Helping breast milk supply
Low Milk Supply | WIC Breastfeeding Support
Many moms worry about low milk supply, but most of the time your body makes exactly what your baby needs, even if you don't realize it. There are also ways to tell if your baby is getting enough milk. If you aren't making enough, there are ways you can build your supply. And your WIC breastfeeding staff is always there to help!
Am I Making Enough Milk?
First, look for these signs that your baby is getting enough milk. For example, pay attention to the number of wet and dirty diapers and your baby's weight gain.
Things you should NOT worry about:
- How your breasts feel. Your breasts will feel softer and less full as your milk supply adjusts to your baby's needs. This does not mean you have low supply.
- If your baby nurses for shorter periods of time, such as only 5 minutes on each breast.
- If your baby's feeds are bunched together. This is called cluster feeding and happens when your baby starts nursing more often and for longer.
This can happen in the evenings or because of growth spurts.
- Not getting much milk when you express. Your baby is much more effective than a pump or hand expression at getting out milk. Find tips to help you pump.
If you are still concerned, talk to your baby's doctor about their growth.
Causes of Low Milk Supply
While most moms make plenty of milk, some do have low milk supply. This might happen if you:
- Limit your baby's breastfeeding sessions. Remember, the more you feed on demand, the more milk you make.
- Give your baby infant formula instead of breastfeeding.
- Introduce solid foods before baby is 4-6 months old.
- Take certain birth control pills or other medicine.
- Don't get enough sleep.
- Drink alcohol or smoke.
- Have had breast surgery.
Talk to your doctor if you have hepatitis B or C, herpes, or diabetes. These conditions may also affect milk supply.
Increasing Your Milk Supply
Breastfeeding frequently—especially in the first hours, days, and weeks—is the main way to increase your milk supply. Your body will make milk to meet your baby's demand.
Try these tips to help you make more milk:
- Breastfeed every time your baby is hungry. In the early weeks, your baby will eat 8-12 times every 24 hours. It's best not to put your baby on a strict feeding schedule. Follow your baby's cues, and let your baby tell you when it's time to eat.
- Make sure your baby is latching well.
- Offer both breasts at each feeding. Let your baby finish the first side, then offer the other side.
- Empty your breasts at each feeding.
 Hand express or pump after a feeding to draw out all the milk and signal your body to make more.
Hand express or pump after a feeding to draw out all the milk and signal your body to make more. - Avoid bottles and pacifiers in the early weeks. Feed your baby from your breast whenever you can.
- Get plenty of sleep, and eat a healthy diet.
- Pump or express your milk. Pumping or expressing milk frequently between nursing sessions, and consistently when you're away from your baby, can help build your milk supply.
- Relax and massage. Relax, hold your baby skin-to-skin, and massage your breasts before feeding to encourage your milk to let down.
- Take care of yourself. Get plenty of rest, eat well, drink enough fluids, and let others help you.
Consider Charting Your Progress
Record how often your baby is breastfeeding, for how long, and on which sides. If you are supplementing with infant formula, record how much your baby is getting and decrease the infant formula as your milk supply increases.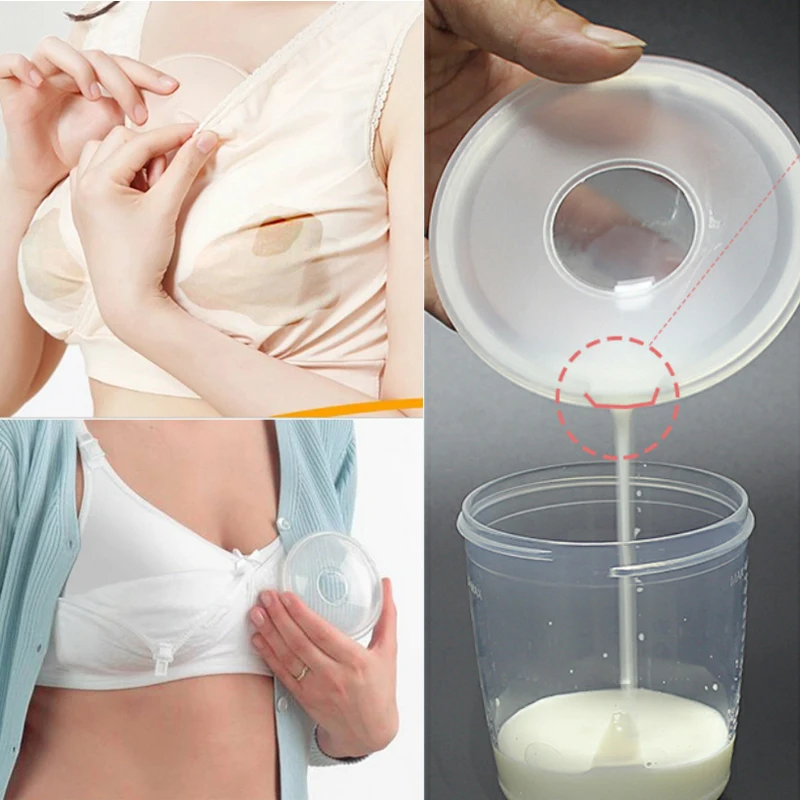 WIC breastfeeding staff can help you determine how much infant formula your baby needs.
WIC breastfeeding staff can help you determine how much infant formula your baby needs.
Still Have Questions?
Contact your WIC breastfeeding expert. They can talk to you about supply concerns and give you tips to increase your supply to meet your baby's needs.
Breastfeeding: Tips to Increase Your Milk Supply l University Hospitals l Northeast Ohio
Signs That a Breastfed Baby Is Being Well Nourished
- Your baby nurses at least 8 to 16 times in 24 hours, or every 2 to 3 hours. Your baby may be fussy once or twice a day. At these times, he or she wants to nurse often for several hours before seeming full. This is called cluster feeding.
- Your baby wets at least 6 cloth or 5 disposable diapers and has at least 1 bowel movement in 24 hours. This occurs by 1 week of age.
- You can hear your baby swallow milk while nursing or you can feel your baby swallow when lightly touching his or her throat.
- Your breasts seem softer after nursing.

- Your baby gains 4 to 8 ounces a week after the first week. There is no need to weigh your baby at home. Your baby’s doctor will do this for you. You may notice that your baby has outgrown his or her clothing.
- Your baby has regained his/her birthweight by 10 to 14 days after birth.
Factors Which Can Cause Your Milk Supply to Decrease
- Your baby feeds fewer than 8 to 16 times in 24 hours. Milk production is affected by how well the breast is drained.
- Your baby has a very weak suck, or has an improper latch.
- Giving bottles of formula or water after nursing. Most babies will suck on a bottle after nursing. This just means they need to suck. It does not mean they are still hungry. Babies cry or fuss for many reasons, such as being tired, bored, wet, hot or cold.
- Giving solid foods too early and/or before you breastfeed. Most babies do not need solid foods for the first 6 months if they are breastfeeding 8 to 16 times a day.

- Smoking can cause a decreased milk supply and interfere with the letdown reflex. Here are some things you should do:
- Try to quit or cut down.
- Smoke after nursing, not before.
- Don’t smoke in the same room with your baby.
- Beginning birth control pills too soon can decrease your milk supply. Wait at least 6 weeks before taking birth control pills and then use only the mini-pill (Progestin). If you still notice a decrease in your milk supply, talk to your doctor about other birth control options. Other medications may also affect milk supply. Check with your doctor. (Refer to PI-682, Breastfeeding and Birth Control: You Have Options.)
- Mothers who are exhausted may notice a decrease in milk supply. To keep yourself from getting too tired:
- Sleep or relax when your baby sleeps.
- Eat balanced diet that includes high-protein food.
- Drink when you are thirsty so that your urine is pale yellow in color.
 Both under and excessive over hydration can decrease milk supply.
Both under and excessive over hydration can decrease milk supply. - Take an iron supplement if your healthcare provider says you are anemic.
- Talk with your doctor or nurse midwife about the need for vitamin supplement.
- Accept help when it is offered.
- Use nipple shields and pacifiers with caution.
- A breast flange that is too small or too large in size can hurt your milk supply.
- Pregnancy
- Breast reduction surgery may reduce milk supply.
If You Notice Your Milk Supply Is Low
You can increase your milk supply by:
- Nursing your baby often. Nurse every 2 hours during the day and every 3 to 4 hours at night (at least 8 to 16 times in 24 hours). If your baby will not nurse, use a good quality double electric breast pump to increase milk production. Pumping after breastfeeding signals your body to produce more milk.
- Nurse your baby at least 15 minutes at each breast.
 Do not limit nursing time. If your baby falls asleep after one breast, wake him or her and offer the second breast. A few babies may benefit from nursing at one breast per feeding to increase the fat content of the feeding. Switch nursing- switching breasts several times during a feeding has been shown to increase milk supply.
Do not limit nursing time. If your baby falls asleep after one breast, wake him or her and offer the second breast. A few babies may benefit from nursing at one breast per feeding to increase the fat content of the feeding. Switch nursing- switching breasts several times during a feeding has been shown to increase milk supply. - Gently massage breast before and during feedings.
- Use relaxation techniques to reduce stress and promote the flow of breast milk.
- Provide skin to skin time with your baby for about 20 minutes after feeds. This “kangaroo care” has been shown to increase milk supply.
- Be sure baby is positioned and latched correctly.
- Offer both breasts at each feeding.
- Try breast compression during the feeding to help drain the breast.
- Pump immediately after breastfeeding during the day. Rest at night. Some mothers find that they get more milk if they pump for 5 minutes, rest for 5 minutes, and pump for another 10 minutes.

Talk to your doctor about using medication or the herb fenugreek.
Works Cited
Wambach, Karen and Riordan, Jan “Breastfeeding and Human Lactation”, Fifth edition, Jones & Bartlett, 2016.
How to get help with breastfeeding | help with breastfeeding
Many mothers need help with breastfeeding, especially in the first days after giving birth. Where can you get it?
Share this information
Some mothers breastfeed easily, but many need help. There are many ways to avoid problems and start breastfeeding successfully.
Before the birth of a child
Every mother-to-be would do well to take courses for pregnant women. In these courses, you will learn the importance of skin-to-skin contact in triggering milk production and receive other helpful breastfeeding tips. The course leader can provide you with a list of local lactation consultants and breastfeeding support groups. If the manager does not have this information, find out about local specialists, hotlines and support services yourself.
If the manager does not have this information, find out about local specialists, hotlines and support services yourself.
Be sure to include breastfeeding and early skin-to-skin contact with your baby in your birth plan. It is important that the medical staff is aware of your wishes.
Who can support breastfeeding?
Seek help immediately after giving birth if you need it. Small problems can quickly turn into big ones, but most of them are easy to fix if you take action right away.
Medical professionals such as obstetricians, nurses and physicians often have basic breastfeeding training. If you have more complex problems, you should contact professionals with a narrow specialization. These are lactation consultants (including self-help and breastfeeding support professionals).
Self-help members
These are mothers who have experienced breastfeeding and have been trained to help with common problems. They can assess whether the baby is latching on well and getting enough milk. If the grip is wrong, they can suggest a more comfortable position for feeding. For more serious problems, they can recommend a qualified technician.
If the grip is wrong, they can suggest a more comfortable position for feeding. For more serious problems, they can recommend a qualified technician.
Breastfeeding support specialists
Breastfeeding support professionals (eg, La Leche Liga, AKEV) have more knowledge and can help with more serious problems, such as if the baby is not gaining enough weight or does not want to latch on.
Lactation Counselors
Lactation Counselors help with more complex problems. It can diagnose insufficient milk production and assist with breastfeeding premature babies.
What problems can experts help with?
Here are some of the most common breastfeeding problems and links to detailed articles on them.
Latching problems
Ideally, a newborn baby will be able to latch on by himself in the first few hours of life. If this does not happen, or if the latch makes you uncomfortable, the obstetrician or self-help member can check that you are properly latching on to your baby. If the maternity hospital has already performed such a check, but the problem has not been solved, do not hesitate to ask for it again. If the baby does not take the breast after a day, and you have already been discharged from the hospital, contact a consultant for further support. Read more in the article on the correct grip on the chest.
If the maternity hospital has already performed such a check, but the problem has not been solved, do not hesitate to ask for it again. If the baby does not take the breast after a day, and you have already been discharged from the hospital, contact a consultant for further support. Read more in the article on the correct grip on the chest.
Sore nipples
This problem is almost always due to the fact that the baby does not latch on properly. A member of the self-help movement or a breastfeeding support specialist will suggest a better position for the baby. If you experience severe pain or inflammation that does not go away even after changing position, seek the help of a consultant to find out the cause. Read more in the article about sore nipples.
Breast swelling
The best way to avoid breast swelling (a condition that occurs two to four days after birth when your breasts are full and hard from incoming milk) is to feed your baby frequently. Your lactation consultant will teach you how to massage your breasts and how to express milk manually or with a breast pump to help relieve discomfort. If you are unable to breastfeed your baby due to swelling of the mammary glands, you should consult an obstetrician. Read more in the article about swelling of the mammary glands.
Your lactation consultant will teach you how to massage your breasts and how to express milk manually or with a breast pump to help relieve discomfort. If you are unable to breastfeed your baby due to swelling of the mammary glands, you should consult an obstetrician. Read more in the article about swelling of the mammary glands.
Problems with milk production
Many mothers in the first days after giving birth worry that they are not producing enough milk. A self-help member, obstetrician or nurse will help you calm down and explain that during this period it is perfectly normal for a child to ask for a breast every one to two hours. If the number of wet and soiled diapers is within the normal range and the baby is gaining weight well, everything is in order. Read more in the article on what to expect in the first week of breastfeeding.
If the baby is not gaining weight, a lactation support specialist or lactation consultant can help develop a feeding plan to ensure the baby is getting enough nutrition and supporting the mother's milk supply. Read more in the article about the lack of milk.
Read more in the article about the lack of milk.
The need to speak out
Sometimes a mother (especially if this is her first child) just needs to be reassured and reassured that her baby's behavior (for example, frequent hunger or waking up at night) is absolutely normal. In this situation, it is helpful to talk to someone who has breastfeeding experience and knows what to expect, such as a self-help member or a breastfeeding support specialist.
It is important to remember that with the right preparation and support, breastfeeding is easy, although tiring at first. And if problems do arise, seeking help in a timely manner will help correct the situation.
Breastfeeding GBUZ VFD Kopeysk
Breastfeeding
is natural, useful, convenient and cheap. Nobody has come up with anything better than breast milk for a baby. And no formula, even the most expensive and enriched with vitamins, will replace mother's milk, because laboratories cannot synthesize or isolate most of the important components that are contained in breast milk from cow's milk. For example, protective cells of maternal immunity.
For example, protective cells of maternal immunity.
Breastfeeding is also good for the mother herself. Long-term breastfeeding is a proven prevention of breast cancer, ovarian cancer, and the development of diabetes.
And one more thing. Any woman can breastfeed, regardless of breast size, the baby was born on time or not, and other factors. True milk deficiency occurs in less than 2-3 percent of cases.
Tips for breastfeeding mothers
There are many difficulties that a breastfeeding mother may face. Here are some important tips for breastfeeding moms from a lactation consultant Anastasia Kulikova .
- It is important to ensure that the baby is properly attached to the breast. Otherwise, he will not completely empty the breast, this may lead to a decrease in milk production, and may also injure the nipples. Please note that the newborn should capture not only the nipple, but also the areola, and its main part is from below, that is, the attachment should not be symmetrical.
 Mom's posture should be comfortable and relaxed.
Mom's posture should be comfortable and relaxed. - For successful breastfeeding, night feedings are very important, namely in the interval from 3 to 6 in the morning. It is at this time that the brain releases large amounts of prolactin, the hormone responsible for milk production.
- Drink plenty of fluids - 2-3 liters per day. It is also very important for a sufficient amount of milk. At night, put a bottle of water near you so as not to run to the kitchen.
- Do not be nervous, try to get enough sleep and be sure that you will be able to feed your baby for a long time. The calmness of the mother, her good emotional state is the key to successful breastfeeding of the newborn.
- If you have problems that you cannot solve yourself: you cannot establish proper attachment, you feel that there is not enough milk and nothing helps to increase lactation, or vice versa, you are experiencing milk stagnation, seek help from a lactation consultant .
 There are such specialists in some antenatal clinics, there are also special services that work on a paid basis.
There are such specialists in some antenatal clinics, there are also special services that work on a paid basis.
How to start breastfeeding correctly
It is important that the newborn is put to the breast immediately after birth, in the delivery room. In most maternity hospitals, the joint stay of mother and child is practiced today, which is also very important for the successful establishment of breastfeeding. In the first 1-3 days, colostrum is produced - it is very small, just a few drops, but enough for a newborn. Then comes the milk.
While in the hospital, breastfeed your baby more often to stimulate milk production. Remember, you need to feed the baby on demand, and not by the hour, as was customary in the past. This is the key to successful and long-term breastfeeding.
In the first month when lactation is established, discard bottles and nipples. Sucking from a bottle is much easier for a newborn, so there is a risk of rejection of the breast.
According to WHO recommendations, newborns should also not be supplemented with water. It is enough in mother's milk. And supplementation can lead to a decrease in milk production, as the baby will eat less of it.
Until what age can a child be fed?
The World Health Organization recommends breastfeeding until two years of age.
- In fact, there is no unambiguously correct answer to this question, - says Anna Levadnaya , pediatrician, PhD, author of the blog about pediatrics on Instagram @doctor_annamama. - I am convinced that you need to feed as long as both the baby and the mother enjoy it. If there are no objective reasons for stopping breastfeeding, up to a year, mother's milk must be present in the baby's diet. It is optimal to keep it up to a year and a half.
There is an opinion that after a year milk no longer brings much benefit to the child, but this is not so.
- Studies show that even after the first year of life in breast milk there is a high amount of protein, the concentration of immunoglobulins, lysozyme and lactoferrin, which help to form immunity, Anna Levadnaya notes. - Long-term breastfeeding reduces the risk of atherosclerosis in adulthood, diabetes and obesity, and many other diseases. Long-term breastfeeding helps the correct formation of the maxillofacial skeleton, the likelihood that the child will not have the correct bite is much lower. And some studies suggest that babies who breastfeed for a long time have higher IQs.
- Long-term breastfeeding reduces the risk of atherosclerosis in adulthood, diabetes and obesity, and many other diseases. Long-term breastfeeding helps the correct formation of the maxillofacial skeleton, the likelihood that the child will not have the correct bite is much lower. And some studies suggest that babies who breastfeed for a long time have higher IQs.
The benefits of breastfeeding
The benefits of breastfeeding cannot be overestimated. It is not only a source of valuable nutrients. During feeding, a strong emotional bond is formed between the newborn and mother. Scientists have conducted many studies on the benefits of breast milk. Here's what they say.
- Breast milk contributes to the maturation of the child's immune system, reduces the risk of cancer.
- Children on breastfeeding have a lower risk of atopic dermatitis, they are less likely to get otitis media, they need to remove the pharyngeal tonsils less often, they have better vision.

- Breastfed babies are less likely to experience constipation, diarrhea and intestinal infections, as well as food allergies (when breastfed for 6 months or more). Adults who were breastfed as children are less likely to develop Crohn's disease (severe inflammation of the intestines), ulcerative colitis (inflammation of the colon), and appendicitis.
- Breast milk contains less protein and salt, so there is less stress on the baby's immature kidneys. Less common are urinary tract infections.
- Improves the growth of nervous tissue - this is facilitated by cholesterol and other fats of breast milk.
- Breast sucking improves jaw muscle development. And if you feed your baby for more than a year, this reduces the risk of malocclusion. In addition, the gradual changes in the taste of breast milk with age prepare the baby for a variety of solid foods.
- Breast-fed babies are less likely to develop respiratory tract infections and are much milder, less likely to develop bronchial asthma, pneumonia, and influenza.

What breast milk should look like
Don't look online for a picture of the "correct" color of breast milk. This is such a unique product that adapts to the needs of the child depending on his age and condition, which can change its composition, fat content and color even during the day. For example, in summer, when a child has a great need to drink, the milk becomes more liquid, the color is more transparent.
But usually with established lactation, the foremilk - the one that the baby receives at the beginning of feeding, is more liquid, it is rich in carbohydrates, its color is less saturated, white-bluish. Back milk, which the baby receives at the end of feeding, is rich in fats, the color is more saturated, yellowish.
If you express milk using a breast pump, you will first see a homogeneous liquid in the bottle. But after standing for quite a bit, it will separate just into these two layers: the top one - the “cream” layer - will be fatter, but smaller in volume.
How to know if a child is hungry
In fact, a child can ask for a breast not only because he is hungry. It helps the newborn to calm down, feel safe, sucking reduces the pain that the baby may experience due to colic. However, there are signs by which you can understand that the child really wants to eat.
- The child is anxious.
- He turns his head from side to side, opens his mouth, as if looking for a nipple, starts doing this especially actively if you pass his hand over his cheek.
- Starts fiddling, groaning, sticking out his tongue.
- When you pick him up, he looks for breasts.
- Cries, does not calm down with motion sickness and other actions.
Remember, it is recommended to breastfeed on demand, but at least once every 3 hours during the day and 5 hours at night. Within 1-2 months, lactation gradually improves, milk is released during feeding, and the breast gets used to working in a certain rhythm of feeding.
Why breast milk is expressed
It is important to remember that when lactation is established, pumping is not necessary. Advice to a nursing mother: do not listen to grandmothers who are convinced that if you do not express milk after each feeding, then it will disappear. This is not true.
- The arrival of milk is carried out according to the so-called "principle of direct feedback": the more milk left, the more it will come, - says Anna Levadnaya. - The child himself regulates the amount he needs. If a woman expresses milk after each feeding, she will be trapped: more milk will come, but the child does not need such an amount, it will stagnate in the chest, which threatens the development of lactostasis and mastitis.
However, there are times when it is necessary to express milk. If your baby was born prematurely and is in intensive care, then the mother should start expressing milk as soon as possible after birth. This will help preserve the milk until the newborn can suckle on his own. In the meantime, the expressed milk will be valuable food for him. Premature babies, as a rule, are fed through a tube, as they are still very weak, they do not have a sucking reflex.
In the meantime, the expressed milk will be valuable food for him. Premature babies, as a rule, are fed through a tube, as they are still very weak, they do not have a sucking reflex.
Another occasion when it is necessary to express milk is when you feel that there is less or not enough milk. You need to pump after each feeding, including at night. In this case, breastfeeding specialists can help you.
If you have to be separated from your baby, you also need to express milk so that dad or someone else in the family can feed the baby. Also, pumping is necessary for lactostasis and mastitis in order to cope with milk stagnation.
What can be done while breastfeeding
How many unreasonable prohibitions today for a nursing mother. In fact, the list of what not to do while breastfeeding is very small. We will dispel myths and tell you what a woman can do while breastfeeding.
- No hypoallergenic diet required. We have long been of the opinion that a nursing mother should follow a special diet so that the child does not have diathesis.
 Meanwhile, in other countries, women eat what they want and how much they want, and the concept of “nursing mother’s diet” simply does not exist. But, despite the widespread practice of diets in pregnant and lactating women, the incidence of allergies continues to grow, and studies have shown that restrictions do not affect its manifestation in any way. Therefore, a nursing mother should eat varied, eat her favorite vegetables, fruits. It is necessary to exclude this or that product from the diet only with a proven food allergy to it.
Meanwhile, in other countries, women eat what they want and how much they want, and the concept of “nursing mother’s diet” simply does not exist. But, despite the widespread practice of diets in pregnant and lactating women, the incidence of allergies continues to grow, and studies have shown that restrictions do not affect its manifestation in any way. Therefore, a nursing mother should eat varied, eat her favorite vegetables, fruits. It is necessary to exclude this or that product from the diet only with a proven food allergy to it. - You can drink coffee, many women love it. But the amount should be limited to 2 cups per day.
- You can play sports. This does not affect the production and quality of milk. But consider important nuances. It is worth returning to full-fledged training not earlier than the child is 6 months old. It is better to give preference to moderate physical activity. During too intense activities, lactic acid accumulates in milk, the child may not like its taste.
 When playing sports, a lot of fluid is lost, so you need to drink more water to avoid dehydration.
When playing sports, a lot of fluid is lost, so you need to drink more water to avoid dehydration. - Can be dyed and curled.
- You can visit the sauna, observing all hygiene measures.
- You can do, if necessary, x-rays, fluorography, treat teeth using anesthesia (it is selected by the doctor, taking into account the fact that you are breastfeeding).
- You can visit beauty salons and get simple facial and body treatments, including massages that do not affect the chest area.
- You can drink alcohol in moderation. Yes, don't be surprised. Sometimes you can afford to have a glass of wine and relax a bit. But remember a few important points. Alcohol penetrates into breast milk, and its maximum concentration in it is reached after 60-90 minutes if you eat, and after 30-60 minutes if you drink on an empty stomach. And the rate of elimination of alcohol from the body depends on the weight of the woman (in full it will happen faster), the amount of alcohol consumed, its strength.
 A glass of wine or a glass of beer is excreted on average in 2-3 hours, strong alcohol - in 13 hours. Therefore, if you want to drink a glass of dry white wine, do it immediately after feeding your baby so that the next alcohol will be out of the body. Or express milk 1-2 feedings ahead if you plan to drink more. But in any case, cut out alcohol until your baby is 3 months old.
A glass of wine or a glass of beer is excreted on average in 2-3 hours, strong alcohol - in 13 hours. Therefore, if you want to drink a glass of dry white wine, do it immediately after feeding your baby so that the next alcohol will be out of the body. Or express milk 1-2 feedings ahead if you plan to drink more. But in any case, cut out alcohol until your baby is 3 months old.
What not to do while breastfeeding
- A breastfeeding mother should not smoke. Continuous smoking reduces the level of prolactin, the hormone responsible for the production of sufficient milk. In a child, it can cause nausea, vomiting, colic, problems with stools, and irritability.
- You can not drink alcohol in large quantities, in a state of intoxication to feed a child.
- You can not do complex cosmetic procedures involving injections, the introduction of various drugs. For example, mesotherapy of the face and scalp, apparatus treatment, photo and laser hair removal, and others, their impact on the body of the mother and child during this period has not been studied.

What to do if the mother gets sick
Unfortunately, mothers get sick during breastfeeding. And often women unreasonably stop breastfeeding because of this. In fact, it is possible and necessary to feed a baby with SARS (perhaps, mothers get sick most often with them). Together with milk, the child will receive the necessary antibodies. And a woman can bring down a high temperature with drugs based on paracetamol or ibuprofen, they are allowed when breastfeeding.
But even more serious illnesses that require medication, including antibiotics, are no reason to stop breastfeeding. First, there are many drugs allowed during this period. And secondly, despite the fact that the instructions for the medicine often say that it can be taken only if the benefit to the woman outweighs the risks to the child, this does not mean at all that the remedy is dangerous and should not be taken.
- The fact is that studies on the safety of drugs during breastfeeding are very expensive, and manufacturers usually do not conduct them, - says Anna Levadnaya. - It is easier for them to write that the drug is not recommended for breastfeeding, for fear of liability. But such studies were carried out by other independent organizations, for example, the World Health Organization, the American Academy of Pediatrics. And in most cases, the drug is allowed during feeding. Or you can choose a safe analogue.
- It is easier for them to write that the drug is not recommended for breastfeeding, for fear of liability. But such studies were carried out by other independent organizations, for example, the World Health Organization, the American Academy of Pediatrics. And in most cases, the drug is allowed during feeding. Or you can choose a safe analogue.
Moreover, this information is publicly available and you can check the compatibility of the drug and breastfeeding yourself.
- There are several sites for this, the simplest is the Spanish site. All data here is based on scientific publications and medical research.
Despite the fact that there is no Russian version of the site, it is not difficult to use it. Here are some tips for breastfeeding moms on how to do this. First determine the Latin name of the drug or active substance. On the site, select English, enter the name of the desired medicine in the search bar. A rectangle of green, yellow, orange or red color with a description will be highlighted. Green means very low risk, which means the drug is safe for the baby. Red - the risk is very high, which means that the drug cannot be used, you need to choose an analogue. But the final decision whether to take this or the drug during breastfeeding or the abolition of breastfeeding, you still need to work with your doctor.
Green means very low risk, which means the drug is safe for the baby. Red - the risk is very high, which means that the drug cannot be used, you need to choose an analogue. But the final decision whether to take this or the drug during breastfeeding or the abolition of breastfeeding, you still need to work with your doctor.
Feeding after caesarean section
Women whose babies are born by caesarean section often worry that they will not be able to breastfeed their baby. Of course it isn't. There are some difficulties that a mother may face, but they are all surmountable. Milk after a cesarean may come a little later than after a natural birth. To speed up this process, take the baby to you from the nursery as soon as you can take care of him yourself, breastfeed more often.
If for some reason it is not possible to stay together with the baby in the maternity hospital after the operation, then the mother needs to express milk in order to maintain lactation, start doing this as soon as possible after the birth. True, in this case, the baby, who will receive the mixture at the maternity hospital, may refuse the breast at home: sucking from it requires much more effort than from a bottle. Do not despair! Try not to use nipples and bottles, offer breasts more often, and you can feed with expressed milk from a spoon or pipette.
True, in this case, the baby, who will receive the mixture at the maternity hospital, may refuse the breast at home: sucking from it requires much more effort than from a bottle. Do not despair! Try not to use nipples and bottles, offer breasts more often, and you can feed with expressed milk from a spoon or pipette.
Feeding premature babies
Breast milk is very important for premature babies. The baby receives the necessary nutrients, protection from infections. Breast milk is easier to digest, which is very important for the still immature digestive system of the baby.
Unfortunately, often children born prematurely can be in intensive care, sometimes for quite a long time. They cannot suckle on their own, they are fed through a tube. In this case, in order to save breast milk, the mother needs to start expressing as soon as possible after childbirth and continue to do this until the baby gets stronger and can not eat on her own. “If a premature baby is discharged from the hospital with a normal weight for his age, then the mother can only feed the baby with breast milk,” says Anna Levadnaya.
- If the baby is underweight, breast milk fortifiers should be used. These are special supplements that give a premature baby extra calories, vitamins, macro- and microelements. They are available in the form of a powder or a ready-made mixture. Add to expressed milk just before feeding.
There are two points of view, in many ways different.
The first is followed by many pediatricians and, in particular, the famous Dr. Komarovsky: it is necessary to wean the baby when he is one year old, and do it quickly, decisively and irrevocably . Doctors assure: by this age the child has already received everything that is needed from mother's milk, and is able to eat coarser food, since teeth are already growing. Not delaying feeding is also good for the mother, in terms of social needs: for example, going to work.
Radical completion methods are proposed. For example, for a few days to leave the baby with his grandmother. Of course, the child will cry and look for his mother, but he will have to be firm. Mom, meanwhile, takes lactation suppressant pills and pumps. If you do everything right, the stress will be minimal and quickly forgotten. Weaning should be postponed if the baby is sick, teething, or there is a change of scenery (moving, going on vacation, etc.). But the time of year doesn't matter here. Previously, pediatricians really dissuaded from completing breastfeeding in the summer to protect the baby from intestinal infections and disorders. Now this is not relevant: it is enough to follow the usual rules of hygiene.
Of course, the child will cry and look for his mother, but he will have to be firm. Mom, meanwhile, takes lactation suppressant pills and pumps. If you do everything right, the stress will be minimal and quickly forgotten. Weaning should be postponed if the baby is sick, teething, or there is a change of scenery (moving, going on vacation, etc.). But the time of year doesn't matter here. Previously, pediatricians really dissuaded from completing breastfeeding in the summer to protect the baby from intestinal infections and disorders. Now this is not relevant: it is enough to follow the usual rules of hygiene.
Lactation consultants and perinatal psychologists (yes, there are some) are strongly opposed to such an early termination, and especially disagree with doctoral methods, considering them ruthless. Like, for a child, separation from his mother is a catastrophe and betrayal, such injuries do not go away without a trace.
Breastfeeding should be completed by 2-3 years, gradually and gently, the authors of the popular BF blog advise. The breast is not only food for the baby, but also contact with the mother, calm falling asleep, confidence that everything is fine.
The breast is not only food for the baby, but also contact with the mother, calm falling asleep, confidence that everything is fine.
The scheme is as follows: from the age of 6 months, small restrictions on feeding are introduced, for example, on the street, at a party - only at home. Then the number of applications during the day is gradually reduced. How? Minimize everything that reminds of mother's milk: do not change clothes in front of the child, choose clothes that make it difficult to access the breast. Distract with something interesting or tasty. Next, we teach the baby to calm down and fall asleep without a breast. First during the day and then at night. Rituals will help here: before going to bed, read a fairy tale, sing a song, stroke ... Night feedings are removed the very last and also gradually, until the attachments become symbolic. This completion of the GW may take several weeks or even months, but it is worth it. And you can “round off” in a day or two, if the child himself is ready and simply outgrew the need for sucking.