Constant migraine while pregnant
Headaches during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Headaches during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content3-minute read
Listen
Headaches in women can often be triggered by a change in hormones during pregnancy. Expectant mothers may experience an increase or decrease in the number of headaches. Unexplained, frequent headaches later in your pregnancy could be a sign of a more serious condition called pre-eclampsia, so tell your doctor if this is the case.
Causes of headache during pregnancy
Many women experience headaches during pregnancy, especially in the first and third trimesters. If you're pregnant, you may notice an increase in the number of headaches you have at around week 9 of your pregnancy.
As well as hormonal changes, headaches in the early stages of pregnancy can be caused by an increase in the volume of blood your body is producing.
Other causes of headaches during pregnancy can include:
- not getting enough sleep
- withdrawal from caffeine (e.g. in coffee, tea or cola drinks)
- low blood sugar
- dehydration
- feeling stressed
- poor posture, particularly as your baby gets bigger
- having depression or anxiety
Migraine
Migraine is a particular type of headache that mostly occurs on one side of the head – it can be either moderate or very painful. People who experience migraine can also feel sick or vomit, and be sensitive to light or sound.
In pregnancy, migraine may get worse for the first few months, but for many women it can improve in the later stages of their pregnancy when the level of the hormone oestrogen stabilises. Other women may experience no change or a decrease in the number of migraine headaches while pregnant. Some women may experience differences in migraine during different pregnancies.
Some women may experience differences in migraine during different pregnancies.
Treatment
It’s not advisable for pregnant women with migraine to use migraine medicine. For other headaches it's also recommended that you try to treat your headache without medicine.
You could try:
- getting more sleep or rest and relaxation
- pregnancy yoga classes or other exercise
- practising good posture, particularly later in your pregnancy
- eating regular, well-balanced meals
- putting a warm facecloth on your eye and nose area, if it is a sinus headache
- putting a cold pack on the back of your neck, taking a bath or using a heat pack, if it is a tension headache
- neck and shoulders massage
Pregnant women who experience migraine should avoid things that may trigger their migraine. This may include:
- chocolate
- yoghurt
- peanuts
- bread
- sour cream
- preserved meats
- aged cheese
- monosodium glutamate (MSG)
- caffeine (withdrawal from)
- bright or flickering lights
- strong smells
- loud sounds
- computer or movie screens
- sudden or excessive exercise
- emotional triggers such as arguments or stress
If you do take medicine for your headache or migraine you should check with your doctor, pharmacist or midwife first. Paracetamol, with or without codeine, is generally considered safe for pregnant women to use but you should avoid using other pain medicine such as aspirin or ibuprofen.
Paracetamol, with or without codeine, is generally considered safe for pregnant women to use but you should avoid using other pain medicine such as aspirin or ibuprofen.
When to contact your doctor
If you experience frequent headaches that don't go away with paracetamol, it could be a sign of a more serious medical condition called pre-eclampsia. This usually involves an increase in the pregnant woman's blood pressure and problems with her kidneys. There are also other serious risks for both you and your baby. Pre-eclampsia mostly occurs in the second half of pregnancy.
Contact your doctor, particularly if, along with your headaches, you have a pain below your ribs, feel like you have heartburn, you suddenly swell in your face, hands or feet, or you have problems with your eyesight.
Further information
- Speak with your doctor or midwife, particularly if you have any concerns about pre-eclampsia
- Phone Pregnancy, Birth and Baby on 1800 882 436 to speak with a maternal child health nurse.

- For more information about headaches during pregnancy, visit Headache Australia.
- For more information about medication during pregnancy, see your doctor or pharmacist, or visit NPS MedicineWise.
Sources:
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (Pre-eclampsia and high blood pressure during pregnancy), Headache Australia (Migraine), Women's and Children's Health Network (Medicines during pregnancy), Headache Australia (Adults and headache), Headache Australia (Migraine – A common and distressing disorder), Raising Children Network (9 weeks pregnant), Raising Children Network (34 weeks pregnant), Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (Perinatal Anxiety and Depression), American Pregnancy Association (Pregnancy and Headaches), NPS Medicinewise (Taking medicines in pregnancy), Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (Is paracetamol safe to use in pregnancy?)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: May 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- Common discomforts during pregnancy
Need further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Migraines & Headaches During Pregnancy: Causes and Treatment
Written by Rebecca Buffum Taylor
In this Article
- Causes of Migraine Headaches
- Tracking Triggers With a Migraine Diary
- Tests for Migraines
- Self-Care of Migraines
- Medications for Migraines
- Acute Migraine Treatment
- Preventive Migraine Treatment
If you're pregnant, you're no doubt experiencing new aches and pains. If you're also one of the millions of pregnant women who experience migraines, you might be glad to know that pregnancy eases migraine headache symptoms for many women. But even if it doesn't for you, the information in this article can help you cope.
But even if it doesn't for you, the information in this article can help you cope.
Causes of Migraine Headaches
Exactly what causes migraine headaches isn't known. But migraines appear to involve changes in nerve pathways, neurochemicals, and blood flow in the brain.
Researchers believe that overly excited brain cells stimulate a release of chemicals. These chemicals irritate blood vessels on the brain's surface. That, in turn, causes blood vessels to swell and stimulate the pain response.
Estrogen is thought to play a role in migraines. That's why pregnancy, menstruation, and menopause often change a woman's pattern of migraine headaches.
The neurotransmitter serotonin also appears to have a key role in migraines.
Tracking Triggers With a Migraine Diary
Hormone changes during pregnancy are not the only thing that can trigger migraine headaches. Most women have a combination of triggers. For instance, stress, skipped meals, and lack of sleep may all trigger a migraine. And something that triggers a migraine one day may not bother you at all the next.
And something that triggers a migraine one day may not bother you at all the next.
Some migraines last a few hours. Others, if left untreated, could last a couple of days. Migraines are quite unpredictable. So while pregnancy may make them worse for one woman, they might completely disappear for another.
A headache diary can let you track your particular triggers. This will help your doctor decide on what treatment will work best to relieve your specific symptoms. It may also help you recognize a pattern that tells you which triggers to avoid while you're pregnant.
Each time you have a headache, write down:
- Your specific symptoms: where you feel the pain, what the pain feels like, and any other symptoms such as vomiting or sensitivity to noise, smells, or bright light
- The time your headache started and ended
- Food and beverages you had during the 24 hours before the migraine
- Any change in your environment, such as traveling to a new place, a change in weather, or trying new kinds of food
- Any treatment you tried, and whether it helped or made the headache worse
Common headache triggers include:
- Chocolate
- Caffeine
- Foods that contain the preservatives MSG (monosodium glutamate) and nitrates
- Aspartame, the sweetener in NutraSweet and Equal
Tests for Migraines
Headaches can be caused by a pregnancy complication called preeclampsia. So your doctor may evaluate you for that condition before making a diagnosis of migraine. Be sure to tell your doctor about all the medications you're taking, including over-the-counter products and natural supplements. Also let your doctor know whether anyone in your family has had migraines.
So your doctor may evaluate you for that condition before making a diagnosis of migraine. Be sure to tell your doctor about all the medications you're taking, including over-the-counter products and natural supplements. Also let your doctor know whether anyone in your family has had migraines.
The doctor often can diagnose migraine from a headache diary and your medical history. CT scans and other radiology tests to rule out other causes of your headaches aren't usually advised in pregnancy. That's because of the potential risks to the fetus.
Self-Care of Migraines
Your first line of defense against migraine headaches is a healthy lifestyle and self-care. Here are some tips to help you manage migraines during pregnancy:
- Avoid your known triggers, such as specific foods, as much as possible.
- Keep a predictable schedule of meals and snacks.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Get plenty of rest.
- Consider taking a class in biofeedback or other relaxation techniques.

- When pain strikes, try ice packs, massage, and resting in a quiet, darkened room.
Medications for Migraines
If you're pregnant -- or planning to get pregnant soon -- your doctor will generally advise you to stay off medications unless they're absolutely needed. Together, you'll have to weigh the potential effects of a drug on your unborn baby. In some cases, a decision will need to be made based on scant or inconclusive research into a particular drug.
Many of the anti-migraine medications to treat or prevent migraine headache and its symptoms should be avoided during pregnancy. Some have been linked to birth defects in babies. Other medications are associated with pregnancy complications. For instance, some have been associated with bleeding, miscarriage, or intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), a condition in which the uterus and fetus don't grow normally.
Acute Migraine Treatment
Acute treatment aims to stop a migraine attack after its first signs appear.
Pain relievers, also called analgesics, may help ease the intense pain of migraines. These general pain-relieving drugs, though, aren't specific to the migraine pain pathway:
- Acetaminophen is generally considered low-risk during pregnancy.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), including aspirin, may carry a risk of bleeding and miscarriage if taken in early pregnancy. There is also a possible risk of heart complications in the baby if they are taken in the third trimester. Aspirin taken near delivery may lead to excess blood loss in mothers during birth.
- Most NSAIDs, including ibuprofen -- sold over the counter under the brand names Advil and Motrin -- and naproxen -- sold as Aleve, Naprosyn and other brands -- don't have enough controlled human research studies to assess all their risks in pregnancy.
- Narcotic pain relievers should generally be avoided. There is a dual risk of addiction in both mothers and babies if they are used for prolonged periods of time.

Ergotamines work specifically for migraine pain. But doctors advise against taking these drugs during pregnancy. They carry a risk of birth defects, especially if taken in the first trimester. These drugs may also stimulate labor contractions and premature birth.
Triptans work specifically on the migraine pain pathway. Triptans aren't known to cause birth defects. But most research to date has focused on animals, not humans. Your doctor can help you decide is it is safe for you and your unborn baby.
Other medications may be prescribed for relief of specific symptoms of a migraine during pregnancy. For instance, antiemetics help soothe the vomiting and nausea that can accompany a migraine. But many of the drugs typically used for migraine haven't been adequately studied in pregnancy, so their safety or risk to the fetus has not been determined.
Preventive Migraine Treatment
If you have severe, recurring attacks, preventive treatment may stop future attacks or reduce their severity.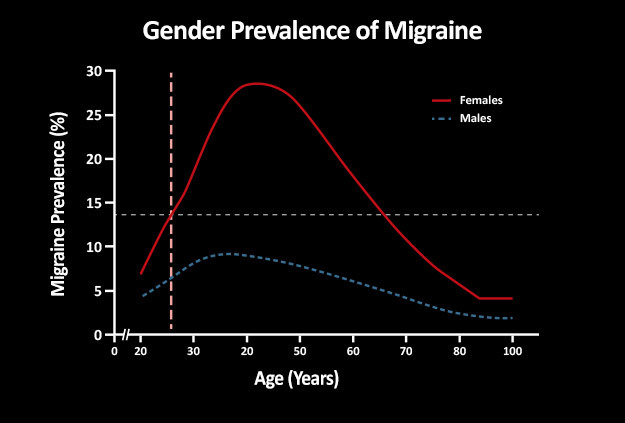 Many of the drugs used for prevention were originally used for other conditions, such as high blood pressure.
Many of the drugs used for prevention were originally used for other conditions, such as high blood pressure.
See a neurologist experienced with treating pregnant women. They'll prescribe a medicine in the lowest dose needed to help you and likely recommend some kind of talk therapy. Relatively safe medications for migraines include beta-blockers, such as metoprolol (Lopressor, Toprol XL) and propranolol (Inderal LA, Inderal XL, InnoPran XL)
When you're pregnant, always talk with your doctor before taking any drug, herbal product, or natural medicine.
If you can't take medications or wish not to, there are some devices which might be worth considering. Cefaly is a portable headband-like device that gives electrical impulses on the skin at the forehead. This stimulates a nerve associated with migraine headaches. Cefaly is used once a day for 20 minutes, and when it's on you'll feel a tingling or massaging sensation.
SpringTMS is a magnet placed on the back of the head at the first sign of a headache. It gives off a split-second magnetic pulse that stimulates part of the brain. It usually has no side effects. Also, gammaCore is a hand-held portable device which is a noninvasive vagus nerve stimulator (nVS). When placed over the vagus nerve in the neck, it releases a mild electrical stimulation to the nerve's fibers to relieve pain.
It gives off a split-second magnetic pulse that stimulates part of the brain. It usually has no side effects. Also, gammaCore is a hand-held portable device which is a noninvasive vagus nerve stimulator (nVS). When placed over the vagus nerve in the neck, it releases a mild electrical stimulation to the nerve's fibers to relieve pain.
If you're seeing a headache specialist, double-check with your obstetrician or certified midwife about the safety of any medications ordevices during pregnancy. While migraine pain may be excruciating, taking a risk with your baby's health could cause lifelong health problems for your child.
Migraine during pregnancy: what to do
Migraine is a benign disease, it does not affect the course of pregnancy and fetal development. However, migraine and pregnancy is a combination that requires a responsible attitude. Especially with frequent migraines (more than 2 times a week) and migraines with aura, because:
-
medicines approved for use, few,
-
and the approach to the treatment and prevention of migraine during this period is extremely individual: it depends on the frequency, severity and duration of headache, the degree of impact on life.

Our neurologist Daria Korobkova conducted a live broadcast on the clinic's Instagram account, where she told how migraine and pregnancy are connected, why attacks become more frequent or disappear, and answered subscribers' questions. The ether was saved, see “Air recording: migraine during pregnancy and GV.
We will tell about migraine during breastfeeding separately.
The statistics of clinical observations of migraine during pregnancy looks like this:
In 60-70% of pregnant women with migraine, headache attacks become less frequent, milder, or even completely disappear in the second and third trimesters. This is due to the stabilization of estrogen levels. By the beginning of the second trimester, it rises 6 times and its fluctuations stop.
In other women, migraines during pregnancy either remain unchanged or worsen. But as the duration of pregnancy increases, the proportion of such women gradually decreases:
If at the end of the first trimester the frequency and intensity of attacks persist, then it is most likely that migraine will disturb the woman throughout the entire period of pregnancy and after childbirth too.
How to manage migraine during pregnancy?
The main thing here is to learn how to control seizures and, if necessary, seek medical help.
-
Follow lifestyle advice:
-
get enough sleep;
-
drink enough fluids;
-
eat fractionally and without long breaks;
-
rest;
-
avoid stressful situations. This is one of the main provocateurs of migraine. Psychotherapy, relaxation and stress management are here to help you.
-
Keep a headache diary. This will help you take control of migraine triggers.
Yes, these simple recommendations are sometimes enough to make seizures less frequent! Pregnancy is a special state of a woman. If in other periods of life we do not take such recommendations so seriously, then in this situation it is worth trying to change the philosophy of life and attitude towards ourselves =)
How to relieve an attack?
-
Favor non-drug methods.
 Sometimes, in order to relieve an attack, it is enough to eliminate an unfavorable factor:
Sometimes, in order to relieve an attack, it is enough to eliminate an unfavorable factor:
-
dry biscuits, ginger, or applesauce may help with nausea;
-
for dehydration - diluted juice or other liquid;
-
sleep, walking or breathing exercises can also help to cope;
-
If the attacks are severe, interfere with your life, then under the supervision of a specialist, you can resort to drug therapy.
PARACETAMOL is considered the safest and can be taken throughout pregnancy.
All other drugs have nuances. For example:
-
ibuprofen can be taken in the second trimester, and in the first trimester it is better to limit, in the third trimester the drug is contraindicated for use;
-
aspirin is prohibited in the 3rd trimester and is undesirable for taking in the first two, as it can cause extremely undesirable consequences;
-
It is strictly forbidden to use ergotamine and opioid analgesics;
-
triptans are not officially approved for use during pregnancy as no controlled studies have been conducted.
 However, clinical observations of women around the world who took them on their own showed no adverse effects on the fetus. We discussed this issue in more detail on the air.
However, clinical observations of women around the world who took them on their own showed no adverse effects on the fetus. We discussed this issue in more detail on the air.
!Other than paracetamol, we do not recommend the use of any drug without a doctor's prescription.
When to see a doctor:
-
migraine occurred for the first time during pregnancy;
-
if migraine attacks suddenly become more frequent and stronger;
-
if the aura became longer or appeared for the first time;
-
if the headache is rapidly increasing and has an unusual character;
-
if the pressure rises during the headache.
Follow our Instagram to read the latest materials on the diagnosis and treatment of headaches!
cluster headache. Rare but painful Holidays without headaches. Real holidays Something about osteochondrosis. An excerpt from the book of Kirill Skorobogatykh.
Rare but painful Holidays without headaches. Real holidays Something about osteochondrosis. An excerpt from the book of Kirill Skorobogatykh.
Headache during pregnancy: where does it come from and how to get rid of it
Share
0When to call an ambulance
Urgently dial 103 or 112 if you have Clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of tension headache the following symptoms:
- sudden and severe headache;
- consciousness Preeclampsia becomes confused or lost altogether;
- pain worsens over 5 minutes;
- flies, spots flash in the eyes;
- throbbing and noisy in the ears;
- speech has become slurred, words are drawn out;
- arms and legs weaken, convulsions set in;
- severe neck stiffness Meningitis, chin cannot reach chest;
- fever ALGORITHMS for providing emergency medical care outside a medical organization 39°C and above;
- increased heart rate at rest;
- severe shortness of breath;
- the child pushes without stopping or stops abruptly;
- leaking High blood pressure and pregnancy: Know the facts of water or blood;
- lower abdomen hurts, as if contractions had begun.

Why pregnant women can get headaches
Pregnancy headaches are not always life threatening. But the doctor needs to be told about it in any case. If the symptom appeared for the first time and does not hurt much, postpone the conversation until a scheduled visit. If your headache is recurring or gets worse, it's best to make an appointment as soon as possible. The gynecologist will decide what needs to be done or refer you to another doctor.
There are many causes of headaches. Scientists have found Characteristics and diagnoses of acute headache in pregnant women — a retrospective cross‑sectional study that in pregnant women in 57% of cases it is primary, that is, not associated with other diseases. The most common are migraines and tension headaches.
Everything else is a secondary headache caused by various pathologies. Usually it is high blood pressure and infections. But there are also more dangerous reasons.
1. Stress and fatigue
A pregnant woman's body experiences increased stress, because it has to work for two. If at the same time the expectant mother is exposed to stress, strong feelings or sleeps little, she gets Clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of tension headache tension headache.
If at the same time the expectant mother is exposed to stress, strong feelings or sleeps little, she gets Clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of tension headache tension headache.
Discomfort lasts from 30 minutes to several days. The head hurts in the forehead, occiput, both temples. But there is no feeling that they put on a tight hoop or helmet. The pain does not get worse when bending over, walking, or climbing stairs, bright lights, or sounds.
What to do
Tension headache can go away on its own: enough Clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of tension headache get some fresh air or sleep. Sometimes pleasant emotions help, which distract from experiences.
If the pain persists for 2-3 consecutive days, see a doctor. He will select painkillers that are safe for the child.
2. Medications
Any medicine that enters the stomach or bloodstream can cause headaches even if the dosage is correct. In pregnant women, this often occurs due to drugs for high blood pressure, heart disease, antibiotics, anticonvulsants.
In pregnant women, this often occurs due to drugs for high blood pressure, heart disease, antibiotics, anticonvulsants.
Long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for headaches may cause Clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of tension-type headache the opposite effect: the pills do not remove, but provoke symptoms.
What to do
If your head hurts a few hours after taking the medicine, you need to see a doctor to change the medicine. Do not drink non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for more than 3-5 days. If they do not help, you need to tell the doctor about it.
3. Love or avoidance of coffee
Headache during pregnancy may be caused by coffee Drug-induced headache: management. Unpleasant symptoms occur if you drink more than 3-4 cups a day.
Abrupt refusal of coffee is also harmful. It is worth finding out about pregnancy and stop brewing a fragrant drink, and after 1-2 days Caffeine-withdrawal headache will appear in the temples and the back of the head. The Vågå study of headache epidemiology aching pain.
The Vågå study of headache epidemiology aching pain.
What to do
Coffee is better Caffeine and adaptive changes in the circulatory system during pregnancy stop during pregnancy. If a headache occurs a day after this, you can drink a small cup of the drink and wait a day again. Gradually, the dependence on coffee will pass.
Coffee drinkers can Caffeine reduce their drink intake to 1-2 cups per day.
4. Infection with fever
Acute viral (usually ARVI) or bacterial (eg, streptococcal tonsillitis) infections cause fever and headache. This is a normal reaction to foreign microorganisms.
But any infection is dangerous for pregnant women The role of infection in miscarriage. It can cause fetal defects, growth retardation and even miscarriage. And with meningitis, especially listeriosis, there is a threat to the life of the mother.
What to do
If you have a headache with fever, call your doctor. He will prescribe safe medications or give you a referral to the hospital if a severe infection is suspected. In this case, Meningitis needs strong antibiotics, drips to maintain the body and sometimes hormones.
In this case, Meningitis needs strong antibiotics, drips to maintain the body and sometimes hormones.
5. Preeclampsia and preeclampsia
After 20 weeks, preeclampsia may develop in pregnant women. This disease is GESTOSIS: THEORY AND PRACTICE, in which one of three symptoms or a combination of them may appear: high blood pressure, edema and protein in the urine.
Without proper treatment, gestosis turns into preeclampsia Preeclampsia. The pressure rises sharply, the head and lower abdomen hurt unbearably, the baby pushes unusually hard or, on the contrary, suddenly subsides Placental abruption. Preeclampsia can lead to placental abruption, damage to the liver and other organs, bleeding, and even seizures. Without urgent medical care, the fetus and mother die.
What to do
When the first signs of preeclampsia appear, the pregnant woman is hospitalized to find treatment. After that, she is discharged home under the supervision of her gynecologist.
But if her health worsens, the doctor again sends the woman to the Preeclampsia hospital, where she is prescribed drugs to reduce pressure, special drips to keep her body functioning. If improvement does not occur within a day, a caesarean section is performed.
6. Migraine
One of the causes of migraine Migraine is a change in estrogen levels. But the disease very rarely appears due to pregnancy. On the contrary, in 70% of women the symptoms subside dramatically Migraine and pregnancy: a particular example of the course of the disease after conception. And yet migraine torments Migraine many.
It may begin with an aura: flashes of light, spots before the eyes, tingling in the hands or numbness of half of the face, sometimes tinnitus. Each symptom can last from 20 minutes to an hour.
A migraine attack develops after the aura. In this case, one side of the head hurts and throbs, nausea or vomiting appears. A woman is irritated by bright lights, loud noises, smells. They make the pain worse.
They make the pain worse.
Seizures last from a few hours to a week or more. After a migraine, there is a feeling of severe fatigue, exhaustion, and an awkward turn of the head can return the pain.
What to do
Any medication for migraine during pregnancy must be prescribed by a doctor. In some cases drugs are used Headache in Pregnancy and the Puerperium from the group of beta-blockers.
Studies have shown Migraine and pregnancy: a particular example of the course of the disease, that often migraine in pregnant women is associated with a lack of magnesium. The doctor will help you choose the appropriate type of vitamin and mineral complex and its dosage.
7. Cerebrovascular disease
Hormone problems in some pregnant women increase blood clotting, which increases the risk of Headache and pregnancy: a systematic review of thrombosis, stroke, or meningeal hemorrhage. These conditions are very dangerous: a woman can die within a few minutes or remain disabled.
Vascular involvement is always accompanied by several symptoms:
- severe headache on one side;
- nausea and vomiting;
- blurred vision;
- loss of consciousness;
- convulsions.
What to do
Urgently call an ambulance. The pregnant woman must be laid or seated so that she does not hit when she falls. You can't give medicine! You can only open the window so that there is more air in the room.
What treatment will prescribe Headache and pregnancy: a systematic review by a physician, depends on the specific disease. These can be drugs that reduce blood clotting and dissolve blood clots. In some cases, urgent surgery is needed.
8. Brain Tumors
Studies show that progesterone and estrogen during pregnancy may cause or accelerate the growth of neoplasms in the brain. Symptoms of the disease appear slowly, over several months, and depend on the size and location of the tumor.
Headache may gradually increase Brain tumor, then vision, speech, hearing deteriorate, limbs go numb and convulsions appear. Sometimes it is difficult for a woman to keep her balance.
Sometimes it is difficult for a woman to keep her balance.
What to do
If a pregnant woman often has a headache or she forgets what she wanted to buy in the store and how to cook her favorite borscht, confuses her way home, you need to go to a neurologist. First, he will prescribe standard treatment, simple and safe medicines, rest, good sleep.
If this does not help, the symptoms do not disappear or worsen, a deep examination is needed Brain tumor. The pregnant woman will be sent for an MRI of the brain. This procedure is safe for the fetus. If the diagnosis is confirmed, surgery may be required.
What to do if the doctor cannot find the cause of the pain
If you have been examined and the doctor cannot tell you why your head hurts and diagnoses you with vascular dystonia, this is a reason to be wary. There is no such disease.
Look for another doctor. Perhaps he uses new diagnostic methods that will help to deal with the problem and choose a treatment.
How to avoid headaches during pregnancy
Experts recommend What can I do about headaches during pregnancy? I'd rather not take medication. next:
- Avoid triggers. For example, if you notice that certain foods, smells, or situations cause headaches, try not to encounter them.
- Protect yourself from stress, do not worry about trifles.
- Move more. During pregnancy, walk every day in the fresh air and do special exercises for expectant mothers.
- Correct Pregnancy nutrition: Healthy‑eating basics to eat. Try to eat a lot of vegetables and fruits, dairy products, drink at least 2.4 liters of liquid. Every day, the menu should include fish, poultry or lean meat. And it is better not to buy sweet, fast food and other junk food.
- Observe Working during pregnancy: Do’s and don’ts daily routine. You need to sleep at least 8 hours a day and go to bed no later than 22-23 hours in order for melatonin to be produced normally.