Dry patches on palms of hands
Palm rash: Causes, pictures, and treatments
Palm rashes can occur due to common skin conditions, such as eczema, or due to irritants and allergens. Most cases are not severe, and depending on the cause, the rash may improve on its own.
This article explores common causes for a rash on the palms, along with their symptoms and treatments.
A rash on the palms of the hands will look and feel differently depending on what causes it.
Most rashes look inflamed and may cause pain or itchiness. In paler skin, they may be red, while in darker skin, they may be grey, violet, or dark brown. Some rashes can also cause blistering, peeling, or flaking.
A palm rash might cause discomfort when closing the hand into a ball, or cause irritation when a person touches certain substances. Frequently washing the hands may dry the skin further.
[Slideshow]
Some possible triggers of palm rashes include:
Eczema
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a common condition that causes dry, sensitive skin. It typically affects young children but may continue into adulthood.
Symptoms include:
- itching
- dry skin that may crack
- red patches in lighter skin, and grey or purple areas in darker skin
Some forms of the condition are more common on the palms, such as dyshidrotic eczema. This type of eczema can cause small blisters on the hands, fingers, and palms.
Eczema treatments vary depending on the severity of the condition. There are many over-the-counter (OTC) moisturizers for mild to moderate cases. More severe cases may require corticosteroids or antihistamines.
Learn more about the causes and treatments for atopic dermatitis.
Contact dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a skin condition that develops when the skin comes into contact with an irritant or allergen. Many different substances can trigger contact dermatitis, including:
- nickel
- latex
- poison ivy
When the skin comes into contact with something the body perceives as dangerous, this can cause a rash. This rash may:
This rash may:
- burn
- blister
- itch
- hurt
The skin may also become dry, and in severe cases, crack. Because the hands touch many different substances each day, they are a common place where contact dermatitis can develop.
The main treatment is to identify and avoid the triggers for this condition. A doctor can perform a patch test on someone to determine what substance is causing the reaction. Some people may also benefit from moisturizers or corticosteroids.
Hives
Hives are raised red or skin-colored welts on the skin. They itch and can appear anywhere on the body, including the palms of the hands.
An allergic reaction to certain substances triggers this condition. These substances include foods, medications, or pollen. However, they can also occur in response to an infection or physical stimuli, such as heat or sun exposure.
Most cases of hives are acute and go away when there is no more exposure to the trigger causing the reaction. Antihistamines can also help reduce swelling and allergy symptoms.
Antihistamines can also help reduce swelling and allergy symptoms.
However, some people have chronic hives. An allergy specialist can help someone manage this and, if possible, identify the cause.
Hand, foot, and mouth disease
A virus causes hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD). It most commonly affects children under 5 years old, but can also affect adults.
The symptoms of HFMD include:
- fever
- sore throat
- a rash on the hands and feet, consisting of painful blisters
- headache
- ulcers in the mouth
- loss of appetite
People sometimes confuse HFMD with foot and mouth disease. However, these are separate conditions. Foot and mouth disease can only affect livestock and does not affect humans.
Usually, HFMD is not serious and resolves without treatment in 7–10 days. In the meantime, OTC pain medication can help relieve symptoms.
However, HFMD is contagious and spreads easily. People can help prevent spreading the virus by practicing hand hygiene and avoiding close contact with others.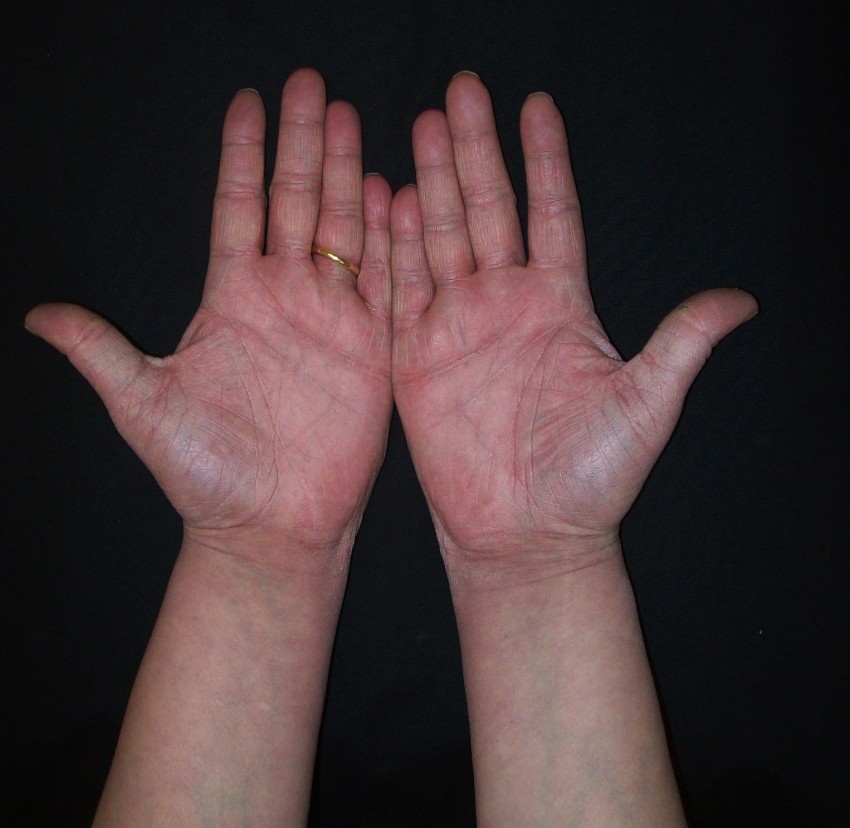
Fungal infection
Tinea manuum is a type of fungal infection that affects the hands. Ringworm triggers this condition, the same fungus that causes athlete’s foot. This condition is contagious, so touching other areas of the body affected with ringworm could lead to an infection on the palms.
Symptoms include:
- a small rash on the hands that gradually gets bigger
- itching
- skin that peels, flakes, or is scaly
A person can treat ringworm with OTC topical creams. A pharmacist can recommend an antifungal product for use on the hands. If the infection persists or is severe, a doctor may prescribe oral medication.
If a person has tinea manuum, they should avoid touching other areas of the body, or other people, as this can spread the infection. If people need to apply topical treatments to other parts of the body, they should wear disposable gloves.
Palmoplantar psoriasis
Palmoplantar psoriasis is an inflammatory condition that causes red, scaly patches to appear on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. It is an autoimmune condition that occurs when the skin grows new cells too quickly.
It is an autoimmune condition that occurs when the skin grows new cells too quickly.
Symptoms of psoriasis include:
- red, scaly patches of skin
- itching
- pain
- cracked skin that may bleed
Psoriasis can also affect the fingernails and toenails and may include pustules.
There is no cure for psoriasis, but there are treatments that can help someone manage it, including:
- moisturizers
- steroid creams
- UV light therapy
- medications to suppress the immune system, such as ciclosporin
Learn more about the symptoms and treatments for psoriasis.
To diagnose rashes on the palms, a doctor will look at the rash to assess its appearance. They may ask if the person has had any other symptoms, such as a fever or pain. They may also take a medical history or ask questions about skin conditions that run in someone’s family.
If a person could have contact dermatitis or hives, a doctor may recommend a skin prick test to determine the triggers.
There are ways to care for a palm rash at home. However, the techniques depend on the underlying cause.
For example, for fungal infections, a person may need to avoid touching the rash or sharing personal items with other people. OTC antifungal creams will help treat the disease.
For allergic reactions, people may need to make changes to their home environment, diet, or lifestyle to avoid triggers.
For dry skin, eczema, and contact dermatitis, there are several home remedies, including:
- taking warm showers or baths, ensuring they are not hot
- using gentle, nonirritating cleansers
- regularly applying a barrier cream, such as E45 or Eucerin
- moisturizing after bathing, showering, or washing the hands
- wearing cotton gloves at night to prevent scratching
Learn more about how to care for dry skin on the hands.
A person may wish to see a doctor so they can identify the cause of a palm rash. A medical professional can help identify the trigger and recommend treatments.
People should also see a doctor if they have ringworm that does not respond to OTC treatments, or their rash shows signs of a bacterial infection. The symptoms of a bacterial infection on the skin include:
- pus
- swelling
- feeling warm to the touch
- fever
People with hives or allergies should contact an emergency department or dial 911 immediately if they have trouble breathing.
Several conditions can trigger a palm rash. Most are not serious and may resolve on their own, or improve with OTC treatments and home care.
If a person has persistent or severe symptoms, or other symptoms accompanying the rash, they should speak to a doctor.
Palm rash: Causes, pictures, and treatments
Palm rashes can occur due to common skin conditions, such as eczema, or due to irritants and allergens. Most cases are not severe, and depending on the cause, the rash may improve on its own.
This article explores common causes for a rash on the palms, along with their symptoms and treatments.
A rash on the palms of the hands will look and feel differently depending on what causes it.
Most rashes look inflamed and may cause pain or itchiness. In paler skin, they may be red, while in darker skin, they may be grey, violet, or dark brown. Some rashes can also cause blistering, peeling, or flaking.
A palm rash might cause discomfort when closing the hand into a ball, or cause irritation when a person touches certain substances. Frequently washing the hands may dry the skin further.
[Slideshow]
Some possible triggers of palm rashes include:
Eczema
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a common condition that causes dry, sensitive skin. It typically affects young children but may continue into adulthood.
Symptoms include:
- itching
- dry skin that may crack
- red patches in lighter skin, and grey or purple areas in darker skin
Some forms of the condition are more common on the palms, such as dyshidrotic eczema. This type of eczema can cause small blisters on the hands, fingers, and palms.
This type of eczema can cause small blisters on the hands, fingers, and palms.
Eczema treatments vary depending on the severity of the condition. There are many over-the-counter (OTC) moisturizers for mild to moderate cases. More severe cases may require corticosteroids or antihistamines.
Learn more about the causes and treatments for atopic dermatitis.
Contact dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a skin condition that develops when the skin comes into contact with an irritant or allergen. Many different substances can trigger contact dermatitis, including:
- nickel
- latex
- poison ivy
When the skin comes into contact with something the body perceives as dangerous, this can cause a rash. This rash may:
- burn
- blister
- itch
- hurt
The skin may also become dry, and in severe cases, crack. Because the hands touch many different substances each day, they are a common place where contact dermatitis can develop.
The main treatment is to identify and avoid the triggers for this condition. A doctor can perform a patch test on someone to determine what substance is causing the reaction. Some people may also benefit from moisturizers or corticosteroids.
Hives
Hives are raised red or skin-colored welts on the skin. They itch and can appear anywhere on the body, including the palms of the hands.
An allergic reaction to certain substances triggers this condition. These substances include foods, medications, or pollen. However, they can also occur in response to an infection or physical stimuli, such as heat or sun exposure.
Most cases of hives are acute and go away when there is no more exposure to the trigger causing the reaction. Antihistamines can also help reduce swelling and allergy symptoms.
However, some people have chronic hives. An allergy specialist can help someone manage this and, if possible, identify the cause.
Hand, foot, and mouth disease
A virus causes hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD). It most commonly affects children under 5 years old, but can also affect adults.
It most commonly affects children under 5 years old, but can also affect adults.
The symptoms of HFMD include:
- fever
- sore throat
- a rash on the hands and feet, consisting of painful blisters
- headache
- ulcers in the mouth
- loss of appetite
People sometimes confuse HFMD with foot and mouth disease. However, these are separate conditions. Foot and mouth disease can only affect livestock and does not affect humans.
Usually, HFMD is not serious and resolves without treatment in 7–10 days. In the meantime, OTC pain medication can help relieve symptoms.
However, HFMD is contagious and spreads easily. People can help prevent spreading the virus by practicing hand hygiene and avoiding close contact with others.
Fungal infection
Tinea manuum is a type of fungal infection that affects the hands. Ringworm triggers this condition, the same fungus that causes athlete’s foot. This condition is contagious, so touching other areas of the body affected with ringworm could lead to an infection on the palms.
Symptoms include:
- a small rash on the hands that gradually gets bigger
- itching
- skin that peels, flakes, or is scaly
A person can treat ringworm with OTC topical creams. A pharmacist can recommend an antifungal product for use on the hands. If the infection persists or is severe, a doctor may prescribe oral medication.
If a person has tinea manuum, they should avoid touching other areas of the body, or other people, as this can spread the infection. If people need to apply topical treatments to other parts of the body, they should wear disposable gloves.
Palmoplantar psoriasis
Palmoplantar psoriasis is an inflammatory condition that causes red, scaly patches to appear on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. It is an autoimmune condition that occurs when the skin grows new cells too quickly.
Symptoms of psoriasis include:
- red, scaly patches of skin
- itching
- pain
- cracked skin that may bleed
Psoriasis can also affect the fingernails and toenails and may include pustules.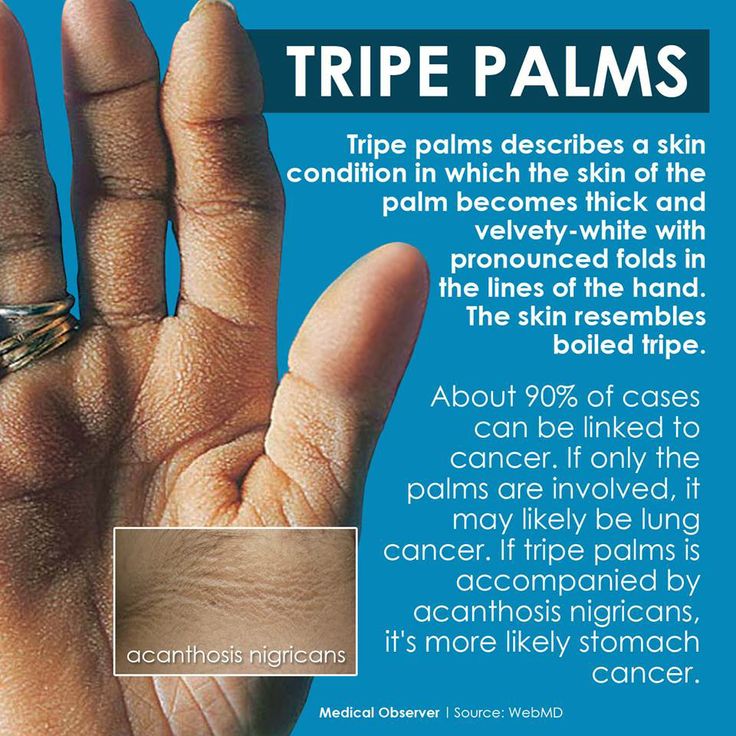
There is no cure for psoriasis, but there are treatments that can help someone manage it, including:
- moisturizers
- steroid creams
- UV light therapy
- medications to suppress the immune system, such as ciclosporin
Learn more about the symptoms and treatments for psoriasis.
To diagnose rashes on the palms, a doctor will look at the rash to assess its appearance. They may ask if the person has had any other symptoms, such as a fever or pain. They may also take a medical history or ask questions about skin conditions that run in someone’s family.
If a person could have contact dermatitis or hives, a doctor may recommend a skin prick test to determine the triggers.
There are ways to care for a palm rash at home. However, the techniques depend on the underlying cause.
For example, for fungal infections, a person may need to avoid touching the rash or sharing personal items with other people. OTC antifungal creams will help treat the disease.
For allergic reactions, people may need to make changes to their home environment, diet, or lifestyle to avoid triggers.
For dry skin, eczema, and contact dermatitis, there are several home remedies, including:
- taking warm showers or baths, ensuring they are not hot
- using gentle, nonirritating cleansers
- regularly applying a barrier cream, such as E45 or Eucerin
- moisturizing after bathing, showering, or washing the hands
- wearing cotton gloves at night to prevent scratching
Learn more about how to care for dry skin on the hands.
A person may wish to see a doctor so they can identify the cause of a palm rash. A medical professional can help identify the trigger and recommend treatments.
People should also see a doctor if they have ringworm that does not respond to OTC treatments, or their rash shows signs of a bacterial infection. The symptoms of a bacterial infection on the skin include:
- pus
- swelling
- feeling warm to the touch
- fever
People with hives or allergies should contact an emergency department or dial 911 immediately if they have trouble breathing.
Several conditions can trigger a palm rash. Most are not serious and may resolve on their own, or improve with OTC treatments and home care.
If a person has persistent or severe symptoms, or other symptoms accompanying the rash, they should speak to a doctor.
Red spots on palms | Prima Medica
Many disease states of a person manifest themselves on the skin. Including red spots on the palms indicate the presence of any trouble in the body. To successfully eliminate a skin defect, it is necessary, without delay, to find out the cause of its occurrence. It is necessary to start the examination with a consultation with a dermatologist.
Epidemiology of red spots on the palms
The epidemiology of this disease is ambiguous; for a long time it was considered as a purely professional one. According to foreign studies, allergic contact dermatitis affects approximately 30% of the adult population, mainly in developed countries. In addition, according to German scientists, no more than 40% of patients come to medical institutions with such problems. Among children, the prevalence of allergic contact dermatitis is lower, however, it was diagnosed in a fifth of all children and adolescents who sought medical help for dermatitis.
Among children, the prevalence of allergic contact dermatitis is lower, however, it was diagnosed in a fifth of all children and adolescents who sought medical help for dermatitis.
Causes of red spots on the palms
Rashes on the palms can be triggered by many factors.
The most common form of this is contact dermatitis. It can be allergic and simple (burns, frostbite, abrasions). The reasons for the simple are almost always obvious; when they are eliminated, dermatitis also disappears. Allergic occurs in the place that was in direct contact with the substance that caused the allergy. For example, with cleaning, detergents. This can lead to sensitization to cold (cold allergy). Rashes appear immediately after a sharp cooling of the skin on the arms or legs. Less commonly, an allergic rash on the palms and/or feet may be caused by a food or drug allergen. In the pathogenesis of sensitization in these cases, mainly not antibodies, but T-lymphocytes take part. Microscopic studies of samples from the lesion show large concentrations of lymphocytes and other immune cells that have moved from the bloodstream to redness.
Microscopic studies of samples from the lesion show large concentrations of lymphocytes and other immune cells that have moved from the bloodstream to redness.
Risk factors for red spots on the palms
Risk factors for the appearance of red spots are nervous strain or severe stress, decreased immunity.
These same factors cause relapses of dyshidrotic eczema. This is a non-contagious chronic disease accompanied by severe itching. Its causes have not yet been fully elucidated, and they presumably include allergic manifestations caused by household chemicals and food products, and a hereditary predisposition. Dyshidrotic eczema can be observed not only on the skin of the palms and feet, but also on the back. Most of those who applied for this disease are younger than 40 years old, among them patients of both sexes. The pathogenesis of dyshidrotic eczema is not actually associated with sweating disorders, as previously thought. In a family history, 50% of patients have a predisposition to allergic reactions. Risk factors, in addition to emotional overstrain, are called high temperature and humidity.
Risk factors, in addition to emotional overstrain, are called high temperature and humidity.
Rashes can be infectious (for example, beginning lichen), viral (herpes), parasitic (scabies) in nature. Such a rash, usually first appearing on the palms, quickly spreads to other parts of the body. It is transmitted by contact with a sick person, a fungal infection (lichen) can also be contracted from a sick animal. Herpes is ubiquitous, 90% of the adult population of the planet has antibodies to it.
A bright crimson rash, localized only on the palms or feet - erythrosis (Lane's disease). Itching for this disease is not typical. Such rashes should be well known to the patient, since the tendency to them is inherited from close relatives. The palms, as well as the feet, have an extensive network of arterial and venous vessels - nature has provided a good blood supply to this part of the body. In the pathogenesis of the disease, the main role is played by hereditary disorders in the vessels that interact between the venous and arterial systems - anastomoses. Through these vessels, blood is discharged into the venous bed with an increase in blood pressure, if the anastomoses are narrowed or completely impassable, then the blood discharge is disturbed, arterioles and capillaries constantly work in overload mode. This contributes to their constant expansion and the appearance of red spots. The disease is quite rare, it manifests itself both from birth and at a later age under the influence of factors provoking its development. Men and women get sick equally often, in one family the disease manifests itself in all or almost all of its members.
Through these vessels, blood is discharged into the venous bed with an increase in blood pressure, if the anastomoses are narrowed or completely impassable, then the blood discharge is disturbed, arterioles and capillaries constantly work in overload mode. This contributes to their constant expansion and the appearance of red spots. The disease is quite rare, it manifests itself both from birth and at a later age under the influence of factors provoking its development. Men and women get sick equally often, in one family the disease manifests itself in all or almost all of its members.
Dysfunction of the heart muscle, vegetative-vascular dystonia causes seizures, leading to a decrease in vascular tone and the appearance of dotted red spots on the palms. They do not itch, do not hurt and pass along with the attack.
Diabetes is a risk factor for skin infection. Changes in the hormonal background during puberty, during pregnancy, taking hormonal drugs can also cause rashes; the rapid growth of itchy rashes on the palms is a signal for a visit to an oncologist.
Symptoms of red spots on the palms
Since red spots on the palms can be caused by a variety of reasons, the symptoms also have some differences.
The clinical signs of allergic contact dermatitis are similar to those of the acute stage of eczema. The first signs are the appearance of sufficiently large reddenings, later small multiple bubbles begin to form against their background. Bursting and getting rid of the contents, they are exudative red spots on the surface of the skin, drying up, they can become covered with scales and crusts. The main focus is located where contact with the allergen occurred. Red spots on the palms itch, making it difficult to sleep and stay awake. Sometimes itching precedes the appearance of rashes - palms itch and red spots appear, as if from scratching. Allergic contact dermatitis can be localized on the feet if you had to walk barefoot on a substance that causes allergies. Since the body is sensitized to the effects of the allergen as a whole, the appearance of secondary foci can occur anywhere in the body, very distant from the primary focus. Secondary lesions may look like red nodules, vesicles, spots, hyperemia and swelling. Allergic dermatitis can also look like one red itchy spot on the palm of your hand (usually at the site of contact with the allergen), single and massive rashes can also appear on the back of the hands and feet.
Secondary lesions may look like red nodules, vesicles, spots, hyperemia and swelling. Allergic dermatitis can also look like one red itchy spot on the palm of your hand (usually at the site of contact with the allergen), single and massive rashes can also appear on the back of the hands and feet.
Dyshidrotic eczema in symptoms resembles contact dermatitis. The first signs are the appearance of grouped small, approximately millimeter-sized, deeply located vesicles, sometimes with vesicles. The newly appeared small red spots on the palms are very itchy. Later - they merge, burst, forming erosive surfaces that peel off and crack. This stage is already accompanied by pain. It is localized in 80% of cases on the hands, sometimes on the soles, red spots on the palms and feet itch. First, the skin surfaces between the fingers, palms and soles of the foot are affected, then the rash can spread to the back surface.
The first signs of erythrosis (Lane's disease) - a significant number of bright rashes of a rich crimson color appear on the palms. At the same time, they appear on the feet, however, they notice them there later. The spots do not differ in soreness and itching. Upon closer inspection, you can see that the spots are not continuous - these are small dots, concentrated very close. Such accumulations are localized on the fingers and between them, palmar tubercles under the extreme fingers - the little finger and thumb. The border with healthy skin is sharply defined and is located on the lateral surface of the hands and feet. Rashes with erythrosis are never located outside the hand or foot. This pathology is not characterized by increased sweating on the inner surface of the palms and feet, which is used to differentiate it from similar diseases.
At the same time, they appear on the feet, however, they notice them there later. The spots do not differ in soreness and itching. Upon closer inspection, you can see that the spots are not continuous - these are small dots, concentrated very close. Such accumulations are localized on the fingers and between them, palmar tubercles under the extreme fingers - the little finger and thumb. The border with healthy skin is sharply defined and is located on the lateral surface of the hands and feet. Rashes with erythrosis are never located outside the hand or foot. This pathology is not characterized by increased sweating on the inner surface of the palms and feet, which is used to differentiate it from similar diseases.
If the hands of the hands down lowered turn red and small white spots appear on them, this indicates a problem with the capillary circulation, but special treatment is usually not prescribed. If a person has red palms with white spots forming a marble ornament, then this indicates circulatory disorders.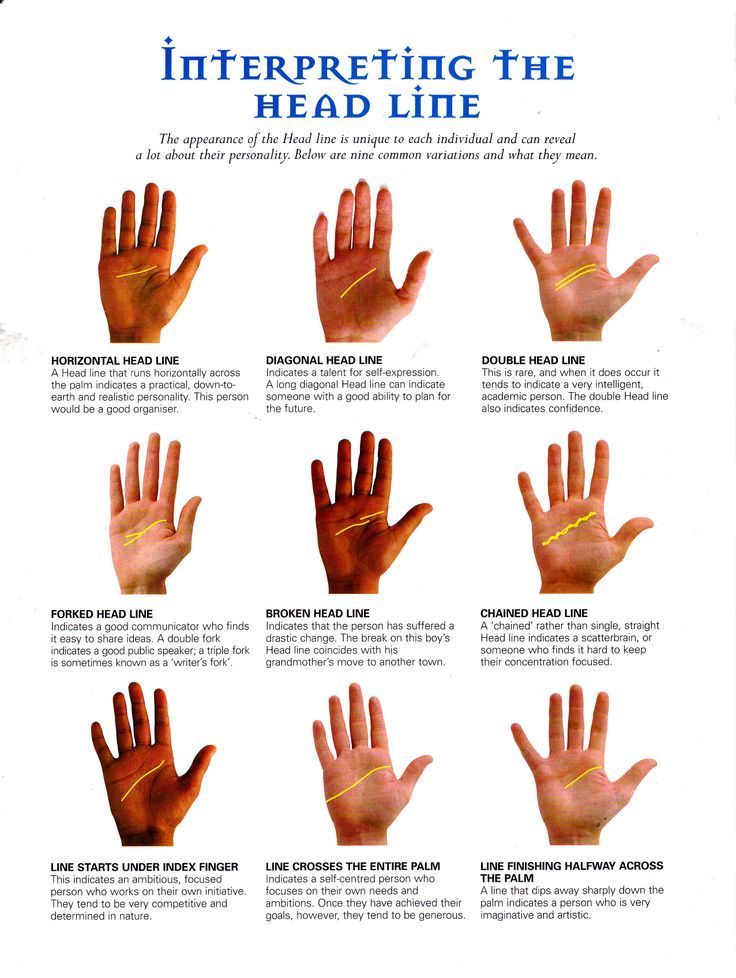
Having found red scaly spots on the back of the hand, one can assume the presence of psoriasis, by the way, this disease also has a palmoplantar form. Ringworm and other infectious skin diseases can also start on the hands, since our hands most often come into contact with infected objects. Such symptoms should be an incentive to contact a dermatologist.
On the hands, lichen can be localized, for example, microsporia (ringworm). Although the palms, and even more so the feet, are extremely rarely affected, however, this cannot be completely ruled out. You can get infected not only from a sick animal, but also from a person. At first, a red pimple appears, which itches, but not too much, grows and brightens in the center, dry scales begin to form there. Along the edges are red small papules, forming a clear border. The formation gradually increases, along the edge of the spot, a limiting roller is formed, consisting of vesicles, nodules and crusts.
Infection with scabies caused by the scabies mite can be suspected by finding characteristic rashes that itch intensely, especially at night or after taking a bath (shower). The rash is characterized by thin, winding light lines connecting the entrance and exit of the tick. At the ends there are small spots or vesicles, which sometimes merge into plaques with exudation. On the skin of the palms, these rashes are localized between the fingers. We need to look for more such rashes. Ticks love thin delicate skin, flexion areas of the arms, external genitalia, abdomen, sides, skin folds. They never settle on the back. In children - palms, feet, buttocks, face and head.
The rash is characterized by thin, winding light lines connecting the entrance and exit of the tick. At the ends there are small spots or vesicles, which sometimes merge into plaques with exudation. On the skin of the palms, these rashes are localized between the fingers. We need to look for more such rashes. Ticks love thin delicate skin, flexion areas of the arms, external genitalia, abdomen, sides, skin folds. They never settle on the back. In children - palms, feet, buttocks, face and head.
Red spots on the palms and temperature in a child may appear at the onset of infectious diseases - measles, chickenpox, rubella, scarlet fever. Allergic contact dermatitis can sometimes be accompanied by fever. Adults are also not immune from childhood illnesses, especially since childhood illnesses in adults often occur in an atypical form and are quite difficult. The presence of such symptoms should be alarming and force you to immediately consult a doctor.
Noticing red spots on the palms of a child, parents, as a rule, seek medical help. Basically, rashes in infectious diseases are localized not only on the palms, they appear after an increase in temperature (measles, scarlet fever) and other symptoms. So, measles is characterized by photophobia - the child asks to draw the curtains on the windows, scarlet fever is a type of sore throat and a rash usually complements the symptoms. Chickenpox and rubella can occur in children in a mild form without an increase in body temperature, and rashes are localized throughout the body, and with chickenpox they also itch a lot.
Basically, rashes in infectious diseases are localized not only on the palms, they appear after an increase in temperature (measles, scarlet fever) and other symptoms. So, measles is characterized by photophobia - the child asks to draw the curtains on the windows, scarlet fever is a type of sore throat and a rash usually complements the symptoms. Chickenpox and rubella can occur in children in a mild form without an increase in body temperature, and rashes are localized throughout the body, and with chickenpox they also itch a lot.
Allergic dermatitis on the palms appears after contact with an allergen, which can be, in principle, any substance. Most often it is chocolate, citrus fruits, medicines, plants (including domestic ones), animal hair (more often cats), insect bites, cosmetics and household chemicals. Rashes, deep red, itchy, may be accompanied by respiratory disorders.
Lana's disease often manifests itself already in childhood. Diseases of the circulatory and hematopoietic organs, accompanied by a hemorrhagic rash, may appear as red spots on the palms.
Non-compliance with hygiene rules in young children manifests itself as sweating, diaper rash, dermatitis. The palms are not the most characteristic part of the body for such rashes, but it cannot be ruled out.
Complications and consequences of red spots on the palms
The consequences and complications of rashes, especially itchy ones, are fraught with an associated secondary infection. Sometimes such rashes, which appeared as an allergic reaction, quickly disappear on their own when contact with the allergen is excluded. However, if the spots do not go away, you should immediately contact a dermatologist so as not to aggravate the course of the disease and avoid possible complications, since the appearance of spots on the palms indicates trouble in the body.
Diagnosis of red spots on the palms
Diagnosis is based on a complete examination of the skin and mucous membranes, based on typical signs of the disease. Laboratory studies: bacterial cultures, urine and blood tests - biochemical and clinical, in some cases a blood test is done for hormones, remoprobes, immunological tests. A medical history is compiled taking into account hereditary predisposition. Instrumental diagnostics is prescribed: ultrasound of internal organs, skin biopsy, microscopy of scrapings and cultures. For differentiation with diseases accompanied by a similar clinic, differential diagnosis is carried out. For example, with a preliminary diagnosis: dyshidrotic eczema, contact dermatitis, fungal infections (dermatophytosis of the feet), palmar-plantar psoriasis, neurodermatitis with localization on the palms and feet, eczematitis, epidermomycosis, spongiosis, scabies and some other skin diseases should be excluded.
A medical history is compiled taking into account hereditary predisposition. Instrumental diagnostics is prescribed: ultrasound of internal organs, skin biopsy, microscopy of scrapings and cultures. For differentiation with diseases accompanied by a similar clinic, differential diagnosis is carried out. For example, with a preliminary diagnosis: dyshidrotic eczema, contact dermatitis, fungal infections (dermatophytosis of the feet), palmar-plantar psoriasis, neurodermatitis with localization on the palms and feet, eczematitis, epidermomycosis, spongiosis, scabies and some other skin diseases should be excluded.
By analyzing complex data, including a detailed medical history, clinical examination data, as well as the results of laboratory and instrumental studies, the doctor can make the correct final diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Treatment of red spots on the palms
In dermatology, with the similarity of symptoms, diseases can have completely different etiologies - from infection by microorganisms to autoimmune aggression, therefore, treatment methods in most cases are based on symptoms. Only certain diseases require radical treatment aimed at eliminating the cause of their occurrence.
Only certain diseases require radical treatment aimed at eliminating the cause of their occurrence.
Most often, in symptomatic therapy, external medicines are used to relieve itching, pain, eliminate rashes, oral preparations or injections are much less commonly used.
In case of recurrence of the disease, water procedures using soap, foam and shower gels are not recommended in order to avoid skin irritation. It is undesirable to use household chemicals, at least you need to wear gloves. It is advisable to avoid prolonged exposure to adverse environmental conditions - solar radiation, rain, wind, snow. Do not wear products made of synthetics, fur, wool on areas of irritation. From the diet of the patient are excluded products that most often cause allergies: citrus fruits, chocolate, coffee.
If red spots on the palms are caused by contact dermatitis, you need to identify and remove the irritant, after which in most cases it goes away on its own or simple rehabilitation is required to eliminate residual irritation on the skin. Patients with an immediate allergic reaction often do not need treatment at all, since the inflammation disappears after contact with the allergen is eliminated as quickly as it arose. It's just that the patient must know his allergens and eliminate the possibility of contact with them throughout his life. It is necessary to take into account the fact that over time the spectrum of substances that cause allergies in a given person usually expands.
Patients with an immediate allergic reaction often do not need treatment at all, since the inflammation disappears after contact with the allergen is eliminated as quickly as it arose. It's just that the patient must know his allergens and eliminate the possibility of contact with them throughout his life. It is necessary to take into account the fact that over time the spectrum of substances that cause allergies in a given person usually expands.
In more complex forms of allergic contact dermatitis, drug therapy is carried out, mainly consisting in the use of local antihistamine or hormonal ointments, lotions with drugs. At the vesiculo-bullous stage of allergy, it is recommended to open the blisters on the patient's bodies, while the upper part (lid) of the blisters is not removed, but impregnated with an antiseptic and left in place. Modern techniques recommend the use of epithelial ointments in such cases.
Patients with a severe form of the disease are prescribed potent drugs both externally and internally, and in order to increase the absorption of the drug, hermetic dressings are used. When dressing, the damaged skin is treated with a salt solution and ice is applied to it.
When dressing, the damaged skin is treated with a salt solution and ice is applied to it.
Difficulties are cases of occupational allergic contact dermatitis, when a radical change in the type of activity is often required to cure the patient.
Treatment of allergic contact dermatitis begins with weaker external preparations, if there is no effect, after a few weeks they switch to stronger ones. They finish the fight against residual phenomena, again using weaker means. When prescribing an external agent, the doctor usually takes into account the factor that ointment works better on dry surfaces with cracks, and cream on wet surfaces. If a secondary infection is suspected, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics, which can cause allergies. You do not need to try to eliminate it yourself, you should consult a doctor to adjust the appointment.
Ointments (creams, gels) and other external preparations are applied to dry, clean skin in a thin layer, without rubbing.
Fenistil gel (active ingredient - dimethindene maleate, blocker of H1-histamine receptors). The drug reduces the production of histamine in the body, eliminates itching, irritation and other symptoms of an allergic reaction. Helps to strengthen the capillary walls, has an analgesic and healing effect.
It is characterized by speed, noticeably improves the condition almost immediately, the highest concentration at the site of application can occur within an hour. 10% of the active ingredient is absorbed into the systemic circulation. It is used for itchy rashes of various etiologies, including simple and allergic contact dermatitis.
It is contraindicated in cases of sensitization to demididene other ingredients, newborns, pregnant women in the first three months, with prostate adenoma, angle-closure glaucoma.
It is used two to four times a day, in severe cases, accompanied by severe itching or extensive areas of damage, it can be combined with taking Fenistil drops or capsules.
May cause adverse reactions at the site of application.
For allergic diseases with an associated secondary infection, the doctor may prescribe Lorinden C ointment. This is a combined preparation containing the glucocorticosteroid flumethasone pivalate, which relieves inflammation, itching, exudation and other allergy symptoms, in combination with iodochloroxyquinoline, which has a bactericidal and fungicidal effect. Can be used by pregnant and lactating women in small areas. It is not prescribed for syphilitic and tuberculous skin lesions, oncological skin diseases, the consequences of vaccination and sensitization to the components of the drug.
Ointments that help accelerate tissue regeneration - Actovegin, Solcoseryl, the active substance of which is a calf blood extract devoid of a protein component.
Solcoseryl ointment is a biogenic stimulator of cellular metabolism, stimulates the absorption and assimilation of oxygen and glucose by the cells of the damaged epidermis, repairs and maintains its viable state. Prevents the formation of trophic changes, accelerating the process of restoration of the epithelial layer. Once or twice a day, a thin layer is lubricated with lesions, can be used in dressings. Can be used by pregnant and lactating women.
Prevents the formation of trophic changes, accelerating the process of restoration of the epithelial layer. Once or twice a day, a thin layer is lubricated with lesions, can be used in dressings. Can be used by pregnant and lactating women.
Actovegin ointment is an activator of intracellular metabolism, stimulates the absorption and assimilation of oxygen and glucose by the cells of the damaged epidermis, repairs and maintains its viable state. Additionally improves blood circulation. Two or three times a day, a thin layer lubricates the lesions. Use by pregnant and lactating women - with caution. May cause side effects in the area of application.
To get rid of residual effects, Methyluracil ointment with the same active ingredient is also prescribed. Stimulates the reproduction of leukocytes and, to a lesser extent, erythrocytes, which leads to cell renewal, accelerated healing and activation of the protective functions of the skin. It is prescribed for people with leukopenia with long-term non-healing skin lesions, the treatment regimen is prescribed by a doctor. Contraindicated in malignant diseases of the blood and bone marrow.
Contraindicated in malignant diseases of the blood and bone marrow.
Therapy with non-hormonal ointments is usually prolonged, hormonal ointments are used for no more than one to two weeks. Ointments with glucocorticosteroids cause many side effects, including vasodilation, atrophy and depigmentation of the skin at the site of application.
Dyshidrotic eczema is treated by conducting all kinds of examinations and finding out the provocateur of this condition. After the diagnosis, they begin treatment: they use antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs inside and out, in severe cases - hormonal drugs and ointments. Diuretics, hemodez are prescribed for the prevention of side effects of glucocorticosteroids.
Small lesions in the initial stage are treated with ointments with Naftalan oil, sulfur, birch tar; with an attached fungal infection - the drug Fukortsin, which is produced in the form of a solution and has a wide range of antimicrobial activity, including against fungi. Contraindicated in allergic dermatoses, children 0-11 years old. Apply to the affected areas of the skin from one to three times a day, apply until the symptoms disappear. May cause overdose effects: dizziness, nausea, weakness, dyspepsia. Contraindicated in sensitization, not used on significant body surfaces.
Contraindicated in allergic dermatoses, children 0-11 years old. Apply to the affected areas of the skin from one to three times a day, apply until the symptoms disappear. May cause overdose effects: dizziness, nausea, weakness, dyspepsia. Contraindicated in sensitization, not used on significant body surfaces.
Elidel cream copes well with eczema of all types, in terms of its effectiveness it can be compared with strong hormonal ointments. The active ingredient is pimecrolimus, a derivative of ascomycin. Provides selective inhibition of the production and release of pro-inflammatory factors from T-lymphocyte and mast cells. It also suppresses the secondary immune response of T-helper epithelium. Does not affect the processes of renewal of the skin, does not cause their atrophy. It helps well with itching, inflammation - exudation, hyperemia, thickening of the skin. Can be used on surfaces of any area, pregnant women and children from 3 months of age. The cream is carefully treated with diseased skin two or more times a day.
It can cause overdrying of the skin, after taking water procedures, a moisturizer is applied before treatment. Contraindicated in case of sensitization to the components, in case of infection of the skin, with the possibility of malignant degeneration.
With non-infectious genesis of dyshidrotic eczema, Advantan ointment with the active ingredient methylprednisolone is also used. The ointment inhibits accelerated cell division, reduces the manifestations of inflammation - redness, rash, swelling, itching. Available for dry, normal and oily skin. Contraindicated in case of sensitization to the active substance, infection with viruses, tuberculosis and syphilitic skin lesions.
Treatment of areas with rashes is carried out once a day, the duration is not more than four months, for children - no more than one.
Side effects are local in nature - from rashes to atrophy of the skin surface, folliculitis, hyperhairy.
Elokom ointment with the active ingredient mometasone furoate, which is active against pro-inflammatory mediators, promotes the binding of histamine and serotonin, strengthens the walls of blood vessels, removes edema, dries and reduces exudation. It can penetrate into the general circulatory system, causing side effects common to all glucocorticosteroids. Usually, a daily one-time treatment of the affected skin areas is recommended. Hormonal ointments are not recommended for pregnant and lactating women.
It can penetrate into the general circulatory system, causing side effects common to all glucocorticosteroids. Usually, a daily one-time treatment of the affected skin areas is recommended. Hormonal ointments are not recommended for pregnant and lactating women.
In case of Lana's disease, which does not cause discomfort (itching, exudation), treatment can not be prescribed. In some cases, glucocorticosteroids are used, orally and topically, to dilate blood vessels, improve additional blood circulation and reduce pressure in the arterial bed. This reduces the redness of the palms and the pressure on the blood vessels.
With an infectious, viral or parasitic etiology of red rashes on the palms and feet, a specific treatment is prescribed to eliminate the causative agent of the disease. The doctor prescribes the treatment regimen and drugs.
For example, with lichen and other fungal infections, Fukortsin solution, Lamisil spray and cream, Lamicon spray and cream are prescribed.
Lamisil (Lamicon) spray and cream have the active ingredient terbinafine. Its action is to interrupt the production process of the main component of the fungal cell membrane - ergosterol. The fungicidal action of the preparations consists in the inactivation of the enzyme squalene epoxidase, the catalyst of the third, penultimate stage of the biosynthesis of ergosterol. Its deficiency with the simultaneous concentration of squalene in the membrane kills fungal cells.
Squalene epoxidase of human skin cells is not susceptible to terbinafine, which explains the selective effect only on fungal cells.
These drugs have a fungicidal effect on the pathogens of epidermophytosis, trichophytosis, microsporia, pityriasis versicolor, candidiasis, as well as on dermatophytes, aspergillus, cladosporium, scopulariopsis, fungicidal or fungistatic - on yeast fungi of various species.
Manifestations of systemic action of the drug are insignificant.
Studies have not revealed adverse effects of terbinafine on intrauterine development of the fetus, however, during pregnancy it is prescribed only under strict indications. Terbinafine is found in breast milk, therefore it is better to refrain from its use during breastfeeding.
Terbinafine is found in breast milk, therefore it is better to refrain from its use during breastfeeding.
Contraindications for use - allergy to the ingredients of the drug; breastfeeding period; age up to 3 years.
Use with caution in cases of: impaired liver and / or kidney function; alcoholism; neoplasms; violations of metabolic processes, hematopoietic processes, patency of the vessels of the extremities.
Recommended duration of use: in case of ringworm and epidermophytosis, the lesion is irrigated once a day for one week; with pityriasis versicolor - twice a day for one week.
For the treatment of fungal infections, especially those located in places covered by shoes, the form of release of the drug is very important. The fatty components of ointments and creams, which are mainly prescribed for topical use, can cause a greenhouse effect in the infection zone, exacerbation of the inflammatory process and its further spread. In order to prevent such a development of the disease, antimycotics in the form of a spray are used to treat the lesion site. With the defeat of the palms, you can use both ointments and sprays.
With the defeat of the palms, you can use both ointments and sprays.
With herpetic lesions of the skin of the palms, Acyclovir cream is used. It has an antiviral effect, blocking the process of viral DNA synthesis, as well as immunomodulatory. This cream is intended for the treatment of rashes caused by the herpes virus. Herpes is treated by smearing the rashes five times a day with an interval of one hour. Repeat this procedure for five to ten days. The tolerability of this remedy is not bad, although local side effects may also occur.
For scabies, antiparasitic ointments, such as benzyl benzoate, are usually prescribed. The treatment regimen is prescribed by the doctor.
For bacterial skin lesions, ointments with antibiotics that are active against the identified microorganisms are used.
If rashes of any etiology are accompanied by severe itching that interferes with the patient's nightly sleep, the doctor may prescribe sedatives or antihistamines with sedative components.
Vitamins A and E are prescribed to reduce the permeability of the vascular membranes, accelerate the processes of restoration and renewal of the skin surface, stabilize the hormonal background and systemic effects on the body.
As part of complex therapy, physiotherapy is prescribed. This can be acupuncture, laser therapy, high frequency currents or magnetic waves, cryotherapy, electrosleep, ultraviolet radiation, paraffin therapy.
Alternative treatment for red spots on palms
Alternative treatment of red spots on the palms can be used rather in the complex of therapeutic measures, it does not exclude a visit to the doctor, diagnosis. How self-treatment can help only in cases of non-infectious skin lesions of a mild degree.
Spots of allergic origin at the very beginning of their appearance can be cooled with water or a cold compress to relieve itching and swelling;
Before going to bed, it is recommended to immerse the hands daily for 15-20 minutes in warm water, combined in a bath with a decoction of medicinal herbs: succession, chamomile, celandine, sage, oak bark in equal proportions. This procedure soothes inflamed skin, disinfects and eliminates itching.
This procedure soothes inflamed skin, disinfects and eliminates itching.
You can make ointments:
- Mix 5 milliliters of whole cow's milk (homemade) with the same amount of purified pharmacy glycerin, add rice starch until a homogeneous slurry is obtained - treat rashes with this ointment at night and wash off in the morning;
- Mix a quarter cup of fresh cranberry juice with 200 g of Vaseline, treat rashes to eliminate itching and irritation;
- Crush 25 fresh leaves of St. John's wort in a wooden mortar, place in a glass jar, pour a quarter liter of homemade sunflower seed oil into it, cover with a lid and infuse for at least 15 and no more than 20 days, shaking occasionally. Then the composition is filtered, stored in a cool place in a dark glass container, well corked. Treat affected skin. Sun exposure to the affected and treated areas is undesirable.
For dyshidrotic eczema, the following recipes are recommended:
- wipe rashes with horseradish tincture: four teaspoons of which are steamed with 0.
 5 l of boiling water and infused for two hours, cooled and used, or blackberry leaves tincture, which are crushed (100g), steamed with two liters of boiling water and infused;
5 l of boiling water and infused for two hours, cooled and used, or blackberry leaves tincture, which are crushed (100g), steamed with two liters of boiling water and infused; - lubricate palms and feet with sea buckthorn oil 3-4 times a day;
- lotions with tincture of eucalyptus: steam four tablespoons of crushed dry eucalyptus leaf? liters of boiling water, simmer for half an hour over low heat, stirring, cool and strain.
Ointment from the branches of black currant. Two currant sprigs are carefully crushed and ground into powder, add 200 g of butter there. Heat in a water bath, stirring for at least five minutes. The cooled ointment is ready for use.
In case of Lana's disease, vasodilating applications can be made with herbal balm prepared according to the following recipe: make an herbal collection from the same amount of dry chopped herbs: sage, St. John's wort, succession, plantain, chamomile. Brew a tablespoon of herbal mix with a glass of boiling water and insist for a long time to make a gruel. Heat this slurry to
Heat this slurry to
Dry spots on the skin: three common dermatological diseases
July 5, 2020
Dry spots on the skin are a common dermatological symptom that can indicate both a temporary failure and a violation of the barrier functions of the epidermis, and a skin disease. It all depends on the size of the spots, the clarity of their boundaries, as well as the duration of their presence on the skin.
The causes of dryness can be divided into two large groups:
- non-specific - allergic reactions to household chemicals, laundry soap, cosmetic products, dehydration due to cold and wind;
- specific - then the spots become a manifestation of dermatological diseases.
Sometimes a person may notice that dry spots appear on his skin after a certain event occurs, for example, after washing clothes with his hands. Then the reason is obvious and easy to eliminate. But if dry spots on the skin do not go away, itch, peel off, you should consult a doctor.
Dry spots with scales
Pink raised dry spots on the body and head may indicate psoriasis. With this dermatological pathology in humans, raised plaques appear on the skin - psoriatic papules. They protrude above the surface of the skin, cause intense itching and flake, tend to spread and merge.
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease in which rashes are most often localized on the elbows, head, knees and groin. Dry pink spots covered with white scales are foci of chronic inflammation. Under the influence of internal autoimmune processes, epidermal cells divide several times faster than necessary. As a result, small scales are constantly separated from dying skin cells.
Atopic dermatitis and its differences from psoriasis
Atopic dermatitis can also cause dry patches on the body. And as with psoriasis, they cause itching. Due to the increased sensitivity of the skin to environmental factors, the mechanisms of its self-regulation are violated, including the barrier function.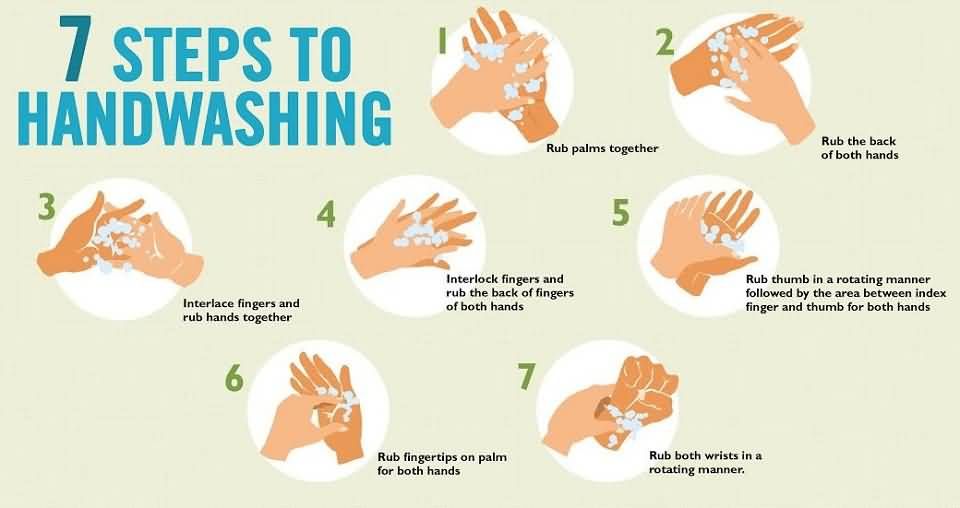 That is, an allergy is a trigger for atopic dermatitis, but the tendency to such a skin reaction is genetically laid down.
That is, an allergy is a trigger for atopic dermatitis, but the tendency to such a skin reaction is genetically laid down.
Most often, atopic dermatitis occurs in children. The disease has a chronic course, when exacerbations are replaced by periods of remission. Here are the typical signs of atopic dermatitis:
- dry skin;
- peeling and redness of the eyelids;
- dry flesh-colored plaques on the trunk and extensor areas of the body;
- cracks.
It is difficult for a person who does not have a medical education to distinguish psoriasis from atopic dermatitis, but a doctor can easily make a differential diagnosis. There are several differences that may speak in favor of a particular pathology. Atopic dermatitis often affects children, psoriasis can debut in adulthood. Psoriatic plaques are raised above the skin, and scales can be seen. Dry spots in atopic dermatitis are flat. It is also important to consider typical localization.
Useful links: State Center of Urology in Moscow - Clinic of Urology named after R. M. Fronshtein of the First Moscow State Medical University named after I.M. Sechenov
Dry eczema
Sometimes white, dry, scaly patches on the skin of the legs can indicate dry eczema. With this disease, dryness and tightness of the skin first occurs, then peeling and unbearable itching join, cracks may occur. In addition to the legs, the hands, the space between the fingers, and even the face are often affected.
Dry eczema can be caused by bacterial and fungal infections, allergens, synthetic clothing, poor hygiene, and other factors.
As you can see, the appearance of dry spots on the skin can be due to a variety of reasons. An important role is played by the features of the immune system and the tendency to allergic reactions. But in any case, when dry spots appear, it is important to contact a dermatologist and establish the cause of this skin condition.