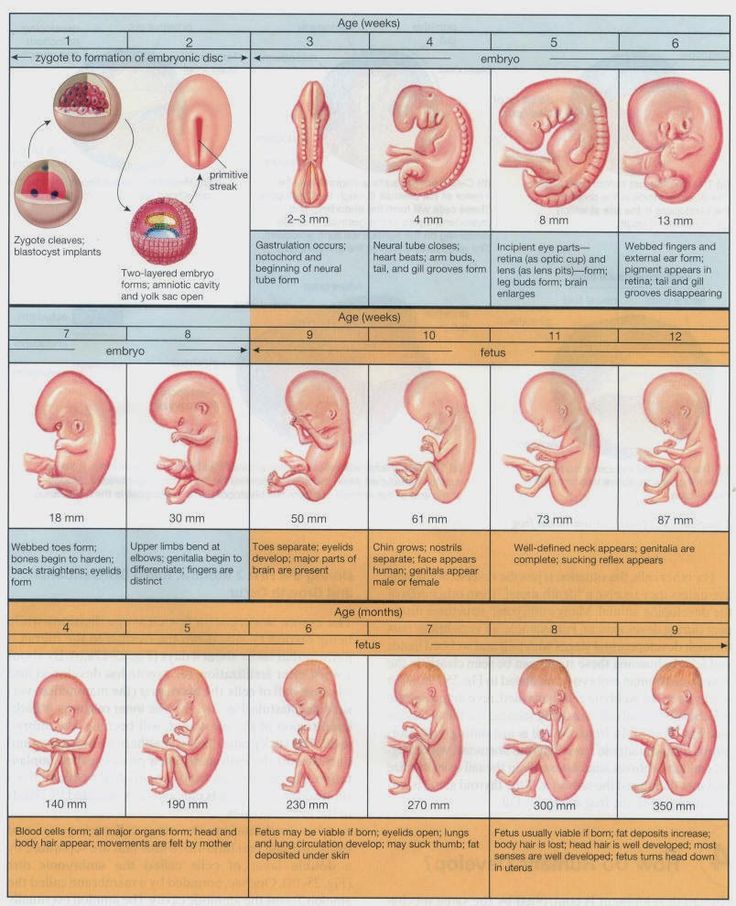
Contractions in early pregnancy
Braxton Hicks contractions | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Braxton Hicks contractions | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content4-minute read
Listen
If you feel tightening or cramping in your abdomen during your pregnancy, you may be having Braxton Hicks contractions. This is normal and not a sign that you’re ready to give birth.
Braxton Hicks contractions are sometimes called ‘false’ or ‘practice’ contractions.
What are Braxton Hicks contractions?
Braxton Hicks contractions are a tightening in your abdomen that comes and goes. They are contractions of your uterus in preparation for giving birth. They tone the muscles in your uterus and may also help prepare the cervix for birth.
Braxton Hicks contractions don’t cause labour and aren’t a sign that labour is beginning.
If you’re not sure whether what you’re experiencing is Braxton Hicks contractions or actual labour, contact your doctor or midwife. They will be able to tell by doing a vaginal examination — if there are no signs that your cervix is changing, it is not labour.
What do they feel like?
Braxton Hicks contractions feel like muscles tightening across your belly, and if you put your hands on your belly when the contractions happen, you can probably feel your uterus becoming hard.
The contractions come irregularly and usually last for about 30 seconds. While they can be uncomfortable, they usually aren’t painful.
If the pain or discomfort of your contractions eases off, they’re probably Braxton Hicks contractions.
When do you get them?
Braxton Hicks contractions occur from early in your pregnancy but you may not feel them until the second trimester. If this is your first pregnancy, you might start to feel them from about 16 weeks. In later pregnancies, you may feel Braxton Hicks contractions more often, or earlier. Some women won’t feel them at all.
Some women won’t feel them at all.
In late pregnancy, you may experience Braxton Hicks contractions more often — perhaps as much as every 10 to 20 minutes. This is a sign that you are preparing for labour — known as prelabour.
How are Braxton Hicks contractions different from labour pain?
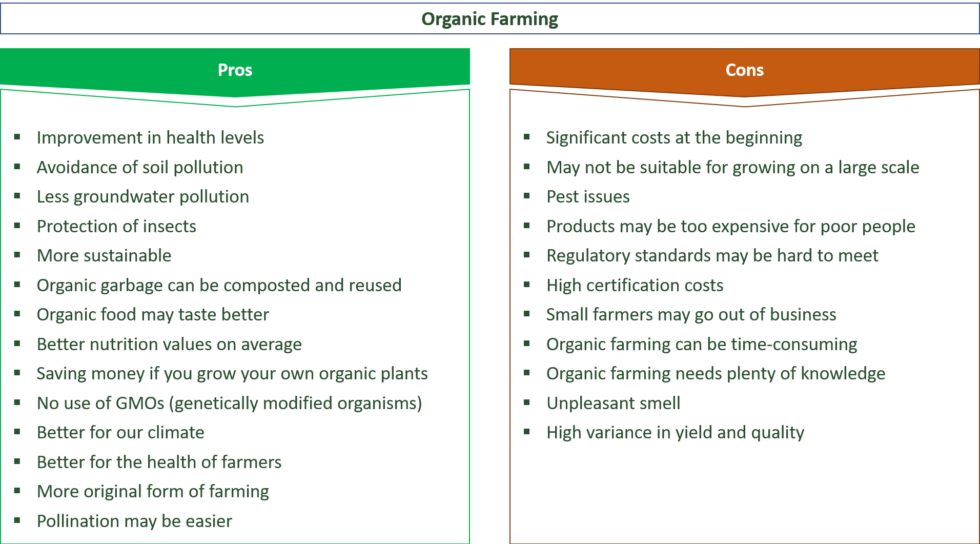
There are some differences between Braxton Hicks contractions and true labour contractions that will help your doctor or midwife decide whether you are in labour:
Braxton Hicks contractions:
- don’t result in your cervix thinning and opening
- usually last for about 30 seconds
- can be uncomfortable, but usually aren’t painful
- come and go at irregular times
- usually occur no more than once or twice an hour (until late in the pregnancy), a few times a day
- usually stop if you change position or activity or go for a walk
- usually go if you have a warm bath or shower
Real labour contractions:
- result in your cervix thinning and opening
- last 30 to 70 seconds
- become very regular
- get closer together
- last longer as time goes by
- get stronger or come more often when you walk
- get stronger over time
Should I call my doctor or midwife?
If you are less than 37 weeks pregnant, contractions can be a sign of premature labour. Contact your doctor or midwife immediately if:
Contact your doctor or midwife immediately if:
- you feel pain, pressure or discomfort in your pelvis, abdomen or lower back
- the contractions become stronger, closer together and more regular
- there is fluid leaking or gushing from your vagina
If you are full-term, you may choose to wait until a bit later in your labour, depending on what you have arranged with your doctor or midwife. If your waters break, or your contractions are strong and 5 minutes apart, it’s time to go to the hospital.
As any stage of pregnancy, you should contact your doctor or midwife immediately if you:
- you have persistent pain in your abdomen
- you have vaginal bleeding
- you notice your baby’s movements have slowed or stopped
- you feel very unwell
If you are in doubt, don’t hesitate to call your doctor or midwife for advice.
How can I ease the discomfort?
Braxton Hicks contractions are normal and don’t need treatment. But if you feel uncomfortable, you can try:
But if you feel uncomfortable, you can try:
- lying down
- taking a walk
- relaxing in a warm bath
- having a massage
It may help to practise your breathing exercises during your Braxton Hicks contractions.
Sources:
Raising Children Network (23 weeks pregnant), RANZCOG (Labour and birth), Elsevier Patient Education (Braxton Hicks Contractions)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: October 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- Giving birth - stages of labour
- Health professionals involved in your pregnancy
- Signs of premature labour
Need more information?
Pregnancy at week 22
By week 22, some parts of your baby’s body are fully formed, while some women experience Braxton Hicks contractions about now.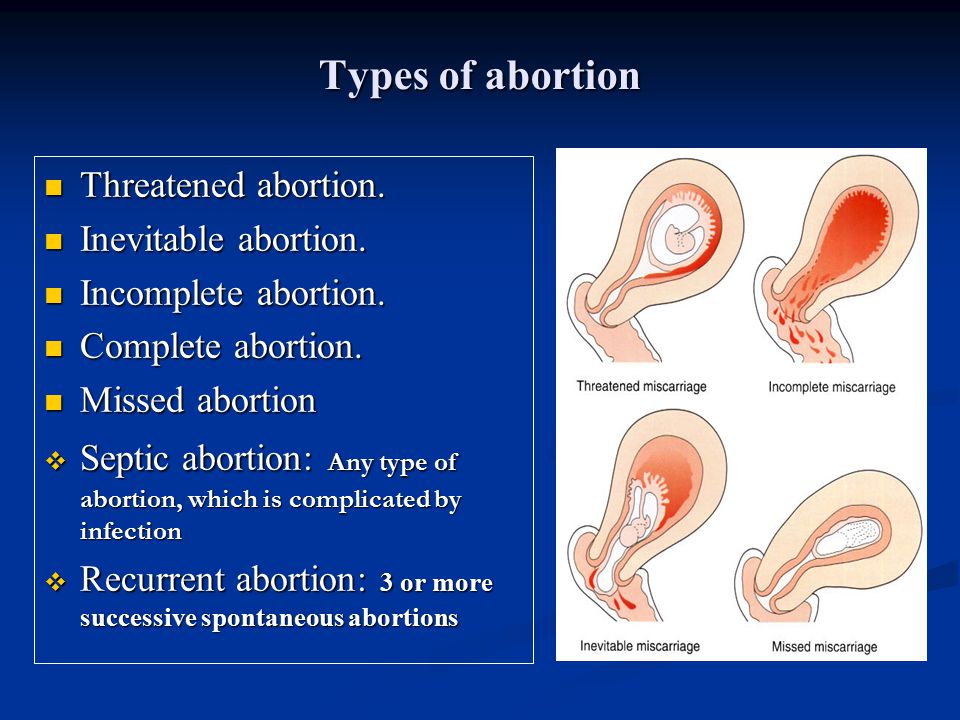
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy at week 35
You'll probably be having lots of Braxton Hicks contractions by now. It's your body's way of preparing for the birth. They should stop if you move position.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Giving birth - contractions
Contractions are when the muscles in your uterus tighten and then relax. They occur throughout the later stages of your pregnancy.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
What happens to your body in childbirth
During childbirth, your body's hormones, ligaments and muscles, as well as the shape of your pelvis, all work together to bring your baby safely into the world.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Anatomy of pregnancy and birth - uterus
The uterus is your growing baby’s home during pregnancy. Learn how the uterus works, nurtures your baby and how it changes while you are pregnant.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Preterm labour - MyDr.com.au
Going into labour before your 37th week of pregnancy is called preterm labour, or premature labour. Find out what it means for you and your baby.
Read more on myDr website
38 weeks pregnant | Raising Children Network
38 weeks pregnant? In this pregnancy week by week guide, find out how your baby is growing, how your body is changing and how to look after yourself.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
26 weeks pregnant | Raising Children Network
26 weeks pregnant? In this pregnancy week by week guide, find out how your baby is growing, how your body is changing and how to look after yourself.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Giving birth - early signs of labour
You can know the early signs of labour, even if you cannot predict when your labour will begin. Find out also what to do if something appears to be wrong.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Anatomy of pregnancy and birth
From conception to giving birth, a woman's body goes through many physical changes.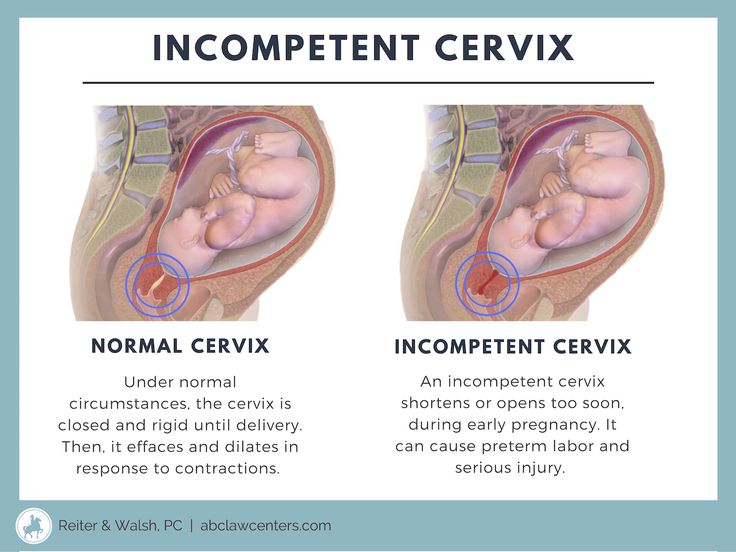 Learn what happens to your body during pregnancy and labour.
Learn what happens to your body during pregnancy and labour.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Contractions and signs of labor
Learning the signs of labor before your due date can help you feel ready for your baby’s birth.
Signs of labor include strong and regular contractions, pain in your belly and lower back, a bloody mucus discharge and your water breaking.
If you think you’re in labor, call your health care provider.

Not all contractions mean you're in true labor. Learning the difference between true and false labor can help you know when it’s the real thing.
What is labor?
Labor (also called childbirth) is the process of your baby leaving the uterus (womb). You’re in labor when you have regular contractions that cause your cervix to change. Contractions are when the muscles of your uterus get tight and then relax. Contractions help push your baby out of your uterus. Your cervix is the opening to the uterus that sits at the top of the vagina. When labor starts, your cervix dilates (opens up).
As you get closer to your due date, learning the signs of labor can help you feel ready for labor and birth. If you have any signs of labor, call your health care provider.
What are the signs of labor?
You know you’re in true labor when:
- You have strong and regular contractions. A contraction is when the muscles of your uterus tighten up like a fist and then relax.
 Contractions help push your baby out. When you’re in true labor, your contractions last about 30 to 70 seconds and come about 5 to 10 minutes apart. They’re so strong that you can’t walk or talk during them. They get stronger and closer together over time.
Contractions help push your baby out. When you’re in true labor, your contractions last about 30 to 70 seconds and come about 5 to 10 minutes apart. They’re so strong that you can’t walk or talk during them. They get stronger and closer together over time. - You feel pain in your belly and lower back. This pain doesn't go away when you move or change positions.
- You have an increase in vaginal discharge that can be clear, pink or slightly bloody (brownish or reddish). This is called bloody show. It can happen a few days before labor or at the beginning of labor. If you have bright red bleeding or if the bleeding is heavy, tell your provider right away.
- Your water breaks. Your baby has been growing in amniotic fluid (the bag of waters) in your uterus. When the bag of waters breaks, you may feel a big rush of water. Or you may feel just a trickle.
If you think you’re in labor, call your health care provider, no matter what time of day or night. Your provider can tell you if it’s time to head for the hospital. To see for sure that you’re in labor, your health care provider measures your cervix.
Your provider can tell you if it’s time to head for the hospital. To see for sure that you’re in labor, your health care provider measures your cervix.
What are signs that you may be close to starting labor?
You may be close to starting labor if:
- Your baby drops or moves lower into your pelvis. This is called lightening. It means that your baby is getting ready to move into position for birth. It can happen a few weeks or even just a few hours before your labor begins.
- You have an increase in vaginal discharge that’s clear, pink or slightly bloody. This is called show or bloody show. It can happen a few days before labor starts or at the beginning of labor.
- At a prenatal checkup, your health care provider tells you that your cervix has begun to efface (thin) and dilate (open). Before labor, your cervix is about 3.5 to 4 centimeters long. When it’s fully dilated (open) for labor, it’s 10 centimeters.
Once labor starts, contractions help open your cervix.
- You have the nesting instinct. This is when you want to get things organized in your home to get ready for your baby. You may want to do things like cook meals or get the baby’s clothes and room ready. Doing these things is fine as long as you’re careful not to overdo it. You need your energy for labor and birth.
If you have any of these signs, you may start labor soon. Learn the signs of labor so you know when to call your provider.
What are false labor and Braxton-Hicks contractions?
Not all contractions mean you’re in labor. You may have contractions on and off before true labor starts. These contractions are called false labor or Braxton-Hicks contractions. They soften and thin the cervix to help your body get ready for labor and birth. You may feel them in the weeks right before your due date. Learning the differences between true labor contractions and false labor contractions can help you know when you’re really in labor.
It can be hard to tell the difference between true labor and false labor. When you first feel contractions, time them. Write down how much time it takes from the start of one contraction to the start of the next. Make a note of how strong the contractions feel. Keep a record of your contractions for 1 hour. Walk or move around to see if the contractions stop when you change positions.
What is preterm labor?
Preterm labor is labor that begins too early, before 37 weeks of pregnancy. Premature babies (born before 37 weeks of pregnancy) can have health problems at birth and later in life. If you’re not to 37 weeks of pregnancy and you have signs or symptoms of preterm labor, call your provider. Getting help quickly is the best thing you can do. Learn about risk factors for preterm labor and what you can do to help reduce your risk.
What are stages of labor?
Stages of labor include the whole process of labor, from your first contractions (stage 1) to pushing (stage 2) to delivery of the placenta (stage 3) after your baby is born.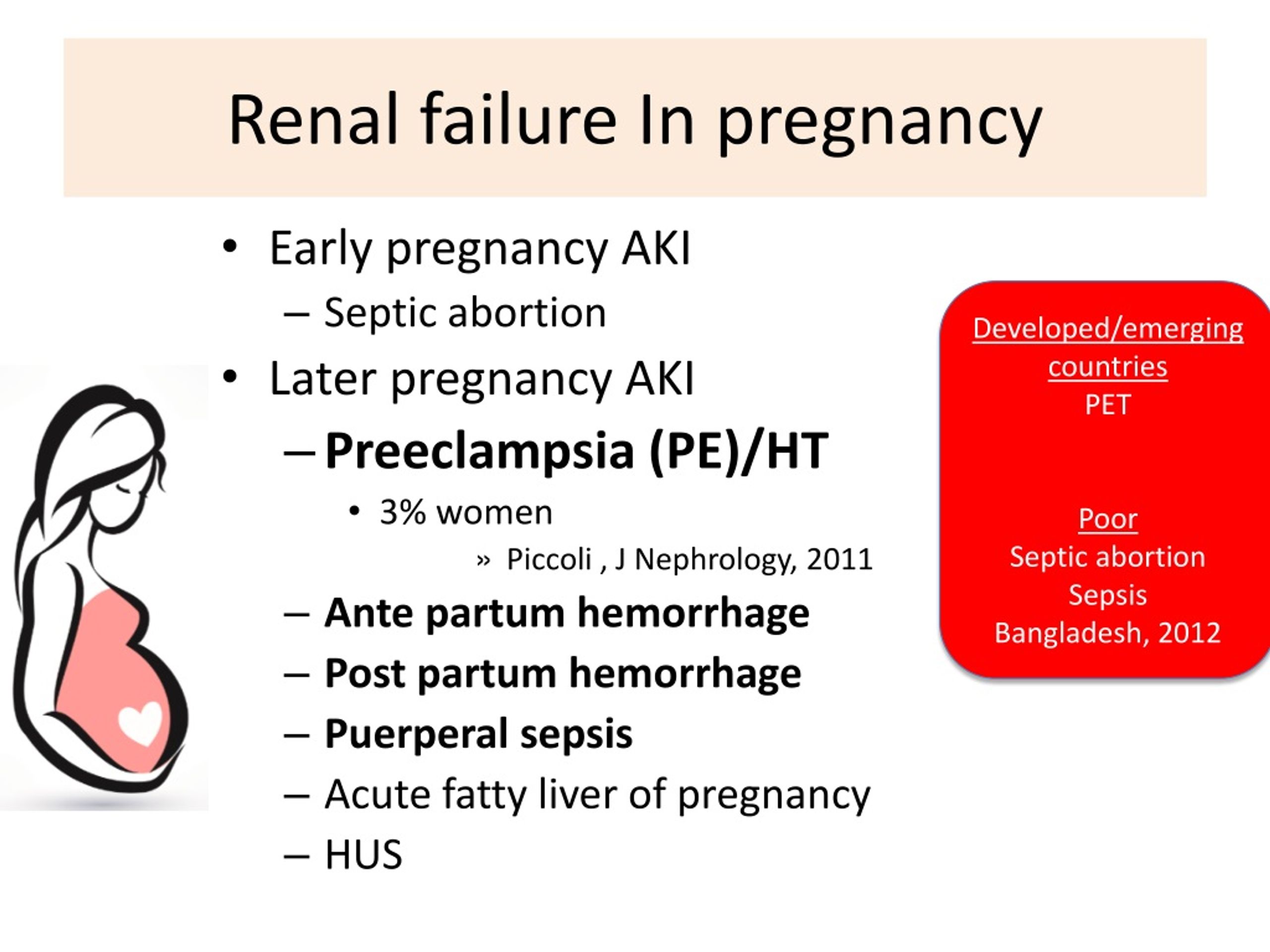 Learning about the stages of labor can help you know what to expect during labor and birth.
Learning about the stages of labor can help you know what to expect during labor and birth.
Last reviewed: December, 2018
Increased tone of the uterus during pregnancy
Nicotine constricts the blood vessels of the expectant mother, as well as the vessels of the placenta and umbilical cord, through which the fetus is nourished. Of course, smoking by itself is unlikely to lead to hypertonicity, but in combination with other factors, it may well
If the work is associated with constant stress, it has harmful effects or it is physically difficult, give it up as soon as possible. If this is not possible, use your rights, which are enshrined in the labor legislation of the Russian Federation
Hypertonicity must be distinguished from Braxton-Hicks contractions: it lasts much longer than these training contractions and usually does not go away on its own (or goes away only after a long time)
what is hypertonicity
, - muscle, and according to the laws of physiology, muscle tissue is reduced under the influence of any factor. Slightly the uterus contracts in women every month during menstruation, much stronger during labor pains. The uterus can also contract during pregnancy, doctors call this condition hypertonicity. What it looks like: suddenly, at some point, a woman feels that her stomach is tense, becomes hard, as if “hardening”. This state lasts for a long time - half an hour, an hour, half a day or even all day. Additionally, discomfort (or pain) in the lower back or sacrum may also appear. It is clear that such tension in the abdomen worries the mother, because since the uterus is contracting, then perhaps there is a threat of termination of pregnancy. But here it all depends on how much and how often the stomach tenses. nine0003
Slightly the uterus contracts in women every month during menstruation, much stronger during labor pains. The uterus can also contract during pregnancy, doctors call this condition hypertonicity. What it looks like: suddenly, at some point, a woman feels that her stomach is tense, becomes hard, as if “hardening”. This state lasts for a long time - half an hour, an hour, half a day or even all day. Additionally, discomfort (or pain) in the lower back or sacrum may also appear. It is clear that such tension in the abdomen worries the mother, because since the uterus is contracting, then perhaps there is a threat of termination of pregnancy. But here it all depends on how much and how often the stomach tenses. nine0003
Braxton-Hicks contractions
It turns out that the stomach can tense up not only when there is a threat of miscarriage. Starting from the end of the second trimester, the expectant mother can feel the so-called training contractions (Brexton-Hicks contractions) - the stomach also tenses with them for a while, as if “hardening”, - in general, the sensations are the same as with hypertonicity. But the main difference between such contractions and hypertonicity is that they last for a very short time (a few seconds - a couple of minutes) and pass by themselves, as well as if you change the position of the body or take a shower. Braxton-Hicks contractions occur up to about ten times a day, and by the end of pregnancy they appear even more often. These contractions are completely normal during pregnancy, and they do not indicate any threat of interruption. It’s just that with their help, the uterus, as it were, prepares (trains) for childbirth. nine0003
But the main difference between such contractions and hypertonicity is that they last for a very short time (a few seconds - a couple of minutes) and pass by themselves, as well as if you change the position of the body or take a shower. Braxton-Hicks contractions occur up to about ten times a day, and by the end of pregnancy they appear even more often. These contractions are completely normal during pregnancy, and they do not indicate any threat of interruption. It’s just that with their help, the uterus, as it were, prepares (trains) for childbirth. nine0003
where does hypertonicity come from
Hypertonicity can appear in any trimester of pregnancy. In the early stages, it occurs more often due to the fact that there is not enough progesterone, a hormone that is needed for the normal course of pregnancy. Another cause of hypertonicity is some changes in the uterine wall, for example, fibroids (a knot of uterine muscle tissue), endometriosis (growth of the uterine mucosa into the thickness of the wall), and inflammatory diseases. In these situations, the wall of the uterus is not able to stretch as it should. At later dates, hypertonicity can develop, on the contrary, with overstretching of the uterus (with polyhydramnios, large fetuses, multiple pregnancies). Very often, hypertonicity is provoked by some kind of physical activity too strong for a woman, for example, if, in a fit of “nesting”, the mother suddenly began to move and rearrange something in the apartment herself, or she simply moved for a very long time without resting. Someone hypertonicity occurs after psychological overstrain. nine0003
In these situations, the wall of the uterus is not able to stretch as it should. At later dates, hypertonicity can develop, on the contrary, with overstretching of the uterus (with polyhydramnios, large fetuses, multiple pregnancies). Very often, hypertonicity is provoked by some kind of physical activity too strong for a woman, for example, if, in a fit of “nesting”, the mother suddenly began to move and rearrange something in the apartment herself, or she simply moved for a very long time without resting. Someone hypertonicity occurs after psychological overstrain. nine0003
how to recognize hypertonicity
Hypertonicity must be distinguished from Braxton-Hicks contractions - as mentioned earlier, it lasts much longer than these training contractions and usually does not go away on its own (or goes away only after some long time). But if the mother cannot understand whether she has hypertension or not, you should consult a doctor. If there is still an increased tone of the uterus, the doctor, simply by placing his hand on his stomach, will feel a seal, tension, up to the feeling of a stone at hand. In addition, you can always do an ultrasound, on which, with hypertonicity, areas of local thickening of the muscular layer of the uterus are visible, and also look at the cervix, by the state of which you can also judge whether there is a threat of abortion or not. nine0003
what to do in case of hypertonicity
If it appears, the first thing you need to do is:
1. Calm down and lie down if possible. Do not panic, extra stress will not bring any benefits, especially since without consulting a doctor it is still not clear whether there is hypertonicity and how pronounced it is. Or maybe it's a false alarm? In addition, you can use relaxation techniques (breathing, auto-training, etc.).
2. Call your doctor. Of course, the doctor will not make a diagnosis in absentia, but since he knows the history of the expectant mother, her real or possible problems, he will be able to give the right direction for further action. nine0003
3. If it is not possible to contact your doctor, you can contact any clinic or antenatal clinic where pregnant women are treated. If medical institutions are already closed (late evening, at night), you can call an ambulance - she will take you to the nearest hospital or maternity hospital (you can also get there by taxi).
If medical institutions are already closed (late evening, at night), you can call an ambulance - she will take you to the nearest hospital or maternity hospital (you can also get there by taxi).
4. Hypertonicity is well eliminated by special medicines that relax the uterus (tocolytics), and if the doctor has prescribed them, then you should not be afraid to take them: they help quickly enough and do not harm the child. nine0003
how to prevent hypertonicity
There are simple rules that can prevent hypertonicity or reduce the risk of its occurrence:
1. Quit smoking, watch your weight, do not eat surrogate foods. No matter how trite it may sound, but it is a healthy lifestyle that is the basis of our well-being.
2. Distribute your forces correctly. Laundry, cooking can wait if the expectant mother suddenly feels that she needs a rest. If any activities require physical or psychological stress, cancel them for a while. Do not attend events or places where you may feel uncomfortable, reduce communication with people that are unpleasant for you. nine0003
nine0003
3. Follow your doctor's recommendations: if he recommends any examination or treatment, do not neglect them.
Listen to your body, follow the doctor's advice, tune in to the positive - this is the key to a successful pregnancy. And then no hypertonicity is terrible for you!
How can you tell real contractions from training contractions?
Shemyakina Natalya Nikolaevna, head of the obstetric department of the Leleka maternity hospital, will help you figure it out .
Training contractions, or as they are also called, fake, or Braxton-Hicks contractions, are irregular contractions that do not have increasing intensity. The uterus may tone up, but normally, it should pass quickly.
For example, the tone appeared once in half an hour and the uterus relaxed rather quickly. Then the tone reappeared only after two hours and again passed. These are training contractions, they do not increase in intensity and do not become more frequent. nine0003
nine0003
Training bouts are physiologically provided by our body. So the uterus is preparing to do the hard work in the process of childbirth. Normally, training contractions appear in terms of pregnancy close to childbirth - from the 37th week of pregnancy.
The appearance of training contractions in the early stages of pregnancy is not the norm
The uterus can tone up with an active lifestyle, physical activity, with a change in body position, but this tone should quickly pass. Normally, the uterus should not often come into tone. And even more so, contractions, as such, should not be until the 37th week of pregnancy. nine0077 Braxton Hicks contractions in the early stages are a threat of preterm labor. If a woman has contractions periodically during the day: after an hour, after 2, then again after an hour, (even if they are not regular), for periods up to 37 weeks, such a tone should alert the expectant mother.
Because this is not the norm, but the threat of premature birth.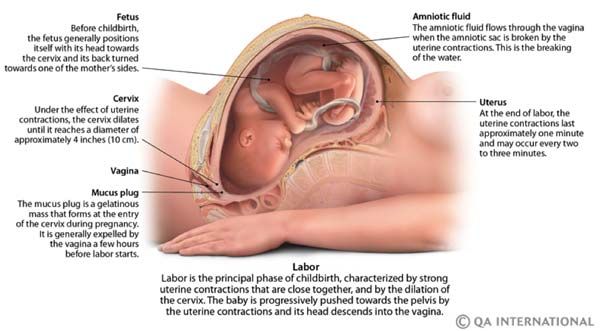 This is an occasion to contact a specialist and change your rhythm of life, put on a bandage. The causes of premature birth are most often internal, caused by hormonal disorders and a violation of the physical health of a woman. But significant physical activity and stress can also cause premature birth. nine0003
This is an occasion to contact a specialist and change your rhythm of life, put on a bandage. The causes of premature birth are most often internal, caused by hormonal disorders and a violation of the physical health of a woman. But significant physical activity and stress can also cause premature birth. nine0003
Labor pains
Unlike training pains, labor pains are regular. The uterus comes to tone first once every 15 minutes, and after a while - once every 7-10 minutes. Contractions gradually become more frequent, longer and stronger. And already occur every 5 minutes, then 3 and finally every 2 minutes.
True labor pains are contractions every 2 minutes, 40 seconds. If within an hour or two the contractions intensify - pains that begin in the lower abdomen or in the lower back and spread to the stomach - most likely, these are real labor pains. nine0003
Training contractions are NOT so much painful as unusual for a woman. When the expectant mother sees how the stomach comes into tone, its shape changes and it becomes dense, like an inflated ball. This might scare you a little. But a woman must understand that in real, labor pains, there must be a clear periodicity, intensification and acceleration over a certain period of time. Real fights never stop, but practice fights do. The uterus then comes to tone, then relaxes. nine0077 Women often confuse contractions with tone, which is caused by other physiological processes in the body. For example, increased intestinal peristalsis, intestinal infections, colic, etc.
What else should alert a woman?! If within an hour or two the uterus periodically becomes toned and mucous, bloody (streaked with blood or brown) discharge appears, then most likely, there are structural changes in the cervix - it opens. Also an important sign to seek help is the discharge of the mucous plug long before childbirth. Her departure in terms of childbirth, a week or two before childbirth is normal. nine0003
Tracking labor pains
There are several methods for determining the types of contractions. A woman can do this herself, writing down the frequency and duration of contractions on paper or tracking them using special programs for a computer and phone. Or you can contact a doctor at antenatal clinic or at the maternity hospital, where a specialist will conduct fetal monitoring (fetal CTG). With the help of 2 sensors, the fetal heartbeat, uterine contractions are monitored and it is determined whether these are training contractions or labor. nine0003
A woman can do this herself, writing down the frequency and duration of contractions on paper or tracking them using special programs for a computer and phone. Or you can contact a doctor at antenatal clinic or at the maternity hospital, where a specialist will conduct fetal monitoring (fetal CTG). With the help of 2 sensors, the fetal heartbeat, uterine contractions are monitored and it is determined whether these are training contractions or labor. nine0003
When should I go to the maternity hospital?
If within an hour or two there is an increase and intensification of pain, its intensity increases, the frequency of contractions is clear and regular, you can go to the maternity hospital. A woman may make a mistake, but it’s better to come and make sure for sure whether these are labor or training contractions.
If the amniotic fluid breaks, you can slowly pack up and go to the maternity hospital. Since, normally, after this labor activity should begin.
The main thing is that a woman should not panic.