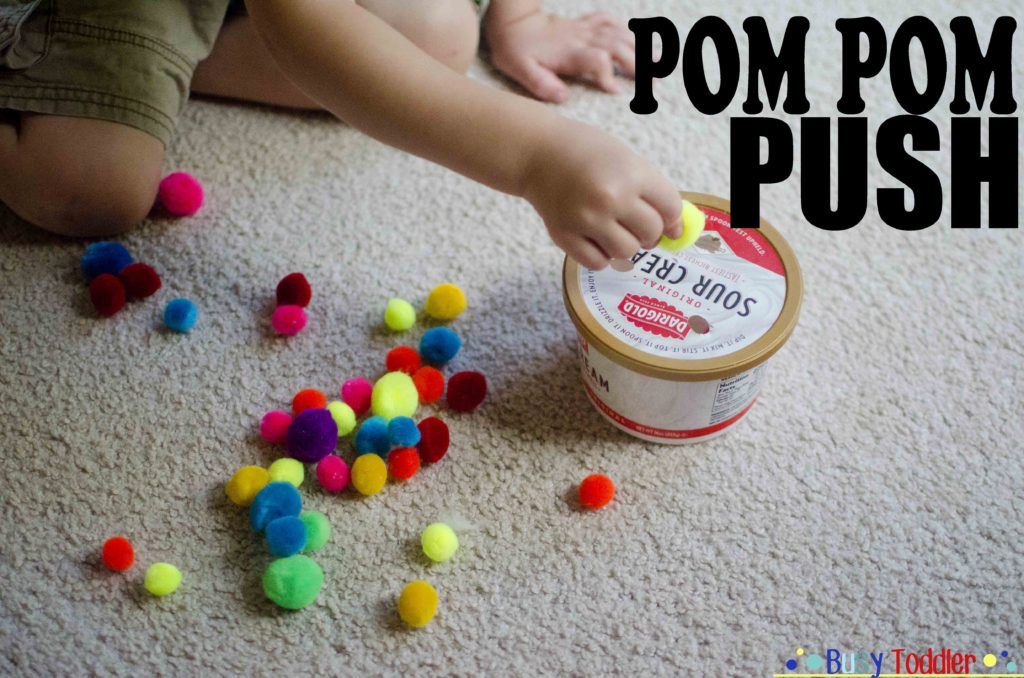
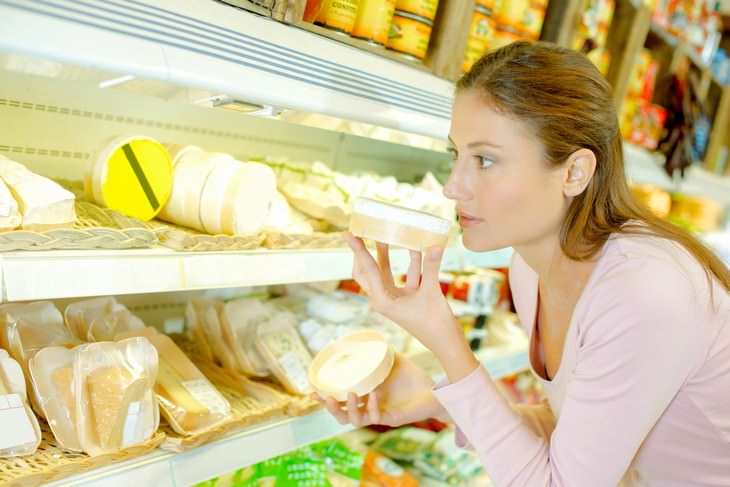
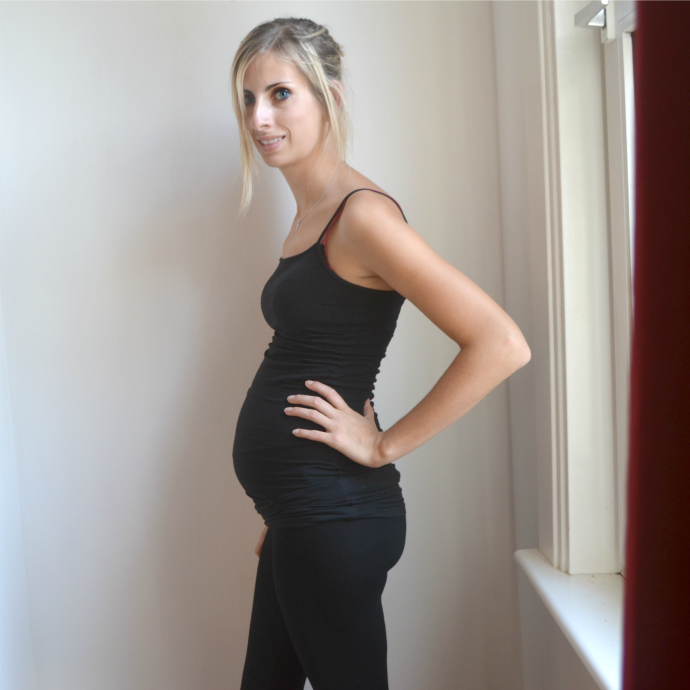
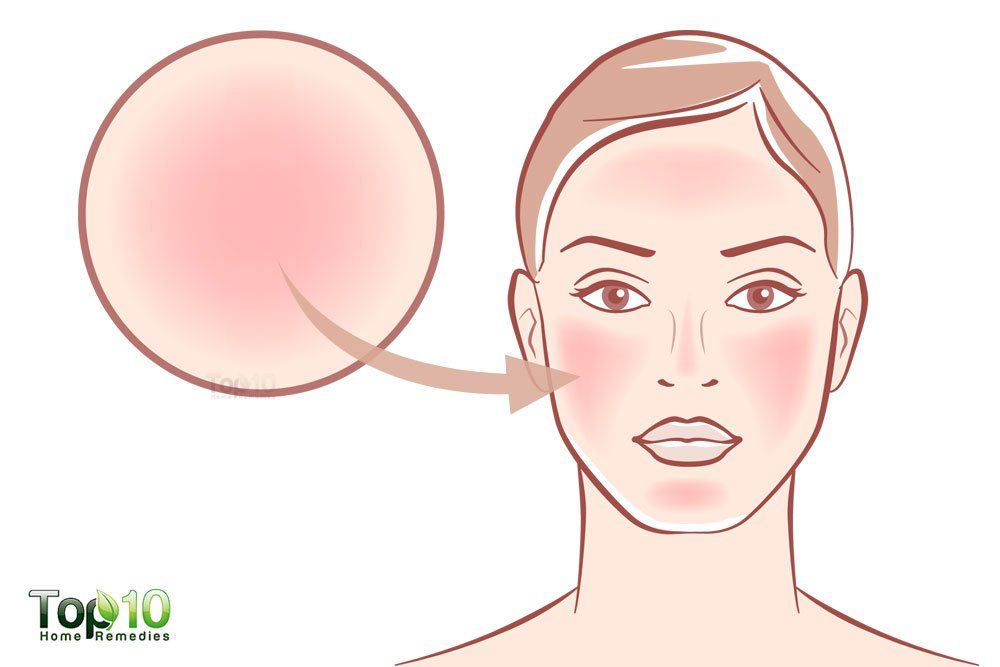
Flat red patches on skin
Petechiae: Causes & Treatment
Written by Stephanie Watson
In this Article
- Causes of Petechiae
- What Does Petechiae Look Like?
- Petechiae Diagnosis
- Petechiae Treatment and Home Remedies
- Petechiae Prevention
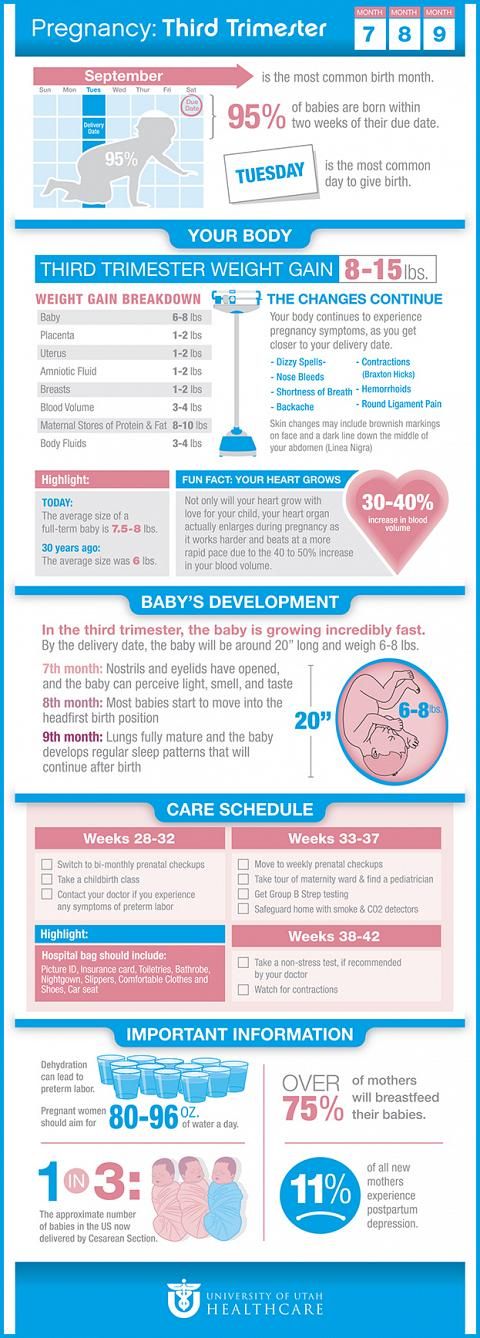
Petechiae are tiny red, flat spots that appear on your skin. They’re caused by bleeding. They sometimes appear in clusters and may look like a rash. If you have tiny red, purple, or brown spots on your skin, they could be petechiae. They're not a disease, but a symptom. A number of things can cause them to happen, from a severe coughing fit to an infection.
Often, petechiae are nothing to worry about. Still, it's always a good idea to check with your doctor if you're not sure where these spots came from. Some conditions that cause petechiae are very serious.
Petechiae are more common in kids. If your child has this rash, especially with a fever, take them to a pediatrician right away.
Causes of Petechiae
Petechiae are a sign of blood leaking from capillaries under your skin. Capillaries are the tiniest blood vessels that connect arteries to veins. They help move oxygen and nutrients from your bloodstream to your organs and tissues. They also carry waste away from your organs and tissues.
Leaking in the capillaries could be due to an illness or a medicine you take. Petechiae may also form on your face, neck, or chest if you strain intensely or for a long time when you do things like:
Cough hard
Vomit
Give birth
Lift heavy weights
Many infections with bacteria, viruses, or fungi can cause these spots, too, including:
Viral infections like cytomegalovirus (CMV), endocarditis, mononucleosis, and the flu
Bacterial infections such as meningitis, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, scarlet fever, and strep throat
Henoch-Schonlein purpura, a disease that causes inflammation in the small blood vessels
Sepsis, a serious, body-wide response to an infection
Viral hemorrhagic fevers like dengue, Ebola, and yellow fever
Blood and immune disorders can also cause petechiae, such as:
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome (HUS), a group of blood disorders
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP), an immune disorder that affects blood clotting
Leukemia, a type of blood cancer
Thrombocytopenia, low levels of platelets that help your blood clot
Vasculitis, or blood vessel inflammation
A lack of vitamin C (scurvy) or vitamin K in your diet can also lead to petechiae.
Reactions to certain medicines can cause these spots, too. Petechiae may be a side effect of drugs like:
Penicillin, an antibiotic
Quinine (Qualaquin), a malaria drug
Phenytoin and valproic acid, which are seizure medications
Blood thinners (warfarin/heparin)
Antidepressants (desipramine)
NSAIDs (naproxen/indomethacin)
Heart rhythm drugs (atropine)
Sedatives (chloral hydrate)
What Does Petechiae Look Like?
Petechiae are flat and look like pinpoint-sized red, brown, or purple dots. Clumps of them on your skin look like a rash. But unlike many rashes, when you press on the spots they don't turn white. And if the spots are larger and red or purple, you may have another type of bleeding problem called purpura.
But unlike many rashes, when you press on the spots they don't turn white. And if the spots are larger and red or purple, you may have another type of bleeding problem called purpura.
Petechiae can form just about anywhere on your body, even your eyelids or inside your mouth.
Petechiae Diagnosis
Petechiae with a fever in children can be a sign of a serious infection like meningococcal disease. Have a doctor check these symptoms right away.
The doctor will examine your child, look at the rash, and ask about their symptoms and recent illnesses. Blood and urine tests may help pinpoint the cause of the spots.
Other serious illnesses can also cause petechiae in your child. If your child has the spots, look out for these other symptoms:
Trouble breathing: If your child has shortness of breath or trouble breathing along with petechiae, it can be a sign of a serious condition called endocarditis.
 Endocarditis means there’s an infection in the lining of the inner chambers of the heart and the valves.
Endocarditis means there’s an infection in the lining of the inner chambers of the heart and the valves.Confusion: Petechiae -- along with confusion -- could indicate that your child has Rocky Mountain spotted fever, an infection caused by the bite of a tick.
Change in consciousness:Some infections caused by viruses, known as viral hemorrhagic fevers, can cause changes in consciousness as well as show signs of petechiae. These diseases include dengue, yellow fever, lassa, marburg, and ebola. They’re found in tropical countries and cases in the U.S. are usually from people who traveled to these areas.
Call their doctor right away if you have any concerns.
Petechiae Treatment and Home Remedies
The rash itself doesn't need treatment. If it’s caused by a virus, the spots should clear up as soon as the infection goes away.
If you think your petechiae might have been caused by a minor incident, like strenuous coughing, vomiting, or weightlifting, you may be able to take care of it at home by doing the following;
However, since petechiae may be the result of a serious underlying condition it is best to consult your doctor when these spots appear.
If you have a bacterial infection, you may need to take antibiotics. Make sure you take the full dose of medicine, even if you start to feel better.
More serious diseases such as meningococcal infections, blood disorders, or cancer may need treatment in a hospital. Your doctor may suggest you see a specialist in infections, blood diseases (hematologist), or cancer (oncologist) to oversee your care.
Petechiae Prevention
The only way to avoid getting petechiae is to try to prevent the various conditions that can cause it. Take good care of yourself:
Practice good hygiene such as washing your hands, brushing your teeth, and sanitizing your living environment.
 Don’t share personal items (straws, utensils, tooth brushes etc).
Don’t share personal items (straws, utensils, tooth brushes etc).Avoid procedures that can lead to skin infections like getting tattoos and piercings. Pay close attention to your health and see your doctor about fevers and infections that don’t resolve quickly.
Eat fruits and vegetables or take supplements to ensure you get enough vitamins in your diet.
Get vaccinated (immunized) to prevent certain types of bacterial meningitis.
Avoid mosquitoes and ticks by wearing long pants and long-sleeve shirts if you’re in an affected area and use insect repellents containing DEET.
Causes, 68 pictures of symptoms, and treatments
A rash is defined as a widespread eruption of skin lesions. It is a very broad medical term. Rashes can vary in appearance greatly, and there are many potential causes.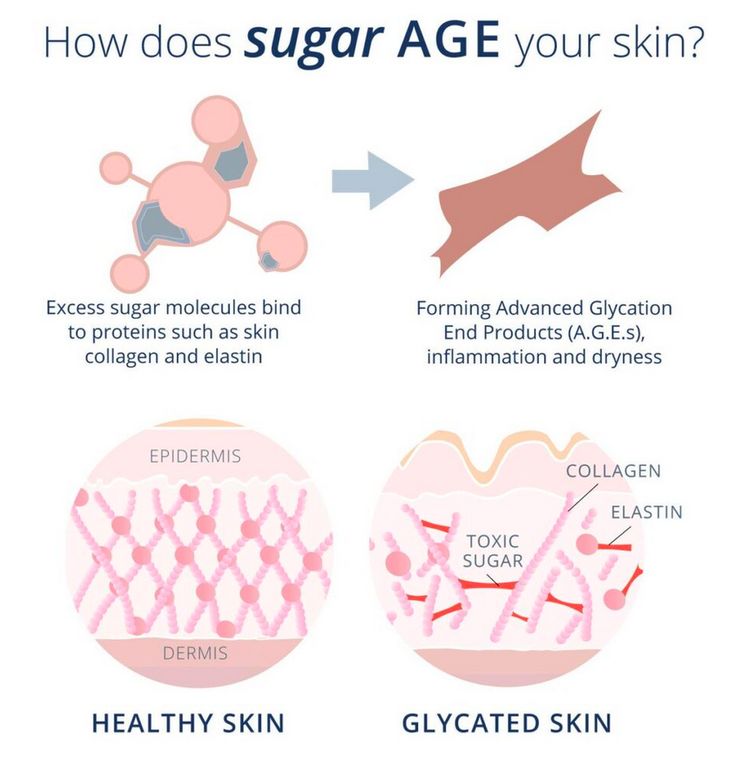 Because of the variety, there is also a wide range of treatments.
Because of the variety, there is also a wide range of treatments.
A rash can be local to just one small part of the body, or it can cover a large area.
Rashes come in many forms, and common causes include contact dermatitis, bodily infections, and allergic reactions to taking medication. They can be dry, moist, bumpy, smooth, cracked, or blistered; they can be painful, itch, and even change color.
Rashes affect millions of people across the world; some rashes may need no treatment and will clear up on their own, some can be treated at home; others might be a sign of something more serious.
There are a number of potential causes of rashes, including allergies, diseases, reactions, and medications. They can also be caused by bacterial, fungal, viral, or parasitic infections.
Contact dermatitisOne of the most common causes of rashes – contact dermatitis – occurs when the skin has a reaction to something that it has touched. The skin may become red and inflamed, and the rash tends to be weepy and oozy. Common causes include:
Common causes include:
- dyes in clothes
- beauty products
- poisonous plants, such as poison ivy and sumac
- chemicals, such as latex or rubber
Certain medications can cause rashes in some people; this may be a side effect or an allergic reaction. Also, some medications, including some antibiotics, cause photosensitivity – they make the individual more susceptible to sunlight. The photosensitivity reaction looks similar to sunburn.
InfectionsInfections by bacteria, viruses, or fungi can also cause a rash. These rashes will vary depending on the type of infection. For instance, candidiasis, a common fungal infection, causes an itchy rash that generally appears in skin folds.
It is important to see a doctor if an infection is suspected.
Autoimmune conditionsAn autoimmune condition occurs when an individual’s immune system begins to attack healthy tissue. There are many autoimmune diseases, some of which can produce rashes.For instance, lupus is a condition that affects a number of body systems, including the skin. It produces a butterfly-shaped rash on the face.
There are many autoimmune diseases, some of which can produce rashes.For instance, lupus is a condition that affects a number of body systems, including the skin. It produces a butterfly-shaped rash on the face.
Share on PinterestA young girl with chickenpox.
Rashes come in many forms and develop for many reasons.
However, there are some basic measures that can speed up recovery and ease some of the discomfort:
- Use mild soap – not scented. These soaps are sometimes advertised for sensative skin, or for baby skin.
- Avoid washing with hot water – opt for warm.
- Try to allow the rash to breathe. Do not cover with a Band-Aid or bandage.
- Do not rub the rash dry, pat it.
- If the rash is dry, for instance, in eczema, use unscented moisturizers.
- Do not use any cosmetics or lotions that may be causing the rash – for instance, newly purchased items.
- Avoid scratching to lessen the risk of infection.
- Cortisone creams that can be purchased over-the-counter or online may ease itching.
- Calamine can relieve some rashes, e.g. poison ivy, chickenpox, and poison oak.
If the rash causes mild pain, acetaminophen or ibuprofen may be useful, but these are not a long-term solution – they will not treat the cause of the rash.
It is important to speak with a doctor before taking any medication. Compare brands before purchasing over-the-counter or online products, to ensure the product is suitable.
If a rash occurs with the following symptoms, it is important to visit a doctor:
- a sore throat
- pain in joints
- if you have had a recent animal or insect bite
- red streaks near the rash
- tender regions near the rash
- a large collection of pus
Although the majority of rashes are not a major cause for concern, anyone experiencing the following symptoms should go to the hospital straight away:
- quickly changing coloration on the skin
- difficulty breathing or feeling like the throat is closing up
- increasing pain or severe pain
- high fever
- confusion
- dizziness
- swelling of the face or extremities
- severe pain in the neck or head
- repeated vomiting or diarrhea
1.
 Bites and stings
Bites and stingsShare on Pinterest
Many insects can cause a rash through a bite or sting. Although the reaction will vary depending on the person and the animal, symptoms often include:
- redness and rash
- itching
- pain
- swelling – either localized to the site of the bite or sting or more widespread
2. Flea bites
Share on Pinterest
Fleas are tiny jumping insects that can live in fabrics within the home. They have a very fast breeding cycle and can take over a home very rapidly.
- flea bites on humans often appear as red spots
- the skin can become irritated and painful
- secondary infections can be caused by scratching
3. Fifth disease
Share on Pinterest
Also known as erythema infectiosum and slapped cheek syndrome, fifth disease is caused by the parvovirus B19. One of the symptoms is a rash, which appears in three stages:
- A blotchy red rash on the cheeks with groups of red papules.
- After 4 days, a net of red marks may appear on the arms and trunk.
- In the third stage, the rash only appears after exposure to sunlight or heat.
4. Impetigo
Share on Pinterest
Impetigo is a highly contagious skin infection that most commonly affects children. The first sign is normally a patch of red, itchy skin. There are two types of impetigo:
- Non-bullous impetigo – red sores appear around the mouth and nose.
- Bullous impetigo – less common, generally affects children under 2. Medium to large blisters appear on the trunk, arms, and legs.
5. Shingles
Share on Pinterest
Shingles is an infection of an individual nerve. It is caused by the same virus as chickenpox – the varicella-zoster virus. Symptoms include:
- A rash similar to chickenpox in a band around the infected nerve.
- Blisters can merge producing a solid red band.
- Rash is often painful.
6. Scabies
Share on Pinterest
Scabies is a skin condition caused by a microscopic mite. It is very contagious and spreads easily through person-to-person contact. Symptoms include:
It is very contagious and spreads easily through person-to-person contact. Symptoms include:
- Intense itching – often worse at night.
- Rash – appears in lines as the mite burrows. Blisters are sometimes present.
- Sores – may appear where the rash has been scratched.
7. Eczema
Share on Pinterest
Eczema is one of the most common skin conditions. It often first develops in childhood. Symptoms depend on the type of eczema and on the age of the individual but they often include:
- dry scaly patches on the skin
- intensely itchy rash
- cracked and rough skin
8. Hay fever
Share on Pinterest
Hay fever, or allergic rhinitis, is an allergic response to pollen. Symptoms can be similar to those of a common cold, such as:
- runny nose
- watery eyes
- sneezing
Hay fever can also cause a rash, similar to hives. These will appear as itchy red patches or eruptions on the skin.
9. Scarlet fever
Share on Pinterest
Scarlet fever is a disease caused by a toxin released by a bacteria – Streptococcus pyogenes – the same bacteria that is responsible for Strep throat. Symptoms include a sore throat, rash, and fever. The rash has the following characteristics:
- red blotches
- blotches turn to fine pink-red rash like sunburn
- skin feels rough
10. Rheumatic fever
Share on Pinterest
Rheumatic fever is an inflammatory reaction to a streptococcal infection, such as Strep throat. It most commonly affects children aged 5-15. Symptoms include:
- small painless bumps under skin
- red skin rash
- swollen tonsils
11. Mono (mononucleosis)
Share on Pinterest
Mono, or mononucleosis, is caused by a virus. It is rarely serious, but symptoms can include:
- a pink, measle-like rash
- body aches
- high fevers
12. Ringworm
Share on Pinterest
Ringworm, despite its name, is caused by a fungus.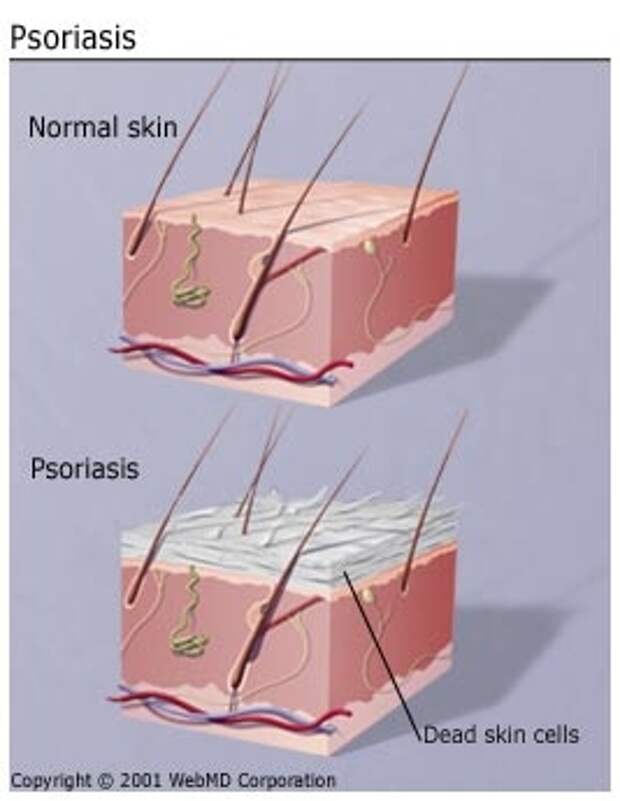 The fungal infection affects the top layer of the skin, scalp, and nails. Symptoms vary depending on the site of the infection, but can include:
The fungal infection affects the top layer of the skin, scalp, and nails. Symptoms vary depending on the site of the infection, but can include:
- itchy, red rash in rings – sometimes slightly raised
- small patches of scaly skin
- hair near patches breaks away
13. Measles
Share on Pinterest
Measles is a highly contagious disease caused by the rubeola virus. Symptoms include:
- a reddish-brown rash
- small grayish-white spots with bluish-white centers in the mouth
- dry cough
14. Yeast infection (candidiasis)
Share on Pinterest
Candidiasis is a common fungal infection of the genitals. It affects both sexes, but more commonly, women. Symptoms include:
- rash
- pain and soreness in the genital area
- itching, burning, and irritation
15. Stasis dermatitis
Share on Pinterest
Stasis dermatitis is also known as varicose eczema. It develops due to poor circulation and most commonly affects the lower legs. Symptoms include:
Symptoms include:
- varicose veins covered in itchy, dry skin
- red, swollen, painful skin, which may weep or crust over
- heavy, aching legs after standing for some time
16. German measles
Share on Pinterest
Also known as rubella, German measles are an infection caused by the rubella virus. Symptoms include:
- rash – less bright than measles, often begins on the face
- inflamed, red eyes
- stuffy nose
17. Sepsis
Share on Pinterest
Sepsis, often called blood poisoning, is a medical emergency. It is the result of a wide scale immune response to an infection. Symptoms vary, but can include:
- a rash that does not fade under pressure
- fever
- increased heart rate
18. West Nile virus
Share on Pinterest
West Nile virus is an infection spread by mosquitos. Often, there are no symptoms, but if they do occur, they can include:
- raised and/or flat, pink skin rash on the trunk, arms, or legs
- excessive sweating
- vomiting
19.
 Lyme disease
Lyme diseaseShare on Pinterest
Lyme disease is a bacterial infection transmitted to humans by the bite of an infected tick. The symptoms include an erythema migrans rash that often appears in the early stages of the disease.
- The rash begins as a small red area that may be warm to the touch but not itchy.
- The center loses color, giving it a bull’s-eye appearance.
- The rash does not necessarily appear at the site of the tick bite.
20. Cellulitis
Share on Pinterest
Cellulitis is a bacterial infection of the deep layer of skin – the dermis. It normally occurs when bacteria enter through a break in the skin. Symptoms include:
- Skin sores or rash that starts suddenly and grows quickly.
- Warm skin around the redness.
- Fever and fatigue.
21. MRSA
Share on Pinterest
MRSA (methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus) is a contagious bacterial infection that is resistant to a range of antibiotics. This makes it difficult to treat. Symptoms include:
This makes it difficult to treat. Symptoms include:
- rash
- swelling and tenderness in the affected part of the body
- wounds that do not heal
Photo credit: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
22. Chickenpox
Share on Pinterest
Chickenpox is an infection by the varicella zoster virus. It is unpleasant, but most people recover within a couple of weeks. Symptoms include:
- An itchy rash of small red spots first appears on the face and trunk, and then spreads across the body.
- Spots then develop blisters on top.
- After 48 hours, the blisters cloud and start to dry out.
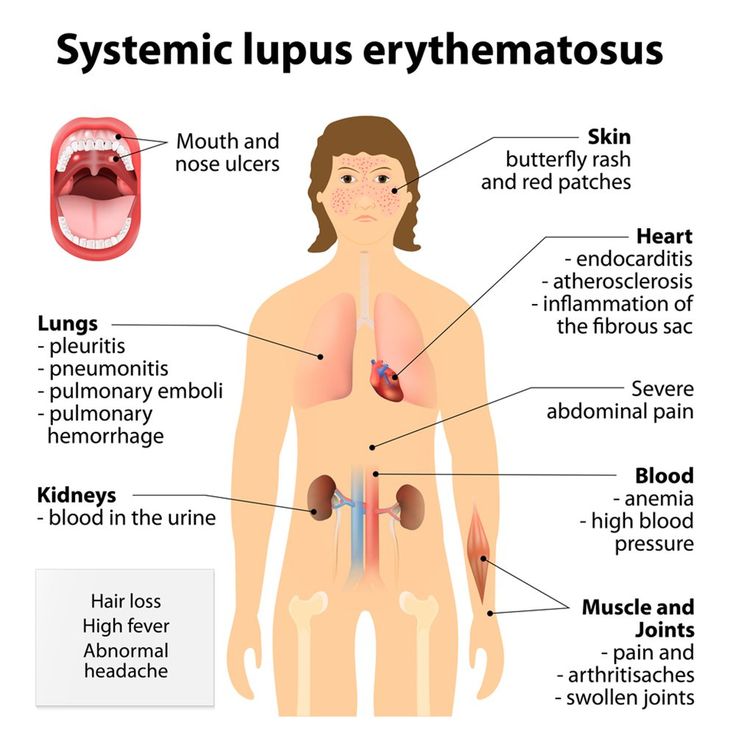
23. Lupus
Share on Pinterest
Lupus is an autoimmune disease, meaning that the immune system attacks healthy tissue. Symptoms vary widely from person to person, but can include:
- Butterfly-shaped rash across the cheeks and the bridge of the nose.
- Flaky red spots or a purple, scaly rash on the face, neck, or arms.

- Skin sensitivity to the sun.
24. Toxic shock syndrome
Share on Pinterest
Toxic shock syndrome is a rare condition sparked by a bacterial infection. It develops quickly and can be life-threatening. All people who have toxic shock syndrome have fever and a rash with the following characteristics:
- looks similar to sunburn and covers most of the body
- flat not raised
- turns white when pressed
25. Acute HIV infection
Share on Pinterest
During the first stages of HIV, levels of the virus in the blood are very high because the immune system has not yet started tackling the infection. Early symptoms include a rash with the following features:
- mostly affects the upper part of the body
- flat or barely raised small red dots
- not generally itchy
26. Hand, foot, and mouth
Share on Pinterest
Hand, foot, and mouth is a childhood illness resulting from a viral infection. Symptoms include:
Symptoms include:
- Rash – flat, non-itchy red blisters on the hands and soles of the feet.
- Loss of appetite.
- Ulcers on the throat, tongue, and mouth.
Image credit: KlatschmohnAcker
27. Acrodermatitis
Share on Pinterest
Acrodermatitis, a type of pustular psoriasis, is also known as Gianotti-Crosti syndrome. It is associated with viral infections. Symptoms include:
- itchy purple or red blisters
- swollen lymph nodes
- bloated abdomen
28. Hookworm
Share on Pinterest
Hookworm is a common intestinal parasite. It can cause a range of complications. Symptoms include:
- Skin rash in one particular area that is red, itchy, and raised.
- Breathing complications.
- Extreme tiredness.
29. Kawasaki disease
Share on Pinterest
Kawasaki’s disease is a rare syndrome that affects children. It is characterized by an inflammation of the walls of the arteries throughout the body. Symptoms include:
Symptoms include:
- A rash on the legs, arms, and torso and between the genitals and anus.
- A rash on the soles of the feet and palms of the hand, sometimes with peeling skin.
- Swollen, chapped, and dry lips.
30. Syphilis
Share on Pinterest
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted bacterial infection. The disease is treatable, but will not go away on its own. Symptoms vary depending on the stage of the disease and include:
- Initially – painless, firm, and round syphilitic sores (chancres).
- Later – non-itchy red/brown rash that starts on the trunk and spreads across the body.
- Oral, anal, and genital wart-like sores.
31. Typhoid
Share on Pinterest
Typhoid is caused by a bacterial infection. It is spread quickly by contact with the feces of an infected person. If untreated, 25 percent of cases end in death. Symptoms can include:
- Rash – rose-colored spots, especially on the neck and abdomen.
- Fever – up to 104 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Abdominal pain, diarrhea, and constipation.
Image credit: Charles N. Farmer, CDC/ Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, 1964
32. Dengue fever
Share on Pinterest
Dengue fever, also called breakbone fever, is transmitted by mosquitos. The condition ranges from mild to severe. Symptoms can include:
- Initially a flat, red rash appears over most of the body.
- Later, a secondary rash appears, similar to measles.
- Severe joint and muscle aches.
Image credit: calliopejen, 2009
33. Ebola
Share on Pinterest
Ebola is a serious viral disease; it spreads rapidly through families and friends and can often be fatal. Often, a rash is one of the symptoms:
- Initially, a short-lived mild rash may be present.
- Rashes begin to peel and look like sunburn.
- Later in the disease, the rash may turn to abscesses.
34. SARS
Share on Pinterest
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is a contagious and sometimes fatal respiratory illness. Symptoms can include:
Symptoms can include:
- skin rash
- chills
- stiff muscles
35. Contact dermatitis
Share on Pinterest
Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin comes in contact with an irritant; it is relatively common, and can be unpleasant. Symptoms include:
- red, flaky rash that stings
- blistered skin
- burning sensation
- cracked skin
36. Fungal infection
Share on Pinterest
Although some fungi live naturally on the human body, sometimes, they can overtake. Symptoms depend on where the infection strikes, but can include:
- a red rash with a circular shape and raised edges
- cracking, flaking, or dry peeling of the skin in the infected area
- chafing, irritation, itching, or burning in the infected area
37. Drug allergy
Share on Pinterest
Certain people have allergic reactions to prescribed drugs. The body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the medication as if it were a pathogen. Symptoms vary depending on the individual and the drug, but can include:
Symptoms vary depending on the individual and the drug, but can include:
- Rash, including hives
- Itchy skin or eyes
- Swelling
38. Atypical pneumonia
Share on Pinterest
Also called walking pneumonia, atypical pneumonia is less severe than the typical form. Symptoms can include:
- rashes (uncommon)
- weakness and fatigue
- chest pain, especially when breathing deeply
39. Erysipelas
Share on Pinterest
Erysipelas is a skin infection. It is a form of cellulitis, however, unlike cellulitis, it only affects the upper layers of the skin, rather than deeper tissue. The skin in a particular area becomes:
- swollen, red, and shiny
- tender and warm to the touch
- red streaks above the affected area
Image credit: CDC/Dr. Thomas F. Sellers/Emory University
40. Reye’s syndrome
Share on Pinterest
Reye’s syndrome is rare and most commonly occurs in children. It can cause serious damage to the body’s organs, particularly the brain and liver (image opposite shows fat accumulation in liver cells). Early symptoms include:
It can cause serious damage to the body’s organs, particularly the brain and liver (image opposite shows fat accumulation in liver cells). Early symptoms include:
- Rash on the palms of the hands and feet.
- Repeated, heavy vomiting.
- Lethargy, confusion, and headaches.
41. Addisonian crisis
Share on Pinterest
Addisonian crisis – also known as an adrenal crisis and acute adrenal insufficiency – is a rare and potentially fatal condition where the adrenal glands stop working correctly. Symptoms include:
- skin reactions, including rashes
- low blood pressure
- fever, chills, and sweating
42. Chemical burns
Share on Pinterest
Chemical burns are relatively common; they can occur when a person comes in direct contact with a chemical or its fumes. Symptoms vary but can include:
- skin that appears black or dead
- irritation, burning, or redness in the affected area
- numbness and pain
43.
 Colorado tick fever
Colorado tick feverShare on Pinterest
Colorado tick fever, also known as mountain tick fever and American tick fever is a viral infection that develops after a bite from a Rocky Mountain wood tick. Symptoms can include:
- a flat or pimply rash
- skin or muscle pain
- fever
44. Accidental poisoning by soap products
Share on Pinterest
Some soap products contain strong chemicals. If they are ingested or inhaled, they can cause serious damage. Symptoms can include:
- chemical burns on the skin
- swelling of the throat, lips, and tongue
- difficulty breathing
45. Adult-onset Still’s disease
Share on Pinterest
Adult-onset Still’s disease is a rare inflammatory disorder that usually affects people in their 30s. Symptoms include:
- A pink rash, mostly affecting the chest and thighs, which tends to fade quickly.
- Joint and muscle pain, commonly affecting the knees, wrists, and ankles.
- Enlarged spleen, liver, or lymph nodes.
46. Juvenile idiopathic arthritis
Share on Pinterest
Juvenile idiopathic arthritis is the most common form of arthritis in children; it used to be called juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Symptoms vary depending on the subtype, but can include:
- fleeting rashes
- a scaly psoriasis-like rash
- spiking fever
47. Histoplasmosis
Share on Pinterest
Histoplasmosis is a fungal infection of the lungs. Sometimes, it presents no symptoms, but in other cases, it produces pneumonia-like symptoms; these include:
- rash
- chest pain
- red bumps on lower legs
48. Dermatomyositis
Share on Pinterest
Dermatomyositis is a medical condition that causes muscle weakness and rashes. The rash may be red and patchy or bluish-purple in color; it appears in a number of places, including:
- shoulders and upper back
- knuckles
- palms and fingers
- around the eyes
49.
 Graft-versus-host disease
Graft-versus-host diseaseShare on Pinterest
People being treated for certain cancers may sometimes undergo a stem cell transplant; in some cases, the donor cells attack the recipient’s healthy cells instead of the cancer cells. Symptoms can include:
- Rashes affecting the palms of the hands, soles of the feet, ears, or face.
- Other skin changes, such as drying, scaling, scarring, hardening, and darkening.
- Hair loss.
50. Icthyosis vulgaris
Share on Pinterest
Ichthyosis vulgaris is a hereditary skin condition that often begins in childhood. It is caused by a mutation in the gene that codes for the protein filaggrin; features include:
- The skin’s surface becomes dry, thick, and scaly.
- The dryness is often accompanied by fine, white, or skin-colored scales.
- It commonly affects the elbows, shins, face, scalp, and torso.
51. Pemphigoid
Share on Pinterest
Pemphigoid is a group of rare autoimmune conditions that primarily cause rashes and skin blistering; there are three main types:
- Bullous pemphigoid – blistering on the lower torso, groin, armpits, inner thighs, soles, and palms.

- Cicatricial pemphigoid – mostly affects mucous membranes.
- Pemphigoid gestationis – develops during pregnancy and mostly affects the upper body.
52. Sarcoidosis
Share on Pinterest
Sarcoidosis is a condition involving the growth of persistent or inappropriate granulomas or clumps of inflammatory cells. Symptoms include:
- Erythema nodosum – a raised red rash on the lower extremities.
- Nodules or growths under the skin, especially around scar tissue.
- Skin discoloration.
53. Phenylketonuria
Share on Pinterest
Phenylketonuria is a genetic condition that affects how phenylalanine is broken down by the body. It affects around 1 in 10,000 babies in the U.S. If left untreated, phenylalanine builds up, causing:
- skin rashes, such as eczema
- lighter skin and eyes due to abnormal levels of melanin
- seizures
54. Porphyria
Share on Pinterest
Porphyria refers to a group of genetic disorders that can affect the nervous system or the skin; symptoms are varied but can include:
- redness and swelling on the skin
- burning pain on the skin
- changes in skin pigmentation
55.
 Dermatitis neglecta
Dermatitis neglectaShare on Pinterest
Dermatitis neglecta is a skin disorder that arises when an individual does not clean themselves sufficiently. It can look similar to other allergic conditions. Symptoms include patches of scaly skin that are collections of:
- sweat and moisture
- dirt
- bacteria and other germs
Image credit: Dr. Piotr Brzezinski Ph.D.
56. Heliotrope rash
Share on Pinterest
Heliotrope rash is often the first noticeable symptom of an inflammatory muscle disease called dermatomyositis. The rash often includes:
- raised and bumpy skin
- red patches
- skin looks dry and irritated
Image credit: Elizabeth M. Dugan, Adam M. Huber, Frederick W. Miller, Lisa G. Rider, 2010.
57. Uric acid skin rash
Share on Pinterest
A person may develop a rash when high levels of uric acid in the blood cause crystals to form and accumulate in and around a joint.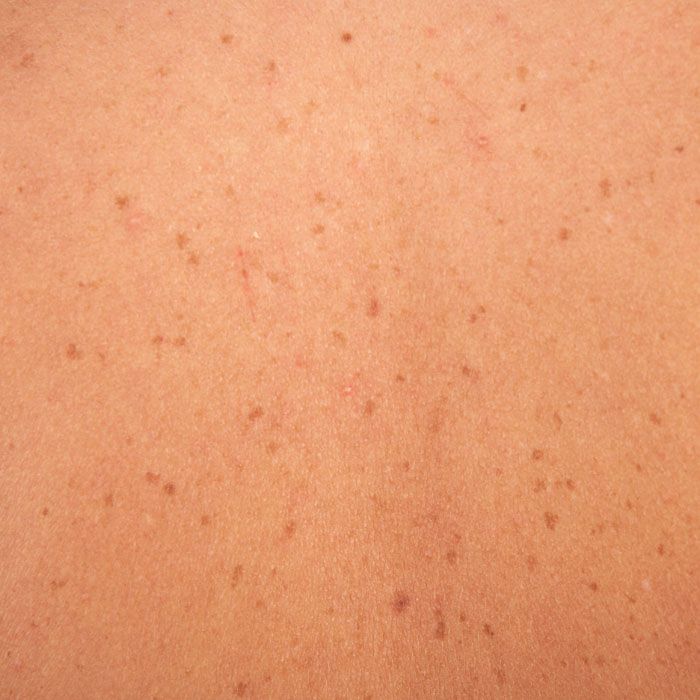 This can also lead to gout. Symptoms include:
This can also lead to gout. Symptoms include:
- A dotted rash on the surface of the skin
- Redness, tenderness, and swelling of the joints
- Prolonged joint pain for weeks following the reaction
Image credit: WNT.
1. Amoxicillin reaction
Share on Pinterest
Some people are allergic to the antibiotic amoxicillin. If a person experiences any of the following symptoms they should stop taking it and report to their doctor:
- skin rash
- blotchy skin
- itchiness
Image credit: Skoch4, 2008.
2. Erythema ab igne (hot bottle rash)
Share on Pinterest
Erythema ab igne is caused by overexposure to heat. Regularly using hot water bottles, or other forms of heat, to relieve pain from muscle or joint damage may lead to developing this skin condition.
Image credit: James Heilman, MD, 2010.
3. Ketoconazole shampoo reaction
Share on Pinterest
Applying ketoconazole shampoo to the scalp can help reduce skin conditions such as dandruff and psoriasis. If a person has an allergic reaction to ketoconazole their symptoms may include:
If a person has an allergic reaction to ketoconazole their symptoms may include:
- enflamed rash covering the area that came into contact with the shampoo
- itchiness
Image credit: Niels Olson, 2010.
4. Beard dye reaction
Share on Pinterest
Some people are allergic to chemicals found in beard or hair coloring dye. Symptoms of an allergic reaction include:
- dry, flaky skin
- redness
- itchiness
Image credit: Yngve Roennike, 2016.
5. Infant milk rash
Share on Pinterest
Breastfed babies may develop a rash if they are allergic to a food group that their mother is consuming. Symptoms of a food allergy can include:
- hives
- itchiness
- coughing
- diarrhea
6. Urticaria (nettle rash)
Share on Pinterest
A person with urticaria will likely develop a raised, itchy rash that is usually triggered by an allergen. Common symptoms of urticaria include:
- pink wheals (swellings) on the skin
- redness
- extreme itchiness
7.
 Grass allergy
Grass allergyShare on Pinterest
A person with a grass allergy may develop hay fever symptoms when coming into contact with grass. It is also common to experience:
- small red dots on the skin
- hives
- itchiness
Image credit: Carolyn, 2009.
8. Poison ivy reaction
Share on Pinterest
Coming into contact with poison ivy plant oil can lead to a person developing contact dermatitis. Symptoms of this include:
- small bumps or blisters on the skin
- redness
- itchiness
Image credit: CDC/ Richard S. Hibbits, 1971.
9. Smallpox vaccination reaction
Share on Pinterest
Following a vaccination, some people may develop the following symptoms:
- small bumps
- redness
- itchiness
- fever
Image credit: CDC/ Arthur E. Kaye, 1969.
10. Hyposensitization therapy reaction
Share on Pinterest
Hyposensitization therapy is used to treat allergic disease.![]() While receiving the course of injections, a person may experience the following symptoms:
While receiving the course of injections, a person may experience the following symptoms:
- redness
- itchiness
Image credit: Bionerd, 2008.
11. Euproctis chrysorrhoea (brown-tail moth) reaction
Share on Pinterest
A person may develop a rash after touching a brown-tail moth. This is caused by a reaction to the toxins found in the moth’s hairs. Symptoms include:
- red, blotchy skin
- raised bumps
Image credit: B kimmel, 2010.
Plaques on the skin - causes, diseases, diagnosis and treatment
- INVITRO
- Library
- Symptoms
- Plaques on the skin
Fungus
Allergy
Psoriasis
Keratoma
Mycosis
Nevus
Melanoma
26035 November 16
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment.
 In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor. nine0031 For a correct assessment of the results of your analyzes in dynamics, it is preferable to do studies in the same laboratory, since different laboratories may use different research methods and units of measurement to perform the same analyzes.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor. nine0031 For a correct assessment of the results of your analyzes in dynamics, it is preferable to do studies in the same laboratory, since different laboratories may use different research methods and units of measurement to perform the same analyzes. Plaques on the skin: the causes of occurrence, in what diseases they occur, diagnosis and methods of treatment.
Definition
A plaque is a pathological element with clear edges that rises above the skin surface or merges with it, more than 5 mm in size. nine0013In dermatology, many types of plaques are distinguished - about 70 diseases occur with the formation of these elements, which makes the plaque one of the most common rashes.
Plaque varieties
The shape of the plaques are round, oval and irregular in shape. Over time, the shape, surface and appearance of this element may change.
Over time, the shape, surface and appearance of this element may change. Due to the occurrence of plaques, they can be both a manifestation of skin diseases and a symptom of diseases of internal organs and systems (autoimmune reactions, liver diseases, oncological processes, allergic reactions). nine0013
Plaques are dry, smooth, red, brown, gray-white, etc.
Possible causes of plaques
Dry plaques on the skin in adults may be a manifestation of the following diseases: plaques with severe itching.
- Allergic reactions are characterized by the appearance on the skin of smooth dry plaques, pink spots, blisters, which are very itchy and cause severe discomfort. They can develop both when the skin comes into contact with the allergen, and when it gets on the mucous membranes (for example, with urticaria, hay fever, food and contact allergies). nine0004
- Psoriasis is a chronic non-infectious skin disease in which scaly dry plaques form on the elbows, knees, scalp, prone to fusion and accompanied by mild itching.
- Dry plaques form on the skin if it is exposed to stress for a long time with the loss of its protective functions.
- Diseases of the digestive tract, accompanied by malabsorption syndrome (impaired absorption of vitamins and trace elements in the small intestine), chronic diseases of the liver and other organs, in which substances that are not normally present in the dermis accumulate, also lead to the appearance of dry plaques. nine0004
- Solar keratoma is a precancerous condition, which is characterized by the presence of many light grayish plaques on the skin.
- Drug toxidermia is an allergic reaction accompanied by the appearance of elements in the form of plaques on the skin. In severe cases, Lyell's syndrome or Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, may develop.
 nine0004
nine0004 - Dühring's dermatitis (herpetiform) is a chronic skin disease with no established etiology, which is characterized by recurrent appearance of a rash of various morphologies on the skin, accompanied by severe skin itching and burning.
- Mycosis fungoides is a primary T-cell lymphoma of the skin, a malignant lymphoid lesion, primarily of the skin. Itchy red plaques appear on the skin, resembling eczema. In the initial stages, they respond well to treatment with hormonal ointments, but the disease itself requires more complex therapy. nine0004
- In children, the appearance of red spots and plaques on the skin is most often associated with an allergic reaction to food.
- Becker's nevus is an anomaly in the development of the dermis, when dark plaques with an uneven surface appear on the skin, on which hair can begin to grow over time.
 nine0004
nine0004 - Pigmentary nevus - "birthmark", may rise above the skin, has a brown or dark color.
- Melanoma is the most malignant skin tumor characterized by rapid metastasis. It develops mainly from nevi and moles. If the nature of the surface, the boundaries of the mole change, its size increases, bleeding occurs, you should immediately contact a dermatologist or oncologist to exclude the development of melanoma. nine0009 Basal cell skin cancer is more often localized on the head, face, neck, does not metastasize, is characterized by slow growth.
- Senile keratoma occurs in elderly people, most likely due to a lack of vitamins, an abundance of animal fats consumed, skin sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation due to a violation of its protective functions. Typical localization - face, neck, open areas of the body.
- Seborrheic keratoma is a yellowish plaque on the skin that eventually transforms into a dark brown growth that tends to flake off, itch severely, crack, bleed, and can serve as an entryway for infection.
 nine0004
nine0004 - change in the shape of the plaque - the edges have become uneven;
- change in the surface of the plaque - cracks, ulcerations appeared;
- change in the size of the plaque - it began to grow rapidly above the surface of the skin or actively spread through it;
- discoloration of the plaque - in cases of malignancy, an uneven color of the formation is usually observed with areas of darker and lighter shades;
- the appearance of bleeding - both contact and spontaneous; nine0004
- enlargement of regional (nearby) lymph nodes.
- Clinical guidelines.
 Dermatitis herpetiformis // Russian Society of Dermatovenerologists and Cosmetologists. 2016.
Dermatitis herpetiformis // Russian Society of Dermatovenerologists and Cosmetologists. 2016. - Clinical guidelines. Urticaria in children // Union of Pediatricians of Russia; Russian Association of Allergists and Clinical Immunologists. 2018.
- Clinical guidelines. Toxidermia // Russian Society of Dermatovenerologists and Cosmetologists. 2016.
- Clinical guidelines. Familial hypercholesterolemia // National Society for the Study of Atherosclerosis. 2018.
-
Cholesterol plaques
5495 November 18th
-
Hepatic colic
3230 09 November
- nine0012 Laryngeal edema
2379 07 November
- Inflammatory (vascular) formations appear as a result of the expansion of the blood vessels of the papillary dermis.
 In this case, bright red or red-bluish rashes appear, which may lighten with time. Spots of small diameter (up to 20-25 mm) are called roseola, in other cases we are talking about erythema. If all skin integuments are included in the pathological process, erythroderma occurs. nine0004
In this case, bright red or red-bluish rashes appear, which may lighten with time. Spots of small diameter (up to 20-25 mm) are called roseola, in other cases we are talking about erythema. If all skin integuments are included in the pathological process, erythroderma occurs. nine0004 - As a result of hemorrhages, hemorrhagic spots appear. Initially they have a purple-red tint, but over time they turn yellow and disappear. The appearance of such formations is preceded by tissue injury.
- Non-inflammatory spots are the result of hemorrhage, disturbances in the content of melanin in cells or the introduction of dyes into the skin. In some cases (for example, with vasodilation) they can also have a red or red-cyanotic tint.
- flat and convex;
- swollen (inflamed) and not inflamed;
- smooth and rough;
- wet and dry; nine0004
- with a clear outline and blurry;
- dark purple or reddish (pink).
- Diseases of the heart or blood vessels.
- Allergic reactions.

- Autoimmune pathologies.
- Dermatological diseases.
- Dysfunction of internal organs.
- Parasitic and bacterial infections.
- Some insect bites.
- Oncological diseases.
- Malnutrition, disturbances in the digestive tract.
- Poor ecological situation in the place of residence. nine0004
- Frequent stress and anxiety.
- Itching or burning.

- Peeling of the skin.
- Increased size or number of spots.
- Soreness on pressure.
- Swelling, weeping.
- The beginning of the inflammatory process.
- Complete blood count.
- Urinalysis.
- Microscopic examination of skin scrapings.
- Ultrasound of internal organs.
- ECG, etc.
- Red rashes that look like mosquito bites but without itching or pain are often the result of stress or anxiety. In rare cases, this may be a manifestation of an allergy or pink lichen Zhibera. nine0004
- Spots associated with soreness or itching may indicate the presence of autoimmune diseases, urticaria or psoriasis.
- A rash that looks like a burn is often a manifestation of atopic dermatitis. They may be accompanied by itching (especially at night).
- Red sores or plaques along the hairline may be a symptom of seborrheic dermatitis.
- Small spots all over the body indicate the presence of measles, chickenpox or lichen. Also, such symptoms occur in some patients with coronavirus. nine0004
- Red rough spots on the skin of the hands indicate a lack of certain vitamins and microelements in the body. In most cases, you can compensate for their lack by changing the diet.
- Medical therapy.
- Local therapy (treatment of the skin).
- Physiotherapy procedures.
- Antihistamines . With a severe allergic reaction or exacerbation of eczema.
- Antibiotics . To combat the infectious nature of different types of red spots on the skin.
- Glucocorticosteroids . Hormonal agents to relieve inflammation.
- Tranquilizers . Used to relieve severe itching.
- Diuretics . Drugs to eliminate puffiness.
- Enterosorbents . To remove the products of intoxication from the intestines.
- B vitamins . They are used to normalize the functioning of the nervous system.
- Karavaeva TA, Korolkova TN Psychological mechanisms and psychosomatic correlations in various dermatoses // Clinical dermatology and venereology. - 2018. - V. 17, No. 5. - S. 7–16.
- Kubanova AA Analysis of the incidence of diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue in the Russian Federation for the period 2003–2016.
The appearance of red plaques on the skin indicates their good blood supply. Possible causes of this condition may be the following nosologies:
Brown plaques occur when melanin is deposited in the affected area of the dermis, which causes a brown (dark) color. Possible causes may be the following diseases:
Which doctors to contact
With the formation of plaques on the skin, it is necessary to contact a dermatologist to determine the causes of the appearance of this element of the rash.
Plaque diagnostics and examinations
For the diagnosis of fungal skin lesions, scraping from the affected area is used for subsequent microscopic examination.
The development of an allergic reaction requires seeking medical help to identify the allergen, prescribing antihistamines, and sometimes hormonal drugs. In clinical cases of allergy, along with skin tests, analyzes are performed using various sets of common allergens and triggers: a panel for respiratory allergens, for food allergens, and for a combination of both. nine0031
Respiratory Panel
Synonyms: Comprehensive Respiratory Allergen Test Panel; Respiratory allergens panel, Allergen respiratory profile, Allergy testing. Brief description of the study "Panel respira...
Brief description of the study "Panel respira...
Up to 5 business days
Available with house call
5 515 RUB nine0013
In garbage
Food Panel, IgE
Food Allergen Panel: hazelnut, peanut, Walnut, almond, cow's milk, egg white, egg ...
Up to 5 working days
Available with house call
5 515 RUB
In garbage
Food and Respiratory Panel
Panel different allergens: A mixture of grass allergens: fragrant spikelet; perennial rye; timothy; rye cultivated; Woolly buckthorn (GP3) IgE . .. nine0013
.. nine0013
Up to 5 business days
Available with house call
5 515 RUB
In garbage
In psoriasis, seeing a dermatologist and a rheumatologist can help reduce the symptoms of the disease if appropriate therapy is prescribed. For the diagnosis, it is usually sufficient to examine, determine, the skin manifestations of psoriasis are so characteristic, but if necessary, a differential diagnosis is carried out, including a clinical blood test, feces for the presence of worm eggs and protozoa, and a histological examination of the skin. nine0013
Clinical blood test: general analysis, leukoformula, ESR (with microscopy of a blood smear in the presence of pathological changes)
Synonyms: Complete blood count, UAC. Full blood count, FBC, Complete blood count (CBC) with differential white blood cell count (CBC with diff), Hemogram. Brief description of the study CBC: general...
Full blood count, FBC, Complete blood count (CBC) with differential white blood cell count (CBC with diff), Hemogram. Brief description of the study CBC: general...
Up to 1 working day
Available with house call
RUB 810
In garbage
Fecal test for helminth eggs
Synonyms: Feces on worm eggs; Analysis of feces for eggs of worms. Ova and Parasite Exam; O&P; Stool O&P test. Brief description of the study "Analysis of feces for eggs of helminths&ra...
Up to 1 business day
Available with house call
RUB 570
In garbage
Fecal analysis for protozoa (PRO stool)
Synonyms: Analysis of faeces for protozoa. Parasite Exam, feces; Parasitic Examination, fecal. Brief description of the study "Analysis of feces for protozoa" Fecal analysis for ...
Parasite Exam, feces; Parasitic Examination, fecal. Brief description of the study "Analysis of feces for protozoa" Fecal analysis for ...
Up to 1 working day
Available with house call
RUB 570
In garbage
Histological examination of biopsy material and material obtained during surgical interventions (endoscopic material; tissues of the female reproductive system; skin, soft tissues; hematopoietic and lymphoid tissue; bone and cartilage tissue)
Taking biomaterial is paid separately. According to the requirements of clause 17 of the Rules for conducting pathological and anatomical studies, approved. Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia. ..
..
Up to 5 business days
Available with house call
2 880 RUB
In garbage nine0013
Diseases of the stomach and intestines can also lead to plaque formation on the skin. To identify the pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, it is enough to refer to therapist or gastroenterologist, conduct a number of endoscopic examinations (gastroscopy, and, if necessary, colonoscopy), ultrasound of the abdominal organs, perform some screening blood tests for diseases of the liver, intestines, stomach.
Gastroscopy
Examination of the mucosa of the upper gastrointestinal tract with the possibility of biopsy or endoscopic removal of small pathological ...
RUB 4,440 Sign up
Colonoscopy
Endoscopic examination of the colon to look for abnormalities, perform biopsies, and remove small polyps and tumors.
RUB 5,740 Sign up
Comprehensive ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs (liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen)
Scanning of the internal organs of the abdominal cavity to assess its functional state and the presence of pathology.
RUB 2,890 Sign up
Liver function tests: screening
Up to 1 business day
Available with house call
RUB 1,935
In garbage
Diagnosis of celiac disease: intolerance to cereal proteins (gluten)
Up to 8 working days
Available with house call
7 520 RUB nine0013
In garbage
Gastropanel
Up to 9 working days
Available with house call
RUB 4,760
In garbage
To clarify the diagnosis of keratoma, a skin biopsy is performed and epithelium scraping is performed, followed by microscopic and histochemical examination. nine0013
nine0013
Histological examination of biopsy material and material obtained during surgical interventions (endoscopic material; tissues of the female reproductive system; skin, soft tissues; hematopoietic and lymphoid tissue; bone and cartilage tissue)
Taking biomaterial is paid separately. According to the requirements of clause 17 of the Rules for conducting pathological and anatomical studies, approved. Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia...
Up to 5 working days
Available with house call
2 880 RUB
In garbage
Examination of scrapings and impressions of tumors and tumor-like formations
Material for research.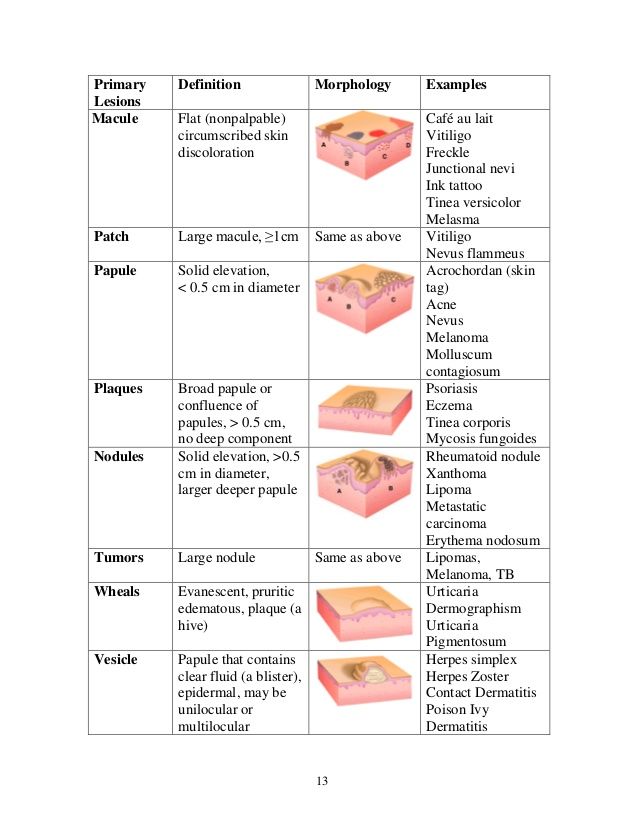 Imprints and scrapings are obtained from pathological lesions of the skin and mucous membranes (except for the cervix and cervical canal). Relative to test...
Imprints and scrapings are obtained from pathological lesions of the skin and mucous membranes (except for the cervix and cervical canal). Relative to test...
Up to 2 working days
Available with house call
RUB 1,030
In garbage
If atypical cells are detected in scrapings or biopsies, immediately contact oncologist.
If xanthoma appears on the skin, it is recommended to consult a cardiologist, take blood tests for lipid profile and blood glucose levels, and screen for diabetes. nine0013
Lipid profile screening
Up to 1 working day
Available with house call
RUB 1,355
In garbage
Glucose (in the blood) (Glucose)
Research material Serum or blood plasma.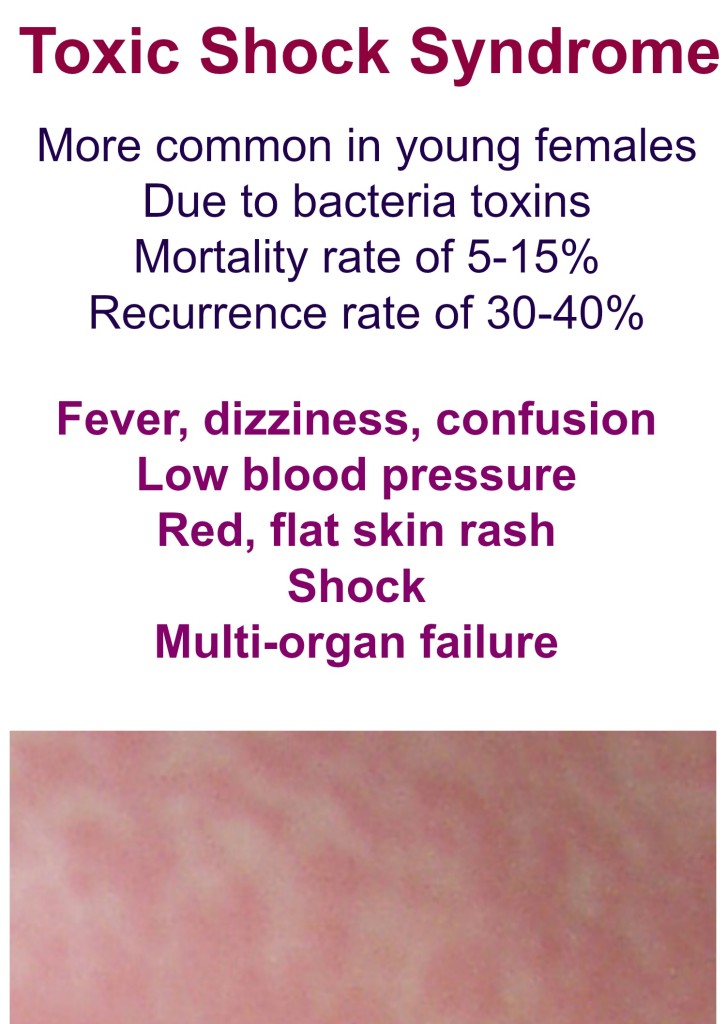 If it is not possible to centrifuge the sample 30 minutes after collection for serum/plasma separation...
If it is not possible to centrifuge the sample 30 minutes after collection for serum/plasma separation...
Up to 1 working day
Available with house call
335 RUB
In garbage
Diabetes management: advanced
Up to 1 working day
Available with house call
RUB 5 820
In garbage
What should I do if plaque appears on the skin?
Any newly appeared neoplasms should be shown to a dermatologist. Their cosmetic removal without prior consultation with a specialist is fraught with serious consequences.
Their cosmetic removal without prior consultation with a specialist is fraught with serious consequences.
In addition, there are symptoms that require immediate medical attention:
Plaque treatment
When plaques of an allergic nature appear on the skin, antihistamines are prescribed, in cases of a severe course of the disease, glucocorticosteroids. In addition, it is important to follow a hypoallergenic diet.
In addition, it is important to follow a hypoallergenic diet.
Mycotic plaques require antifungal drugs, both local (ointments, creams) and systemic (tablets). Taking these drugs is associated with a high risk of side effects, and therefore it is possible only after consulting a doctor, accurate verification of the diagnosis and confirmation of the etiology of the disease. nine0013
Treatment of psoriasis is multi-stage and complex, it involves constant monitoring by a rheumatologist, taking cytostatics and other drugs, using ointments and shampoos to improve skin condition, using antihistamines to reduce itching, including physiotherapy and a hypoallergenic diet in the treatment regimen.
When confirming the presence of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, properly selected therapy can stop the appearance of new plaques on the skin, as well as prevent the development of complications of the underlying disease. nine0013
Sources:
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor.
For a correct assessment of the results of your analyzes in dynamics, it is preferable to do studies in the same laboratory, since different laboratories may use different research methods and units of measurement to perform the same analyzes. nine0013
nine0013
Recommendations
Show more
Fungus
Gastritis
nine0012 HIVSeborrhea
Psoriasis
Avitaminosis
Rosacea
Dermatitis
Oily hair
Oily hair: causes, diseases, diagnosis and treatment.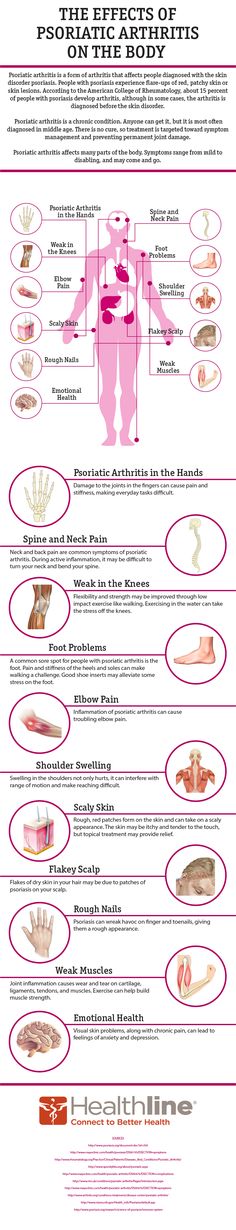
More
Gastritis
Diarrhea
Flatulence
Dysbacteriosis
Allergy
Worms
Ascites
Bloating
In most cases, bloating is associated with flatulence - excessive accumulation of gases in the intestines. Bloating (enlargement) of the abdomen can be due to various reasons. nine0013
More
Atherosclerosis
Iron deficiency
Diabetes mellitus
Fungus
Calf hair reduction
Reducing the amount of hair on the legs: the causes of occurrence, in what diseases it occurs, diagnosis and methods of treatment.
More
Atherosclerosis
Diabetes mellitus
Fungus
nine0026 Hemorrhage in the eyeHemorrhage in the eye: causes, in which diseases it occurs, diagnosis and methods of treatment.
More
Fungus
Diarrhea
Vomiting
nine0012 UlcerGreen feces
Green feces: causes, diseases, diagnosis and treatment.
More
Nothing found
Try editing your query or select a doctor or service from the list.
Doctor not found
Try changing your query or select doctor from the list
Medical office not found
Try changing the query or select medical office from the list
Therapist Traumatologist-orthopedist Endocrinologist Urologist Gynecologist Ultrasound doctor Cardiologist Pediatrician
Nothing found
Please try editing your query
Thank you!
You have successfully made an appointment
Detailed information has been sent to your e-mail
reasons for the appearance of spots on the legs, head, hands
Publication: 09/13/2022 Change: 09/19/2022
Many doctors consider the skin to be an indicator of health, as it signals the onset of pathological processes within the body. Therefore, even such a common symptom as red spots indicates various diseases. Possible causes include skin diseases, allergic reactions, infectious pathologies or autoimmune processes. However, in some cases, red spots on the skin can be a cosmetic defect, which is why it is so important to understand the causes of the appearance and choose the right method of treatment. nine0013
Therefore, even such a common symptom as red spots indicates various diseases. Possible causes include skin diseases, allergic reactions, infectious pathologies or autoimmune processes. However, in some cases, red spots on the skin can be a cosmetic defect, which is why it is so important to understand the causes of the appearance and choose the right method of treatment. nine0013
Author:
Ibraev Anatoly Tomasovich
Head of the Department of Cosmetology and Laser Technologies. Dermatologist-cosmetologistImportant!
The information in this article should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. For staging correct diagnosis and treatment should always consult a doctor. nine0013
Types of red spots on the skin
A macula or macula is a localized discoloration of the skin that is either inflammatory or non-inflammatory in nature:
A cosmetic defect in the form of red spots occurs in people of any gender and age, often spots are found even in infants. At the same time, such rashes have a different appearance: they differ not only in shape, size and quantity, but also in shade. Conditionally red spots are divided into the following groups:
Conditionally red spots are divided into the following groups:
The localization of spots also differs. In rare cases, they appear on almost all parts of the body. More often you can find an option when the rashes are concentrated on a separate area: face, neck, arms, back, genitals.
Symptoms and causes
We have already noted that there are a huge number of possible reasons for the appearance of such formations. More often we are talking about the development of skin or infectious diseases, but sometimes spots are the result of mental disorders or other malfunctions in the body. The following factors can provoke the appearance of rashes:0013
Because there are many causes for red rashes, symptoms will vary from case to case. Spots can be all over the body or only in certain areas, itching, burning or peeling are additionally manifested, but sometimes they may not be. It is impossible to talk about the presence of a single clinical picture, so a separate diagnosis will be required.
If we talk about the most common conditions that provoke the appearance of red spots, then it is worth highlighting the following pathologies:
Allergy . The external manifestation of this problem is itchy reddish spots of various sizes and shapes. Their appearance is accompanied by swelling and peeling of the skin. Some patients experience general malaise, weakness, chills. As a rule, symptoms appear immediately after contact with the allergen: they can be certain products, cosmetics, medicines, plants. In rare cases, the appearance of rashes is associated with exposure to low temperatures. nine0013
Their appearance is accompanied by swelling and peeling of the skin. Some patients experience general malaise, weakness, chills. As a rule, symptoms appear immediately after contact with the allergen: they can be certain products, cosmetics, medicines, plants. In rare cases, the appearance of rashes is associated with exposure to low temperatures. nine0013
Allergies often show up as pink patches where skin contacts clothing, which may indicate the use of inappropriate detergent or personal care products.
Rubella . Red small spots on the skin can be the result of rubella measles. They occur throughout the body, but the maximum localization is noted on the back, face and neck. As a rule, the formations disappear within a few days, but only with treatment.
nine0012 Scarlet fever . This infectious disease is caused by group A streptococcus. One of the symptoms of the disease is small spots all over the body, the size of which does not exceed a few millimeters. Rashes appear after the onset of a sore throat, more often located on the lower abdomen or in the groin area. The skin appears reddened and inflamed.
Rashes appear after the onset of a sore throat, more often located on the lower abdomen or in the groin area. The skin appears reddened and inflamed. Pityriasis rosea Gibert . This pathology is most often encountered by patients with weakened immunity. For this reason, the risk of disease in spring and autumn increases significantly. Lichen may appear as pink, reddish or crimson spots up to 5 cm in diameter. Outwardly, such formations resemble plaques. First, one spot appears, after 5–7 days, others, smaller in size, are found near it. At the same time, peeling of the skin may appear, less often - swelling of the tissues is observed. nine0013
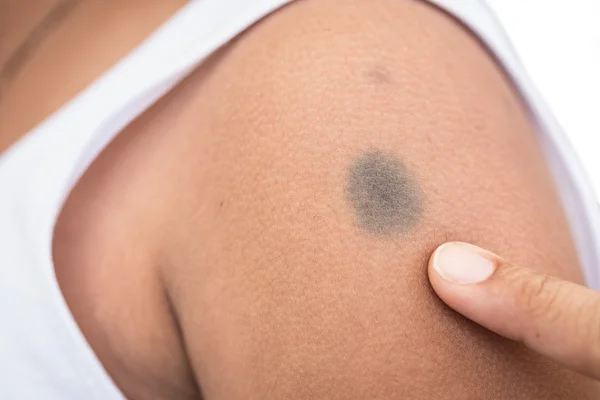
Erythema . This condition is characterized by reddening of the skin, which occurs after the activation of blood circulation and the expansion of capillaries. As a rule, this is the result of heavy physical exertion or excitement. Often, redness is observed on the face after massage, peeling or masks. The spots are relatively large, but do not require treatment, as they quickly disappear on their own.
Less common is persistent erythema, characterized by extensive areas of redness resembling bruising or bruising. Such a problem can lead to the development of rosacea, therefore, it requires an examination and consultation with a dermatologist. nine0013
Urticaria . A fairly common cause of skin rashes, which is often characterized by a long course. Under the urticaria understand a whole group of diseases that lead to the formation of angioedema and blisters. Urticaria can result from medications, certain foods, and supplements. In rare cases, pathology occurs as a result of infections.
Chicken pox . Chickenpox is infectious and can be dangerous to health. This pathology is complicated by pustular lesions, stomatitis and conjunctivitis, in rare cases, damage to internal organs and the brain occurs. nine0013
Chicken pox is one of the common causes of red spots on the skin. As a rule, the rashes are small, localized throughout the body. Further, bubbles up to 5 mm in diameter are formed, which after 2–3 days become covered with a dry crust. Both spots and vesicles can be present on the skin at the same time.
Both spots and vesicles can be present on the skin at the same time.
Ringworm . This is a pathology of fungal origin, which is known in dermatology under the term "microsporia". The causative agent of pathology is a fungus of the genus Microsporum, which parasitizes in the stratum corneum of the epidermis. It is because of it that the skin is covered with rounded spots that have a non-uniform color: the center is lighter, while the edges of the formation may have a bright red tint. As a rule, rashes are found on the head, arms and legs. nine0013
Pityriasis versicolor . Another type of infectious disease that leads to damage to the upper layers of the skin. However, this form of the disease is not contagious and rarely leads to serious consequences, but it is characterized by fairly large lesions. Pathology occurs as a result of some autoimmune disorders, excessive sweating, hormonal problems, etc.
Eczema . This inflammatory skin disease has an allergic nature, but the causes and prerequisites for its development are still not fully understood. Often the disease is called "weeping lichen" due to the presence of characteristic symptoms. nine0013
Often the disease is called "weeping lichen" due to the presence of characteristic symptoms. nine0013
Initially, inflamed areas appear on the skin in the form of red spots, which gradually merge into a separate affected area. After that, characteristic nodules with a bright red color and clear boundaries are formed. Bubbles quickly open, which leads to the appearance of point erosions, which are replaced by crusts and peeling.
Photodermatitis . The reason for the development of such a pathology is the increased sensitivity of the epidermis to ultraviolet radiation. As a result, persistent redness of the skin appears, which can be accompanied by itching, burning, and even blisters. Often there are large red spots on the skin. It should be noted that the symptoms of the condition are very similar to a number of dermatological diseases (for example, in many patients, photodermatitis has all the signs of systemic lupus erythematosus), which complicates the diagnostic process.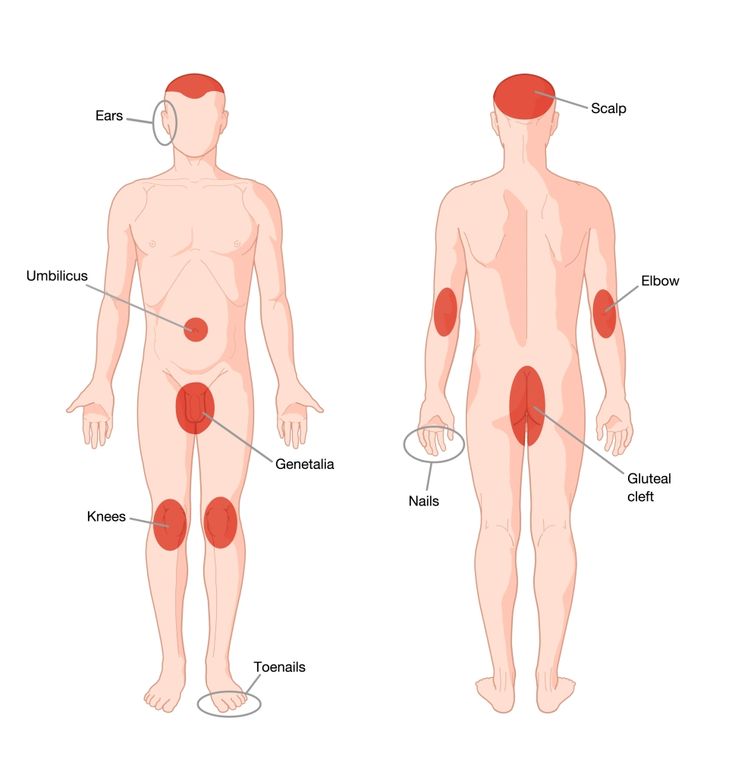 nine0013
nine0013
Important!
The information in this article should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. For staging correct diagnosis and treatment should always consult a doctor.
Psoriasis . One of the most common dermatological diseases is psoriasis. Pathology has an autoimmune origin, the causes of its development can be infectious, psychosomatic, hereditary or mixed. nine0013
Characteristic raised spots with a smooth surface appear on the skin. After a few days, they become covered with white scales, itching occurs. Many patients note dryness and flaking of the skin, and cracks and blisters are also found in advanced cases.
Atopic dermatitis . This chronic inflammatory disease is confused with eczema, although there are a number of differences between the pathologies. AtD is characterized by the appearance of red spots with peeling on various parts of the body. Most often, rashes are localized on the bend of the elbow and knee joints, neck and face. nine0013
nine0013
As a rule, pathology occurs in childhood and its appearance is facilitated by a whole range of factors (both external and genetic). In half of the cases, atopic dermatitis disappears over time, in the remaining patients it persists and recurs throughout life.
Helminthiases . One of the causes of red rashes is exposure to toxic substances that are released during the life of parasites. The size and location of the formations vary depending on the degree of intoxication of the body. As a rule, a rash appears first, which is accompanied by itching and skin irritation. In the future, purulent boils may appear. nine0013
Fungal mycosis . A fairly serious disease, a malignant lymphoid lesion, which is characterized by the appearance of red dry plaques (that is, large-sized elements that rise above the surface of the skin). Outwardly, the formations resemble eczema, but have a rounded shape and clear boundaries.
Hyperhidrosis .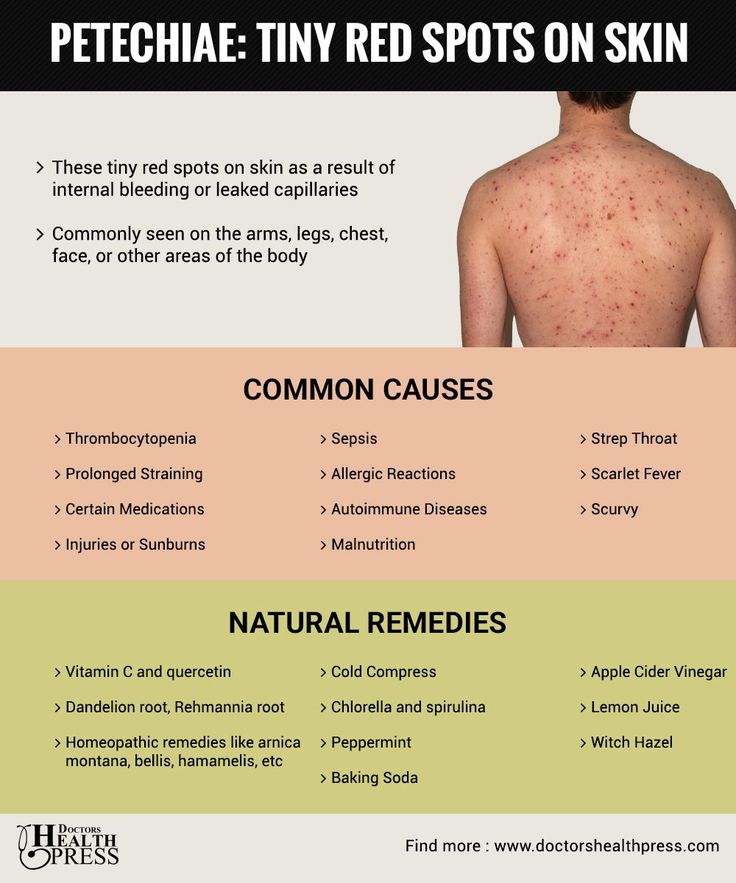 An unobvious cause of red round spots on the skin is hyperhidrosis. This is a functional disorder of sweating, characterized by the release of an increased amount of sweat. As a result of this, redness appears in the armpits and in other areas that are affected by the pathology. nine0013
An unobvious cause of red round spots on the skin is hyperhidrosis. This is a functional disorder of sweating, characterized by the release of an increased amount of sweat. As a result of this, redness appears in the armpits and in other areas that are affected by the pathology. nine0013
Emotional experiences . As a result of psychological disorders and excitement, characteristic redness periodically appears on the neck and face. This problem is the result of depression, emotional overload, chronic lack of sleep. In rare cases, the problem is accompanied by itching, swelling and peeling.
Diagnostic methods
In the event that a red spot appears on the skin that does not go away within a few days or changes its shape / appearance, it is better to seek the advice of a dermatologist. Such a measure will not be superfluous, as it will identify the causes of rashes and exclude serious pathologies. The presence of the following symptoms should alert:
To determine the nature and characteristics of the formations, the doctor performs an examination using a dermatoscope. Of key importance is the collection of anamnesis, clarification of symptoms, identification of concomitant diseases. After the examination, the specialist appoints the patient a number of additional studies, among which may be:
If necessary, the patient is assigned a consultation with other specialists: for example, a therapist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, etc. As a result of such an examination, it will be possible to identify comorbidities and determine which diseases provoked red spots on the skin. nine0013
nine0013
Differential diagnosis is important at this stage, since sometimes rashes in various pathologies can be identical. That is why it is required to exclude the presence of other diseases and allergic reactions.
Already during the examination, the doctor may suspect the presence of a particular pathology. The existing symptoms and the appearance of the spots are taken into account. For example:
Methods of treatment
Treatment of the problem is individual, since when drawing up the scheme, the doctor takes into account the patient's health status, identified pathologies and the presence of symptoms. An integrated approach is always used for the treatment of spots, which includes various conservative methods:
Radical removal procedures are required in rare cases. During treatment, the patient may need to adjust the diet and avoid interaction with allergens. At the same time, in most cases, the use of traditional medicine is unacceptable, since they aggravate the course of the disease and lead to the development of a chronic process. nine0013
nine0013
Different groups of drugs are used for drug therapy. Most often it is:
As for radical methods of treatment, they include electrocoagulation, laser removal and cryosurgery (exposure to liquid nitrogen). Such procedures are used in cases where conservative treatment did not bring relief to the patient or cosmetic defects remained after the therapy. nine0013
nine0013
If we talk about the prevention of red spots, then there are no universal recommendations, since it is always necessary to take into account the cause of the pathology. In order to reduce the likelihood of rashes, it is best to exclude contact with stray animals, refuse products that cause allergies, and regularly undergo preventive examinations with doctors. This will allow early detection of any disturbances in the functioning of the immune system and prevent possible diseases of the internal organs. nine0013