Breech positions pregnancy
Causes, Complications, Turning & Delivery
Overview
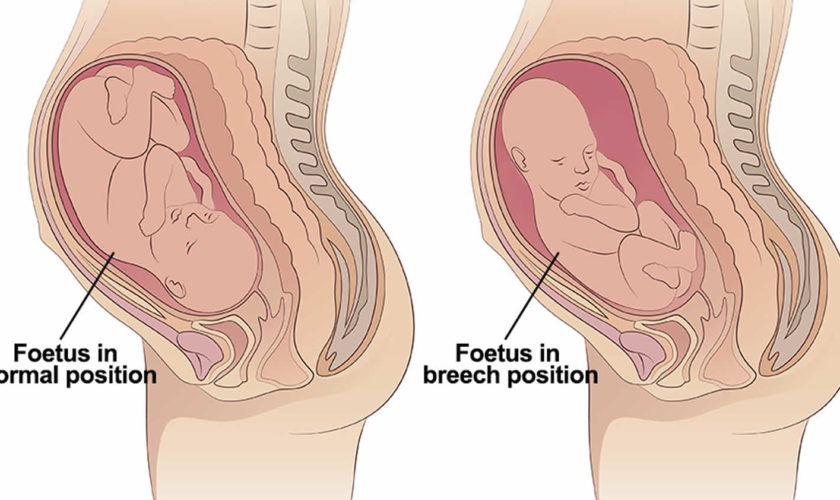
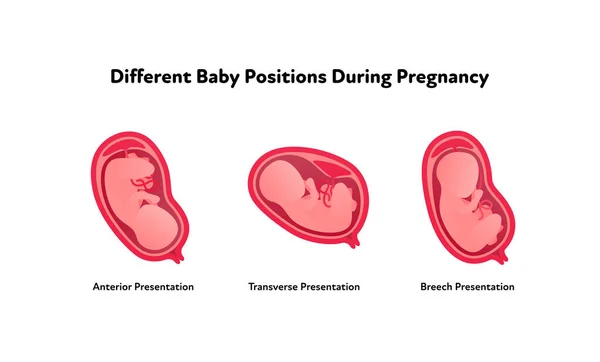
Types of breech positions during pregnancy.What is a breech baby?
A breech baby, or breech birth, is when your baby’s feet or buttocks are positioned to come out of your vagina first. Your baby’s head is up closest to your chest and its bottom is closest to your vagina. Most babies will naturally move so their head is positioned to come out of the vagina first during birth. Breech is common in early pregnancy and most babies will move to a head-first position by 36 weeks of pregnancy. This head-first position is called vertex presentation and is the safest position for birth.
How common is a breech baby?
There is a small chance that your baby will not move into a head-first position before 37 weeks of pregnancy. Breech babies account for about 3% to 4% of all full-term pregnancies.
What are the types of breech position a baby can be in?
There are several fetal positions your baby may present in. Ideally, your baby is positioned head-down, facing your back, with their chin tucked to their chest.
Breech babies can be in a few different positions:
- Frank breech: The baby’s buttocks are aimed at the vaginal canal with its legs sticking straight up in front of their body and the feet near their head.
- Complete breech: The baby’s buttocks are pointing downward and both the hips and the knees are flexed (folded under themselves).
- Footling breech: One or both of the baby’s feet point downward and will deliver before the rest of their body.
- Transverse lie: This is a form of breech presentation where your baby is positioned horizontally across your uterus instead of vertically. This would make their shoulder enter the vagina first.
How does a breech baby affect pregnancy?
Your pregnancy is usually not affected. Most breech babies are born healthy, although there is a slightly elevated risk for certain birth defects.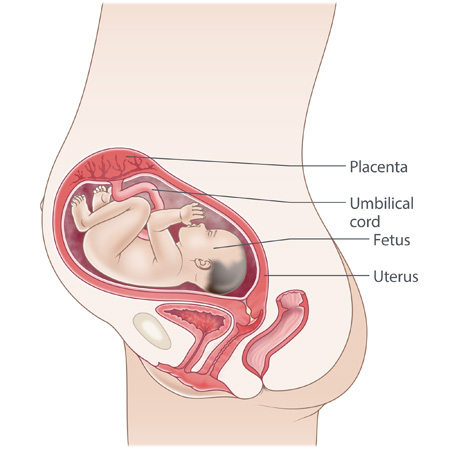 Your baby’s movements may feel a little different. You will feel your baby’s kicks lower in your belly. You may feel a hard lump closer to your ribs. This is your baby’s head.
Your baby’s movements may feel a little different. You will feel your baby’s kicks lower in your belly. You may feel a hard lump closer to your ribs. This is your baby’s head.
If you planned a vaginal delivery, a breech baby could change these plans. When your baby is breech, a vaginal delivery can be complicated and dangerous. Your healthcare provider may feel comfortable attempting a vaginal breech delivery, but in most cases, they will recommend a Cesarean birth (C-section).
How does a breech baby affect delivery?
If your baby presents in a breech position after 36 weeks of pregnancy, your birthing plan will likely change. It's usually unsafe for a breech baby to be born vaginally due to risks of injury. In most cases, a planned C-section is the safest way to deliver your baby. Some healthcare providers may be comfortable with a vaginal breech birth. In some cases, turning your baby to a head-down position while they are still inside your uterus is an option. Your baby is then born head first.
Symptoms and Causes
How can you tell if your baby is breech?
You may be able to tell if your baby is breech, especially if you have had past pregnancies where your baby was head-first. The places where you feel lumps and kicks might indicate that your baby is breech. Let your healthcare provider know where you feel movement. They will feel your belly or do an ultrasound to confirm that your baby is breech.
What causes a baby to be breech?
It’s not always known why a baby is breech. Some factors that may contribute to this position are:
- You are expecting multiples (twins or more). This makes it harder for each baby to get into the right position.
- There is too much or too little amniotic fluid.
- The uterus is not normal in shape or has abnormal growths such as fibroids. Most of the time, the uterus is shaped like an upside-down pear. If it's shaped differently, there might not be enough room for a full-grown baby to move into position.
- The placenta covers all or part of the cervix (a condition called placenta previa).
- The baby is preterm. This means they are less than 37 weeks gestation and may not have turned to a head-first position.
- Your baby has a birth defect that causes them to not turn head-down.
Diagnosis and Tests
How is a breech baby diagnosed?
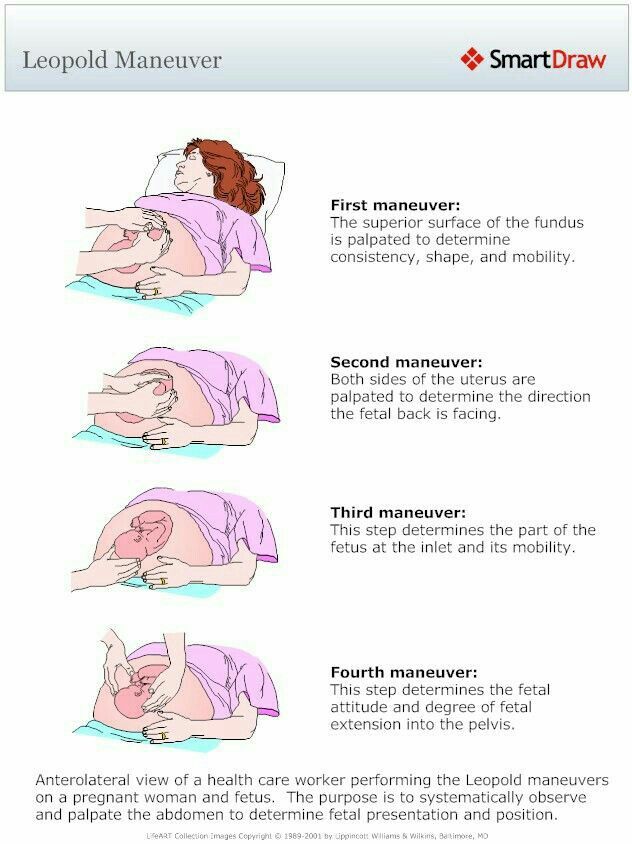
Your healthcare provider may be able to tell which way your baby is facing by placing their hands at certain places on your abdomen. By feeling where the baby’s head, back and buttocks are, it’s usually possible to find out what part of the baby is positioned to come out of the vagina first. An ultrasound may be used to confirm the baby’s position.
When is a breech baby diagnosed?
Almost all babies are breech at some point. As your pregnancy progresses, your baby will naturally move to a head-down position — probably between 32 and 36 weeks. Your healthcare provider will feel your belly and determine where your baby is positioned.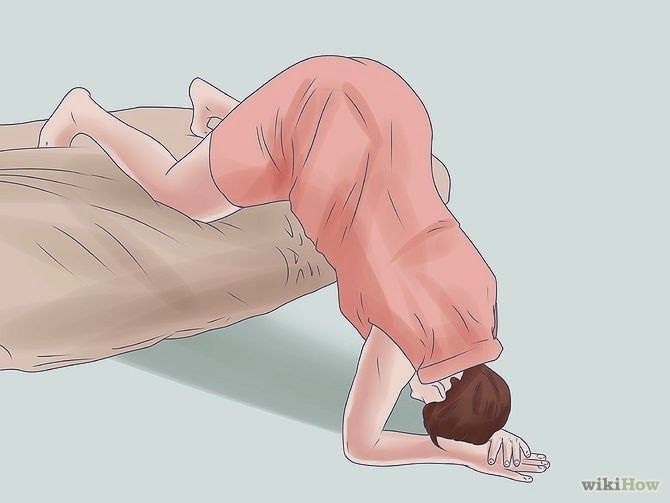 This will happen during most of your appointments in the third trimester. After 37 weeks, a breech baby usually does not turn on their own. Your healthcare provider will discuss delivery options with you.
This will happen during most of your appointments in the third trimester. After 37 weeks, a breech baby usually does not turn on their own. Your healthcare provider will discuss delivery options with you.
Management and Treatment
What are the options for treating a breech baby?
If your baby is breech at 37 weeks of pregnancy, your healthcare provider may:
- Try turning your baby in your uterus into the head-first position.
- Plan a C-section birth.
- Plan a vaginal breech birth.
What are some complications of having a breech baby?
The complications of having a breech baby usually do not occur until it's time to deliver. Some breech babies can be safely delivered through the vagina.
The risks of attempting a vaginal breech birth are:
- Injuries to your baby’s legs or arms such as dislocated or broken bones.
- Umbilical cord problems. The umbilical cord can be flattened or twisted during delivery. This can cause nerve or brain damage due to a lack of oxygen.
Will my doctor try to flip my baby if it's breech?
If your baby is breech, your healthcare provider may consider turning your baby so that you can have a vaginal delivery. In some cases, trying to turn your baby may not be safe or the risks outweigh the benefits.
Flipping your baby may not be safe if you have any of the following:
- Bleeding from your vagina.
- Placenta previa. This is when your placenta covers all or part of your cervix.
- A nonreactive nonstress test.
- An abnormally small baby.
- Low level of amniotic fluid.
- Low or high fetal heart rate.
- Premature rupture of the membranes.
- Twins or multiples.
The most common method used to turn a breech baby is called external cephalic version (ECV). It's performed by your healthcare provider around 37 weeks of pregnancy. This procedure is performed in the hospital just in case an emergency occurs. It involves placing hands on your abdomen and applying firm pressure to turn your baby to a head-down position while your baby is still in your uterus.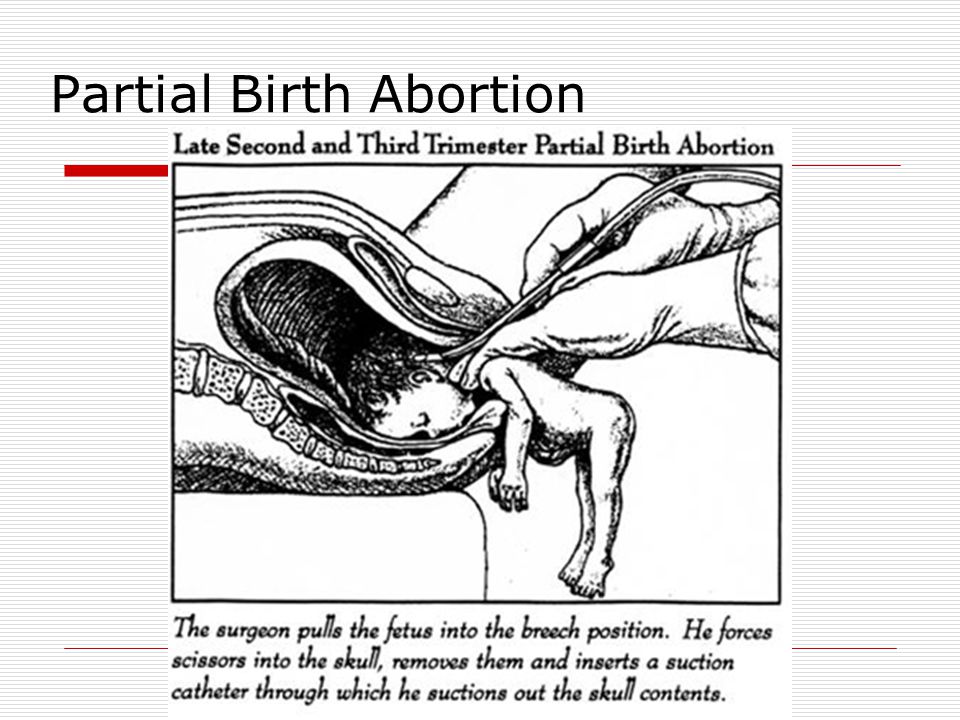 It is about 65% effective and carries some risks.
It is about 65% effective and carries some risks.
What are the risks of turning my breech baby?
The risks of ECV include the following:
- Premature labor.
- Premature rupture of the amniotic sac.
- Blood loss for either you or your baby.
- Emergency C-section.
- Your baby might turn back to the breech position.
Although the risk of having these complications is small, some healthcare providers prefer not to try to flip a breech baby.
Will my breech baby flip on their own?
Most babies will flip to a head-down position before they reach full term (37 weeks). If your baby is still in a breech position at this time, your healthcare provider will determine if you can deliver vaginally or if you will need a C-section.
How can I flip my baby if it's breech?
Some women will try at-home methods to flip their baby to a head-first position. They may help, but there is no scientific evidence that they work.
- Bridge position: Lie on the floor with your legs bent and your feet flat on the ground. Raise your hips and pelvis into a bridge position. Hold this position for 10 or 15 minutes several times a day.
- Child’s pose: Rest in the child’s pose for 10 to 15 minutes. It can help relax your pelvic muscles and uterus. You can also rock back and forth on your hands and knees or make circles with your pelvis to promote activity.
- Music: Place headphones or a speaker at the bottom of your uterus to encourage your baby to turn.
- Temperature: Try placing something cold at the top of your stomach where your baby’s head is. Then, place something warm at the bottom of your stomach.
A chiropractic technique, called the Webster technique, can also help your uterus relax. Some providers even recommend acupuncture. Both of these techniques need to be done by a professional that your healthcare provider has recommended.
Prevention
How can I reduce my risk of having a breech baby?
There is nothing you can do to prevent your baby from being in a breech position. If your baby is in a breech position, it’s not because you did anything wrong.
Outlook / Prognosis
Can you deliver vaginally with a baby breech?
It's possible to deliver a breech baby vaginally. It can be more dangerous for the baby and the risk of injury is much higher. If the umbilical cord is compressed during birth, the baby could be deprived of oxygen and this could harm their brain and nerves. The cord could also slip around the baby’s neck or arms, causing injury. Healthcare providers have various levels of comfort with vaginal deliveries of breech babies. Talk to your provider about the risks and benefits of different types of birth for a breech baby.
Living With
When should I see my healthcare provider?
Contact your healthcare provider if you experience any of the following symptoms during pregnancy:
- Severe cramping or contractions.
- Vaginal bleeding.
What questions should I ask my doctor?
Learning your baby is breech may give you concerns about your delivery. It’s completely natural to have questions. Some questions to ask your doctor can include:
- How can I tell if my baby is breech?
- Is my baby OK?
- What are the benefits and risks of turning my baby?
- What are my options for delivery if my baby remains in the breech position?
- What are the health risks to my baby and me if they are born breech?
Frequently Asked Questions
Do birth defects cause breech position?
Birth defects are slightly more common in breech babies. It might be the reason that the baby didn’t move to the head-down position. Most babies who are breech at delivery are born without any health complications.
Will I need a C-section if my baby is breech?
Most of the time, a C-section is the safest way to deliver a breech baby. Your risks of developing complications are much higher if you try to deliver a breech baby through the vagina.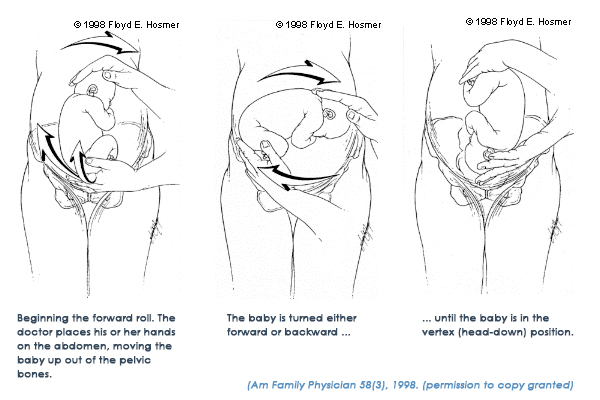 However, some healthcare providers may feel comfortable performing a vaginal breech birth.
However, some healthcare providers may feel comfortable performing a vaginal breech birth.
How does labor start if your baby is breech?
Having a breech baby doesn’t change some of the first signs of labor like contractions or rupturing of your membranes. In most cases, your healthcare provider will recommend a planned C-section. If your delivery is planned, you may not have any labor symptoms.
If you are in labor and go to the hospital for delivery, your provider will confirm your baby’s position a final time. Your provider could attempt a vaginal delivery, but it's more likely they will proceed with a C-section to be safe.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Having a breech baby can be unexpected and change the vision you had for childbirth. Talk to your healthcare provider about what to expect during a breech delivery. They can help you understand the risks and benefits of a breech birth so that you and your baby are kept safe.
Breech pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Breech pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content8-minute read
Listen
How will I know whether my baby is in the breech position or not?
Most babies settle into a head-down position, ready for birth, by about the last month of pregnancy. Health professionals call this a ‘vertex’ or ‘cephalic’ position.
Health professionals call this a ‘vertex’ or ‘cephalic’ position.
When a baby is positioned bottom-down late in pregnancy, this is called the breech position.
It is fairly common for a baby to be in a breech position before 35 to 36 weeks gestation, but most gradually turn to the head-down position before the last month.
Your doctor or midwife will feel your abdomen when you have your pregnancy check-ups in second and third trimesters — this is called an 'abdominal palpation'. When they feel your abdomen at 35 to 36 weeks, they will assess whether the baby has settled into a head-down position in preparation for birth. If they suspect your baby might be in a breech position, they can confirm this with an ultrasound scan.
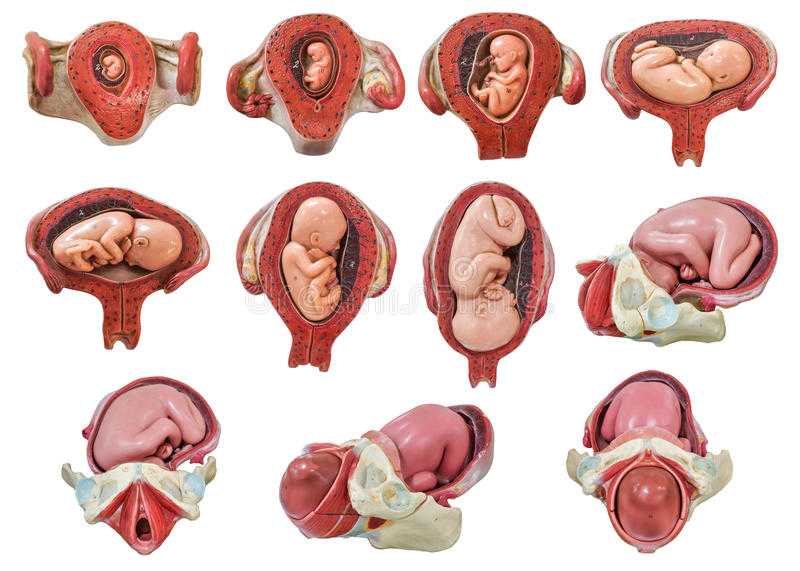
There are 3 main types of breech position. All of them involve the baby being in a bottom-down, head up, position. The variations of breech include:
- frank breech — the baby’s legs are straight up in front of its body in a V shape, so its feet are up near its face
- complete or flexed breech — the baby is in a sitting position with its legs crossed in front of its body and its feet near its bottom
- footling breech — one or both of the baby’s feet are hanging below its bottom, so the foot or feet are coming first
What does it mean for my baby?
While your baby is still in the womb, it is just as safe for them to be in a breech position as it is for them to be head-down. There are no long-term effects on children who were in a breech position during pregnancy. The birth process, however, is often more challenging when babies are still breech at the start of labour.
Why do some babies remain in a breech position?
Often it is unclear why a baby remains in a breech position. Some of the common reasons include:
- too much or too little amniotic fluid around the baby
- the length of the umbilical cord
- multiple pregnancy — for example, often one twin will be in a head-down position and the other in a breech position
- uterine fibroids
- an irregular size or shape of the mother’s uterus
Can my baby still turn after 36 weeks?
Some breech babies turn themselves naturally in the last month of pregnancy. If this is your first baby and they are breech at 36 weeks, the chance of the baby turning itself naturally before you go into labour is about 1 in 8.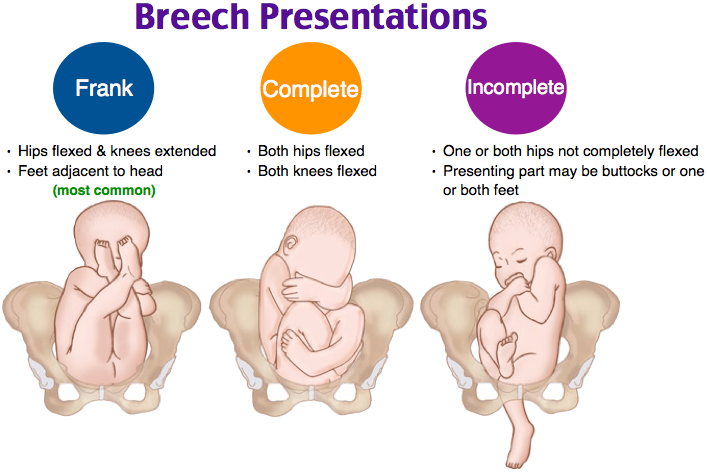 If you’ve already had a baby and this one is breech at 36 weeks, the chance of them turning naturally is about 1 in 3.
If you’ve already had a baby and this one is breech at 36 weeks, the chance of them turning naturally is about 1 in 3.
If your baby is in a breech position at 36 weeks, your doctor or midwife might suggest you think about an ECV, or external cephalic version, after 37 weeks. This will increase your chances of your baby turning to a head-down position. However, ECV is not suitable for everyone, so it’s important to discuss this option with your doctor or midwife.
Some people think that you might be able to encourage your baby to turn by holding yourself in certain positions, such as kneeling with your bottom in the air and your head and shoulders flat to the ground. Other options you might hear include acupuncture, a Chinese herb called moxibustion and chiropractic treatment. There is no good evidence that these work.
Talk to your doctor or midwife before trying any techniques to be sure they do not harm you or your baby.
What are my options if my baby is breech?
If you don’t have an ECV, or if you have it but it doesn’t work, then your options are to have an elective caesarean birth or to have a vaginal birth. Things may be different if you have had a caesarean section before — in this case, if you wish to explore the option of vaginal breech birth, you will need to discuss this with your obstetrician. You may be advised to have a caesarean section again.
Things may be different if you have had a caesarean section before — in this case, if you wish to explore the option of vaginal breech birth, you will need to discuss this with your obstetrician. You may be advised to have a caesarean section again.
Often, women are encouraged to have a caesarean birth if their baby is breech because it might be safer for the baby. But a vaginal birth is still an option in the right circumstances, such as:
- no other issues that would suggest a vaginal birth is unsafe, such as placenta praevia
- you are giving birth in facilities that can handle an emergency caesarean, if necessary
- you have an obstetrician or midwife who is skilled in vaginal breech births
What is involved in a vaginal breech birth?
When babies are in a cephalic (head-down position) ready for birth, the birth process is more straightforward because the crown of the baby’s head is born first. The head is the largest part of the baby’s body, so it makes way for the rest of the body to follow.
The birth process might be more challenging if your baby is breech. When a baby is born bottom first, the baby’s body is born before the largest part, its head. Often this doesn’t cause a problem. But there is a chance that the head, or the head and arms, may not follow easily, once the body is born. In this case, it is important that a midwife or obstetrician with skills and experience in breech births is present to assist your baby to be born.
Upright maternal positions, such as kneeling or a hands and knees position, are recommended when you give birth to a breech baby. The obstetrician or midwife will be standing by, observing closely, with a ‘hands off‘ approach, unless your baby's progress during the birthing process slows down. In such cases, there are a number of techniques that can be used to assist your breech baby to complete the birth vaginally, or it may be necessary to proceed to an emergency caesarean section.
The progress of your labour will be monitored closely.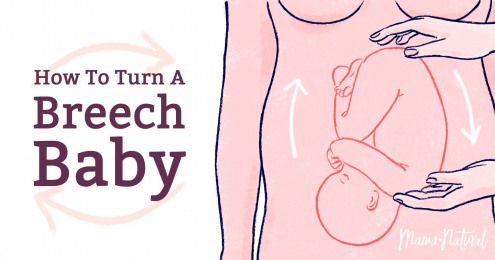 If there is any delay in the descent of your baby, a caesarean section might be recommended. This is because a delay in the baby’s descent inside may be an indication that the birth process could also be delayed, which is more risky for your baby.
If there is any delay in the descent of your baby, a caesarean section might be recommended. This is because a delay in the baby’s descent inside may be an indication that the birth process could also be delayed, which is more risky for your baby.
In many settings where vaginal breech births are offered, it is preferred that your baby is monitored continuously with a cardiotocograph (CTG). If available, you may prefer a cordless, waterproof CTG so you can remain upright and mobile, and so you can use the bath or shower for pain management during labour.
What should I ask my doctor or midwife?
It is worth discussing whether you might benefit from an ECV, because if this is successful, you can go on to try a vaginal birth.
You should also ask if:
- a vaginal birth is safe for the type of breech position your baby is in
- the health service you are planning to use can manage a breech vaginal birth
- your doctor or midwife has training and experience in managing a breech vaginal birth
Do all hospitals offer vaginal breech birth?
Not all hospitals have obstetricians and midwives on staff with the skills and experience in assisting women with a vaginal breech birth. If it is important to you, and your doctor or midwife can’t offer you a vaginal breech birth, you can ask to be referred to another health service.
If it is important to you, and your doctor or midwife can’t offer you a vaginal breech birth, you can ask to be referred to another health service.
What if I am planning a home birth and my baby is breech?
If you are planning a home birth, discuss options for your care with your midwife. The Australian College of Midwives and the Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists recommend that you should be referred to an obstetrician if your baby is breech at the start of labour. This usually means being transferred to give birth in a hospital. In most cases, your midwife will be able to continue supporting you during your birth in hospital and also continue postnatal care at home after your baby is born.
Sources:
The Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists Canada (Breech childbirth), BioMed Central (Does moxibustion work? An overview of systematic reviews (BMC Research Notes 20103:284)), Department of Health (Clinical practice guidelines: Pregnancy care), Cochrane Library (Planned caesarean section for term breech delivery), NSW Health (Breech baby at term), SA Department for Health and Ageing (Perinatal practice guideline: Breech presentation), Australian College of Midwives (Transfer from planned birth at home guidelines), Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (Breech Presentation at the End of your Pregnancy)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: April 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- External cephalic version (ECV)
Need more information?
Breech presentation and turning the baby
In preparation for a safe birth, your health team will need to turn your baby if it is in a bottom first ‘breech’ position.
Read more on WA Health website
Malpresentation
Malpresentation is when your baby is in an unusual position as the birth approaches. Sometimes it’s possible to move the baby, but a caesarean maybe safer.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Labour complications
Even if you’re healthy and well prepared for childbirth, there’s always a chance of unexpected problems. Learn more about labour complications.
Learn more about labour complications.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
External cephalic version (ECV)
ECV is a procedure to try to move your baby if they are in a breech position to the head-down position.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy at week 35
You'll probably be having lots of Braxton Hicks contractions by now. It's your body's way of preparing for the birth. They should stop if you move position.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy at week 28
You are now in the third trimester and you'll probably be feeling many of the common discomforts of pregnancy, like a sore back, swelling, heartburn or cramps.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Glossary of pregnancy and labour
Glossary of common terms and abbreviations used in pregnancy and labour.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Anatomy of pregnancy and birth - pelvis
The pelvis helps carry your growing baby and is especially tailored for vaginal births. Learn more about the structure and function of the female pelvis.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy at week 32
Your baby doesn't have a lot of room, but they will still be moving. The extra weight might cause you some back and pelvic pain which can make it difficult for you to move around.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy at week 39
Your baby's weight gain should slow down since they are now ready to be born. You might soon start to notice the early signs of labour.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.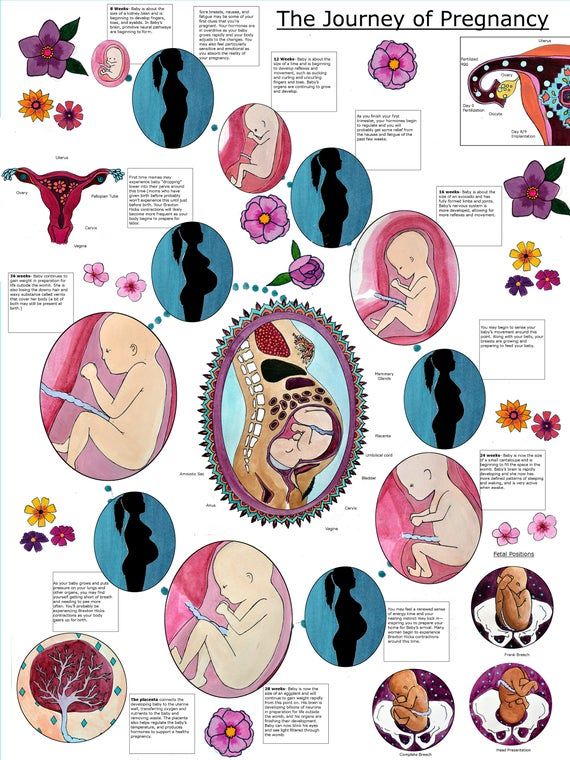
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.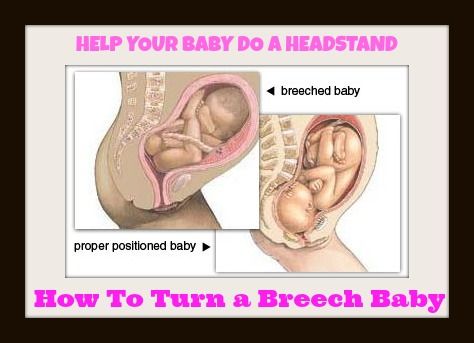
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Breech presentation of the fetus: signs, diagnosis
Consultation with a specialist:
Breech presentation of the fetus is one of the options for the location of the child in the womb. In this case, the fetus, as it were, "sits" in the uterus, and its head is directed upwards. Normally, breech presentation is observed up to 32 weeks, after this period such an arrangement of the fetus is considered pathological.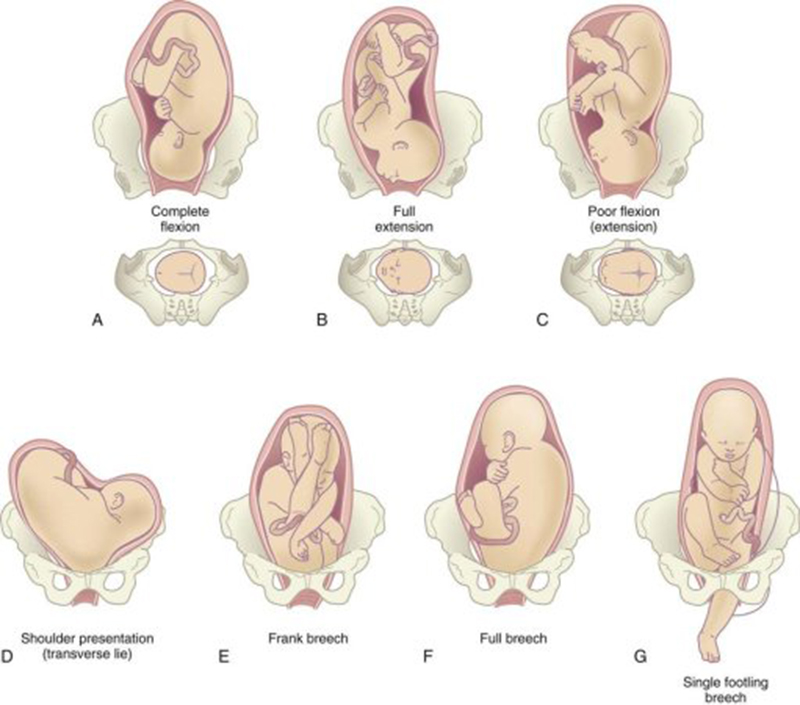
Only a gynecologist can determine the breech presentation during an examination or according to the results of an ultrasound scan. If the baby is positioned incorrectly, the doctor may prescribe special exercises or manipulations to correctly position the fetus. nine0003
To determine whether the baby has taken the correct position for childbirth, it is necessary to undergo an examination by a gynecologist and ultrasound at 32-34 weeks.
Types of breech presentation of the fetus
Breech presentation of the fetus is divided into types:
- gluteal;
- foot.
In breech presentation of the fetus during childbirth, the baby's buttocks are the first to appear. At the same time, its legs are located along the body and straightened at the knees. In such a situation, we can say that the woman is lucky, since in this case she practically does not need additional help, and the risk of complications is reduced to a minimum.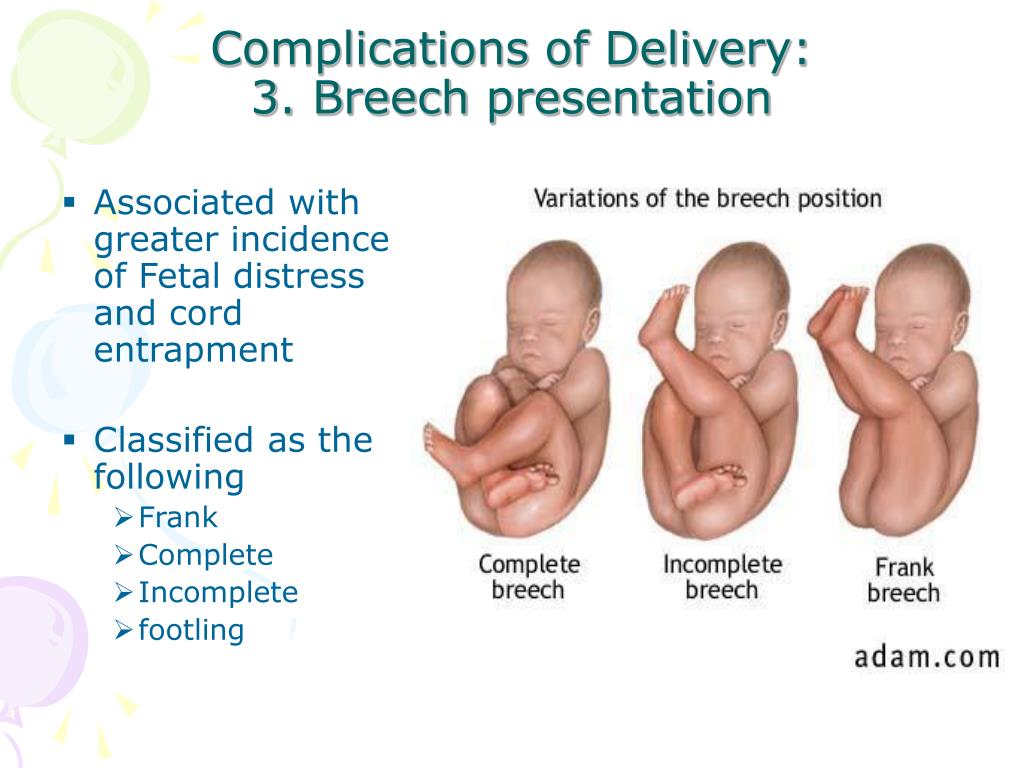 With a mixed breech presentation, the legs and pelvis may appear at the same time. nine0003
With a mixed breech presentation, the legs and pelvis may appear at the same time. nine0003
Foot presentation is considered more unfavorable. According to statistics, up to 15% of children with breech presentation are born this way. In the foot position, the first of the birth canals are the legs, not the pelvis. Usually in the case of a foot presentation, a caesarean section is performed.
Call now
+7 (495) 215-56-90
Make an appointment
Causes of breech presentation
The reasons that caused the pelvic presentation of the fetus can be quite a lot, but the most common are: nine0003
- polyhydramnios - usually in this case, the baby is highly mobile and simply does not have time to take the desired position by the time of birth;
- oligoamnios - in this case, the child's ability to change his position is limited, as a result of which the baby simply cannot take a physiological position;
- twin pregnancy - in this case, it is very difficult for babies to move due to lack of space, it is worth noting that the "traditional" head presentation of the fetus in multiple pregnancy is rare regardless of the week of pregnancy; nine0016
- umbilical cord entanglement - sometimes a very active baby can wrap the umbilical cord around himself so much that it becomes completely impossible for him to take the correct position for childbirth;
- uterine pathology - some diseases of the uterus (for example, fibroids) can directly affect the position of the fetus.
In some cases, in the presence of the problems described above, the breech presentation of the fetus can threaten the following dangers: nine0003
- premature birth;
- hypoxia - if the child in the gluteal position pinched the umbilical cord;
- difficult delivery with the risk of injury to both mother and child..
Breech diagnosis
It is almost impossible to independently suspect a breech presentation of the fetus without understanding obstetrics and gynecology. In addition, such a situation before a certain period should not bother the expectant mother at all. Usually, the first symptoms of breech presentation in the uterus are determined by the obstetrician at the examination at 32-34 weeks. In this case, the doctor pays attention to the area where the child's heartbeat is heard and palpates the abdomen. In the event that the symptoms indicate a breech presentation of the fetus, the specialist will prescribe an additional examination that will either confirm or refute his conclusion. nine0003
nine0003
There are several ways that experienced obstetricians resort to in order to determine the presence of a breech presentation in a fetus.
- First, it is a visual inspection and palpation of the abdomen. Usually, it is not difficult for a specialist to determine the position where the child's head is and where his feet are. In addition, the obstetrician may resort to listening to the heart. If his sounds are heard above the navel, then the child is in a breech presentation. This is the simplest and most affordable method of research and diagnosis. nine0016
- Secondly, the obstetrician can determine the presentation of the fetus and the location of the head at the time of the onset of labor. Usually, this method is resorted to if a woman goes into labor urgently and she has no data on previous examinations, and on the position of the fetus - pelvic or head. In this case, the specialist probes the position of the child through the vagina.
- Thirdly, the surest and most reliable way is to conduct ultrasound.
 It is best to perform an ultrasound scan in breech presentation at 32-34 weeks, when the baby takes its final position. nine0016
It is best to perform an ultrasound scan in breech presentation at 32-34 weeks, when the baby takes its final position. nine0016
Treatment
In fact, in the absence of pathology, breech presentation of the fetus is not some kind of terrible diagnosis that needs to be feared. In addition, in some cases, correcting such a situation can be quite simple.
Remember that any exercises and manipulations aimed at giving the child the desired position must be fully coordinated with the specialist. Otherwise, you risk causing irreparable harm to the unborn baby. nine0077
- Exercise "Turns". To turn, lie on your back and bend your knees slightly. After that, you need to smoothly turn on your side and lie down in this position for about 2 minutes. Then the manipulation must be repeated, but on the other side. The number of repetitions in such an exercise should not exceed 8-10.
- Butt Lift Exercise. This exercise is contraindicated in women with placenta previa or with a scar on the uterus.
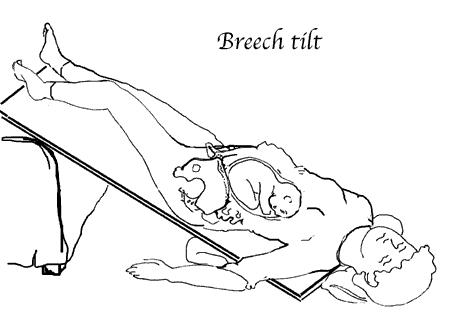 Its essence is to lift the pelvis and put a soft roller under it. In this position, you need to spend 10-15 minutes. nine0016
Its essence is to lift the pelvis and put a soft roller under it. In this position, you need to spend 10-15 minutes. nine0016
All exercises in breech presentation must be performed carefully. Otherwise, premature birth can be provoked. During pregnancy, you should carefully listen to the doctor's recommendations and not neglect visits to the gynecologist. Remember that with a breech presentation of the fetus, a woman needs more careful observation.
If the methods described above did not give a positive result, then at about 35-38 the doctor can perform an "obstetric coup". In this case, the specialist, with the help of special manipulations, by pressing on the woman's stomach, gives the fetus the desired position. However, most babies rotated in this way will soon return to the pelvic position again. nine0003
Breech presentation increases the chance of delivery by caesarean section, but many women give birth safely by vaginal delivery. A contraindication for vaginal delivery in this case may be a too large fetus or entanglement with the umbilical cord.
Share:
Call now
+7 (495) 215-56-90
Make an appointment
The problem of breech presentation of the fetus. External obstetric rotation of the fetus on the head. nine0001
Breech presentation of the fetus occurs in 3% -5% of cases at full-term pregnancy. Vaginal delivery with breech presentation is associated with high risks both on the mother's side and on the fetus's side. Thus, breech presentation is currently considered pathological, even if the conditions necessary for childbirth through the birth canal are ideally met, and the fetus is relatively small relative to the size of the mother's pelvis. During vaginal delivery, the arms and head of the fetus may tilt back, which can lead to injury. nine0003
Currently the most common method of delivery in breech presentation is a caesarean section (90%). Among the indications for the use of caesarean section, breech presentation ranks third among others in the world. However, this the operation does not make it possible to completely eliminate the risk of trauma to the fetus, since when it is removed, it is also possible to tilt the arms and head of the fetus, and their release requires the use of complex manipulations. nine0003
However, this the operation does not make it possible to completely eliminate the risk of trauma to the fetus, since when it is removed, it is also possible to tilt the arms and head of the fetus, and their release requires the use of complex manipulations. nine0003
To correct breech presentation today, the world is using EXTERNAL OB-HEAD TURN proposed at the end the century before last by the Russian obstetrician Arkhangelsky B.A.
External obstetric cephalic rotation (EFRT) is a procedure during which the doctor turns the fetus from the outside through the wall of the uterus breech presentation in the head. A successful attempt at NAPP allows women to give birth on their own, avoiding a caesarean section. nine0003
What is required for external cephalic fetal rotation?
External obstetric rotation of the fetus on the head is performed before the onset of labor, usually starting from 36 weeks of pregnancy.
It is necessary to consult a doctor and conduct an ultrasound examination to confirm the fact breech presentation of the fetus and determine the conditions for NAPP, starting from 34-35 weeks of pregnancy.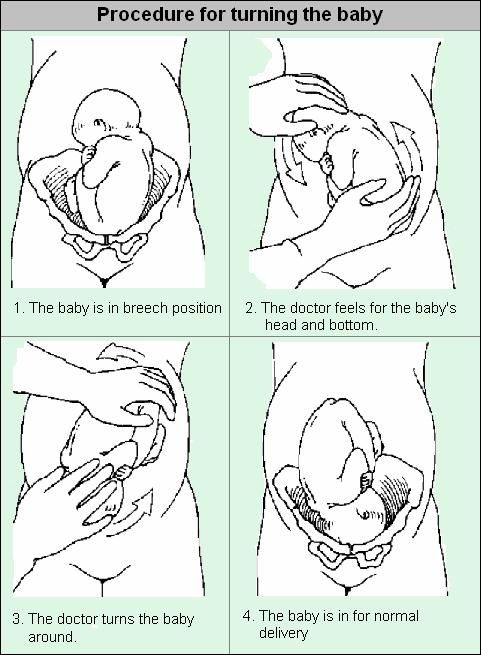
| The operation of external rotation of the fetus on the head in breech presentation |
When NAPP is possible:
- From 36 to 37 weeks, since with earlier use, it is likely that it will return to the breech presentation.
- In the presence of a singleton pregnancy.
- Subject to the mobility of the buttocks of the fetus (if they are tightly pressed against the entrance to the mother's pelvis, it will be extremely difficult to change the position of the fetus). nine0016
- Sufficient amount of amniotic fluid. With oligohydramnios, this manipulation can be traumatic for the fetus, while with polyhydramnios there is a high probability of a reverse rotation of the fetus in a breech presentation.
- Sufficient amount of amniotic fluid. With oligohydramnios, this manipulation can be traumatic for the fetus, while with polyhydramnios there is a high probability of a reverse rotation of the fetus in a breech presentation.
- Fetal head flexed
When NAPP is not possible:
- With the outflow of amniotic fluid.
- If the patient has contraindications to the use of drugs used to relax the uterus (tocolysis).
- In the presence of obstetric indications or indications from the health of the mother for delivery by caesarean section.
- With the extensor position of the fetal head.
- If the fetus has congenital developmental features. nine0016
- With multiple pregnancy.
- In the presence of structural features of the uterus in a pregnant woman
However, in addition to this, there are a number of factors that may favor or, on the contrary, serve as a contraindication to external obstetric turning the fetus on the head, and which can only be determined by a doctor during a direct examination of a pregnant woman.
How NAPP is conducted
For manipulation, hospitalization in the maternity hospital is necessary. Preliminarily, an additional examination of the pregnant woman is carried out in the required volume, including ultrasound. nine0003
Preliminarily, an additional examination of the pregnant woman is carried out in the required volume, including ultrasound. nine0003
When carrying out an NAPP:
Immediately before the start of the manipulation, a CTG is recorded to assess the condition of the fetus.
Drugs are administered to prevent uterine contractions (tocolytics).
Further, under constant ultrasound and KGT control, as well as the continued administration of drugs that relax the uterus, the doctor performs a turn.
Holding both hands on the surface of the pregnant woman's abdomen, one on the head of the fetus, and the other on the buttocks of the fetus, the doctor pushes and rotates the fetus to the upside down position. A pregnant woman may feel some discomfort during the procedure. The degree of discomfort depends on the individual sensitivity of each patient.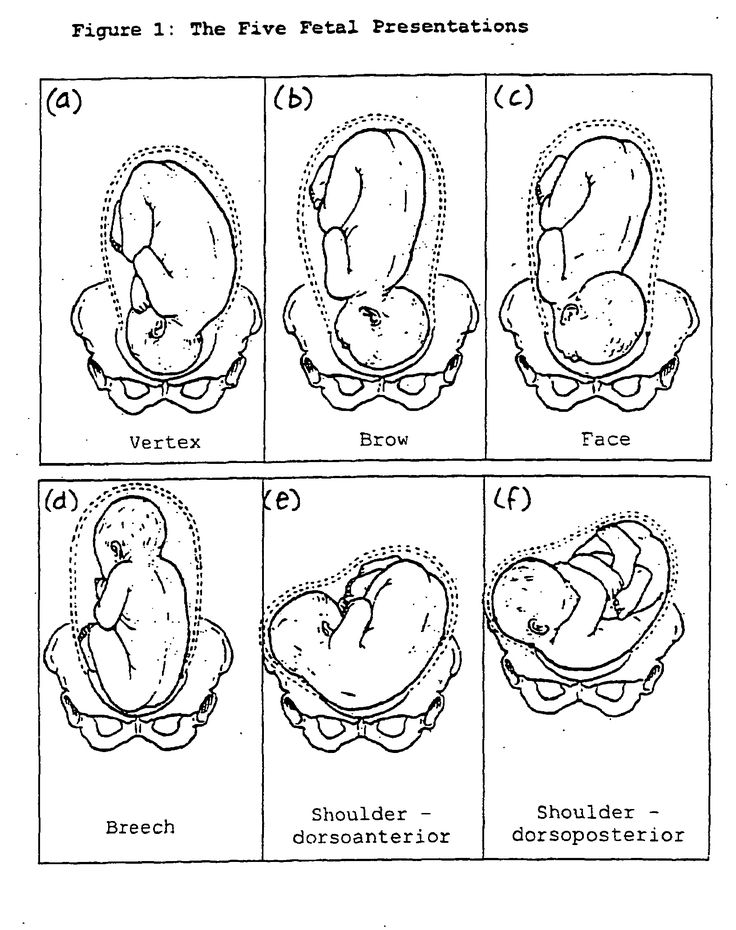 nine0003
nine0003
After the procedure is successfully completed, the CTG is recorded again, to make sure that the fetus feels well and has successfully undergone the procedure. Usually during the day, the condition of the mother and fetus is monitored, after which the patient is discharged and continues the pregnancy until spontaneous delivery occurs.
If the doctor notices a deterioration in the condition of the fetus according to the monitoring data, then the procedure is immediately stopped.
If the first attempt was not successful, your doctor may suggest another attempt if the fetus is in good health. nine0003
APP is performed ONLY in a maternity ward where there is an opportunity for an emergency delivery, if necessary.
Risks associated with NAPP
Subject to constant monitoring of the condition of the fetus, constant tocolysis (administration of drugs that relax the uterus) The risks associated with this procedure are minimal.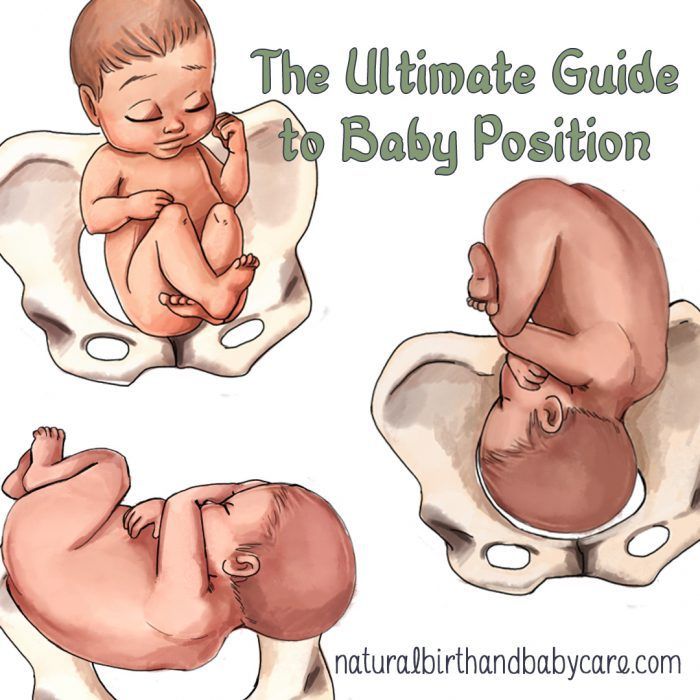 Complications from its use occur in less than 1-2% of cases.
Complications from its use occur in less than 1-2% of cases.
Complications of NAPP include: nine0213 - compression or "twisting" of the umbilical cord. In this case, constant monitoring of the condition of the fetus allows you to immediately fix its deterioration and stop the procedure.
- discharge of amniotic fluid or the development of labor. This complication can be considered relative, since the rotation in most cases is carried out at full-term pregnancy.
Any deviation from the normal course of the procedure serves as a reason to stop the manipulation and decide on the choice of further management tactics. nine0003
Carrying out NAPP with Rh-negative mother's blood.
The presence of Rh isoimmunization (that is, the presence of anti-Rh antibodies in the mother's blood) is a contraindication to this procedure, as it increases the risk of anemia in the fetus.
In the absence of isoimmunization (absence of anti-Rhesus antibodies) it is possible to carry out NAPP with prophylaxis by introducing anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin.