First trimester sick all day
Severe Morning Sickness (Hyperemesis Gravidarum) (for Parents)
What's Morning Sickness?
During the first trimester of pregnancy, many women have the bouts of nausea and vomiting known as morning sickness.
Despite its name, morning sickness can happen day or night. It usually starts around the 6th week of pregnancy, is at its worst around week 9, and stops by weeks 16 to 18. Although unpleasant, morning sickness is considered a normal part of a healthy pregnancy.
What’s Severe Morning Sickness?
Severe morning sickness is when nausea and vomiting get so serious that a pregnant woman vomits several times a day, loses weight, and gets dehydrated or is at risk for dehydration.
If this rare pregnancy-related condition isn’t treated, it can affect a woman's health and her baby's ability to thrive.
The medical term for severe morning sickness is "hyperemesis gravidarum" (hi-per-EM-eh-sis grav-ih-DARE-um), which means "excessive vomiting during pregnancy. " It usually follows a similar timeline to normal morning sickness. But it can go longer, sometimes lasting for the whole pregnancy. Often, the symptoms get less severe as the pregnancy continues.
Most cases of hyperemesis gravidarum affect a woman's first pregnancy. But women who have it in one pregnancy are more likely to have it in future pregnancies.
What Causes Severe Morning Sickness?
The cause of severe morning sickness isn’t known. But it might be related to the hormone changes of pregnancy. A hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin, or HCG, might be to blame because severe morning sickness most often happens when HCG levels are at their highest in a pregnant woman's body.
Severe morning sickness also might run in families. It’s more common in women whose close family members (such as mothers and sisters) have had it.
Other things that can increase a woman's chances of having severe morning sickness include:
- carrying multiples (twins, triplets, etc.
 )
) - history of motion sickness
- migraine headaches with nausea or vomiting
What Problems Can Happen?
The nausea and vomiting that happen in severe morning sickness are so extreme that they can harm the mother and the baby. Not being able to keep down food makes it hard for the mom to meet her nutritional needs. So she might lose weight. And a loss of fluids, combined with the loss of stomach acid from vomiting, can cause dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
If severe morning sickness isn’t treated, it can cause many problems, including organ failure and the early birth of her baby.
When Should I Call the Doctor?
Call the doctor right away if you’re pregnant and have any of these symptoms:
- nausea that lasts throughout the day, making it impossible to eat or drink
- vomiting three to four times per day or not being to keep anything in the stomach
- brownish vomit or vomit with blood or streaks of blood in it
- weight loss
- fainting or dizziness
- peeing less than usual
- a fast heart rate
- a lot of headaches
- unpleasant, fruity mouth or body odor
- extreme tiredness
- confusion
How Is Severe Morning Sickness Treated?
Treatments used for morning sickness, such as eating dry crackers in the morning or a bland diet, may be recommended for women with extreme morning sickness. But these might not help with severe symptoms.
But these might not help with severe symptoms.
Medical treatment can include:
- a short period of not eating to rest the gastrointestinal system
- intravenous (IV) fluids
- vitamin and nutritional supplements
Some women might get medicine to stop the vomiting, either by mouth or through an IV. The doctor might recommend eating foods with ginger or taking vitamin B6 supplements to help ease nausea. It can also help to:
- Eat a bland diet.
- Eat frequent small meals.
- Drink plenty of liquids when not feeling nauseated.
- Avoid spicy and fatty foods.
- Eat high-protein snacks.
- Avoid sensory stimuli that can act as triggers (like specific smells or noises).
If a woman feels anxious or depressed about her condition, talking to a therapist or counselor might help her cope with her feelings.
What Else Should I Know?
With treatment, women with severe morning sickness can feel better and get the nourishment they need so they and their babies thrive. And lifestyle changes can help ease nausea and vomiting and make the pregnancy more enjoyable.
And lifestyle changes can help ease nausea and vomiting and make the pregnancy more enjoyable.
With time, symptoms usually do improve. And, of course, they stop by the time a woman's next journey starts: parenthood.
Vomiting and morning sickness - NHS
Nausea and vomiting in pregnancy, often known as morning sickness, is very common in early pregnancy.
It can affect you at any time of the day or night or you may feel sick all day long.
Morning sickness is unpleasant, and can significantly affect your day-to-day life. But it usually clears up by weeks 16 to 20 of your pregnancy and does not put your baby at any increased risk.
There is a chance of developing a severe form of pregnancy sickness called hyperemesis gravidarum. This can be serious, and there's a chance you may not get enough fluids in your body (dehydration) or not get enough nutrients from your diet (malnourishment). You may need specialist treatment, sometimes in hospital.
You may need specialist treatment, sometimes in hospital.
Sometimes urinary tract infections (UTIs) can also cause nausea and vomiting. A UTI usually affects the bladder, but can spread to the kidneys.
Non-urgent advice: Call your midwife, GP or 111 if:
you're vomiting and:
- have very dark-coloured urine or have not had a pee in more than 8 hours
- are unable to keep food or fluids down for 24 hours
- feel severely weak, dizzy or faint when standing up
- have tummy (abdominal) pain
- have a high temperature
- vomit blood
- have lost weight
Treatments for morning sickness
Unfortunately, there's no hard and fast treatment that will work for everyone’s morning sickness. Every pregnancy will be different.
Every pregnancy will be different.
But there are some changes you can make to your diet and daily life to try to ease the symptoms.
If these do not work for you or you're having more severe symptoms, your doctor or midwife might recommend medicine.
Things you can try yourself
If your morning sickness is not too bad, your GP or midwife will initially recommend you try some lifestyle changes:
- get plenty of rest (tiredness can make nausea worse)
- avoid foods or smells that make you feel sick
- eat something like dry toast or a plain biscuit before you get out of bed
- eat small, frequent meals of plain foods that are high in carbohydrate and low in fat (such as bread, rice, crackers and pasta)
- eat cold foods rather than hot ones if the smell of hot meals makes you feel sick
- drink plenty of fluids, such as water (sipping them little and often may help prevent vomiting)
- eat foods or drinks containing ginger – there's some evidence ginger may help reduce nausea and vomiting (check with your pharmacist before taking ginger supplements during pregnancy)
- try acupressure – there's some evidence that putting pressure on your wrist, using a special band or bracelet on your forearm, may help relieve the symptoms
Find out more about vitamins and supplements in pregnancy
Anti-sickness medicine
If your nausea and vomiting is severe and does not improve after trying the above lifestyle changes, your GP may recommend a short-term course of an anti-sickness medicine, called an antiemetic, that's safe to use in pregnancy.
Often this will be a type of antihistamine, which are usually used to treat allergies but also work as medicines to stop sickness (antiemetic).
Antiemetics will usually be given as tablets for you to swallow.
But if you cannot keep these down, your doctor may suggest an injection or a type of medicine that's inserted into your bottom (suppository).
See your GP if you'd like to talk about getting anti-sickness medication.
Risk factors for morning sickness
It's thought hormonal changes in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy are probably one of the causes of morning sickness.
But you may be more at risk of it if:
- you're having twins or more
- you had severe sickness and vomiting in a previous pregnancy
- you tend to get motion sickness (for example, car sick)
- you have a history of migraine headaches
- morning sickness runs in the family
- you used to feel sick when taking contraceptives containing oestrogen
- it's your first pregnancy
- you're obese (your BMI is 30 or more)
- you're experiencing stress
Visit the pregnancy sickness support site for tips for you and your partner on dealing with morning sickness.
Find maternity services near you
Sign up for pregnancy emails
Sign up for Start4Life's weekly emails for expert advice, videos and tips on pregnancy, birth and beyond.
Video: how can I cope with morning sickness?
In this video, a midwife gives advice on how to deal with morning sickness during your pregnancy.
Media last reviewed: 27 February 2017
Media review due: 27 March 2020
Page last reviewed: 13 April 2021
Next review due: 13 April 2024
Critical stages of pregnancy - why are they dangerous?
Services
Virtual tour. Clinic "ARNIKA"
The wonderful period of waiting for a baby for almost every woman is far from serene: how many anxieties, worries and doubts arise in expectant mothers at this time - they simply cannot be counted. In most cases, all fears are in vain - the baby develops and grows safely. However, it must be remembered that there are also so-called critical periods of pregnancy, when inattention to oneself and one's body can lead to a disastrous result - its spontaneous termination.
In most cases, all fears are in vain - the baby develops and grows safely. However, it must be remembered that there are also so-called critical periods of pregnancy, when inattention to oneself and one's body can lead to a disastrous result - its spontaneous termination.
First trimester
The beginning of a new life in a woman's body, or 2-3 weeks of pregnancy, is considered the first critical period. This is due to the fact that the egg can be fertilized, but due to changes as a result of inflammation, hormonal imbalances, the presence of nodes, scars, fibroids or synechia on the inner mucous membrane of the uterus, implantation does not occur, the embryo dies and is removed from the mother's body during menses. However, even if implantation has occurred, the embryo may stop developing and early miscarriage , and the main reason for this course of events is chromosomal abnormalities.
The second critical period of the first trimester begins at 8 and ends at 12 weeks of gestation. At this time, the main cause of interruption is considered to be hormonal deficiency, which disrupts the process of placental formation. This condition may be associated with reduced work of the corpus luteum of the ovaries, excessive production of androgens by the adrenal glands - male sex hormones, as well as malfunctions of the pituitary gland or thyroid gland. The threat of abortion can be eliminated with the help of properly selected and timely prescribed hormonal treatment, which will allow the baby to safely reach the due date.
At this time, the main cause of interruption is considered to be hormonal deficiency, which disrupts the process of placental formation. This condition may be associated with reduced work of the corpus luteum of the ovaries, excessive production of androgens by the adrenal glands - male sex hormones, as well as malfunctions of the pituitary gland or thyroid gland. The threat of abortion can be eliminated with the help of properly selected and timely prescribed hormonal treatment, which will allow the baby to safely reach the due date.
In addition, throughout the first trimester of pregnancy, the fetus may stop developing due to the following adverse environmental factors:
- harmful working conditions
- bad habits
- physical effects - radiation, vibration, intense sports training, etc.
- acute infectious diseases (influenza, cytomegalovirus, herpes, rubella and others)
- severe stressful situations
And even if the fetus develops further, the negative impact of most of these factors may appear after a few months of pregnancy or even after the baby is born: these may be anatomical disorders or severe malformations. Therefore, the entire first trimester of the development of a new life can be considered "critical".
Therefore, the entire first trimester of the development of a new life can be considered "critical".
Second trimester
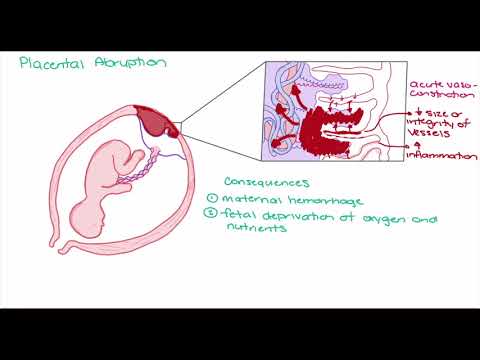
The third critical period of pregnancy occurs at 18-24 weeks of gestation and is largely associated with the active growth of the uterus. At this time, spontaneous interruption most often occurs due to isthmic-cervical insufficiency (ICI), as a result of which the fetal egg descends under the influence of gravity, loses its integrity and triggers the mechanism of labor activity. However, shortening and expansion of the cervical canal, detected in time, allows suturing the cervix or installing an obstetric pessary and safely prolonging the pregnancy. Here we should also remember about infectious diseases, including intrauterine infection, which can disrupt the functions of the placenta, lead to the outflow of water from the fetal bladder and late miscarriage.
Another common reason for interrupting the process of bearing a fetus at this time is placenta previa or its low location: for various reasons, it can exfoliate, cause severe bleeding and death of the fetus. In addition, at this time, pregnancy may stop developing due to violations in the development of the brain and the most important functional systems of the baby, caused by the harmful effects of various negative factors on them in the first trimester.
In addition, at this time, pregnancy may stop developing due to violations in the development of the brain and the most important functional systems of the baby, caused by the harmful effects of various negative factors on them in the first trimester.
Third trimester
In this trimester - at 28-32 weeks - the fourth critical period takes place. The threat of premature birth may occur due to insufficiency of the placenta, its premature detachment, severe forms of late toxicosis of pregnant women, ICI and various hormonal disorders. In addition, due to the overdistension of the uterus, most multiple pregnancies end at this time. Children born during this period are already viable, but they need long-term qualified medical care.
In addition to all the periods listed above, the critical periods for women who have had reproductive losses in the past are the days of planned menstruation, miscarriages or "fading" pregnancies. Doctors believe that during these periods the body can “remember” the need for hormonal changes, so they carefully monitor the condition of the expectant mother and baby and prescribe treatment in a timely manner if any threat arises.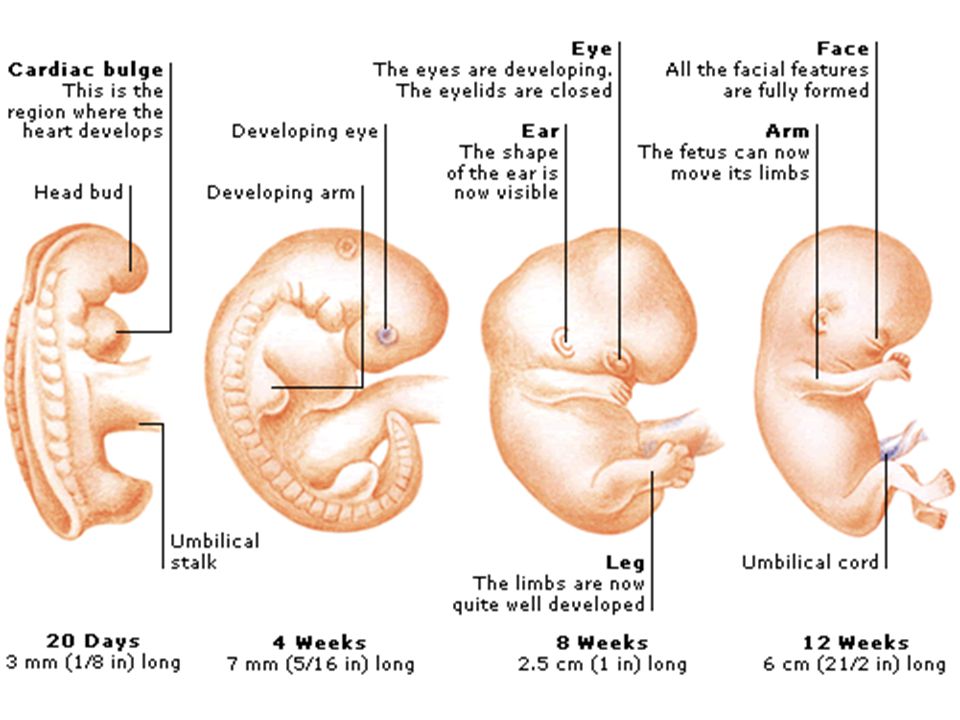
In order to safely overcome the dangerous periods of pregnancy , it is necessary to avoid any physical exertion, stress, and, if necessary, visit a doctor when these dates are approaching. In addition, if you experience pain, bleeding or other warning signs, you should also seek medical attention as soon as possible. Only an attentive attitude to oneself will help to safely endure a healthy baby and give birth to him at the time set by nature.
Take care of yourself and your baby!
Early pregnancy | Shchelkovsky perinatal center
Pregnancy is a wonderful period! However, the changes taking place in the body at this time can greatly frighten you. The phenomena characteristic of pregnancy are different for all women, and will not necessarily be repeated during each subsequent gestation. Let's analyze the most common symptoms, their causes and possible methods of correction.
1. Frequent urination.
Frequent urination.
Frequent, painless (!) urge to urinate is one of the signs of pregnancy. This is due to increased secretion of progesterone (pregnancy hormone), changes in metabolism and pressure from the growing uterus on the bladder.
Be sure to see a doctor if:
- urination is painful (this may be a sign of an infection)
- urine of strange color (stained with blood, brown)
- the amount of urine excreted per day is much less than the liquid drunk per day
Life hack! Under no circumstances should fluid intake be restricted! To alleviate the condition and reduce the frequent urge to urinate, it is necessary to exclude products that have a diuretic effect: tea, coffee, zucchini, watermelon; as well as salty, spicy and fried foods. It is better to drink water or juice. Wear comfortable cotton underwear that does not squeeze the lower abdomen.
2. Nausea, vomiting, heartburn, increased susceptibility to smells.
Nausea is one of the common symptoms of early pregnancy. The range of issues related to nausea and vomiting during pregnancy is quite wide. From "it's good, I don't even feel sick" (with relief), "I don't feel sick, what's wrong with me?" (with anxiety) to "when will this nausea pass" (with hope). Indeed, these symptoms are not at all a mandatory accompaniment of gestation, they can manifest at 7-8 weeks and last up to 12-14 weeks. The duration of this condition can sometimes be delayed, but rarely persists throughout pregnancy.
Life hack! For nausea, eat before feeling hungry. Solid, non-hot food and drinks at a cool temperature are best. With heartburn, you should eat small portions of food and often, and most importantly, sit, stand or walk for at least 30 minutes after eating, but do not lie down.
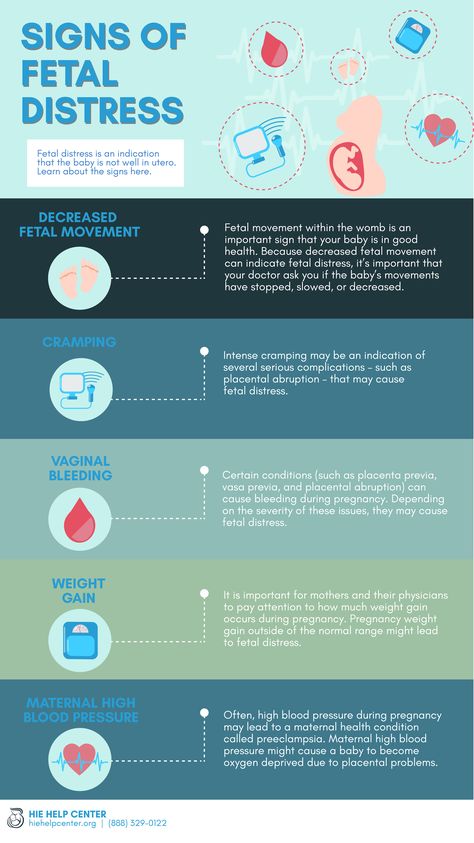
You should definitely consult a doctor if:
- vomiting occurs even after drinking water
- vomiting is exhausting, accompanied by dizziness, weakness
- dryness, jaundice and flaking of the skin appear
- Nausea and vomiting interfere with proper nutrition, accompanied by weight loss
To reduce nausea and vomiting in the morning, try eating something before you get out of bed. It can be a cracker, a cookie, a piece of hard cheese. And salty food is preferable to sweet. You can have a snack in the same way at night when you get up to go to the toilet. Do not lie down immediately after eating, this will only increase nausea. Vitamins for pregnant women with nausea should be taken in the evening after meals. Cool water with lemon, ginger, mint tea, or ginger or mint candies can alleviate the condition. It is necessary to exclude those foods, drinks and smells that are unpleasant to you. Brushing your teeth and rinsing your mouth often can also reduce nausea.
It can be a cracker, a cookie, a piece of hard cheese. And salty food is preferable to sweet. You can have a snack in the same way at night when you get up to go to the toilet. Do not lie down immediately after eating, this will only increase nausea. Vitamins for pregnant women with nausea should be taken in the evening after meals. Cool water with lemon, ginger, mint tea, or ginger or mint candies can alleviate the condition. It is necessary to exclude those foods, drinks and smells that are unpleasant to you. Brushing your teeth and rinsing your mouth often can also reduce nausea.
3. Pain or cramps in the lower abdomen, constipation, pain in the lumbar region.
The simplest and most easily controlled cause of pain is delayed and incomplete bowel movements. An increase in the concentration of progesterone relaxes the smooth muscles, which are located not only in the uterus, but also in other hollow organs. In this case, the correction of the diet and the restoration of the passage of feces will help. If the measures are ineffective, the doctor may prescribe safe drugs for you. A special type of pain that occurs during exclusivity in pregnant women is pain in the round ligament of the uterus. This acute, rather intense pain occurs, as a rule, on the one hand with a sharp change in body position (for example, when getting up from a chair or leaving a car). This pain occurs due to stretching, and then a sharp contraction, like a spring, of the round uterine ligaments. The pain quickly passes if you immediately take a comfortable position and does not require special treatment.
If the measures are ineffective, the doctor may prescribe safe drugs for you. A special type of pain that occurs during exclusivity in pregnant women is pain in the round ligament of the uterus. This acute, rather intense pain occurs, as a rule, on the one hand with a sharp change in body position (for example, when getting up from a chair or leaving a car). This pain occurs due to stretching, and then a sharp contraction, like a spring, of the round uterine ligaments. The pain quickly passes if you immediately take a comfortable position and does not require special treatment.
You should definitely consult a doctor if:
- pain is accompanied by spotting bloody discharge from the external genitalia
- increasing duration and intensity of pain
- abdominal pain accompanied by dizziness, fever, loss of consciousness
Life hack! To improve bowel movements, eat more vegetables and fruits, drink water and move more during the day. Try to eat often and in small portions.
Try to eat often and in small portions.
4. Enlargement and soreness of the mammary glands.
Hormonal restructuring of the body during gestation is accompanied, among other things, by an increase in the size of the mammary glands and an increase in their sensitivity. By the end of the first trimester, the soreness usually disappears, no additional methods of treatment are needed.
Life hack! Choose comfortable supportive underwear (it should not leave marks on the skin at the end of the day). You may need a larger size or a sports bra. Pain in the mammary glands is relieved by a warm shower at the end of the day.
You should definitely see a doctor if:
- the pain is severe
- mammary glands are very dense with redness and body temperature is increased
- there is discharge from the nipples (purulent, bloody)
5. Increased body temperature.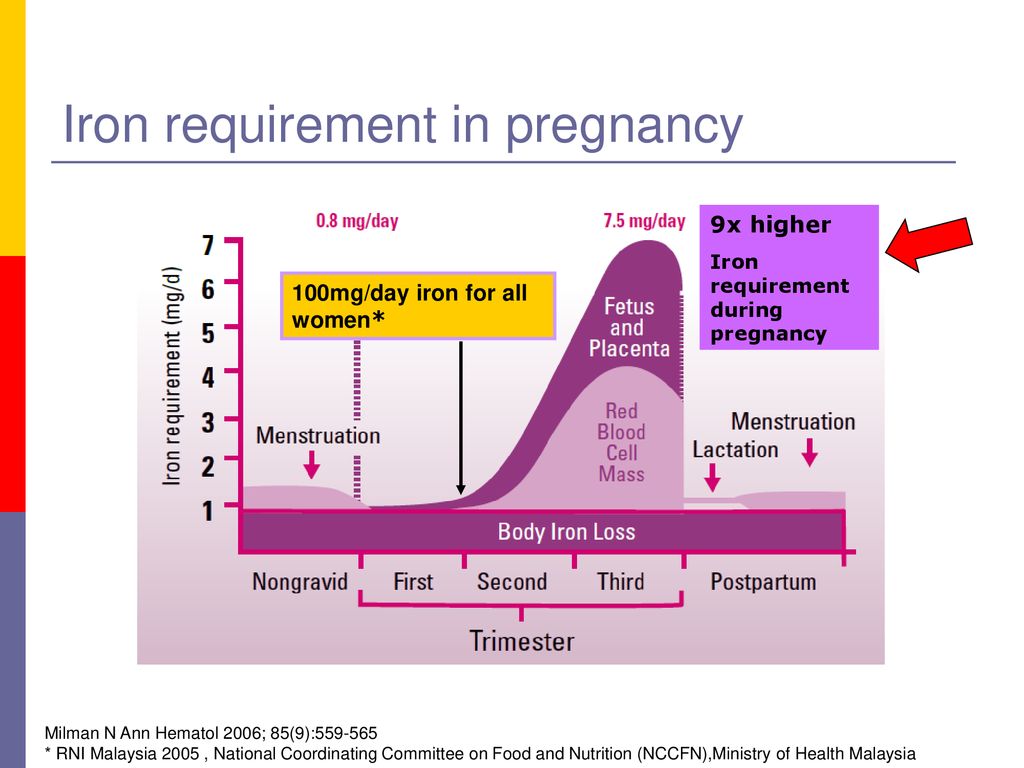
In early pregnancy, an increase in body temperature to 37.5 ° C is not necessary, but is possible due to the peculiarities of the action of progesterone. Because of this, it is difficult for pregnant women to endure stuffy, hot rooms. Self-medication is dangerous: an attempt to bring down the temperature even with a seemingly harmless folk method - tea with raspberries - can mask the true cause of hyperthermia and delay the diagnosis. Due to the increased body temperature, pregnant women should dress in layers and avoid stuffy and hot rooms and spaces so that they can always “adjust” their temperature on their own.
- temperature above 37.5 °C
- along with fever, any pain occurs
- runny nose, cough, body aches appear
6. Nasal congestion, shortness of breath, nosebleeds.
These symptoms can be explained by the individual reaction of the vascular system to the increase in blood volume that occurs during pregnancy. Another possible reason is dry air in the room, the operation of central heating batteries.
Another possible reason is dry air in the room, the operation of central heating batteries.
Life hack! The easiest way to deal with nasal congestion is to use a humidifier. If you don't have one, you can put a damp towel on the battery - less effective, but better than nothing. It is possible to use sprays with sea salt, but you need to carefully read the instructions and especially the "Indications" section, it should contain information about the safety of the product during pregnancy.
You should definitely see a doctor if:
- symptoms of a cold occur
- nasal congestion accompanied by ear congestion
- These symptoms appeared after exposure to the allergen known to you
7. Blood pressure fluctuations.
An ideal option for the course of any pregnancy is the stability of the blood pressure throughout the gestation. However, this is extremely rare. A small (up to 10 units) increase in pressure from the usual reference may be due to an increase in the load on the cardiovascular system as a result of changes in body weight, hormonal changes, and uterine pressure on the vessels. Normal pressure: systolic below 130 mm Hg, diastolic no more than 85 mm Hg. Blood pressure in the range of 130-139/ 85–89 mm Hg considered high to be normal. High numbers are often observed in patients of older reproductive age, suffering from diabetes mellitus and kidney disease, obesity, etc. However, it is imperative to tell the doctor about all these concomitant pathological conditions at the first appointment and, if necessary, consult a neurologist, cardiologist, endocrinologist and other related specialists . Reasonable physical activity, adherence to sleep and wakefulness, a balanced diet, and the rejection of coffee and strong tea allow you to keep pressure within limits. Of the completely exotic for our days, but no less significant - the prevention of stress.
Normal pressure: systolic below 130 mm Hg, diastolic no more than 85 mm Hg. Blood pressure in the range of 130-139/ 85–89 mm Hg considered high to be normal. High numbers are often observed in patients of older reproductive age, suffering from diabetes mellitus and kidney disease, obesity, etc. However, it is imperative to tell the doctor about all these concomitant pathological conditions at the first appointment and, if necessary, consult a neurologist, cardiologist, endocrinologist and other related specialists . Reasonable physical activity, adherence to sleep and wakefulness, a balanced diet, and the rejection of coffee and strong tea allow you to keep pressure within limits. Of the completely exotic for our days, but no less significant - the prevention of stress.
Life hack! If you are experiencing high normal blood pressure for the first time, repeat the measurement after 15 minutes. If the pressure remains elevated, see a doctor.
Be sure to see a doctor if:
- your blood pressure is above 140/90 mmHg
- pressure increased by more than 10 mm Hg.
 relative to your regular
relative to your regular - an increase in the pressure indicator is accompanied by edema, the appearance of "flies" before the eyes
NB! You should also pay attention to lowering blood pressure. Numbers less than 90/60 mmHg - an excuse to see a doctor.
Life hack! Keep a blood pressure diary, especially if you are prone to hypertension. Show your diary to your doctor at every appointment.
8. Heaviness and pain in the legs.
Heaviness and pain in the legs, especially in the evening, are frequent companions of pregnancy. There is an explanation for the occurrence of symptoms: an increase in load due to growing weight and a shift in the center of gravity of the body.
Life hack! Ask your partner/husband to give you a foot massage, relax with your limbs elevated (not too much!) A therapeutic pedicure, dousing the legs with cool water, a contrast shower, a cream or gel for legs with cooling components (menthol, essential oils), as well as compression stockings or stockings of the lightest degree of compression will help.
Be sure to see a doctor if:
- one or both legs are severely swollen or discolored
- previously diagnosed varicose veins, family history of thrombosis
9. Skin changes.
During pregnancy, you may notice dark spots on your skin. Especially often such darkening (hyperpigmentation) is observed in the nipple area, along the white line of the abdomen. Stretch marks (stretch marks) may appear on the skin of the abdomen and thighs. These are normal signs and do not require any treatment. In most cases, skin color will return to normal after breastfeeding ends, and stretch marks will shrink and fade. Itching can be associated with stretching of the skin, especially in the abdomen and mammary glands. This symptom occurs infrequently and is usually successfully stopped by the use of special products to moisturize and soften the skin. By the way, these same remedies usually help in the fight against stretch marks.
Life hack! Oils and moisturizing creams to increase skin elasticity, contrast showers, massage with a hard brush will help reduce the likelihood of skin changes.
You should definitely consult a doctor if:
- along with itching there are areas of redness, spots, peeling
- itching increases
10. Bleeding gums.
Changes in the characteristics of blood circulation in the body of a pregnant woman can cause bleeding gums. The appearance of minor blood impurities during brushing your teeth, when eating solid foods (for example, an apple) is acceptable. However, the key provision is "insignificant". If you find it difficult to assess your own condition, consult a specialist.
You should definitely consult a doctor if:
- you have loose teeth, sore gums, bad breath
- bleeding in the gum area increases
11.