How do i know contractions have started
Signs that labour has begun
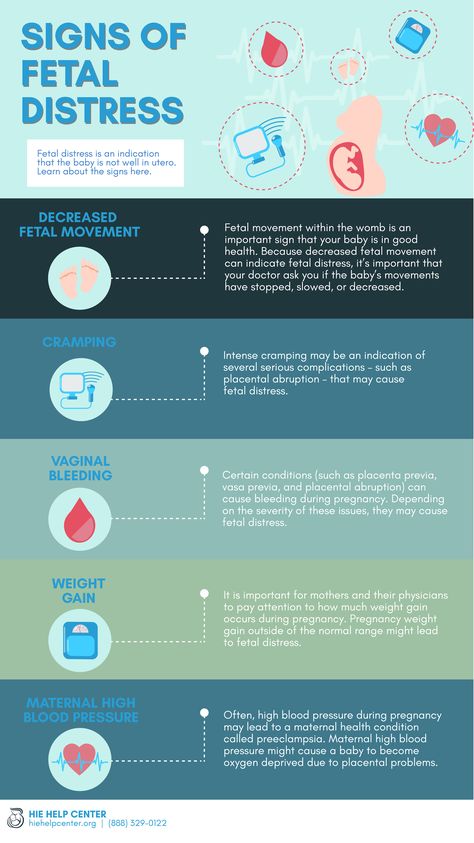
Know the signs
There are several signs that labour might be starting, including:
- contractions or tightenings
- a "show", when the plug of mucus from your cervix (entrance to your womb, or uterus) comes away
- backache
- an urge to go to the toilet, which is caused by your baby's head pressing on your bowel
- your waters breaking
The early (latent) stage of labour can take some time.
Urgent advice: Call your midwife or maternity unit if:
- your waters break
- you have vaginal bleeding
- your baby is moving less than usual
- you're less than 37 weeks pregnant and think you might be in labour
These signs mean you need to see a midwife or doctor.
Latent phase of labour
The start of labour is called the latent phase. This is when your cervix becomes soft and thin, and starts opening for your baby to be born. This can take hours or sometimes days.
You'll probably be advised to stay at home during this time. If you go to the hospital or maternity unit, they may suggest you go back home.
Find out more about the stages of labour and what you can do at home during the latent phase.
Call your midwife if you're unsure or worried about anything.
What do contractions feel like
When you have a contraction, your womb tightens and then relaxes. For some people, contractions may feel like extreme period pains.
You may have had contractions during your pregnancy, particularly towards the end. These tightenings are called Braxton Hicks contractions and are usually painless.
These tightenings are called Braxton Hicks contractions and are usually painless.
Your contractions tend to become longer, stronger and more frequent as your labour progresses. During a contraction, the muscles tighten and the pain increases. If you put your hand on your abdomen, you'll feel it getting harder; when the muscles relax, the pain fades and you will feel the hardness ease.
The contractions are pushing your baby down and opening the entrance to your womb (the cervix), ready for your baby to go through.
Your midwife will probably advise you to stay at home until your contractions become frequent.
Call your midwife or maternity unit for guidance when your contractions are in a regular pattern and:
- last at least 60 seconds
- come every 5 minutes or
- you think you are in labour
Read more information on when to go to hospital
Backache often comes on in labour
You may get backache or a heavy, aching feeling.
A "show" can signal the start of labour
During pregnancy, there's a plug of mucus in your cervix. This mucus comes away just before labour starts, or when in early labour, and it may pass out of your vagina. This sticky, jelly-like pink mucus is called a show.
It may come away in 1 blob or in several pieces. It's pink because it contains a small amount of blood.
If you're losing more blood, it may be a sign something is wrong, so phone your hospital or midwife straight away.
A show indicates that the cervix is starting to open. Labour may quickly follow or may take a few days. Sometimes there is no show.
What happens when my waters break
It's likely your waters will break during labour, but it can also happen before labour starts.
Your baby develops and grows inside a bag of fluid called the amniotic sac. When it's time for your baby to be born, the sac usually breaks and the amniotic fluid drains out through your vagina. This is your waters breaking. Sometimes when you're in labour, a midwife or doctor may offer to break your waters.
When it's time for your baby to be born, the sac usually breaks and the amniotic fluid drains out through your vagina. This is your waters breaking. Sometimes when you're in labour, a midwife or doctor may offer to break your waters.
If your waters break naturally, you may feel a slow trickle or a sudden gush of water you cannot control. To prepare for this, you could keep a sanitary towel (but not a tampon) handy if you're going out, and put a protective sheet on your bed.
Amniotic fluid is clear and pale. Sometimes it's difficult to tell amniotic fluid from urine. When your waters break, the water may be a little bloodstained to begin with.
Tell your midwife immediately if:
- the waters are smelly or coloured
- you're losing blood
This could mean you and your baby need urgent attention.
If your waters break before labour starts, call your midwife.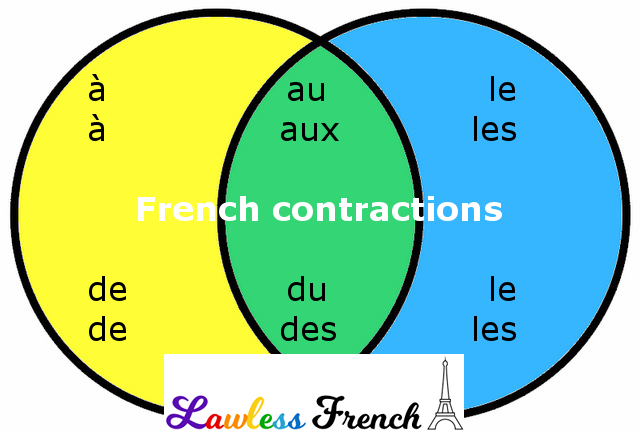 Use a sanitary pad (not a tampon) so your midwife can check the colour of the waters.
Use a sanitary pad (not a tampon) so your midwife can check the colour of the waters.
If labour does not start after your waters break
It's usual to go into labour within 24 hours of the waters breaking. You'll be offered an induction if you do not because, without amniotic fluid, there's an increased risk of infection for your baby.
Until your induction, or if you choose to wait for labour to start naturally, tell your midwife immediately if:
- your baby moves less than usual
- there's any change in the colour or smell of any fluid coming from your vagina
You should take your temperature every 4 hours when you're awake, and tell your midwife if it's raised. A raised temperature is usually above 37.5C, but you may need to call before this – check with your midwife.
There's no evidence that having a bath or shower after your waters have broken increases your risk of infection, but having sex might.
How to cope when labour begins
At the beginning of labour, you can:
- walk or move about, if you feel like it
- drink fluids – you may find sports (isotonic) drinks help keep your energy levels up
- have a snack, if you feel like it
- try any relaxation and breathing exercises you've learned to deal with contractions as they get stronger and more painful – your birth partner can help by doing these with you
- have your birth partner rub your back – this can help relieve pain
- take paracetamol according to the instructions on the packet – paracetamol is safe to take in labour
- have a warm bath
Find out what happens during labour and birth, and what you can do for pain relief in the early stages of labour.
Get Start4Life pregnancy and baby emails
For information and advice you can trust, sign up for weekly Start4Life pregnancy and baby emails.
Video: How will I know I am in labour?
In this video, a midwife describes the signs that mean labour may be starting.
Media last reviewed: 1 November 2019
Media review due: 1 November 2022
Contractions and signs of labor
Donate
Contact
Events
DONATE
- Home >
- Pregnancy >
- Labor & birth > Contractions and signs of labor
Topics
In This Topic
KEY POINTS
Learning the signs of labor before your due date can help you feel ready for your baby’s birth.
Signs of labor include strong and regular contractions, pain in your belly and lower back, a bloody mucus discharge and your water breaking.
If you think you’re in labor, call your health care provider.
Not all contractions mean you're in true labor. Learning the difference between true and false labor can help you know when it’s the real thing.
What is labor?
Labor (also called childbirth) is the process of your baby leaving the uterus (womb). You’re in labor when you have regular contractions that cause your cervix to change. Contractions are when the muscles of your uterus get tight and then relax. Contractions help push your baby out of your uterus. Your cervix is the opening to the uterus that sits at the top of the vagina. When labor starts, your cervix dilates (opens up).
Contractions help push your baby out of your uterus. Your cervix is the opening to the uterus that sits at the top of the vagina. When labor starts, your cervix dilates (opens up).
As you get closer to your due date, learning the signs of labor can help you feel ready for labor and birth. If you have any signs of labor, call your health care provider.
What are the signs of labor?
You know you’re in true labor when:
- You have strong and regular contractions. A contraction is when the muscles of your uterus tighten up like a fist and then relax. Contractions help push your baby out. When you’re in true labor, your contractions last about 30 to 70 seconds and come about 5 to 10 minutes apart. They’re so strong that you can’t walk or talk during them. They get stronger and closer together over time.
- You feel pain in your belly and lower back. This pain doesn't go away when you move or change positions.
- You have a bloody (brownish or reddish) mucus discharge.
 This is called bloody show.
This is called bloody show. - Your water breaks. Your baby has been growing in amniotic fluid (the bag of waters) in your uterus. When the bag of waters breaks, you may feel a big rush of water. Or you may feel just a trickle.
If you think you’re in labor, call your health care provider, no matter what time of day or night. Your provider can tell you if it’s time to head for the hospital. To see for sure that you’re in labor, your health care provider measures your cervix.
What are signs that you may be close to starting labor?
You may be close to starting labor if:
- Your baby drops or moves lower into your pelvis. This is called lightening. It means that your baby is getting ready to move into position for birth. It can happen a few weeks or even just a few hours before your labor begins.
- You have an increase in vaginal discharge that’s clear, pink or slightly bloody. This is called show or bloody show.
 It can happen a few days before labor starts or at the beginning of labor.
It can happen a few days before labor starts or at the beginning of labor. - At a prenatal checkup, your health care provider tells you that your cervix has begun to efface (thin) and dilate (open). Before labor, your cervix is about 3.5 to 4 centimeters long. When it’s fully dilated (open) for labor, it’s 10 centimeters. Once labor starts, contractions help open your cervix.
- You have the nesting instinct. This is when you want to get things organized in your home to get ready for your baby. You may want to do things like cook meals or get the baby’s clothes and room ready. Doing these things is fine as long as you’re careful not to overdo it. You need your energy for labor and birth.
If you have any of these signs, you may start labor soon. Learn the signs of labor so you know when to call your provider.
What are false labor and Braxton-Hicks contractions?
Not all contractions mean you’re in labor. You may have contractions on and off before true labor starts. These contractions are called false labor or Braxton-Hicks contractions. They soften and thin the cervix to help your body get ready for labor and birth. You may feel them in the weeks right before your due date. Learning the differences between true labor contractions and false labor contractions can help you know when you’re really in labor.
These contractions are called false labor or Braxton-Hicks contractions. They soften and thin the cervix to help your body get ready for labor and birth. You may feel them in the weeks right before your due date. Learning the differences between true labor contractions and false labor contractions can help you know when you’re really in labor.
It can be hard to tell the difference between true labor and false labor. When you first feel contractions, time them. Write down how much time it takes from the start of one contraction to the start of the next. Make a note of how strong the contractions feel. Keep a record of your contractions for 1 hour. Walk or move around to see if the contractions stop when you change positions.
What is preterm labor?
Preterm labor is labor that begins too early, before 37 weeks of pregnancy. Premature babies (born before 37 weeks of pregnancy) can have health problems at birth and later in life. If you’re not to 37 weeks of pregnancy and you have signs or symptoms of preterm labor, call your provider. Getting help quickly is the best thing you can do. Learn about risk factors for preterm labor and what you can do to help reduce your risk.
Getting help quickly is the best thing you can do. Learn about risk factors for preterm labor and what you can do to help reduce your risk.
What are stages of labor?
Stages of labor include the whole process of labor, from your first contractions (stage 1) to pushing (stage 2) to delivery of the placenta (stage 3) after your baby is born. Learning about the stages of labor can help you know what to expect during labor and birth.
Last reviewed: December, 2018
') document.write('
Nutrition, weight & fitness
') document.write('') }
') document.write('
Prenatal care
') document.write('') }
How to distinguish real contractions from training ones?
Shemyakina Natalya Nikolaevna, head of the obstetric department of the Leleka maternity hospital will help you figure it out.
Training contractions, or as they are also called, fake, or Braxton-Hicks contractions, are irregular contractions that do not have increasing intensity. The uterus may tone up, but normally, it should pass quickly.
For example, the tone appeared once in half an hour and the uterus relaxed rather quickly. Then the tone reappeared only after two hours and again passed. These are training contractions, they do not increase in intensity and do not become more frequent.
Training bouts are physiologically provided by our body. So the uterus is preparing to do the hard work in the process of childbirth. Normally, training contractions appear in terms of pregnancy close to childbirth - from the 37th week of pregnancy.
The appearance of training contractions in the early stages of pregnancy is not the norm
The uterus can tone up with an active lifestyle, physical activity, with a change in body position, but this tone should quickly pass. Normally, the uterus should not often come into tone. And even more so, contractions, as such, should not be until the 37th week of pregnancy.
And even more so, contractions, as such, should not be until the 37th week of pregnancy.
Braxton Hicks contractions in the early stages are a threat of preterm labor. If a woman has contractions periodically during the day: after an hour, after 2, then again after an hour, (even if they are not regular), for periods up to 37 weeks, such a tone should alert the expectant mother.
Because this is not the norm, but the threat of premature birth. This is an occasion to contact a specialist and change your rhythm of life, put on a bandage. The causes of premature birth are most often internal, caused by hormonal disorders and a violation of the physical health of a woman. But significant physical activity and stress can also cause premature birth.
Labor pains
Unlike training contractions, labor pains are regular. The uterus comes to tone first once every 15 minutes, and after a while - once every 7-10 minutes. Contractions gradually become more frequent, longer and stronger. And already occur every 5 minutes, then 3 and finally every 2 minutes.
And already occur every 5 minutes, then 3 and finally every 2 minutes.
True labor pains are contractions every 2 minutes, 40 seconds. If within an hour or two the contractions intensify - pains that begin in the lower abdomen or in the lower back and spread to the stomach - most likely, these are real labor pains.
Training contractions are NOT so much painful as unusual for a woman. When the expectant mother sees how the stomach comes into tone, its shape changes and it becomes dense, like an inflated ball. This might scare you a little. But a woman must understand that in real, labor pains, there must be a clear periodicity, intensification and acceleration over a certain period of time. Real fights never stop, but practice fights do. The uterus then comes to tone, then relaxes.
Often women confuse contractions with tone, which is caused by other physiological processes in the body. For example, increased intestinal peristalsis, intestinal infections, colic, etc.
What else should alert a woman?! If within an hour or two the uterus periodically comes into tone and mucous, bloody (streaked with blood or brown) discharge appears, then most likely there are structural changes in the cervix - it opens. Also an important sign to seek help is the discharge of the mucous plug long before childbirth. Her departure in terms of childbirth, a week or two before childbirth is normal.
Tracking labor pains
There are several methods for determining the types of contractions. A woman can do this herself, writing down the frequency and duration of contractions on paper or tracking them using special programs for a computer and phone. Or you can contact a doctor at antenatal clinic or at the maternity hospital, where a specialist will conduct fetal monitoring (fetal CTG). With the help of 2 sensors, the fetal heartbeat, uterine contractions are monitored and it is determined whether these are training contractions or labor.
When should I go to the maternity hospital?
If within an hour or two there is an increase and intensification of pain, its intensity increases, the frequency of contractions is clear and regular, you can go to the maternity hospital. A woman can make a mistake, but it’s better to come and make sure for sure whether these are labor or training contractions.
If the amniotic fluid breaks, you can slowly pack up and go to the maternity hospital. Since, normally, after this labor activity should begin.
The main thing is that a woman should not panic. The latent phase of labor can last 8-10 hours until the cervix is fully dilated. Labor activity does not proceed in 30 seconds. In the process of labor, the cervix of the uterus in women giving birth for the first time opens about 1 cm in an hour. She needs to open up to 10 cm, that is, a woman has about 10:00 by the time the baby is born.
Happy pregnancy and childbirth!
How contractions start: the signals your body sends
“You will immediately understand that it is them,” say women who already have children. But this is not always the case. We figure out how to recognize real contractions and distinguish them from false ones.
But this is not always the case. We figure out how to recognize real contractions and distinguish them from false ones.
What are contractions
pixabay.com
Pregnant women are often very worried about the approach of the due date. Expectant mothers are wondering how to understand that contractions have begun. How not to miss the right moment and arrive at the hospital on time? There are several clear signs.
Types of contractions
@umkina_berloga
Training
Some women already feel slight contractions a few weeks before giving birth, which means that training contractions (or Braxton-Hicks contractions) have begun. With their help, the uterus prepares for childbirth.
The first training sensations are barely noticeable, but towards the end of pregnancy they become stronger. Unlike real ones, they do not lead to the opening of the cervix. There are only pulling sensations in the lower abdomen or in the lower back, the uterus seems to turn to stone - if you put your hand on the stomach, you can clearly see this. Training sessions are irregular and less painful. You feel them for a minute once an hour or several times a day. You need to worry if they repeat more and more often. If they occur more often than three to four times an hour or ten times a day, then it is recommended to consult a doctor.
Do not miss
-
Do not miss
7 gadgets that will make life easier for a modern mother (grandmother will envy)
If they are accompanied by pressure or pain in the abdomen or back, or heavy vaginal discharge or bleeding, tell your doctor immediately as this may indicate the onset of preterm labor.
Walking helps to completely relieve the discomfort and tension of the uterus. The role of false ones is not yet fully understood. Their appearance is associated with an increase in the excitability of the uterus, it is believed that shortly before childbirth they contribute to the softening and shortening of its neck.
Premature
If a woman has contractions before the 36th week of pregnancy (and they are accompanied by bleeding or vaginal discharge, pain in the abdomen or back), then they are called premature. According to the WHO recommendation, a woman should immediately consult a doctor. If the contractions started prematurely, then doctors will try to stop them with the help of appropriate medications, and thus give the child more time for intrauterine development.
Real
This is the name given to regular involuntary contractions of the uterine muscles that a woman cannot control. The shortest real contractions last 20 seconds with pauses of 15 minutes. The longest ones last 60 seconds with pauses of two to three minutes.
The longest ones last 60 seconds with pauses of two to three minutes.
At first, the intervals are about half an hour (sometimes more), gradually their frequency, intensity and duration increase. The last contractions occur at intervals of five to seven minutes and turn into attempts. On average, the whole process lasts 12 hours for those giving birth for the first time, and up to nine hours for repeated births.
Do not miss
-
Do not miss
5 signs of an outdated maternity hospital, in which it is better not to give birth
Just before the birth of the child, the contractions become so frequent that they pass one into the other almost without intervals. Further, they are joined by attempts, which are contractions of the muscles of the uterus, abdominal wall and perineum. At this time, the child presses his head on the small pelvis, and the woman in labor has a desire to push, and the pain moves to the perineum. When the cervix is fully dilated, the birth process begins.
At this time, the child presses his head on the small pelvis, and the woman in labor has a desire to push, and the pain moves to the perineum. When the cervix is fully dilated, the birth process begins.
How to understand that real contractions have begun
How do contractions start? Quite often, even before the sensations begin, women intuitively feel that childbirth will begin soon. Pain does not appear immediately, it is usually preceded by discomfort in the abdomen or lower back. Some women experience menstrual-like pain.
Gradually, these sensations become stronger, spread to the entire abdomen and lower back, pain appears - from rather strong pressure to twitching sensations. The pain is paroxysmal, its occurrence, intensification, reaching a peak and a gradual decrease are clearly felt, then a period without pain begins.
Do not miss
-
Do not miss
Uterine tone during pregnancy: everything you need to know about it
Doctors recommend paying attention to the first signs that may signal that the first contractions are starting.
- Real contractions before childbirth are regular and are repeated at shorter intervals and with greater intensity, and their duration also increases gradually.
- The length of real contractions is different, but the intervals between them are almost always equal.
- False contractions are painless, with a feeling of constriction in some part of the abdomen or in the groin. With real pain, sensations spread to the entire abdomen and hip joints.
- Slight bleeding indicates a possible opening of the cervix.
- The main symptom is that with real contractions before childbirth, other symptoms are also observed: discharge of water, mucous plug, pain in the lower back, diarrhea.
References
- World Health Organization (WHO), United Nations Population Fund, UNICEF, World Bank Normal birth and delivery.