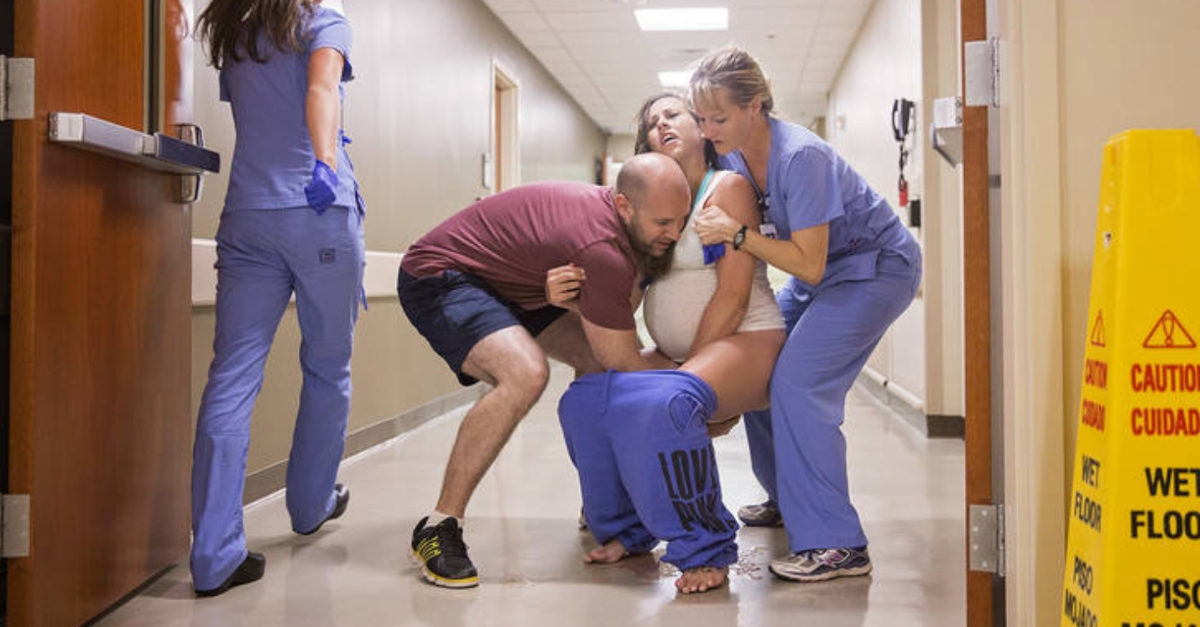
Give birth process
What happens to your body during childbirth
What happens to your body during childbirth | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content7-minute read
Listen
Key facts
- Female bodies are designed to give birth, and changes during the last weeks of pregnancy help prepare your body for labour and delivery.
- The shape of the pelvis, hormones, powerful muscles and more all work together to help you bring your baby into the world.
- Many different types of hormones work together to prepare your body for labour and birth.
- Your baby’s skull can also change shape to better pass through your birth canal.
How does my body prepare for labour?
Here are some of the ways your body will prepare both you and your baby for the birth ahead.
Braxton Hicks contractions
In the weeks or days before you start having proper contractions, you may experience Braxton Hicks contractions. This is your uterus tightening then relaxing. These contractions don't usually hurt and are thought to help your uterus and cervix get ready for labour. Braxton Hicks contractions are sometimes referred to as 'false labour'.
Braxton Hicks contractions may become more regular as you get closer to the time of birth. Unlike labour contractions, they don't change the shape of the cervix. Your midwife can tell you if you're experiencing Braxton Hicks contractions or if you are in labour by doing a vaginal examination.
Changes to the cervix
As labour gets closer, your cervix softens and becomes thinner, getting ready to dilate (widen). This will allow your baby to enter your vagina during birth. You may also see a ‘show’, which is a pinkish plug of mucus that may be bloodstained.
Engagement
Your baby may move further down your pelvis as the head engages, or sits in place over your cervix, ready for the birth. You may feel that you have more room to breathe after the baby has moved down. This is called ‘lightening’.
You may feel that you have more room to breathe after the baby has moved down. This is called ‘lightening’.
Rupture of the membranes, or ‘waters breaking’
During labour, the sac of amniotic fluid containing the baby breaks, and the fluid leaks (or gushes) out of the vagina. This is called rupture of the membranes or 'waters breaking'. In some cases, this happens before labour.
Let your maternity team know when your waters have broken and take notice of the colour of the fluid. It is usually clear or tinged pink. If it is green or red, tell your maternity team since this could mean the baby is having problems.
If your labour doesn’t start within 24 hours of your waters breaking, there is a risk of infection. If this happens, your doctor or midwife may recommend inducing your labour.
How will I know when labour has started?
Movies often show labour starting with sudden, painful contractions and a rush to hospital. In real life, labour usually starts gradually. It’s common not to be sure if your labour has actually started.
It’s common not to be sure if your labour has actually started.
You may feel restless, have back pain or period-like pain, or digestive issues such as diarrhoea.
Labour officially begins with contractions, which start working to open up (dilate) the cervix. It’s a good idea to phone your midwife when your contractions start. However, you may not be encouraged to come to the hospital or birthing centre until your contractions are closer together.
In preparation for labour, your baby may move further down your pelvis as the head engages, or sits in place over your cervix.You and your baby’s bodies work together during labour and birth.
Your pelvis is located between your hip bones. Females typically have wider, flatter pelvises than males, as well as a wider pelvic cavity (hole) to allow a baby to pass through.
During childbirth, the muscles at the top of your uterus contract and push your baby towards your cervix. If your baby is facing head-down, the head will press on your cervix.
This, along with the release of the hormone oxytocin (see 'How hormones help you give birth', below), brings on contractions. The bones and ligaments of your pelvis also move or stretch as the baby travels into the vagina.
Your baby’s skull is made up of 5 separate bones, which can cross over each other during labour. This allows your baby's head to fit more easily through your birth canal.
Which hormones help me give birth?
Your body produces hormones that trigger changes in your body before, during and after childbirth. Here's how they work to help you deliver your baby.
- Prostaglandin — Before childbirth, a higher level of prostaglandin will help open the cervix and make your body more receptive to another important hormone, oxytocin.
- Oxytocin — This hormone causes contractions during labour, as well as the contractions that deliver the placenta after the baby is born, and during breastfeeding.
- Relaxin — The hormone relaxin helps soften and stretch the cervix for birth.
 It helps your waters break and allows the ligaments in your pelvis to stretch to allow the baby to come through.
It helps your waters break and allows the ligaments in your pelvis to stretch to allow the baby to come through. - Beta-endorphins — During childbirth, this type of endorphin helps with pain relief and may cause you to feel joy or euphoria.
- Adrenaline and noradrenaline — These ‘fight or flight’ hormones are released just before birth, causing several strong contractions and a surge of energy that help you birth your baby.
When childbirth doesn’t go to plan
Despite your best efforts, sometimes, labour and birth do not go to plan. This could be because of complications before the labour, such as your waters breaking early, problems with your placenta, or issues with your baby’s position, health or progress during labour. If this happens, your midwife or doctor may recommend intervening to ensure a safe birth for both you and your baby.
Some of the more common interventions include:
- external cephalic version (turning your baby so they are in a better position for birth)
- induction or augmentation of labour
- assisted delivery
- episiotomy
- caesarean section
It’s your choice whether to have interventions in your labour. You can ask your doctor or midwife about the benefits and risks of any intervention they recommend.
You can ask your doctor or midwife about the benefits and risks of any intervention they recommend.
Talk to your doctor or midwife if you have questions about your body. They can give you more information and help you understand what you're experiencing.
You can also call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby for free advice, support and guidance from our maternal child health nurses.
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Sources:
Mater Mothers’ Hospital (Labour and birth information), National Childbirth Trust (Hormones in labour: oxytocin and the others – how they work), NSW Government (Having a baby), QLD Health (How your body prepares for labour), Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (Labour and birth), Stat Pearls (Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis), You and Your Hormones from the Society for Endocrinology (Hormones of pregnancy and labour)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: August 2022
Back To Top
Need more information?
Pregnancy: premature labour & birth | Raising Children Network
Are you likely to be having a premature birth? Here’s all you need to know about preparing for and recovering from premature labour and birth.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Pregnancy: labour & birth | Raising Children Network
Pregnant? Here’s all you need to know to decide where to give birth and prepare for labour and vaginal birth or caesarean birth.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Labour & birth: what to expect | Raising Children Network
Early labour signs include a show, waters breaking and pain. During labour, your contractions increase and your cervix dilates, so you can birth your baby.
During labour, your contractions increase and your cervix dilates, so you can birth your baby.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Premature birth & premature babies | Raising Children Network
This essential guide for parents of premature babies covers gestational age, premature birth risk factors, premature labour and premature development.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Premature birth: questions & checklist | Raising Children Network
Our checklist has answers to questions about premature birth and labour, covering where and how premature babies are born, and things to ask medical staff.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Labour and Birth
Read more on RANZCOG - Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists website
Developing a birth plan - Better Health Channel
A birth plan is a written summary of your preferences for when you are in labour and giving birth.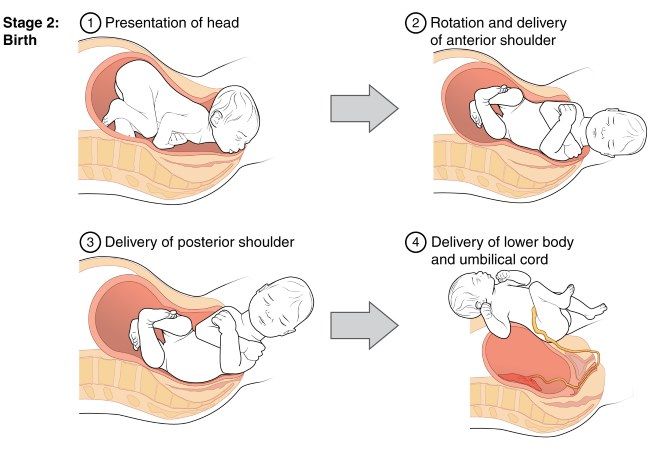
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Premature babies and birth | Raising Children Network
Premature babies are born before 37 weeks of pregnancy. Our essential guide covers premature birth, babies, development, NICU and more.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Premature birth: emotional preparation | Raising Children Network
If you know your baby will be born early, you can prepare yourself mentally and emotionally. Practise relaxation and take a tour of the NICU. Find out more.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Dads: premature birth and premature babies | Raising Children Network
After a premature birth, it can be hard for dads. Our dads guide to premature babies and birth covers feelings, bonding, and getting involved with your baby.
Our dads guide to premature babies and birth covers feelings, bonding, and getting involved with your baby.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.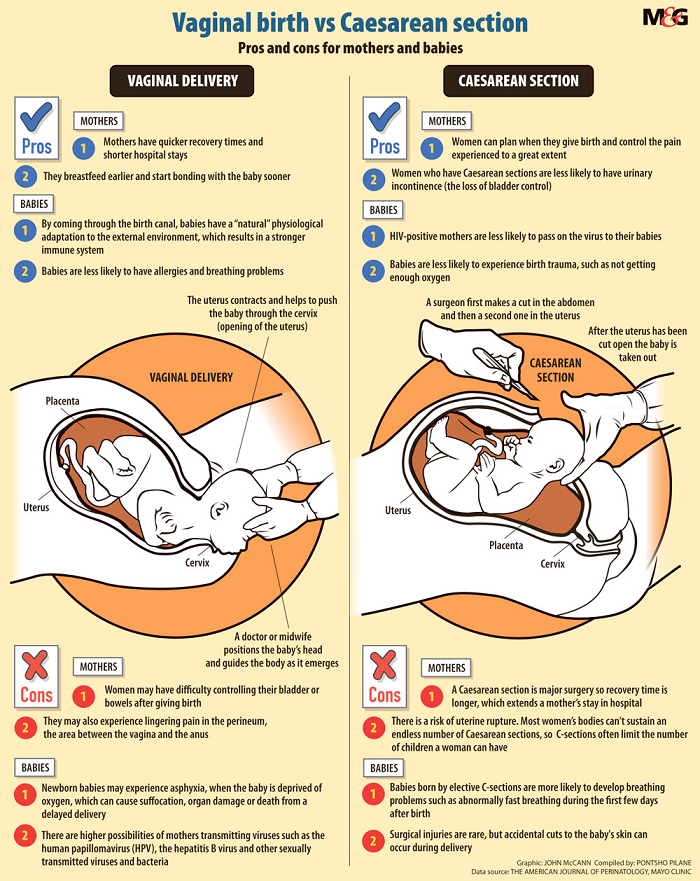
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Childbirth | Stages of Labor | Effacement
On this page
Basics
- Summary
- Start Here
- Diagnosis and Tests
- Treatments and Therapies
Learn More
- Related Issues
- Specifics
See, Play and Learn
- Images
Research
- Statistics and Research
- Clinical Trials
- Journal Articles
Resources
- Find an Expert
For You
- Patient Handouts
When you are ready to have your baby, you'll go through labor. Labor is the process of giving birth. Signs that you might be going into labor include:
- Contractions that are regular then start to come closer together
- Leaking fluid or bleeding from the vagina
- Low, dull backache
- Abdominal cramps
Call your health care provider if you have any of these signs, even if it is before your due date. Preterm labor can start before 37 completed weeks of pregnancy.
Labor happens in three stages. The first stage begins with contractions. It continues until your cervix has become thinner and dilated (stretched) to about 4 inches wide. The second stage is the active stage, in which you begin to push downward. Crowning is when your baby's scalp comes into view. Shortly afterward, your baby is born. In the third stage, you deliver the placenta. The placenta is the organ that supplied food and oxygen to your baby during pregnancy.
Mothers and babies are monitored closely during labor. Most women are able to have a baby through normal vaginal delivery. If there are complications, the baby may need to be delivered surgically by a Cesarean section.
NIH: National Institute of Child Health and Human Development
- Labor and Birth (Department of Health and Human Services, Office on Women's Health) Also in Spanish
- Stages of Labor (March of Dimes Birth Defects Foundation) Also in Spanish
- What Is Labor? (Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development) Also in Spanish
- Contractions and Signs of Labor (March of Dimes Birth Defects Foundation)
- Cord Blood Testing and Banking (National Library of Medicine) Also in Spanish
- Monitoring Baby's Heart Rate during Labor (American Academy of Family Physicians) Also in Spanish
- Water Breaking: Understand This Sign of Labor (Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research) Also in Spanish
- Dealing with Pain during Childbirth (Nemours Foundation) Also in Spanish
- Apgar Scores (American Academy of Pediatrics) Also in Spanish
- Birthing Centers and Hospital Maternity Services (Nemours Foundation) Also in Spanish
- Birthing Classes (American Academy of Family Physicians) Also in Spanish
- Elective Deliveries Before 39 Weeks: Is It Worth It? (American Academy of Pediatrics)
- Why at Least 39 Weeks Is Best for Your Baby (March of Dimes Birth Defects Foundation)
- Assisted Vaginal Delivery (American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists)
- Cesarean Section: MedlinePlus Health Topic (National Library of Medicine) Also in Spanish
- Episiotomy: When It's Needed, When It's Not (Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research) Also in Spanish
- Induction of Labor at 39 Weeks (American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists)
- Labor Pain (American Society of Anesthesiologists)
- Natural Childbirth (Nemours Foundation) Also in Spanish
- FastStats: Births -- Method of Delivery (National Center for Health Statistics)
- PeriStats: Perinatal Statistics (March of Dimes Birth Defects Foundation)
- ClinicalTrials.
 gov: Delivery, Obstetric (National Institutes of Health)
gov: Delivery, Obstetric (National Institutes of Health) - ClinicalTrials.gov: Labor, Obstetric (National Institutes of Health)
- Article: A comparison of the effect of Swedish massage with and without.
 ..
.. - Article: Effect of implementing a birth plan on maternal and neonatal outcomes:...
- Article: Micturition in the toilet compared with bedpan in laboring Nulliparas: a.
 ..
.. - Childbirth -- see more articles
- Department of Health and Human Services, Office on Women's Health Also in Spanish
- Find an Ob-Gyn (American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists)
The process of childbirth
This event must be approached with self-confidence, one's strengths, capabilities and reliability of information received about childbirth during pregnancy. Tuning in the right way and doing everything right, knowledge helps. It is incomparably easier for pregnant women who have a good idea of all the stages of the birth process and are psychologically prepared for the upcoming event than for those expectant mothers who are poorly aware of what will happen to them.
Tuning in the right way and doing everything right, knowledge helps. It is incomparably easier for pregnant women who have a good idea of all the stages of the birth process and are psychologically prepared for the upcoming event than for those expectant mothers who are poorly aware of what will happen to them.
Childbirth is divided into three periods:
- Disclosure period . As a result of regular contractions (involuntary contraction of the muscles of the uterus), the cervix opens.
- The period of expulsion of the fetus from the uterine cavity. Attempts are added to the contractions - arbitrary (that is, controlled by the woman in labor) contractions of the abdominal muscles. The baby moves through the birth canal and is born.
- Follow-up period . The placenta and membranes are born.
First stage of labor
The fact that labor has already begun or is about to begin is indicated by the appearance of regular contractions and / or the outflow of amniotic fluid. Contractions are involuntary periodic contractions of the muscles of the uterus, aimed at shortening and opening the cervix. Normally, the length of the cervix is 3-5 cm, and the diameter is only a few millimeters. And for the birth of a child, it is necessary that the cervix completely shorten and open up to 9-10 cm.
Contractions are involuntary periodic contractions of the muscles of the uterus, aimed at shortening and opening the cervix. Normally, the length of the cervix is 3-5 cm, and the diameter is only a few millimeters. And for the birth of a child, it is necessary that the cervix completely shorten and open up to 9-10 cm.
The period of dilation is the longest in the process of childbirth. In the natural course of childbirth, this period lasts 10-11 hours for primiparas, 6-7 hours for multiparous ones.
At the beginning of this period there are regular contractions that last 15-20 seconds with an interval of about 15 minutes. As the cervix dilates, the contractions intensify, become longer, and the intervals between them shorten. When the break between contractions is 10 minutes, you need to go to the maternity hospital.
During the opening period, it is recommended to walk, move, breathe properly, take a warm shower or bath. These measures contribute to a faster opening of the cervix, while reducing pain.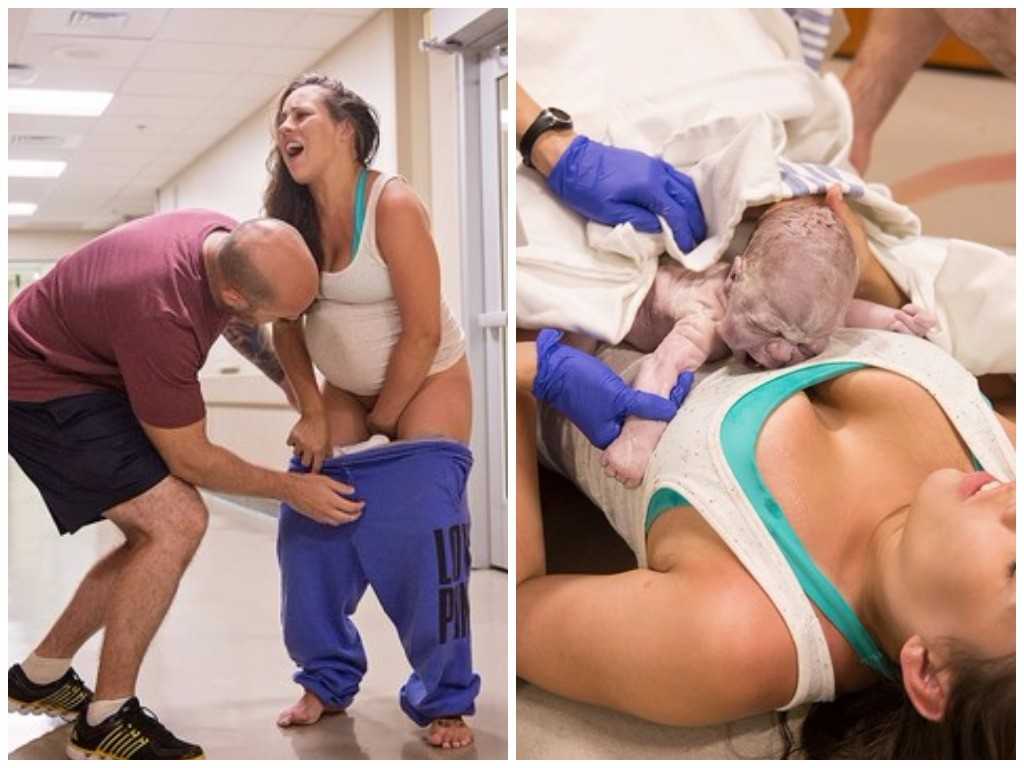 You can ask your husband or midwife to massage the lumbar region - this will reduce the discomfort from contractions.
You can ask your husband or midwife to massage the lumbar region - this will reduce the discomfort from contractions.
Second stage of labor
Most women agree that the end of the dilation phase, before the onset of the second stage of labor, is the most difficult. Contractions become frequent and painful, anesthesia by this moment usually ceases to act, fatigue accumulates, it is still impossible to push. The state of many women at this moment is described by one single phrase: “That's it! I can not anymore!". The only consolation is that it doesn't last long.
After the cervix is fully dilated, the doctor allows the mother to push. A woman usually herself feels strong urges to "push" the child out of the birth canal. These urges are called pushes.
In order for pushing to be effective, you need to push properly and breathe properly. Before pushing, you need to get more air into the lungs, hold your breath and try to push effectively. It is important not to strain your face and legs during attempts, but on the contrary - to relax as much as possible. Between attempts, you also need to relax and rest.
Between attempts, you also need to relax and rest.
The second stage of labor lasts from 15 minutes to two hours, and in multiparous this stage is shorter than in primiparas. During this period, doctors especially carefully monitor the condition of the mother and fetus (they regularly listen to heartbeats, etc.).
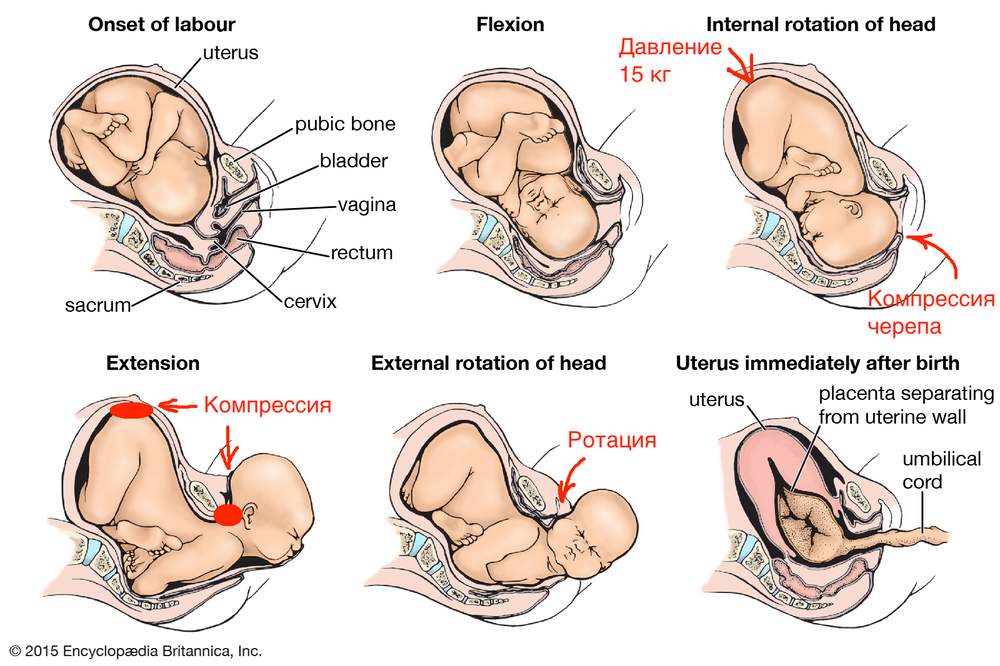
Meanwhile, the baby is moving along the genital tract. At the height of one of the attempts from the genital slit, the lower pole of the head (or buttocks - in breech presentation) is shown, after the end of the attempt, the head is hidden in the genital slit. This process - cutting the head - continues for some time. At a certain moment, the pole of the head remains in the genital gap and in between attempts. Under the influence of continuing attempts, the eruption of the head begins, which continues until its full birth. There is very little left. A few more attempts - and the whole child is born.
The newborn is placed on the mother's belly (ideally) and they get to know each other for a while, resting after the birth.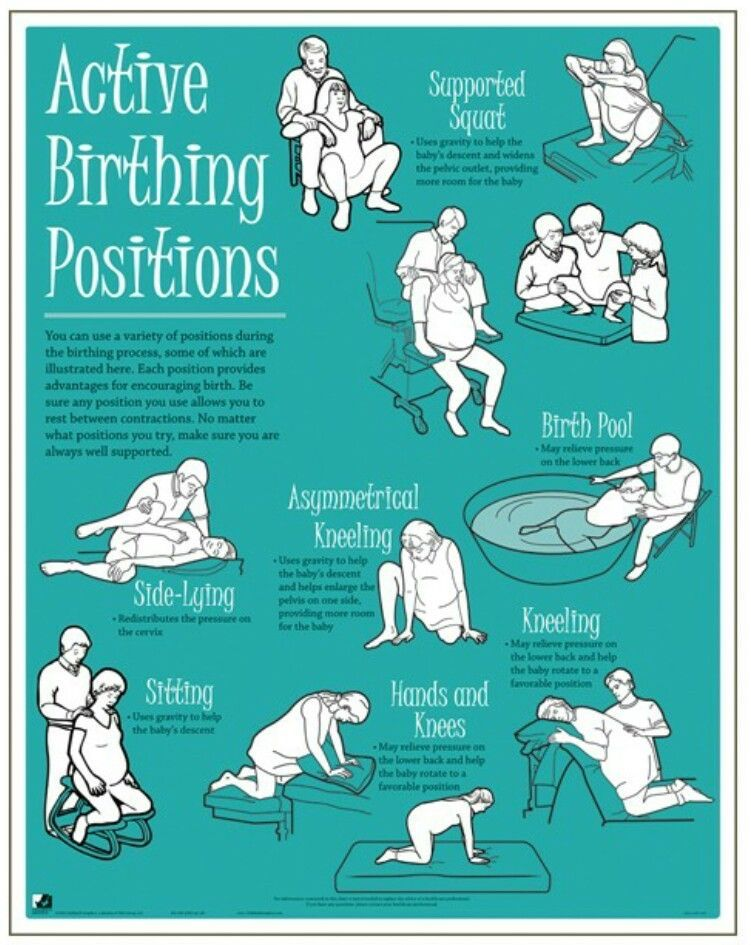 The midwife or doctor then cuts the umbilical cord and takes the baby away for proper treatment, bathing, weighing and examination by a pediatrician.
The midwife or doctor then cuts the umbilical cord and takes the baby away for proper treatment, bathing, weighing and examination by a pediatrician.
10-15 minutes after the birth of the baby can be applied to the breast. This promotes uterine contraction and milk production.
Third stage of labor
The last stage of labor - the birth of the placenta - is the shortest. Usually, the afterbirth is born 10-20 minutes after the birth of the baby. Mom might need to push a little for this.
If the placenta does not separate for more than 30 minutes, doctors diagnose the retention of the placenta in the uterus and begin to take emergency measures.
The delivered placenta is carefully examined for its integrity. If everything is fine, that is, the placenta has separated completely, the woman is sewn up with tears or incisions (if any). After that, a heating pad with ice is placed on her stomach and observed for some time in the delivery room (1.5-2 hours).
This is where the birth process ends and a new life begins for mother and baby.
References
- Florian S., Ichou M., Panico L. Parental migrant status and health inequalities at birth: The role of immigrant educational selectivity. // Soc Sci Med - 2021 - Vol278 - NNULL - p.113915; PMID:33905985
- Naja S., Al Kubaisi N., Singh R., Abdalla H., Bougmiza I. Screening for antenatal depression and its determinants among pregnant women in Qatar: revisiting the biopsychosocial model. // BMC Pregnancy Childbirth - 2021 - Vol21 - N1 - p.330; PMID:33902481
- Shchepin VO., Khabriev RU. [The characteristics of population mortality of the Russian Federation, the Central Federal Okrug and City of Moscow in 2020]. // Probl Sotsialnoi Gig Zdravookhranenniiai Istor Med - 2021 - Vol29 - N2 - p.189-193; PMID:332
- Saavedra LPJ., Prates KV., Gonçalves GD., Piovan S., Matafome P., Mathias PCF. COVID-19 During Development: A Matter of Concern.
 // Front Cell Dev Biol - 2021 - Vol9 - NNULL - p.659032; PMID:33898461
// Front Cell Dev Biol - 2021 - Vol9 - NNULL - p.659032; PMID:33898461 - Caparros-Gonzalez RA., Romero-Gonzalez B., Puertas-Gonzalez JA., Quirós-Fernandez S., Coca-Guzman B., Peralta-Ramirez MI. [Midwives and psychologists as professionals to screen and prevent pregnancy-specific stress.] // Rev Esp Salud Publica - 2021 - Vol95 - NNULL - p.; PMID:33896933
- Burakowska K., Gorka P., Penner GB. Effects of canola meal inclusion rate in starter mixtures for Holstein heifer calves on dry matter intake, average daily gain, ruminal fermentation, plasma metabolites, and total-tract digestibility. // J Dairy Sci - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33896627
- Toker E., Aktaş S. The childbirth experiences of Syrian refugee mothers living in Turkey: a qualitative study. // J Reprod Infant Psychol - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.1-17; PMID:33896296
- Mérillet L., Pavoine S., Kopp D., Robert M., Mouchet M. Biomass of slow life history species increases as local bottom trawl effort decreases in the Celtic sea.
 // J Environ Manage - 2021 - Vol290 - NNULL - p.112634; PMID:33895454
// J Environ Manage - 2021 - Vol290 - NNULL - p.112634; PMID:33895454 - Patskun E., Yevtushok L., Zymak-Zakutnia N., Lapchenko S., Akhmedzhanova D., Wertelecki W. A teratology information system in vernacular: Closing an information gap. // Birth Defects Res - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33893758
- Fu A., Liu C. Is Pregnancy Following a TRAM or DIEP Flap Safe? A Critical Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. // Aesthetic Plast Surg - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33893518
How to behave in childbirth? Learning to give birth quickly and with problems
Childbirth is a natural process, laid down by nature. The whole sequence of events that take place during this period is predetermined, but by your actions you can either speed up the birth of a baby, or complicate his birth.
Childbirth is the final and most important stage of pregnancy. How you behave and how accurately and skillfully you follow the instructions of the obstetrician depends on how you will feel and how quickly your baby will be born.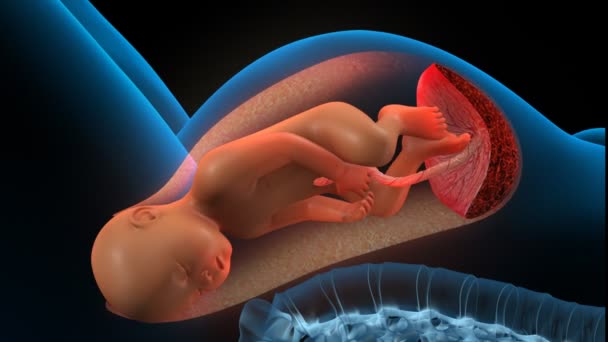 What does a newborn need to know? Let's try to answer the most important questions.
What does a newborn need to know? Let's try to answer the most important questions.
1. When is it time to go to the maternity hospital?
Childbirth is a natural result of hormonal changes that occur in your body during the final stages of pregnancy. The sagging belly and heaviness in its lower part and the lumbar region speak of the imminent denouement of the story. Periodically, weak contractions occur, the stomach tenses and pulls down, but these sensations quickly pass, the uterus relaxes again and becomes soft. Such contractions are harbingers of childbirth, but they are far from real labor activity.
The signal to call an ambulance should be sufficiently strong contractions that are repeated at regular intervals, the appearance of mucous secretions from the genital tract, slightly stained with blood, or the outflow of amniotic fluid.
2. First stage of childbirth: we breathe for two!
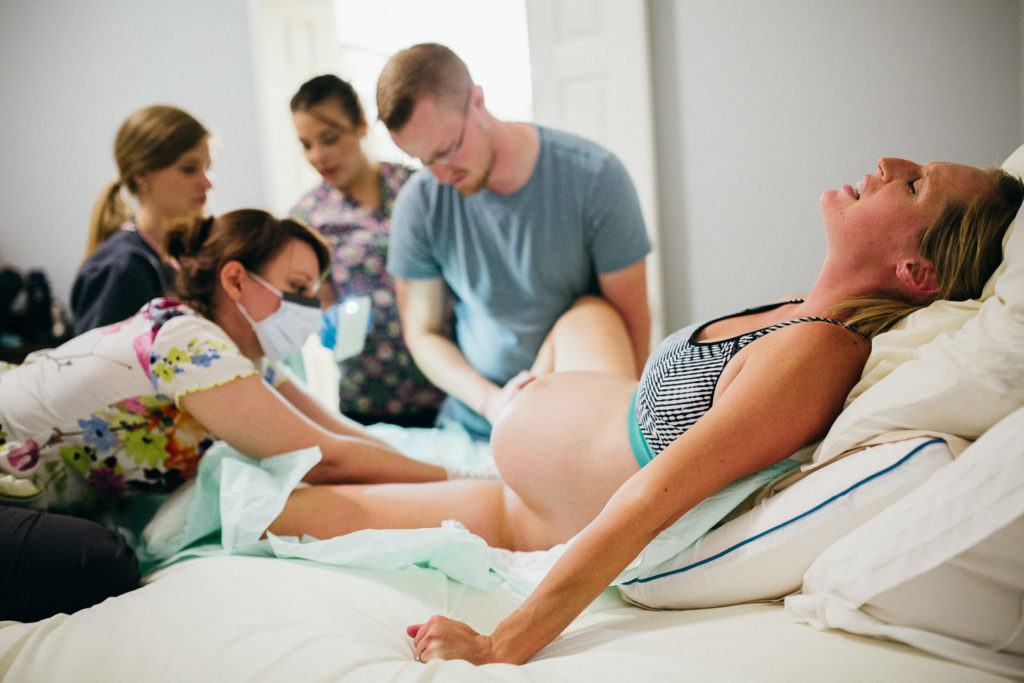
From the moment the contractions become regular, the first stage of labor begins, during which the strength, frequency and duration of uterine spasms increases and the cervix opens.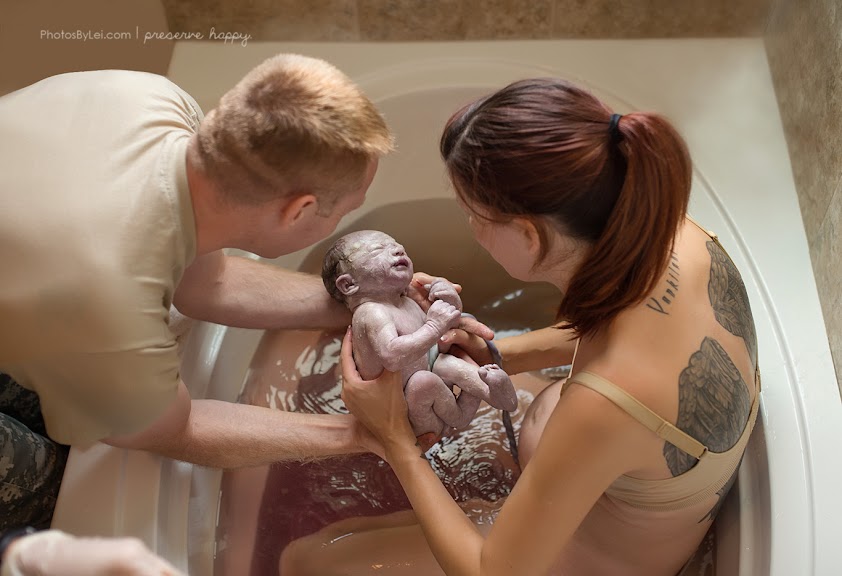
During spastic contraction of the uterine muscle fibers, the blood vessels that carry arterial blood to the placenta and fetus are compressed. The fetus begins to experience a lack of oxygen, and this involuntarily makes you breathe deeper. The reflex increase in the rate of contractions of your heart will ensure the delivery of oxygen to the child. Nature has provided that these processes take place regardless of your consciousness, but you should not completely rely on it.
In the first stage of labor, during each contraction, you need to breathe calmly and deeply, trying not to hold your breath while inhaling. At the same time, the air should fill the upper sections of the lungs, as if raising the chest. You need to inhale through the nose, slowly and smoothly, exhale through the mouth, just as evenly.
3. Auto-training in the prenatal ward
To speed up the opening of the cervix, you need to walk more, but sitting is not recommended, while blood flow in the limbs is disturbed and venous blood stagnation occurs in the pelvis.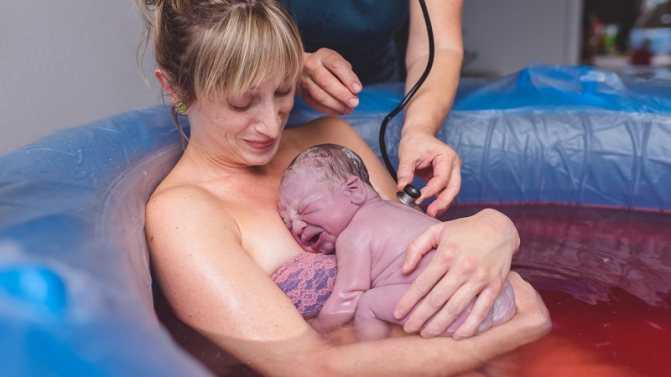 From time to time it is useful to lie on your side, stroking your lower abdomen with both hands in the direction from the center to the sides, focusing on breathing and saying to yourself: "I am calm, I am in control of the situation, each contraction brings me closer to the birth of a baby."
From time to time it is useful to lie on your side, stroking your lower abdomen with both hands in the direction from the center to the sides, focusing on breathing and saying to yourself: "I am calm, I am in control of the situation, each contraction brings me closer to the birth of a baby."
4. To relieve pain
Acupressure of the lower back can help relieve pain. Find the outer corners of the sacral rhombus on your lower back and massage these points with clenched fists.
Monitor the frequency and duration of contractions and if they weaken or sharply increase, immediately inform your doctor. In case of severe pain, you can ask for an anesthetic, but you should remember that you should not take the medicine too often, this is fraught with narcotic depression of the newborn and a decrease in his adaptive abilities.
If dilatation of the cervix has caused reflex vomiting, rinse the mouth with water and then drink a few sips to replace the lost fluid.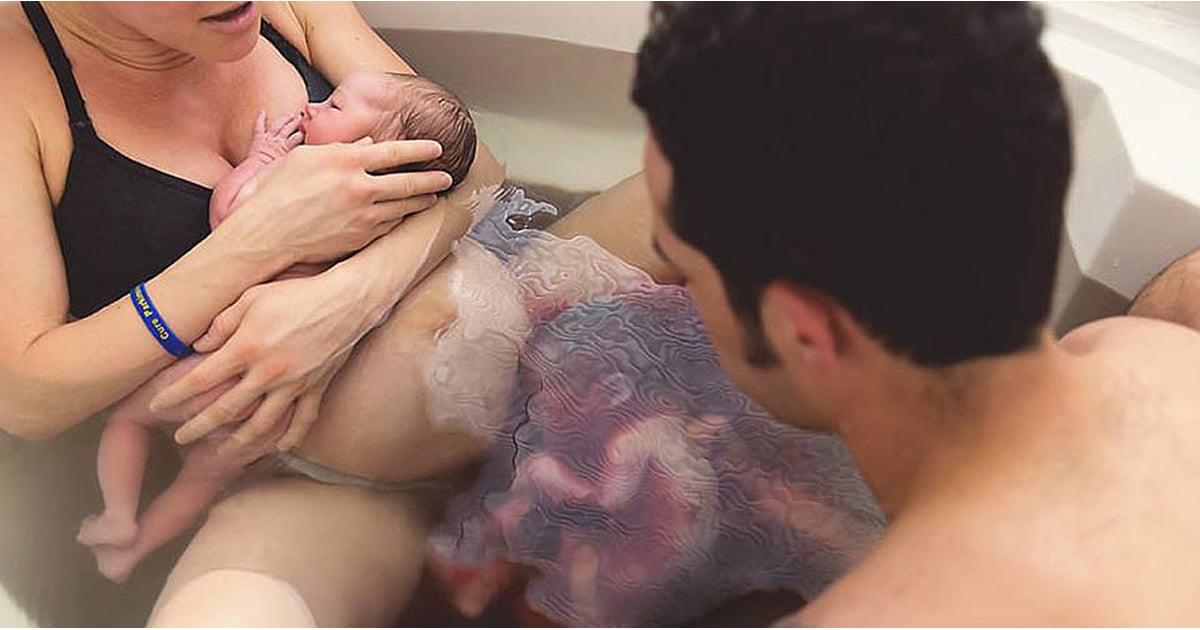 Do not drink a lot, this can provoke a recurrence of vomiting.
Do not drink a lot, this can provoke a recurrence of vomiting.
5. The maternity ward is not a place for tantrums
They say that difficult childbirth is a person's retribution for walking upright. Childbirth is actually a painful process, but the presence of reason allows us, representatives of the genus Homo sapiens, to control our emotions. Screaming, crying, tantrums and swearing have no place in the maternity ward. This creates a tense environment, interferes with the normal course of childbirth, complicates diagnostic and therapeutic measures, and ultimately affects their outcome.
6. Second stage of labor - pushing and expulsion of the fetus
After the baby's head slips through the dilated cervix and finds itself on the bottom of the pelvis, the pushing period of labor begins. At this time, there is a desire to push, as it usually happens during a bowel movement, but at the same time many times stronger. At first, the attempts are controllable, they can be "breathed", but by the beginning of the third stage of labor, the expulsion of the fetus, they become unbearable.
With the beginning of the straining period, you will be transferred to the delivery room. Having settled down on the delivery table, rest your feet on the special steps, firmly grasp the handrails and wait for the midwife's command.
While pushing, inhale deeply, close your mouth, clench your lips tightly, pull the handrails of the birthing table towards you and direct all the exhalation energy down, squeezing the fetus out of you. When the top of the baby appears from the genital slit, the midwife will ask you to ease your efforts. With gentle movements of her hands, she will first release the baby’s forehead, then his face and chin, after which she will ask you to push again. At the moment of the next attempt, the baby's shoulders and torso will be born. After the newborn is born, you can breathe freely and rest a little, but the birth is not over.
7. Third stage of labor and final
Third stage of labor - afterbirth.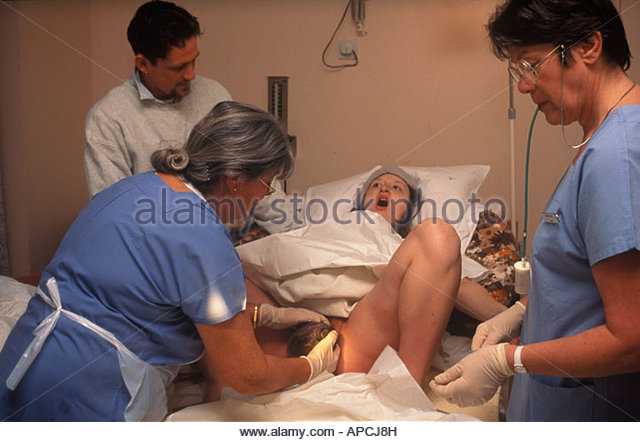 At this time, weak contractions are observed, due to which the fetal membranes gradually exfoliate from the walls of the uterus.
At this time, weak contractions are observed, due to which the fetal membranes gradually exfoliate from the walls of the uterus.
About 10 minutes after your baby is born, your midwife will ask you to push again to deliver your afterbirth. The doctor will carefully examine it and make sure that all parts of the membranes have come out. After that, with the help of mirrors, he will examine the cervix and make sure that it is intact. If necessary, all tears will be closed with absorbable sutures.
You will have to spend a couple more hours in the delivery room with an ice-filled bladder on your stomach. To quickly contract the uterus, you will be given injections of special drugs. When the threat of postpartum hemorrhage has passed, you will be transferred to the postpartum ward to the baby.
Childbirth completed. Ahead of the postpartum period, during which your body will recover after pregnancy.
Read more at Medkrug.