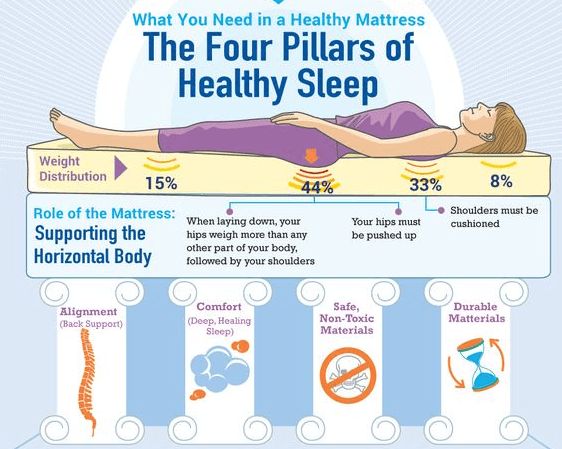
Is having headaches a sign of pregnancy
Am I pregnant? Early signs and symptoms | Pregnancy articles & support
If you’ve not done a test yet but you suspect you could be pregnant, here are the signs that could spill the beans.
When you think you could be pregnant, it’s natural to obsess over signs. Do you normally have that much discharge? Is that nausea really because of how much spag bol you devoured?
What are the early pregnancy signs and symptoms?
Here are the pregnancy signs that could give the game away:
- Changes of appetite
- Feeling of sickness, nausea and vomiting
- Strange taste in your mouth
- Constipation
- Needing to wee more often
- Headaches
- Breast changes
- Tiredness
- Mood swings
- Spotting
- Cramps. (Healthline 2018)
This video looks at the early pregnancy symptoms and signs:
"The best way to confirm though is to pick up a pregnancy test".
![]()
Changes of appetite
In the early stages of being pregnant, you may crave certain foods or go off others (Patient, 2017; NHS Choices, 2016).
The morning cuppa that you used to love might seem repulsive now, while you’re pining for Marmite despite previously being a hater (NHS Choices, 2016).
Things should settle back to normal in your second trimester. So as long as you’re getting a reasonable amount of nutrition, it won’t harm you to go with your new (and sometimes quirky) preferences (American Pregnancy Association, 2018).
Sickness, nausea and vomiting
If you’re sitting in meetings fighting the urge to vomit, you’re definitely not alone. About 50% to 80% of pregnant women will throw up or feel nauseous (Koren et al, 2002). That can start happening any time from two to eight weeks after you conceive your baby.
The most likely cause is fluctuating levels of pregnancy hormones (Fantasia, 2014).
Oh, and the term morning sickness is a bit misleading too. Nausea or vomiting can happen at any time during the day (American Pregnancy Association, 2018).
Nausea or vomiting can happen at any time during the day (American Pregnancy Association, 2018).
A small number of women might find themselves with a severe form of nausea and vomiting called hyperemis gravadarum (HG). HG can lead to pregnancy complications like dehydration, weight loss and electrolyte imbalance so you might need to be admitted to hospital (Fantasia, 2014; RCOG, 2016).
Strange taste in your mouth
Some women get a strange metallic taste in their mouth when they’re pregnant (NHS Choices, 2016; Patient, 2017), which can be an early sign.
Sensitivity to smells
You might also notice that you’re more sensitive to the smell of food or cooking (NHS Choices, 2016; Healthline, 2018). This can make you a little queasy and might put you off some foods.
Constipation
In a lot of women, being pregnant can lead to constipation and bloating (Li et al, 2015). This could be because you’re producing a large amount of progesterone so your digestive system slows down (Li et al, 2015; Mayo Clinic, 2017). For more on how to prevent constipation in pregnancy, see here.
For more on how to prevent constipation in pregnancy, see here.
Going to the toilet a lot
When you’re pregnant, the urge to wee will come over you often, sometimes even leaking out before you get there.
This happens as your body pumps more blood than normal when you’re pregnant. That means the kidney processes more fluid than usual, leading to more fluid in your bladder (Healthline, 2018).
In the later stages of pregnancy, you’ll run to the loo even more often because of the increased pressure of your baby’s head (Mayo Clinic, 2017; Patient, 2017).
Headaches
One of your earliest pregnancy symptoms can be headaches, which might be down to rising hormone levels. It could also be because of increased blood flow (American Pregnancy Association, 2018).
Speak to your midwife if you’re suffering as in some cases, they can be a sign of something more worrying. Your midwife will also advise you on what you can and can’t use to treat your headaches when you’re pregnant (Negro et al, 2017).
Breast changes
Because of the changes in – you guessed it – hormone levels, changes in your boobs can be one of the earliest pregnancy symptoms. You might find your breasts change between four and six weeks of pregnancy.
These changes can include:
- breasts getting bigger (see our article about bras for pregnancy if your old bras are getting too tight)
- breasts feeling tender
- breasts tingling
- veins becoming more visible
- areola (area around your breast) darkening. (NHS Choices, 2016; Healthline, 2018)
Tiredness
Anyone fancy a nap? Yep, tiredness and fatigue are some of the most common symptoms in early pregnancy. Try to make sure you get as much rest as you can.
Your sleepiness is caused by increased levels of progesterone (NHS Choices, 2016; Mayo Clinic, 2017; Patient 2017; Healthline, 2018). But if you're struggling to get a good night's sleep, see our article about how to sleep better during pregnancy.
Mood swings
Changes in your hormone levels during pregnancy can make you feel irritable and moody (Patient, 2017; Healthline 2018). So yes, you do have an excuse. Because your oestrogen and progesterone levels are up, you might feel more emotional or feel depressed, anxious and even euphoric (Healthline, 2018).
Spotting
In early pregnancy, some women get a small amount of blood or spotting, known as implantation bleeding (Mayo Clinic, 2017; American Pregnancy Association, 2018).
Implantation happens when the fertilised egg attaches to the lining of the uterus 10 to 14 days after you conceived your baby. The spotting will probably last for less than three days (Healthline, 2018). For more information, see our articles on discharge during pregnancy and bleeding or spotting during pregnancy.
Cramps
You might get light stomach cramps or pain if you have implantation bleeding (Healthline, 2018). Some women get mild cramping in their uterus in early pregnancy too (Mayo Clinic, 2017).
This page was last reviewed in September 2018
Further information
Our support line offers practical and emotional support with feeding your baby and general enquiries for parents, members and volunteers: 0300 330 0700.
We also offer antenatal courses which are a great way to find out more about birth, labour and life with a new child.
The HER Foundation provides information about hyperemesis gravidarum (HG).
References
American Pregnancy Association. (2018) Pregnancy symptoms – early signs of pregnancy. Available from: http://americanpregnancy.org/getting-pregnant/early-pregnancy-symptoms/ [Accessed 24th September 2018]
Fantasia HC. (2014) A new pharmacologic treatment for nausea and vomiting of pregnancy. Nursing for women’s health 18(1). Available from: https://www.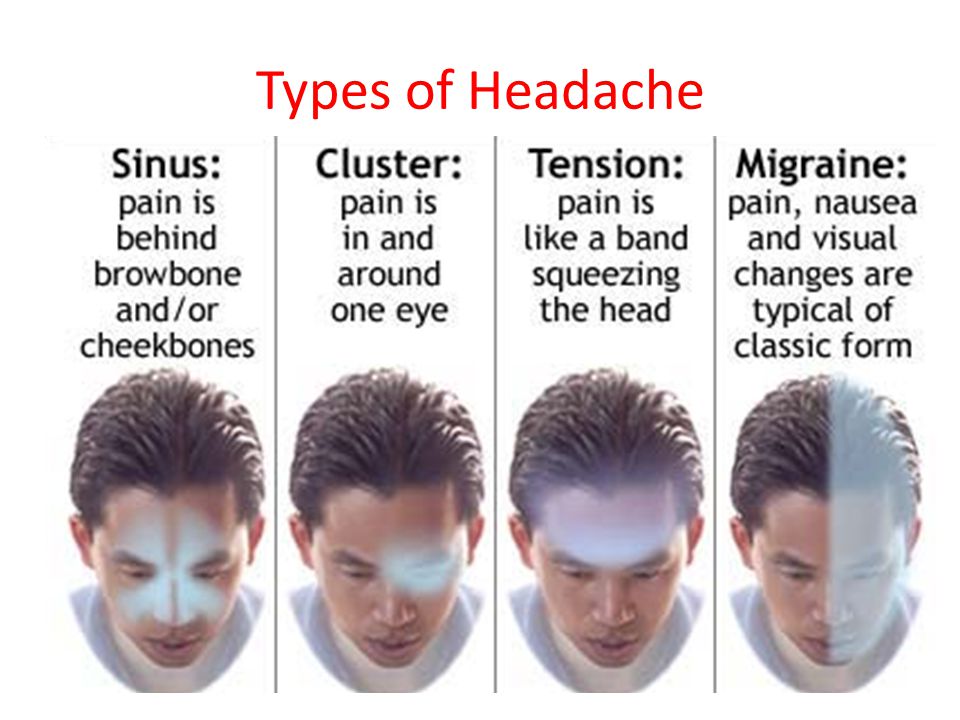 ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24548499 [Accessed 24th September 2018]
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24548499 [Accessed 24th September 2018]
Healthline. (2018) Early pregnancy symptoms. Available from: https://www.healthline.com/health/pregnancy/early-symptoms-timeline [Accessed 24th September 2018]
Hyperemis RCOG. (2016) The management of nausea and vomiting of pregnancy and hyperemesis gravidarum. The Green Top Guideline No. 69. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23863612 [Accessed 24th September 2018]
Koren G, Boskovic R, Hard M, Maltepe C, Navioz Y, Einarson A. Motherisk- PUQE (pregnancy-unique quantification or emesis and nausea) scoring system for nausea and vomiting of pregnancy. (2002) American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 186(5). Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12011891 [Accessed 24th September 2018]
Li Z, Pergolizzi JV, Huttner RP, Zampogna G, Breve F, Raffa RB. (2015) Management of opioid-induced constipation in pregnancy: a concise review with emphasis on the PAMORAs. Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeautics. 40: 615-619. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26573866 [Accessed 24th September 2018]
40: 615-619. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26573866 [Accessed 24th September 2018]
Mayo Clinic. (2017) Getting pregnant. Available from: https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/getting-pregnant/in-depth/symptoms-of-pregnancy/art-20043853 [Accessed 24th September 2018]
Negro A, Delaruelle Z, Ivanova TA, Khan S, Ornello R, Raffaelli B, Terrin A, Reuter U, Mitsikostas DD. (2017) Headache and pregnancy: a systematic review. J Headache Pain. 18(1):106. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29052046 [Accessed 24th September 2018]
NHS Choices. (2016) Signs and symptoms of pregnancy. Available from: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/pregnancy-and-baby/signs-and-symptoms-pregnancy/#strange-tastes-smells-and-cravings [Accessed 24th September 2018]
Patient. (2017) Early pregnancy signs and symptoms. Available from: https://patient.info/health/early-pregnancy-signs-and-symptoms [Accessed 24th September 2018]
Further reading
Gartland D, Brown S, Donath S, Perlen S. (2010) Women’s health in early pregnancy: Findings from an Australian nulliparous cohort study. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology. 50 (5). Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21039372 [Accessed 24th September 2018]
(2010) Women’s health in early pregnancy: Findings from an Australian nulliparous cohort study. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology. 50 (5). Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21039372 [Accessed 24th September 2018]
When To Take, Types & Accuracy
Overview
How Does a Pregnancy Test Work?What is a pregnancy test?
A pregnancy test is a way to determine if you’re pregnant. If your pregnancy test is positive, it means you’re pregnant. If the test is negative, it means you aren’t pregnant. Pregnancy tests work by detecting human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), a hormone your body makes when you’re pregnant.
From the very beginning of pregnancy, your body starts to go through changes to support the cells that will develop into your baby. One thing that happens very quickly is the production of HCG. If you’re pregnant, your body starts to produce more HCG. Your HCG levels start to build up once the fertilized egg implants in your uterus — about six to 10 days after conception.
There are two main types of pregnancy tests — urine tests and blood tests. Often, you’ll take a urine test at home with a home pregnancy test. This type of test is available over the counter (you don’t need a prescription from your healthcare provider) and in a variety of price ranges. Blood tests to check for pregnancy happen in your healthcare provider’s office and involve giving a sample of your blood. The other way to confirm a pregnancy is by using an ultrasound. Your provider performs an ultrasound in their office.
There are several reasons why you might take a pregnancy test. You could be trying to get pregnant and hoping for a positive result. You might have experienced an issue with your birth control. You might even be about to have a medical procedure or start a new medication that could be complicated by pregnancy. No matter what the reason, if you ever have any questions about your test results, the best thing to do is reach out to your healthcare provider.
What hormone levels are checked for a pregnancy test?
Pregnancy tests look for an elevated amount of HCG. Levels of HCG rise quickly – doubling every few days in the first weeks of pregnancy. The placenta produces HCG. Only pregnant people have a placenta, which develops shortly after a fertilized egg attaches to your uterine wall.
Levels of HCG rise quickly – doubling every few days in the first weeks of pregnancy. The placenta produces HCG. Only pregnant people have a placenta, which develops shortly after a fertilized egg attaches to your uterine wall.
When should I take a pregnancy test?
If you think you could be pregnant, it’s a good idea to take a test and make sure. Home pregnancy tests can differ in how early they’ll detect a pregnancy. In many cases, you might get a positive result from an at-home test as early as 10 days after conception. For a more accurate result, wait until after you’ve missed your period to take a test. Remember, if you take a test too soon, it could be negative even if you’re pregnant. If you get a negative test and then miss your period, take another test.
What time should I take a pregnancy test?
In general, the best time is when you have your first morning pee. However, some pregnancy tests are sensitive enough to detect HCG no matter what time of day you take the test. When possible, try to wait until it’s been three hours since your last pee before you take the test. You could also take two pregnancy tests to confirm you get the same result.
When possible, try to wait until it’s been three hours since your last pee before you take the test. You could also take two pregnancy tests to confirm you get the same result.
Test Details
How do pregnancy tests work?
When you take a pregnancy test, it’s looking for the amount of human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) in your body. You can find HCG in your pee or blood. HCG needs time to build up in your body. Each day of early pregnancy, your body will create more HCG. As the weeks go on, you’ll have more and more HCG in your body, which will make it more likely that a pregnancy test will show as positive. This means if you take a test too soon, it will come back negative.
Pregnancy tests work by reacting to the amount of HCG in either your pee or blood. In a urine test, a piece of reactive paper detects the HCG. This test might show a plus sign, double vertical lines or even the word “pregnant.” Different tests will show a positive result in unique ways. Read the directions that come with the test to know what a positive result will look like. For example, most tests have a control window that shows up first. Seeing a symbol in this window will tell you that the test is working. Keep in mind that different brands of tests will take different amounts of time to show a result.
For example, most tests have a control window that shows up first. Seeing a symbol in this window will tell you that the test is working. Keep in mind that different brands of tests will take different amounts of time to show a result.
If you take a blood test, your provider will take a sample of your blood and send it to a lab. The lab will determine the amount of HCG in your blood. Your provider will contact you with your results.
What are the different types of pregnancy tests?
There are two main types of pregnancy tests: urine and blood tests.
Urine tests are typically done at home — though you can have a urine test done at your healthcare provider’s office — while your provider performs a blood test.
At-home pregnancy test
An at-home test uses your pee to look for HCG. They contain special strips that detect HCG. Most at-home pregnancy tests are about 99% effective when used correctly. That’s about the same accuracy rate as pregnancy tests done in your healthcare provider’s office. These tests are available in most drug or grocery stores. They’re easy to use and inexpensive. It’s important to read the instructions on these tests before taking them.
These tests are available in most drug or grocery stores. They’re easy to use and inexpensive. It’s important to read the instructions on these tests before taking them.
There are three ways to take an at-home pregnancy test:
- Pee in a clean cup. Then, place one to several drops of your pee on a chemical strip.
- Place the pregnancy test strip in your urine stream while you pee.
- Pee in a clean cup and then dip the test strip in the pee while it’s still in the cup.
For many of these tests, HCG can be detected in your urine about 10 days after conception. However, taking it after you miss your period reduces the chance of getting a false-negative result. A missed period typically happens around 14 days after conception.
There are a few things to keep in mind when you take a home pregnancy test, including:
- Use your first morning pee if you can. This is the time of day when your HCG levels will be the most concentrated and easily detected.
 If you do it at another time of day, try to make sure your pee has been in your bladder for at least three hours.
If you do it at another time of day, try to make sure your pee has been in your bladder for at least three hours. - Don’t drink excessive amounts of fluids before you take a pregnancy test. This can dilute (thin out) your HCG levels.
- Check the expiration date on the package.
- Read the directions that come with the test thoroughly before starting the test, and follow every step exactly.
Blood test
Another type of pregnancy test is a blood test. Blood tests are rarely done because they’re expensive and tend to have the same result as a urine test. This type of pregnancy test is done using a small sample of blood from a vein in your arm. This blood test not only detects whether the pregnancy hormone is in your body, but can also determine how much of the hormone is present. This is helpful for when your provider needs to know the exact amount of HCG in your blood, not just if there’s HCG in your blood.
A blood test for pregnancy might be done in special circumstances, such as for people who are having fertility treatments or when the healthcare provider thinks there might be a problem.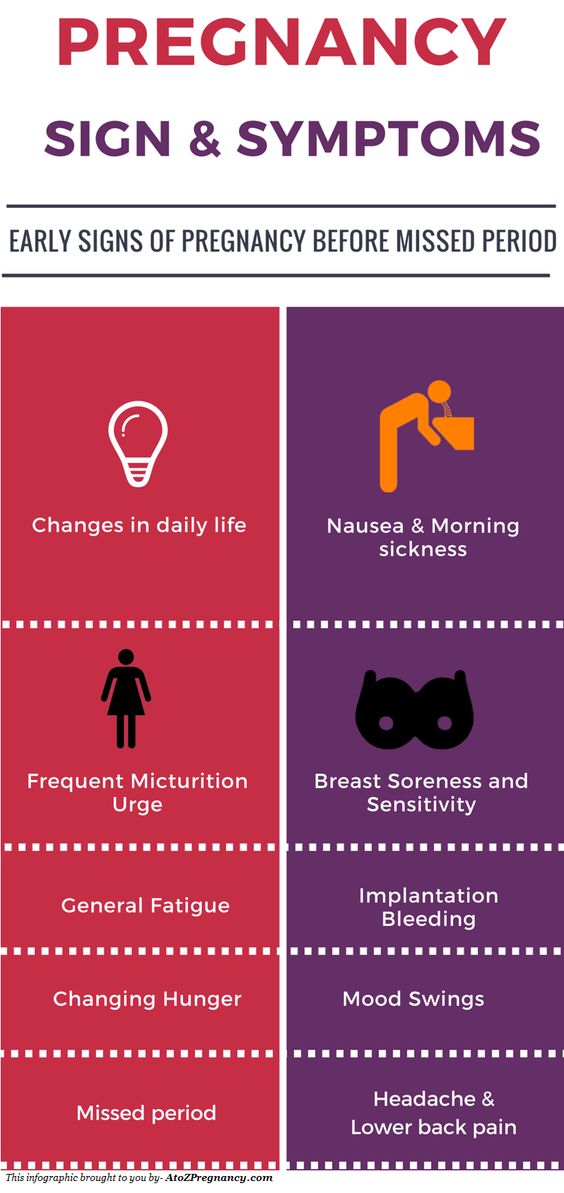
These blood tests are slightly more sensitive than urine tests because they can detect very small levels of HCG. That means they can provide a more accurate answer very early on in pregnancy — within seven to 10 days after conception. For this test, your blood sample is taken at your provider’s office or the hospital, then sent to a lab for analysis. Results might take anywhere from a few hours to two days.
Your provider might also choose to use a blood test to compare HCG levels during the pregnancy. Your HCG levels usually double about every two days during the first few weeks of pregnancy. If the levels don’t rise, it might suggest a problem with the pregnancy. Extremely high HCG levels might mean that you’re carrying twins or that there’s an issue with the pregnancy.
Are all home pregnancy testing methods the same?
Most brands of at-home pregnancy tests are reliable. Although the exact testing method of different pregnancy tests can differ from one type to the other, they all look for HCG in your body. If you’re using an at-home test, most will give you the same result. The difference with your at-home tests will be the sensitivity of the test. Some might be more sensitive than others and produce a positive result (detect HCG in your urine) sooner than others. For the most accurate reading, it’s still recommended that you wait until you’ve missed your period. At that point, all tests should be accurate.
If you’re using an at-home test, most will give you the same result. The difference with your at-home tests will be the sensitivity of the test. Some might be more sensitive than others and produce a positive result (detect HCG in your urine) sooner than others. For the most accurate reading, it’s still recommended that you wait until you’ve missed your period. At that point, all tests should be accurate.
What are the advantages of using a home pregnancy test?
There are quite a few advantages to using a home pregnancy test, including:
- Pregnancy tests are inexpensive.
- They’re easy to use.
- Home tests provide results quickly.
According to pregnancy kit manufacturers, most at-home pregnancy tests are 98% to 99% accurate when you use them exactly as instructed. Positive results can be trusted, but you can get a false negative result if you take the test too soon.
Blood tests tend to be more expensive and inconvenient. However, blood tests can detect pregnancy sooner and are the only tests to show specific amounts of HCG in your body.
Is there anything you shouldn’t do before a pregnancy test?
Most pregnancy tests don’t ask you to avoid activities or change your lifestyle. The only medication that may interfere with your results is fertility medication containing HCG.
Here are some helpful tips you should follow for the best results:
- Read the instructions carefully before doing anything.
- Wait until you miss your period to take the test.
- Use your first pee or pee from a full bladder. Chugging water before your test in order to pee may affect your results.
Results and Follow-Up
How long does it take to get results of a pregnancy test?
Each home pregnancy test is different. Read the instruction manual carefully. It will tell you how many minutes to wait for your result. In most cases, you can expect to wait three minutes for your result. Keep in mind that if you wait too long to check your result, it may be inaccurate.
Even a faint line on a pregnancy test could mean you’re pregnant.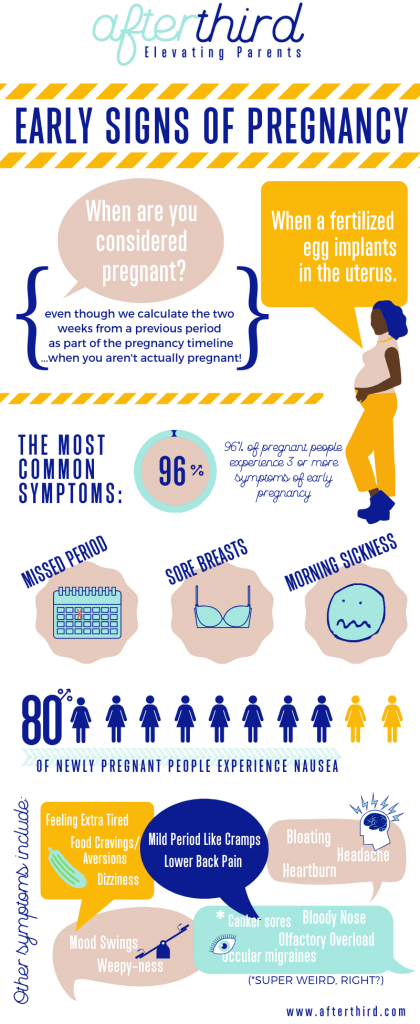 Your test will also have a control window that indicates that you took the test correctly. The instructions with your test will outline all of this. If you have any questions or remain unsure of your result after several tests, please contact your healthcare provider.
Your test will also have a control window that indicates that you took the test correctly. The instructions with your test will outline all of this. If you have any questions or remain unsure of your result after several tests, please contact your healthcare provider.
A faint line is different than an evaporation line. An evaporation line may appear if you wait too long to check your results — meaning your pee is dry. Most tests ask you to read your results before 10 minutes. This ensures the pee doesn’t dry up and you don’t get an evaporation line.
How soon will a pregnancy test be positive?
It depends on which type of test you use. Some at-home pregnancy tests may be able to detect pregnancy before you miss your period. However, if you want the most accurate result, it’s best to wait until you have missed your period.
How accurate are pregnancy tests?
Pregnancy tests are about 99% accurate when you use them correctly.
How common are false results on pregnancy tests?
False results — either a false negative or a false positive — mainly happen due to using the test incorrectly. The main reason for a false-negative is testing too early. You might also get a false-negative if you use a home test incorrectly, such as using too much or too little pee. It’s important to follow the directions on your test kit to make sure you get an accurate result.
The main reason for a false-negative is testing too early. You might also get a false-negative if you use a home test incorrectly, such as using too much or too little pee. It’s important to follow the directions on your test kit to make sure you get an accurate result.
Can a positive test be wrong?
A false positive is rare, but it can happen. This may be the case if you experience a chemical pregnancy or lose the pregnancy shortly after the fertilized egg attaches to your uterine wall.
What type of pregnancy test confirms pregnancy first?
A blood test confirms pregnancy first because it can detect a smaller amount of HCG as compared to a test that uses your pee.
Are there any medications that can change the result of my pregnancy test?
For the most part, medications don’t change your pregnancy test results. Antibiotics, pain relievers and alcohol don’t impact your test results.
However, fertility drugs are one exception. These medications can sometimes cause a false-positive on your pregnancy test. If you’re taking fertility medications, reach out to your healthcare provider about your results to make sure they’re accurate.
If you’re taking fertility medications, reach out to your healthcare provider about your results to make sure they’re accurate.
What should I do after getting a positive pregnancy test?
If you take a pregnancy test at home and it’s positive, there are a few things you should do, including:
- Take your prenatal vitamins. Pick a vitamin with folic acid included in the ingredient list. Start taking these while you’re trying to conceive, if possible. This is because the folic acid can help prevent complications during fetal development.
- Call your healthcare provider for an appointment. This appointment might not happen for several weeks — but it’s a good idea to call your provider and make an appointment.
- Make sure to pursue healthy habits like not drinking alcohol or smoking during pregnancy. You may also want to limit the amount of caffeine you consume each day during pregnancy.
Additional Details
Will an ectopic pregnancy show up on a pregnancy test?
Yes, you’ll still have a positive result on a pregnancy test if you have an ectopic pregnancy.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Pregnancy tests are how a person finds out if they’re pregnant. Most people take a pregnancy test at home using their pee. However, you can also take a pregnancy test at your provider’s office using a blood sample or pee. For the most accurate results, wait until you miss your period to take a home pregnancy test. If you use pregnancy tests correctly, the results are 99% accurate. Contact your healthcare provider if you have questions about the results of your pregnancy test.
Are you pregnant? / "Shape-mama"
Return to list
Yes or no? If your period is still far away, 9 simple, but very “bright” signs will tell you about the presence or absence of your pregnancy.
Many women notice only a textbook symptom - a delay in menstruation, and some do not even suspect about pregnancy until the strong changes in the figure and the first movements of the child. But in fact, even before you are happy with two stripes on the test, the body gives you signals about the emergence of a new life. Listen to yourself!
Listen to yourself!
1. Breast Augmentation
Have you noticed that the lace on the bra is suspiciously folded over? Breast filled and added in size? This is one of the main signs of pregnancy. Breasts can begin to grow early - 1-2 weeks after conception, which is associated with increased secretion of hormones: estrogen and progesterone. There may be a feeling of tension in the chest area or even slight pain. The nipples become extremely sensitive to touch.
What to do: Buy a supportive bra. Discard tight underwear and synthetics that do not allow the skin to “breathe”.
2. Easily fatigued
Do you feel sleepy at work after lunch, yawn all day and can't concentrate? In the first weeks of pregnancy, your body is working twenty-four hours a day, seven days a week, preparing for pregnancy; the heart pumps blood in an enhanced mode, so fatigue and drowsiness are completely normal. Body temperature may rise to 37-37.2 degrees. In combination with nasal congestion (also one of the possible signs of pregnancy), this condition can easily be mistaken for a cold.
What to do: Try to get more rest, sleep at least 8 hours a day, and completely eliminate harmful foods from your diet. If you smoke, it's time to give up cigarettes.
3. Dizziness
Suddenly, in a stuffy room, you feel very dizzy? If you didn’t notice such symptoms before, then your body is signaling you about pregnancy. Increased or decreased, sudden pressure drops leading to fainting and dizziness are also a common thing for the first trimester of pregnancy.
What to do: Buy a blood pressure monitor and take your blood pressure regularly. In the morning, do not abruptly get out of bed, try to do without sudden movements. Monitor your blood sugar levels - drink plenty of fluids and eat every 3-4 hours. If the head begins to spin, you can drink some tea or coffee, with severe weakness, take 10-15 drops of cordiamine.
4. Headaches
Do you have a headache in the morning, regardless of the weather and mood? This is also associated with an increase in progesterone levels. Fortunately, migraines recede with an increase in duration - in the second trimester you will forget about them.
Fortunately, migraines recede with an increase in duration - in the second trimester you will forget about them.
What to do: Drink plenty of fluids and be sure to donate blood to rule out anemia. If your headaches don't stop, ask your doctor to prescribe medication (such as Tylenol).
5. Nausea
Does the wine feel fermented, but does the smell of cooking make you feel sick? In most women, toxicosis begins at about 7 weeks and continues until the 12th week of pregnancy. But sometimes nausea makes itself felt from a very early date - two weeks after conception. The culprit is the same hormone progesterone. There is another version: nausea and a change in eating habits are a defense reaction, because the mother's body protects the child. The proof is the fact that it is usually “dangerous” foods that cause dislike: alcohol, spicy, fatty, fried foods.
What to do: nutritionists recommend eating something else in bed in the morning, and eating little but often all day. Drink vitamin B6, it will help to cope with toxicosis. Not bad relieves nausea acupuncture massage of the wrist.
Drink vitamin B6, it will help to cope with toxicosis. Not bad relieves nausea acupuncture massage of the wrist.
6. Mood Swings
Suddenly burst into tears while watching Sex and the City, and then flew into a rage when you learned that your husband would be late at work. Hormones are to blame for everything - they are now raging in your blood, and your mood changes from tearfulness to aggressiveness.
What to do: be patient, this state will pass quickly. Tell family and friends about the pregnancy. So that they do not worry and do not take offense at you.
7. Hypersensitivity to smells
Do you think that your husband overuses cologne, the neighbors obviously overcooked the fish, and cigarette smoke causes severe nausea? If before you could not boast of a scent like a dog, your new abilities indicate pregnancy.
What to do: Avoid smoking areas, ask your husband and friends not to wear perfume, avoid public transport during rush hours if possible.
8. Frequent urination
You may know that frequent urination is inevitable in the third trimester of pregnancy, but the same symptom is also relevant for the first weeks after conception.
What to do: if there is no burning sensation and pain, it is not terrible. Will soon pass!
9. Pain in the back
Pain in the back, stretching or tingling below, and increased discharge are caused by hormonal changes and fetal growth.
What to do: if the pain does not become unbearable and there is no bleeding, it is not dangerous, but if you have at least one of the signs, be sure to consult a doctor.
Marina Ukolova, Consultant Physician, Independent Laboratory INVITRO
“A blood test for a specific pregnancy hormone, chorionic gonadotropin (beta-hCG), will help confirm or refute suspicions. Of course, it is best to do this analysis on the 2-3rd day of a delay in menstruation, but if because of this you literally do not sleep at night, then an hCG analysis will help you calm down. He can diagnose pregnancy as early as 6-8 days after conception. However, in this case, there is a risk of getting a false negative result: due to the characteristics of your body, the level of hCG may initially be quite low, but pregnancy can still take place.
He can diagnose pregnancy as early as 6-8 days after conception. However, in this case, there is a risk of getting a false negative result: due to the characteristics of your body, the level of hCG may initially be quite low, but pregnancy can still take place.
Signs of pregnancy - Health Clinic 365 Yekaterinburg
Symptoms of pregnancy - what is it?
Pregnancy symptoms or signs of pregnancy are, as a rule, a combination of certain physiological changes in the body that a woman notices already in the early stages of pregnancy.
Sometimes we hear that it is wrong to say “pregnancy symptoms”, because if there are symptoms, then there is a disease, and pregnancy is not a disease. But if we dig into dictionaries, we find that the word “symptom” comes from the Greek sýmptoma, i.e. "sign", "case", "coincidence". Thus, "pregnancy symptoms" is just a synonym for the phrase "signs of pregnancy", which is absolutely correct. The symptoms of early pregnancy or the first symptoms of pregnancy are different from the symptoms that occur in the later stages.
The symptoms of early pregnancy or the first symptoms of pregnancy are different from the symptoms that occur in the later stages.
Knowing the signs of pregnancy allows a woman in the early stages to show increased attention to her health, and, consequently, to the health of the unborn baby, a pregnant woman will be able to determine pregnancy in the earliest possible time and, accordingly, resolve the issue for herself in time about its prolongation (preservation, continuation).
Every woman is remarkably different, so the symptoms a woman may experience during pregnancy may vary. Some women feel pregnant even before the test is positive. Below are nine symptoms of pregnancy.
The first symptom of pregnancy is implantation bleeding.
This is one of the earliest symptoms. On the sixth - twelfth day after conception, the introduction (attachment, implantation) of the embryo into the wall of the uterus occurs. Some women notice a small amount of red discharge (spots), which may be pink or reddish brown. If you have pain along with spotting or bleeding, see your doctor immediately as this could be a sign of an ectopic pregnancy.
Some women notice a small amount of red discharge (spots), which may be pink or reddish brown. If you have pain along with spotting or bleeding, see your doctor immediately as this could be a sign of an ectopic pregnancy.
The second symptom of pregnancy, also the main one, is the delay in menstruation
This symptom must be present during a normal pregnancy. You should be aware that sometimes bleeding occurs during pregnancy. The main thing is not to confuse them with menstruation, especially on those days when you should have started your period, that is, at 4, 8, 12 weeks of pregnancy. Bleeding during pregnancy is a sign of a threatened abortion. Therefore, if you notice this symptom in yourself, then immediately contact a specialized medical institution. With timely treatment, there is every chance to save the desired pregnancy. Menstruation does not occur throughout pregnancy and, as a rule, during breastfeeding.
The third symptom of pregnancy is increased basal body temperature.
Basal body temperature rises above 37 degrees during pregnancy. If you notice some symptoms of pregnancy in yourself or even confirmed it with a doctor and at the same time observe a decrease in basal temperature, consult a doctor. A decrease in basal temperature may be due to the threat of miscarriage. For the result to be reliable, measure the temperature correctly. It should be measured in the rectum, immediately after waking up, in the morning.
The fourth symptom of pregnancy is profuse discharge.
In this case, we do not mean bleeding. Women know that normal vaginal discharge is odorless and almost colorless. Their number increases during ovulation and, as you now know, during pregnancy. On 9/10, you are pregnant if you have a missed period, heavy discharge, and an elevated basal body temperature.
The fifth symptom of pregnancy - swelling and (or) increased sensitivity of the mammary glands.
Many women say that the sensitivity of the mammary glands changes. This symptom may appear 1 to 2 weeks after conception. Swelling and increased sensitivity of the breast may appear not only as a result of pregnancy. Other causes are: premenstrual syndrome (PMS), birth control pills, or hormonal imbalances.
The sixth symptom of pregnancy is toxicosis.
Nausea or vomiting in the morning usually does not occur early in pregnancy, but some women experience nausea as early as the third week. Many women believe that toxicosis is morning sickness and vomiting. But it is not so. In addition to nausea and vomiting, signs of toxicosis include a heightened sense of smell and aversion to certain foods. Many pregnant women cannot tolerate certain smells during early pregnancy. A heightened sense of smell is a side effect of a rapidly rising level of estrogen in your blood. Aversion to certain foods is even more common than cravings for certain foods during pregnancy. You may suddenly find that certain foods, even your favorites, disgust you.
You may suddenly find that certain foods, even your favorites, disgust you.
The feeling of fatigue, which will be discussed below, is also referred to by some obstetricians as manifestations of toxicosis. Toxicosis, most often, goes away on its own by 12-14 weeks of pregnancy.
The seventh symptom of pregnancy is feeling tired.
Fatigue can be as pronounced as if you had run a marathon. Fatigue is caused by increased levels of progesterone and other hormones necessary for the development of the child.
The eighth symptom of pregnancy is frequent urination and constipation.
You may suddenly become aware that you are going to the bathroom with alarming frequency.
The ninth symptom of pregnancy is headache and migraine.
Usually headaches are caused by hormonal changes in the body. If headaches occur, you should not self-medicate, since most known painkillers are contraindicated during pregnancy, especially in the early stages.