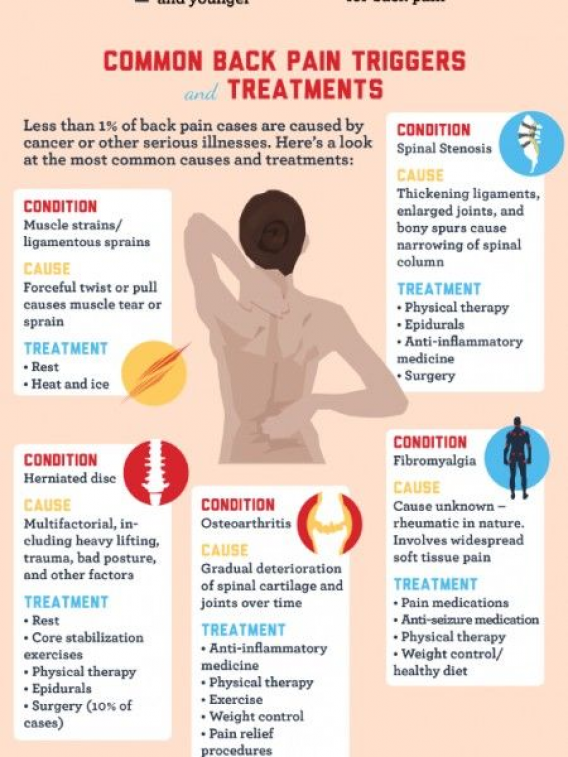
Do epidurals work
What It Is, Procedure, Risks & Side Effects
Overview
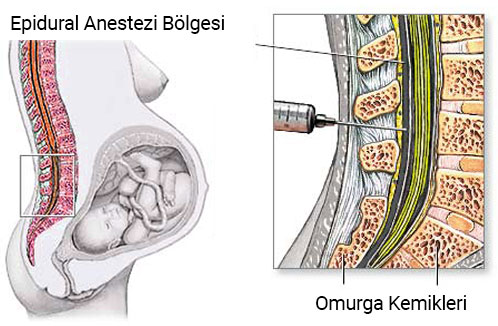
An epidural injects medication into the space around your spinal nerves known as the epidural space.What is an epidural?
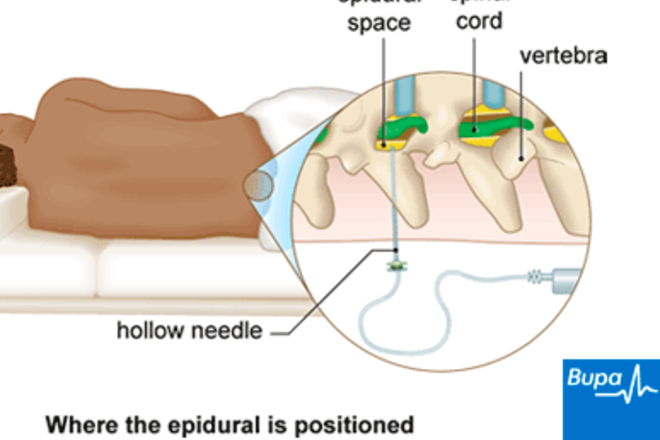
An epidural is a procedure that involves injecting a medication — either an anesthetic or a steroid — into the space around your spinal nerves known as the epidural space. The goal of an epidural procedure is to provide pain relief (analgesia) or a complete lack of feeling (anesthesia) for one region of your body, such as your legs or belly.
An epidural is commonly called the following terms:
- Epidural anesthesia.
- Epidural block.
- Epidural steroid injection (ESI).
- Regional anesthesia.
- Neuraxial anesthesia.
How does an epidural work?
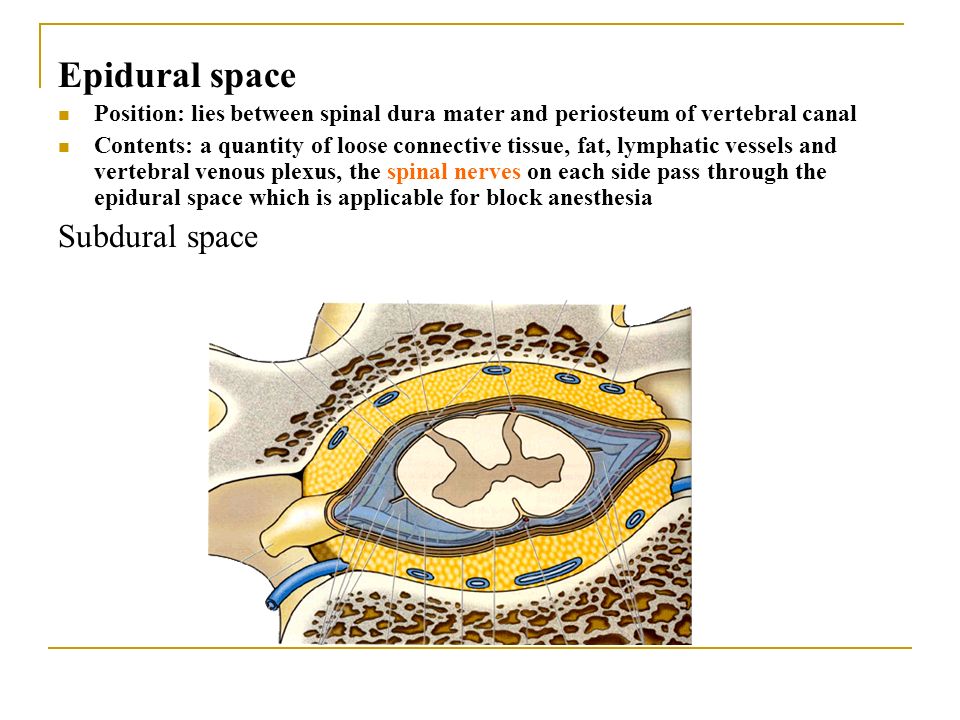
An epidural anesthesia injection works by injecting an anesthetic into the epidural space around your spine so that it can stop pain signals from traveling from your spine to your brain. The epidural space is filled with fluid and surrounds your spinal cord. Think of it as a liquid sleeve around your spinal cord.
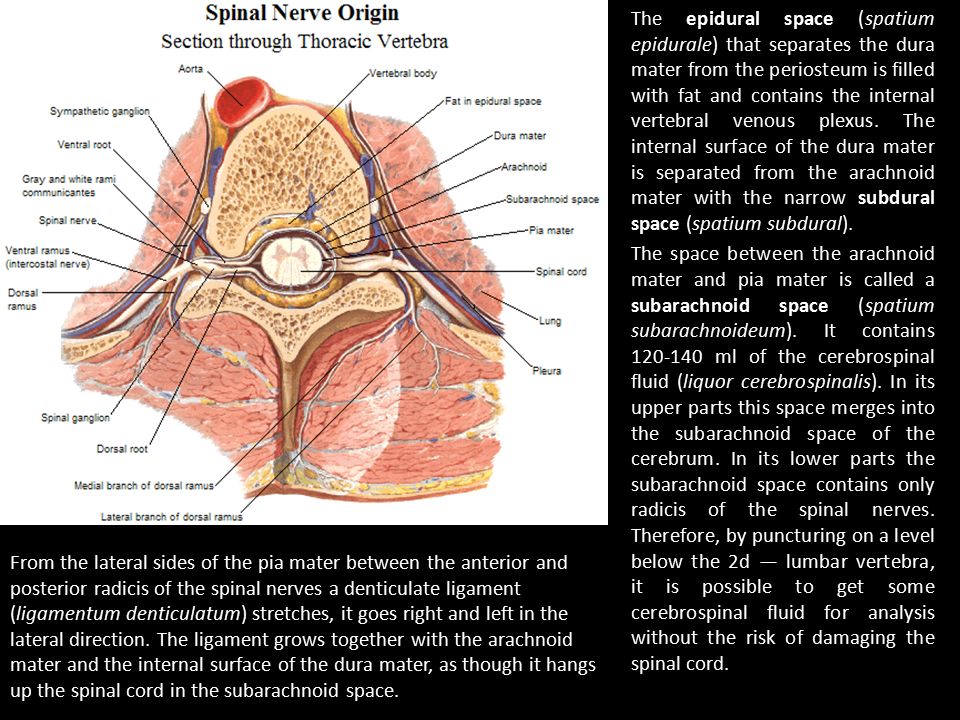
Your spinal cord acts like a highway that connects the nerves located all over your body to your brain. When you get injured, for example, the nerve in that area of your body sends a pain signal that travels through your spinal cord to your brain and back. An epidural anesthetic temporarily numbs the spinal nerves, which then blocks pain signals in a certain region of your body depending on where along your spine your provider injected the epidural.
Epidural anesthesia can provide temporary pain relief or a temporary total lack of feeling. The following factors contribute to how much feeling you temporarily lose from an epidural:
- The type of anesthetic drug your provider uses.
- The concentration of the drug (how strong it is).
- The dosage of the drug.
An epidural steroid injection (ESI) works slightly differently and is used for chronic pain management. Instead of anesthetic medication, your provider injects a steroid or corticosteroid medication into the epidural space around your spine.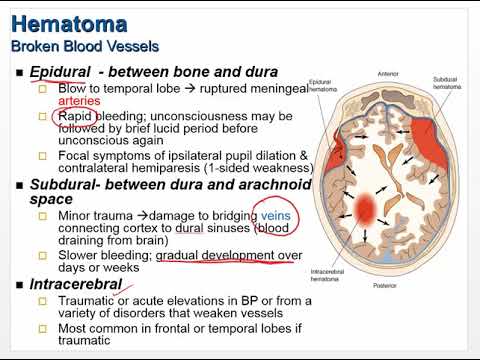 Instead of blocking pain or feeling in a region of your body, the steroid coats the irritated nerve(s) that are causing you pain and works to reduce swelling. The steroid allows the nerve(s) time to heal. Epidural steroid injections can lead to temporary, long-term or permanent pain relief.
Instead of blocking pain or feeling in a region of your body, the steroid coats the irritated nerve(s) that are causing you pain and works to reduce swelling. The steroid allows the nerve(s) time to heal. Epidural steroid injections can lead to temporary, long-term or permanent pain relief.
Who performs an epidural?
An anesthesiologist or certified registered nurse anesthetist usually performs an epidural procedure. Anesthesiologists have special training in the field of anesthesiology, which is a medical specialty that involves the care of people before, during and after their surgery or procedure. Anesthesiology covers anesthesia, pain medicine, intensive care medicine and critical emergency medicine.
Healthcare providers of other specialties, such as neurology, may also perform an epidural. Again, they’re specially trained to properly and safely perform an epidural procedure.
For epidural procedures that use a catheter, a supporting healthcare provider is usually present to help as needed.
What’s the difference between epidural analgesia and epidural anesthesia?
Analgesia is pain relief without losing consciousness (going to sleep) and without complete loss of feeling or movement. Anesthesiologists use epidural analgesia for people who are in labor and are delivering a baby. They inject the epidural into your lower back to provide pain relief for the lower part of your body due to contractions and childbirth.
Anesthesia is the loss of physical sensation with or without loss of consciousness. Epidural anesthesia itself won’t cause a loss of consciousness, but if you’re having a certain kind of surgery, your anesthesiologist may give you epidural anesthesia so you don’t feel any pain or don’t move during the surgery and a different medication to make you go to sleep (lose consciousness).
What are epidurals used for?
Your healthcare provider may recommend an epidural procedure for the following situations:
- To provide pain relief (analgesia) for labor and childbirth.
- To provide anesthesia for certain surgeries as an alternative to general anesthesia.
- To provide pain relief after certain surgeries.
- To manage certain causes of back pain and other forms of chronic pain (through epidural steroid injections).
What are the different kinds of epidurals?
There are different variations of epidurals based on certain factors. This section will explain different kinds of epidurals grouped into the following categories:
- How the medication is delivered.
- Labor and childbirth epidurals.
- Epidural steroid injections (ESI).
Epidural medication delivery options
There are a few ways your healthcare provider can deliver medication with an epidural, including:
- Single-injection epidural: This type of epidural involves one injection of a medication (an anesthetic or a steroid) into the epidural space around your spine. If you get a single injection of an anesthesia epidural, the feeling in your affected area usually returns within a few hours.
 A single injection anesthesia epidural is for short-term pain relief. Most epidural steroid injections are single injections.
A single injection anesthesia epidural is for short-term pain relief. Most epidural steroid injections are single injections. - Epidural with a catheter: Most epidural procedures involve the use of a catheter in your epidural space so that your healthcare provider can give you a continuous flow of anesthetic medication, multiple separate doses or both. A catheter is a small, flexible tube that’s inserted through a narrow opening into a body cavity. In this case, your provider places a catheter that opens into the epidural space in your spinal area. This way, your provider can administer more than just one injection of medication. Providers usually recommend this type of epidural for longer operations, for providing pain relief over several days and for labor and childbirth.
- Epidural with patient-controlled analgesia (PCA): For recovery from certain kinds of surgery, your healthcare provider may allow you to control the amount of pain relief you’re receiving through your epidural catheter.
 This is called patient-controlled analgesia (PCA). Your healthcare provider sets controls on the PCA pump, which are programmed for the pain-relieving drug your provider orders based on your age, weight and the type of surgery you had. The PCA pump is safe to use because you receive medication by pressing a button when you feel pain, but the pump won’t give you the medication if it’s not time to receive another dose yet.
This is called patient-controlled analgesia (PCA). Your healthcare provider sets controls on the PCA pump, which are programmed for the pain-relieving drug your provider orders based on your age, weight and the type of surgery you had. The PCA pump is safe to use because you receive medication by pressing a button when you feel pain, but the pump won’t give you the medication if it’s not time to receive another dose yet.
Labor and delivery epidurals
There are two general kinds of epidurals that you may choose during labor and childbirth. These include:
- Epidural with a catheter: Your provider will administer medicine through a catheter in your lower back that they insert with an epidural injection. The catheter remains in your epidural space so that your provider can give you more medication if needed.
- Combined spinal-epidural (CSE): A CSE is a combination of two injections: a spinal injection (spinal block) and an epidural.
 A CSE provides pain relief much faster than just an epidural. Because it involves a lower dose of medication, you’ll have a bit more feeling in your lower half. This allows you to move around more easily and change positions. This type of epidural is often called a “walking” epidural, but most people aren’t able to fully walk with this kind of epidural.
A CSE provides pain relief much faster than just an epidural. Because it involves a lower dose of medication, you’ll have a bit more feeling in your lower half. This allows you to move around more easily and change positions. This type of epidural is often called a “walking” epidural, but most people aren’t able to fully walk with this kind of epidural.
Epidural steroid injections (ESI)
An epidural steroid injection (ESI) involves an injection of a steroid or corticosteroid into your epidural space. It can help relieve neck, arm, back and leg pain caused by inflamed spinal nerves due to certain conditions or injuries. Pain relief from an ESI may last for several days or even years.
People who have pain in their neck, arm, lower back or leg due to the following conditions may benefit from epidural steroid injections:
- Spinal stenosis.
- Spondylolisthesis.
- Herniated disk (slipped, ruptured or bulging disk).
- Degenerative disk disease.

- Sciatica.
How common are epidurals?
Epidurals are a common procedure. An epidural is the most popular method of pain relief during labor and childbirth. More than 50% of people who give birth at a hospital choose to receive epidural analgesia. Epidural steroid injections (ESI) are one of the most commonly performed pain relief procedures.
Who shouldn’t get an epidural?
Due to certain medical conditions, not everyone can have an epidural. Because of this, it’s important to talk to your healthcare provider about your medical history and any questions you have. If you have any of the following conditions, you may not be able to get an epidural:
- Anesthetic drug allergies.
- Blood clotting issues.
- An infection.
- Poorly managed diabetes (for epidural steroid injections).
If you’re unable to undergo an epidural procedure, your healthcare provider may recommend another type of pain relief or anesthesia for you, or they may have you wait until a better time to have your surgery, if possible.
Procedure Details
How do I prepare for an epidural?
Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions about what you need to do to prepare for your epidural. Be sure to follow their instructions. Your provider may:
- Have you not eat or drink for a certain amount of time before your epidural.
- Adjust certain medications you’re taking, especially blood thinner medications.
- Make sure you have someone with you to drive you home after your epidural.
Questions that may be helpful to ask your healthcare provider before you get an epidural include:
- How often do you perform epidurals?
- What do I need to do to prepare for my epidural?
- What are the risks of getting an epidural?
- What will my epidural feel like?
- How long will my epidural last?
- How long will it take to recover from my epidural?
What happens during the epidural procedure?
This section will explain the general procedure for two kinds of epidurals: epidurals that use a catheter and epidural steroid injections.
Single-injection epidurals are similar in procedure to epidurals that use a catheter except there’s no catheter placement. Your provider will inject one dose of medication when they insert the needle into your epidural space.
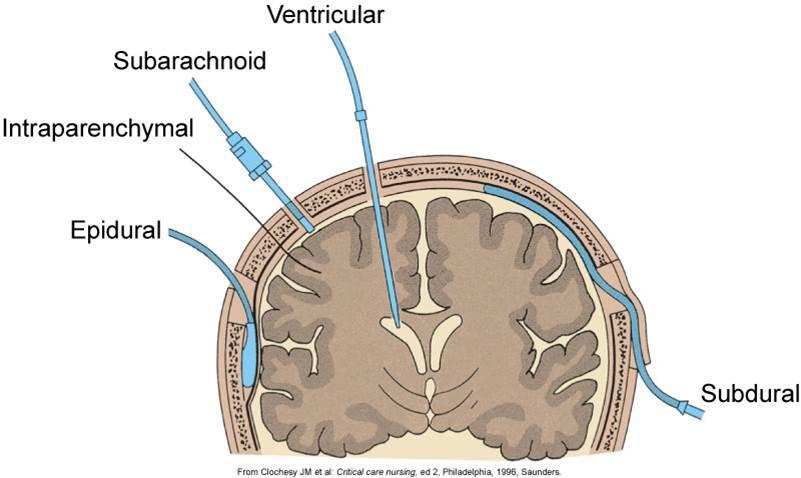
Epidural with a catheter procedure
The steps involved in an epidural procedure that uses a catheter include:
- Before your epidural procedure, a healthcare provider will likely insert a cannula into a vein in your arm so that a medical drip can be attached to it if needed. This is a safety precaution in case your blood pressure drops during the epidural. If this happens, your provider can access the cannula very quickly to give you medication to help stabilize your blood pressure.
- You will likely have to lie on your side or sit up — either way, you’ll need to tuck in your chin to your chest and hunch your back so that your provider can more easily see and access the area where they’ll insert the epidural.
- Your provider will thoroughly clean the area of your back where they’ll insert the epidural to minimize the risk of infection.

- They will then inject local anesthesia with a small needle near the area where they’ll insert the epidural. This is so you won’t feel as much pain when they insert the epidural needle, which is larger than a standard shot needle, such as a vaccine shot needle.
- Your provider will then insert the epidural needle into your back in the epidural space just outside of your spinal cord. If you’re getting an epidural for labor and childbirth, it’ll be in your lower back.
- They’ll then thread a small, soft tube called a catheter through the needle and into your back where the needle went in
- They’ll remove the epidural needle, and the catheter will remain in your back.
- Now your provider can give you anesthetic medicine through the catheter for as long as it’s needed.
- Once you no longer need the epidural, your provider will remove the catheter, clean the area again with an antiseptic and apply a dressing over the site.
Epidural steroid injection procedure
Epidural steroid injections are often used to manage or treat chronic pain.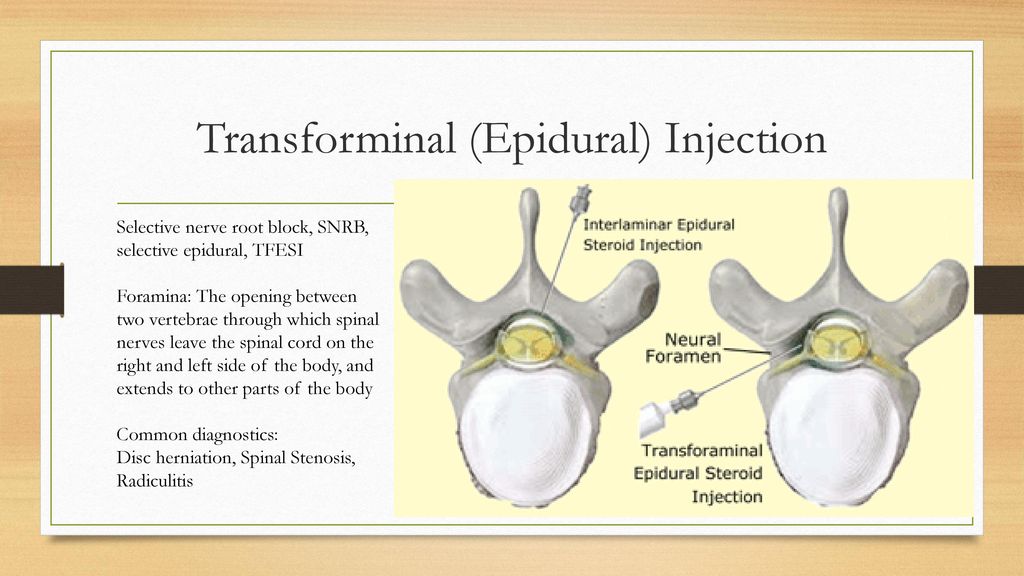 Depending on what’s causing your pain, your healthcare provider will inject the epidural somewhere along your spine. Here are the general steps of an epidural steroid injection procedure:
Depending on what’s causing your pain, your healthcare provider will inject the epidural somewhere along your spine. Here are the general steps of an epidural steroid injection procedure:
- You will lie on a comfortable table on your stomach or side.
- Your healthcare provider will thoroughly clean the area of your back where they’ll insert the epidural to minimize the risk of infection.
- Your provider will inject local anesthesia with a small needle near the area where they’ll insert the epidural. This is so you won’t feel as much pain when they insert the epidural needle, which is larger than a standard shot needle.
- Once the area is numb, your provider will most likely use an imaging machine, such as fluoroscopy equipment or a CT scanner (both are radiology imaging) to help guide the epidural needle to exactly the right position.
- When the epidural needle is in place in the epidural space around your spinal cord, your provider will inject the contrast material.
 The contrast material will make it easier for your provider to see the area they’re targeting on the screen of the imaging machine. This helps to make sure that the medication will reach the inflamed nerves they are targeting.
The contrast material will make it easier for your provider to see the area they’re targeting on the screen of the imaging machine. This helps to make sure that the medication will reach the inflamed nerves they are targeting. - Your provider will then slowly inject the medication, which is usually an anti-inflammatory medication, such as a steroid or corticosteroid. Some providers may inject a mixture of a corticosteroid and a long-acting anesthetic.
- When your provider is done with the injection they’ll clean the area again and apply a dressing to the site. You’ll move into a chair or bed to rest for a few minutes to an hour. This is so your provider can make sure you don’t have any reactions to the medication before you go home.
What will I experience during my epidural procedure?
You’ll likely experience a minor pinch when your provider injects the local anesthetic to numb the area before the epidural procedure.
You may feel pressure, tingling, a burning sensation or momentary shooting pain when your provider injects the epidural. Or you may not feel anything. If you have any discomfort during the injection, it usually disappears once the injection is finished.
Or you may not feel anything. If you have any discomfort during the injection, it usually disappears once the injection is finished.
If you feel intense sharp pain during or after your epidural procedure, tell your provider immediately.
What happens after the epidural procedure?
If you’ve had an epidural with anesthetic medication, it’ll take 20 to 30 minutes for your pain relief and/or loss of feeling to take full effect.
Epidural steroid injections start working within two to seven days, and the pain relief can last several days or longer.
Risks / Benefits
What are the advantages of getting an epidural?
There are different advantages of getting an epidural depending on why you’re getting it.
The advantages of getting epidural analgesia during labor and childbirth include:
- They are usually very effective in minimizing pain felt during labor and delivery.
- They are generally very safe.
- You can often still move around in your bed and push when you need to.
- If you’re experiencing prolonged labor, having an epidural helps you to sleep and recover your strength.
- If you're undergoing a cesarean birth (C-section), you can stay awake during the birth, and your partner can be there as well.
- You can usually get an epidural at any time during your labor.
The advantages of epidural anesthesia injections for surgery include:
- You’ll likely experience less nausea and vomiting than you might with general anesthesia.
- You’ll have a quicker recovery after the surgery than you would with general anesthesia.
- You may have a lower risk of developing a blood clot in one of your leg veins (deep vein thrombosis, or DVT) than you would if you had general anesthesia.
The advantages of epidural steroid injections include:
- You’ll likely experience temporary or long-term pain relief.
- You’ll likely have a better quality of life and an improved ability to do daily activities without the restrictions previously caused by pain.

- Epidural steroid injections may help confirm the origin of your pain. This is often a problem in people who have more than one possible cause of pain.
- Epidural steroid injections may reduce the need for more invasive procedures for pain management.
What are the risks or complications of getting an epidural?
Epidurals are usually safe, but there are risks of certain side effects and complications. Although rare, risks and complications that apply to all types of epidural procedures include:
- Having low blood pressure, which can make you feel lightheaded.
- Experiencing a severe headache caused by spinal fluid leakage. Less than 1% of people experience this side effect.
- Getting an infection from the epidural procedure, such as an epidural abscess, discitis, osteomyelitis or meningitis.
- Having a negative reaction to the medications, such as hot flashes or a rash.
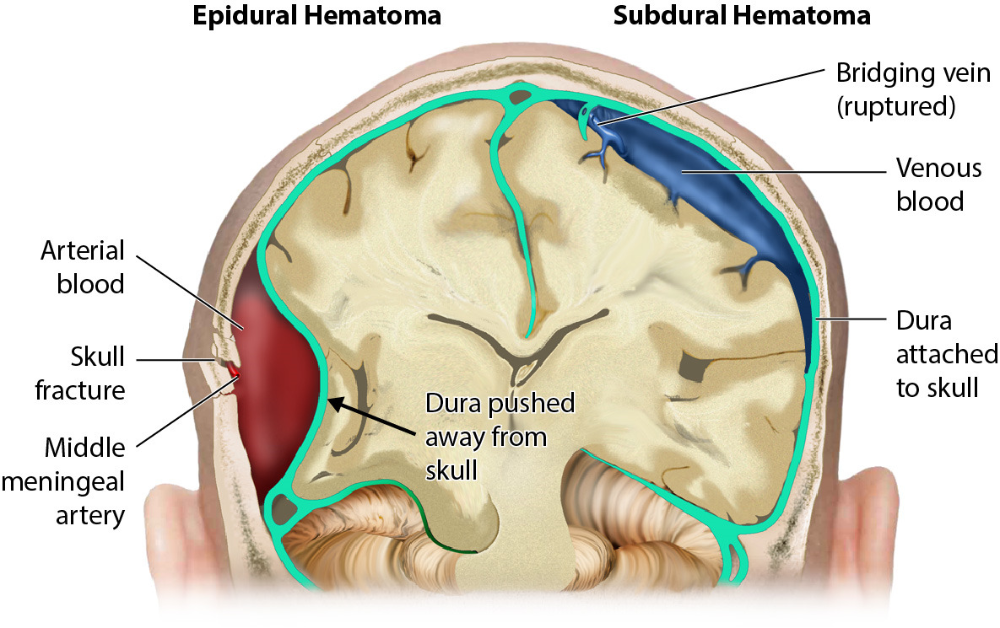
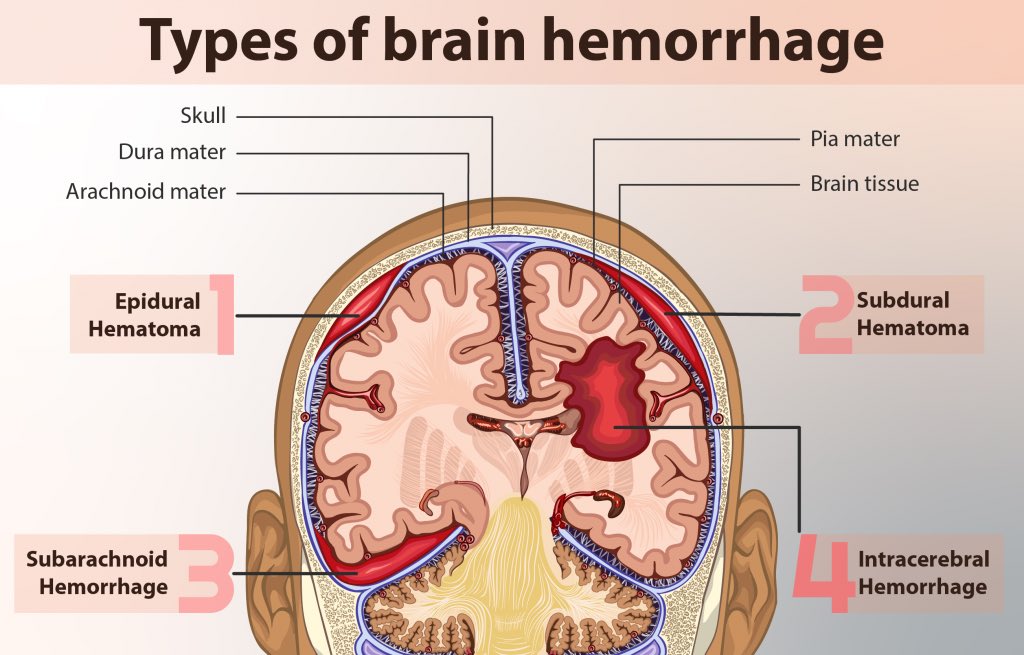
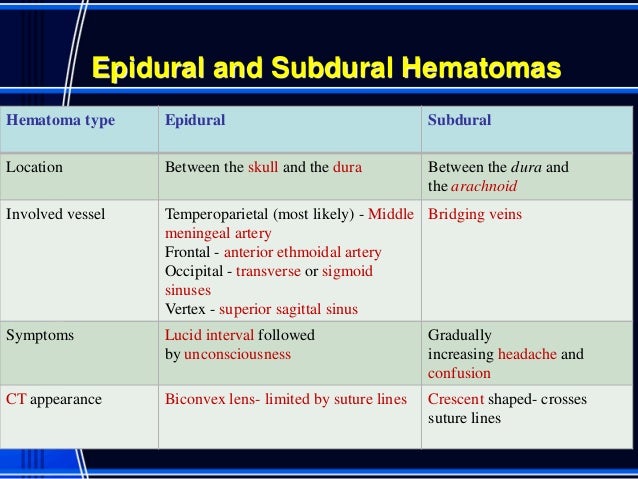
- Experiencing bleeding if a blood vessel is accidentally damaged during the injection, which could cause a hematoma or a blood clot to form.
- Having damage to the nerves at the injection site.
- Temporarily losing control of your bladder and bowels. You might need a catheter (a small tube) in your bladder to help you pee.
Disadvantages and risks that apply to epidural analgesia for labor and delivery specifically include:
- You might lose feeling in your legs for a few hours.
- It might slow down the second stage of labor.
- You might not be able to push and need help to give birth. Your provider may need to use forceps or a vacuum to help deliver your baby.
- Your baby will need to be closely monitored during your labor.
Risks and complications that apply to epidural steroid injections specifically include:
- Experiencing a temporary increase in pain.
- If your provider uses fluoroscopy or a CT scan for imaging guidance, there will be minimal low-level radiation exposure due to the X-rays.
- If you have diabetes, a steroid injection will likely cause high blood sugar (hyperglycemia).
 This could last for several hours or even days.
This could last for several hours or even days.
Can getting an epidural cause back problems?
There’s a common belief that getting an epidural will lead to back pain, but it’s very rare for an epidural to cause long-term or chronic back problems.
It’s normal to experience temporary back pain or tenderness at the site of your epidural. This usually goes away within a few days.
This belief likely stems from the fact that many people who go through childbirth experience back pain after labor and delivery — whether they’ve had an epidural or not. This is because the bones and ligaments in your pelvis are shifting back into their original positions from before your pregnancy, which can cause back pain and discomfort.
Can getting an epidural cause long-term side effects?
While it’s very rare, having an epidural procedure can lead to some long-term complications, including:
- Permanent neurologic deficit due to spinal cord or nerve root damage from the epidural injection.
- Chronic pain due to due to spinal cord or nerve root damage from the epidural injection.
- Permanent paralysis from a hematoma that occurs when there’s a buildup of blood between the dura mater and the spinal cord.
Recovery and Outlook
How long does an epidural last?
How long an epidural lasts depends on what kind of epidural you got and what kind of medicine your healthcare provider injected. Your provider will let you know what to expect. In general, here’s how long certain types of epidurals last:
- Epidural with a catheter: If you have an epidural with a catheter, your provider can give you a continuous flow of anesthetic medicine or multiple separate doses, depending on your situation and pain level. Once your provider has stopped the medication, you’ll likely experience numbness for a few hours before the effect of the medicine begins to wear off. You’ll likely have to rest in a lying or sitting position until you have full feeling in your legs again.
 You may feel a slight tingling sensation while you’re waiting.
You may feel a slight tingling sensation while you’re waiting. - Single-injection epidural: Single injection epidurals usually last a few hours before you begin to regain feeling in the area that was numb.
- Epidural steroid injection: The length of time an epidural steroid injection can provide pain relief varies. Some people experience permanent pain relief if they have a new disk herniation. For people who have chronic pain, epidural steroid injections usually last 3 to 6 months or more.
When can I return to my normal activities after an epidural?
If you’ve had an epidural, do not drive, operate machinery or drink alcohol for at least 24 hours after. Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions about when you can return to your normal activities depending on your type of epidural and your situation. Be sure to follow them.
When to Call the Doctor
When should I see my healthcare provider?
If you experience any of the following symptoms after you’ve returned home from your epidural procedure, be sure to contact your healthcare provider or go to the nearest hospital as soon as possible:
- Experiencing a severe headache while you’re standing up or sitting that feels better after lying down.
 This could be a sign of a dural puncture.
This could be a sign of a dural puncture. - Having a fever, which could be a sign of an infection.
- Having a reduced or complete loss of bladder or bowel control.
- Feeling numbness and/or weakness in your legs, which could be a sign of nerve injury.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between an epidural and a spinal block?
An epidural and a spinal block both provide pain relief through an injection in the area around your spine. The differences are the placement and the effect.
With an epidural, your healthcare provider injects anesthesia into the epidural space around your spinal nerves. With a spinal block, your provider injects the anesthesia into the dural sac around your spinal nerves that contains cerebrospinal fluid. This placement of a spinal block injection means that it gives immediate relief. Epidural injections usually take 20 to 30 minutes before you feel the full effect of pain relief or lack of feeling.
What are the side effects of an epidural after childbirth?
If you get an epidural for labor and childbirth, you may experience the following side effects, which aren’t very common, after delivery:
- Severe headache.
- Temporary difficulty with peeing.
- Temporary difficulty with walking.
- Fever.
You will likely have a small bruise and some tenderness at the site of the epidural after delivery. This should get better in one to two days.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Epidurals are a common, effective and generally safe procedure to deliver quick pain relief and/or a temporary lack of feeling. If you’re feeling anxious about the possibility of receiving an epidural, don’t be afraid to ask your healthcare provider about it and the procedure. They can answer any questions you may have.
Epidurals: Meaning and Side Effects of Anesthesia During Labor
An epidural is the most common type of anesthetic used for pain relief during labor. Here’s what you should know before having an epidural, including information that dispels some common myths.
Here’s what you should know before having an epidural, including information that dispels some common myths.
If you choose to have an epidural, an anesthesiologist will insert a needle and a tiny tube, called a catheter, in the lower part of your back. The needle is removed and the catheter left in place for delivery of the medication through the tube as needed. You can begin an epidural at any time during your labor — in the beginning, in the middle, or even toward the end — in consultation with your physician.
Does it hurt when the epidural is administered?The anesthesiologist will numb the area where the epidural is administered, which may cause a momentary stinging or burning sensation. But because of this numbing, there is very little pain associated with an epidural injection. Instead, most patients will feel some pressure as the needle is inserted.
What does an epidural do?An epidural provides anesthesia that creates a band of numbness from your bellybutton to your upper legs. It allows you to be awake and alert throughout labor, as well as to feel pressure. The ability to feel second-stage labor pressure enables you to push when it’s time to give birth to your baby. It can take about 15 minutes for the pain medication to work.
It allows you to be awake and alert throughout labor, as well as to feel pressure. The ability to feel second-stage labor pressure enables you to push when it’s time to give birth to your baby. It can take about 15 minutes for the pain medication to work.
You can continue to receive pain relief through an epidural for as long as you need it. The amount of medication you receive through the epidural can be increased or decreased as necessary.
Can an epidural slow labor or lead to a cesarean delivery (C-section)?There is no credible evidence that it does either. When a woman needs a C-section, other factors usually are at play, including the size or position of the baby or slow progression of labor due to other issues. With an epidural, you might be able to feel contractions — they just won’t hurt — and you’ll be able to push effectively. There is some evidence that epidurals can speed the first stage of labor by allowing the mother to relax.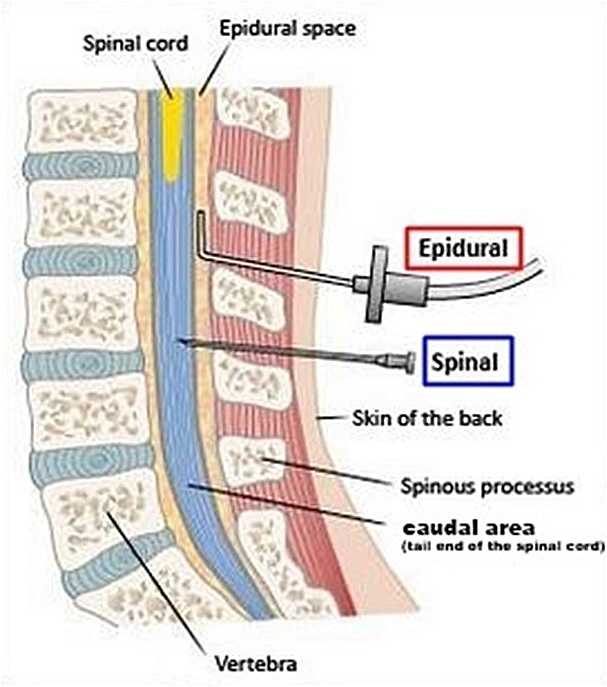
The amount of medication that reaches the baby from the epidural is very small, and there is no evidence that it causes any harm.
Are there risks and side effects?Epidurals are very safe; serious complications are extremely rare. However, as with all medications and medical procedures, there are potential side effects:
- Decrease in blood pressure – The medication may lower your blood pressure, which may slow your baby’s heart rate. To make this less likely, you will be given extra fluids through a tube in your arm (IV), and you may need to lie on your side. Sometimes, your anesthesiologist will give you a medication to maintain your blood pressure.
- Sore back – Your lower back may be sore where the needle was inserted to deliver the medication. This soreness should last no more than a few days. There is no evidence that an epidural can cause permanent back pain.
- Headache – On rare occasions, the needle pierces the covering of the spinal cord, which can cause a headache that may last for a few days if left untreated. If this situation arises, discuss the treatment options with your anesthesiologist.
A spinal block is sometimes used in combination with an epidural during labor to provide immediate pain relief. A spinal block, like an epidural, involves an injection in the lower back. While you sit or lie on your side in bed, a small amount of medication is injected into the spinal fluid to numb the lower half of the body. It brings good relief from pain and starts working quickly, but it lasts only an hour or two and is usually given only once during labor. The epidural provides continued pain relief after the spinal block wears off.
Anesthesiologists are committed to patient safety and high-quality care, and have the necessary knowledge to understand and treat the entire human body.
Epidural anesthesia | ROSTOV REGIONAL CLINICAL HOSPITAL
Font size:
- +
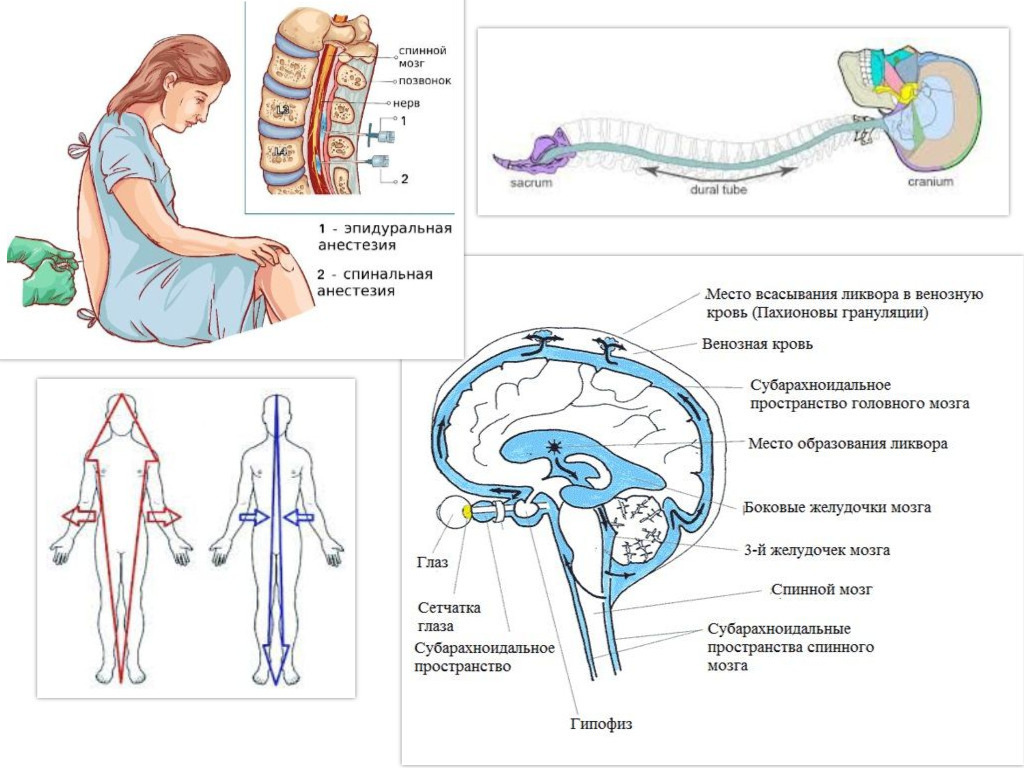
Epidural anesthesia is a method of pain relief for surgical intervention by injecting appropriate drugs directly into the epidural space of the spinal column through a catheter. In the course of such anesthesia, it is also possible to achieve muscle relaxation. Epidural anesthesia of the chest, groin, legs and abdomen is less risky than the neck and arms, and the use of such anesthesia for the head is basically impossible.
An epidural may also be used:
- as a local anesthetic if surgery is not expected, eg during labor;
- as an adjunct to general anesthesia to reduce the amount of opioids used;
- in the postoperative period to relieve pain;
- for the treatment of back pain (in this case, steroid drugs and analgesics are injected into the epidural region).

When an anesthesiologist is faced with the choice of general or epidural anesthesia, the latter is preferred whenever possible. A large selection of drugs for its implementation allows you to choose the most suitable option for each patient, there are also drugs that perfectly stop the pain syndrome, but retain mobility and clarity of consciousness.
Epidural anesthesia is considered the most suitable for operations on the legs. It allows not only to relieve pain and relax the muscles as much as possible, but also to reduce blood loss. It is widely used during surgery on the organs of the abdominal cavity and small pelvis.
The method has been proven to be safe for the kidneys and prostate. The cardiovascular system works stably, since the drug acts gradually, it can be used for heart defects, as well as diabetes. There is no irritation of the upper respiratory tract, as with general anesthesia, which is especially advantageous for asthma patients. However, this does not mean that epidural anesthesia is always used for such pathologies. The decision in each case is made by the anesthesiologist strictly individually.
The decision in each case is made by the anesthesiologist strictly individually.
Among the absolute contraindications for the use of epidural anesthesia:
- tuberculous spondylitis or its complications;
- inflammatory process on the back;
- state of shock due to trauma;
- hypersensitivity to the drugs used;
- pathology of the nervous system;
- spinal deformity;
- violation of the process of blood clotting;
- certain diseases of the abdominal cavity;
- intestinal obstruction.
Overweight, hypotension, some neurological diseases can also become a problem. As a rule, epidural anesthesia is not used in childhood.
The quality of epidural anesthesia depends not only on the state of health of the patient, but also on the drug used, and on the qualifications of the anesthesiologist - the epidural method of anesthesia is considered one of the most difficult. An anesthesiologist's mistake when administering the drug, when the drug enters the vessel, can lead to convulsions, a sharp decrease in blood pressure, there is a danger of subarachnoid administration, as a result of which a total spinal block develops.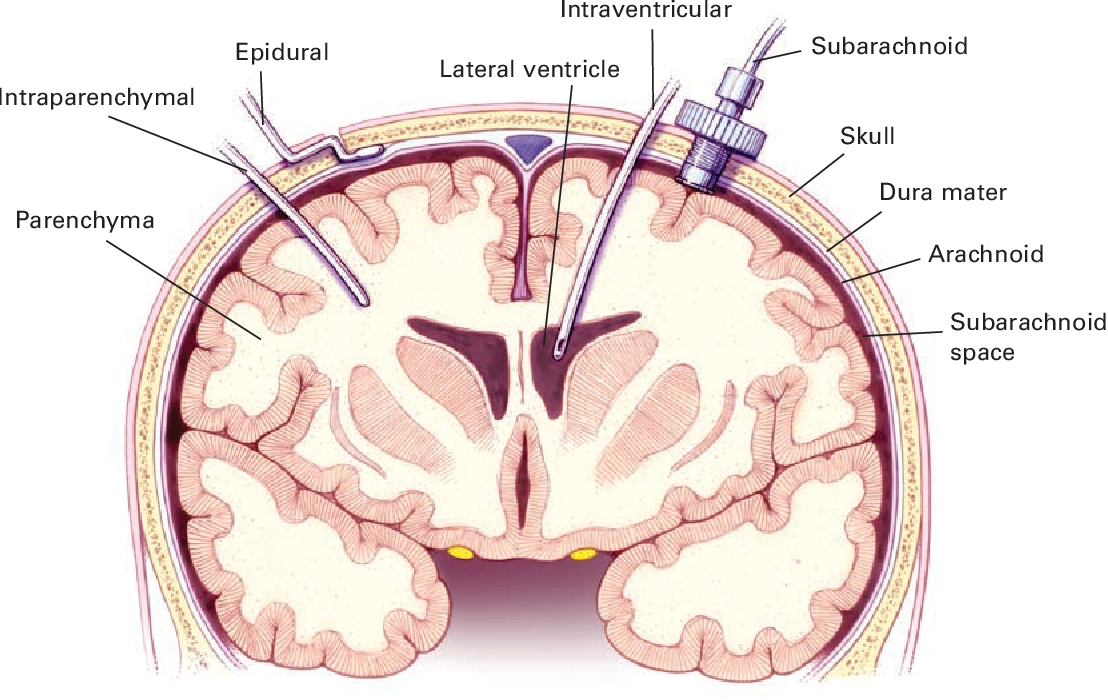 However, with proper conduct, complications as a result of epidural anesthesia are extremely rare.
However, with proper conduct, complications as a result of epidural anesthesia are extremely rare.
← To the list of surgeries and procedures
Top
Not Found (#404)
Paracelsus Medical Center
Page not found.
The above error occurred while the Web server was processing your request.
Please contact us if you think this is a server error. thank you.
Leave feedback Write to management
Please wait, download may take time
Loading...
You know which doctor you want to book
You know the service you want to book
Service selection
A second consultation is considered to be a consultation of one specialist within 30 days from the date of the previous appointment.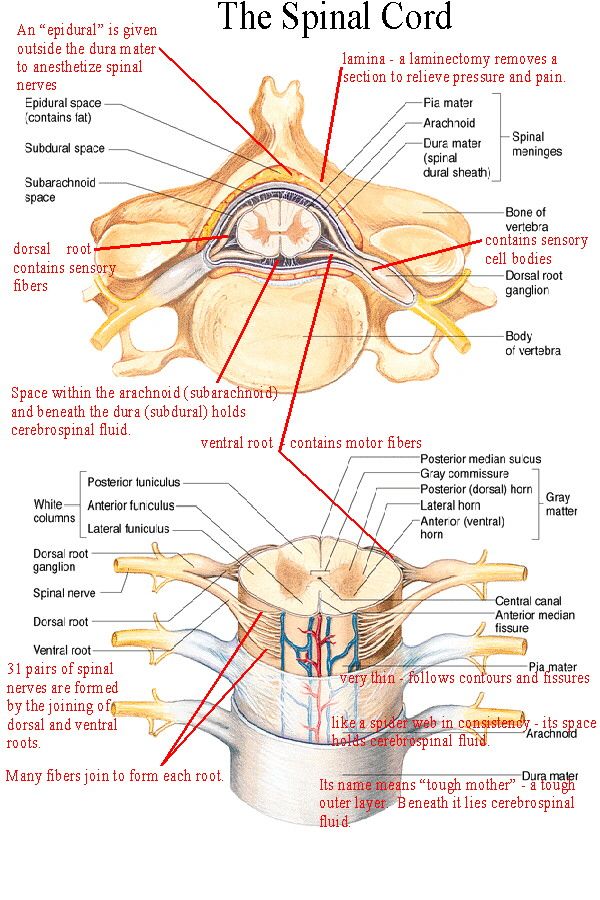 On the 31st day from the previous visit to a specialist of this profile, the consultation will be primary.
On the 31st day from the previous visit to a specialist of this profile, the consultation will be primary.
The choice of a specialist
Service selected:
Choosing a specialist service
A second consultation is considered to be a consultation of one specialist within 30 days from the date of the previous appointment. On the 31st day from the previous visit to a specialist of this profile, the consultation will be primary.
Address selection:
st.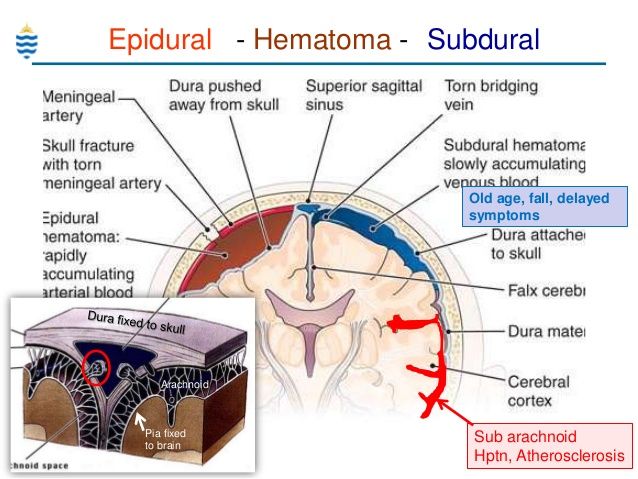 Vikulova, 33, building 2 st. Bolshakova, d. 68
Vikulova, 33, building 2 st. Bolshakova, d. 68
Date selection:
Time of receipt:
Password
Password
Register Can't login? account activation
To gain access to your personal account, enter the e-mail that was specified during registration, we will send instructions for password recovery
To gain access to your personal account, enter the e-mail that was specified during registration, we will send instructions for reactivating your account
Your application has been accepted, our specialists will answer your question as soon as possible!
Telephone
Commentary
By clicking on the confirmation button, I agree with personal data processing policy
Dear patients!
Multidisciplinary Clinic and Maternity Hospital "Paracelsus" informs you, according to the Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation to the Federal Tax Service dated March 25, 2022.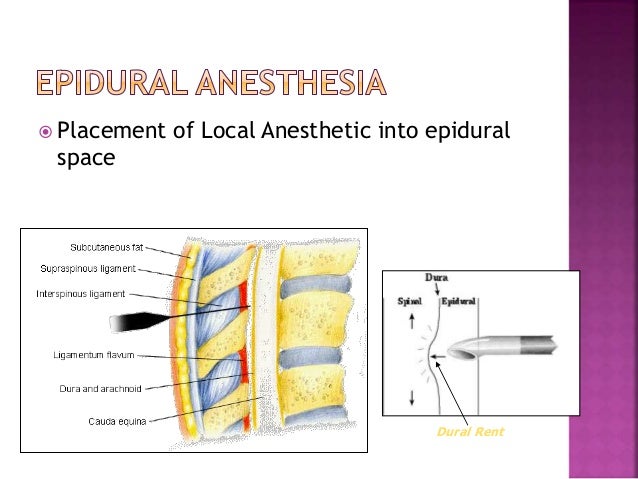 N BS-4-11 / 3605, that subparagraph 3 of paragraph 1 of Article 219 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for the taxpayer's right to receive a social tax deduction in the amount paid by him in the tax period for medical services provided by medical organizations engaged in medical activities , him, his spouse, parents, children (including adopted children) under the age of 18, wards under the age of 18 (in accordance with the list of medical services approved by the Government of the Russian Federation).
N BS-4-11 / 3605, that subparagraph 3 of paragraph 1 of Article 219 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for the taxpayer's right to receive a social tax deduction in the amount paid by him in the tax period for medical services provided by medical organizations engaged in medical activities , him, his spouse, parents, children (including adopted children) under the age of 18, wards under the age of 18 (in accordance with the list of medical services approved by the Government of the Russian Federation).
Joint order of the Ministry of Taxation of Russia and the Ministry of Health of Russia of July 25, 2001 N 289 / BG-3-04 / 256 (hereinafter - the order of July 25, 2001) approved the form of the Certificate of payment for medical services for submission to the tax authorities of the Russian Federation (hereinafter - the Certificate payment for medical services).
This certificate certifies the fact of receiving a medical service and paying for it through the cash desk of a healthcare institution at the expense of the taxpayer.