condition called twin-twin-transfusion-syndrome (TTTS). This is the consequence of vascular communications at the placenta level between the twins. Due to these communications, the twins may share their blood. When this happens — if nothing is done — there is a 90% risk that the twins will die in-utero. In-utero procedures are performed to decrease the fetal death risk for the twins.
Another complication that can happen in identical twins with one placenta is called twin-anemia-polycythemia sequence (TAPS). This is due to blood that goes from one twin to the co-twin because of vascular communications at the placental level. In this condition, one twin becomes anemic (low red-blood cells), whereas the co-twin becomes polycythemic (too many red-blood cells).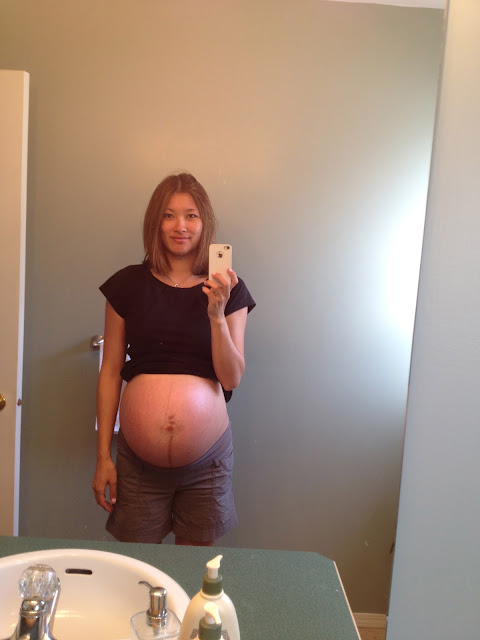 Several treatments/interventions are performed when this happens.
Several treatments/interventions are performed when this happens.
A third condition that can occur in identical twins with one placenta is called” selective IUGR”. One twin grows well, whereas the co-twin does not experience much growth.
Another condition typical of identical twins is called twin-reversed-arterial-perfusion syndrome. In this condition, the heart of one twin pumps blood for the circulation of both twins. One twin does not have the heart and will not survive following birth. The outcome of the twin with the normal heart varies. Fortunately, this syndrome is rare (1 in 20,000 to 40,000) and it is amenable to in-utero procedures.
Identical twins with one placenta may also be in the same sac. They are called monochorionic (one placenta)-monoamniotic (one gestational sac). This pregnancy occurs in 1% of multiple gestations and it’s associated with an increased risk for one or both twins.
Your healthcare provider will diagnose the above conditions with an ultrasound.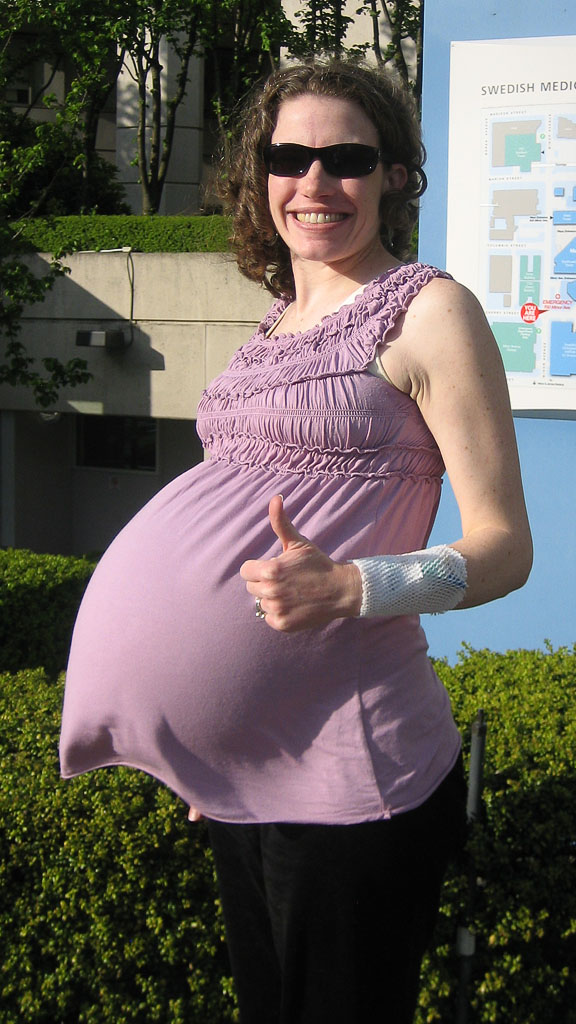
Am I more likely to have a C-section delivery if I’m carrying multiples?
A cesarean section is a procedure used to deliver a baby through an incision (cut) in the abdomen. This type of delivery might be used for a variety of reasons, but it’s fairly common in multiple births. Your chance of having a C-section for a multiple birth is higher than if you were pregnant for only one baby. However, even in single births, a C-section can sometimes be the safest option for delivery.
Often, the babies aren’t in the right position for birth — head down. A C-section can also happen if you have a complication during pregnancy that means a vaginal birth isn’t the safest option for you or your babies. Your healthcare provider will monitor you leading up to your due date and talk to you about the best option for delivery.
What can I do to stay healthy during a multiple pregnancy?
Eating nutritious foods, getting enough rest, and visiting the doctor regularly are important steps for any pregnant woman to take toward a healthy pregnancy. These steps are especially important during multiple pregnancies.
These steps are especially important during multiple pregnancies.
If you’re expecting multiples, you have additional dietary needs to meet. Getting enough protein and enough hydration (fluids) is important. You’ll also need to make sure you get enough extra calories for the developing fetuses. One rule of thumb is to eat an extra 300 calories a day per baby. That means that if you’re pregnant with twins, you will need to add 600 calories to your daily diet. Talk to your healthcare provider about your diet and the specific amounts you’ll need for a healthy pregnancy.
Moms of multiples might also experience the typical discomforts of pregnancy more intensely. It’s important to take good care of yourself and get plenty of rest to help ease the stresses of pregnancy.
In some cases, you might want to find a healthcare provider who has experience with multiple births. Specialized healthcare can help ensure that you and your babies are receiving the best care available. The need for frequent, intensive prenatal care is very important in a multiple pregnancy. Talk to your family doctor or OBGYN about their recommendations for specialists.
Talk to your family doctor or OBGYN about their recommendations for specialists.
Can I be active and exercise during a multiple pregnancy?
Exercise and activity is an important part of any pregnancy. In most cases, you can absolutely exercise during a multiple pregnancy. Low-impact exercises are a great way to stay in shape and maintain your health throughout pregnancy. Some low-impact exercises to try during a multiple pregnancy can include:
- Swimming.
- Walking.
- Prenatal yoga.
Even though activity is wonderful during pregnancy, you should talk to your healthcare provider about the best activities for you. Some more strenuous activities might not be a good idea during a multiple pregnancy, including:
- Jogging.
- Aerobics that involve jumping.
It’s also important to remember that your exercise routine might need to change over time if you experience any complications.
Nine symptoms of multiple pregnancy in early pregnancy
Hello, dear friends and subscribers. Yesterday I found out that my girlfriend is pregnant with triplets. She suspected her interesting position in an unusual way, looked through the educational literature and read there what are the symptoms of multiple pregnancy in the early stages. A friend has long dreamed of a baby, and now imagine, she will have three of them!
Yesterday I found out that my girlfriend is pregnant with triplets. She suspected her interesting position in an unusual way, looked through the educational literature and read there what are the symptoms of multiple pregnancy in the early stages. A friend has long dreamed of a baby, and now imagine, she will have three of them!
Causes of multiple pregnancy
Recently, twins, triplets and even quadruplets are born more and more often. So my friend lives in anticipation of her triplets.
Statistics say that 1% of all pregnancies are multiples. Why has this figure grown so much? What contributes to this? If we take the case of my friend, then the hormonal drugs that she took to stimulate superovulation most quickly affected. When the follicle bursts, mature eggs are released and meet with sperm. The probability of multiple pregnancy in this case is high.
Reasons for having twins or triplets:
- IVF. To obtain a positive result of the procedure, doctors introduce several grown embryos into the uterus.

- The structure of the uterus. If the organ is "two-horned" or "forked", then twins are born more often.
- Age - 35 years. At this time, the work of the reproductive function is rebuilt in a woman, and hormonal fluctuations occur.
- Heredity. Multiple pregnancy is inherited both maternally and paternally.
- Lactation. During this period, the likelihood of conceiving and subsequently giving birth to twins or triplets increases.
- Rebound effect. When a woman uses oral contraceptives for a long time, then after their cancellation, fertilization may occur in the next month.
I was surprised to learn that the largest multiple pregnancy in the world occurred in Russia in the city of Kursk. The woman gave birth to ten children at once!
What symptoms can be used to suspect multiple pregnancies
Talking with a friend and remembering my interesting situation, I can say that the symptoms of carrying more than two embryos are similar to a singleton pregnancy. However, they are more pronounced and a few more specific manifestations are added to them.
However, they are more pronounced and a few more specific manifestations are added to them.
Early signs of multiple pregnancy:
- High blood pressure values.
- Severe toxicosis at the initial stage.
- Early manifestation of preeclampsia.
- Rapidly growing tummy.
- The size of the uterus in multiple pregnancies is not proportional to the term.
- Rapid weight gain.
- HCG in multiple pregnancy is overestimated.
- More than two heartbeats are heard on an electrocardiogram.
- A pronounced state of fatigue.
If a pregnancy test is performed a few days after the fertilization of the egg, that is, even before the delay, it will show a positive answer.
Multiple pregnancy is confirmed by ultrasound as early as the fifth week. But quite recently, a woman found out that she was carrying more than one baby under her heart only at the end of the second trimester.
Medical confirmation
How to detect multiple pregnancy? Ultrasound is considered the most reliable way to confirm multiple pregnancy. It will determine the number of developing eggs in the uterus and where they are located already in the fifth week.
It will determine the number of developing eggs in the uterus and where they are located already in the fifth week.
Ultrasound helps doctors monitor the development of embryos. This method allows you to notice a stop or pathology in the development of one of the fetuses in time. Of course, laboratory tests can also show these deviations, but their result will not be so informative.
During the first screening, the specialist determines the nature of multiple pregnancies, listens to the baby's heartbeat, and evaluates developmental features. The veracity of the survey results by this method is more than 99%.
When a woman is pregnant with more than one baby, a biochemical blood test will show elevated levels of estriol, hCG, AFP and PAPP-A.
However, this may also indicate abnormalities in the development of one of the embryos. Therefore, ultrasound is considered the most accessible and truthful method for determining multiple pregnancy. With its help, the existing pathologies in the development of the fetus are identified.
In this article, I told you how long a multiple pregnancy is determined, the causes and symptoms of multiple pregnancy were considered.
This concludes our conversation. If you liked my article, then invite your friends to read it on social networks. And I remind you of the opportunity to subscribe to blog updates.
See you soon!
Multiple pregnancy
Author: Mikheeva Natalya Grigorievna, Malyshok magazine
A multiple pregnancy is a pregnancy in which two or more fetuses develop simultaneously in the uterus. Multiple pregnancy occurs in 0.4 - 1.6% of all pregnancies. Recently, there has been an obvious trend towards an increase in the incidence of such pregnancies due to the active use of assisted reproduction technologies, including in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Types of multiple pregnancies
Children born in multiple pregnancies are called TWINS. There are two main types of twins: monozygotic (identical, homologous, identical, similar) and dizygotic (fraternal, heterologous, different).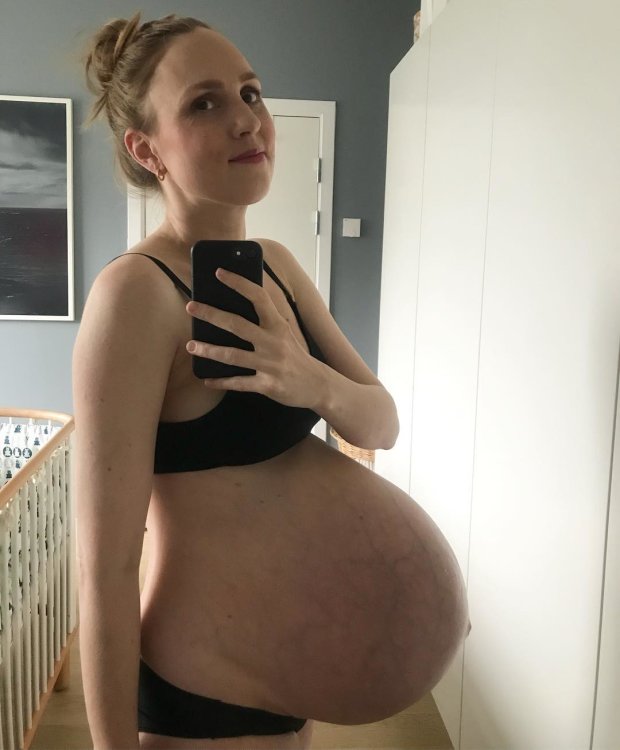 African countries have the highest twin birth rate, Europe and the USA have an average rate, and Asian countries have a low rate.
African countries have the highest twin birth rate, Europe and the USA have an average rate, and Asian countries have a low rate.
Dizygotic (fraternal) twins are more common (in 66-75% of all twins). The birth rate of dizygotic twins varies from 4 to 50 per 1000 births. Dizygotic twins occur when two separate eggs are fertilized. The maturation of two or more eggs can occur both in one ovary and in two. The predisposition to develop dizygotic twins may be maternally inherited. Dizygotic twins can be either same-sex or opposite-sex, they look like each other like ordinary brothers and sisters. With fraternal twins, two placentas are always formed, which can be very close, even touching, but they can always be separated. Two fruit spaces (i.e., fetal bladders or two “houses”) are separated from each other by a septum consisting of two chorionic and two amniotic membranes. Such twins are called dizygotic dichorionic diamniotic twins.
Monozygotic (identical) twins are formed as a result of the separation of one fetal egg at various stages of its development. The frequency of birth of monozygotic twins is 3-5 per 1000 births. The division of a fertilized egg into two equal parts can occur as a result of a delay in implantation (immersion of the embryo in the uterine mucosa) and oxygen deficiency, as well as due to a violation of the acidity and ionic composition of the medium, exposure to toxic and other factors. The emergence of monozygotic twins is also associated with the fertilization of an egg that had two or more nuclei. If the separation of the fetal egg occurs in the first 3 days after fertilization, then monozygotic twins have two placentas and two amniotic cavities, and are called monozygotic diamniotic dichoriones (Fig. A). If the division of the ovum occurs between 4 - 8 days after fertilization, then two embryos will form, each in a separate amniotic sac. Two amniotic sacs will be surrounded by a common chorionic membrane with one placenta for two. Such twins are called monozygotic diamniotic monochorionic twins (Fig. B). If division occurs by 9- 10th day after fertilization, then two embryos are formed with a common amniotic sac and placenta.
The frequency of birth of monozygotic twins is 3-5 per 1000 births. The division of a fertilized egg into two equal parts can occur as a result of a delay in implantation (immersion of the embryo in the uterine mucosa) and oxygen deficiency, as well as due to a violation of the acidity and ionic composition of the medium, exposure to toxic and other factors. The emergence of monozygotic twins is also associated with the fertilization of an egg that had two or more nuclei. If the separation of the fetal egg occurs in the first 3 days after fertilization, then monozygotic twins have two placentas and two amniotic cavities, and are called monozygotic diamniotic dichoriones (Fig. A). If the division of the ovum occurs between 4 - 8 days after fertilization, then two embryos will form, each in a separate amniotic sac. Two amniotic sacs will be surrounded by a common chorionic membrane with one placenta for two. Such twins are called monozygotic diamniotic monochorionic twins (Fig. B). If division occurs by 9- 10th day after fertilization, then two embryos are formed with a common amniotic sac and placenta.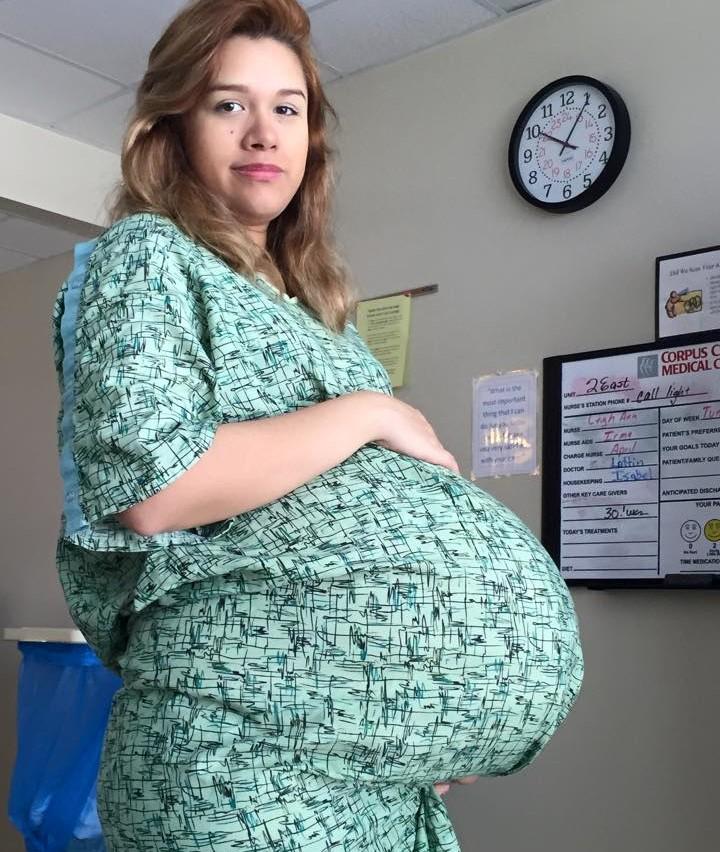 Such twins are called monozygotic monoamniotic monochorionic (Fig. B) If the egg is separated at a later date on the 13th - 15th day after conception, the separation will be incomplete, which will lead to the appearance of conjoined (undivided, Siamese) twins. This type is quite rare, approximately 1 observation in 1500 multiple pregnancies or 1: 50,000 - 100,000 newborns. Monozygotic twins are always the same sex, have the same blood type, have the same eye color, hair, skin texture of the fingers, and are very similar to each other.
Such twins are called monozygotic monoamniotic monochorionic (Fig. B) If the egg is separated at a later date on the 13th - 15th day after conception, the separation will be incomplete, which will lead to the appearance of conjoined (undivided, Siamese) twins. This type is quite rare, approximately 1 observation in 1500 multiple pregnancies or 1: 50,000 - 100,000 newborns. Monozygotic twins are always the same sex, have the same blood type, have the same eye color, hair, skin texture of the fingers, and are very similar to each other.
Twin births occur once in 87 births, triplets - once in 87 2 (6400) twins, quadruples - once in 87 3 (51200) triplets, etc. (according to the Gallin formula). The origin of triplets, quadruplets, and more twins varies. So, triplets can be formed from three separate eggs, from two or one egg. They can be monozygotic and heterozygous. Quadruples can also be identical and fraternal.
Features of the course of multiple pregnancy
In case of multiple pregnancy, the woman's body is subject to increased demands. All organs and systems function with great tension. In connection with the displacement of the diaphragm by the enlarged uterus, the activity of the heart becomes difficult, shortness of breath, fatigue occur. Enlargement of the uterus, especially towards the end of pregnancy, leads to compression of the internal organs, which is manifested by impaired bowel function, frequent urination, and heartburn. Almost 4-5 times more often there is the development of preeclampsia, which is characterized by an earlier onset, a protracted and more severe clinical course, often combined with acute pyelonephritis of pregnant women. Due to the increased need and consumption of iron, iron deficiency anemia often develops in pregnant women. Significantly more often than with a singleton pregnancy, complications such as bleeding during pregnancy and childbirth, anomalies in labor, and a low location of the placenta are observed. Often, with multiple pregnancies, abnormal positions of the fetus occur. One of the most common complications in multiple pregnancy is its premature termination.
All organs and systems function with great tension. In connection with the displacement of the diaphragm by the enlarged uterus, the activity of the heart becomes difficult, shortness of breath, fatigue occur. Enlargement of the uterus, especially towards the end of pregnancy, leads to compression of the internal organs, which is manifested by impaired bowel function, frequent urination, and heartburn. Almost 4-5 times more often there is the development of preeclampsia, which is characterized by an earlier onset, a protracted and more severe clinical course, often combined with acute pyelonephritis of pregnant women. Due to the increased need and consumption of iron, iron deficiency anemia often develops in pregnant women. Significantly more often than with a singleton pregnancy, complications such as bleeding during pregnancy and childbirth, anomalies in labor, and a low location of the placenta are observed. Often, with multiple pregnancies, abnormal positions of the fetus occur. One of the most common complications in multiple pregnancy is its premature termination. Preterm birth is observed in 25-50% of cases of such pregnancies.
Preterm birth is observed in 25-50% of cases of such pregnancies.
The development of term twins is normal in most cases. However, their body weight is usually less (by 10% or more) than in singleton pregnancies. With twins, the weight of children at birth less than 2500 g is observed in 40-60%. The low weight of twins is most often due to insufficiency of the uteroplacental system, which is not able to adequately provide several fetuses with nutrients, trace elements and oxygen. The consequence of this is a delay in the development of the fetus, which is a common occurrence in multiple pregnancies. The mass of twins, respectively, decreases in proportion to their number (triplets, quadruplets, etc.).
With monochorionic twins in the placenta, anastomoses are often formed between the fetal vascular systems, which can lead to a serious complication - feto-fetal transfusion syndrome. In this case, there is a redistribution of blood from one fetus to another, the so-called "stealing". The severity of feto-fetal transfusion (mild, moderate, severe) depends on the degree of redistribution of blood through the anastomoses, which vary in size, number and direction.
The severity of feto-fetal transfusion (mild, moderate, severe) depends on the degree of redistribution of blood through the anastomoses, which vary in size, number and direction.
Diagnosis in multiple pregnancy
The most reliable method for diagnosing multiple pregnancies is ultrasound, which allows not only early diagnosis of multiple pregnancies, but also to determine the position and presentation of fetuses, localization, structure and number of placentas, the number of amniotic cavities, the volume of amniotic fluid, congenital malformations and antenatal fetal death, the state of the fetus from a functional point of view, the nature of the uteroplacental and fetal-placental blood flow.
In multiple pregnancies, due to the higher risk of complications, ultrasound monitoring is performed more frequently than in singleton pregnancies. With dizygotic twins, about once every 3-4 weeks, with monozygotic twins - once every 2 weeks.
In addition, examinations and control of clinical tests are carried out with great care, and CTG is regularly recorded from 28 weeks of pregnancy.
Birth management
Indications for caesarean section associated with multiple pregnancy are triplets (quadruple), the transverse position of both or one of the fetuses, breech presentation of both fetuses or the first of them, and not associated with multiple pregnancy - fetal hypoxia, anomalies labor activity, prolapse of the umbilical cord, extragenital pathology of the mother, severe gestosis, placenta previa and abruption, etc.
-
ECO
In the department of assisted reproductive technologies of the Maternity Hospital No. 2
, IVF is performed at the expense of the Republican budget for couples
who have received a positive decision from the Minsk city or regional commissions to provide one free IVF attempt.
No problem with drug supply. There is no waiting list.The largest number of children
The largest number of children born to one mother, according to official data, is 69.
 According to reports made in 1782, between 1725 and 1765. The wife of a Russian peasant, Fyodor Vasiliev, gave birth 27 times, giving birth to twins 16 times, triplets 7 times and 4 twins 4 times. Of these, only 2 children died in infancy.
According to reports made in 1782, between 1725 and 1765. The wife of a Russian peasant, Fyodor Vasiliev, gave birth 27 times, giving birth to twins 16 times, triplets 7 times and 4 twins 4 times. Of these, only 2 children died in infancy. The most prolific mother of our contemporaries is Leontina Albina (or Alvina) of San Antonio, Chile, who at 1943-81 years gave birth to 55 children. As a result of the first 5 pregnancies, she gave birth to triplets, and exclusively male.
Most Birth
The record 38 births are claimed to be Elizabeth Greenhillies Abbots-Langley, c. Hertfordshire, UK. She had 39 children - 32 daughters and 7 sons.
The largest number of multiple births in one family
Maddalena Pomegranate from Italy (b. 1839) had triplets born 15 times.
There is also information about the birth on May 29, 1971 in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA, and in May 1977 in Bagarhat, Bangladesh, 11 twins. In both cases, no child survived.
Most fertile pregnancies
Dr. Gennaro Montanino, Rome, Italy, claimed to have removed, in July 1971, the embryos of 10 girls and 5 boys from the uterus of a 35-year-old woman who was 4 months pregnant. This unique case of 15-fertility was the result of infertility pills.
9 children - the largest number in one pregnancy - were born on June 13, 1971 by Geraldine Broadrick in Sydney, Australia. 5 boys and 4 girls were born: 2 boys were stillborn, and none of the rest survived more than 6 days.
Births of 10 twins (2 boys and 8 girls) are reported from Spain (1924), China (1936) and Brazil (April 1946).The father with the largest number of children
The largest father in the history of Russia is Yakov Kirillov, a peasant from the village of Vvedensky, who in 1755 was presented to the court in connection with this (he was then 60 years old). The first wife of a peasant gave birth to 57 children: 4 times four, 7 times three, 9once twice and 2 times once.