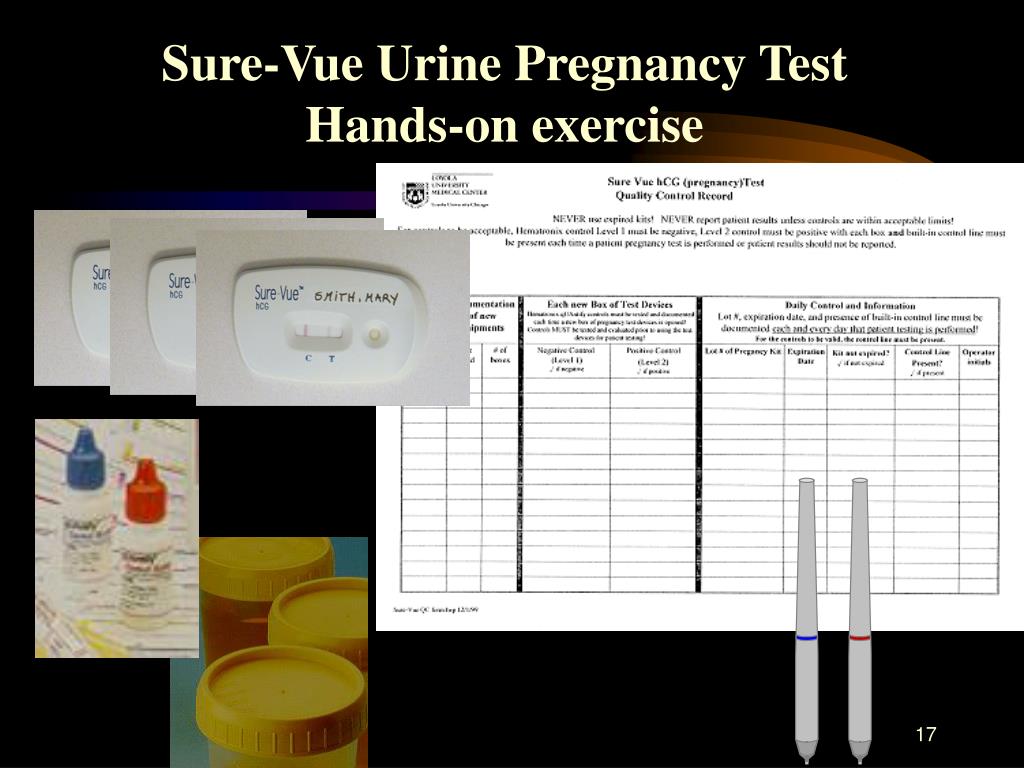
Excess urine during pregnancy
Frequent urination during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
beginning of content4-minute read
Listen
What is frequent urination during pregnancy?
Frequent urination is when you need to urinate (wee) more often than usual when pregnant. Needing to go to the toilet more often during your pregnancy is normal and is caused by the hormonal and physical changes occurring in your body. Your bladder (which stores urine), your bowel (which your poo passes through) and your uterus (where your baby grows) are all located in the small space of your abdomen, so changes that occur in one organ are also likely to affect the others.
What causes frequent urination during pregnancy?
You experience frequent urination because when you are pregnant, your body produces more fluids than at other times. Your kidneys, which produce urine, also become more efficient. Your uterus – situated directly behind your bladder – becomes larger to accommodate your growing baby and as a result, it pushes against your bladder.
For some women, weak pelvic floor muscles are another cause of frequent urination during pregnancy. Pelvic floor muscles support the organs of the pelvis, which include the bladder, uterus and bowel.
When am I more likely to experience frequent urination during pregnancy?
Frequent urination is common at every stage of pregnancy. During the first stages, hormonal changes increase the frequency with which you need to use the toilet. Later in pregnancy, it is more likely to be caused by your baby pressing against your bladder, while in the last few weeks of pregnancy, you may struggle to empty your bladder completely.
Towards the end of your pregnancy, it is common to wet yourself a little while coughing, sneezing or lifting things. This happens because these actions place more pressure on your pelvic floor, and for many women, the pelvic floor becomes weakened during pregnancy.
Am I likely to experience frequent urination if I have had it before pregnancy?
If you have had bladder problems before pregnancy, unfortunately these are likely to worsen after the birth. Women can also develop new bladder problems after having a baby.
How can I reduce frequent urination during my pregnancy?
While you cannot do much to lessen your need to urinate frequently, you can strengthen your pelvic floor muscles. Strengthening these muscles can help you ‘hold in’ your urine until you are able to get to the toilet. The best way to strengthen your pelvic floor muscles is through exercise. Exercising the muscles will also provide a sturdy support system for your bowel, uterus and bladder.
Ideally, women should do pelvic floor exercises before becoming pregnant, but it's never too late. Remember to keep up your pelvic floor exercises after your baby is born too.
The Continence Foundation of Australia have produced this video on how to do pelvic floor exercises:
While, in most cases, frequent urination during pregnancy is quite normal and not a concern, in some situations it is best to see a doctor. If you feel a stinging, burning sensation or if you feel any pain when you use the toilet, it is important that you discuss this with your doctor. It might indicate you have an infection that needs to be treated promptly.
Will it continue after I’ve had the baby?
While you may continue to urinate more than usual after your baby is born, you will usually see an improvement in the first 6 months after the birth. This is because pelvic floor nerves, tissues and muscles are beginning to recover from pregnancy and birth. Make sure you keep up your pelvic floor exercises — your midwife can also guide you with what to expect over the first few weeks and months after your baby’s birth.
Where to get help
- Call the Continence Foundation of Australia on 1800 33 00 66
- Talk to your GP — Click here to find a doctor near you
- Check in with your midwife
- Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby on 1800 882 436 to speak to a maternal child health nurse
Sources:
The Royal Women's Hospital (Common concerns in early pregnancy), Better Health Channel (Pregnancy - signs and symptoms), Continence Foundation of Australia (Pregnancy and childbirth), The Royal Women’s Hospital (Pelvic floor exercises)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: January 2021
Back To Top
Related pages
- Incontinence during pregnancy
- Pelvic floor exercises
- Bladder weakness after birth
- Bladder and bowel problems during pregnancy
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Causes and what to do
Urinating more frequently than normal is common during pregnancy. As a standalone symptom, it is not a cause for concern, but a pregnant person should consult their doctor if they experience pain while urinating or other symptoms of a urinary tract infection (UTI).
Frequent urination is a common early sign of pregnancy. Urinary frequency initially occurs due to increased levels of the hormones progesterone and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
Urinary frequency initially occurs due to increased levels of the hormones progesterone and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
While some pregnant people may experience mild changes, others may feel the need to continuously run to the bathroom throughout the day and night.
Frequency can also reappear later in the pregnancy as the uterus and baby continue to grow, creating pressure on the bladder.
Pregnant people who have a fever or chills, or notice a burning sensation while urinating, should seek immediate medical attention as it could be a urinary tract infection (UTI). Other symptoms may include back pain or a sharp increase in the need to urinate in a small period of time.
In this article, we discuss the causes and symptoms of frequent urination during pregnancy, how to manage and prevent frequent urination, how long it lasts, and outlook.
Although symptoms may vary from person to person, many pregnant people notice they begin to need to urinate more frequently during their first trimester (week 1 to week 12). Some people may also experience leakage or stress urinary incontinence (SUI) while pregnant as the fetus grows and presses down on the bladder, urethra, and pelvic floor muscles.
Some people may also experience leakage or stress urinary incontinence (SUI) while pregnant as the fetus grows and presses down on the bladder, urethra, and pelvic floor muscles.
The Office on Women’s Health notes that leakage may occur when:
- sneezing
- coughing
- laughing
- exercising
- lifting something
- walking
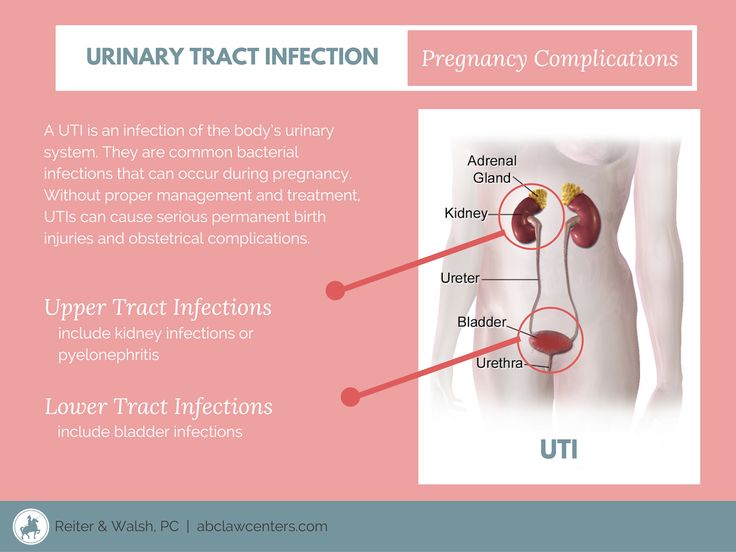
Sometimes urinary frequency symptoms indicate an underlying condition, such as a UTI — an infection of the urinary system.
In addition to urgency, other symptoms of a UTI include:
- blood in the urine
- cloudy or foul-smelling urine
- lower abdominal pain
- nausea
- pain or burning when urinating
- loss of bladder control
Pregnant people are at increased risk for UTIs. According to one study from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately 8% of pregnant people develop a UTI.
If left untreated, a UTI can pose a serious health risk to a pregnant person and their developing fetus.
Doctors can often diagnose urinary frequency based on a person’s symptoms. In addition to doing a physical examination, they may ask a series of questions about how often the person is going to the restroom and how much they are urinating with each trip.
They may also ask about:
- changes in the smell, color, or consistency of the urine
- daily fluid consumption
- the pattern of frequency (i.e. when it started and what time of day symptoms occur)
If a doctor suspects that the symptoms are not pregnancy-related, they may order one or more diagnostic tests.
Tests may include:
- urinalysis
- ultrasound
- cystoscopy
- bladder stress test
- sexually transmitted infection (STI) tests
Frequent urination is an early sign of pregnancy and can begin as early as the first couple of weeks following conception.
Most people, however, may begin to experience urgency in weeks 10 to 13, as this is when the uterus begins to push on the bladder.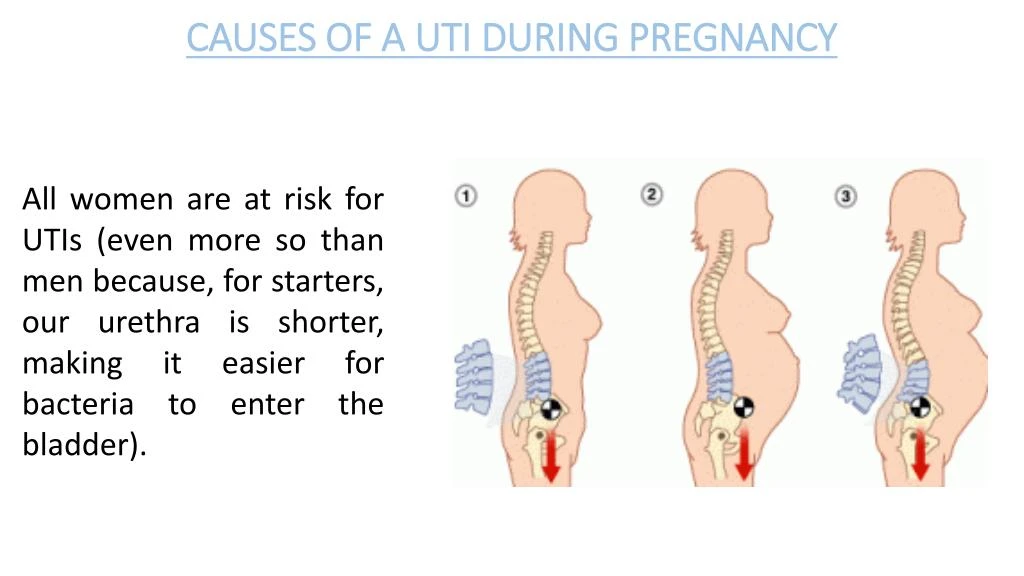
After an embryo implants in the uterus, the body produces progesterone and hCG, both of which are pregnancy hormones that can lead to urgency.
During pregnancy, the body’s blood supply increases to support the fetus. Approximately 20–25% of a person’s blood filters through the kidneys and leaves the body as waste or urine. The more blood a person’s body produces, the harder their kidneys have to work to flush the extra fluid.
Pressure is another contributing factor. As the uterus expands, it pushes down on the bladder, urethra, and pelvic floor muscles, increasing the urge to urinate.
Pelvic floor exercises, also known as Kegel exercises, can strengthen the muscles of the pelvis and urethra and support the bladder. Performing Kegel exercises during pregnancy may help some people regain control over their urine flow.
Kegel exercises are safe to perform during pregnancy and after childbirth.
To perform Kegel exercises, empty the bladder and then follow these steps:
- Relax the abdomen, chest, thighs, and buttocks.

- Tighten the pelvic floor muscles and hold for 5 to 10 seconds.
- Relax the muscles for 5 to 10 seconds.
- Repeat 10 times.
The National Association for Continence (NAFC) recommends doing 10 repetitions three times per day.
Staying hydrated by drinking eight to 12 cups of water per day is vital during pregnancy. However, there are a few things a pregnant person can do to ease the flow, including:
- cutting down on fluids before bed
- avoiding caffeinated drinks
- leaning forward when urinating
- keeping a bladder journal or recording bathroom breaks
The average person goes to the bathroom between 6 and 7 times per day, though this number can vary depending on what the person drinks and how often.
Urinating between four and 10 times per day can also be “normal” as long as the person is healthy and comfortable with how often they visit the restroom.
For pregnant people, this number will depend on the individual’s “normal. ” For example, if a person typically uses the restroom eight times per day, becoming pregnant may increase their visits to 10 times per day.
” For example, if a person typically uses the restroom eight times per day, becoming pregnant may increase their visits to 10 times per day.
Pregnancy-related urinary frequency may ease up in the second trimester but usually returns in the final weeks of the pregnancy. Once the baby is born, a more frequent than usual urge to go to the bathroom should go away.
Frequent urination is a normal pregnancy symptom. However, it also can be a sign of an underlying condition that may require medical treatment.
Pregnant people who show additional symptoms of a UTI, including painful urination, should contact their doctor as soon as possible.
Frequent urination is a part of being pregnant and should resolve after childbirth.
However, some pregnant people may experience symptoms up to six weeks after giving birth.
Pregnant people who experience pain with urination or who are still having bladder problems following birth should make an appointment to see their doctor.
Many people experience urinary frequency during pregnancy, especially in the first and third trimesters.
Unless the frequency is accompanied by burning or painful urination, or other potential signs of a UTI, there is usually no need for concern.
Urinary frequency generally will subside once the baby is born.
Urinalysis during pregnancy - what to watch
- Why take a urine test during pregnancy
- How to properly pass urine for analysis
- What a urine test shows and how it is assessed
- Special urine tests
During pregnancy, a woman undergoes many different tests. The most frequent, and at the same time the simplest study is a urinalysis. It is taken regularly, before each visit to the doctor of the antenatal clinic, that is, at least 12 times during pregnancy.
Why take a urine test during pregnancy
Urine is formed in the kidneys during blood filtration, with it the decay products formed during metabolism, salts, vitamins, hormones are excreted from the body. Based on this analysis, one can judge the work of the kidneys and other organs. The main component of urine is water (92-99%). Approximately 50-70 dry substances are removed from the body with urine every day, most of which are urea and sodium chloride. The composition of urine varies significantly even in healthy people, depending on the diet, drinking regimen and medication. During pregnancy, a regular study of a general urine test allows you to suspect in time the initial pathological processes in the body of a future mother, for example, the development of a urinary tract infection or toxicosis in the second half of pregnancy. For a correct assessment of the results of the analysis, urine must be collected correctly.
Based on this analysis, one can judge the work of the kidneys and other organs. The main component of urine is water (92-99%). Approximately 50-70 dry substances are removed from the body with urine every day, most of which are urea and sodium chloride. The composition of urine varies significantly even in healthy people, depending on the diet, drinking regimen and medication. During pregnancy, a regular study of a general urine test allows you to suspect in time the initial pathological processes in the body of a future mother, for example, the development of a urinary tract infection or toxicosis in the second half of pregnancy. For a correct assessment of the results of the analysis, urine must be collected correctly.
How to donate urine for analysis
On the eve of the test, it is recommended to refrain from intense physical activity, do not eat a lot of meat products, salty, sour and spicy foods, as well as coloring foods (beets, carrots, etc.). This can lead to a distortion of the result - the appearance of protein and salts in the urine. For a general urinalysis, it is preferable to collect the morning portion of urine.
For a general urinalysis, it is preferable to collect the morning portion of urine.
Preliminary thorough toileting of the external genitalia with warm water and soap. It is better to close the vagina with a cotton swab to prevent secretions from entering the urine sample. Urine is collected in a clean, dry container. For analysis, an average portion of urine is used, that is, for the first few seconds you need to urinate into the toilet, then into a jar, and the remains again into the toilet.
Urine must be delivered to the laboratory within two hours of collection and it is advisable to try not to subject it to strong shaking during transport. It is allowed to store urine in the refrigerator at a temperature of +2-+4 degrees, but not more than 1.5 hours. It is desirable that the amount of material collected for the study be at least 70 ml.
What a urinalysis shows and how it is evaluated
In a urinalysis, many parameters are evaluated.
Color
Normal urine has a yellow color of various shades. The shade depends on the degree of saturation of urine with a special pigment - urochrome. A change in the color of urine can occur when taking certain medications (for example, vitamins can give a bright yellow color, aspirin - pink). However, much more often a change in the color of urine indicates the presence of any pathological processes in the body. When blood appears in the urine, which occurs in diseases of the kidneys and bladder, the urine becomes bright red (with renal colic, cystitis) or the so-called “color of meat slops” (with acute inflammatory kidney damage). With increased destruction of red blood cells (erythrocytes), urine acquires a reddish-brown hue. Yellow-brown (or beer-colored) urine occurs with liver diseases.
The shade depends on the degree of saturation of urine with a special pigment - urochrome. A change in the color of urine can occur when taking certain medications (for example, vitamins can give a bright yellow color, aspirin - pink). However, much more often a change in the color of urine indicates the presence of any pathological processes in the body. When blood appears in the urine, which occurs in diseases of the kidneys and bladder, the urine becomes bright red (with renal colic, cystitis) or the so-called “color of meat slops” (with acute inflammatory kidney damage). With increased destruction of red blood cells (erythrocytes), urine acquires a reddish-brown hue. Yellow-brown (or beer-colored) urine occurs with liver diseases.
Transparency
Transparency should normally be complete. Turbidity of urine can be the result of the presence in the urine of erythrocytes, leukocytes, epithelium, bacteria, fat droplets, precipitation of salts.
Relative density (specific gravity)
This is an indicator that characterizes the amount of trace elements, salts, various compounds. Normally, the specific gravity is 1003 - 1035 g / l. This indicator may decrease in the presence of glucose or protein in the urine, with toxicosis of the first half of pregnancy, dehydration. An increase in specific gravity occurs in chronic renal failure, diabetes insipidus, and heavy drinking.
Normally, the specific gravity is 1003 - 1035 g / l. This indicator may decrease in the presence of glucose or protein in the urine, with toxicosis of the first half of pregnancy, dehydration. An increase in specific gravity occurs in chronic renal failure, diabetes insipidus, and heavy drinking.
Protein
Protein content in urine is one of the most important indicators of kidney function. Normally, it shouldn't be. A small amount of protein in the urine (physiological proteinuria) can also be found in healthy people, while the protein concentration does not exceed 0.033 g / l, in modern laboratories with more sensitive equipment - 0.14 g / l. The appearance of protein in the urine is noted in diseases of the kidneys, inflammatory diseases of the bladder and urinary tract. The presence of protein in the urine, combined with increased blood pressure and edema, is a sign of a serious complication of pregnancy - late preeclampsia, which can lead to seizures and even death of a pregnant woman and fetus.
Glucose
Normally, there is no glucose in the general urine test. However, in the second half of pregnancy, the presence of glucose in the urine (glucosuria) can normally be detected. This is due to increased filtration of glucose in the kidneys. Since the appearance of glucose in the urine can be a sign of a serious illness - diabetes mellitus, acute inflammation of the pancreas, all patients with glucosuria need an additional examination - blood glucose control, sometimes even a glucose tolerance test with a sugar load - determination of blood glucose on an empty stomach and 2 hours after taking 75 grams of glucose.
Bilirubin
This is a blood pigment that is formed as a result of metabolic processes in the body and is excreted with bile into the gastrointestinal tract. With an increase in the concentration of bilirubin in the blood, it begins to be excreted by the kidneys and found in the urine. This occurs mainly with liver damage or mechanical obstruction of the outflow of bile.
Urobilinogen
This is a conversion product of bilirubin. Normally, it is excreted in the bile and practically does not enter the urine. The appearance of urobilinogen in the urine occurs in liver diseases, poisoning, increased decay of red blood cells - erythrocytes.
Ketone bodies
These are products formed during the breakdown of fatty acids in the body. Normally, there are no ketone bodies in the urine test. Determining them is very important in diagnosing the adequacy of diabetes therapy. The appearance of ketones can occur in the first trimester of pregnancy with early toxicosis and indicate dehydration.
Nitrites
These are salts of nitrous acid and are not normally found in urine. Their appearance indicates the presence of a urinary tract infection.
Leukocytes
These are white blood cells. Normally, in the general analysis of urine, leukocytes are found up to 5 in the field of view. If the number of leukocytes is increased, this indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the kidneys, bladder or urethra, while the higher the number of leukocytes, the more pronounced the inflammation. A slight increase in the number of leukocytes can be observed if vaginal discharge enters the urine with a poor toilet of the external genital organs.
Erythrocytes
Red blood cells. Normally, in the general analysis of urine there should be no more than 2 erythrocytes in the field of view. An increase in their number occurs in the presence of stones in the kidneys or urinary tract, inflammation of the kidneys, injuries.
Cylinders
Cylindrical elements of urine sediment, consisting of protein or cells, may also contain various inclusions. Normally absent. They are found mainly in diseases of the kidneys.
Salts
These are inorganic substances which may precipitate on standing urine. Normally, there are no salts in the urine. The appearance of urates in the urine occurs with kidney diseases, as well as in the first trimester of pregnancy with vomiting of pregnant women.
Amorphous phosphates
Also found in vomiting of pregnant women, in inflammation of the bladder, and can occur normally with a predominance of vegetable and dairy foods in the diet.
Oxalates
Occurs in inflammation of the kidneys, diabetes mellitus, as well as in the predominance of foods rich in oxalic acid in the diet (spinach, sorrel, tomatoes, asparagus).
Bacteria
Isolation of bacteria in the urine is of significant diagnostic value in pregnancy. The appearance of bacteria in the urine indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the kidneys, bladder or urethra and requires mandatory treatment, even if the expectant mother is not worried about anything. Bacteria can also enter the urine from the vagina when the toilet of the external genitalia is poor. To determine the number of bacteria, their type and sensitivity to antibiotic therapy, an additional urine culture for flora is mandatory. To obtain the correct result of this analysis, after a thorough toilet of the external genital organs, close the vagina with a cotton swab, collect the middle portion of urine in a sterile container, tighten the lid tightly and deliver it to the laboratory within one and a half to two hours. Urine culture is prepared on average from 7 to 10 days and allows the doctor to decide whether it is necessary to carry out antibacterial treatment, and with what drugs.
Urine culture is prepared on average from 7 to 10 days and allows the doctor to decide whether it is necessary to carry out antibacterial treatment, and with what drugs.
Special urinalysis
Urine culture
Mandatory if bacteria are detected in the general urinalysis.
The purpose of the study. Performed to determine the number of bacteria, their type and sensitivity to antibacterial drugs.
Rules for collecting urine for analysis. To obtain a correct result from this test, urine must be collected after thorough toileting of the vulva by covering the vagina with a cotton swab. It is necessary to collect an average portion of urine in a sterile container, screw the lid tightly and deliver it to the laboratory within one and a half to two hours.
Urine culture is prepared on average from 7 to 10 days and allows the doctor to decide whether to carry out antibacterial treatment and with what drugs. If there is a clinical picture of inflammation, before the results of the culture are obtained, antibacterial treatment with a broad-spectrum antibiotic (acts on a large range of bacteria) is carried out, and in case of asymptomatic course of the disease or mild inflammation, treatment is not carried out until the results of the analysis are obtained.
Nechiporenko urinalysis
This is a special urinalysis that shows the amount of red blood cells, white blood cells and cylinders in 1 ml of urine.
The purpose of the study. This analysis is prescribed if there is a suspicion of an inflammatory process in the organs of the urinary system in a pregnant woman, if there are changes in the general analysis of urine. It gives more accurate results than a general urinalysis, and also allows you to control the ongoing treatment in dynamics.
Urine collection rules. Urine for analysis according to Nechiporenko is collected in the same way as for a general urine test.
Investigated parameters
- The number of leukocytes - normally they should be less than 2 thousand in 1 ml . An increase of in the number of leukocytes indicates the presence of pyelonephritis (an inflammatory disease of the pelvis and cups of the kidneys).

- The number of erythrocytes is normally less than 1 thousand per 1 ml. An increase in the number of red blood cells indicates the development of glomerulonephritis (inflammation of the renal glomeruli).
- The number of cylinders is normally less than 20 in 1 ml. The detection of an increased content of cylinders indicates arterial hypertension, diseases of the cardiovascular system, and can occur with early toxicosis of pregnant women.
Urinalysis according to Zimnitsky
Purpose of the study. This analysis is prescribed to clarify the ability of the kidneys to concentrate and dilute urine, to identify latent edema. The study may be needed if you suspect the development of preeclampsia, renal failure, infections of the urinary system, as well as diabetes.
Urine collection rules. For urine analysis according to Zimnitsky, urine is collected during the day (24 hours) in 8 containers (jars), while the amount of fluid drunk is taken into account (the pregnant woman writes down how much fluid she drinks during the day, taking into account soups, fruits and vegetables). At 6 am, a woman urinates into the toilet, then all subsequent urine is collected in jars.
At 6 am, a woman urinates into the toilet, then all subsequent urine is collected in jars.
Total 8 servings:
- 1 serving - 6:00 a.m. to 9:00 a.m.,
- 2 portion - from 9-00 to 12-00 hours,
- 3 portion - from 12-00 to 15-00 hours,
- 4 portion - from 15-00 to 18-00 hours,
- 5 portion - from 18-00 to 21-00 hours,
- 6 portion - from 21-00 to 24-00 hours,
- 7 portion - from 24-00 to 3-00 hours,
- 8 portion - from 3-00 to 6-00 hours.
Jars are signed and delivered to the laboratory.
Test parameters. The amount and specific gravity of urine in each portion is estimated. Normal kidney function is characterized by:
- daily urine volume about 1.5 liters;
- predominance of daytime urination over nighttime;
- urinary excretion of approximately 70--80% of the liquid drunk per day;
- the specific gravity of urine in at least one of the portions is not lower than 1.
 020--1.022;
020--1.022; - significant fluctuations during the day the amount of urine in individual portions (from 50 to 400 ml) and the specific gravity of urine (from 1.003 to 1.028).
Deviations from these standards indicate a violation in the work of the kidneys.
Rehberg's test
Purpose of the study. This test is used to determine the ability of the kidneys to filter urine. It must be carried out for all pregnant women with preeclampsia, with urinary tract infections, with kidney diseases, and with diabetes.
Urine collection rules. Before the test, intense physical activity, strong tea and coffee are excluded. Urine is collected during the day in one container, which is stored in the refrigerator during the entire collection time. After completing the collection of urine, measure the contents of the container, be sure to mix and immediately pour 70-100 ml into a special container or jar and deliver it to the laboratory, reporting the total volume of urine collected per day.
At the time of delivery of urine to the laboratory, blood is taken for creatinine from a vein.
Test parameters. The method is based on the assessment of glomerular filtration by the rate of purification of blood plasma from creatinine, a special product of protein breakdown. This indicator can be determined if you know the concentration of creatinine in the blood, in the urine and the daily volume of urine. This indicator is calculated using a special formula and is called creatinine clearance. Normally, the value of this indicator ranges from 75 to 134 ml / min / 1.7 m2. A decrease in the level of renal filtration indicates kidney damage and occurs with severe complications of pregnancy - gestosis, kidney diseases (pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis), diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, urolithiasis.
Urine for 17-KC
This test was previously widely prescribed to pregnant women to determine the hormones produced by the adrenal cortex. For analysis, urine was collected during the day, mixed, a small part of it was poured, which was delivered to the laboratory with an indication of the total amount of urine collected. An increase in the concentration of 17-ketosteroids in the urine indicated an excess production of hormones in the body of a pregnant woman, on the basis of which the doctor prescribed hormonal drugs. However, at present, the determination of these substances in urine is considered uninformative and is not used during pregnancy.
For analysis, urine was collected during the day, mixed, a small part of it was poured, which was delivered to the laboratory with an indication of the total amount of urine collected. An increase in the concentration of 17-ketosteroids in the urine indicated an excess production of hormones in the body of a pregnant woman, on the basis of which the doctor prescribed hormonal drugs. However, at present, the determination of these substances in urine is considered uninformative and is not used during pregnancy.
Urine tests are very easy to perform and very informative for the doctor, they allow you to timely detect the slightest changes in the body of the expectant mother and start treatment in a timely manner, which helps prevent serious complications from the pregnant woman and the unborn baby.
The purpose of the study of the general analysis of urine during pregnancy
The main purpose of a woman, determined by nature itself, is the birth of a child. However, its bearing is a complex physiological process that has a huge impact on the female body.
During pregnancy, the kidneys work with a double load, removing not only the metabolic products of the mother, but also the fetus. Also, the growing uterus compresses the abdominal organs, including the ureters, which can lead to stagnation of urine, swelling of the kidneys and an ascending infection penetrating the kidneys from the bladder.
In addition, immunity during gestation is weakened, hormonal changes lead to relaxation of the ureters, which also provokes an infectious process or exacerbation of chronic infectious diseases of the urinary system.
Urinalysis during pregnancy is prescribed by practicing obstetrician-gynecologists:
- for the timely diagnosis of various pathological processes in the urinary system and other internal organs;
- monitoring the course of the detected disease and evaluating the rationality of the course of ongoing medical therapy.
Urinalysis during pregnancy helps not to miss the alarming signs of a specific pathology of the prenatal period - late toxicosis (preeclampsia), which can pose a threat to the life of the mother and child. Together with certain complaints and symptoms, a general urinalysis is important in identifying the severity of preeclampsia and directing the efforts of doctors to prevent this formidable pathology.
Together with certain complaints and symptoms, a general urinalysis is important in identifying the severity of preeclampsia and directing the efforts of doctors to prevent this formidable pathology.
Frequency of urinalysis
Pregnant women are prescribed a urinalysis more often than other laboratory tests.
Urinalysis for pregnant women:
- every 4 weeks in the first trimester, 90,003 times every 2 weeks in the second and early third trimester;
- weekly starting at 35 weeks.
Usually, a general urine test during pregnancy is given at each visit to the gynecologist, from the moment of registration to the birth itself.
Urine during pregnancy.
In the analysis of urine during pregnancy, the doctor evaluates both physical and chemical parameters - color, transparency, density (specific gravity) and pH , and inorganic urine sediment - the number of formed elements, salts, microbes, protein.
The acidity or pH of the urine will depend on nutrition: with a predominantly vegetable and dairy diet, urine will be slightly alkaline, with an abundance of meat - acidic. An increase in the acidity of urine, together with an increase in the number of leukocytes, is an early sign of an infectious process in the urinary tract. Timely intervention allows you to stop the inflammatory process at the initial stage, which reduces the dose and duration of taking antibacterial drugs used to combat urinary tract infections. The easiest way to monitor urine pH at home is to use a portable urine analyzer.
The specific gravity of urine indicates the degree of dissolution of salts and other substances (glucose, protein) in it. A sharp increase in specific gravity may indicate a violation of kidney function or the presence of serious diseases (diabetes, nephropathy).
Main indicators and possible deviations from the norm in the analysis
Consider the main indicators of urine analysis.
- Acetone in urine during pregnancy.
The acidity of the urine changes with toxicosis with vomiting, causing both acidification of the urine and its alkalinization, depending on the activities carried out and the severity of vomiting. One of the signs of toxicosis and its rather pronounced condition is the appearance of acetone (ketone bodies) in the urine. They change the pH of urine to the acid side.
- Cloudy urine during pregnancy.
If the transparency of urine is disturbed, the presence of mucus, microbes or leukocytes, protein in it can be suspected, which indicates a serious inflammatory process in the kidneys or urinary system. The appearance of a precipitate may indicate urolithiasis or metabolic disorders.
- Protein in urine during pregnancy.
One particularly worrisome indicator in the urine of pregnant women is protein. In a healthy woman, it should normally be absent, but during pregnancy, especially in its later stages, traces of protein in the urine are quite acceptable. These are the features of the blood circulation of the kidneys and the result of increasing loads on them.
These are the features of the blood circulation of the kidneys and the result of increasing loads on them. An increase in the amount of protein in the general urine test serves as a signal for a more detailed examination of the woman. An increase in the protein level above 0.033 g/l may indicate the development of a serious pregnancy complication - nephropathy or preeclampsia. Also, the appearance of protein in the urine can be a sign of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the kidneys - glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis.
In such conditions, immediate hospitalization is required, a comprehensive examination and treatment is required, and with a gestational age of more than 32 weeks and a progressive deterioration in kidney function, early delivery is necessary to save the life of the child and mother. Nephropathy leads to increased pressure, the development of dangerous complications in the form of preeclampsia and eclampsia, which can dramatically disrupt the nutrition of the placenta, cause convulsions in the mother and fetal death.
Timely detection of an increase in the level of protein in the urine allows you to identify preeclampsia in the early stages and avoid the terrible complications associated with it. For monitoring at home, a portable urine analyzer is best.
- Bacteria in urine during pregnancy.
During pregnancy, urinalysis of women often reveals bacteria. This phenomenon is quite common and is due to the peculiarities of the structure of the genitourinary system of women, the proximity to the genital organs of the rectum and the weakening of the immune defense of the mucous membranes from microbial attacks during pregnancy. The appearance of microbes in the urine may be a defect in the collection of urine and a consequence of insufficient hygiene of the genital organs, or it may be a symptom of a serious urinary tract infection - pyelonephritis, cystitis. Especially often in the urine is sown E. coli or staphylococcus aureus.
A separate option may be asymptomatic bacteriuria : the appearance of microbes in the urine in the complete absence of signs of inflammation from the urogenital area.
 This condition requires close monitoring by a doctor, as it can be the initial stage of serious infections of the kidneys and bladder. Asymptomatic bacteriuria with a large number of microbial bodies per milliliter of urine can lead to premature birth, threatened abortion, intrauterine infection of the fetus, and other complications.
This condition requires close monitoring by a doctor, as it can be the initial stage of serious infections of the kidneys and bladder. Asymptomatic bacteriuria with a large number of microbial bodies per milliliter of urine can lead to premature birth, threatened abortion, intrauterine infection of the fetus, and other complications. If microbes are found in the general urine test, an additional urine culture is performed during pregnancy. This analysis is carried out according to the general rules, but urine is collected in a sterile cup and sown on special media, detecting the number and type of microbes in the urine, as well as determining the sensitivity of these microbes to antibiotics.
- Leukocytes in urine during pregnancy.
The presence of leukocytes in the urine indicates an inflammatory process in the genitourinary system. This is accompanied by a serious condition of the pregnant woman, and is extremely dangerous for the fetus - it can threaten intrauterine death, premature birth, fetal hypoxia, and placental problems.
The easiest way to monitor your white blood cell count at home is to use a portable urine analyzer.
- Erythrocytes in urine during pregnancy.
The appearance of erythrocytes in the urine is an unfavorable symptom, since normally they should be completely absent in a pregnant woman. Blood in the urine may appear as microhematuria, which is a very small number of red blood cells. This happens with cystitis, urolithiasis, pyelonephritis, in the initial stage of preeclampsia.Sometimes blood in the urine is visible to the naked eye, which is called gross hematuria. This occurs with nephritis, glomerunonephritis with nephrotic syndrome, with severe gestosis. These conditions are extremely dangerous for the mother and fetus, require immediate hospitalization and active therapy, and sometimes an emergency caesarean section to save the baby and the mother herself.
- Urine sugar during pregnancy
If diabetes or gestational diabetes is suspected, urine glucose (sugar) is measured. In case of violation of carbohydrate metabolism, associated both with the pregnancy itself and with the onset of diabetes, as a result of an increase in the level of glucose in the blood, its excess is filtered into the urine. Usually, an increase in sugar levels is accompanied by an increase in the density of urine, a sharp increase in the volume of urine released (up to three to five liters) and intense thirst.
In case of violation of carbohydrate metabolism, associated both with the pregnancy itself and with the onset of diabetes, as a result of an increase in the level of glucose in the blood, its excess is filtered into the urine. Usually, an increase in sugar levels is accompanied by an increase in the density of urine, a sharp increase in the volume of urine released (up to three to five liters) and intense thirst. The easiest way to monitor the level of red blood cells and urine sugar at home is to use a portable urine analyzer.
How to collect urine for analysis?
It is necessary to collect the average portion of the morning (immediately after sleep) urine in a special sterile container for analysis.
On the eve of sampling, avoid taking medications (vitamins, diuretics, hormones, antibiotics and other medicines) and coloring foods (carrots, beets, asparagus, cranberries, blueberries, etc.).
The last sexual intercourse should be at least 12 hours before the collection of the urine sample.
First of all, before collecting urine, it is necessary to carefully perform hygiene of the external genital organs. To prevent the vaginal environment from entering the urine sample, a swab must be inserted into the vagina. Avoid touching the urine collection container with your body.
When urinating, flush the first portion of urine (1-2 seconds) down the toilet, and then, without interrupting urination, collect the second part of the urine, interrupting at the end of the process and finishing urinating into the toilet.
Poor urinalysis during pregnancy
The presence of a “bad” urinalysis during pregnancy may indicate asymptomatic bacteriuria of pregnant women, preeclampsia, pyelonephritis of pregnant women, cystitis, urethritis and other diseases. In most cases of intense proteinuria, micro- and macrohematuria, the detection of bacteria, a large number of leukocytes and cylinders in the urine, it requires additional diagnostics (ultrasound, urine culture for flora with antibiotic sensitivity), and, sometimes, observation of a pregnant woman in a hospital.