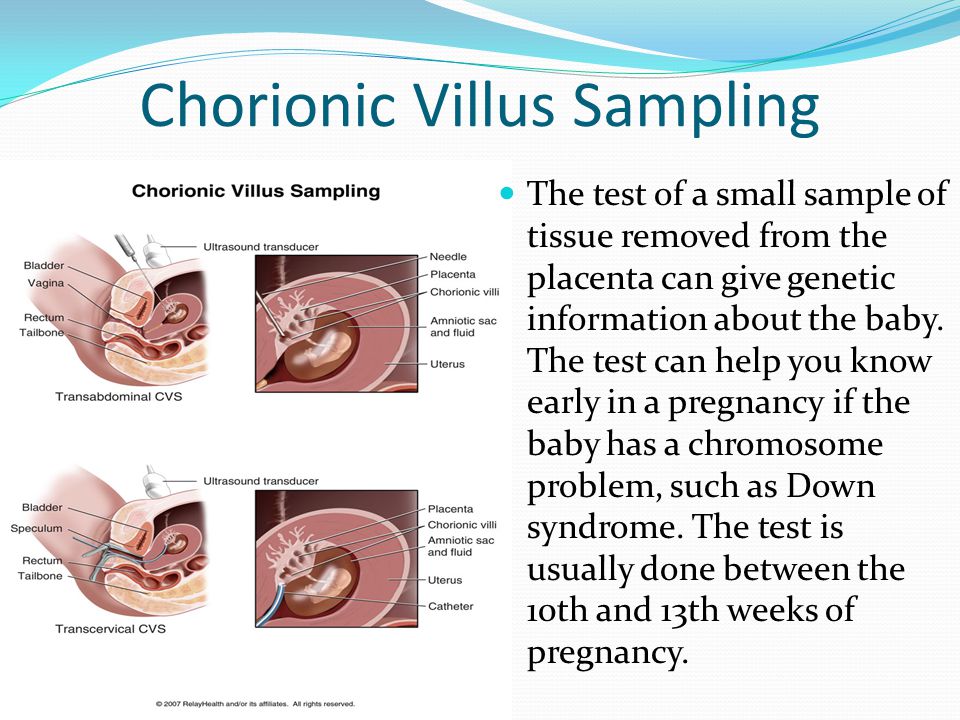
Fetal tissue miscarriage 5 weeks
5 Weeks Pregnant Miscarriage - MyBump2Baby
A miscarriage is defined as “the loss of a pregnancy during the first 23 weeks”. Somewhere between 8 and 20 percent of pregnancies end in miscarriage.
Most miscarriages happen before the 12th week of pregnancy, or during your first trimester.
In this article:
- Can You Have A Miscarriage at 5 Weeks?
- Why Am I Having Cramps at 5 Weeks Pregnant? – Is it Normal to Have Cramping at 5 Weeks Pregnant?
- 5 Weeks Early Pregnancy Symptoms
- Different Types of Miscarriage
- How Long Does Vaginal Bleeding from a Miscarriage Last?
- Different Types of Miscarriage
- How Heavy is 5 Week Miscarriage Bleeding?
- Miscarriage Risk Factors
- FAQs – Miscarriages at 5 Weeks Pregnant
Can You Have A Miscarriage at 5 Weeks?
You can have a miscarriage at any point of your pregnancy, although they are much more likely within the first 12 weeks (first trimester) of pregnancy.
Depending on the point of pregnancy you are in, depends on whether it may be considered a chemical pregnancy or early miscarriage.
A miscarriage at 5 weeks pregnant is considered to be a very early miscarriage.
A chemical pregnancy is a pregnancy loss that happens within the first 5 weeks of pregnancy, so a miscarriage at 5 weeks pregnant may be considered a chemical pregnancy.
Why Am I Having Cramps at 5 Weeks Pregnant? – Is it Normal to Have Cramping at 5 Weeks Pregnant?
Cramping at 5 weeks pregnant is usually nothing to worry about; it usually means that the embryo has implanted into your uterus (implantation has occured), or that your uterus is expanding nicely, to prepare to accomodate your developing embryo, or baby, for the next 8 months or so. If you are worried you can book a 5 week ultrasound scan!
If your cramps are severe or painful, you should contact your nearest healthcare professional to ensure that it’s not a sign of a problem. If they suspect a miscarriage, they may want to perform an early 4 week ultrasound scan.
If they suspect a miscarriage, they may want to perform an early 4 week ultrasound scan.
Below are more miscarriage symptoms at 5 weeks:
Signs of an Early Miscarriage – 5 Weeks
- Cramping that is slightly more severe than in your normal menstrual period
- Sharp or Severe Pain
- Bleeding from your vagina
- Loss of your usual pregnancy symptoms
5 Weeks Early Pregnancy Symptoms
Experiencing a loss of your usual pregnancy symptoms is a sign of miscarriage.
- Fatigue
- Morning Sickness
- Spotting
- Mild Cramping
- Bloating
- Mood swings
- Heightened Sense of Smell
- Breast Tenderness
Different Types of Miscarriage
There are several different kinda of miscarriage: complete, missed, incomplete, threatened and inevitable.
Complete
When a miscarriage occurs during the first 5 weeks of pregnancy, it is considered a very early miscarriage.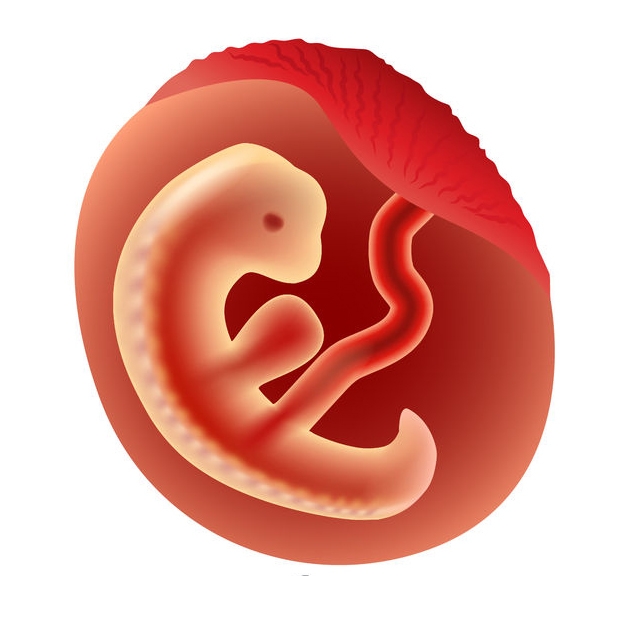 It is called a chemical pregnancy. At this stage, you may not have even known that you were pregnant.
It is called a chemical pregnancy. At this stage, you may not have even known that you were pregnant.
During a miscarriage, your bleeding may start as light spotting and develop into gushes of blood.
As the cervix dilates to prepare for the miscarriage, you will begin bleeding more heavily.
During very early pregnancy loss, you will only experience bleeding similar in strength to your period.
The colour of your blood during a miscarriage can vary: pink blood usually appears during light bleeding, red blood is fresh blood which has left the uterus instantly (like on your period) and brown blood is old blood that has taken longer to release. During a miscarriage, you may also see discharge like coffee grounds or nearly black in colour.
Missed Miscarriage
A missed miscarriage is when loss of pregnancy occurs, but the products of conception remain inside of the uterus. Due to there being no bleeding, a missed miscarriage is usually diagnosed via an ultrasound scan.
Incomplete Miscarriage
An incomplete miscarriage is when all of the products of conception are not passed through the cervix.
Signs of incomplete miscarriages are unusually heavy bleeding and a fever. An incomplete miscarriage can be diagnosed via an ultrasound scan- as the ultrasound reveals whether there is any pregnancy tissue remaining in your uterus.
To remove the rest of the pregnancy tissue, surgery may be performed. This surgery is also known as a dilation and curettage, or D & C.
Threatened Miscarriage
A threatened miscarriage is when vaginal bleeding occurs during pregnancy. Bleeding from your vagina does not always lead to miscarriages.
Mild cramping at 5 weeks pregnant may also be a sign of a threatened miscarriage at 5 weeks, although cramping is not always present.
After a threatened miscarriage, there is an 83% chance of your pregnancy resuming. If you experience bleeding during pregnancy, you should consult your doctor.
Inevitable
An inevitable miscarriages can either come after a a threatened miscarriage or without any warning at all.
In an inevitable miscarriage, there usually a larger amount of vaginal bleeding and painful lower abdominal cramps.
How Long Does Vaginal Bleeding From A Miscarriage Last?
How long a miscarriage (and bleeding) lasts, depends on how far along you were in the pregnancy and how long it takes for your body to expel the fetal tissue.
In many cases, it takes around two weeks for a miscarriage to pass naturally. Once a miscarriage starts, the majority of tissue and blood will be expelled in approximately 3 and 5 hours.
How Heavy is 5 Week Miscarriage Bleeding?
At 5 weeks pregnant, miscarriage bleeding may be brown and resemble coffee grounds, or can be bright red to pink.
This vaginal bleeding may be light, stop intermittently, or be like a heavy period.
Miscarriage Risk Factors
There are some factors which can increase your chances of having a miscarriage. You can read about these risk factors below.
You can read about these risk factors below.
Age
Women who are above 35 years of age are at higher risk of miscarriage.
At 35 years old, you have a miscarriage risk of 20%. At 40 years old, the risk doubles to around 40% and at around 45 years old, the risk doubles again to around 80%.
Weight
Having an unhealthy weight (underweight or overweight) increases the risk of miscarriage.
Previous Miscarriages
If you have experienced three or more miscarriages (recurrent miscarriage), you are at a high risk of miscarrying during pregnancy.
Uterine or Cervical Problems
Uterine or cervical issues (such as uterine abnormalities or an incompetent cervix) may increase the risk of miscarriage.
Smoking, Alcohol or Drugs
Unsafe, or unhealthy habits, such as smoking, drinking alcohol heavily or using other recreational or illicit drugs increases your risk of miscarriage.
Chronic Medical Conditions
Chronic Conditions, such as uncontrolled diabetes or high blood pressure, can increase your risk of miscarriage.
Can you still get a positive pregnancy test after a miscarriage?
After a miscarriage, you may still receive positive pregnancy test results on a home pregnancy test for days or weeks after your miscarriage. This is due to the fact that the pregnancy hormone- hCG- is still present in your body- the hormone that allows you to test positive on a pregnancy test.
FAQs – Miscarriages at 5 Weeks Pregnant
How Long Does a Miscarriage Last at 5 Weeks?
At 5 weeks pregnant, the amount of time it takes for the miscarriage to pass naturally can vary.
For some women, bleeding and cramping may last for a few hours, whilst another woman may experience miscarriage bleeding for a few days.
If You Miscarry at 5 Weeks What Happens?
A miscarriage at 5 weeks pregnant is a very early miscarriage.
When you have a miscarriage, you are likely to experience symptoms that are similar to a heavy period- including heavy vaginal bleeding, painful abdominal cramping, nausea and headaches.
If you believe you may have had a miscarriage, you should consult your health care provider.
What Does a Miscarriage Look Like at 5 Weeks?
At 5 weeks, there will likely not be any recognisable shape.
Your miscarriage will be pink or brown vaginal discharge with a consistency like coffee grounds, or bright red vaginal bleeding with clots.
What Does a Miscarriage Feel Like at 5 Weeks?
A miscarriage at 5 weeks pregnant often feels like a heavy period- and often goes unnoticed by women.
Follow Carla on her Pregnancy Journey
Join Carla, MyBump2Baby’s founder, on her pregnancy journey, where she shares her real experience week-by-week throughout her pregnancy.
Louise McCamily
Hi, I’m Louise- mum of one to a little boy called Mason.
I am the Digital Marketing and Admin Assistant for MyBump2Baby.
I enjoy working to provide excellent service to MyBump2Baby’s growing families.
Nice to meet you!
You can email me at [email protected]
What Does a Miscarriage Look Like? Bleeding, Duration, and More
A miscarriage is a spontaneous pregnancy loss before 20 weeks of gestation. Some 8 to 20 percent known pregnancies end in miscarriage, with the majority happening before the 12th week.
The signs and symptoms of miscarriage vary from person to person. Symptoms may also vary depending on how far along you are. For example, a fetus at 14 weeks will be much larger than a fetus at 5 weeks of gestation, so there may be more bleeding and tissue loss with a later miscarriage.
Miscarriage symptoms may include:
- spotting or bleeding from the vagina
- abdominal cramping or pain in the lower back
- passage of tissue, fluid, or other products from the vagina
Read on to learn more about identifying a miscarriage and what to do if you suspect you’re experiencing one.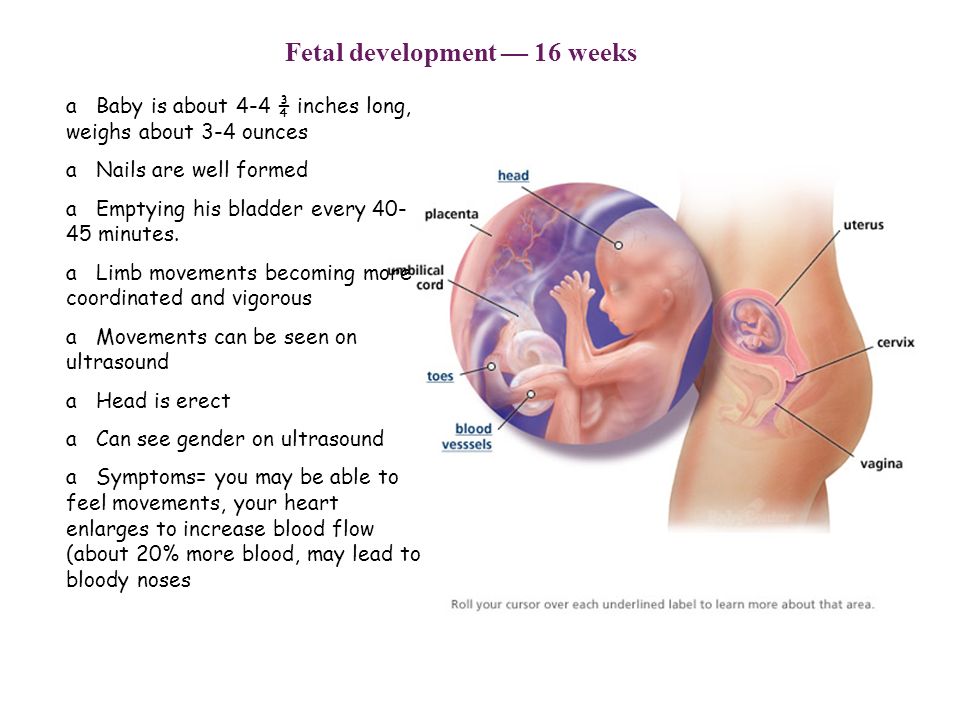
Bleeding may start as light spotting, or it could be heavier and appear as a gush of blood. As the cervix dilates to empty, the bleeding becomes heavier.
The heaviest bleeding is generally over within three to five hours from the time heavy bleeding begins. Lighter bleeding may stop and start over one to two weeks before it completely ends.
The color of the blood can range from pink to red to brown. Red blood is fresh blood that leaves the body quickly. Brown blood, on the other hand, is blood that’s been in the uterus a while. You may see discharge the color of coffee grounds, or near black, during a miscarriage.
Exactly how much bleeding you’ll experience depends on a variety of circumstances, including how far along you are and whether or not your miscarriage is progressing naturally.
While you may see a lot of blood, let your doctor know if you fill more than two sanitary pads an hour for two or more hours in a row.
What does a missed miscarriage look like?
You may not experience bleeding or other symptoms with a miscarriage, at least at first.
A missed miscarriage, also referred to as a missed abortion, happens when the fetus has died but the products of conception remain in the uterus. This type of miscarriage is usually diagnosed via ultrasound.
Just as with the amount of blood you’ll see, the duration of a miscarriage will vary from person to person and even from pregnancy to pregnancy.
In many cases, a miscarriage will take around two weeks to pass naturally. Your doctor may prescribe the medication misoprostol (Cytotec) to help a miscarriage pass more quickly. Bleeding may start within two days of beginning the medication. For others, it may take up to two weeks.
Once the miscarriage has started, the tissue and heaviest bleeding should be passed in about three to five hours. After the fetus has passed, you may still experience spotting and mild tissue loss for one to two weeks.
It may be difficult to tell a very early miscarriage from a late period. In fact, many miscarriages happen before a person even knows they’re pregnant.
In general, a miscarriage will cause more intense symptoms than a menstrual period. For example:
- Your menstrual flow may be relatively similar from month to month with heavy days and light days. A miscarriage can also have heavy and light days, but bleeding may be especially heavy at times and last longer than you’re used to.
- Bleeding from a miscarriage may also contain large clots and tissue you don’t normally see during your period.
- Cramps can be a part of your normal monthly cycle, but with a miscarriage, they may be particularly painful as the cervix dilates.
- The color of blood during your period can range from pink to red to brown. If you see a color you’re not used to seeing, it may be a sign of miscarriage.
Always contact your doctor if you’re pregnant and experience bleeding. While a miscarriage can’t be stopped once it starts, you doctor can run tests to help determine if you’re experiencing the loss of your pregnancy or something else.
To diagnose a miscarriage, your doctor will likely perform an ultrasound to look for the baby’s heartbeat, if you’re far enough along to see a heartbeat. Your doctor may also order a blood test to check human chorionic gonadotropin (hcG) levels to see if they’re rising or falling.
If a miscarriage is confirmed, your doctor may suggest “expectant management” or waiting for the miscarriage to pass naturally. This generally happens within two weeks.
Incomplete miscarriage
The miscarriage may be incomplete if:
- your bleeding is particularly heavy
- you have a fever
- an ultrasound reveals there’s still tissue in your uterus
If this is the case, your doctor may suggest a dilation and curettage (D and C), which is a surgical procedure done to remove remaining tissue. The procedure is done under general or regional anesthesia, and is considered safe. D and C doesn’t usually lead to long-term complications.
Threatened miscarriage
It’s important to report any bleeding or pain you experience in your pregnancy to your doctor. In some cases, you may have what’s called a threatened miscarriage, and there may be certain treatments that can help. These include:
In some cases, you may have what’s called a threatened miscarriage, and there may be certain treatments that can help. These include:
- hormone supplements if the bleeding is caused by low progesterone
- a cerclage (stitch in the cervix) if the issue is with the cervix opening prematurely
Speak with your healthcare provider if you’re looking to get pregnant again after a miscarriage. While it may be safe to start trying after your first normal period, you may want to schedule a checkup depending on the cause or the number of miscarriages you’ve had.
The reason for loss isn’t always known, but around half of miscarriages are caused by issues with the baby’s chromosomes.
Other possible causes include:
- uterine issues
- hormonal imbalances
- other health conditions, such as diabetes, autoimmune disorders, or polycystic ovary syndrome
After a miscarriage, you may have hcG in your blood for one to two months, which could lead to a false positive pregnancy test. In most cases, your period will return within four to six weeks, though you may start ovulating almost immediately following a miscarriage.
In most cases, your period will return within four to six weeks, though you may start ovulating almost immediately following a miscarriage.
Speak with your doctor about birth control options if you don’t wish to become pregnant after a miscarriage.
Will I miscarry again?
Having one miscarriage doesn’t necessarily increases your chances of having another. The risk remains around 20 percent.
Two or more miscarriages is referred to as recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL). The risk of miscarriage after two losses is 28 percent. After three consecutive losses, it increases to 43 percent.
Only 1 percent of people experience three or more miscarriages. About 65 percent of those with unexplained RPL go on to have successful pregnancies.
Activities like exercise, work, morning sickness, and sex don’t cause miscarriages. Even things like smoking or drinking alcohol or caffeine, which can lead to other complications, are also unlikely to lead to early pregnancy loss.
A miscarriage can be physically painful, and it may also cause a variety of emotions. While your body may recover in a few weeks, be sure to take time to process your feelings, grieve, and reach out for help when you need it.
Early miscarriage - City Hospital No. 12, Barnaul: articles
Early miscarriage is a spontaneous abortion for up to 12 obstetric weeks, often in the absence of cardiac activity in the fetus or an empty embryonic sac. Usually, an early miscarriage is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen or lower back of a different nature, bloody discharge from the vagina with a possible admixture of purulent masses or amniotic fluid. Diagnosis includes confirmation of pregnancy, physical examination of the patient, examination of the birth canal, and transvaginal ultrasound scanning. Treatment for an early miscarriage depends on its form and may include medical prolongation, termination of pregnancy, or vacuum aspiration.
General information
Early miscarriage is a pathological condition in obstetrics and gynecology, which is characterized by spontaneous abortion for up to 12 weeks. According to official statistics, about 15-20% of all confirmed pregnancies end in spontaneous termination. Early miscarriage is the most common complication in obstetrics, it accounts for about 80% of all spontaneous abortions and in 70% of cases occurs before the clinical manifestation of pregnancy. About a third of all cases of early miscarriages occur before 8 obstetric weeks due to the absence of an embryo. This condition is most common among mothers over the age of 40. This is due to the high frequency of chromosomal abnormalities, which are responsible for over 50% of all early miscarriages.
According to official statistics, about 15-20% of all confirmed pregnancies end in spontaneous termination. Early miscarriage is the most common complication in obstetrics, it accounts for about 80% of all spontaneous abortions and in 70% of cases occurs before the clinical manifestation of pregnancy. About a third of all cases of early miscarriages occur before 8 obstetric weeks due to the absence of an embryo. This condition is most common among mothers over the age of 40. This is due to the high frequency of chromosomal abnormalities, which are responsible for over 50% of all early miscarriages.
Causes of early miscarriage
More than half of early miscarriages are caused by fetal chromosomal mutations, in particular, autosomal trisomies, X-chromosome monosomies and polyploidies. A minority of cases are provoked by factors that have a teratogenic effect on the fetus and create an unfavorable environment for its development. This includes the mother's use of alcohol, cigarettes, large amounts of caffeine (more than 4 cups per day) or drugs, infectious diseases (syphilis, chlamydia, toxoplasmosis), certain medications (NSAIDs, retinoids, antimycotics, antidepressants), occupational hazards (ionizing radiation, toxins, etc.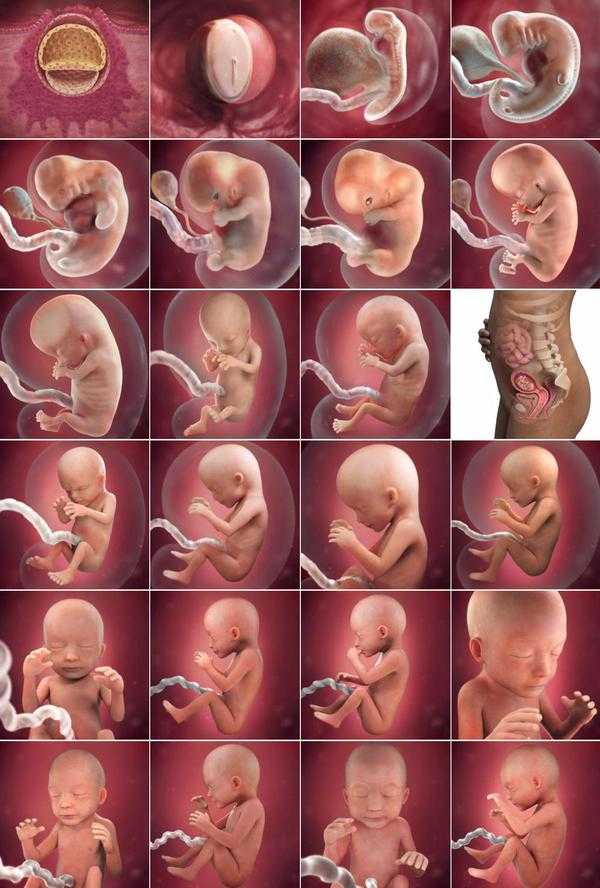 ).
).
Also, the cause of early miscarriage may be the mature age of the mother (after 40 years, the risk of spontaneous abortion is more than 40%), anomalies in the development of the genital organs, severe obesity, direct abdominal trauma, chronic diseases (antiphospholipid syndrome, polycystic ovaries, thyroid disease, etc.). ).
Symptoms of early miscarriage
There are several clinical variants of early miscarriage: threatening, incipient, septic and incomplete miscarriage, miscarriage in progress. A threatened miscarriage is manifested by pain in the suprapubic and lumbar regions of a pulling nature, scanty bloody discharge from the vagina. At the same time, hypertonicity of the uterus is observed, its dimensions correspond to the gestational age, and the internal pharynx is closed. An early miscarriage that has begun has the same symptoms, but they are more pronounced, and the cervical canal goes into an ajar state. A miscarriage in the course is characterized by recurring pains in the lower abdomen of a cramping nature, more pronounced bloody discharge, less often with an admixture of amniotic fluid. During the examination, the uterus is smaller than it should be for a given gestational age, the external and internal os are open. In the lumen of the vagina or cervix, elements of the fetal egg can be determined.
During the examination, the uterus is smaller than it should be for a given gestational age, the external and internal os are open. In the lumen of the vagina or cervix, elements of the fetal egg can be determined.
Incomplete early miscarriage (incomplete abortion) is a woman's condition in which, after termination of pregnancy, elements of the fetal egg remain in the uterus. It is accompanied by moderate pain in the lumbar region and lower abdomen, massive bleeding, which can lead to hemorrhagic shock. Septic or infected early miscarriage - termination of pregnancy, characterized by signs of infection of the genital organs: a sharp increase in body temperature, general weakness, pain in the pelvic area, purulent discharge from the vagina, increased heart rate and respiratory rate, muscular defense of the anterior abdominal wall.
Diagnosis of early miscarriage
Diagnosis of early miscarriage is based on the collection of anamnestic data and complaints of the patient, an objective examination, data from laboratory and instrumental research methods.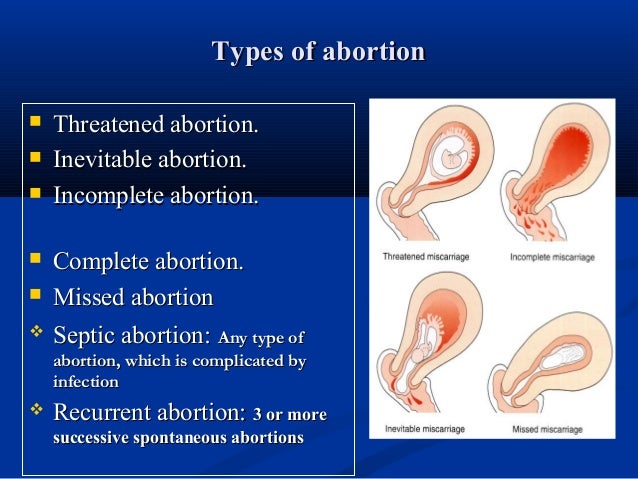 When interviewing a woman, an obstetrician-gynecologist pays attention to the date of the last menstruation, bad habits, occupational hazards, chronic diseases present, recent infections, medications and the results of past pregnancies. Collecting complaints, the specialist specifies the amount of bleeding from the vagina, the presence of pus or amniotic fluid, the nature and localization of the pain syndrome. At the baseline examination of a woman with suspected early miscarriage, the general condition, body temperature, heart rate, respiratory rate and blood pressure are assessed. Next, an examination of the abdomen is performed, followed by a vaginal examination using speculums and a bimanual examination to assess the size and consistency of the uterus. Among the laboratory tests, in addition to basic tests, the level of progesterone and β-human chorionic gonadotropin (β-hCG) is measured to determine a possible ectopic pregnancy.
When interviewing a woman, an obstetrician-gynecologist pays attention to the date of the last menstruation, bad habits, occupational hazards, chronic diseases present, recent infections, medications and the results of past pregnancies. Collecting complaints, the specialist specifies the amount of bleeding from the vagina, the presence of pus or amniotic fluid, the nature and localization of the pain syndrome. At the baseline examination of a woman with suspected early miscarriage, the general condition, body temperature, heart rate, respiratory rate and blood pressure are assessed. Next, an examination of the abdomen is performed, followed by a vaginal examination using speculums and a bimanual examination to assess the size and consistency of the uterus. Among the laboratory tests, in addition to basic tests, the level of progesterone and β-human chorionic gonadotropin (β-hCG) is measured to determine a possible ectopic pregnancy.
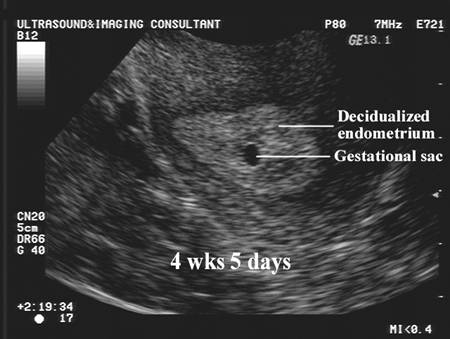
The leading place in the diagnosis of early miscarriage is occupied by ultrasound (ultrasound). Currently, transvaginal ultrasound (TVS) is the "gold standard" in the diagnosis of pregnancies in the early stages. Only if it is impossible to carry out a transabdominal scan (TAS) is used. Signs of early miscarriage include an average internal diameter of the fetal egg over 20 mm on the TVS and 25 mm on the TAS, respectively, the absence of cardiac activity or the complete absence of its visualization. Differential diagnosis of early miscarriage is carried out with benign and malignant neoplasms of the cervix and vagina, chorionepithelioma and ectopic pregnancy.
Currently, transvaginal ultrasound (TVS) is the "gold standard" in the diagnosis of pregnancies in the early stages. Only if it is impossible to carry out a transabdominal scan (TAS) is used. Signs of early miscarriage include an average internal diameter of the fetal egg over 20 mm on the TVS and 25 mm on the TAS, respectively, the absence of cardiac activity or the complete absence of its visualization. Differential diagnosis of early miscarriage is carried out with benign and malignant neoplasms of the cervix and vagina, chorionepithelioma and ectopic pregnancy.
Treatment of early miscarriage
The treatment regimen for early miscarriage directly depends on the clinical form of the pathology and the decision of the mother. With a threatened or incipient miscarriage, prolongation of pregnancy is possible, with intrauterine death of the fetus, medical abortion is indicated. In order to maintain pregnancy and prevent early miscarriage, gestagens are used. Tranexamic acid is also used for hemostatic purposes, and drotaverine is used to relieve pain. If it is impossible to prolong the pregnancy, medical curettage is indicated. There are various options for its implementation, in which prostaglandin analogues can be combined with an antiprogestin.
If it is impossible to prolong the pregnancy, medical curettage is indicated. There are various options for its implementation, in which prostaglandin analogues can be combined with an antiprogestin.
Surgical treatment is indicated in cases of infected and incomplete early miscarriage, as well as massive bleeding caused by the latter. The essence of the surgical intervention is to remove the remaining tissues of the chorion or placenta and complete hemostasis. As a rule, such interventions are performed using a vacuum aspirator or other sources of vacuum, less often they resort to instrumental curettage. According to modern research, before surgery for early miscarriage, it is effective to preliminarily (1-1.5 hours) use of NVPS and drugs from the benzodiazepine group.
Forecast and prevention of early miscarriage
The prognosis for early miscarriage is favorable in most cases. The risk of repeated miscarriage increases slightly and is 19-20% compared to the average of 15%. Among couples in whom it was not possible to identify the cause of early miscarriage, in more than 65% of cases, re-pregnancy goes well.
Among couples in whom it was not possible to identify the cause of early miscarriage, in more than 65% of cases, re-pregnancy goes well.
There is no specific prevention of early miscarriage. Non-specific preventive measures involve the exclusion of etiological factors through full antenatal protection of the fetus and rational pregnancy planning. If a couple wants to have a child, it is recommended to visit specialized centers and consult a geneticist. After confirming the fact of pregnancy, in order to prevent early miscarriage, a woman should exclude all teratogenic factors, completely abandon bad habits and undergo all control examinations according to the recommendations of an obstetrician-gynecologist.
Threatened abortion is the risk of abortion before 22 weeks of gestation. The condition is accompanied by aching or pulling pain in the lower abdomen, the release of a small amount of blood, but the cervix retains its structure. Diagnosis is based on the complaints of the pregnant woman, clinical symptoms, examination, ultrasound data. The goal of treatment is to preserve the fetus and prolong childbearing as much as possible. Hormonal drugs, antispasmodics are used to relieve the tone of the myometrium, symptomatic treatment aimed at stopping bleeding.
The goal of treatment is to preserve the fetus and prolong childbearing as much as possible. Hormonal drugs, antispasmodics are used to relieve the tone of the myometrium, symptomatic treatment aimed at stopping bleeding.
ICD-10
General
Clinical protocols recommend not using the term "threatened abortion" to reduce the psychological burden on a woman at risk of losing a desired pregnancy. Instead, it is proposed to call this condition a threatened miscarriage. The definition includes cases when detachment of the fetal egg occurs at an early stage - up to 12 weeks. The appearance of uterine tone and bleeding from 12 to 22 weeks is considered a late threat of abortion. Later this period, similar symptoms are called the threat of premature birth. It is erroneously believed that a miscarriage is provoked by sexual activity, blunt abdominal trauma, and physical activity. The main causes are chromosomal abnormalities, infections, endocrine disorders.
Causes
Spontaneous threat of short-term pregnancy termination in 50% of patients is associated with chromosomal abnormalities of the embryo. After 16 weeks, threatened miscarriage is the result of genetic defects in 10% of cases. The shorter the gestational age, the higher the likelihood that a threatened abortion will turn into a spontaneous miscarriage. The infection can cause a violation of the development of the fetal egg and a threatening abortion in chronic endometritis, viral infection during childbearing. The danger is higher at an early stage, until the placenta is formed, which acts as a protective filter.
After 16 weeks, threatened miscarriage is the result of genetic defects in 10% of cases. The shorter the gestational age, the higher the likelihood that a threatened abortion will turn into a spontaneous miscarriage. The infection can cause a violation of the development of the fetal egg and a threatening abortion in chronic endometritis, viral infection during childbearing. The danger is higher at an early stage, until the placenta is formed, which acts as a protective filter.
Identifies factors that significantly increase the risk of threatened abortion. They are associated with endogenous conditions, features of the lifestyle of the expectant mother. Of great importance are the transferred acute and chronic diseases, as well as the action of external stimuli and pathogens. These factors are taken into account when registering a woman with an obstetrician-gynecologist and managing pregnancy:
- Mother's age . In women 20-30 years of age, threatening abortion occurs in 9-15%, after 30 years this figure increases to 20%, and in 45-year-olds - up to 80%.
 Young girls under 18 years of age also often face the development of a threat of interruption of gestation due to the immature hypothalamic-pituitary system, physiological dysfunction of the ovaries.
Young girls under 18 years of age also often face the development of a threat of interruption of gestation due to the immature hypothalamic-pituitary system, physiological dysfunction of the ovaries. - Maternal endocrine disorders . Pathology of the thyroid gland, uncompensated diabetes mellitus, polycystic ovary syndrome cause endocrine changes that worsen the condition of the endometrium, the production of hormones of the corpus luteum of the ovaries. Obesity leads to a change in the synthesis of steroid hormones, which leads to their imbalance.
- History of pregnancy loss . In women with recurrent miscarriage, the risk is 30%. If there was a history of normal childbirth and there are no spontaneous miscarriages, then the risk of interruption of gestation in a pregnant woman is only 5%.
- Taking medicines. The use of drugs with teratogenic effects (retinoids, anticoagulants), large doses of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs inhibit the synthesis of prostaglandins and impair embryo implantation, which may later cause a threatened miscarriage.
- Effects of toxic substances . The threat of interruption of gestation may occur in women working in hazardous conditions, in hazardous industries. Alcohol has a toxic effect on the endometrium and the fetus with systematic use, smoking 10 cigarettes a day, and cocaine use. Dose-dependent effect has coffee, soft drinks with caffeine. The danger is the use of 4-5 cups of strong drink or 100 mg of caffeine per day.
- Autoimmune diseases. Antiphospholipid syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus is associated with the formation of antibodies to phospholipids and other cell structures. A woman is more prone to microthrombosis. Thrombi form in the vessels of the endometrium, which disrupts the nutrition of the embryo, leading to a threatening abortion or death of the fetal egg.
Pathogenesis
The mechanism of development of threatened miscarriage is associated with increased uterine contractility. In the event of an infection, the blood flow in the vessels that feed the embryo is disturbed, their spasm occurs. The embryo does not receive the right amount of nutrients and oxygen. At this stage, his death may occur. Spasm of microvessels leads to their rupture, there is a slight bleeding into the wall of the uterus, a retrochorial hematoma is formed. It exfoliates the fetal egg from the endometrium. If the bleeding is not stopped in time, a threatened abortion turns into a miscarriage in the course. Pregnancy loss in the 1st and early 2nd trimester occurs without rupture of the membranes.
The embryo does not receive the right amount of nutrients and oxygen. At this stage, his death may occur. Spasm of microvessels leads to their rupture, there is a slight bleeding into the wall of the uterus, a retrochorial hematoma is formed. It exfoliates the fetal egg from the endometrium. If the bleeding is not stopped in time, a threatened abortion turns into a miscarriage in the course. Pregnancy loss in the 1st and early 2nd trimester occurs without rupture of the membranes.
Symptoms of threatened abortion
Unpleasant symptoms appear against a background of complete well-being. The pregnant woman begins to feel a feeling of discomfort in the lower abdomen, which gradually turns into a pulling, aching pain. The pain is localized indistinctly above the pubis, may radiate to the sacrum, lower back, perineum. With a threatened abortion, sensations do not turn into contractions, otherwise this indicates the progression of the pathology and a developing miscarriage.
There may be no discharge from the genital tract at the initial stage. This is typical for the formation of a small hematoma behind the fetal egg, which is not emptied into the uterine cavity. If its detachment occurs along the edge, then the pregnant woman notices bloody spotting or bloody-bloody discharge on the linen, which looks like streaks of dark blood mixed with mucus. With the threat of a miscarriage, they do not transform into massive bleeding with scarlet or dark blood. Allocations appear several times a day, gradually their number decreases under the influence of therapy. If this does not happen, the progression of the pathology is assumed.
This is typical for the formation of a small hematoma behind the fetal egg, which is not emptied into the uterine cavity. If its detachment occurs along the edge, then the pregnant woman notices bloody spotting or bloody-bloody discharge on the linen, which looks like streaks of dark blood mixed with mucus. With the threat of a miscarriage, they do not transform into massive bleeding with scarlet or dark blood. Allocations appear several times a day, gradually their number decreases under the influence of therapy. If this does not happen, the progression of the pathology is assumed.
Violation of general well-being is not typical. Pain in the lower abdomen does not reduce the working capacity of the pregnant woman, but there is a desire to lie down and relax. Often this helps to reduce the intensity of discomfort. Increased pain is provoked by nervous experiences, physical activity or lack of proper rest. Sexual relations can also become a factor in the progression of threatened abortion.
Complications
If you do not consult a gynecologist in time, a threatened miscarriage can turn into an unstoppable abortion. In this case, severe cramping pains appear, which can lead to the opening of the cervix. At week 22, the fetus is not viable, so the birth leads to its death. Termination of pregnancy is accompanied by bleeding. A woman needs medical care to reduce the risk of massive blood loss, the addition of infectious complications. Temperature or signs of intoxication indicate a septic abortion.
An incomplete miscarriage is an incomplete process in which the fetus separates but the membranes remain in the uterus. This disrupts uterine contractions, the vessels of the uterus gape, so there is a high probability of bleeding. Complications of this condition can be hemorrhagic shock, DIC, endometritis. Inflammation of the mucous membrane in the future becomes the cause of infertility, resistant to treatment.
Diagnosis
If characteristic complaints appear, you should contact an obstetrician-gynecologist for examination and diagnosis. After confirming the diagnosis, hospitalization may be required for treatment and follow-up. Examination of a pregnant woman includes:
After confirming the diagnosis, hospitalization may be required for treatment and follow-up. Examination of a pregnant woman includes:
- Inspection on chair . Physical examination shows that the cervix is tightly closed, but there may be a small amount of brown discharge in the vagina. Bimanual examination does not cause pain, the vaginal vaults are free. On palpation, the uterus remains unexcitable, soft, but there is a slight soreness. The ovaries are not palpable.
- Laboratory diagnostics . Needed to evaluate ovarian function and monitor pregnancy. Blood is taken for hCG, to confirm a progressing pregnancy, the analysis is carried out in dynamics with an interval of several days. Determine the level of progesterone. According to the indications, an estrogen test may be prescribed.
- Pelvic ultrasound . The "gold standard" for diagnosing a threatened miscarriage is an ultrasound transvaginal probe, the accuracy of the technique is higher than in transabdominal examination.
 According to ultrasound, signs of fetal viability are determined. A fetal egg is visualized in the uterine cavity, a heartbeat is determined in the embryo or fetus. With doubtful results, the study is repeated twice by different specialists with an interval of 7-10 days.
According to ultrasound, signs of fetal viability are determined. A fetal egg is visualized in the uterine cavity, a heartbeat is determined in the embryo or fetus. With doubtful results, the study is repeated twice by different specialists with an interval of 7-10 days.
Treatment of threatened miscarriage
A pregnant woman with bleeding and a threat of miscarriage in the short term should be urgently hospitalized in the gynecology department. She is assigned a medical-protective regime, it is not recommended to get out of bed. In some institutions, as an additional method of therapy, raising the foot of the bed by 5 cm is practiced. Medical preservation therapy is prescribed:
- Progesterone preparations . Use dydrogesterone or micronized progesterone. They are prescribed to maintain the function of the placenta according to an individual scheme. For women who have had interruptions for a short period in the past, drugs are prescribed preventively until signs of danger appear.
- Estrogens . They are included in the treatment regimen from the 6th week of gestation, if, according to the results of the tests, their deficiency is revealed. Needed to improve the action of progesterone. The dosage is selected individually.
- Relieving uterine tone . For the relief of pain and muscle spasm in pregnant women, it is allowed to use drotaverine, papaverine. They are prescribed intramuscularly, later they switch to tablet forms. A solution of magnesium sulfate has a pronounced tocolytic effect. It is used to reduce uterine tone, lower blood pressure and improve fetal nutrition.
- Hemostatic therapy . To stop bleeding, sodium etamsylate is used in the form of a solution intramuscularly or intravenously. Aminocaproic and tranexamic acid are approved for use.
Forecast and prevention
With timely access to an obstetrician-gynecologist and proper treatment, the prognosis is favorable. The fetus can be saved if the area of detachment of the fetal egg is small, the bleeding has stopped, and the hematoma gradually resolves. The remaining period of gestation, the woman is under the close supervision of a doctor in order to notice the deterioration in time and take measures to prevent complications. Prevention of threatening spontaneous abortion consists in preconception preparation, sanitation of foci of infection in the body. Women need to start taking folic acid and vitamin E 2 months before conception.
The remaining period of gestation, the woman is under the close supervision of a doctor in order to notice the deterioration in time and take measures to prevent complications. Prevention of threatening spontaneous abortion consists in preconception preparation, sanitation of foci of infection in the body. Women need to start taking folic acid and vitamin E 2 months before conception.
1. Miscarriage in early pregnancy: diagnosis and tactics. Clinical guidelines / ed. Serova V.N. – 2016.
3. The procedure for providing medical care in the profile "Obstetrics and Gynecology" / Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated November 1, 2012 No. 572n.
When a woman is pregnant, the safety of her unborn child is her number one priority, so she should be aware of the early signs and symptoms of a miscarriage. Since the risk of miscarriage in early pregnancy is especially high, up to 12/13 weeks, you need to carefully monitor the health of the expectant mother.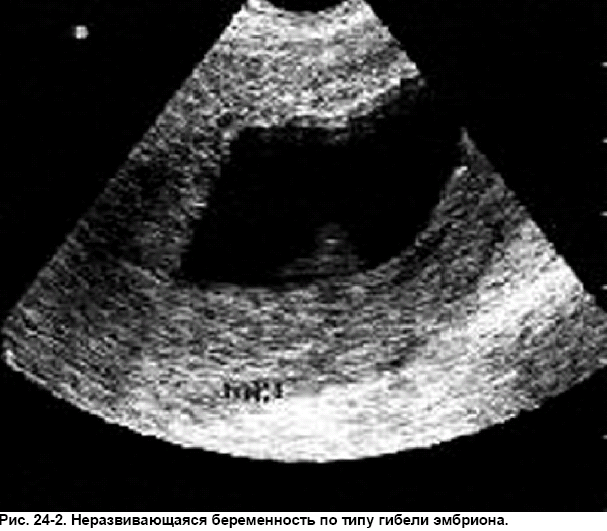 It is believed that in the first week after conception, up to 50% of fertilized eggs die, when a woman is not yet aware of the changes taking place in her body.
It is believed that in the first week after conception, up to 50% of fertilized eggs die, when a woman is not yet aware of the changes taking place in her body.
At this time, dangerous symptoms that indicate a threat of pregnancy are so implicitly expressed that they can be ignored. Later, after the conception becomes known, and the test confirms that fertilization has occurred, at least 10-20% of pregnancies end tragically.
According to statistics, from 1 to 4% of women have two miscarriages in the early stages in a row. Even more rarely, threats of miscarriage lead to three or more miscarriages. This condition is referred to as habitual miscarriage. A synonym for the word "miscarriage" is "spontaneous abortion", when it means that the body itself gets rid of the embryo.
Signs of a threatened miscarriage - warning signs
Signs of a threatened miscarriage in early pregnancy include the following conditions: The blood may have a brown or brownish tint, or it may be bright scarlet;
If you are in danger of having a miscarriage and some of the symptoms listed above have made you wary, don't waste your time. Contact your doctor immediately who is monitoring your pregnancy. The specialist will examine you, send you for an ultrasound, and then diagnose whether there is a threat and what treatment will be effective. Or he will say that fears are in vain.
Types of early miscarriage
If we talked about the signs of early pregnancy termination, it is necessary to understand how doctors classify the condition. The typology is based on the following groups:
- Threatened miscarriage - slight bleeding in the first trimester. About 1/3 of women will bleed during this period, and only half of them are diagnosed with spontaneous abortion;
- Complete miscarriage - symptoms of a threatened early miscarriage are confirmed by a medical examination, which shows that a spontaneous abortion has occurred. In this case, all embryonic tissues come out of the uterus.
 Subsequently, no additional treatment or observation by specialists is required;
Subsequently, no additional treatment or observation by specialists is required; - Incomplete miscarriage - the threat of miscarriage in early pregnancy is confirmed. The embryo dies, but its tissues do not completely leave the uterus, which threatens to provoke an infection and can cause sepsis. Some women may need emergency surgery due to heavy bleeding. Medications may be used to provoke the uterus into contractions and ejection of fetal debris. In some cases, waiting tactics are acceptable without taking any action;
- Anembryony - a condition in which the symptoms of a threatened miscarriage in the early stages may not be observed. Fertilization of the egg occurs, its implantation in the wall of the uterus, but there is no formation of the fetus. In some cases, even a gestational sac is formed;
- Missed miscarriage - with a frozen pregnancy, when it stops developing, the embryonic tissue does not leave the uterus for at least 4 weeks. One of the main symptoms of a miscarriage in the early stages is absent - heavy bleeding.
 There may be slight spotting;
There may be slight spotting; - Septic miscarriage - accompanied by infection in the uterine cavity. A serious illness that requires immediate treatment to prevent the death of the failed mother. Early signs of a threatened septic miscarriage are fever, abdominal pain, and foul-smelling bleeding. It is important to start injecting antibiotics as soon as possible and remove the foreign contents of the uterus.
Many women are interested in the logical question of what to do with the threat of miscarriage in early pregnancy and how to prevent a dangerous condition. We will talk about this a little later, first we will designate the factors provocateurs of spontaneous abortion.
Miscarriage provocateurs in early pregnancy
Among the factors that future parents can influence are smoking, alcohol, drugs, excessive physical labor of the mother during pregnancy. This can be corrected by minimizing their effect. However, there are reasons that are difficult to influence:
- Genetics - about half of spontaneous abortions are due to genetic abnormalities that are incompatible with the life of the fetus;
- Maternal diseases - even a banal increase in temperature to extreme values \u200b\u200bcan harm the developing embryo, but there are more dangerous infections - measles, rubella, cytomegalovirus and others;
- Hormonal imbalance - women with irregular periods have a higher risk of threatened miscarriage in early pregnancy than those who have regular periods;
- Placental problems - disturbances in the blood supply to the placenta, which provokes a lack of nutrition of the embryo;
- Early dilatation of the cervix, fibroids, an unusual shape of the organ that prevents the fetus from developing;
- Mechanical injuries - can provoke spontaneous abortion in the early stages, the threat of miscarriage at 20 weeks and later.
One of the common threats of miscarriage in early pregnancy is an ectopic pregnancy, when the embryo develops in one of the fallopian tubes or elsewhere - outside the uterus. Equally important is the age of the mother:
There are other reasons why there is a single miscarriage and two miscarriages in the early stages in a row. Finding out the reasons is better to entrust to specialists, if necessary, visit a genetics consultation, pass the necessary tests and undergo examinations. This is especially true for women who have had two miscarriages in the early stages. However, this is not a reason to put a sentence on a woman's ability to bear children. The chance to endure and give birth to a healthy baby is great even after three unsuccessful pregnancies.
What to do if there is a threat of miscarriage – getting ready for a new conception
If you have had two miscarriages in the early stages, but you are striving for the birth of a healthy baby, it is important to carefully plan your pregnancy, avoid stress, overload, hypothermia and other negative factors. You do not need to be alone with your misfortune, it is important to find a specialist you will trust, who knows what to do with a threatened miscarriage and how to reduce the risks when planning a new conception.
You do not need to be alone with your misfortune, it is important to find a specialist you will trust, who knows what to do with a threatened miscarriage and how to reduce the risks when planning a new conception.
One of the important points is to find the root cause of what is happening. It is important to remember the symptoms of a threatened miscarriage, when they occurred, whether they were preceded by some events that could play a decisive role. On the recommendation of a doctor, undergo special examinations:
- Blood tests - deciphering the results in the laboratory will help you find hormonal problems or identify negative features of the immune system;
- Chromosomal tests - to detect signs of a threatened miscarriage in the early stages, it is enough for partners to donate blood, in which chromosomal abnormalities can be detected. Ideally, fetal tissue should be submitted for analysis, which will also be scrupulously checked.
To find out how to prevent the threat of miscarriage in the early stages, resulting from the pathology of the uterus, you need to go through:
- Ultrasound - thanks to the action of high-frequency sound waves, an image is formed on a computer monitor, which accurately reflects the features of the examined areas, tissues, organs.
 The specialist conducts an examination by external scanning and examination through the vagina. Thanks to the ultrasound method, fibroids and other anomalies can be detected;
The specialist conducts an examination by external scanning and examination through the vagina. Thanks to the ultrasound method, fibroids and other anomalies can be detected; - Hysteroscopy - the introduction of a hysteroscope through the cervix into the internal cavity of the organ. Thanks to special illumination, the doctor clearly sees structural transformations in tissues, which allows him to diagnose the problem and prescribe effective treatment to prevent miscarriage in the early stages;
- Hysterosalpingography and sonohysterography - a contrast agent is injected into the uterus through a catheter. That allows you to make visible the structure of the organ and the fallopian tubes on an X-ray image and through ultrasound. Using this method, the uterine contour is examined and the presence of obstructive formations in the fallopian tubes is revealed.
If the cause of spontaneous abortion is not found, every effort is made to re-conceive. Knowing the symptoms of a threatened miscarriage, a woman treats her health with particular care, watches the change of states. It is important during the pregnancy planning period to rest more, eat right, take vitamin and mineral complexes prescribed by a doctor.
It is important during the pregnancy planning period to rest more, eat right, take vitamin and mineral complexes prescribed by a doctor.
It is necessary to get rid of bad habits, get enough sleep, not expose yourself to stress. Try not to appear in public places unnecessarily, so as not to become a victim of an airborne infection that can adversely affect pregnancy. If there are factors harmful to health at work, it is better to exclude their influence.
Late miscarriage is a spontaneous abortion at 13 to 22 weeks of gestation. Depending on the stage, a woman experiences pains of a pulling or cramping type in the lower back and lower abdomen, bloody vaginal discharge is noted, a fetal egg or its fragments depart. For diagnosis, bimanual palpation, transabdominal gynecological ultrasound, analysis for the content of hCG are used. With a threatening late abortion, a protective regimen, hormonal, antispasmodic, sedative drugs are prescribed. Patients with incipient and ongoing miscarriage are shown emptying the uterine cavity, antibacterial and antianemic therapy.
General information
Late spontaneous abortion (miscarriage) occurs in 2-4% of women with clinically confirmed pregnancy, which is about 1/5 of all cases of premature termination. The key difference between late miscarriage and preterm birth is the non-viability of the fetus, which weighs up to 500 g during abortion and cannot independently develop outside the uterine cavity, which approximately corresponds to the 22nd week of gestation. There is a certain difference in the approaches of domestic and foreign obstetricians to the management of pregnant women with the threat of miscarriage. While expectant management is practiced abroad, in Russia, patients with threatened abortion are prescribed medication.
Causes of late miscarriage
Unlike early miscarriage, premature termination of pregnancy at 13-22 weeks in extremely rare cases is caused by genetic abnormalities. By this time, the main organs of the fetus have already been formed, so miscarriage is usually caused by:
- Isthmic-cervical insufficiency .
 Cervical insufficiency is caused by genetic abnormalities, hormonal disorders or mechanical damage in previous births. The descent of the fetal bladder and the opening of its membranes provokes the premature onset of labor. ICI is detected in 15-40% of patients with recurrent miscarriage.
Cervical insufficiency is caused by genetic abnormalities, hormonal disorders or mechanical damage in previous births. The descent of the fetal bladder and the opening of its membranes provokes the premature onset of labor. ICI is detected in 15-40% of patients with recurrent miscarriage. - Uterine pathology . The normal course of pregnancy is hampered by developmental anomalies (unicornuate, bicornuate, saddle uterus), inflammatory processes, adenomyosis, submucosal fibroids, and other benign and malignant neoplasms.
- Pathology of the placenta and umbilical cord . Late miscarriage can occur due to delayed maturation or hypoplasia of the placenta, the presence of cysts and areas of calcification in its tissues, inflammation and premature detachment. True nodes and thrombosis of the vessels of the umbilical cord also lead to the death of the fetus.
- Immunological factors . Spontaneous late abortion may be the result of incompatibility of the blood of the mother and fetus according to the Rh factor or the AB0 system.
In addition to the immediate causes leading to late abortion, there are a number of predisposing factors. So, pregnancy is more often spontaneously interrupted in patients with sexually transmitted infections, dyshormonal conditions, concomitant somatic diseases (diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension), and gestosis. The risk of miscarriage increases in women who have previously undergone induced abortions, gynecological surgeries, invasive diagnostic procedures, and complicated births with cervical damage. Late abortion can also be provoked by injuries, intoxications, infectious diseases, significant physical and psychological stress.
Pathogenesis
The mechanism of late spontaneous interruption of the gestational period is determined by the causes that caused it. In this case, the tone of the uterus usually first increases and the contractile activity of the myometrium increases, which leads to shortening and opening of the cervix, rejection of the fetal egg from the uterine wall, followed by death and expulsion. Sometimes fetal death precedes a late abortion. At the beginning of the second trimester, the membranes during a miscarriage usually do not open, the fetal egg comes out entirely. After the expulsion of all parts of the fetal egg is completed, the myometrium contracts, bleeding stops.
Sometimes fetal death precedes a late abortion. At the beginning of the second trimester, the membranes during a miscarriage usually do not open, the fetal egg comes out entirely. After the expulsion of all parts of the fetal egg is completed, the myometrium contracts, bleeding stops.
Classification
Definition of the form (stage) of late miscarriage is based on the symptoms and reversibility of the pathological process. Domestic specialists in the field of obstetrics and gynecology distinguish the following types of spontaneous late abortions:
- Threat of abortion . Threatened abortion is characterized by an increase in the tone of the muscular layer of the uterus with the preservation of the placenta, fetus and membranes.
- Incipient miscarriage . Against the background of an ajar or open cervix, fetal rejection begins.
- Abortion in progress . The fetus and the membranes surrounding it are partially or completely expelled from the uterus.
 Accordingly, there are incomplete and complete miscarriages.
Accordingly, there are incomplete and complete miscarriages. - Miscarriage (missed pregnancy) . It is observed with the death of the fetus and failure of the contractile function of the myometrium.
Foreign experts offer a slightly different approach. In the WHO classification, a late abortion that has begun and a miscarriage in progress constitute a general category - an inevitable miscarriage, in which the pregnancy cannot be maintained.
Symptoms of late miscarriage
Clinical manifestations depend on the stage of abortion. Patients with a threat of late miscarriage complain of pulling pains in the lower abdomen and lower back. Vaginal discharge is usually absent, less often spotting bloody. With the onset of a miscarriage, pain increases, discharge with an admixture of blood appears or intensifies. At the stage of abortion during the course, the uterine muscles contract regularly, which is subjectively perceived by the patient as cramping pain, abundant spotting is observed, the fetal egg departs completely or partially. After the expulsion of the fetus, placenta and membranes, the pain disappears, the bleeding stops, and scant discharge may persist for some time.
After the expulsion of the fetus, placenta and membranes, the pain disappears, the bleeding stops, and scant discharge may persist for some time.
In late miscarriage that has not taken place, there are no characteristic pains and spotting. At the expected time, fetal movement does not appear, and if such movements were noted earlier, they stop. The patient notes the disappearance of subjective signs of a previously diagnosed pregnancy and softening of the mammary glands. 3-4 weeks after the death of the fetus, signs of general malaise with weakness, dizziness, fever to subfebrile numbers may appear. In some cases, it is during this period that typical symptoms of a miscarriage develop.
Complications
Retention in the uterine cavity of the elements of the fetus, its membranes or placenta causes massive bleeding, leading to significant blood loss and can cause hypovolemic shock. Accession to a miscarriage of the inflammatory process is manifested by the clinic of an infected abortion - a serious condition characterized by chills, fever, general malaise, bloody or purulent discharge from the vagina, severe pain in the lower abdomen.![]() Subsequently, in such patients, the risk of developing inflammatory and dyshormonal gynecological diseases increases. A distant consequence of a late miscarriage is an increased likelihood of spontaneous termination of subsequent pregnancies. In addition, the stress experienced by a woman sometimes provokes the development of depression and psychological problems.
Subsequently, in such patients, the risk of developing inflammatory and dyshormonal gynecological diseases increases. A distant consequence of a late miscarriage is an increased likelihood of spontaneous termination of subsequent pregnancies. In addition, the stress experienced by a woman sometimes provokes the development of depression and psychological problems.
Diagnosis
Late abortion may be suspected by the presence of typical clinical symptoms in women 13-22 weeks pregnant. To confirm the diagnosis and determine the stage of miscarriage, the patient is prescribed:
- Bimanual palpation . With the threat of abortion, the size of the uterus corresponds to the gestational age, the tone of the myometrium is increased, the cervix is normal in size, closed. At the beginning of a miscarriage, bloody discharge comes through the slightly opened cervical canal. In late abortion, an open external and internal os is palpated in the course, a whole or fragmented fetal egg is detected in the canal and / or vagina.
 Upon completion of the expulsion of the fetus, the size of a well-contoured uterus is less than the previously established gestational age, the cervical canal is partially or completely closed.
Upon completion of the expulsion of the fetus, the size of a well-contoured uterus is less than the previously established gestational age, the cervical canal is partially or completely closed. - Transabdominal ultrasound . With a likely threat of miscarriage, an increase in uterine tone is determined. In cases where the fetus is alive, its heartbeat is recorded. The main echo-signs of an abortion that has begun or a process in progress are myometrial hypertonicity, impaired placental circulation, opening of the internal uterine os, and rejection of the fetal egg. If the abortion turned out to be incomplete, fragments of the placenta and / or fetal egg are detected inside the uterus. A complete miscarriage is characterized by a closed uterine cavity.
- Determination of hormonal status . Conducting a study is especially important for the choice of treatment tactics for the threat of miscarriage. To assess the level of hormones, the patient is prescribed a blood test for estrogens, progesterone, testosterone, a urine test for 17-ketosteroids.
 A decrease in estrogen levels is indirectly indicated by an increase in the karyopyknotic index (KPI) of more than 10% during a colpocytological study.
A decrease in estrogen levels is indirectly indicated by an increase in the karyopyknotic index (KPI) of more than 10% during a colpocytological study.
Highly informative is the determination of the level of human chorionic gonadotropin, which decreases in the event of fetal death. In case of a threatened miscarriage, to identify its causes, an additional examination for intrauterine infection of the fetus (herpes, toxoplasmosis, rubella, cytomegalovirus), bacteriological examination of a smear, laboratory blood tests for genital infections (PCR, RIF, ELISA), standard or extended tests for chromosomal anomalies, coagulogram. Differential diagnosis of late miscarriage is carried out with ectropion, benign and malignant neoplasia of the genital organs, cystic mole, acute surgical pathology. If necessary, an oncogynecologist, surgeon, therapist is involved in the diagnosis.
Treatment of late miscarriage
Therapeutic tactics for spontaneous abortion depends on its form.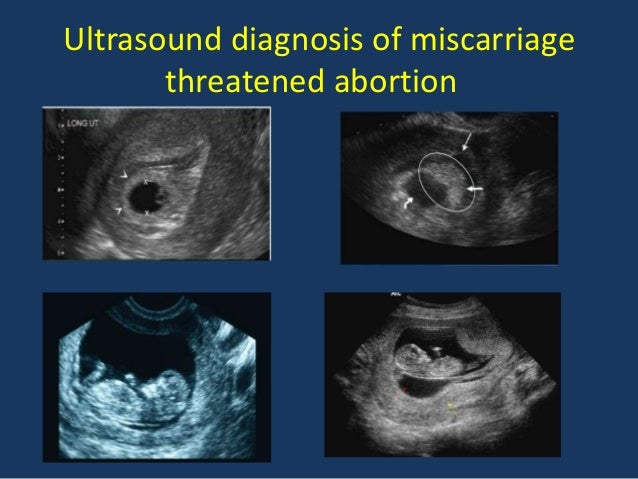 If there is a threat of miscarriage, drug treatment and a protective regimen with the refusal of physical activity and sexual relations are recommended. The patient is prescribed:
If there is a threat of miscarriage, drug treatment and a protective regimen with the refusal of physical activity and sexual relations are recommended. The patient is prescribed:
- Hormonal preparations . The use of gestagens in combination with vitamin E is especially effective.
- Antispasmodics . Drugs can lower the tone of the myometrium and, accordingly, reduce pain.
- Methylxanthines . Medicines of this group relax the myometrium, reduce the risk of thrombosis, improve blood circulation in the tissues of the uterus and placenta.
- Sedatives . To reduce the psychological stress experienced by a pregnant woman, magnesium preparations, a decoction of motherwort or valerian are used.
After the threat of late termination of pregnancy has been eliminated, further management of the patient depends on what causes provoked this condition. If isthmic-cervical insufficiency is detected, sutures are applied to the cervix or an unloading obstetric pessary (Meyer's ring) is installed in the vagina. The tactics of treating identified gynecological and concomitant diseases should take into account the peculiarities of prescribing various groups of drugs during pregnancy. The management of a pregnant woman in the diagnosis of intrauterine infection of the fetus or chromosomal aberrations is determined by the type of pathogen and genetic abnormalities.
The tactics of treating identified gynecological and concomitant diseases should take into account the peculiarities of prescribing various groups of drugs during pregnancy. The management of a pregnant woman in the diagnosis of intrauterine infection of the fetus or chromosomal aberrations is determined by the type of pathogen and genetic abnormalities.
Late incomplete abortion is a direct indication for emergency surgical care to avoid significant blood loss. In such cases, the remnants of the fetal egg are removed with fingers, a curette or a vacuum aspirator. In parallel, a dropper with oxytocin is prescribed. With a probable complete abortion at 13-16 weeks of gestation, ultrasound control and curettage of the uterus are recommended if decidual tissue and elements of the fetal egg are found in its cavity. If the miscarriage occurred at a later gestational age, and the uterus has contracted well, you can do without curettage.
The management of a patient with a failed miscarriage and a dead fetus depends on the timing of pregnancy. Until the 16th week, the fetal egg is removed by instrumental methods, with a longer period, labor activity is stimulated with medication. For this purpose, sodium chloride solution is administered intraamnially, antiprogestogens and prostaglandins are prescribed. After a spontaneous abortion, antianemic and preventive antibiotic therapy is indicated. Patients with Rh-negative blood recommended the introduction of anti-Rh immunoglobulin.
Until the 16th week, the fetal egg is removed by instrumental methods, with a longer period, labor activity is stimulated with medication. For this purpose, sodium chloride solution is administered intraamnially, antiprogestogens and prostaglandins are prescribed. After a spontaneous abortion, antianemic and preventive antibiotic therapy is indicated. Patients with Rh-negative blood recommended the introduction of anti-Rh immunoglobulin.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis for the fetus and the pregnant woman is determined by the causes that provoked a late miscarriage. In the absence of developmental anomalies and gross anatomical changes in the uterus, the timely appointment of a protective regimen and drug treatment in most cases allows you to save the pregnancy. With an abortion that has begun, incomplete, complete and failed, it is impossible to maintain pregnancy, and the main efforts of obstetricians and gynecologists are aimed at helping the woman. After a miscarriage, the risk of recurrent spontaneous abortion increases by 3-5%. As a preventive measure, women with a likely threat of termination of pregnancy are recommended to plan conception, preventive treatment of inflammatory diseases of the female genital area, timely registration and regular monitoring in the antenatal clinic.
As a preventive measure, women with a likely threat of termination of pregnancy are recommended to plan conception, preventive treatment of inflammatory diseases of the female genital area, timely registration and regular monitoring in the antenatal clinic.
Miscarriage, how to avoid - Planning and management of pregnancy in the gynecology of the Literary Fund polyclinic after a miscarriage
- Gallery
- News
- Blog
- Reviews
- Jobs
- Licenses
- Insurance partners
- Controlling organizations
- Schedule of reception of citizens on personal appeals
- What you need to know about coronavirus infection?
- Rules for patients
- Online doctor's consultation
- to corporative clients
- The documents
A miscarriage is always associated with serious consequences for the whole body of a woman and for her reproductive organs in particular, it also affects the family situation, disrupts the woman's work schedule.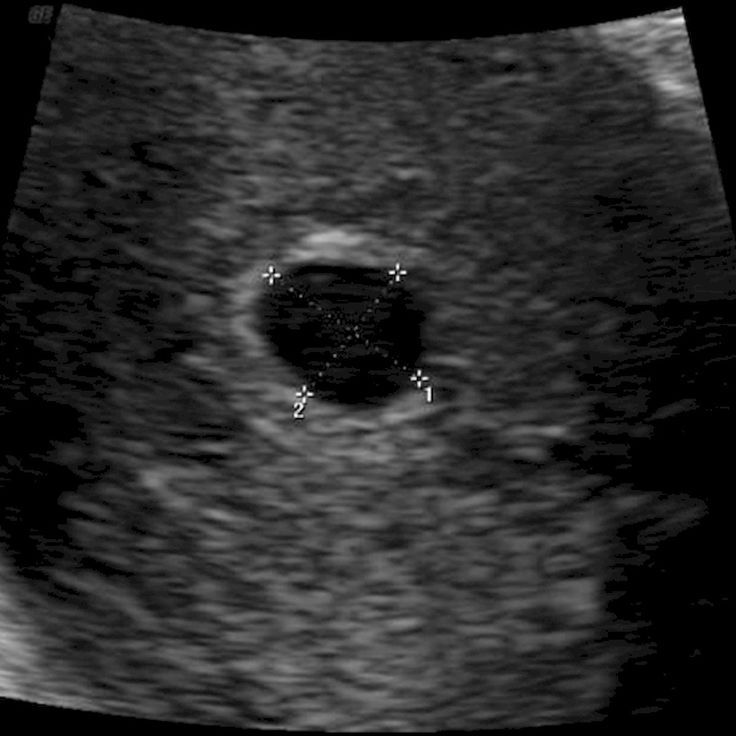 An unfavorable outcome of pregnancy requires great mental and physical costs on the part of parents. Therefore, contacting doctors to find out the causes of the problem is the very first and correct step towards the birth of a child.
An unfavorable outcome of pregnancy requires great mental and physical costs on the part of parents. Therefore, contacting doctors to find out the causes of the problem is the very first and correct step towards the birth of a child.
Any competent gynecologist will tell you that the problem of miscarriage can be solved. With proper preparation for pregnancy and its management, the next time you will have a successful pregnancy. Most girls after a miscarriage go to extremes: they try to get pregnant again as soon as possible. And if this succeeds, then the miscarriage is very often repeated. And you need to give the body a rest for 2-3 months, then identify and eliminate the cause. And only then try.
Causes of miscarriage
Many are convinced that miscarriages are due to a fall, injury, or some other physical shock. Any woman who has had a miscarriage can remember that not long before she either fell or lifted something heavy. And I am sure that she lost her unborn child precisely because of this. However, those women whose pregnancy was normal also fall and lift heavy things. Most sudden miscarriages do not occur for this reason. The reason is in violations of the pregnancy itself. Approximately half of miscarriages are due to abnormal genetic development of the fetus, which can be hereditary or accidental. Merciful nature, following the principles of natural selection in everything, destroys the defective and unviable fetus. But you should not be afraid of this. The fact that there is a defect in one embryo does not mean at all that all the others will be the same.
However, those women whose pregnancy was normal also fall and lift heavy things. Most sudden miscarriages do not occur for this reason. The reason is in violations of the pregnancy itself. Approximately half of miscarriages are due to abnormal genetic development of the fetus, which can be hereditary or accidental. Merciful nature, following the principles of natural selection in everything, destroys the defective and unviable fetus. But you should not be afraid of this. The fact that there is a defect in one embryo does not mean at all that all the others will be the same.
The woman's body is almost always to blame for the other half of miscarriages. They are caused by various known and unknown factors, such as: acute infectious diseases suffered in the first trimester of pregnancy, poor environment or difficult working conditions, excessive psychological or physical stress, abnormal development of the uterus, radiation, alcohol, smoking and certain types of drugs.
The causes of early and late miscarriage may differ, although they may overlap. The most important thing is to find out and eliminate or compensate for your own cause of miscarriage. Having discovered the cause, the gynecologist will tell you how to avoid another loss.
The most important thing is to find out and eliminate or compensate for your own cause of miscarriage. Having discovered the cause, the gynecologist will tell you how to avoid another loss.
Miscarriage
Miscarriage statistics also include “missed pregnancy”. Sometimes it happens that the embryo dies and lingers in the uterine cavity. Most often, this fact is detected by ultrasound. The dead fetus may begin to decompose, and this, thereby, will lead to poisoning of the mother's body.
Doctors resort to surgical curettage, which is associated with a risk of inflammation and complications. With such a miscarriage, the next pregnancy is planned after the body is fully restored - not earlier than a year. During this year, you will have to find out the cause of the missed pregnancy and treat it.
Miscarriage up to 6 weeks
The main causes of miscarriage on this line are malformations of the embryo itself. Statistics say that from 70-90% of embryos had chromosomal abnormalities: they are random and will not occur in other pregnancies. You may have been ill, taken medication, or were under the influence of other harmful factors. Fate saved you from a child with malformations.
You may have been ill, taken medication, or were under the influence of other harmful factors. Fate saved you from a child with malformations.
The human body is perfect and finds a way to correct the situation by miscarriage. Today is a tragedy for you. The real tragedy would be the preservation and birth of a sick, non-viable child. So don’t cry and understand: everything is for the best, you won’t help grief with tears ... And after three months, try again - it will almost certainly turn out to be successful.
It should also be noted that the fact of a miscarriage does not mean that you have lost something. So for a period of 7-8 weeks, the absence of an embryo in the fetal egg is found - "anembryony". It is believed that in 80-90% of cases, miscarriages are undiagnosed non-developing pregnancies.
Miscarriage between 6 and 12 weeks
Miscarriage in this period is also considered early. Its most common causes are:
Endocrine disorders
Endocrine disorders, when the ovaries do not synthesize enough hormones to keep the fetus in the womb, or the amount of male sex hormones is increased, is one of the most common causes of miscarriage and miscarriage.
Hormone imbalance in a woman's body is likely to lead to an early termination of pregnancy. With a lack of the main hormone progesterone produced by the ovaries, this happens most often. Another hormonal problem is an increase in the tone of the uterus, which provokes the expulsion of the fetus.
Progesterone prepares the uterine mucosa for implantation and is the hormone for maintaining pregnancy in the first months. If conception occurs, the fetus cannot properly establish itself in the uterus. As a result, the fertilized egg is rejected. But pregnancy can be saved with the help of progesterone preparations if this problem is detected in time.
An excess of male sex hormones that suppress the production of estrogen and progesterone can also be the cause of an early miscarriage. Often, the cause of recurrent miscarriages are androgens that affect the formation and development of pregnancy; as well as thyroid and adrenal hormones. Therefore, a change in the function of these glands can lead to miscarriage.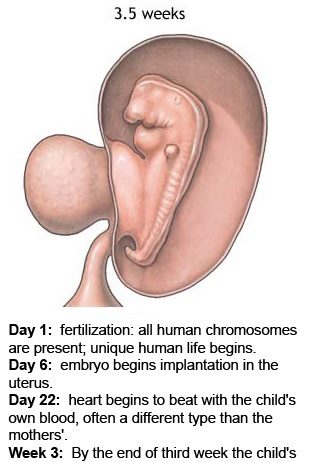
Undertreated sexual infections
This problem must be solved before conception. Often the cause of miscarriage is sexually transmitted infections: syphilis, trichomoniasis, toxoplasmosis, chlamydia, cytomegalovirus and herpetic infections. Their effect on the fetus and the course of pregnancy is different for each woman and depends on the timing of infection, the activity of the microorganism, the degree of immune protection and the presence of other adverse factors. Depending on the situation, they can lead to the formation of fetal malformations, intrauterine infection, feto-placental insufficiency, early miscarriage or premature birth. Infection of the fetus and damage to the membrane of the fetus leads to miscarriage. To avoid this, infections should be treated before pregnancy. The use of therapy is possible during pregnancy as prescribed by a doctor.
Viral infections and other diseases
Any disease accompanied by intoxication and fever above 38 o C can lead to a miscarriage.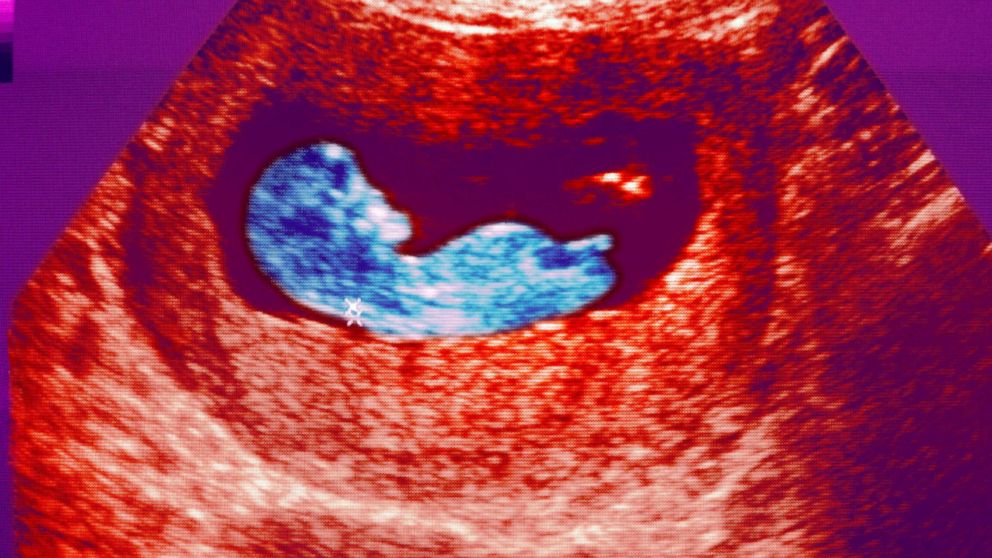 Rubella, influenza and viral hepatitis occupy a leading position in this list. At a period of 4-10 weeks for pregnancy, ordinary tonsillitis can also become tragic, pneumonia carries a more serious risk. Pyelonephritis and appendicitis can cause early labor. When planning a pregnancy, it is imperative to undergo a medical examination in order to identify and treat foci of infections.
Rubella, influenza and viral hepatitis occupy a leading position in this list. At a period of 4-10 weeks for pregnancy, ordinary tonsillitis can also become tragic, pneumonia carries a more serious risk. Pyelonephritis and appendicitis can cause early labor. When planning a pregnancy, it is imperative to undergo a medical examination in order to identify and treat foci of infections.
Extremely dangerous during pregnancy rubella - it leads to severe fetal malformations, so infection during pregnancy is an indication for medical abortion.
Any disease during pregnancy can lead to non-viability of the fetus. And the body, through a miscarriage, insures you against unwanted offspring. With such a miscarriage, the next pregnancy has every chance of going well.
Immune causes of miscarriage
Sometimes antibodies that are hostile to the fetus are formed in the blood of a pregnant woman. This cause can be predicted and eliminated in advance. Most often, the conflict occurs when the embryo inherits the positive Rh factor of the father, and the negative Rh factor, the mother's body rejects the embryonic tissues that are alien to it. Constant monitoring of antibody titer and the introduction of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulins allows you to maintain and maintain pregnancy. In case of an immune conflict, progesterone preparations are also used to prevent miscarriage, which in this case has an immunomodulatory effect.
Most often, the conflict occurs when the embryo inherits the positive Rh factor of the father, and the negative Rh factor, the mother's body rejects the embryonic tissues that are alien to it. Constant monitoring of antibody titer and the introduction of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulins allows you to maintain and maintain pregnancy. In case of an immune conflict, progesterone preparations are also used to prevent miscarriage, which in this case has an immunomodulatory effect.
Reduced immunity
Reduced immunity during pregnancy also refers to immune causes. The body is simply not able to grow a new life in itself. You need to take care of yourself and recover before the next conception.
Anatomical causes of miscarriage
Anatomical causes of miscarriage are the most intractable. Malformations of the uterus are a serious reason for miscarriage. Sometimes you just have to deal with it.
Miscarriage between 12 and 22 weeks
Such a miscarriage is considered late. Its causes coincide with the causes of miscarriages in the early stages (anatomical, immune, infectious, endocrine).
Its causes coincide with the causes of miscarriages in the early stages (anatomical, immune, infectious, endocrine).
At this time, miscarriage also occurs due to isthmic-cervical insufficiency - a weak cervix cannot hold the fetus and opens. For this reason, a miscarriage can occur in the 2nd or 3rd trimester. Isthmic-cervical insufficiency is observed in 15.0-42.7% of women suffering from miscarriage. Careful monitoring of the pregnant woman allows you to identify the problem in time and make surgical correction of the cervix before the onset of childbirth.
In isthmic-cervical insufficiency, there is only one method of treatment - a mechanical narrowing of the cervical canal. To do this, the neck is either sewn up or a special ring is put on it. However, the latter method is less efficient, because the ring can easily slide off the neck, then it will no longer hold back the process of opening it.
After suturing, if necessary, it is possible to use antibiotics and drugs that normalize the microflora of the vagina.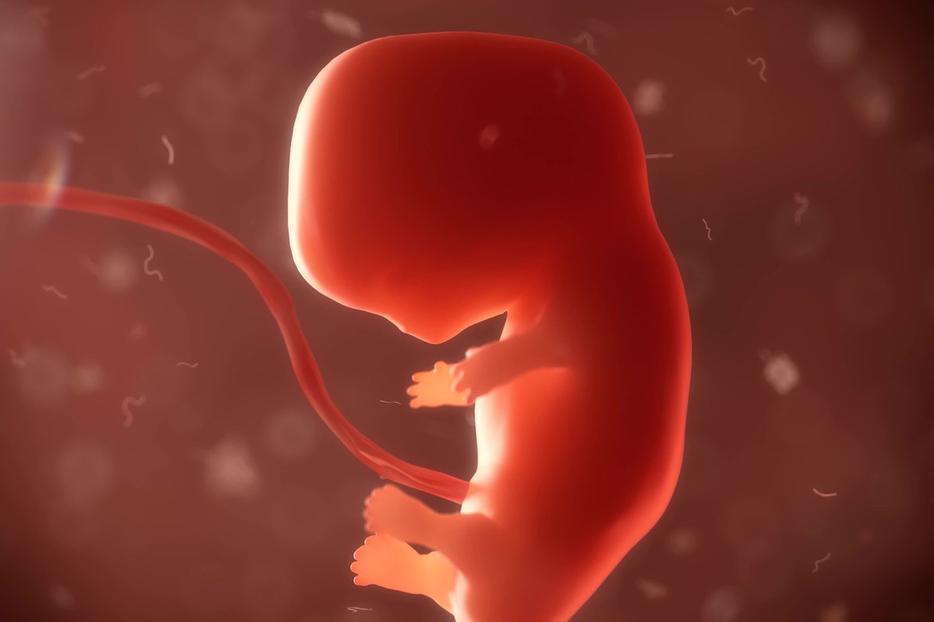 The treatment of the vagina and the control of the state of the seams are carried out daily for 5 days. Stitches are removed at 37-38 weeks and with premature onset of labor.
The treatment of the vagina and the control of the state of the seams are carried out daily for 5 days. Stitches are removed at 37-38 weeks and with premature onset of labor.
Isthmic-cervical insufficiency may be primary (for no apparent reason), may be the result of abortion or hormonal disorders (increased levels of androgens - male sex hormones or their precursors).
Miscarriage after 22 weeks
Such a loss is hard to forget. Obstetricians talk about premature birth after the 28th week of pregnancy. Traditionally, a child born after this period is considered viable. But medicine knows many cases when it was possible to save the life of earlier children.
We recommend that you be carefully examined for miscarriage, check the above factors. In addition to them, the cause of a miscarriage can be antiphospholipid syndrome, while the woman's body perceives the child as something alien and rejects it. This disease, like the others listed, can be corrected; you have a very real chance of bearing a child.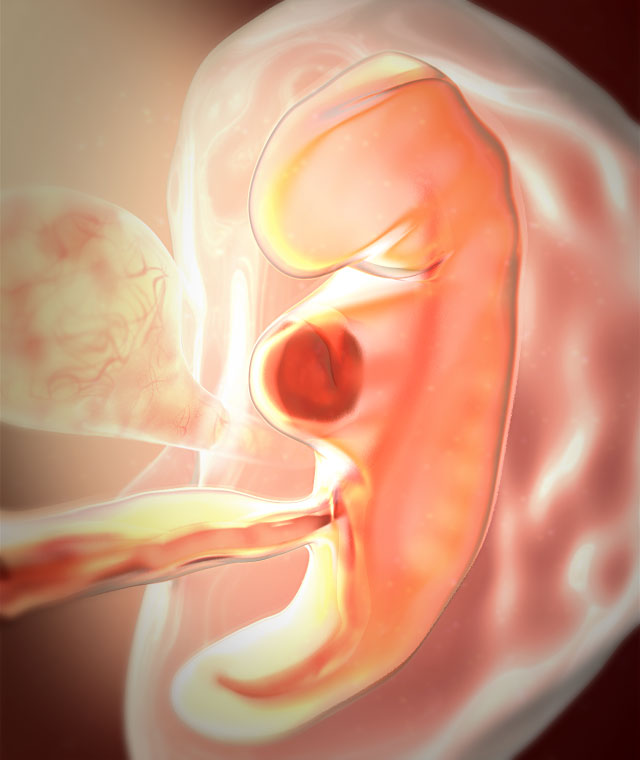
Miscarriages due to hemostasis disorders
All of the above causes account for only 30-40%. Up to 70% of miscarriages are caused by disorders in the blood coagulation system (hemostasis).
Blood coagulation disorders leading to pregnancy loss can be divided into thrombophilic (increased clotting) and hemorrhagic (bleeding tendencies). Both of these extremes are dangerous to the fetus. Various disorders leading to the formation of small blood clots lead to the fact that the fetus loses sufficient blood supply, development is disturbed and the fetus is rejected.
The main hemorrhagic changes can appear even in childhood in the form of increased bleeding during cuts, tooth extractions, the onset of menstruation. But sometimes they declare themselves only during pregnancy and are the cause of a miscarriage. Bleeding in the early stages and detachment of the chorion is difficult to stop.
You may not guess, but incomprehensible headaches, weakness, fatigue, temporary loss of smell or hearing may be symptoms of disorders in the blood clotting system.