How much breastmilk by age
Baby Feeding Chart - How Many Ounces By Age
As newborns, babies seem to eat, sleep, and poop all day – every day. But, as your baby gets older, you may be wondering how much your baby should be eating, how often, and how many ounces by age. Keep in mind that milk should be your baby’s primary form of nutrition for the first year. Even after you’ve begun to offer solid foods, your baby’s milk intake should not decrease much, if at all. Also, babies are very good at self-moderation, so it is usually unnecessary to limit your baby’s milk intake for fear of him or her becoming overweight. Your baby’s growth and development depend on a large consumption of fat and calories.
These baby feeding charts for breastfeeding babies, formula-fed babies, and solids will help guide you to know if your baby is eating enough and how to help your baby sleep through the night sooner rather than later. You may want to bookmark this page for future reference or pin it on Pinterest.
Quick Links:
Breastmilk Amounts by Age
Formula Amounts by Age
Solid Food Amounts by Age
Breastmilk Feedings and Amounts by Age
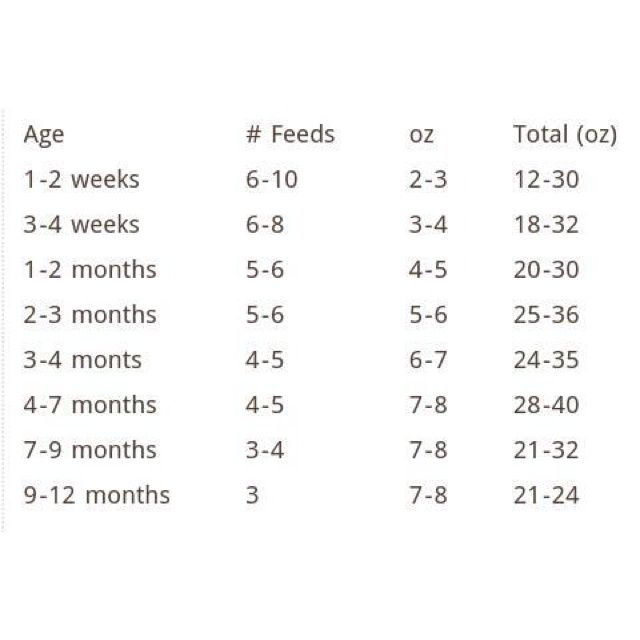
All breastfed babies need between 20-35 ounces of breast milk per day, on average. In younger newborns and up to 2-3 months old, your baby should breastfeed on-demand, which usually means every 2-3 hours.
If you are pumping, breastmilk bottles vary in size from 3 to 6 ounces, usually, with 4 ounces being the average size once a baby is at least 3-4 months old. Keep in mind that some babies simply have larger appetites than others. The most important aspect is that your baby’s weight gain stays on his or her growth curve. Do not withhold milk from your baby in fear he or she will become overweight. Babies are very good at self-moderation and should be fed when hungry.
Keep in mind that the number of times your baby breastfeeds in a 24-hour period will depend on the combination of:
a) how much milk your baby can hold in their stomach (i. e. stomach capacity).
e. stomach capacity).
b) how much milk you can store in your breasts (which has nothing to do with breast size).
c) your baby’s personality as well as if they have any digestion issues such as reflux.
We find babies who have reflux tend to eat more frequent, smaller meals. Also, some baby’s personalities are to overfill themselves while others eat until content and stop. My two boys were different than one another. While my first son would only ever eat 4-ounce bottles when we weren’t breastfeeding, his brother would take up to 5 to 5 1/2 ounce bottles at times. They were just different and even as my first son got older, he would simply NOT overeat or overfill his stomach and is still this way to this day.
Here is a handy baby feeding chart with breastmilk amounts by age, though keep in mind that many breastfeeding mothers feed their babies on-demand throughout their breastfeeding journey. This is just a rough guide to consider, especially if you feel like you are having to feed your baby excessively given his or her age.
If you ever have any concerns about your baby and your baby’s feeding habits, please be sure to seek out a healthcare provider and/or lactation consultant.
| Age | # of feedings per day / 24 hours | Feeding Frequency | Average Bottle Sizes (if applicable) | Night Feedings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-4 weeks | on-demand | on-demand* | ~2-3 ounces / 60-90 ml | on-demand |
| 5-8 weeks | on-demand | every 2-3 hours** | ~2-4 ounces / 60-120 ml | 3-4 |
| 9-12 weeks/3 months | ~8-10 | every 2-3 hours | 3-4 ounces / 90-120 ml | 2-3 |
| 13-16 weeks/4 months | ~6-10 | every 2-3 hours | 3-4 ounces / 90-120 ml | 2-3 |
| 5 months | ~6-10 | every 2-3 hours | 3-4 ounces / 90-120 ml | 2, maybe 3 |
| 6 months | ~6-9 | every 3 hours | 4-5 ounces / 120-150 ml | 1-2 |
| 7 months | ~5-8 | every 3-4 hours | 4-6 ounces / 120-180 ml | 1-2 |
| 8 months | ~5-8 | every 3-4 hours | 4-6 ounces / 120-180 ml | 1, maybe 2 |
| 9 months | ~5-8 | every 3-4 hours | 4-6 ounces / 120-180 ml | 1 |
| 10 months | ~4-6 | every 3-4 hours | 4-6 ounces / 120-180 ml | 0-1 |
| 11 months | ~4-6 | every 3-4 hours | 4-6 ounces / 120-180 ml | 0 |
| 12 months | ~4-6 | every 3-4 hours | 4-6 ounces / 120-180 ml | 0 |
* If your baby goes longer than 4 hours without eating, be sure to wake him or her to feed them.
** Many newborns cluster feed in the evenings, which means they may nurse every hour for several hours or practically remain on the breast for several hours. Some say they are “tanking up” for the night.
You may also be interested in:
- Baby Night Feedings By Age Chart
- Baby Sleep and Breastfeeding Series
- Breastfeeding and Sleep Training – Can They Go Together?
Formula Feeding Amounts by Age
Formula fed infants typically need 2 1/2 ounces or 74 ml of formula for each pound of weight, on average. Some babies have larger appetites than others, though. I have worked with a lot of families, personally, and some babies take small bottles and consume around 24 oz a day total while others consume over 30 oz. The most important thing to remember is that your baby should stay on his or her own growth curve.
In the newborn days, it’s important to feed your baby on-demand whenever he or she shows signs of hunger. As your baby grows older, you can consider putting your baby on a schedule.
As your baby grows older, you can consider putting your baby on a schedule.
While some parents and babies thrive on schedules, some people prefer to allow the daily routine to be flexible. Keep in mind that the more your baby eats during the day, the sooner your baby will sleep through the night.
Here is a formula-feeding chart to tell you the average frequency and bottle sizes of formula by age, but keep in mind that some babies eat a variable amount at different times of the day. You should use this chart simply as a guide while also adapting your daily routine to fit your unique baby.
If you ever have any concerns about your baby and your baby’s feeding habits, please be sure to seek out a healthcare provider and/or lactation consultant.
| Age | # of feedings per day / 24 hours | Feeding Frequency | Average Bottle Size | Night Feedings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-4 weeks | on-demand | on-demand* | ~2-4 ounces / 60-120 ml | on-demand |
| 5-8 weeks | 6-7 | every 3 hours | ~4 ounces / 120 ml | 2-3 |
| 9-12 weeks/3 months | 5 | every 3 hours | 4-6 ounces / 120-180 ml | 2, maybe 3 |
| 13-16 weeks/4 months | 5 | every 3-4 hours** | 4-6 ounces / 120-180 ml | 1-2 |
| 5 months | 4-5 | every 3-4 hours | 6-7 ounces / 180-210 ml | 1-2 |
| 6 months | 4-5 | every 3-4 hours | 6-8 ounces / 180-240 ml | 0-1 |
| 7 months | 4-5 | every 3-4 hours | 6-8 ounces / 180-240 ml | 0*** |
| 8 months | 4-5 | every 3-4 hours | 6-8 ounces / 180-240 ml | 0 |
| 9 months | 4-5 | every 3-4 hours | 6-8 ounces / 180-240 ml | 0 |
| 10 months | 3-5 | every 3-4 hours | 6-8 ounces / 180-240 ml | 0 |
| 11 months | 2-4 | every 3-4 hours | 6-8 ounces / 180-240 ml | 0 |
| 12 months | 2-3 | every 3-4 hours | 6-8 ounces / 180-240 ml | 0 |
* If your baby goes longer than 4 hours without eating, be sure to wake him or her to feed them.
** Not all babies get to 4 hours between milk feedings by this age or ever. Some babies will always eat every 3 hours until 9-10+ months old.
*** Some formula-fed babies still eat at night even past 6 months old, especially if they have reflux.
You may also be interested in:
- Baby Night Feedings By Age Chart
- Baby Feeding Schedule: Rigid, Flexible, or On-Demand?
- How to Put Your Baby on a Schedule
Solid Foods by Age
As you start solids, your baby’s milk intake should not decrease much, if at all, until 10+ months old when he or she is eating 3 solid meals per day plus one snack. For the first year, solid food is a lot about practice and introducing a variety of flavors and textures. Keep in mind that until your baby is consuming significant amounts of solid food, starting solids won’t necessarily help your baby sleep. In fact, so many sleep problems have nothing to do with hunger that starting solids doesn’t change sleep whatsoever.
Here is a baby feeding chart for solid foods. Keep in mind that if you are practicing baby led weaning, whether by choice or because your baby doesn’t like pureed foods, your baby will likely consume a lot less solid food than other babies his or her age. That is just fine as milk should still be your baby’s primary source of nutrition.
| Age | Grains (per day) | Fruit (per day) | Vegetables (per day) | Meat and Dairy (per day) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Birth-5 months | None | None | None | None |
| 6 months (1 solid feeding per day) | 1-2 tablespoons dry infant cereal, mixed with breastmilk or formula | 1-2 tablespoons pureed fruit | 1-2 tablespoons pureed vegetables | None |
| 7-8 months (2 solid feedings per day) | 1-6 tablespoons dry infant cereal, mixed with breastmilk or formula | 1-6 tablespoons pureed/mashed fruit | 1-6 tablespoons pureed/mashed vegetables | Meat: 1-2 tablespoons pureed/mashed protein (offer at 8 months) Dairy: 1/4-1/2 cup yogurt or cottage cheese; 1 oz. 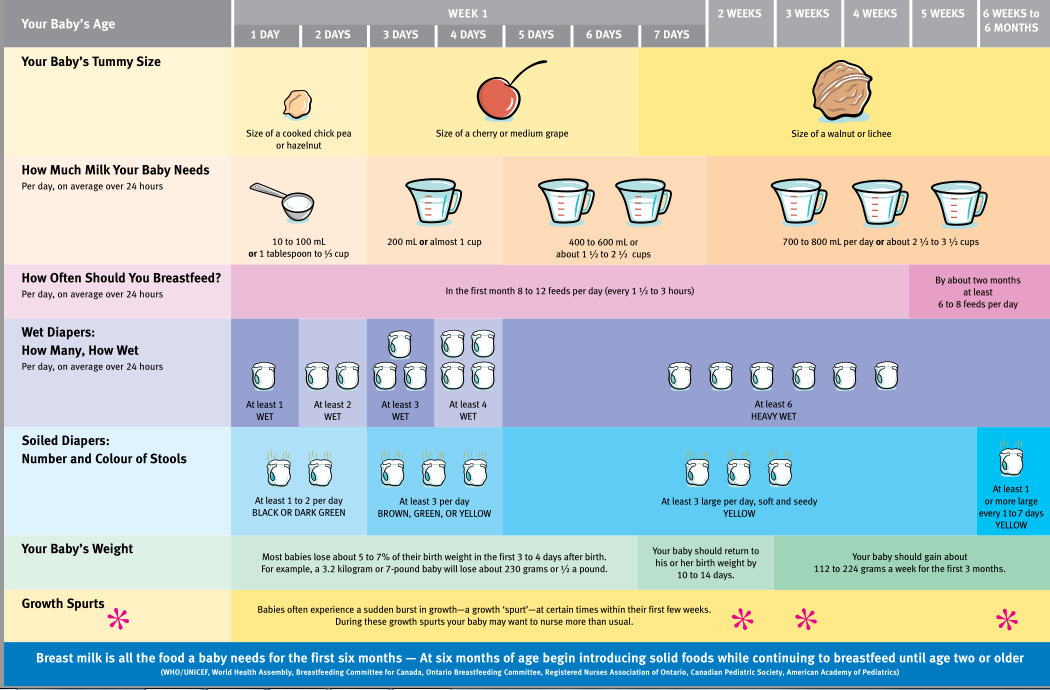 shredded cheese shredded cheese |
| 9-10 months (3 solid feedings per day) | 2-4 tablespoons dry infant cereal, mixed with breastmilk or formula. 1-2 servings other grains* | 4-8 tablespoons mashed/chopped fruit | 4-12 tablespoons mashed/chopped vegetables | Meat: 2-6 tablespoons mashed/chopped protein Dairy: Same as 7-8 month recommendations. |
| 11-12 months (3 solid feedings per day) | Same as above, except increase “other grains” to 2 servings | 6-8 tablespoons mashed/chopped fruit, or 1/2 cup diced | 6-12 tablespoons mashed/chopped vegetables, or 1/2 – 3/4 cup diced | Meat: 2-6 tablespoons mashed/chopped protein, or 1/4 cup diced Dairy: Same as 7-8 month recommendations. |
* 1 serving of “other grains” = 1/2 slice of bread, 2 crackers, 1/2 cup Cheerios, or 1/2 cup whole wheat pasta
You might also be interested in:
- When to Start Solids
- How to Feed Your Baby Solids
- Your Baby’s Start On Solid Foods: A Comprehensive Guide
Share your experience with feeding your baby!
The Baby Sleep Site® is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program and other product affiliate programs. If you click on a product link and make a purchase, The Baby Sleep Site® may (but not always) receive a small commission from the company selling the product, but will not affect your purchase price. We only recommend products that we believe are quality products and are good for our readers.
If you click on a product link and make a purchase, The Baby Sleep Site® may (but not always) receive a small commission from the company selling the product, but will not affect your purchase price. We only recommend products that we believe are quality products and are good for our readers.
If you are tired of wading through stacks of baby sleep books that just aren't working, if you are beyond exhausted and just can't solve your child's sleep problems on your own...then personalized sleep consulting is for you. We have been around since 2008 and invite you to tap into our MANY years of experience. Our team of expert consultants will create a Personalized Sleep Plan® just for your family and then support you through every step of implementing your plan. We encourage you to consider our personalized, one-on-one baby and toddler sleep consultation packages if you want to see real, meaningful results now. Your consultation package also includes ample follow-up help, designed to help you troubleshoot problems and tweak your plan as needed.
Your consultation package also includes ample follow-up help, designed to help you troubleshoot problems and tweak your plan as needed.
Learn More About Services
For those persistent nighttime struggles, check out The 3 Step System to Help Your Baby Sleep. Using the same unique approach and practical tools for success, this e-book helps you and your baby sleep through the night.
Learn More About The 3-Step System
If you’re looking for ways to get your baby or toddler into a healthy sleeping routine during the day, explore Mastering Naps and Schedules, a comprehensive guide to napping routines, nap transitions, and all the other important “how-tos” of good baby sleep. With over 45 sample sleep schedules and worksheets, Mastering Naps and Schedules is a hands-on tool ideal for any parenting style.
Learn More About Mastering Naps
For those persistent toddler sleep struggles, check out The 5 Step System to Help Your Toddler Sleep. Using the same unique approach and practical tools for success, this e-book helps you and your toddler sleep through the night and enjoy a better daytime schedule.
Using the same unique approach and practical tools for success, this e-book helps you and your toddler sleep through the night and enjoy a better daytime schedule.
Learn More About The 5-Step System
Join our VIP Members Area packed with exclusive content and resources: e-Books, assessments, detailed case studies, expert advice, and more. As a VIP member, you'll also enjoy a weekly chat with an expert sleep consultant.
Learn More About VIP Membership
How much expressed milk will my baby need? • KellyMom.com
By Kelly Bonyata, BS, IBCLC
- How much milk do babies need?
- What if baby is eating solid foods?
- Is baby drinking too much or too little expressed milk?
- Other ways of estimating milk intake
- References
Image credit: Jerry Bunkers on flickr
How much milk do babies need?
Many mothers wonder how much expressed breastmilk they need to have available if they are away from baby.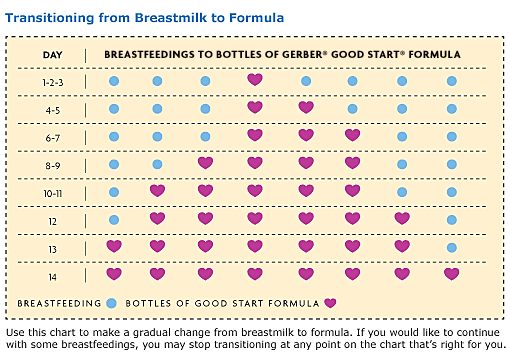
.
In exclusively breastfed babies, milk intake increases quickly during the first few weeks of life, then stays about the same between one and six months (though it likely increases short term during growth spurts). Current breastfeeding research does not indicate that breastmilk intake changes with baby’s age or weight between one and six months. After six months, breastmilk intake will continue at this same level until — sometime after six months, depending in baby’s intake from other foods — baby’s milk intake begins to decrease gradually (see below).
The research tells us that exclusively breastfed babies take in an average of 25 oz (750 mL) per day between the ages of 1 month and 6 months. Different babies take in different amounts of milk; a typical range of milk intakes is 19-30 oz per day (570-900 mL per day).
We can use this information to estimate the average amount of milk baby will need at a feeding:
- Estimate the number of times that baby nurses per day (24 hours).

- Then divide 25 oz by the number of nursings.
- This gives you a “ballpark” figure for the amount of expressed milk your exclusively breastfed baby will need at one feeding.
Example: If baby usually nurses around 8 times per day, you can guess that baby might need around 3 ounces per feeding when mom is away. (25/8=3.1).
What if baby is eating solid foods?
Sometime between six months and a year (as solids are introduced and slowly increased) baby’s milk intake may begin to decrease, but breastmilk should provide the majority of baby’s nutrition through the first year. Because of the great variability in the amount of solids that babies take during the second six months, the amount of milk will vary, too. One study found average breastmilk intake to be 30 oz per day (875 ml/day; 93% of total intake) at 7 months and 19 oz (550 ml/day; 50% of total energy intake) at 11-16 months.
Several studies have measured breastmilk intake for babies between 12 and 24 months and found typical amounts to be 14-19 oz per day (400-550 mL per day).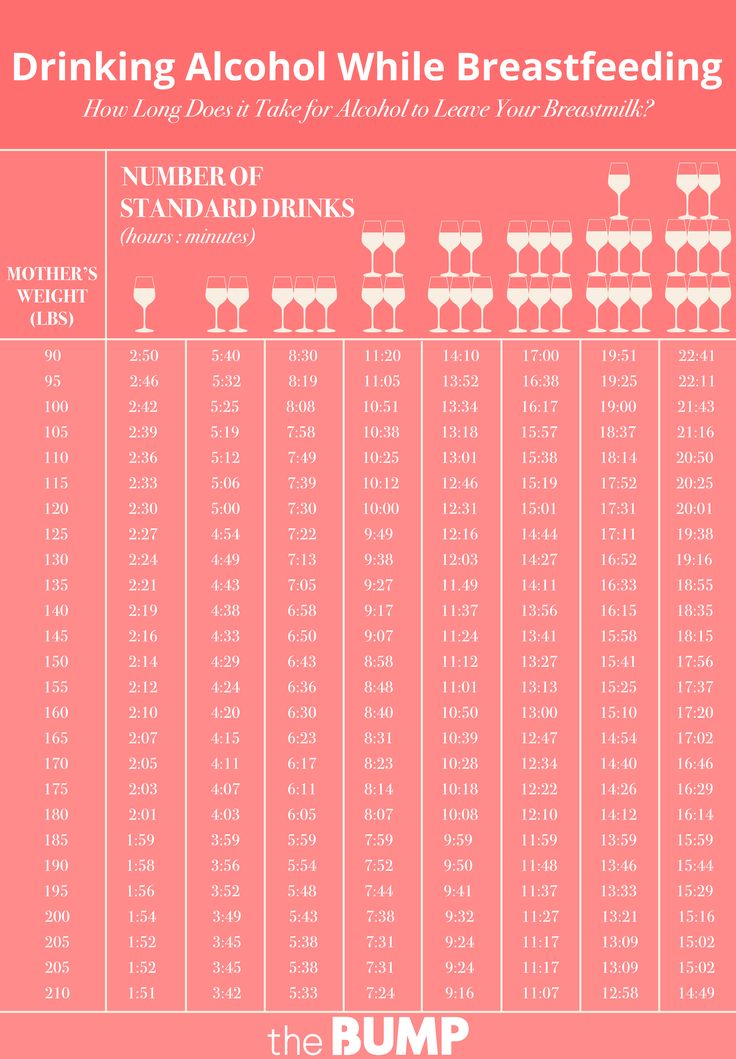 Studies looking at breastmilk intake between 24 and 36 months have found typical amounts to be 10-12 oz per day (300-360 mL per day).
Studies looking at breastmilk intake between 24 and 36 months have found typical amounts to be 10-12 oz per day (300-360 mL per day).
Is baby drinking too much or too little expressed milk?
Keep in mind that the amount of milk that baby takes at a particular feeding will vary, just as the amount of food and drink that an adult takes throughout the day will vary. Baby will probably not drink the same amount of milk at each feeding. Watch baby’s cues instead of simply encouraging baby to finish the bottle.
If your baby is taking substantially more than the average amounts, consider the possibility that baby is being given too much milk while you are away. Things that can contribute to overfeeding include:
- Fast flow bottles. Always use the lowest flow bottle nipple that baby will tolerate. Even with a slower flowing nipple, it is important to pace the bottle feed to allow baby to better control his intake.
- Using bottle feeding as the primary way to comfort baby.
 Some well-meaning caregivers feed baby the bottle every time he makes a sound. Use the calculator above to estimate the amount of milk that baby needs, and start with that amount. If baby still seems to be hungry, have your caregiver first check to see whether baby will settle with walking, rocking, holding, etc. before offering another ounce or two.
Some well-meaning caregivers feed baby the bottle every time he makes a sound. Use the calculator above to estimate the amount of milk that baby needs, and start with that amount. If baby still seems to be hungry, have your caregiver first check to see whether baby will settle with walking, rocking, holding, etc. before offering another ounce or two. - Baby’s need to suck. Babies have a very strong need to suck, and the need may be greater while mom is away (sucking is comforting to baby). A baby can control the flow of milk at the breast and will get minimal milk when he mainly needs to suck. When drinking from a bottle, baby gets a larger constant flow of milk as long as he is sucking. If baby is taking large amounts of expressed milk while you are away, you might consider encouraging baby to suck fingers or thumb, or consider using a pacifier for the times when mom is not available, to give baby something besides the bottle to satisfy his sucking needs.
- If, after trying these suggestions, you’re still having a hard time pumping enough milk, see I’m not pumping enough milk.
 What can I do?
What can I do?
If baby is taking significantly less expressed milk than the average, it could be that baby is reverse-cycling, where baby takes just enough milk to “take the edge off” his hunger, then waits for mom to return to get the bulk of his calories. Baby will typically nurse more often and/or longer than usual once mom returns. Some mothers encourage reverse cycling so they won’t need to pump as much milk. Reverse cycling is common for breastfed babies, especially those just starting out with the bottle.
If your baby is reverse cycling, here are a few tips:
- Be patient. Try not to stress about it. Consider it a compliment – baby prefers you!
- Use small amounts of expressed milk per bottle so there is less waste.
- If you’re worrying that baby can’t go that long without more milk, keep in mind that some babies sleep through the night for 8 hours or so without mom needing to worry that baby is not eating during that time period.
 Keep an eye on wet diapers and weight gain to assure yourself that baby is getting enough milk.
Keep an eye on wet diapers and weight gain to assure yourself that baby is getting enough milk. - Ensure that baby has ample chance to nurse when you’re together.
Other ways of estimating milk intake
There are various ways of estimating the amount of milk intake related to the weight of the baby and the age of the baby, based upon formula intake – research has shown that after the early weeks these methods overestimate the amount of milk that baby actually needs. These are the estimates that we used for breastfed babies for years, with the caveat that most breastfed babies don’t take as much expressed milk as estimated by these methods. Current research tells us that breastmilk intake is quite constant after the first month and does not appreciably increase with age or weight, so the current findings are validating what moms and lactation counselors have observed all along.
More:
- Breast Versus Bottle: How much milk should baby take? By Nancy Mohrbacher, IBCLC, FILCA
- Supplementation Guidelines from LowMilkSupply.
 org
org
References
Onyango, Adelheid W., Receveur, Olivier and Esrey, Steven A. The contribution of breast milk to toddler diets in western Kenya. Bull World Health Organ, 2002, vol.80 no.4. ISSN 0042-9686.
Salazar G, Vio F, Garcia C, Aguirre E, Coward WA. Energy requirements in Chilean infants. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2000 Sep;83(2):F120-3.
Kent JC, Mitoulas L, Cox DB, Owens RA, Hartmann PE. Breast volume and milk production during extended lactation in women. Exp Physiol. 1999 Mar;84(2):435-47.
Persson V, Greiner T, Islam S, and Gebre-Medhin M. The Helen Keller international food-frequency method underestimates vitamin A intake where sustained breastfeeding is common. Food and Nutrition Bulletin, vol.19 no.4. Tokyo, Japan: United Nations University Press, 1998.
Cox DB, Owens RA, Hartmann PE. Blood and milk prolactin and the rate of milk synthesis in women. Exp Physiol. 1996 Nov;81(6):1007-20.
Dewey KG, Heinig MJ, Nommsen LA, Lonnerdal B. Maternal versus infant factors related to breast milk intake and residual milk volume: the DARLING study. Pediatrics. 1991 Jun;87(6):829-37.
Maternal versus infant factors related to breast milk intake and residual milk volume: the DARLING study. Pediatrics. 1991 Jun;87(6):829-37.
Neville MC, et al. Studies in human lactation: milk volumes in lactating women during the onset of lactation and full lactation. Am J Clin Nutr. 1988 Dec;48(6):1375-86.
Dewey KG, Finley DA, Lonnerdal B. Breast milk volume and composition during late lactation (7-20 months). J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1984 Nov;3(5):713-20.
Butte NF, Garza C, Smith EO, Nichols BL. Human milk intake and growth in exclusively breast-fed infants. J Pediatr. 1984 Feb;104(2):187-95.
Dewey KG, Lonnerdal B. Milk and nutrient intake of breast-fed infants from 1 to 6 months: relation to growth and fatness. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1983;2(3):497-506.
Brown K, Black R, Robertson A, Akhtar N, Ahmed G, Becker S. Clinical and field studies of human lactation: methodological considerations. Am J Clin Nutr 1982;35:745-56.
Jelliffe D, Jelliffe E. The volume and composition of human milk in poorly nourished communities: a review. Am J Clin Nutr 1978;31:492-515.
The volume and composition of human milk in poorly nourished communities: a review. Am J Clin Nutr 1978;31:492-515.
| Summary of Research Data | ||||
| Baby’s Age | Average Milk Intake per 24 hours | Reference | ||
| g | ml | oz | ||
| 5 days | 498 +/- 129 g | 483 ml | 16 oz | Neville 1988 |
| 1 mo | 728 g | 706 ml | 24 oz | Salazar 2000 |
| 1 mo | — | 673 ml | 23 oz | Dewey 1983 |
| 1 mo | 708 +/- 54.7 g | 687 ml | 23 oz | Cox 1996 |
| 1-6 mo | 453.6+/-201 g per breast | 440 ml x2 = 880 ml | 30 oz | Kent 1999 |
| 3 mo | 818 g | 793 ml | 27 oz | Dewey 1991 |
| 3-5 mo | 753 +/- 89 g | 730 ml | 25 oz | Neville 1988 |
| 6 mo | — | 896 ml | 30 oz | Dewey 1983 |
| 6 mo | 742 +/- 79. 4 g 4 g | 720 ml | 24 oz | Cox 1996 |
| 7 mo | — | 875 ml (93% of total energy intake) | 30 oz | Dewey 1984 |
| 11-16 mo | — | 550 ml (50% of total energy intake) | 19 oz | Dewey 1984 |
| 11-16 mo | 502 +/- 34 g | 487 ml (32% of total energy intake) | 16.5 oz | Onyango 2002 |
| 12-17 mo | 563 g | 546 ml | 18 oz | Brown 1982 |
| 12-23 mo | 548 g | 532 ml | 18 oz | Persson 1998 |
| 15 mo | 208.0+/-56.7 g per breast | 202 ml x2 = 404 ml | 14 oz | Kent 1999 |
| 18-23 mo | 501 g | 486 ml | 16 oz | Brown 1982 |
| >24 mo | 368 g | 357 ml | 12 oz | Brown 1982 |
| 24-36 mo | 312 g | 303 ml | 10 oz | Persson 1998 |
Specific Gravity of Mature Human Milk = 1. 031, so Density of Mature Human Milk ~ 1.031 g/ml;1 oz = 29.6 ml;Numbers in gray were derived using the above conversion factors. 031, so Density of Mature Human Milk ~ 1.031 g/ml;1 oz = 29.6 ml;Numbers in gray were derived using the above conversion factors. | ||||
how much milk a child needs for 1 feeding, the rate of formula and breast milk
The birth of a baby is a very joyful event. However, along with the joy of parents, many more questions arise. After all, it is so important that the baby grows up healthy and actively develops. One of the first such questions is usually: "How much does a newborn eat per feeding?" It would seem that feeding is such a natural process that it should not cause difficulties. However, most mothers are concerned that the baby does not have enough milk or, on the contrary, he overeats. How to strike a balance? Let's talk about it in this article.
Content: Hide
- Features of breastfeeding
- On colostrum
- Consumption norms
- How to calculate the volume of feeding
- What is important to take into account artificial feeding
Precipility.
 As a rule, the most difficult in the matter of feeding is the first week after childbirth. At this time, mother and child are only learning to understand each other. But there is no doubt that breast milk is the best food for a baby. This product is perfect by nature and has everything you need at every stage.
As a rule, the most difficult in the matter of feeding is the first week after childbirth. At this time, mother and child are only learning to understand each other. But there is no doubt that breast milk is the best food for a baby. This product is perfect by nature and has everything you need at every stage. Breastfeeding is good for both the baby and the mother:
- it helps the baby to get the substances necessary for growth, development and immunity and just satisfy hunger;
- promotes active contraction of the woman's uterus (under the influence of sucking movements) and a faster recovery process after childbirth.
About colostrum
Newborns eat little, their sucking reflex is just developing and is beginning to be put into practice. In addition, a woman's milk is not produced immediately. In the mammary glands at the end of pregnancy and in the first hours after childbirth, colostrum is formed. This is not exactly milk, it even outwardly differs from mature milk, and in its chemical composition it is similar to blood. This is a very valuable product. It is high in fat and contains immunoglobulins and antitoxins, which strengthen the immune system and protect the baby's body from infections. After a few days, colostrum is replaced by transitional milk. It is lighter, but also quite oily.
This is a very valuable product. It is high in fat and contains immunoglobulins and antitoxins, which strengthen the immune system and protect the baby's body from infections. After a few days, colostrum is replaced by transitional milk. It is lighter, but also quite oily.
Read also: Complementary foods for artificial feeding
Consumption rates
This is important!
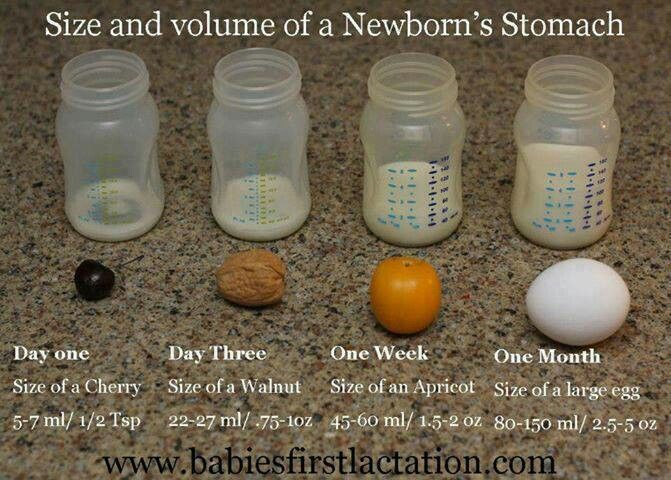
A mother should not worry that her baby was hungry, even if she applied it 10 times to the breast, but it seems that he did not eat almost a drop. The size of the stomach of a newborn is very small, so only about 10 ml is eaten per feeding. Thus, for the whole day the baby can drink up to 100 ml.
On average, milk arrives 3-4 days after birth and its quantity gradually increases. The stomach of the baby also grows. This means that the amount of milk consumed also increases. So, for the first day, a newborn can drink 10 ml per feeding, for the second day - 20 ml, and for the third - 30 ml. But remember that each organism is individual and there are no strict limits here. However, if by the 4-5th day of life the child's body weight does not increase, but only decreases (by more than 8%), then this requires the attention of a specialist.
But remember that each organism is individual and there are no strict limits here. However, if by the 4-5th day of life the child's body weight does not increase, but only decreases (by more than 8%), then this requires the attention of a specialist.
There is a folk way to determine the rate of consumption of breast milk. You need to multiply the number of days that have passed since the day of birth by 10. But this method is inaccurate and has no scientific confirmation.
So how much should a newborn eat per feeding? The table shows the daily and one-time volume of milk by months for children under 1 year old.
| Child's age | Molo volume for one feeding (ml) | Milk rate per day (ml) |
| 3-4 days | 20-60 | 9000 200-300 | 666
| 1 week | 50–80 | 400 |
| 2 weeks | 60–90 | 20 % of body weight |
| 9000 1 month 1 month 1 month 1 months0002 100–110 | 600 | |
| month | 120–1503 | 800 |
9000 3 months | 9000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 15000 150000061 | 1/6 body weight | |
| 4 months | 180–210 | |
| 9000 month | 210–24000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 | 1/7 body weight |
| 7–12 months | 210–240 | 1/8–1/9 body weight |
do not forget that children with children located breastfeeding, complementary foods are introduced at about 6 months. This means that the amount of milk consumed is reduced, giving way to more adult food.
This means that the amount of milk consumed is reduced, giving way to more adult food.
How to calculate the amount eaten
In terms of measuring the amount eaten, formula feeding seems to be just perfect. Here is a bottle with a scale, here is water, here is a measuring spoon. However, in terms of its benefits, formula milk will never be compared with breast milk. And besides, making measurements is not as difficult as it seems at first glance. Babies just need to be weighed before and after feeding on a baby scale. To ensure the accuracy of the result, you need to weigh several times a day. If nothing threatens the health of the baby, he does not look thin and pale, develops according to age, and the mother has enough milk, then monthly weighing in the clinic is usually enough.
Feeding schedule
For breastfed babies, there is a rule - to put the baby to the breast on demand. Previously, it was believed that it was necessary to maintain an interval of 3 hours, but now pediatricians agree that the breaks between feedings can be 1. 5–2 hours. This does not mean at all that the baby will overeat.
5–2 hours. This does not mean at all that the baby will overeat.
Video: Does a baby get enough food in the first months of life?
Author: pediatrician, Ph.D. Komarovsky E.O.
The duration of one feeding is usually 15-30 minutes. Although there are deviations from the norm. For example, a woman has a lot of milk, and the child is full in 5-10 minutes. Or, on the contrary, there is not enough milk, and the baby can suck out the remains for a long time. Some babies just enjoy suckling and use their mother's breast as a pacifier.
What is important to consider
At first, mother and baby are just getting used to the ongoing changes, so the feeding regimen may not be ideal. However, you should adhere to the following rules.
- In the first couple of weeks, a woman needs a lot of dedication, because the interests of the child in the matter of satisfying hunger come to the fore.
 You can’t refuse food to a baby, even if it costs a sleepless night.
You can’t refuse food to a baby, even if it costs a sleepless night. - If there is any doubt that the baby is undernourished or overeating, it is best to start monitoring the frequency of feedings. So, you need to mark the time at which the baby was really hungry, mark the intervals between feedings. This information may also be useful at the appointment with the pediatrician.
- It is impossible to establish a clear feeding regime, as with artificial feeding, especially in the first weeks after birth. Maintaining intervals of more than 2–3 hours during the day and 3–4 hours at night is highly discouraged.
- Do not try to force feed your baby. He is still too young to realize the need for food, and is guided solely by his feeling of hunger. If the baby persistently refuses the breast, you need to try to offer him to eat a little later. If the interval is too large, it is better to contact a specialist for advice.
- It is important that your baby latch on correctly.
 His mouth should capture not only the nipple, but also the areola. Thus, the milk will properly enter the mouth, and the woman will reduce the risk of cracked nipples.
His mouth should capture not only the nipple, but also the areola. Thus, the milk will properly enter the mouth, and the woman will reduce the risk of cracked nipples. - Soothers and bottles are not recommended for breastfed babies. Such products can reduce the intensity of sucking movements.
- It is best to give your baby only one breast at a time. In the mammary gland, fore milk is formed, with which the baby quenches his thirst, and hind milk, with which he "eats up", since it is more nutritious in composition.
- Hold the baby upright for about 10 minutes after each feed. This helps to free the tummy from air and excess milk.
As a rule, with a normal feeding regimen and a sufficient amount of milk from the mother, by the month the weight of the child increases by 500–600 g. Now consider the situation when the mother does not have the opportunity to breastfeed the baby. In this case, it is necessary to choose a quality milk formula that will cover the nutritional needs. The pediatrician should help in this matter. The doctor will always take into account the peculiarities of the child's health and will be able to advise a regular or medicinal product. Do not forget that when breastfeeding, the baby makes more effort. He drinks milk gradually and feels full. When feeding with a formula, a strict dosage is needed, since usually saturation does not come immediately, and the baby may require a supplement that he does not really need (the feeling of hunger should disappear after a few minutes).
The pediatrician should help in this matter. The doctor will always take into account the peculiarities of the child's health and will be able to advise a regular or medicinal product. Do not forget that when breastfeeding, the baby makes more effort. He drinks milk gradually and feels full. When feeding with a formula, a strict dosage is needed, since usually saturation does not come immediately, and the baby may require a supplement that he does not really need (the feeling of hunger should disappear after a few minutes).
Consumption rates
Almost all known mixtures require 8 or 7 meals a day with an interval of 3 hours. Night feedings are also included. When the baby grows up a little, it will be possible to skip them and sleep 5-6 hours until morning. With regard to formula milk, the principle of feeding on demand is not suitable. Therefore, it is necessary to observe both the dosage indicated by the manufacturer and the regimen.
It will not be difficult to calculate how much the baby eats for feeding.
| Age | Daily milk rate from body weight |
| 10 days - 1.5 months | 9000 1/5 | 9000 9000 1.5–4 months | 1/6 |
| 4–6 months | 1/7 |
| 6-8 months | 1/8 |
| 9000 8 months - 1 year 9000 | 1/9 |
For example, a baby is 2 months old and weighs 4800 grams. According to the table, we divide 4800 by 6 and get the daily rate - 800 ml of milk formula per day. To calculate the volume of one feeding, divide 800 by 6 (number of feedings per day). Thus, the child eats about 130 ml of formula at a time.
Not everyone can find the right mixture right away, but do not despair. Even with allergies, digestive problems, cow's milk protein intolerance, you can find a suitable product, but only under the strict supervision of a doctor.
#Nutrition for children up to a year
Breastfeeding norms for newborns
When a child is born in a family, parents have many questions about the proper care of the baby. One of the most frequently asked questions is related to breastfeeding norms.
Dry initial milk formula adapted by Valio Baby 1 NutriValio for feeding children from birth to 6 months Read more
Follow-up dry milk formula adapted by Valio Baby 2 NutriValio for feeding children from 6 to 12 months More
Dry milk drink "Baby milk" Valio Baby 3 NutriValio for feeding children over 12 months Read more
Starting from the first feeding and in the first days of life, the child receives colostrum. It is very nutritious.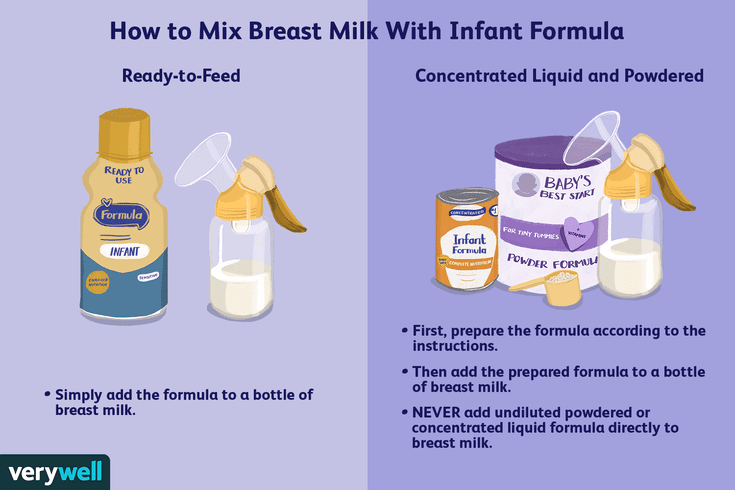 The newborn eats little, but remains full. The volume of the stomach in babies in the first days of life does not exceed 10 ml. In one day, a baby eats about 100 ml of breast milk. This volume is increasing every day. For a baby older than 10 days, it is very easy to calculate the feeding rate. To do this, you need to multiply the number of days lived by 10. The amount of food eaten per day should be 1/5 of the baby's body weight.
The newborn eats little, but remains full. The volume of the stomach in babies in the first days of life does not exceed 10 ml. In one day, a baby eats about 100 ml of breast milk. This volume is increasing every day. For a baby older than 10 days, it is very easy to calculate the feeding rate. To do this, you need to multiply the number of days lived by 10. The amount of food eaten per day should be 1/5 of the baby's body weight.
To determine the rate of feeding children from the first month of life to a year, experts have developed the following table for calculating the volume of feeding:
You can also determine the correct amount of food for feeding a baby, focusing on the age, weight, behavior and development of the child.
At present, the so-called free-feeding regimen is recommended, i.e., to give the child a breast not according to the schedule, but at his first request, including at night. This allows the baby to take full advantage of the first milk - colostrum, which is characterized by a high concentration of antimicrobial factors, which prevents the possibility of infection of the newborn.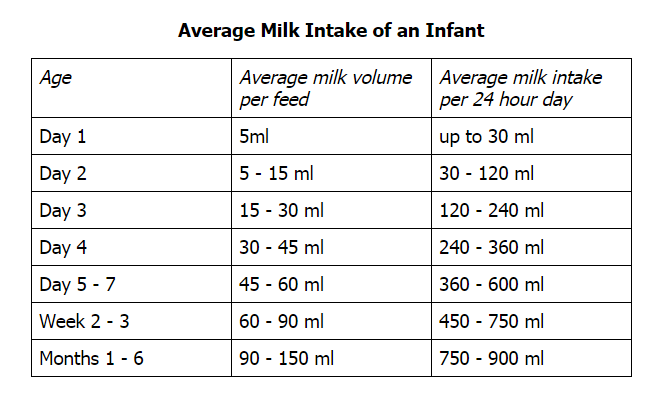 Colostrum, which contains a high percentage of protein and minerals, even in small quantities satisfies the nutritional needs of the child. In addition, the entry of colostrum into the child's digestive tract ensures a faster "maturation" of the intestinal mucosa. A mother can learn to correctly identify the "hungry" cry of her child: at the same time, he turns his head in search of the mother's breast, smacks his lips, cries loudly, insistently. Usually, with a free-feeding regimen, a newborn baby receives breasts up to 10-12 times a day. on, initiating the secretion and release of milk. It has been shown that with free feeding, the volume of milk is 1.5 times higher than with hourly feeding. Subsequently, as the child grows, he usually develops his own feeding regimen by 2-3 months - from 6 to 8 times a day and, as a rule, without a night break. Observations show that with this feeding regime, children are distinguished by calm behavior, good mood, sleep soundly, give normal weight gain, and mothers produce more breast milk and the ability to secrete it lasts longer.
Colostrum, which contains a high percentage of protein and minerals, even in small quantities satisfies the nutritional needs of the child. In addition, the entry of colostrum into the child's digestive tract ensures a faster "maturation" of the intestinal mucosa. A mother can learn to correctly identify the "hungry" cry of her child: at the same time, he turns his head in search of the mother's breast, smacks his lips, cries loudly, insistently. Usually, with a free-feeding regimen, a newborn baby receives breasts up to 10-12 times a day. on, initiating the secretion and release of milk. It has been shown that with free feeding, the volume of milk is 1.5 times higher than with hourly feeding. Subsequently, as the child grows, he usually develops his own feeding regimen by 2-3 months - from 6 to 8 times a day and, as a rule, without a night break. Observations show that with this feeding regime, children are distinguished by calm behavior, good mood, sleep soundly, give normal weight gain, and mothers produce more breast milk and the ability to secrete it lasts longer.
How can you tell if your baby is getting enough milk?
There is a so-called "wet diaper test". If the baby receives the necessary daily nutritional intake, he pees an average of 16-18 times. At the same time, 6-8 or more richly filled diapers are usually spent per day.
You can also determine if a child is getting enough nutrition by observing how much weight he gains each month. Infants from 2 to 13 weeks of age should gain between 170 and 200 grams per week.
Keep track of whether the baby grows out of the clothes he wears and out of diapers. If the baby eats properly, then on the 10-14th day of life, he returns to his original weight at birth. Babies who get enough food also sleep well and look cheerful and cheerful.
#PROMO_BLOCK#
Learn more about proper breastfeeding and check out our blog for tips.
3.08 38
Power supplyShare:
Author: Reetta Tikanmäki
Palm oil in baby food
Infant milk formulas are made from cow's milk.