Does early pregnancy feel like a uti
12 early signs that you might be pregnant
We include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Here’s our process.
Medical News Today only shows you brands and products that we stand behind.
Our team thoroughly researches and evaluates the recommendations we make on our site. To establish that the product manufacturers addressed safety and efficacy standards, we:
- Evaluate ingredients and composition: Do they have the potential to cause harm?
- Fact-check all health claims: Do they align with the current body of scientific evidence?
- Assess the brand: Does it operate with integrity and adhere to industry best practices?
We do the research so you can find trusted products for your health and wellness.
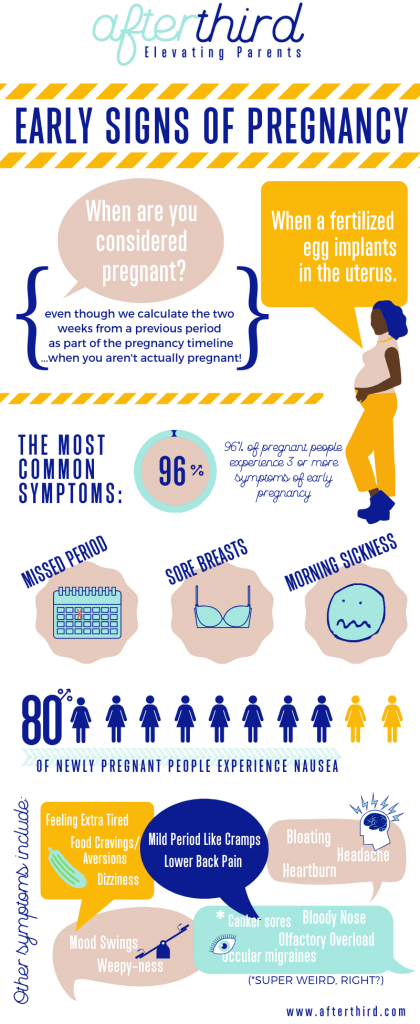
Read more about our vetting process.A missed period may be the first noticeable sign of pregnancy, but there are many other early signs.
Early pregnancy and premenstrual symptoms are often similar, and it can be hard for a person to tell whether they might be pregnant or about to get their period. Also, some pregnant people do not experience the typical early signs.
The article explores 12 changes that can point to pregnancy in the early stages.
Missing one or more periods is often the clearest early sign of pregnancy. We explore these and other signs below.
1. A missed period
This is often the first sign that a person notices, but missing a period does not always point to pregnancy.
A person might miss a period for many reasons, such as changes to birth control medication or sudden weight loss. A missed period can also indicate a health issue, such as polycystic ovary syndrome.
For this reason, anyone who unexpectedly misses a period should contact a healthcare professional as soon as they can.
2. Nausea
Nausea during pregnancy, or morning sickness, is common.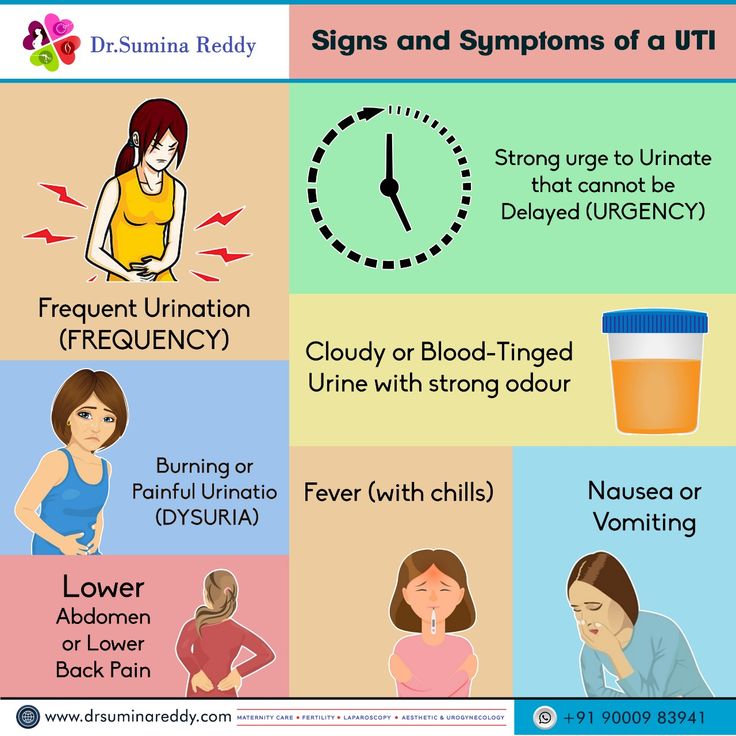 It can begin as early as 4 weeks into the pregnancy.
It can begin as early as 4 weeks into the pregnancy.
For some people, it eases early on, and others experience it throughout their pregnancy. Most pregnant people experiencing some degree of nausea.
A note about sex and gender
Sex and gender exist on spectrums. This article will use the terms “male,” “female,” or both to refer to sex assigned at birth. Click here to learn more.
3. Breast changes
These may occur within 2 weeks of conception.
The amount of breast tissue increases in preparation for milk production. The veins of the breasts become more noticeable, and the nipples may darken.
The breasts and nipples may feel tingly, sore, and extra sensitive.
4. Frequent urination
This often begins early in pregnancy, and it results from various changes, including:
- the uterus expanding
- hormonal changes
- an increase in blood volume
- an increase in blood circulation to the pelvis
- an increase in kidney size
Later in the pregnancy, the pressure of the growing fetus and uterus on the bladder may result in even more frequent and urgent urination.
Learn more about pregnancy trimesters here.
Contact a healthcare professional if urination becomes painful, as this can stem from a urinary tract infection.
5. Fatigue
Fatigue is one of the most common early pregnancy symptoms. It may be most intense in the first 12 weeks.
During pregnancy, the body produces more of the hormone progesterone. This is essential for a healthy pregnancy, but it may also contribute to fatigue.
In addition, the body needs to pump more blood to the fetus as it grows. This, coupled with the increased physical demands in the later stages of pregnancy can lead to more fatigue.
6. Cramping
Mild cramping without bleeding is common in the first trimester, and it may feel like menstrual cramps. It results from the uterus expanding.
Abdominal bloating, constipation, and heartburn also tend to develop early in a pregnancy, and they may last throughout.
7. Nasal congestion
Hormonal changes during pregnancy can cause a stuffy nose. While this can occur early in pregnancy, it is more common in the third trimester.
While this can occur early in pregnancy, it is more common in the third trimester.
8. Food cravings and aversions
These are common throughout pregnancy, and they may result from hormonal and physical changes, rather than shifting nutritional requirements.
The underlying cause of food cravings and aversions is still unclear. Different people seek out and avoid different foods.
Regardless, it is important to take in the right amounts of nutrients and calories.
Learn more about the diet during pregnancy here.
9. Mood changes
Sudden shifts in mood can stem from hormonal changes, fatigue, and stress in early pregnancy. It is normal to feel increased emotional sensitivity and abrupt fluctuations in mood during pregnancy.
Pregnancy can also cause relapses of existing mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety.
10. Lightheadedness
This can result from a range of factors, including:
- changes in hormones
- changes in blood pressure and volume
- altered balance due to weight changes
- iron deficiency anemia and other health issues
A person may be more lightheaded when they change positions, such as standing up, quickly.
While some lightheadedness may be expected, a person should contact a healthcare professional if it persists after they sit or lie back down.
11. Headaches
These are common in early pregnancy and can result from changes in hormones.
Typically, headaches cause no harm to the fetus. However, headaches can be a symptom of preeclampsia, which can lead to serious complications without treatment.
Anyone who experiences strong headaches, especially with changes in vision, should contact their doctor.
Learn more about preeclampsia here.
12. Bleeding
Bleeding may be common during early pregnancy. While it may be harmless, a doctor should investigate the cause.
Implantation bleeding occurs when the embryo attaches to the wall of the uterus. This can cause light bleeding or spotting. It may happen around the time when the person would have expected a period.
Early pregnancy symptoms are general — they can also stem from health problems. For this reason, it is important for a healthcare professional to confirm the cause as soon as possible.
For this reason, it is important for a healthcare professional to confirm the cause as soon as possible.
Blood and urine tests
Pregnancy tests check for the presence of the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). A person might take an over-the-counter test at home, or they might visit a clinic and provide a urine or blood sample for testing.
The body produces hCG after implantation. Some rare conditions and diseases can also raise levels of this hormone.
It is a good idea for anyone who has received a positive test result to have this confirmed by a healthcare professional.
Various pregnancy tests are available for purchase online.
Ultrasound
An ultrasound scan produces an image of the fetus using sound waves.
Doctors typically use these scans to check the progress of a known pregnancy, but they can also confirm whether a person is pregnant and help detect multiple pregnancies.
If a person has any pregnancy symptoms, they should contact a healthcare professional.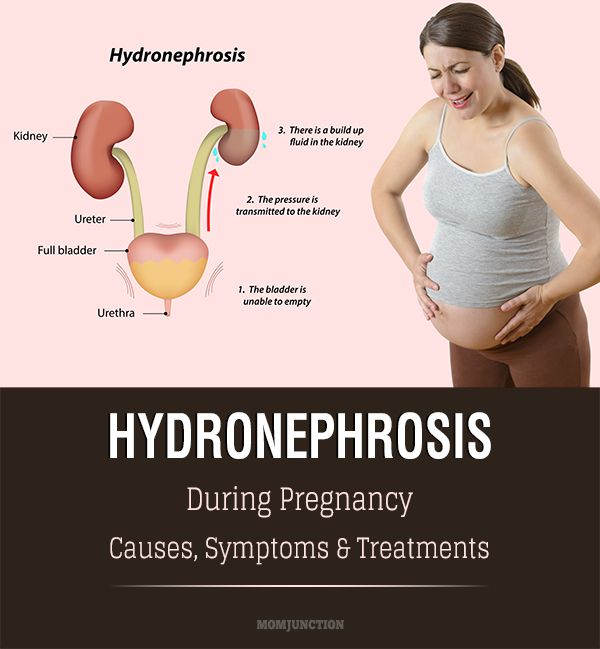 Once the pregnancy is confirmed, having consistent prenatal care improves outcomes for the pregnant person and the fetus.
Once the pregnancy is confirmed, having consistent prenatal care improves outcomes for the pregnant person and the fetus.
Among the many early signs of pregnancy are missed periods, breast changes, fatigue, sudden shifts in mood, and frequent urination.
If a person has any pregnancy symptoms, they might take an at-home pregnancy test or visit a healthcare professional. Anyone who receives a positive result at home should have it confirmed by a doctor, who will then draw up a plan for prenatal care.
UTIs During Pregnancy: Symptoms, Treatment, Common Questions
Urinary tract infections (UTIs), also known as bladder infections, are the most common type of bacterial infection diagnosed today, according to research published in the American Journal of Medicine. Roughly 31 percent of pregnant women will have either a symptomatic or an asymptomatic (without symptoms) UTI during pregnancy, research suggests. UTIs occur when bacteria enters into the usually sterile urinary tract and multiplies, causing painful urination and other symptoms. Certain factors during pregnancy make this occurrence more likely to happen. Here’s what you need to know to keep you and your baby healthy.
Certain factors during pregnancy make this occurrence more likely to happen. Here’s what you need to know to keep you and your baby healthy.
RELATED: 8 Home Remedies for Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) Symptoms
Why Are UTIs Common in Pregnant Women?When you’re pregnant, the anatomy of your urinary tract actually changes. For instance, your kidneys become larger and your growing uterus can compress your ureters and bladder. Because of this compression, fully emptying your bladder during pregnancy becomes more difficult. In addition, your progesterone and estrogen levels increase during pregnancy, which can weaken your bladder and ureters. Pregnancy also alters the makeup of your urine, reducing the acidity and increasing the amount of protein, hormones, and sugar in your urine. That excess sugar, for one, can encourage bacterial growth. All of the above contribute to a heightened chance of developing a UTI in pregnancy. And that is why it’s recommended that all pregnant women receive a urinalysis and urine culture at 12 to 16 weeks or during the first prenatal visit.
And that is why it’s recommended that all pregnant women receive a urinalysis and urine culture at 12 to 16 weeks or during the first prenatal visit.
RELATED: 7 Things an Anesthesiologist Wants You to Know About Pain
UTIs by Pregnancy TrimesterYour risk of UTI goes up beginning at week 6 of your pregnancy; the chances you’ll have a UTI vary by trimester.
First TrimesterAbout 41 percent of UTIs are diagnosed during the first trimester. Because getting a UTI during the first trimester is so common, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that your healthcare provider obtain a urinalysis and urine culture at your first prenatal visit. That recommendation holds whether you present with UTI symptoms or not.
Second TrimesterAccording to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, about half as many pregnant women are diagnosed with a UTI during their second trimester compared with the first trimester.
Compared with the second trimester, the number of women who experience a UTI during the third trimester is almost halved. However, 80 to 90 percent of acute kidney infections in pregnancy (many caused by the progression of an untreated UTI) occur in the second and third trimesters, according to research published in the Archives of Medical Science. Thus, it’s recommended to do a repeat urine culture during the third trimester, too.
Common UTI Symptoms in Pregnant Women“While mildly painful urination during pregnancy can often mean a yeast infection, not a UTI, it’s always best to see your healthcare provider if you experience any symptoms,” says Heather Bartos, MD, an ob-gyn in Cross Roads, Texas. After all, research suggests that about 18 percent of UTIs that occur during pregnancy are symptomatic UTIs, meaning the telltale UTI signs and symptoms are present:
- Strong and frequent urge to use the bathroom
- Burning while urinating
- Regularly passing only small amounts of urine
- Cloudy, red, pink or cola-colored urine
- Foul-smelling urine
- Pelvic pain, usually in the center of the pelvis
In pregnancy, women are also more susceptible to asymptomatic UTIs, meaning you have significant bacteria in your urine but your urinary tract is free of signs and symptoms. Experiencing no symptoms, however, does not mean that asymptomatic UTIs are benign. “An asymptomatic UTI can lead to a symptomatic UTI or even a kidney infection,” says Dr. Bartos. In fact, research shows that if asymptomatic UTIs are left untreated, 30 percent of pregnant women will go on to develop a symptomatic UTI, and half of those women will eventually be diagnosed with acute pyelonephritis (a kidney infection). Up to 23 percent will have a kidney infection recurrence during the same pregnancy. It’s important to note that classic UTI signs, like frequent and painful urination, may or may not occur with a kidney infection. Here, some signs to look out for:
Experiencing no symptoms, however, does not mean that asymptomatic UTIs are benign. “An asymptomatic UTI can lead to a symptomatic UTI or even a kidney infection,” says Dr. Bartos. In fact, research shows that if asymptomatic UTIs are left untreated, 30 percent of pregnant women will go on to develop a symptomatic UTI, and half of those women will eventually be diagnosed with acute pyelonephritis (a kidney infection). Up to 23 percent will have a kidney infection recurrence during the same pregnancy. It’s important to note that classic UTI signs, like frequent and painful urination, may or may not occur with a kidney infection. Here, some signs to look out for:
- High-grade fever
- Chills and rigors (sudden feeling of cold with shivering)
- Headache
- Nausea or vomiting
- Lower back pain
- Flank pain (often right side)
- Possible reduced urine output
“UTIs can rapidly progress to a kidney infection in pregnancy, which can be much more dangerous than a kidney infection in nonpregnant women,” says Bartos.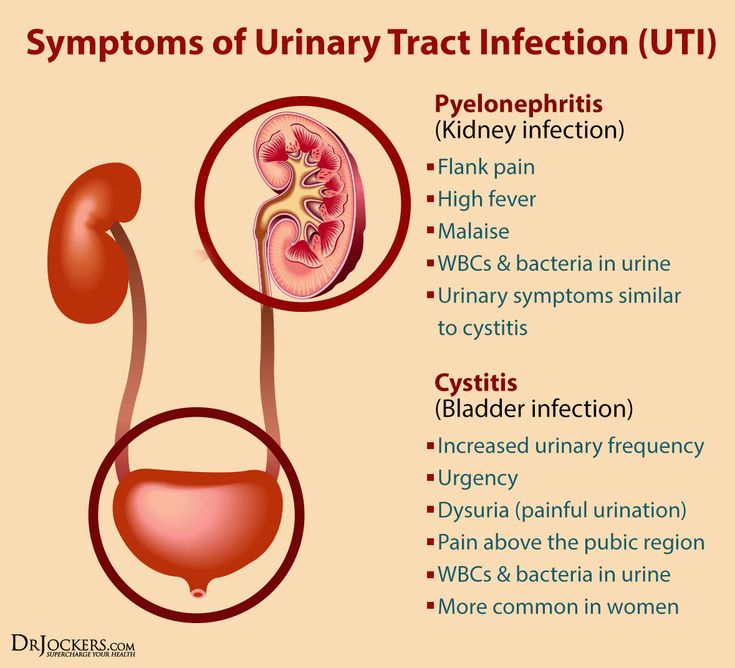 “Severe infections can lead to respiratory problems and sepsis, which can then lead to preterm labor or even the need to urgently deliver the baby.” Beyond a kidney infection, simply having a UTI during pregnancy appears to possibly be a contributing factor to low birth weight. Women who have a UTI in pregnancy also have a 1.31-fold higher risk of developing preeclampsia, a pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure, according to a meta-analysis published in September 2018 in the journal Medicine. It’s thought that a UTI may alter a pregnant woman’s inflammatory response, which can spur preeclampsia.
“Severe infections can lead to respiratory problems and sepsis, which can then lead to preterm labor or even the need to urgently deliver the baby.” Beyond a kidney infection, simply having a UTI during pregnancy appears to possibly be a contributing factor to low birth weight. Women who have a UTI in pregnancy also have a 1.31-fold higher risk of developing preeclampsia, a pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure, according to a meta-analysis published in September 2018 in the journal Medicine. It’s thought that a UTI may alter a pregnant woman’s inflammatory response, which can spur preeclampsia.
RELATED: National Period Day Is October 19
Can Having a UTI While Pregnant Hurt the Baby?Possibly. “A UTI itself doesn’t hurt the baby directly,” says Bartos. “It’s the failure to treat a UTI that can cause things like preterm birth or, rarely, infection of the amniotic sac. ” For example, research published in American Family Physician shows that treating pregnant women who have asymptomatic UTIs decreases the incidence of preterm birth and low-birth-weight infants. That’s why screening and prompt treatment are important.
” For example, research published in American Family Physician shows that treating pregnant women who have asymptomatic UTIs decreases the incidence of preterm birth and low-birth-weight infants. That’s why screening and prompt treatment are important.
Urinary tract infections are not associated with preterm labor, according to research published in the Journal of the Chinese Medical Association. However, if a urinary tract infection is left untreated, it can progress to a kidney infection. And a kidney infection (pyelonephritis) during pregnancy can modestly increase your chances of early contractions and delivery. Research published in the American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology notes that women diagnosed with acute pyelonephritis in pregnancy have a 10.3 percent chance of preterm delivery compared with the 7.9 percent chance among women without a kidney infection during pregnancy.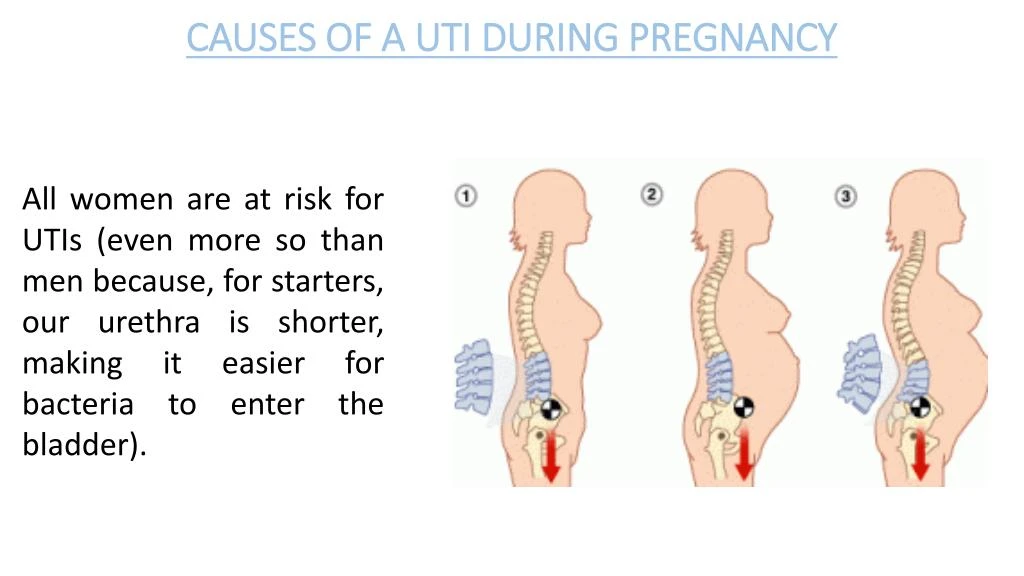
RELATED: Common Types of Vaginal Infections
Do UTIs Differ by Trimester?At week 6, UTI risk starts to go up, with two-fifths of UTIs occurring during the first trimester. Because of the likelihood of getting a UTI during the first trimester, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that pregnant women have a urinalysis and urine culture at their first prenatal visit — whether they have UTI symptoms or not. In the second trimester, about half as many pregnant women are diagnosed with a UTI as in the first trimester, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and that number is almost halved again for the third trimester. However, 80 to 90 percent of acute kidney infections in pregnancy (many caused by the progression of an untreated UTI) occur in the second and third trimesters, according to data published in the Archives of Medical Science, so pregnant women should have a repeat urine culture during the third trimester.
RELATED: March Is Endometriosis Awareness Month
What Are Pregnancy-Safe UTI Treatment Options?How do you treat a UTI when pregnant? It’s similar to how you treat a UTI when not pregnant — with a few key differences. A short-course of antibiotics is the standard treatment for asymptomatic and symptomatic urinary tract infections that occur during pregnancy. There are, however, two important contrasts in treating UTIs in pregnant women versus nonpregnant women. First, asymptomatic UTIs diagnosed during the first trimester are treated with antibiotics, whereas nonpregnant women’s infections are often not treated in this manner. (Outside of pregnancy, asymptomatic bacteriuria is usually not treated with antibiotics.) Also, the preferred antibiotic drugs used to treat UTI in pregnancy often differ than what would be used while not pregnant. For instance, the following antibiotics have not been associated with any birth defects, thus are likely safe to use at any point during pregnancy:
- Penicillins Amoxicillin, ampicillin, and augmentin are in this group.
- Erythromycin Some of the brand names include Ery-Tab, Akne-Mycin, E.E.S. Eryc, and Pediamycin.
- Cephalosporins Keflex (cephalexin) is a cephalosporin.
UTI history and resistance patterns must be considered before prescribing any of these drugs.
Because certain antibiotics pose a potential risk for birth defects (anencephaly, heart defects, and cleft palate) when taken during the first trimester, they are only considered a first-line treatment for UTIs occurring during the second and third trimesters, according to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Prescribing the antibiotics listed below during the first trimester is considered appropriate only when no other suitable alternative treatments are available:
- Nitrofurantoin Macrobid, Furadantin, and Macrodantin are in this category.
- Sulfonamides Bactrim (trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole) is part of this class.

Be sure to double-check what your healthcare provider is prescribing, since despite the warnings, nitrofurantoin remains the most frequently prescribed antibiotic during the first trimester.
Diagnosing UTI: Tests and Screenings, Early Diagnosis, and Your Doctors
By Holly PevznerSigns and Symptoms of Urinary Tract Infections
Symptoms of a UTI may include a constant urge to urinate, frequent urination, or discomfort while urinating.
By Holly Pevzner
How to Prevent Urinary Tract Infections, or UTIs
Urinary tract infections, or UTIs, are the most common type of bacterial infection diagnosed today, with more than half of all women experiencing at least...
By Holly Pevzner
What Is a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)? Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention
By Holly PevznerTreatment for Urinary Tract Infections: Antibiotics, Medication, and Home Remedies
By Holly PevznerCauses and Risk Factors of UTIs
Urinary tract infections occur when harmful bacteria enter the urethra—the tube that carries urine out of the body. Risk factors for UTIs may differ between...
Risk factors for UTIs may differ between...
By Lindsey Konkel
"False pregnancy" in women. What's this?
Home/About clinic/Useful/ "False pregnancy" in women. What's this?
July 25, 2019
False (imaginary) pregnancy has been described by doctors since the time of Hippocarat. In Latin, this phenomenon is called pseudocyesis. In this case, a woman can feel all the signs of pregnancy, but in fact there is no developing fetus in the uterus. Most often, this condition appears in women who are suspicious and susceptible, with a mobile psyche, an overly excitable central nervous system, who have experienced stress or shock. nine0009
False pregnancy sometimes occurs in those women who strongly want to have a child. It may be the other way around - the fear of motherhood becomes the ground for its development. Patients who suffer from infertility for many years and undergo long-term treatment for this often feel falsely pregnant.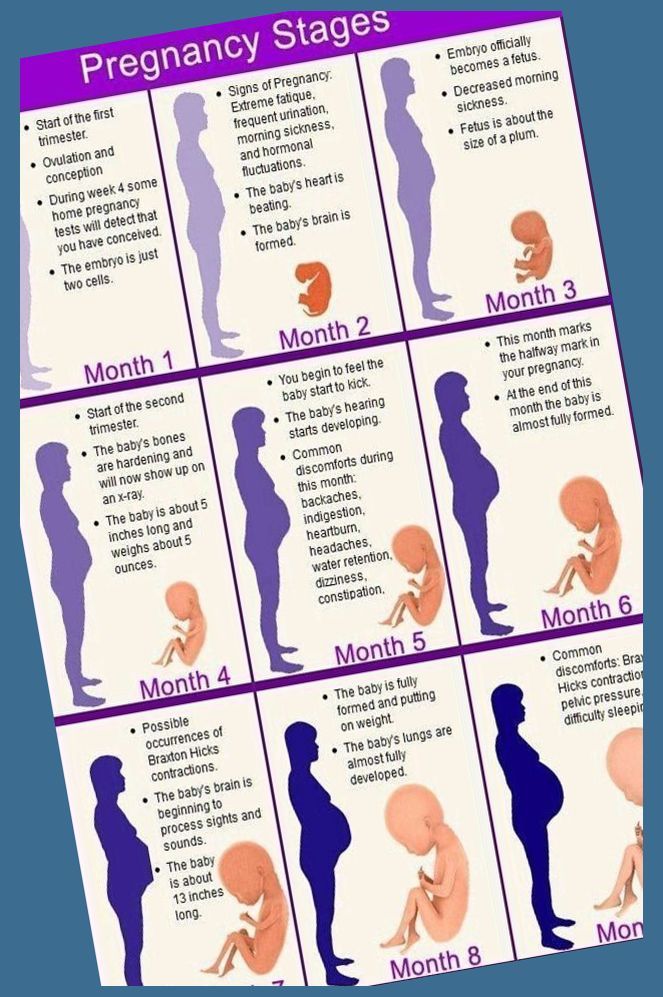 Reaching despair, they begin, through self-hypnosis, to look for symptoms in themselves that indicate pregnancy.
Reaching despair, they begin, through self-hypnosis, to look for symptoms in themselves that indicate pregnancy.
A false pregnancy can be caused by a hormonal imbalance. Regular stress causes the body to produce a lot of pituitary hormones, the increase in which is also observed during real pregnancy. nine0003
Women may lag behind in the development of the mammary glands or uterus ("baby uterus"). Under these conditions, doctors may prescribe a long course of taking hormonal drugs that lead to menstrual irregularities. The absence of menstruation is often taken by a woman as a sign of pregnancy.
False pregnancy manifests itself in the same way as a real one.
Main (doubtful) signs of false pregnancy:
- Morning sickness or vomiting
- Increases the perception of smells, changes in taste sensations and preferences
- Mood swings occur
- In rare cases, a woman even feels the movements of a non-existent fetus
The above signs are considered doubtful because the woman herself talks about them. The situation becomes more convincing if there are likely signs. These include the following:
The situation becomes more convincing if there are likely signs. These include the following:
- Cessation of menses, long delays
- Enlargement and engorgement of the mammary glands, sometimes there is the appearance of characteristic pigmentation in the area of the halo and nipples
- There may be a discharge from the nipples similar to colostrum
- Belly increases in size
The condition of a false pregnancy is so similar to a real pregnancy that the woman is firmly convinced that she is expecting a child. nine0008 Claiming her interesting position, she does not deceive anyone!
The most surprising thing is that a test for the presence of hCG in the urine can also show a positive result. This fact will further convince the woman of a real pregnancy. However, hCG can also increase if there is a cyst, a pelvic tumor, or some other pathology.
Women may sometimes see two lines on the test during a false pregnancy.
nine0008 This is possible if they take a course of hormonal fertility drugs that contain hCG. It is also impossible to exclude the situation in which the test is damaged (marriage or improper storage).
Obstetrician-gynecologists of the IVF and reproductive health clinic "Genome-Don" recommend to confirm the presence of pregnancy with the help of transvaginal ultrasound, starting from the 1st week
menses delay.
Share information:
Previous news
Go back
Make an appointment with the specialists of the clinic "Genome"
in Rostov-on-Don:
Phone: +7 (863) 295-35-80
WhatsApp: ask a question, make an appointment
call Navigator Request a call
Volgograd
Kaliningrad
Moscow
Astana
Rostov-on-Don
Tomsk
Ulyanovsk
Cherepovets
Remember my choice
Choose a convenient clinic
Volgograd
Kaliningrad
Moscow
,000
9000
Ulyanovsk
Cherepovets
Remember my choice
How to distinguish PMS from pregnancy symptoms?
The symptoms of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and early pregnancy are quite similar.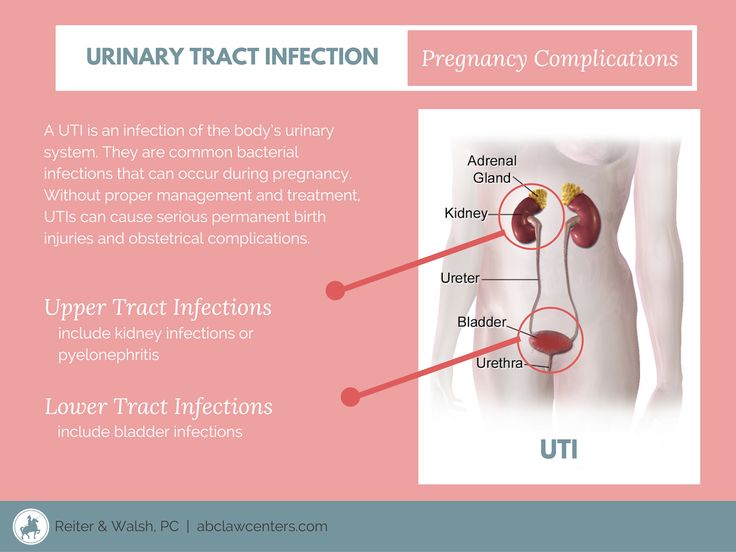 In this regard, a woman may have difficulty in determining her condition. nine0003
In this regard, a woman may have difficulty in determining her condition. nine0003
General symptoms of PMS and pregnancy
- Changes in mood: irritability, anxiety, tearfulness. With PMS, these symptoms disappear after the onset of menstruation. Signs of pregnancy will be the persistence of this condition and the absence of menstruation. It is worth noting that a depressed mood can be a sign of depression. If the symptoms do not disappear within 2 weeks, you should consult a doctor.
- Constipation. Hormonal fluctuations slow down bowel movements, which is a common cause of constipation. In pregnant women, this symptom is noted during the first two trimesters. With PMS, constipation goes away after the onset of menstruation. nine0125
- Changes in the chest. These changes may include:
- pain;
- sensitivity;
- swelling;
- size increase.
In PMS, these symptoms are usually most pronounced just before the period and disappear immediately after it ends.
In the early stages of pregnancy, the breasts become tender and enlarge. Veins may protrude on the surface of the breast and there may be pain around the nipples. nine0003
- Fatigue. This symptom is associated with the action of one of the sex hormones - progesterone. With PMS, the condition returns to normal after the end of menstruation.
Fatigue is also a common symptom of early pregnancy. The duration of this symptom depends on the individual characteristics of the woman's body. In addition, fatigue can be a sign of iron deficiency anemia.
- Bleeding. As you know, menstruation is accompanied by a period of bleeding, which lasts an average of 4-5 days. nine0125
In early pregnancy, light bleeding may also occur, which is usually associated with the period of embryo implantation (10-14 days after fertilization).
- Spasms. This symptom is characteristic of both PMS and pregnancy. However, in the case of pregnancy, cramps occur closer to the stomach.
 They can appear throughout the entire pregnancy. This is due to the process of embryo implantation and expansion of the uterus.
They can appear throughout the entire pregnancy. This is due to the process of embryo implantation and expansion of the uterus.
- Headache and back pain. These symptoms are characteristic of both the PMS period and pregnancy. nine0125
- Appetite changes. Increased appetite is a common pregnancy symptom, but it is also common during PMS.
Cravings for sugary or fatty foods are associated with fluctuations in sex hormones such as estrogen and progesterone.
Symptoms most likely to indicate pregnancy include:
- cessation of the menstrual cycle. This is one of the most obvious symptoms that indicates pregnancy, but there are other reasons for a change in the menstrual cycle:
- stress;
- low body weight;
- polycystic ovarian syndrome;
- thyroid disease or diabetes mellitus;
- menopause;
- Nausea and vomiting are common symptoms in early pregnancy.