First stage of labor symptoms
Signs that labour has begun
Know the signs
There are several signs that labour might be starting, including:
- contractions or tightenings
- a "show", when the plug of mucus from your cervix (entrance to your womb, or uterus) comes away
- backache
- an urge to go to the toilet, which is caused by your baby's head pressing on your bowel
- your waters breaking
The early (latent) stage of labour can take some time.
Urgent advice: Call your midwife or maternity unit if:
- your waters break
- you have vaginal bleeding
- your baby is moving less than usual
- you're less than 37 weeks pregnant and think you might be in labour
These signs mean you need to see a midwife or doctor.
Latent phase of labour
The start of labour is called the latent phase. This is when your cervix becomes soft and thin, and starts opening for your baby to be born. This can take hours or sometimes days.
You'll probably be advised to stay at home during this time. If you go to the hospital or maternity unit, they may suggest you go back home.
Find out more about the stages of labour and what you can do at home during the latent phase.
Call your midwife if you're unsure or worried about anything.
What do contractions feel like
When you have a contraction, your womb tightens and then relaxes. For some people, contractions may feel like extreme period pains.
You may have had contractions during your pregnancy, particularly towards the end. These tightenings are called Braxton Hicks contractions and are usually painless.
These tightenings are called Braxton Hicks contractions and are usually painless.
Your contractions tend to become longer, stronger and more frequent as your labour progresses. During a contraction, the muscles tighten and the pain increases. If you put your hand on your abdomen, you'll feel it getting harder; when the muscles relax, the pain fades and you will feel the hardness ease.
The contractions are pushing your baby down and opening the entrance to your womb (the cervix), ready for your baby to go through.
Your midwife will probably advise you to stay at home until your contractions become frequent.
Call your midwife or maternity unit for guidance when your contractions are in a regular pattern and:
- last at least 60 seconds
- come every 5 minutes or
- you think you are in labour
Read more information on when to go to hospital
Backache often comes on in labour
You may get backache or a heavy, aching feeling.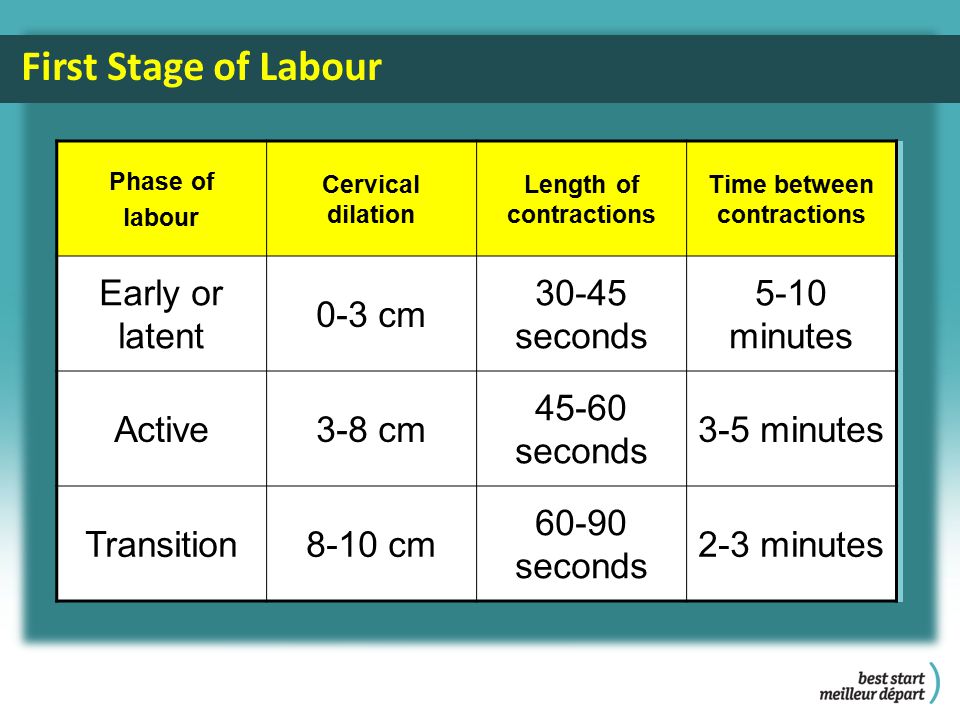
A "show" can signal the start of labour
During pregnancy, there's a plug of mucus in your cervix. This mucus comes away just before labour starts, or when in early labour, and it may pass out of your vagina. This sticky, jelly-like pink mucus is called a show.
It may come away in 1 blob or in several pieces. It's pink because it contains a small amount of blood.
If you're losing more blood, it may be a sign something is wrong, so phone your hospital or midwife straight away.
A show indicates that the cervix is starting to open. Labour may quickly follow or may take a few days. Sometimes there is no show.
What happens when my waters break
It's likely your waters will break during labour, but it can also happen before labour starts.
Your baby develops and grows inside a bag of fluid called the amniotic sac. When it's time for your baby to be born, the sac usually breaks and the amniotic fluid drains out through your vagina. This is your waters breaking. Sometimes when you're in labour, a midwife or doctor may offer to break your waters.
When it's time for your baby to be born, the sac usually breaks and the amniotic fluid drains out through your vagina. This is your waters breaking. Sometimes when you're in labour, a midwife or doctor may offer to break your waters.
If your waters break naturally, you may feel a slow trickle or a sudden gush of water you cannot control. To prepare for this, you could keep a sanitary towel (but not a tampon) handy if you're going out, and put a protective sheet on your bed.
Amniotic fluid is clear and pale. Sometimes it's difficult to tell amniotic fluid from urine. When your waters break, the water may be a little bloodstained to begin with.
Tell your midwife immediately if:
- the waters are smelly or coloured
- you're losing blood
This could mean you and your baby need urgent attention.
If your waters break before labour starts, call your midwife.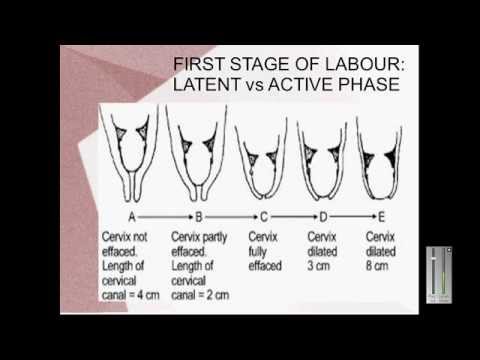 Use a sanitary pad (not a tampon) so your midwife can check the colour of the waters.
Use a sanitary pad (not a tampon) so your midwife can check the colour of the waters.
If labour does not start after your waters break
It's usual to go into labour within 24 hours of the waters breaking. You'll be offered an induction if you do not because, without amniotic fluid, there's an increased risk of infection for your baby.
Until your induction, or if you choose to wait for labour to start naturally, tell your midwife immediately if:
- your baby moves less than usual
- there's any change in the colour or smell of any fluid coming from your vagina
You should take your temperature every 4 hours when you're awake, and tell your midwife if it's raised. A raised temperature is usually above 37.5C, but you may need to call before this – check with your midwife.
There's no evidence that having a bath or shower after your waters have broken increases your risk of infection, but having sex might.
How to cope when labour begins
At the beginning of labour, you can:
- walk or move about, if you feel like it
- drink fluids – you may find sports (isotonic) drinks help keep your energy levels up
- have a snack, if you feel like it
- try any relaxation and breathing exercises you've learned to deal with contractions as they get stronger and more painful – your birth partner can help by doing these with you
- have your birth partner rub your back – this can help relieve pain
- take paracetamol according to the instructions on the packet – paracetamol is safe to take in labour
- have a warm bath
Find out what happens during labour and birth, and what you can do for pain relief in the early stages of labour.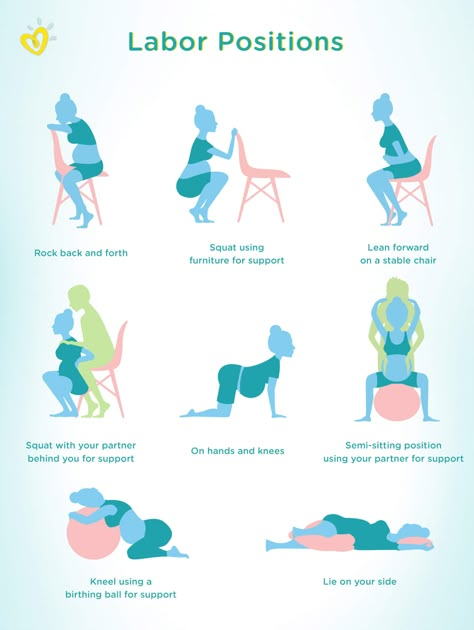
Get Start4Life pregnancy and baby emails
For information and advice you can trust, sign up for weekly Start4Life pregnancy and baby emails.
Video: How will I know I am in labour?
In this video, a midwife describes the signs that mean labour may be starting.
Media last reviewed: 1 November 2019
Media review due: 1 November 2022
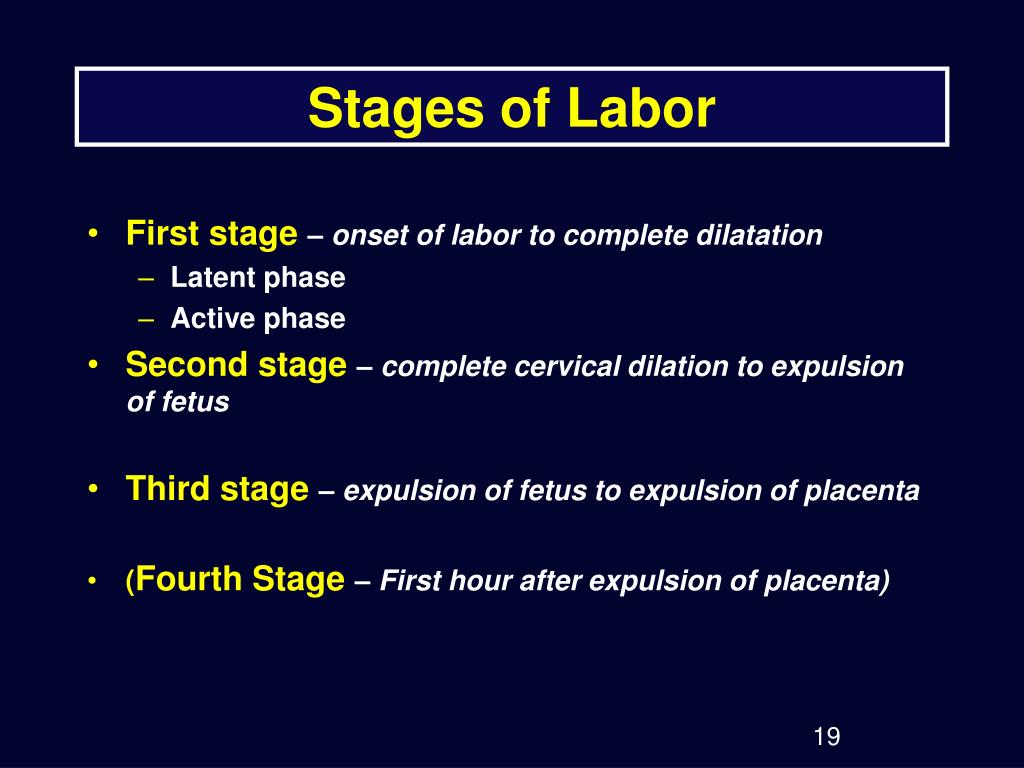
Stages of labor
Topics
In This Topic
KEY POINTS
Every woman’s labor is different. And it may be different each time you have a baby.
Learning about stages of labor before your due date can help you know what to expect so you can feel ready for your baby’s birth.
Use a birth plan so your health care provider and hospital staff know what your plans are for labor and after birth.
Having a professional support person, like a doula, during labor can help you have a better experience with labor and birth.
Try to stay comfortable and relaxed through labor. Move around and try different positions to find what works best for you.
What are stages of labor?
Labor (also called childbirth) is the process of your baby leaving the uterus (womb). Labor is divided into three stages:
- Labor
- Pushing and birth
- Delivery of the placenta
Every woman’s labor is different. And your labor may be different each time you have a baby. But there are patterns to labor that are true for most women. Learning about the stages of labor and what happens during each one can help you know what to expect once labor begins.
What is a birth plan?
A birth plan is a set of instructions you make about your baby’s birth. It includes things like:
It includes things like:
- Where you want to have your baby
- Who you want to be with you during labor and birth
- If you want medicine to help with labor pain
- If there are cultural traditions you’d like to follow during labor and birth
- If you plan to breastfeed
Before your due date, use the March of Dimes birth plan to help you think about how you want your labor to be. Share the completed plan with your partner, your health care provider and the staff at the hospital where you plan to give birth.
What is a doula?
A doula is a trained professional who provides information and physical and emotional care and support to women before, during and after childbirth, including continuous support through labor and birth. For example, a doula can:
- Help you stay comfortable during labor
- Explain what’s happening during labor and birth and any procedures you may have
- Encourage you and give you confidence
- Support your family and friends who are with you during labor
- Let hospital staff know what you need
- Help you get started breastfeeding
Having a support person like a doula can be good for you, your baby and your family. It can help you feel good about your birth experience. Having a doula can help:
It can help you feel good about your birth experience. Having a doula can help:
- Shorten your labor
- Reduce your need for pain medicine during labor
- Reduce your risk of needing a cesarean birth or the need for your provider to use forceps or suction with a vaginal birth
- Your baby get a good Apgar score at birth. Your baby gets an Apgar test right after birth to check his overall health. The test checks his heart rate, breathing, muscle tone, reflexes and skin color.
To find a certified doula, ask your provider or go to DONA International.
You also may want to have your partner, a friend or a family member be a support person to help you through labor. They can go to childbirth education classes with you to learn ways to help, like timing your contractions, helping you relax and helping you move around to find a comfortable position. Ask your provider about childbirth education classes in your area.
If you decide to have a doula or another support person help you with labor and birth, put their names and contact information in your birth plan. Share your plan with your provider and with hospital staff.
Share your plan with your provider and with hospital staff.
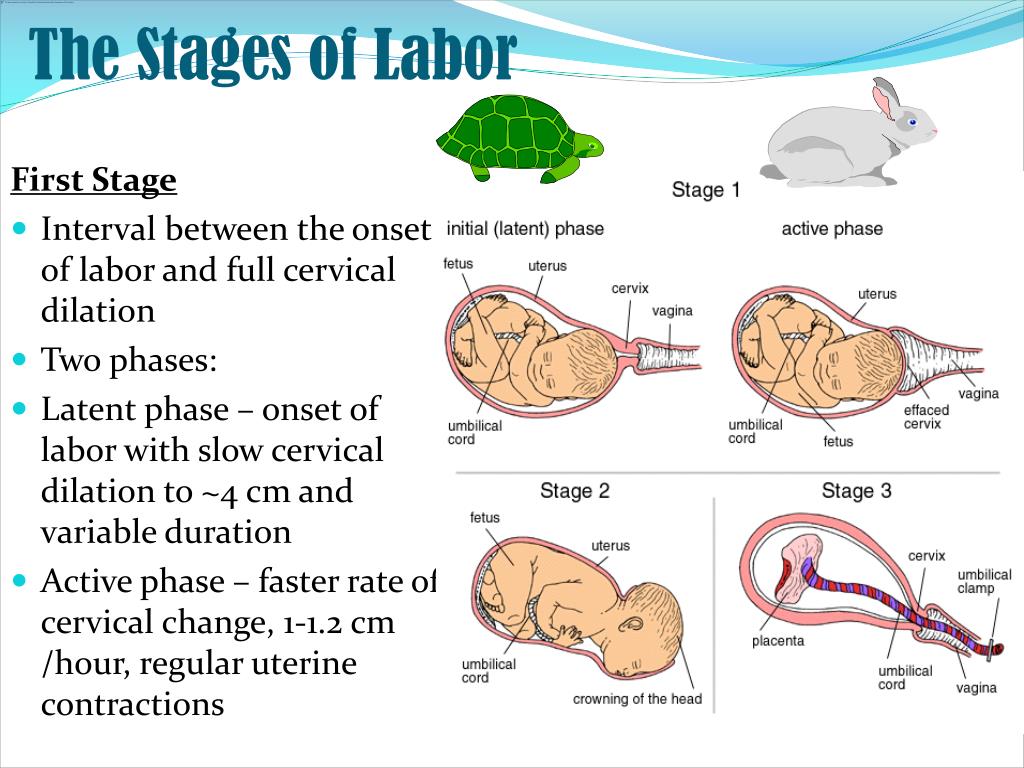
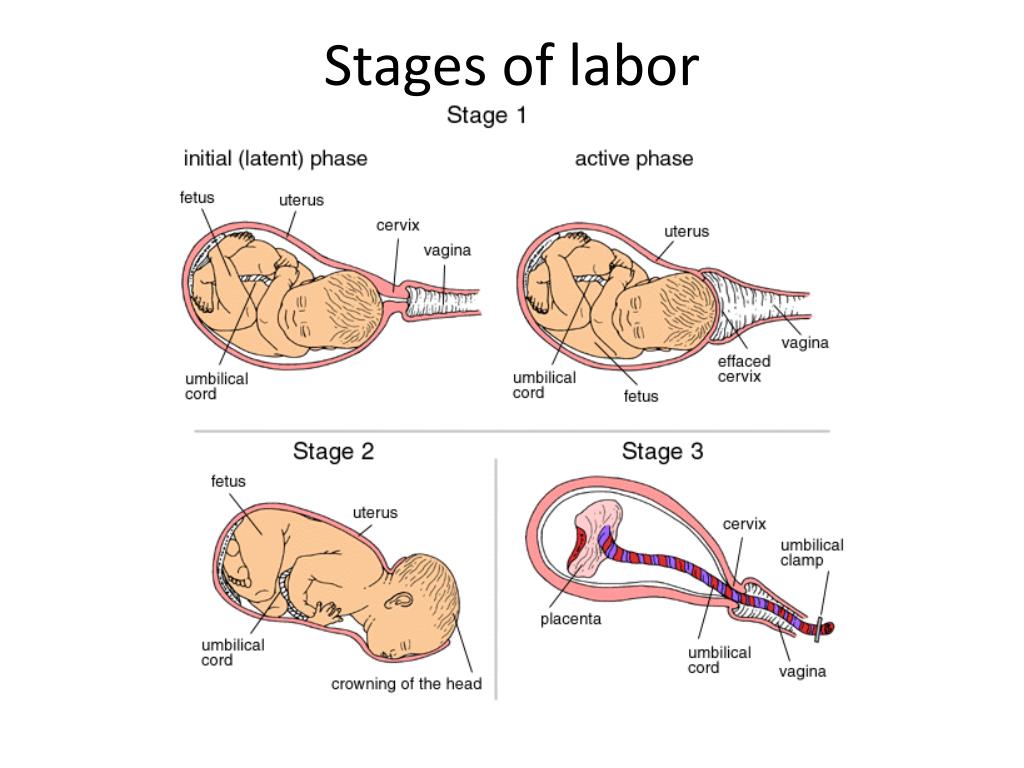
What happens in the first stage of labor?
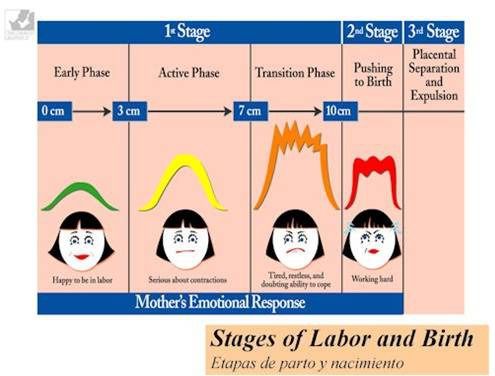
The first stage of labor is the longest stage. For first-time moms, it can last from 12 to 19 hours . It may be shorter (about 14 hours) for moms who’ve already had children. It’s when contractions become strong and regular enough to cause your cervix to dilate (open) and thin out (efface). This lets your baby move lower into your pelvis and into your birth canal (vagina). This stage of labor ends when you are 10 centimeters dilated. The first stage is divided into three parts: early labor, active labor and transition to stage 2 of labor.
Early labor
For most first-time moms, early labor lasts about 6 to 12 hours. You can spend this time at home or wherever you’re most comfortable. During early labor:
- You may feel mild contractions that come every 5 to 15 minutes and last 60 to 90 seconds.
- You may have a bloody show. This is a pink, red or bloody vaginal discharge.
 If you have heavy bleeding or bleeding like your period, call your provider right away.
If you have heavy bleeding or bleeding like your period, call your provider right away.
What you can do in early labor:
This is a great time for you to rely on your doula or labor support person. Try the methods you learned about in childbirth education classes about how to relax and cope with pain. During early labor:
- Rest and relax as much as you can.
- Take a shower or bath.
- Go for a walk.
- Change positions often.
- Make sure you’re ready to go to the hospital.
- Take slow, relaxing breaths during contractions.
Active labor
This is when you head to the hospital! Active labor usually lasts about 4 to 8 hours. It starts when your contractions are regular and your cervix has dilated to 6 centimeters. In active labor:
- Your contractions get stronger, longer and more painful. Each lasts about 45 seconds and they can be as close as 3 minutes apart.
- You may feel pressure in your lower back, and your legs may cramp.
- You may feel the urge to push.
- Your cervix will dilate up to 10 centimeters.
- If your water hasn’t broken, it may break now.
- You may feel sick to your stomach.
What you can do in active labor:
- Make sure the hospital staff has a copy of your birth plan.
- Try to stay relaxed and not think too hard about the next contraction.
- Move around or change positions. Walk the hallways in the hospital.
- Drink water or other liquids. But don’t eat solid foods.
- If you’re going to take medicine to help relieve labor pain, you can start taking it now. Your choice about pain relief is part of your birth plan.
- Go to the bathroom often to empty your bladder. An empty bladder gives more room for your baby’s head to move down.
- If you feel like you want to push, tell your provider. You don’t want to start pushing until your provider checks your cervix to see how dilated it is.
Transition to the second stage of labor
This can be the toughest and most painful part of labor. It can last 15 minutes to an hour. During the transition:
It can last 15 minutes to an hour. During the transition:
- Contractions come closer together and can last 60 to 90 seconds. You may feel like you want to bear down.
- You may feel a lot of pressure in your lower back and rectum. If you feel like you want to push, tell your provider.
What happens in the second stage of labor?
In the second stage of labor, your cervix is fully dilated and ready for childbirth. This stage is the most work for you because your provider wants you to start pushing your baby out. This stage can be as short as 20 minutes or as long as a few hours. It may be longer for first-time moms or if you’ve had an epidural. And epidural is pain medicine you get through a tube in your lower back that helps numb your lower body during labor. It's the most common kind of pain relief used during labor. The second stage ends when your baby is born.
During the second stage of labor:
- Your contractions may slow down to come every 2 to 5 minutes apart.
 They last about 60 to 90 seconds.
They last about 60 to 90 seconds. - You may get an episiotomy. This is a small cut made at the opening of the vagina to help let the baby out. Most women don't need an episiotomy.
- Your baby’s head begins to show. This is called crowning.
- Your provider guides your baby out of the birth canal. She may use special tools, like forceps or suction, to help your baby out.
- Your baby is born, and the umbilical cord is cut. Instructions about who’s cutting the umbilical cord are in your birth plan. What you can do:
- Find a position that is comfortable for you. You can squat, sit, kneel or lie back.
- Push during contractions and rest between them. Push when you feel the urge or when your provider tells you.
- If you’re uncomfortable or pushing has stopped, try a new position.
What happens in the third stage of labor?
In the third stage of labor, the placenta is delivered. The placenta grows in your uterus and supplies your baby with food and oxygen through the umbilical cord.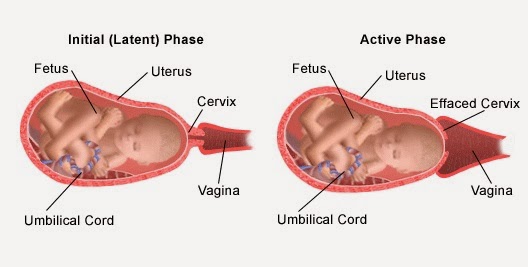 This stage is the shortest and usually doesn’t take more than 20 minutes.
This stage is the shortest and usually doesn’t take more than 20 minutes.
During the third stage of labor:
- You have contractions that are closer together and not as painful as earlier. These contractions help the placenta separate from the uterus and move into the birth canal. They begin 5 to 30 minutes after birth.
- You continue to have contractions even after the placenta is delivered. You may get medicine to help with contractions and to prevent heavy bleeding.
- Your provider squeezes and presses on your belly to make sure the uterus feels right.
- If you had an episiotomy, your provider repairs it now.
- If you’re storing your umbilical cord blood, your provider collects it now. Umbilical cord blood is blood left in the umbilical cord and placenta after your baby is born and the cord is cut. Some moms and families want to store or donate umbilical cord blood so it can be used later to treat certain diseases, like cancer. Your instructions about umbilical cord blood can be part of your birth plan.
- You may have chills or feel shaky. Tell your provider if these are making you uncomfortable.
What you can do:
- Enjoy the first few moments with your baby.
- Start breastfeeding. Most women can start breastfeeding within 1 hour of their baby’s birth.
- Give yourself a big pat on the back for all your hard work. You've made it through childbirth!
What happens after your baby is born?
Congratulations! It’s time to hold your baby! Right after birth your provider places your baby skin-to-skin on your chest and covers him with a blanket. Holding your baby skin-to-skin helps your baby stay warm as he gets used to being outside the womb. It’s also a great way to get started breastfeeding. You can start breastfeeding even within an hour of your baby’s birth. Even if you don’t plan to breastfeed, hold your baby skin-to-skin so you get to know each other right away. Your baby will welcome your gentle touch, and this closeness can help you and your baby bond.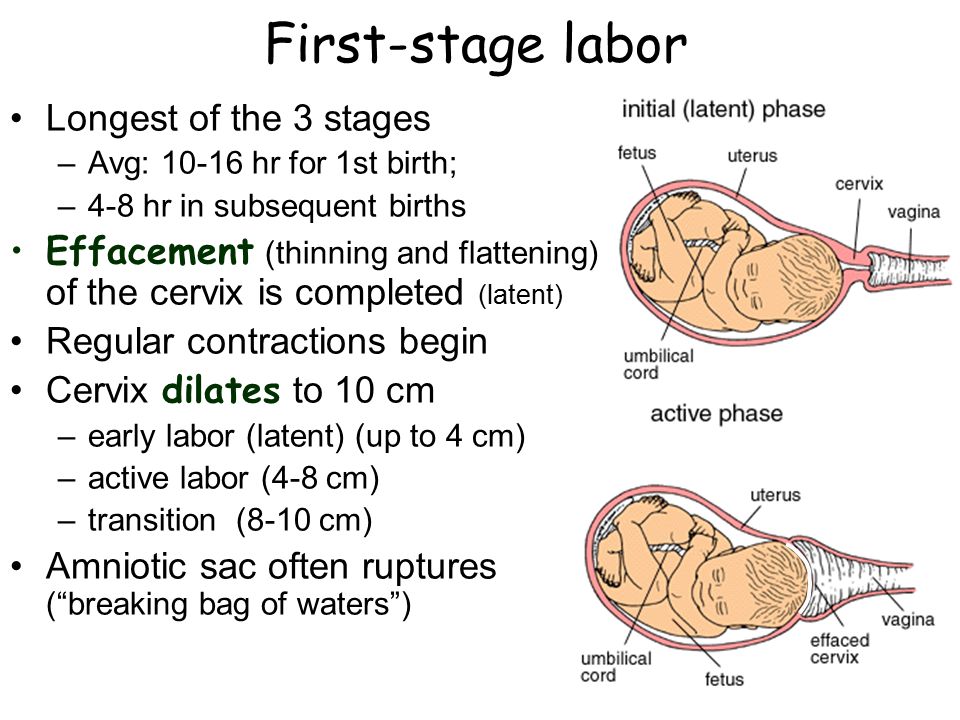
After birth, your body starts to change to help you heal. Your provider takes your temperature and checks your heart and blood pressure to make sure you’re doing well. If you had anesthesia during labor, your provider makes sure you’re recovering without any complications.
Last reviewed: March, 2019
') document.write('
Nutrition, weight & fitness
') document.write('') }
') document.write('') }
Important to know - Health of a Petersburger
The total duration of childbirth and their course
The total duration of childbirth depends on many factors: age, physique and physical condition of the woman, her psychological mood, the speed of cervical dilatation, first pregnancy or repeated, the size of the child, the type of presentation and a number of other points.
Labor activity proceeds differently for all women, but the main periods of childbirth are clearly distinguished: 1st period - the period of contractions, the longest and most intense, 2nd period - the direct birth of a baby, 3rd period - the birth of the afterbirth (placenta).
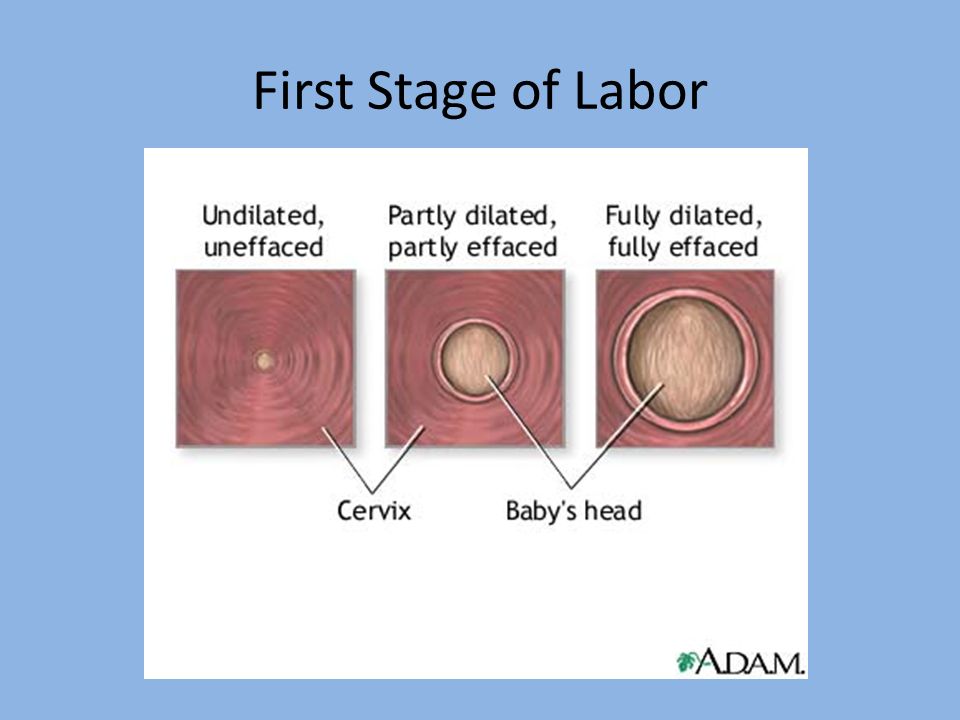
First stage of labor (opening period)
As the name implies, during this period there is a gradual opening of the cervix as a result of regular contractions of the uterine muscles. Contractions occur with a decreasing interval, while they themselves become longer and more frequent.
The dilation period is the time elapsed from the onset of regular contractions until the cervix is fully dilated. During this period, the birth canal is prepared for the passage of the fetus through them with all the fetal formations.
Cervical dilatation occurs gradually: at first the cervix is smoothed out, then the pharynx opens up to 3-4 cm and at the end of the first stage of labor up to 10 cm.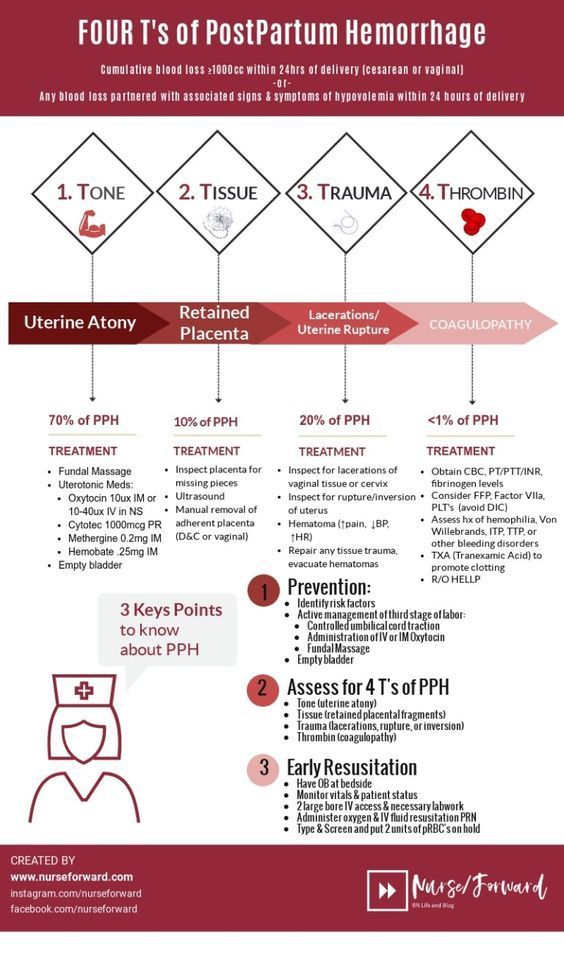 This is already a complete dilatation of the cervix. With it, during contractions, the fetal bladder becomes tense and bursts at the height of one of them, the anterior portion of amniotic fluid is poured out.
This is already a complete dilatation of the cervix. With it, during contractions, the fetal bladder becomes tense and bursts at the height of one of them, the anterior portion of amniotic fluid is poured out.
The first stage of labor is the longest and consists of three phases:
1. Latent phase (lasts 5-6 hours). It is characterized by the establishment of regular contractions, with an interval between them of 10-15 minutes. Latent, or hidden, this phase is called because the contractions of the uterus during it are painless or slightly painful. By the end of the phase, the cervix is definitively flattened and opens about 4 cm.
2. Active phase (lasts 3-4 hours). Contractions become more intense, last at least 20 seconds, and the interval between them is reduced to 5-6 minutes. Normally, during the active phase, amniotic fluid is poured out, which contributes to a faster full disclosure of the uterine pharynx. By the end of the phase, the uterus opens by 8 cm. This phase is not always clearly manifested, but it is nevertheless distinguished due to the usual weakening of contractions during disclosure from 8 to 10 cm. The child's head descends and stands in the narrow part of the small pelvis, which necessitates a slower and smoother process. Already in the transitional phase, the woman in labor feels the desire to push, to push the baby out. But in order for the head to pass through the birth canal without the risk of injury, it is necessary to achieve cervical dilatation up to 10 cm.
This phase is not always clearly manifested, but it is nevertheless distinguished due to the usual weakening of contractions during disclosure from 8 to 10 cm. The child's head descends and stands in the narrow part of the small pelvis, which necessitates a slower and smoother process. Already in the transitional phase, the woman in labor feels the desire to push, to push the baby out. But in order for the head to pass through the birth canal without the risk of injury, it is necessary to achieve cervical dilatation up to 10 cm.
Second stage of labor (exile period)
The period of exile is the time from the moment of full opening of the pharynx until the birth of the fetus.
It is the second stage of childbirth that is their culmination, because for a short time (compared to contractions) the long-awaited birth of the baby takes place.
After the discharge of amniotic fluid, contractions temporarily stop. The volume of the uterine cavity decreases, the uterine cavity and vagina appear as a single birth canal.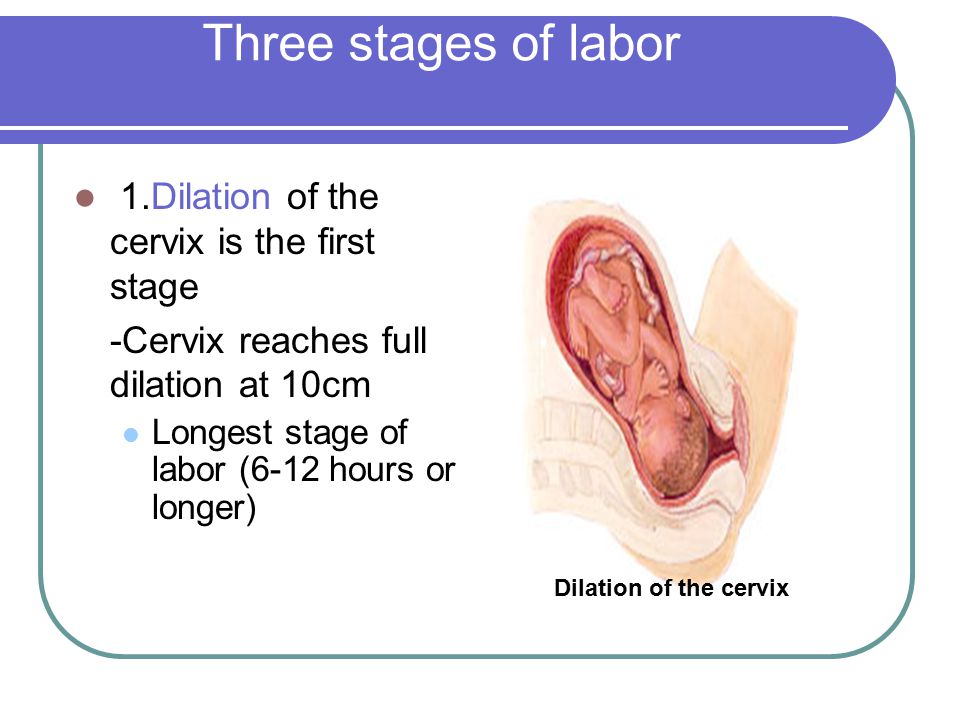 Contractions reappear and become more intense. They are joined by attempts - contractions of the muscle press (abdominal wall, diaphragm and pelvic floor). The frequency and intensity of contractions and attempts are constantly increasing. The head descends and compresses the nerves of the sacral plexus. A woman has a strong desire to squeeze the head out of the birth canal, she is looking for supports for her arms and legs to strengthen her efforts.
Contractions reappear and become more intense. They are joined by attempts - contractions of the muscle press (abdominal wall, diaphragm and pelvic floor). The frequency and intensity of contractions and attempts are constantly increasing. The head descends and compresses the nerves of the sacral plexus. A woman has a strong desire to squeeze the head out of the birth canal, she is looking for supports for her arms and legs to strengthen her efforts.
Pushing is a lot of physical work. During attempts, a woman experiences maximum physical stress (blood pressure rises, pulse and respiration become more frequent). During the attempts, the woman holds her breath, and in the intervals between them she rests and "gathers her strength for a new attempt."
In the process of one of the attempts, the head is born. Next, the shoulders are born (first the front, then the back) and the torso. Following the fetus, the posterior amniotic fluid is poured out with an admixture of cheese-like lubricant.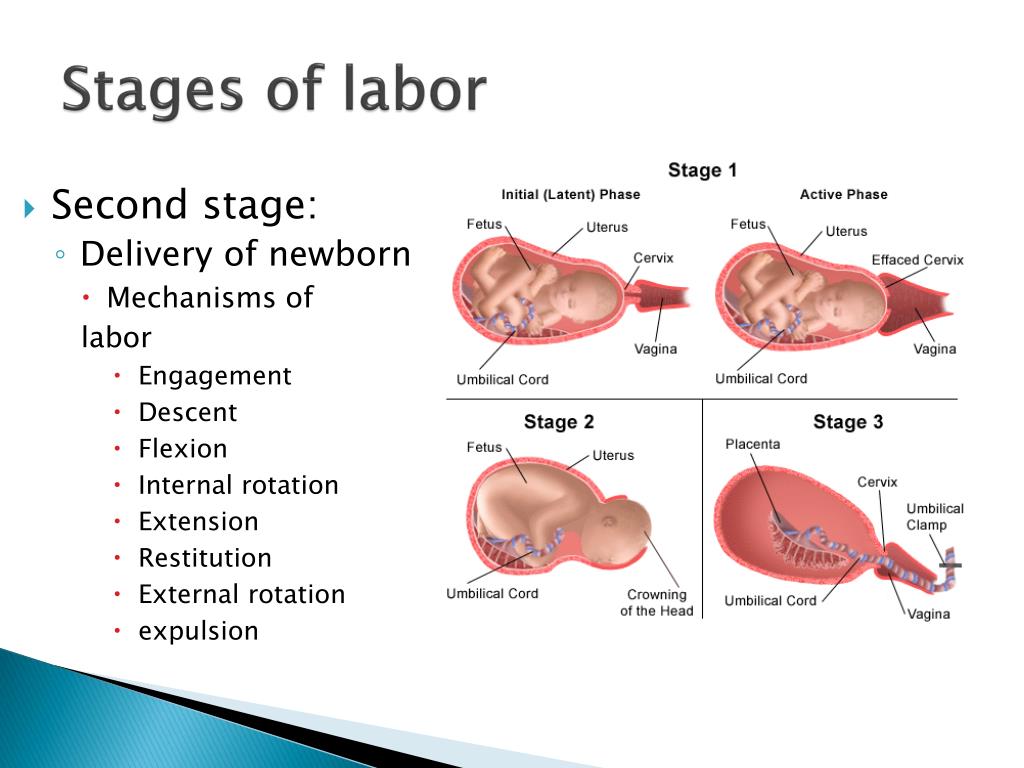
A woman in labor, having experienced severe fatigue, rests after hard work (pulse and respiration rate decrease).
Third stage of labor (postpartum period).
The afterbirth period is the time from the birth of the fetus to the birth of the placenta. During this period, the placenta separates from the walls of the uterus and the birth of the placenta (placenta with membranes and umbilical cord).
In the process of separation of the placenta from the walls of the uterus, the uteroplacental vessels are damaged, which is normally accompanied by blood loss in the amount of 100-200 ml, without adversely affecting the woman's condition. After the birth of the placenta, the uterus contracts sharply, becomes dense, which is necessary to stop bleeding in the area of the placental site; its bottom is in the middle between the womb and the navel.
During this period, the woman's pulse and respiration normalize. Her demeanor is calm. Sometimes chills can be observed (as a reaction to the transferred strong physical stress).