Hands swell after walking
Why Do My Hands Swell When I Walk? 4 Causes + Advice To Avoid It
Walking does a lot of wonderful things for the body. In the final few steps of a good walk, any muscle stiffness you had before the walk might be all but a distant memory, your mood might be lighter, and you will likely feel more energized and ready to conquer the rest of the day.
But, some people also find that their fingers swell when walking. Swollen hands or fingers after walking can be concerning the first time you notice it if you don’t know why it’s happening.
In this guide, we will try to answer the common question, “Why do my hands swell when I walk?” and discuss ways to potentially prevent your hands and fingers from swelling when you exercise.
We will take a look at:
- Why Do My Hands Swell When I Walk Or Run?
- How to Prevent Your Hands From Swelling When You Walk Or Run
Ready?
Let’s jump in!
Why Do My Hands Swell When I Walk Or Run?
If your fingers and hands get swollen and puffy when you walk or run, you’re not alone. Many people, particularly women, report that their fingers swell when they are walking, although studies about fingers and hand swelling during walking are limited.
However, despite the fact that this seems to be a relatively common phenomenon, medical professionals and exercise physiologist researchers have yet to fully understand why this occurs.
The potential theories and hypotheses to answer your question, why do my hands swell when I walk or run are as follows:
#1: Changes In Blood Flow
When you exercise, blood flow increases to the heart, lungs, and working muscles in order to deliver an adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients to the working muscles.
To compensate, some of the normal blood flow to your extremities—like your toes, fingers, and hands—is diverted to supply the increase in relative blood flow to your muscles.
This reduced blood flow to the fingers and hands can cause a decrease in their temperature. As your hands cool down, the intricate network of blood vessels in your fingers and hands dilate. This can cause your fingers to swell.
As your hands cool down, the intricate network of blood vessels in your fingers and hands dilate. This can cause your fingers to swell.
#2: Swinging Your Arms
Some people theorize that fingers and hands swelling during walking and running is a product of the arm swing during these movements.
This concept can be compared to the experience of swollen ankles or feet after standing for hours, perhaps at the end of a long shift at work on your feet.
Blood and lymph circulate through your body at all times. However, when you are standing upright for a long time, the veins and lymphatic vessels that return fluids from the feet to your heart have to pump these fluids against gravity.
Despite the opposing force of gravity, your body typically does a good job and can usually maintain adequate circulation back to the heart. However, some amount of fluid can pool in the feet, causing visible swelling.
Unless you have venous insufficiency or some other circulation issue, usually, once you are lying down or have the chance to elevate your feet somewhat, this excess blood plasma and lymph fluid are flushed back to the heart, and the swelling subsides.
Similarly, a vigorous arm swing used during walking or running may push extra blood and lymph fluids into your hands and fingers.
Then, in the same way that these fluids have to fight gravity to return to the heart from the feet when you are standing, these fluids must work against the centrifugal force of your arm, thrusting them towards the fingers with every swing of your arm.
Each time your arm pumps back and forth, the momentum propels the blood into the fingers instead of squeezing it back up the arm to the heart.
Again, most of the blood and lymph are able to oppose this force and successfully circulate out of the hands, but some amount of excess fluid can accumulate over the duration of a longer walk or run, making your fingers and hands appear puffy and swollen.
#3: Temperature Regulation
Many people who ask themselves why do my hands swell when I walk, note that the problem is usually exacerbated when exercising at either temperature extreme.
Studies show that our hands often swell while walking when it’s cold outside. As mentioned, the temperature in your extremities drops when you exercise. This causes all the many capillaries and larger blood vessels in your fingers and hands to dilate or widen.
When this occurs, more fluid fills the blood vessels, causing a visible puffiness.
Interestingly enough, a similar phenomenon can occur when you are exercising in the heat. Anytime you are exercising, but particularly when it’s hot outside, your body generates excess heat.
In an effort to maintain homeostasis and keep your core body temperature within a finite range, your body employs thermoregulatory mechanisms to cool you down.
These mechanisms include sweating and increasing the circulation to your skin and extremities to try and move more blood to regions away from the core where it can cool down.
Again, the blood vessels in the fingers and hands dilate to accommodate more blood. Vasodilation then causes your fingers to swell when you walk.
Vasodilation then causes your fingers to swell when you walk.
#4: Hyponatremia
Hyponatremia refers to a condition when your electrolytes, mainly sodium, get too diluted, usually due to an excessive intake of water.
Decades ago, runners only ever seemed to receive the advice to drink, drink, drink. The importance of hydration was stressed, but the conversation largely centered around drinking plain water.
While clean water is typically acceptable, if not preferred, for exercise lasting an hour or less, when running or working out in the heat or for more than an hour, drinking fluids with electrolytes becomes essential to maintain the electrolyte balance in your body.
Electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and chloride are lost through sweat, and simply replacing fluids but not these key minerals can cause the concentration of these ions in the blood to drop.
As electrolytes are vital for many physiological processes such as nerve conduction and heart and muscle contraction, imbalances or a significant dilution in sodium and potassium can cause a cascade of adverse consequences and physiological dysfunctions, ranging from mild muscle cramping and headaches to coma and death.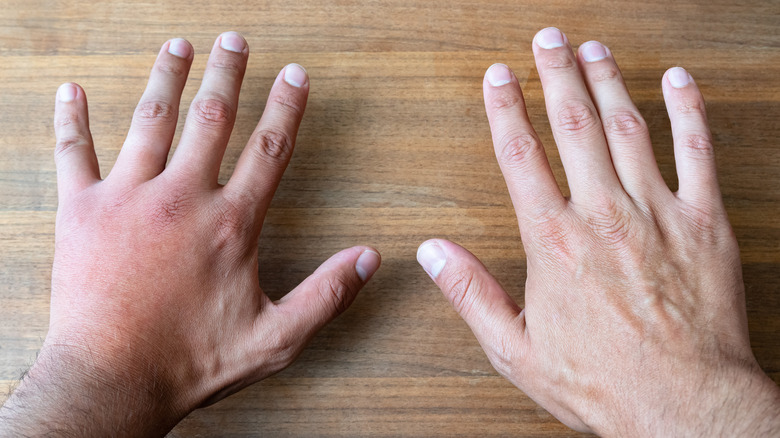
Exercise-induced hyponatremia can occur when runners (or occasionally walkers) drink too much water without taking in electrolytes. Coupled with the simultaneous loss of electrolytes in sweat, this causes the relative amount of sodium in your blood to drop too much.
One of the first signs and symptoms of hyponatremia is swelling, bloating, or puffiness, which may occur in your hands when you walk or run.
Hyponatremia is more likely to occur when people run or walk for a long time (think long runs or marathons), drink a lot of water, sweat a lot, and generally don’t take in a lot of salt.
How to Prevent Your Hands From Swelling When You Walk Or Run
So, the natural follow-up question to “Why do my hands swell when I walk?” is “What can I do about it?”
Particularly because scientists aren’t entirely sure why exactly our fingers swell when walking or running, it’s not necessarily clear that there’s a guaranteed cure-all or preventative measure.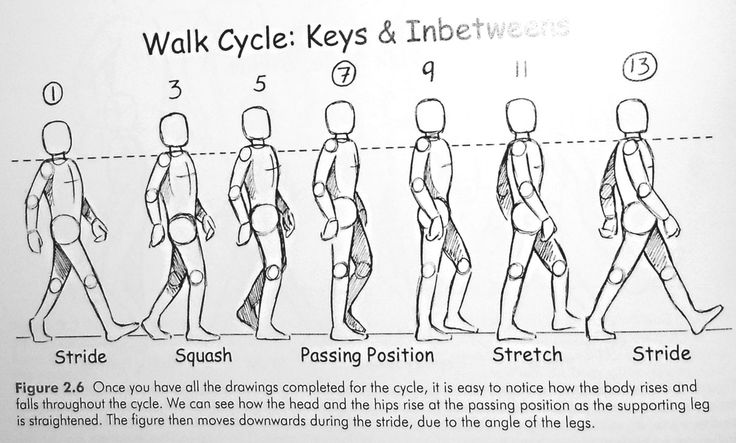
However, the following can potentially help reduce the severity of the swelling or prevent your hands from swelling when you walk or run:
Keep Your Hands Comfortable
In cold weather, wear gloves or mittens while you walk to keep your fingers warm. If it’s really hot or really cold outside, consider walking inside on a treadmill.
Examine Your Hydration
Make sure you’re taking in electrolytes during longer workouts.
Raise Your Arms Above Your Head
Though not a preventative measure, raising your hands above your heart (or head) after your walk can help resolve swelling in your fingers quicker.
Even though the answer to the question, why do my hands swell when I walk and run isn’t as clear as we would like it to be, give these tips a try the next time you go out and hopefully avoid that uncomfortable swelling in your hands.
If you feel your hands swelling may be a consequence of a lack of proper hydration, we can help you delve into your strategies and ensure you are hydrating well with the following articles:
Hydration For Runners: Everything You Need To Know!
Hydration And Salt Levels For Runners – Explained
Fluid And Electrolytes: A Complete Runner’s Guide
0 shares
- Share
- Tweet
Why Do My Hands Swell When I Walk or Run? Is Swelling a Concern?
- Hands swelling is a common issue runners experience in hot weather.

- Swinging your arms while you run and increased blood flow are two additional reasons it might occur.
- Moving your workouts to cooler parts of the day can help decrease your odds of experiencing this.
If you’ve ever noticed your hands swelling midrun or plopped down after the fact to see some swollen fingers, you’re definitely not alone. While it’s often only subtle, it’s actually a pretty common occurrence, so we tapped William O. Roberts, M.D., professor in the Department of Family Medicine and Community Health at the University of Minnesota, to give us the details on this phenomenon.
According to Roberts, your hands usually swell when it’s hot out—but it’s not a sign of dehydration. Rather, it’s the opposite: Hands and fingers swelling can be a sign of hyponatremia, which occurs when you drink too much fluid over the course of a run, he says.
Related Story
- Every Hydration Question, Answered
“During exercise, circulation increases, and the hand has a large network of small blood vessels that open up,” he tells Runner’s World.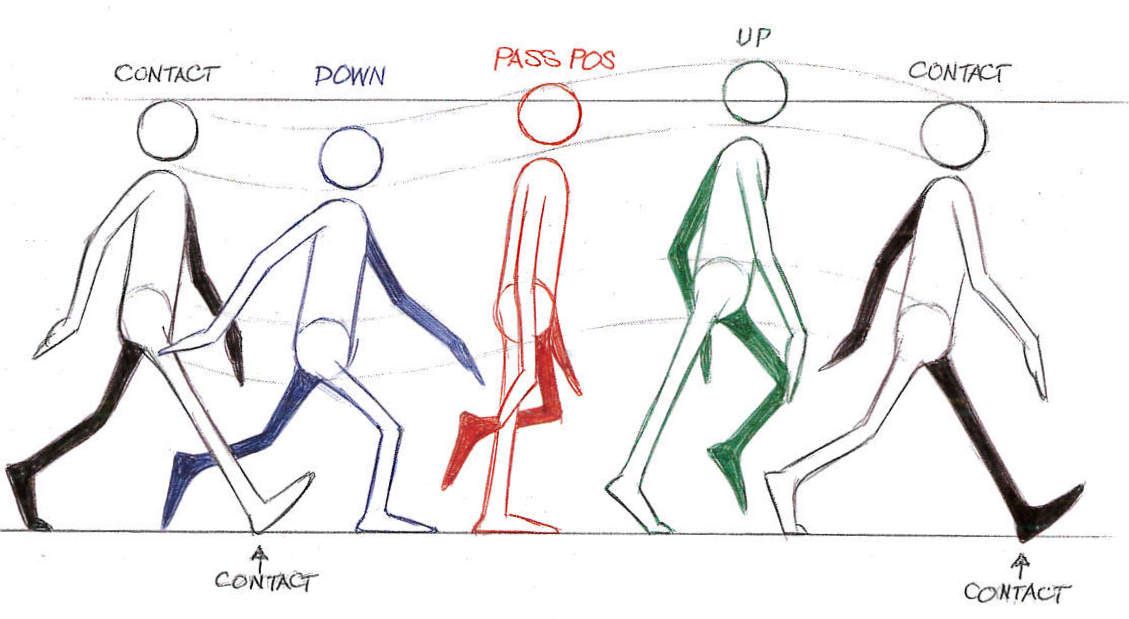 “With the increased blood flow, there is some fluid leak between the cells. This leakage is probably the cause of your fingers swelling.”
“With the increased blood flow, there is some fluid leak between the cells. This leakage is probably the cause of your fingers swelling.”
Additionally, swinging your arms as you run may also contribute to fluid retention in your hands, since this motion increases air movement across your skin to improve heat exchange with the air.
“This fluid is eventually reabsorbed into the cells or cleared by the lymph system,” he says. “This process is going on while you are running, but the rate of removal is slower than the rate of accumulation. Once you stop exercising, the fluid will reabsorb into the vascular system or surrounding cells or be removed by lymph flow.”
The solution? Roberts says if you notice that your hand swelling is worse when you run in the heat, moving your hard or long workouts to the cooler parts of the day—mornings or night—could help.
Related Story
- How to Carry Water on a Run
Taking off any rings you’re wearing is also not a bad idea—the last thing you want to deal with after a 20-miler is wrestling to get them off of your swollen fingers.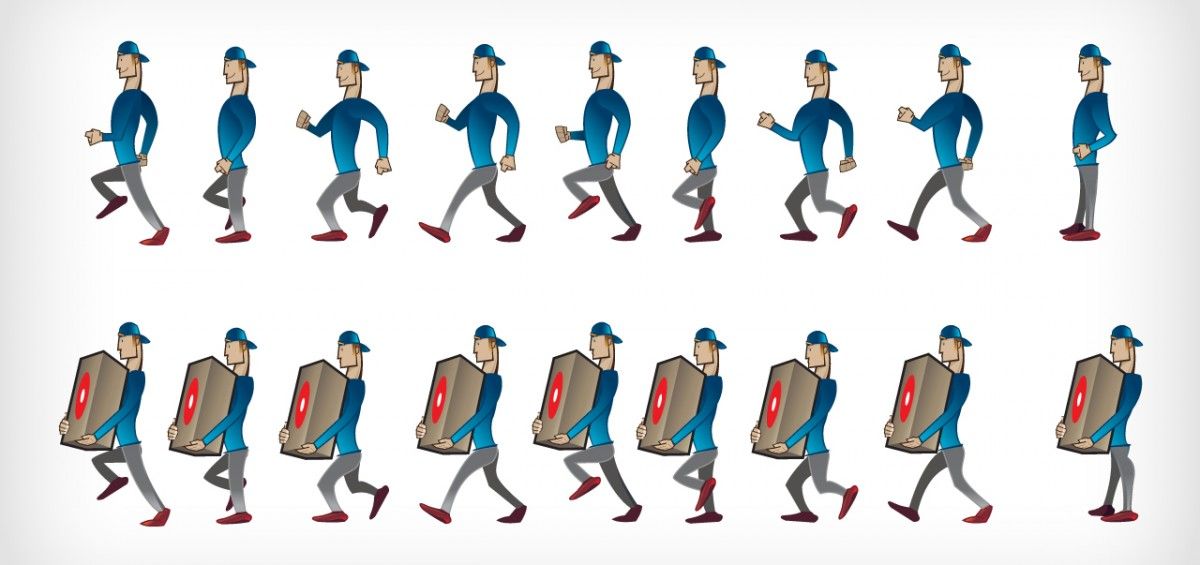 (If you really like to keep something like a wedding ring on, you can opt for a rubber version.)
(If you really like to keep something like a wedding ring on, you can opt for a rubber version.)
And most importantly, dial in your hydration plan, especially for long runs that last over an hour or have to happen in heat and humidity. One recent study, published in the European Journal of Applied Physiology, suggests that drinking water whenever you want (when you feel thirst) will lead to adequate hydration at the end of a two-hour run despite the temperature. Listen closely to your body to prevent over-hydrating which can lead to symptoms of hyponatremia.
4 Great Hydration Belts to Consider for Your Runs
Danielle Zickl
Senior Editor
Danielle Zickl for Runner's World and Bicycling.
SM-Clinic cardiologist spoke about the causes of hand swelling in adults
Edema of the hands occurs quite often, and can be a manifestation of physiological changes or one of the symptoms of pathology. When should edema alert and where to address the problem?
When should edema alert and where to address the problem?
ALENA PARETSKAYA
Pathophysiologist, immunologist, member
St. Petersburg Society of Pathophysiologists
ANDREY GRACHEV
Leading cardiologist of the holding
SM-Clinic, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences
Swelling of the hand is a cause for concern if it occurs frequently or almost daily, is accompanied by additional symptoms, is aggravated or is not eliminated by simple methods.
What you need to know about arm swelling
- Why your arm swells
- How to remove swelling
- Questions and answers
Why the hand swells in adults
Swelling of the arm or both at once may be physiological or be a sign of pathology. It may be localized or spread to surrounding tissues. With swelling, the limb increases in volume, discomfort, soreness, and inconvenience when performing precise finger movements may be felt. It is difficult to remove the rings from the fingers or the watch from the wrist.
With swelling, the limb increases in volume, discomfort, soreness, and inconvenience when performing precise finger movements may be felt. It is difficult to remove the rings from the fingers or the watch from the wrist.
Swelling in the right or left arm occurs when the blood or lymphatic vessels are compressed by items of clothing during sleep. Swelling of the fingers and hands, which is especially noticeable if you remove rings or watches, occurs after alcohol or excess salty foods, fluids at night. nine0009
Right hand
A small local edema, if the mobility of the limb is preserved, is possible with bruises. In the area of edema, there may be soreness, redness, bruises or abrasions may appear. If it is a hematoma, the edema will be more pronounced, a seal is determined under the skin, in the center of which fluctuation (fluid movement) is felt. Swelling is typical for sprains in the area of the carpal, elbow or shoulder joint, with torn ligaments or their rupture.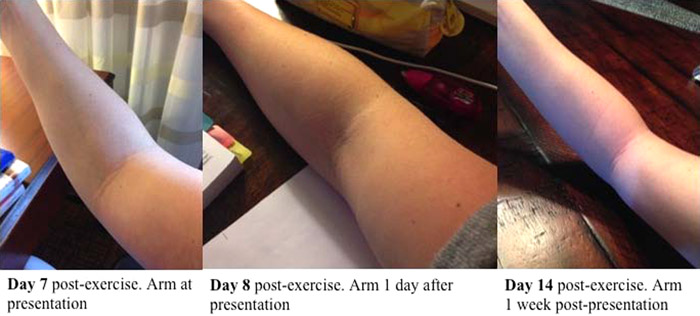 Severe pain is characteristic, which increases with movement, if the ligaments are torn, it is almost impossible to move the hand. nine0003
Severe pain is characteristic, which increases with movement, if the ligaments are torn, it is almost impossible to move the hand. nine0003
Edema is possible with fractures of bones, dislocations of joints. Then there is pain, limb deformity, complete impossibility of movement.
Edema may appear with frostbite of the fingers, burns, infectious processes in the area of the hand, forearm or shoulder.
Left hand
Swelling of the finger of the left hand (as well as the right one) is possible with panaritium - suppuration in the phalanx. If it is a deeper lesion, the edema passes to the hand. Carbuncles or boils on any part of the arm can also lead to swelling. In this case, cyanosis or a purple area with suppuration is visible in the center of the inflamed focus. Edema is possible with suppuration of wounds, erysipelas, purulent arthritis and osteomyelitis. nine0003
Joint damage in other forms of arthritis also leads to tissue swelling.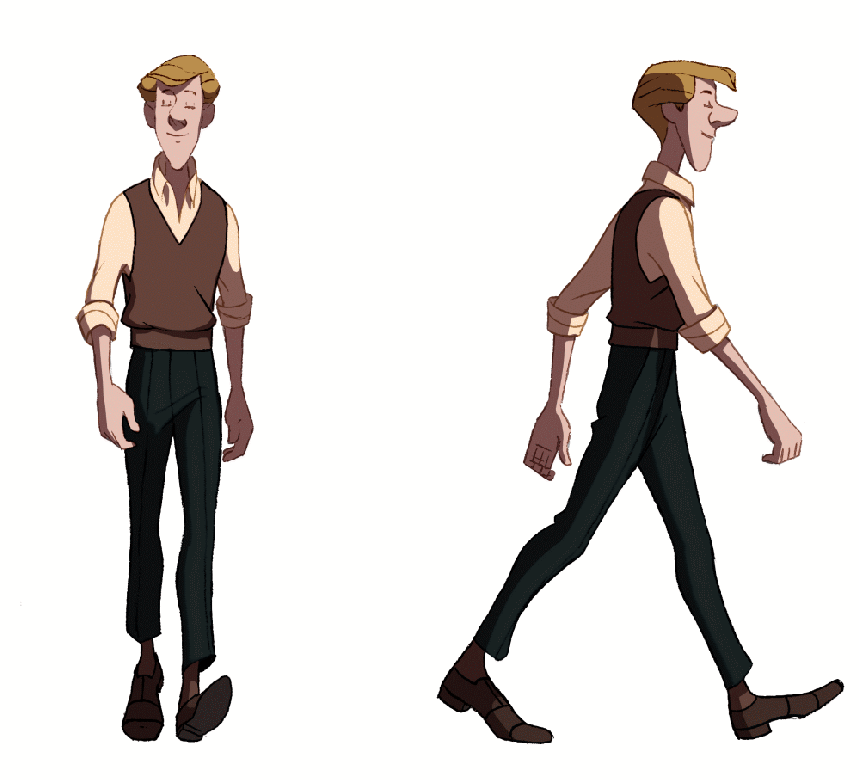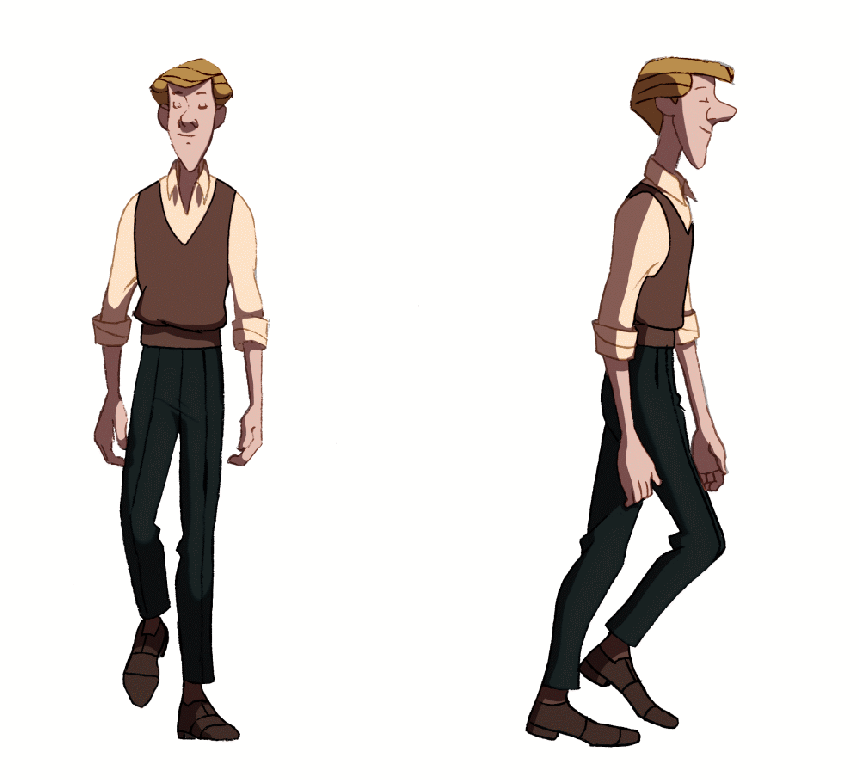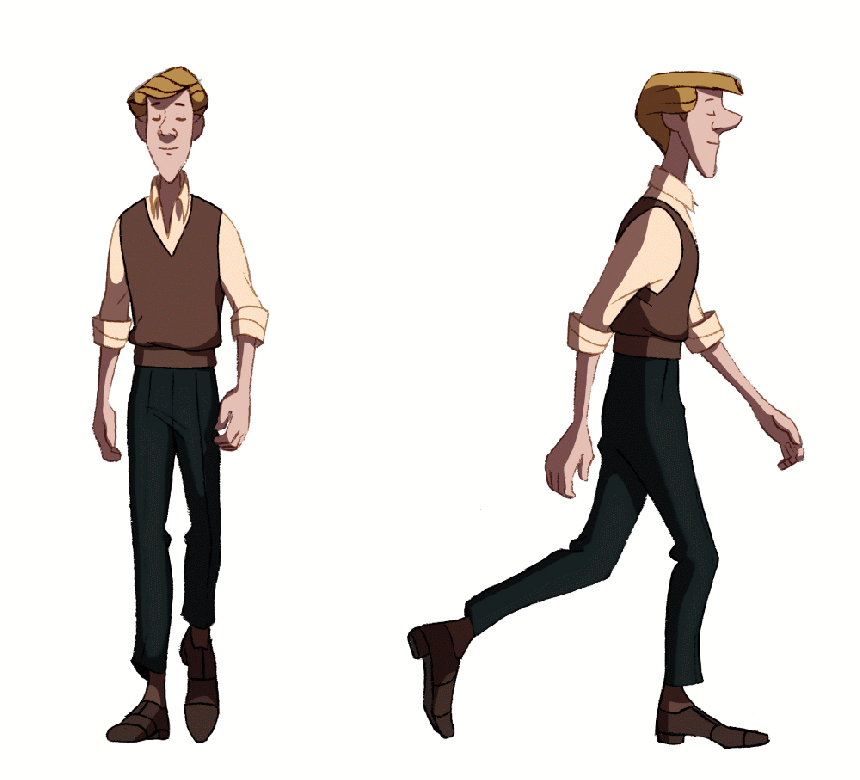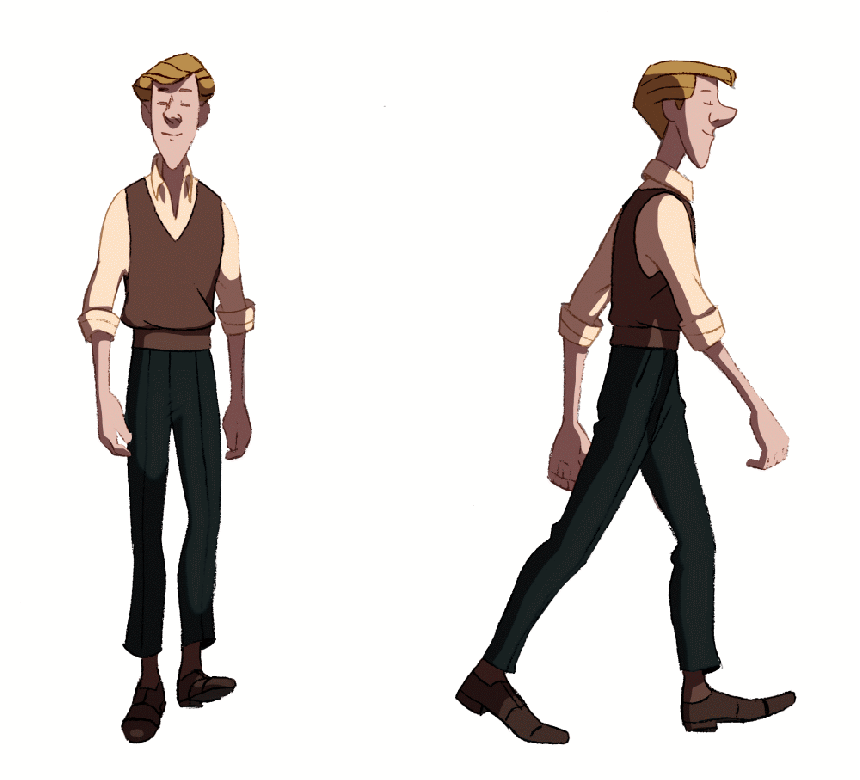 With rheumatoid arthritis, the joints of both hands are symmetrically affected, with gout, the fingers swell, with psoriasis, the joints of the fingers and hand.
With rheumatoid arthritis, the joints of both hands are symmetrically affected, with gout, the fingers swell, with psoriasis, the joints of the fingers and hand.
Edema is typical for joint damage - thrombosis. In addition to edema, a feeling of fullness, pain, thickening of tissues, discoloration of the skin, crawling, and a change in sensitivity are typical.
Morning
Lymphatic edema is possible after operations to remove the mammary gland, if the axillary lymph nodes were excised. Puffiness may increase or appear in the morning with malformations of the lymphatic capillaries, with post-burn scars, thrombophlebitis, lymphadenitis. Without treatment, swelling can become permanent. nine0003
Hand edema also occurs against the background of heart failure. In the morning they are minimal, intensify in the evening. In contrast, renal swelling of the hands is most pronounced in the morning and decreases or disappears during the day.
Pregnancy
Puffiness in the fingers or hands is due to hormonal changes, especially as the pregnancy progresses. In the first trimester, a slight swelling of the fingers is typical, which is almost not noticeable. By the third trimester, swelling can be pronounced, making it difficult to wear rings, watches, bracelets. Puffiness gradually disappears in the first days after childbirth. nine0003
However, in pregnant women, pathological edema associated with hypertension, overweight and the development of preeclampsia is also possible. Then the appearance of protein in the urine, a pronounced weight gain per week, severe swelling of the arms and legs, face, and body are typical.
How to relieve hand swelling in adults
At home or for first aid, you need to give your hand an elevated position.
If this is an injury, the hand should be immobilized with a bandage or splint, a cold compress should be applied to the affected area, and an anesthetic should be taken. nine0003
nine0003
If these are diseases of the joints, it is necessary to use painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs locally and orally. If the swelling develops quickly, with severe pain and dysfunction of the hand, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Doctors have two options for treating edema - conservative and surgical. It depends on the cause, the severity of the condition, and possible complications. In case of injuries, emergency care, bandages, anti-inflammatory drugs, anesthesia are indicated.
In vascular edema, antispasmodic, angioprotective and phlebotonic drugs are used.
Physiotherapy, gymnastics, massage or manual therapy are also prescribed.
If the injury is serious or severe lesions of blood vessels, bones, joints are detected, the edema is not eliminated, surgical interventions are used.
Popular questions and answers
Edema can be a short-term phenomenon and does not threaten anything. But sometimes they are symptoms of dangerous conditions. Andrey Grachev, a cardiologist, helped us figure out the problem. nine0003
But sometimes they are symptoms of dangerous conditions. Andrey Grachev, a cardiologist, helped us figure out the problem. nine0003
Why is hand swelling dangerous?
Swelling is often a sign of a serious infection, cancer, heart or kidney problems. And if the swelling is persistent, then the disease has worsened or is rapidly progressing. Edema can be complicated by tissue malnutrition, skin inflammation, stretch marks, and discoloration.
When should I see a doctor for swollen hands?
In any situation when you notice swelling of the hands - in the morning, in the evening or during the day, you need a doctor's consultation and at least a minimal set of tests and examinations. Edema itself is a symptom of problems in the body, and you need to find out what caused it. nine0003
Is it possible to remove swelling of the hands with folk remedies?
There are a number of diuretic decoctions and infusions, but it is extremely dangerous to use them on your own, not knowing what the causes of edema are. This can lead to a worsening of the situation, an electrolyte imbalance, a sharp decrease in pressure, dehydration and malaise.
This can lead to a worsening of the situation, an electrolyte imbalance, a sharp decrease in pressure, dehydration and malaise.
In addition, various traditional medicines can cause allergies, worsen the condition, negatively affect the effects of the drugs taken and have a number of contraindications for taking. Folk remedies are not equal to the concept of "safe". nine0003
What if only one arm is swollen?
If one arm is swollen, see a surgeon or physician, depending on the suspected cause. At the time of the examination, it is worth disturbing the sore arm less, giving it an elevated position so that the liquid flows more easily, do not sleep on this side, do not press the arm to the body. Also, do not massage the swollen hand, carry out any activities without the permission of the doctor.
Published on the portal kp.ru
Why hands and fingers swell: the therapist called 9 reasons
Health
- Photo
- iStockphoto
In the heat, we often notice a slight swelling of the fingers or hands in the morning or in the evening. Most often, this phenomenon is associated with the use of fluids to quench thirst, which leads to water retention in the tissues and slight swelling.
Most often, this phenomenon is associated with the use of fluids to quench thirst, which leads to water retention in the tissues and slight swelling.
But sometimes the hands swell due to the development of various, including quite serious, pathologies. "Doctor Peter" asked Sergei Lopatin, a therapist, gastroenterologist, doctor of the first category, to clarify the main causes of swelling of the hands. nine0003
therapist, gastroenterologist "SM-Clinic" in St. Petersburg, doctor of the first category
Personal website
Why hands swell
Most often, swelling of the hands is caused by external causes and after a while goes away on its own. Fluid retention can be determined by traces left by rings and other jewelry on hands, watch straps, or by subjective sensations. Against the background of puffiness, swelling of the phalanges, the rear of the hand occurs, and when the fingers are clenched into a fist, there is a slight resistance of the tissues and pressure. This feeling usually goes away after a few hours. nine0003
This feeling usually goes away after a few hours. nine0003
However, swelling of the hands can sometimes indicate various health problems. Where to look for the cause of edema? We have identified nine of the most common changes in the body that can be accompanied by edema.
Kidney problems
The kidneys control the excretion of excess fluid from the body. If their work fails, the fluid begins to gradually accumulate in the tissues. This is an extremely dangerous condition, therefore, with regular edema, it is necessary to consult a nephrologist and undergo basic examinations that will help identify abnormalities in the functioning of the organs. nine0003
Fluid retention
The most common physiological cause of hand edema is excess fluid retention in the body (mainly in the intercellular space). Various factors can influence it. So, the effect of "resting hand" is often the result of sleeping in an uncomfortable position. Squeezing the hand with hair ties, jewelry, watch straps, etc. can also lead to swelling.
can also lead to swelling.
The second popular reason is the abuse of salty foods and excessive drinking at night. Eating a pickled cucumber at night, we break the water-salt balance of the body, and wake up with swelling in the morning. In women, hormonal changes sometimes lead to a failure in the water balance. For example, before menstruation in the female body, the amount of the hormone estrogen increases, which can retain water in the tissues. nine0003
Pregnancy
Pregnant women often face the problem of swollen hands: the later in pregnancy, the swelling becomes more severe. Fluctuations in the hormonal background, as well as a change in the size of the uterus, should be blamed for this. As the organ enlarges, it begins to put pressure on the venous vessels, which disrupts blood flow in the tissues.
Problems with the musculoskeletal system
Edema can also be caused by diseases of the musculoskeletal system. First of all, we are talking about arthritis - acute inflammatory processes inside the joints. In this case, swelling of the tissues is usually accompanied by pain and discomfort in the hands. nine0003
In this case, swelling of the tissues is usually accompanied by pain and discomfort in the hands. nine0003
In addition, edema may be associated with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, where the branches of the spinal nerve are located. These nerve roots are responsible for the condition of the vessels in the area of the hands: their clamping contributes to stagnation of blood and the formation of edema.
Allergy
Swelling is a common symptom of contact allergy. A variety of hand creams, ointments, and household chemicals can provoke them. Slightly less often, an allergic reaction occurs to foods, insect bites, or certain medications. nine0003
Skin infections
Skin infections can cause redness and swelling in the hands. Thus, the problem of swollen hands and wrists in the morning is well known to patients with erysipelas. This skin inflammation is caused by the microbe Streptococcus.
Thrombosis
Blockage of arm vessels by thrombi prevents normal blood outflow.