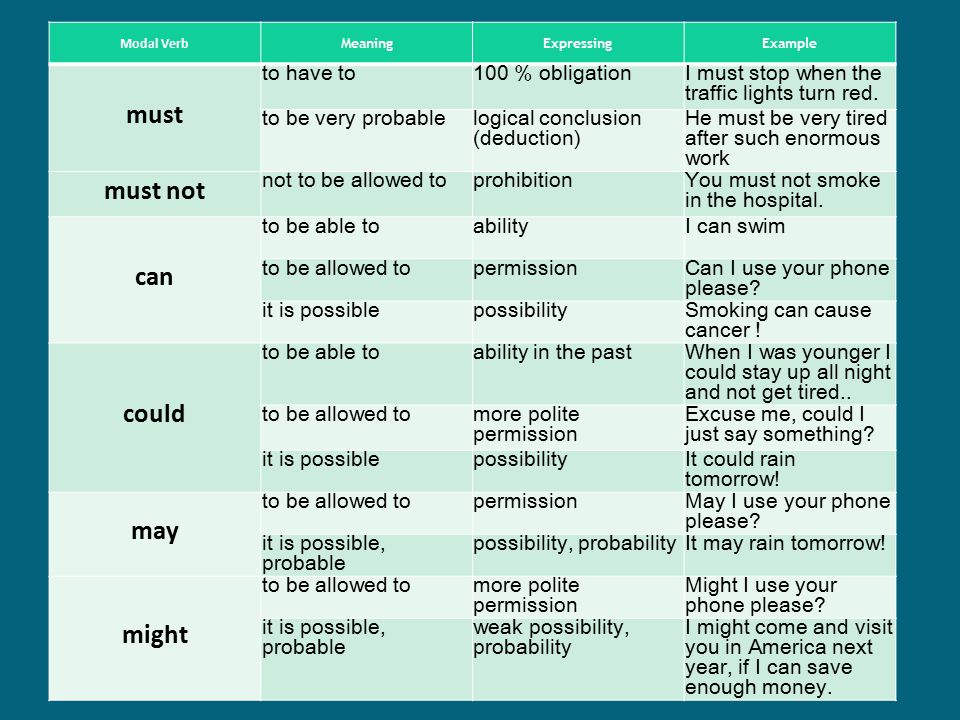
Heavy bleeding 3 weeks after miscarriage
How Long Does a Miscarriage Last? Physical Symptoms Last 2-8 Weeks
- Symptoms of a miscarriage, primarily heavy bleeding and cramping, can last up to two weeks, while lighter bleeding may continue another one to two weeks.
- It can take four to six weeks to get a normal period again, and irregular periods immediately following miscarriages are common.
- The emotional effects of a miscarriage, which are less often discussed, can be long-lasting and difficult.
Miscarriage is medically defined as the loss of pregnancy up to 20 weeks. After that point, it is technically considered a stillbirth.
However, miscarriage is often used as an umbrella term for pregnancy loss at any point. Miscarriage occurs in about 15%-25% of pregnancies in the United States, and most happen within the first 10 weeks of gestation. Only 5% of women will experience two consecutive miscarriages, and 1% will experience three or more.
There are likely more miscarriages than we know because some occur before the pregnancy is detected by a test, says Amanda Kallen, assistant professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at Yale School of Medicine.
Here are some signs of pregnancy loss, and what to expect if you're experiencing a miscarriage.
How long does a miscarriage last?Symptoms of miscarriage — primarily heavy bleeding and cramping — can last up to two weeks. Lighter bleeding can last an additional one to two weeks. Depending on how far along the pregnancy was, pregnancy hormone levels can remain high for days or several weeks.
It can take four to six weeks to get a normal period again, though irregular periods immediately following miscarriages are common.
Sometimes, even more complicated than the physical symptoms are the emotional consequences of miscarriage, says Kallen, who herself has had two losses. The psychological pain is complicated by the tendency for women to suffer in silence because there is a societal taboo surrounding miscarriages, Kallen says.
According to research, social support has shown to be crucial in the emotional healing that occurs after pregnancy loss.
"There can be a significant grieving process, and it is often not linear," Kallen says. "Depending on how much time has passed, or if someone has invested time and energy into fertility treatments — or even for someone who got pregnant easily and feels a connection to that pregnancy — the process can last a long time and be complex."
Types of miscarriage and symptomsSpotting in the first trimester — the initial 12 weeks of the pregnancy — is quite common. But if the bleeding is heavy and accompanied by cramping, it could be a sign of something worse.
"Any bleeding that is soaking a pad within an hour should be carefully evaluated," says Kallen. "Initial instances of bleeding should be at least discussed with a provider. That can be managed with more observation and discussion."
Different types of pregnancy loss:
Chemical pregnancy – Also called "biochemical pregnancy," this is a pregnancy loss that occurs within the first five weeks of gestation. The body makes enough of the reproductive hormone – human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) – to result in a positive test but does not progress into a clinical pregnancy. About 50%-75% of all miscarriages are believed to be chemical pregnancies. Potential causes include advanced maternal age and chromosomal abnormalities.
The body makes enough of the reproductive hormone – human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) – to result in a positive test but does not progress into a clinical pregnancy. About 50%-75% of all miscarriages are believed to be chemical pregnancies. Potential causes include advanced maternal age and chromosomal abnormalities.
Missed miscarriage – In a missed miscarriage – also known as a silent miscarriage or missed abortion – tissues from the placenta and embryo remain in the uterus, but the embryo has died or never properly formed. People who experience this have three options. They can wait it out to see if the body naturally passes the tissue, or take misoprostol, a medication that prevents stomach ulcers but can also help manage miscarriages. The third option is a D&C, or dilation and curettage, which uses either surgical instruments or suctions to remove the tissue manually. The decision depends on each individual's preferences, the circumstances of the miscarriage, and the doctor's recommendation, Kallen says.
First-trimester loss – Missed miscarriages and chemical pregnancies both fall under the umbrella of first-trimester loss. These miscarriages occur in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy. Risk factors include maternal age of 35 or older, chronic conditions like diabetes or thyroid disease, and obesity, along with cigarette smoking and illicit drug use. About 80% of pregnancy loss occurs in the first trimester.
Second-trimester loss – Miscarriages that occur between 12 and 24 weeks of gestation are far less common – only 2%-3% of pregnancies are lost during this time. Unlike earlier miscarriages, the loss is more likely caused by trauma, infections, or clotting disorders, Kallen says. There may also be problems with fetal development or issues with the uterus, such as abnormalities in shape.
Late pregnancy loss – Losses that occur in the final term are often caused by problems with the placenta, birth defects, infections in the fetus or placenta, or umbilical cord complications.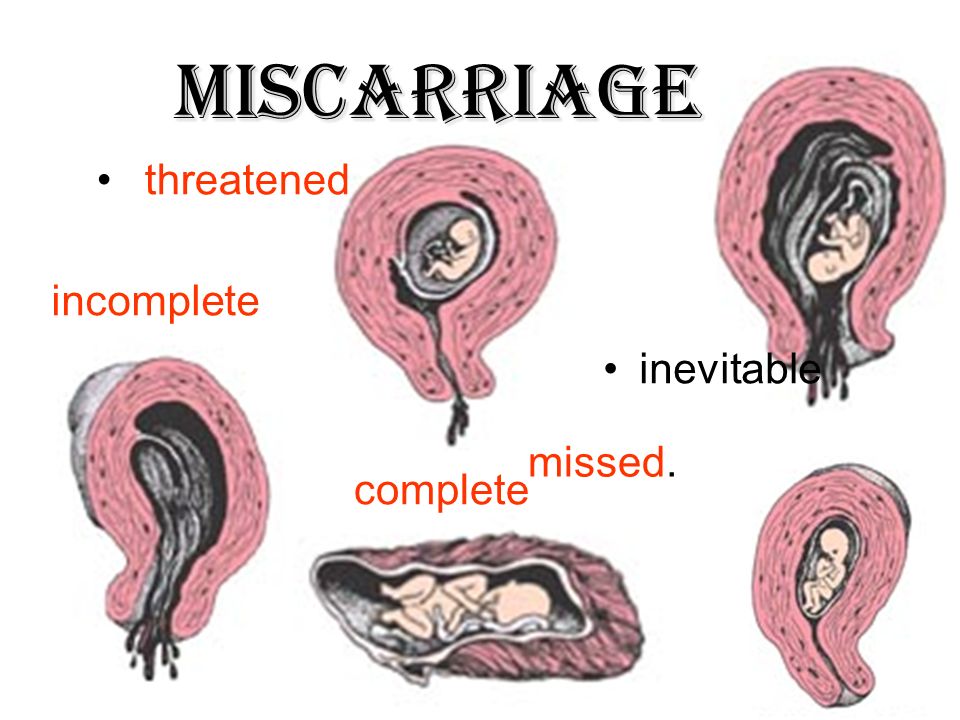 Like second trimester miscarriage, diabetes or preeclampsia can also play a role. The use of marijuana, cigarettes, and illicit drugs increases the risk of stillbirth.
Like second trimester miscarriage, diabetes or preeclampsia can also play a role. The use of marijuana, cigarettes, and illicit drugs increases the risk of stillbirth.
Kallen says if you experience any bleeding after a positive pregnancy test, tell your doctor, who can further evaluate the status of the pregnancy.
If there are no signs of infection, also called a septic miscarriage, it can be safe to allow the early miscarriage to happen naturally, Kallen says.
But if symptoms of septic miscarriage are present, such as fever, chills, lower abdominal tenderness, and foul-smelling vaginal discharge, an individual should seek immediate medical attention.
If a doctor deems it necessary to use medication to manage the miscarriage at home, some options include:
- Misoprostol pills: These are placed in the vagina, which usually leads to cramps and bleeding that will start within two to six hours afterward.
 Misoprostol may also be prescribed orally.
Misoprostol may also be prescribed orally. - Ibuprofen: Taking ibuprofen can help with cramps.
"For miscarriages in the second and third trimester, there will need to be medical intervention," Kallen says.
For those having a D&C, doctors will often recommend taking pain medicine beforehand. The procedure usually takes less than 10 minutes and may take place in a doctor's office on an outpatient basis or in the hospital. General or local anesthetic will be used, and most women experience minor cramping and bleeding for a few days after.
Insider's takeawayMiscarriages are relatively common, and each woman's experience will vary depending on the circumstances. Early pregnancy loss is more common than later miscarriage and can often be managed at home.
If you suspect you are having a miscarriage, always contact your doctor to discuss options. The physical effects can last for several weeks, but the emotional effects, which are seldom discussed, can be long-lasting and difficult.
"Pregnancy loss is different for each individual," Kallen says. "It can be sort of a secret experience because women can go through it without many people knowing. The silence around it is the hardest part."
- What causes miscarriages, and disproving common myths
- You cannot prevent a miscarriage but there are steps you can take to reduce your risk
- A chemical pregnancy is a miscarriage, but doctors say it's a good sign if you're trying to get pregnant
- You've had a miscarriage. Here's how long doctors recommend you wait before trying again
- How many periods you can miss before you should worry
Lindsay Kalter
Lindsay Kalter is a health freelance writer and contributor to Insider who has held positions with Politico, the Boston Herald, and the American Heart Association. Her work has appeared in publications including The Washington Post, Hour Detroit Magazine, The Dallas Morning News, and WebMD. She has covered topics from mental health and opioid use to cutting-edge medical research and the COVID-19 pandemic.
Her work has appeared in publications including The Washington Post, Hour Detroit Magazine, The Dallas Morning News, and WebMD. She has covered topics from mental health and opioid use to cutting-edge medical research and the COVID-19 pandemic.
Read moreRead less
Miscarriage - What happens - NHS
If there's no pregnancy tissue left in your womb, no treatment is required.
However, if there's still some pregnancy tissue in your womb, your options are:
- expectant management – wait for the tissue to pass out of your womb naturally
- medical management – take medicine that causes the tissue to pass out of your womb
- surgical management – have the tissue surgically removed
The risk of complications is very small for all these options.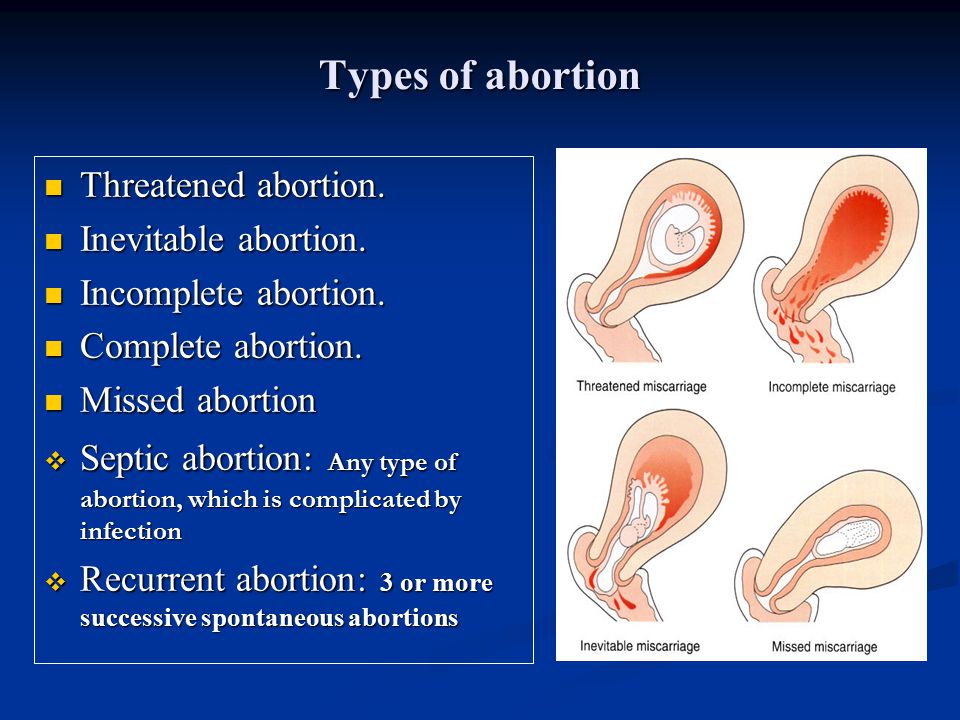 It's important to discuss them all with the doctor in charge of your care.
It's important to discuss them all with the doctor in charge of your care.
Expectant management
If you have a miscarriage in your first trimester, you may choose to wait 7 to 14 days after a miscarriage for the tissue to pass out naturally. This is called expectant management.
If the pain and bleeding have lessened or stopped completely during this time, this usually means the miscarriage has finished. You should be advised to take a home pregnancy test after 3 weeks.
If the test shows you're still pregnant, you may need to have further tests.
If the pain and bleeding have not started within 7 to 14 days or are continuing or getting worse, this could mean the miscarriage has not begun or has not finished. In this case, you should be offered another scan.
After this scan, you may decide to either continue waiting for the miscarriage to occur naturally, or have drug treatment or surgery. If you choose to continue to wait, your healthcare professional should check your condition again up to 14 days later.
If you choose to continue to wait, your healthcare professional should check your condition again up to 14 days later.
Contact your hospital immediately if the bleeding becomes particularly heavy, you develop a high temperature (fever) or you experience severe pain.
Medicine
You may choose to have medicine to remove the tissue if you do not want to wait, or if it does not pass out naturally within 2 weeks. This involves taking tablets that cause the cervix to open, allowing the tissue to pass out.
In most cases, you'll be offered tablets called pessaries that are inserted directly into your vagina, where they dissolve.
The tablets usually begin to work within a few hours. You'll experience symptoms similar to a heavy period, such as cramping and heavy vaginal bleeding. You may also experience vaginal bleeding for up to 3 weeks.
In most units, you'll be sent home for the miscarriage to complete. This is safe, but ring your hospital if the bleeding becomes very heavy.
You should be advised to take a home pregnancy test 3 weeks after taking this medicine. If the pregnancy test shows you're still pregnant, you may need to have further tests.
You may be advised to contact your healthcare professional to discuss your options if bleeding has not started within 24 hours of taking the medicine.
Surgery
In some cases, surgery is used to remove any remaining pregnancy tissue. You may be advised to have immediate surgery if:
- you experience continuous heavy bleeding
- there's evidence the pregnancy tissue has become infected
- medicine or waiting for the tissue to pass out naturally has been unsuccessful
Surgery involves removing any remaining tissue in your womb with a suction device. You should be offered a choice of general anaesthetic or local anaesthetic if both are suitable.
You should be offered a choice of general anaesthetic or local anaesthetic if both are suitable.
After a miscarriage
A miscarriage can be very upsetting, and you and your partner may need counselling or support. You may also have questions about trying for another baby and what happens to the miscarried foetus.
For more information, read what happens after a miscarriage.
Page last reviewed: 09 March 2022
Next review due: 09 March 2025
norm or cause for panic
- Home
- Useful articles
Bleeding after abortion: normal or cause for alarm
Uterine bleeding after termination of pregnancy is a common phenomenon in obstetric practice that occurs on the first day after the operation. The intensity and duration of blood loss are individual and depend not only on the characteristics of the female body, but also on the type of abortion.
 nine0017
nine0017 Features of bleeding after abortion
Bleeding may be completely absent during the first two days after surgical termination of pregnancy, but later increases to menstrual bleeding and continues in some clinical pictures up to 6 weeks. This pathology indicates a hormonal imbalance, that is, there is insufficient "support" of endometrial tissues, which supports the development of pregnancy. As a result of this bleeding after termination of pregnancy can only intensify, and continue intermittently for several weeks. It is important to understand that here we are talking about pathology.
Most women of reproductive age are concerned about the main question, how long will the bleeding after an abortion last? The question is individual, but if it does not pass more than two weeks after getting rid of the fetus, it is important to urgently contact the local gynecologist. The duration of the hemorrhage also depends on the gestational age: the earlier an abortion is performed, the more likely it is to solve such a piquant problem in a gentle “mode” and without serious consequences.
 nine0017
nine0017 Cause of abnormal bleeding after an abortion
The occurrence of bleeding after an abortion should not confuse the patient, but its duration should be a cause for concern. Among the pathological causes of this symptom, the following should be singled out:
- Perforation of the uterus;
- Injury of the cervix;
- Presence of residual fetal tissue;
- Blood clotting disorder;
- The reaction of the female body to individual anesthetics. nine0004
With such diagnoses, along with hemorrhage, there is an obvious violation of the temperature regime, convulsions, general weakness, fainting, hypotension, increased heart rate. It is important not to ignore such signs of shock, but to visit a medical center and a qualified specialist in a timely manner.
How to deal with bleeding after a miscarriage
It is important to understand that to stop prolonged bleeding after a miscarriage at home is impossible, only a competent gynecologist can determine an accurate and effective treatment regimen.
 Delay in this matter can cost the patient her life.
Delay in this matter can cost the patient her life. If the appeal to the doctor is timely, then the first thing the patient is referred for is an ultrasound scan. This accurate clinical examination allows to determine the etiology of the pathological process and the future treatment regimen. If it became known that there is residual fetal tissue in the uterus, additional surgical intervention is necessary to properly clean its cavity. In case of mechanical damage to the uterus or its cervix after interruption, the gynecologist prescribes the repair of the injured area of the uterus, bladder or intestines. nine0017
Possible complications
Bleeding after an abortion is dangerous for women's health and causes serious damage to the woman's reproductive system. Among the potential complications, doctors distinguish infertility, malignant tumors and even death of the patient. Therefore, the problem needs to be addressed in a timely manner, and early termination of pregnancy in order to avoid heavy bleeding.
Return to list
Miscarriage. What to do after a miscarriage? nine0001
When a woman finds out about her pregnancy, she changes her rhythm of life, especially if the pregnancy is desired. However, depending on many circumstances, miscarriage may occur, that is, a natural termination of pregnancy. Statistics say that up to 20 percent of pregnancies end in pathological abortions. Often a woman may not know that she was pregnant, as a miscarriage sometimes occurs at a very early stage and seems to be just a normal delay in menstruation followed by heavy discharge. nine0017
If a woman finds out that she is pregnant and wants to become a mother, she should be very attentive to her condition. The threat of miscarriage often occurs in the early stages of pregnancy and therefore it is necessary to know what symptoms and signs precede a sudden miscarriage.
Signs
The main sign of a suspected miscarriage is bleeding from the uterus.
 They happen not abundant, pale scarlet or gray-brown. The discharge most often gradually increases and is characterized by sudden spasms or pulling pains in the lower abdomen. These symptoms may last for some time. nine0017
They happen not abundant, pale scarlet or gray-brown. The discharge most often gradually increases and is characterized by sudden spasms or pulling pains in the lower abdomen. These symptoms may last for some time. nine0017 The pains are often so weak that the woman simply does not pay attention to them. They are able to be interrupted, and the woman simply forgets about them, especially if the discharge also stopped, and before that they were insignificant. Meanwhile, the very first symptoms should alert you and you should urgently go to the gynecologist for examination and consultation. Even if the process has stopped, after a few days you can feel a sharp deterioration in health, and then you can no longer save the life of the unborn child. Be sure to pay attention to what exactly comes out with the discharge, if there are tissue fragments, it means that miscarriage has already occurred. Therefore, one should not hesitate to go to the doctor, the fetus may come out, in whole or in parts, there may be white particles or a round gray bubble.
 When the body is completely cleansed, the pain will subside, but before that it may continue for some time.
When the body is completely cleansed, the pain will subside, but before that it may continue for some time. Terms of miscarriage
A miscarriage is classified as early if it occurred before twelve weeks from the onset of pregnancy. Starting from the 22nd week, if a spontaneous miscarriage has occurred, it is considered late. If the termination of pregnancy occurred before thirty-seven weeks, then this is already called premature birth. All subsequent fetal rejections are called term births and are generally considered normal, since during this period, mostly able-to-survive children are born. In modern medicine, children born after 22 weeks are nursed and subsequently do not differ from those born at term with normal weight. nine0017
Types of miscarriages
Specialists have identified several types of miscarriages.
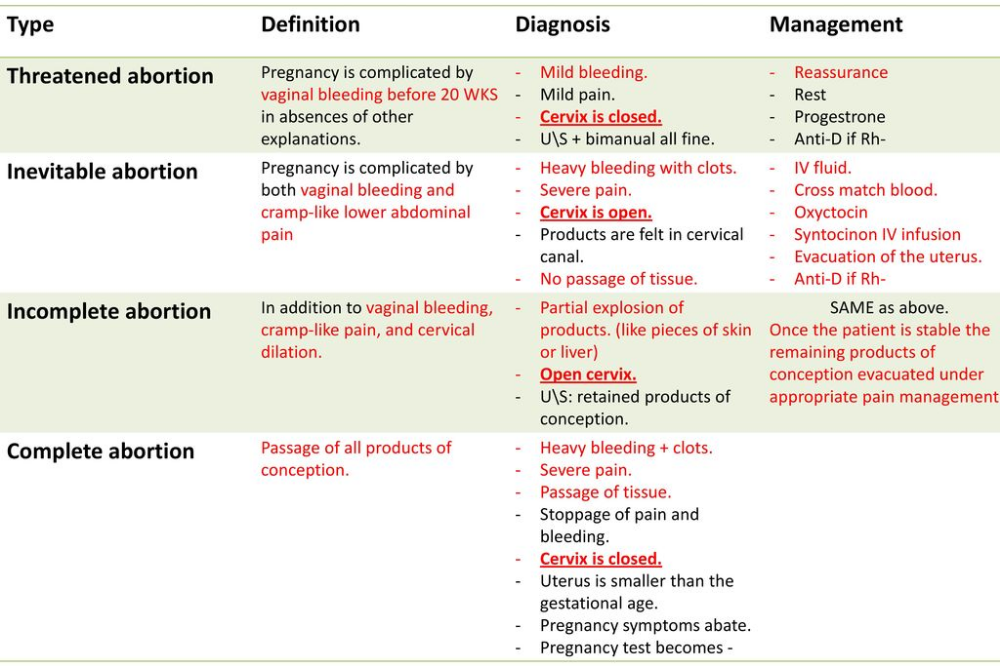
- Complete or inevitable - characterized by pain in the lower back and dilatation of the cervix, hemorrhages from it.
 The fetal membrane necessarily bursts, and the pregnancy is terminated. The fetus comes out of the uterus, and all discomfort in the form of pain and bleeding stops.
The fetal membrane necessarily bursts, and the pregnancy is terminated. The fetus comes out of the uterus, and all discomfort in the form of pain and bleeding stops. - Miscarriage is different in that the fetus died, but remained in the mother's body. This can be detected by a doctor when examining a woman and when listening to the fetal heartbeat. nine0004
- Repeated miscarriage is rare, it occurs only some time after the first and can occur up to three times in a row in the early stages.
Causes of spontaneous abortion
The vast majority of women, having learned about their pregnancy, want to give birth to a healthy baby. And if there is a spontaneous miscarriage , then for a failed mother this is a real tragedy. Many, having experienced an abortion, try to conceive a child faster again, but first you need to know the reasons for what happened in order to save the fetus in the future.
 According to statistics, the largest number of miscarriages occurs precisely in the early stages. nine0017
According to statistics, the largest number of miscarriages occurs precisely in the early stages. nine0017 There are several reasons for this:
- Violations in genetics.
This is the most common cause of miscarriage. This is not due to heredity, it is a consequence of the mutation of parent germ cells, which accidentally ended up in unfavorable conditions. This is also the influence of radiation, poisoning, viruses, that is, temporary situations that affected the quality of germ cells. The body thus gets rid of a weak non-viable fetus. It is impossible and unnecessary to prevent such spontaneous abortion. It is only necessary, having decided to become pregnant, to try to cleanse your body of possible harmful influences. nine0017
- Hormonal disorders
The cause of a miscarriage at a very early stage also lies in the lack of the hormone progesterone, or in the fact that a woman has an excess of male sex hormones that suppress the production of estrogen and progesterone in her body.
 In this case, the fetus can be saved medically by administering the necessary medicines to the woman. The work of the adrenal glands, as well as the thyroid gland, affects the production of hormones, so a lot depends on the work of these glands throughout the pregnancy process. nine0017
In this case, the fetus can be saved medically by administering the necessary medicines to the woman. The work of the adrenal glands, as well as the thyroid gland, affects the production of hormones, so a lot depends on the work of these glands throughout the pregnancy process. nine0017 - Immunological causes .
In this case, the vitality of the fetus is directly affected by the Rh conflict. The embryo will inherit the positive Rh of the man, and if the partner has a negative Rh, then her body simply rejects cells that are foreign to him. A similar situation can be prevented by injecting the expectant mother with a variety of progesterone, a process called immunomodulation.
Sexually transmitted infections such as toxoplasmosis, syphilis, trichomoniasis, chlamydia and others are of great danger. External infection: bacteria and viruses infect the fetal membranes, and the body will inevitably reject the embryo. Therefore, before becoming pregnant, you should be examined to know for sure that there are no infections, and if the result is positive, undergo treatment.
 nine0017
nine0017 In addition, all inflammatory processes, various diseases of the internal organs, which are accompanied by a persistent high temperature, can also lead to unexpected rejection of the fetus. Rubella is especially dangerous, and viral hepatitis is common. But even a sore throat, mild pneumonia, appendicitis sometimes play a key role and lead to a miscarriage, so the expectant mother must undergo a thorough examination even before the child is conceived, and then beware of all kinds of infections and weakening of the body. nine0017
- Medical abortion.
If a woman had an abortion in a hospital and then became pregnant and decided to give birth, there is a risk that she will have a miscarriage. Abortion is a stress factor for the body, ovarian dysfunction is often observed, inflammatory processes in the female genital organs can begin, and all this will lead, at best, to a miscarriage and subsequent repeated miscarriages, and at worst, to infertility.
 Therefore, you need to think very seriously before going for an abortion. nine0017
Therefore, you need to think very seriously before going for an abortion. nine0017 - Medicines and certain herbs.
It is advisable for a pregnant woman not to take any medication at all, especially during the first three calendar months. Medicines and herbs can cause various defects in the fetus, which in turn will lead to its rejection. Analgesics and uncontrolled hormonal contraceptives are especially dangerous. Parsley and nettle should be eaten with caution - they cause a high tone of the uterus, which in turn can reject the fetus. nine0017
- Stress.
It is no coincidence that in ancient times pregnant women were protected from unrest, they were created comfortable conditions, and they tried to give as many positive emotions as possible. Now the direct dependence of the health of the unborn baby on the mental state during pregnancy has already been proven. Any stress, fear and overstrain can cause an unexpected termination of pregnancy.
 If you have a problem (death of a loved one, divorce, etc.), you need to find sedatives with the help of a doctor, they will help you cope with this period. nine0017
If you have a problem (death of a loved one, divorce, etc.), you need to find sedatives with the help of a doctor, they will help you cope with this period. nine0017 - Unhealthy lifestyle.
Of course, the intake of alcoholic beverages, an unhealthy lifestyle, smoking, even coffee consumption in large quantities, improper diet - all this can lead to a transient miscarriage. Therefore, the expectant mother should prioritize and change her rhythm of life in advance in order to give birth to a healthy child.
- Sexual intercourse, falling, heavy lifting. nine0009
All of these factors can affect the fetus, so you should protect yourself and your baby by avoiding these activities.
What to do after a miscarriage?
Having experienced the tragedy of losing a child, parents often intend to immediately conceive a new baby, but they are afraid that everything will happen again.
 In this case, you do not need to make independent decisions, but consult a doctor. And first of all, it is necessary to identify the cause that led to the miscarriage. For this, the expectant mother needs to undergo as thorough an examination as possible. nine0017
In this case, you do not need to make independent decisions, but consult a doctor. And first of all, it is necessary to identify the cause that led to the miscarriage. For this, the expectant mother needs to undergo as thorough an examination as possible. nine0017 If no obvious cause is found, the fetus most likely has a chromosomal abnormality. In this case, you should not worry, since the next conception will occur with a different set of chromosomes, which means that there will be no repeated miscarriage. If the miscarriage was repeated, it is necessary to contact a geneticist and conduct a study of the set of chromosomes of both parents. If it turns out that the cause was an infection, then it is necessary to fully recover. If we are talking about sexual infections, then both parents need to undergo therapy. It is necessary to take tests for hormonal studies, hemostasis systems and determine the immune status. nine0017
After a miscarriage, should be treated, if necessary, and pause between conceptions.
 During pregnancy, you should not take medications to prevent re-spontaneous pathological termination of pregnancy. Therefore, you can become pregnant only after the end of the course of treatment. If the cause was hormonal abnormalities, then the expectant mother should take special drugs to stabilize the background, and at this time she should never become pregnant. During the pause, you need to choose contraceptives with the help of a doctor. You can go to a specialized clinic where you will be prescribed a full course of rehabilitation. nine0017
During pregnancy, you should not take medications to prevent re-spontaneous pathological termination of pregnancy. Therefore, you can become pregnant only after the end of the course of treatment. If the cause was hormonal abnormalities, then the expectant mother should take special drugs to stabilize the background, and at this time she should never become pregnant. During the pause, you need to choose contraceptives with the help of a doctor. You can go to a specialized clinic where you will be prescribed a full course of rehabilitation. nine0017 The first week after a miscarriage women often experience pain in the lower abdomen, heavy bleeding, so you should refrain from sexual intercourse with a man. If there is severe bleeding, acute pain in the lower abdomen, convulsions, high fever, palpitations, nausea, vomiting, then you should immediately consult a doctor to identify the cause of this condition. It is necessary to plan a subsequent pregnancy not earlier than three months after this situation, but preferably six months later.
Until that time, it is worth reconsidering your outlook on life, giving up hard work, eating right and wisely, taking vitamins, exercising, losing weight if you are overweight, stop smoking, drinking alcohol, think over your daily routine. nine0017
It is very important during this recovery period to have a positive attitude and confidence that the next attempt will be successful. It is more difficult to do than to say, because after a miscarriage the woman is in a depressed state and is afraid of a repetition of the situation. You can’t get hung up on your problem, during this period it’s better to do some favorite thing, relax, change the situation, travel, visit the city more often. The modern ecological situation in cities has a bad effect on women's health, so private trips to nature, a trip to the sea, to friends in another city can distract from painful thoughts. An important role in this case is played by the woman's relatives and, above all, the husband, who can surround her with care and attention, creating peace of mind.