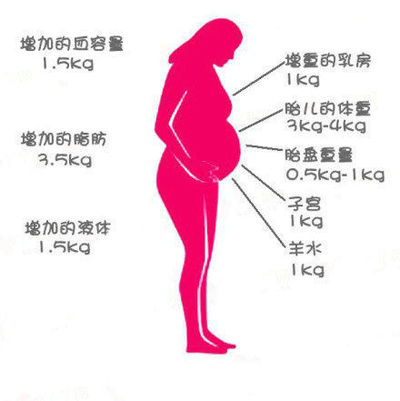
Colds and pregnancy on the first trimester
Association of the common cold in the first trimester of pregnancy with birth defects
Save citation to file
Format: Summary (text)PubMedPMIDAbstract (text)CSV
Add to Collections
- Create a new collection
- Add to an existing collection
Name your collection:
Name must be less than 100 characters
Choose a collection:
Unable to load your collection due to an error
Please try again
Add to My Bibliography
- My Bibliography
Unable to load your delegates due to an error
Please try again
Your saved search
Name of saved search:
Search terms:
Test search terms
Email: (change)
Which day? The first SundayThe first MondayThe first TuesdayThe first WednesdayThe first ThursdayThe first FridayThe first SaturdayThe first dayThe first weekday
Which day? SundayMondayTuesdayWednesdayThursdayFridaySaturday
Report format: SummarySummary (text)AbstractAbstract (text)PubMed
Send at most: 1 item5 items10 items20 items50 items100 items200 items
Send even when there aren't any new results
Optional text in email:
Create a file for external citation management software
. 1993 Oct;92(4):559-63.
J Zhang 1 , W W Cai
Affiliations
Affiliation
- 1 Carolina Population Center, Chapel Hill, NC 27516-3997.
- PMID: 8414827
J Zhang et al. Pediatrics. 1993 Oct.
. 1993 Oct;92(4):559-63.
Authors
J Zhang 1 , W W Cai
Affiliation
- 1 Carolina Population Center, Chapel Hill, NC 27516-3997.
- PMID: 8414827
Abstract
Objective: To examine the association between the common cold with or without fever in the first 3 months of pregnancy and birth defects in offspring.
Design: A case-control study.
Setting: Data are from the Shanghai Birth Defects Monitoring Program, conducted in 29 hospitals in Shanghai, China from October 1, 1986 to September 30, 1987.
Subjects: A total of 986 birth defects cases, 990 frequency-matched live birth controls, and 159 stillbirth controls.
Results: Modestly elevated risk of birth defects was identified among women who reported having a cold with or without fever in the first trimester of pregnancy. Notably increased relative risks were observed for anencephalus (odds ratio [OR] = 3.9, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 2.0 to 7.7), spina bifida (OR = 4.1, 95% CI = 1.7 to 9.7), hydrocephalus (OR = 2.3, 95% CI = 1.1 to 5.1), cleft lip (OR = 2. 2, 95% CI = 1.4 to 3.4), and undescended testicle (OR = 1.8, 95% CI = 1.0 to 3.0). Our study further found that the overall relative risks were consistent by using two different control groups, suggesting that this association was unlikely to be due to recall or report bias.
2, 95% CI = 1.4 to 3.4), and undescended testicle (OR = 1.8, 95% CI = 1.0 to 3.0). Our study further found that the overall relative risks were consistent by using two different control groups, suggesting that this association was unlikely to be due to recall or report bias.
Conclusion: Common cold in the first trimester of pregnancy may be associated with an increased risk of birth defects in offspring. However, these findings should be interpreted cautiously.
Similar articles
-
[A case-control study on birth defects of newborns in Tangshan].
Xu YJ. Xu YJ. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 1989 Aug;10(4):223-6. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 1989. PMID: 2805050 Chinese.
-
Maternal fever and birth outcome: a prospective study.
Chambers CD, Johnson KA, Dick LM, Felix RJ, Jones KL. Chambers CD, et al. Teratology. 1998 Dec;58(6):251-7. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9926(199812)58:63.0.CO;2-L. Teratology. 1998. PMID: 9894674
-
Anencephaly and maternal common cold.
Kurppa K, Holmberg PC, Kuosma E, Aro T, Saxén L. Kurppa K, et al. Teratology. 1991 Jul;44(1):51-5. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420440109. Teratology. 1991. PMID: 1957263
-
Vitamin supplements and the risk for congenital anomalies other than neural tube defects.
Botto LD, Olney RS, Erickson JD. Botto LD, et al. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2004 Feb 15;125C(1):12-21. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.30004. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2004. PMID: 14755429 Review.

-
The safety of quinolones--a meta-analysis of pregnancy outcomes.
Bar-Oz B, Moretti ME, Boskovic R, O'Brien L, Koren G. Bar-Oz B, et al. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2009 Apr;143(2):75-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2008.12.007. Epub 2009 Jan 31. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2009. PMID: 19181435 Review.
See all similar articles
Cited by
-
First-Trimester Maternal Folic Acid Supplementation Modifies the Effects of Risk Factors Exposures on Congenital Heart Disease in Offspring.
Qu Y, Lin S, Bloom MS, Wang X, Nie Z, Ou Y, Mai J, Gao X, Wu Y, Chen J, Justino J, Tan H, Zhuang J, Liu X. Qu Y, et al. Life (Basel). 2021 Jul 21;11(8):724. doi: 10.3390/life11080724.
 Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34440469 Free PMC article.
Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34440469 Free PMC article. -
Gene Environment Interactions in the Etiology of Neural Tube Defects.
Finnell RH, Caiaffa CD, Kim SE, Lei Y, Steele J, Cao X, Tukeman G, Lin YL, Cabrera RM, Wlodarczyk BJ. Finnell RH, et al. Front Genet. 2021 May 10;12:659612. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.659612. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34040637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maternal fever during preconception and conception is associated with congenital heart diseases in offspring: An updated meta-analysis of observational studies.
Yang G, Deng X, Xiao J, Huang P, Zhang K, Li Y. Yang G, et al. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Mar 5;100(9):e24899. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000024899. Medicine (Baltimore).
 2021. PMID: 33655950 Free PMC article. Review.
2021. PMID: 33655950 Free PMC article. Review. -
Environmental mechanisms of orofacial clefts.
Garland MA, Reynolds K, Zhou CJ. Garland MA, et al. Birth Defects Res. 2020 Nov;112(19):1660-1698. doi: 10.1002/bdr2.1830. Epub 2020 Oct 30. Birth Defects Res. 2020. PMID: 33125192 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Associations of maternal upper respiratory tract infection/influenza during early pregnancy with congenital heart disease in offspring: evidence from a case-control study and meta-analysis.
Xia YQ, Zhao KN, Zhao AD, Zhu JZ, Hong HF, Wang YL, Li SH. Xia YQ, et al. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2019 Dec 2;19(1):277. doi: 10.1186/s12872-019-1206-0. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2019. PMID: 31791237 Free PMC article.
 Review.
Review.
See all "Cited by" articles
MeSH terms
Cite
Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Add to Collections
- Create a new collection
- Add to an existing collection
Name your collection:
Name must be less than 100 characters
Choose a collection:
Unable to load your collection due to an error
Please try again
Send To
Pregnant with a cold: Treatments, risks, and prevention
Catching a cold during pregnancy will not harm the fetus, but it can be uncomfortable for the person who is pregnant, and they may also worry about which treatments and medications they can use safely.
Colds are very common. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimate that adults have an average of 2–3 colds per year.
The chances of catching a cold while pregnant are higher because the immune system is less robust during pregnancy.
According to March of Dimes, catching a cold will not harm a developing fetus, and the pregnant person will typically recover in a week or so.
People are also more likely to catch potentially more serious infections, such as the flu, during pregnancy. This means that taking steps to prevent illness is important during pregnancy.
This article looks at what to consider when treating the symptoms of a cold during pregnancy, how to prevent a cold, and when to see a doctor.
Treating a cold usually means using over-the-counter (OTC) medications. However, many pregnant people worry about whether drugs will affect the fetus.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recommend always talking to a doctor before using any pain medication during pregnancy.
Most OTC drugs contain the same few ingredients to treat cold symptoms. The following sections look at the safety of different types of cold treatments.
Pain relievers
Pain relievers are a group of drugs that reduce pain. Some types also reduce inflammation and fever.
OTC pain medications include:
- acetaminophen, under brand names such as Tylenol
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), including naproxen, ibuprofen, and aspirin
Research suggests that acetaminophen is the safest pain relief drug to use during pregnancy, with recommendations to use the lowest effective dosage for the shortest time.
An article published in American Family Physician (AFP) reports acetaminophen to be safe to use during all trimesters on its own, but not necessarily in combination with other cold remedies that contain a range of other ingredients.
However, the article states that NSAIDs may carry risks. They recommend avoiding aspirin during pregnancy except for specific uses and avoiding naproxen and ibuprofen during the third trimester.
Prescription drugs tend to be stronger than OTC drugs and are more likely to carry risks.
The FDA note that prescription NSAIDs may increase the risk of pregnancy loss during the first half of pregnancy and that prescription opioids may increase the risk of birth abnormalities when taken in the first trimester.
Severe and persistent pain can lead to serious effects, such as high blood pressure, depression, and anxiety. It is important to weigh the benefits of taking pain relief drugs during pregnancy against the potential risks.
Always talk to a healthcare professional before deciding to take any medication that relieves pain during pregnancy.
Cough suppressants
OTC cough suppressants often contain medications such as dextromethorphan and guaifenesin.
According to the AFP, these medications appear to be safe during pregnancy in the correct doses. However, it may be best to consider drug-free options as the first line of defense.
For example, before using a cough suppressant medication, people can try using herbal or mentholated throat lozenges to ease a cough or sore throat.
Read more about natural cough remedies here.
Antihistamines
Antihistamines are a popular allergy medication that may relieve a runny nose, watery eyes, or sneezing caused by a cold.
Up to 15% of people use antihistamines during pregnancy, and experts generally consider them safe.
According to the American College of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology (ACCAI), people can use the following during pregnancy:
- diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
- chlorpheniramine (ChlorTrimeton)
- loratadine (Claritin)
- cetirizine (Zyrtec)
Most OTC antihistamines are safe to take in pregnancy as long as a doctor approves them.
Read about some natural antihistamines here.
Decongestants
According to one source, it is safe to take decongestants, such as pseudoephedrine, when directed by a healthcare provider.
However, research has not yet established that decongestants are safe during pregnancy. Some studies suggest that some decongestants, including pseudoephedrine and phenylephrine, may increase the risk of birth abnormalities.
The overall evidence suggests that people use decongestants sparingly during pregnancy, especially during the first trimester.
Saline nasal sprays and nasal strips are safe alternatives for nasal congestion.
Natural remedies
Resting while sick is important to give the body time to focus on recovery. Lying down with the head elevated may help with breathing and stuffiness.
Drinking plenty of water can help people recover from a cold. Juices and smoothies can also provide nutritional intake when people have no appetite.
Many people also use room humidifiers to help clear a stuffy nose and promote a productive cough.
Applying warm compresses to the head, sinuses, and shoulders may help reduce pain and congestion.
Read more about natural remedies for a cold or flu here.
People are also more likely to catch colds and the flu during pregnancy, so it is important to take steps to prevent illness.
To prevent the common cold, the CDC recommend:
- washing the hands often with soap and water for 20 seconds, or using an alcohol-based hand sanitizer when this is not possible
- avoiding touching the face with unwashed hands because viruses that cause colds can enter the body through the eyes, nose, and mouth
- staying away from people who are sick as close contact with others can spread cold viruses.

Light to moderate pregnancy-safe exercises, such as swimming and indoor cycling, can boost the immune system and increase metabolism.
Healthful eating is another important factor in preventing a cold. Focusing on eating a variety of fresh foods can help ensure the body gets the nutrients it needs.
Taking a prenatal vitamin that includes zinc and vitamin C may also help support the immune system and prevent colds.
Many people experience pregnancy rhinitis, which has symptoms similar to a cold.
This occurs due to inflammation and swelling of the mucous membranes in the nose, extra fluid in the body, and changing hormone levels.
Pregnancy rhinitis occurs in around 20% of people. Some people may find it difficult to distinguish rhinitis from a common cold.
The symptoms of pregnancy rhinitis include:
- a runny nose
- congestion
- sneezing
- difficulty breathing
- snoring
A cold during pregnancy is the same as any other cold. The common cold is not likely to not harm the mother or fetus.
The common cold is not likely to not harm the mother or fetus.
People may catch a cold or flu from being around others who are sick. The CDC provide guidance on how to avoid catching the flu.
It is important to know the difference between a cold and the flu. The two have similar symptoms, but the flu tends to be more severe, and a person will usually have a fever.
Read more about pregnancy and the flu here.
If someone experiences a fever during pregnancy, they should contact their doctor to see what steps they can take to reduce the fever to safe levels as quickly as possible.
Having a cold during pregnancy will not usually affect the fetus. Colds are mild illnesses that a person’s immune system can handle relatively easily.
However, the person’s temperature and infections can affect the fetus. If a person is experiencing a fever or other signs of infection, it is essential to speak with a doctor immediately to find the best way to reduce these symptoms.
When a person is pregnant, their body deals with a cold in much the same way as it does at any other time. The symptoms are temporary, and in most cases, the cold will be gone in 7–10 days.
If someone experiences the following symptoms during pregnancy, they should talk to a doctor right away:
- a fever of over 100.4° F
- severe or unusual symptoms
- symptoms that last more than 10 days
- symptoms of the flu
- violent coughing that makes it hard to breathe
Colds are very common during pregnancy, and they are unlikely to harm the pregnant person or fetus.
While there are some uncertainties over the safety of OTC cold remedies during pregnancy, most people can relieve their symptoms using gentle home remedies. Most people will feel better in around a week.
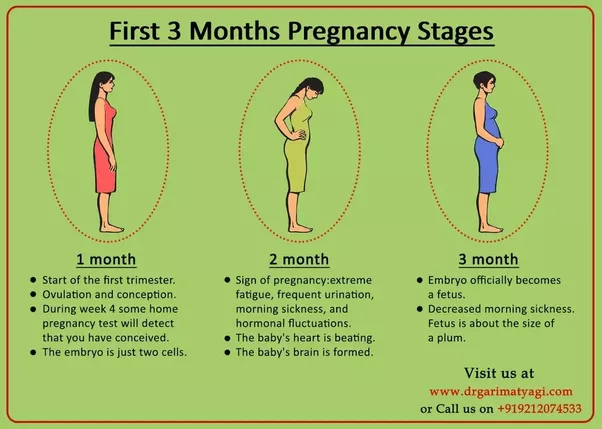
Colds during pregnancy: how to treat?
Any cold or respiratory disease in early pregnancy, during the primary formation of the fetus, can lead to unpredictable consequences and complications. The matter is complicated by the fact that most medications are absolutely contraindicated for use during gestation.
The matter is complicated by the fact that most medications are absolutely contraindicated for use during gestation.
In this regard, the treatment and prevention of colds in pregnant women is an important issue, which should be approached especially responsibly! The main thesis is: be careful with medicines and apply mild preventive measures based on alternative medicine methods to avoid respiratory diseases and flu. nine0003
"One for two - immunity"
This is a very fragile system, it is not necessary to interfere in its work, but it is necessary to support and strengthen it. Pregnancy belongs to the category of special, albeit temporary, conditions during which a woman needs additional protection.
This issue will help simple recommendations that are available to everyone:
• During the period of frequent weather changes, it is necessary to dress warmer, paying special attention to shoes. nine0017 • During an epidemic, it is better for a pregnant woman to refrain from being in crowded places - transport, metro, shops and hospitals. If there is an urgent need, to prevent possible infection, a protective respiratory mask should be worn before leaving the house.
If there is an urgent need, to prevent possible infection, a protective respiratory mask should be worn before leaving the house.
• Be especially careful about hygiene after visiting the street and public places. Upon returning home, the first thing to do is wash your hands thoroughly.
Interesting: More than 90% of all acute respiratory infections are caused by viruses, about 10% are bacteria and other pathogens. Accordingly, any soap can be used, not necessarily antibacterial.
• Before going outside, you can lubricate the nasal mucosa with oxolinic ointment. Upon returning home, flush the upper respiratory tract with soda solution.
• Rationalization of nutrition and intake of vitamins will strengthen the immune defense. It is especially useful to eat fruits and vegetables that are enriched with vitamins and have not undergone heat treatment. nine0003
Interesting: our grandmothers used to say: in order not to get sick, you need to drink chicken broth! Strange, but until recently, scientists did not attach much importance to this prophylactic. Pulmonologist Stefan Rennard decided to find out if this was true or not. The professor conducted a study and proved that the use of chicken broth affects the mobility of neutrophils, white blood cells that protect the body from infections and activate the immune system.
Pulmonologist Stefan Rennard decided to find out if this was true or not. The professor conducted a study and proved that the use of chicken broth affects the mobility of neutrophils, white blood cells that protect the body from infections and activate the immune system.
- Vitamins can be taken using ready-made pharmaceutical multivitamin complexes. Before choosing a drug, you should consult your doctor. nine0035
- Compliance with the regimen and duration of sleep - at least 9 hours a day. The possibility of psychotraumatic situations should be minimized.
- Maintaining cleanliness in the living quarters (ventilation, wet cleaning).
- Air humidification is an important aspect in the prevention of influenza and respiratory diseases. If air conditioners or heaters are used in the house of a pregnant woman, it would be best to purchase a mechanical humidifier. nine0035
Medications for prevention
- Grippferon - a drug in the form of drops for the nose, which provides prevention and treatment of influenza, is not contraindicated for pregnant and lactating women.
 The medicine stimulates an increase in immunity, has a pronounced antiviral effect that can protect against colds, infections and influenza varieties.
The medicine stimulates an increase in immunity, has a pronounced antiviral effect that can protect against colds, infections and influenza varieties. - Ascorbic acid - can be used as a separate source of vitamin C in a synthetic version, with a reduced daily intake from food. Ascorbic acid not only prevents infection, but also fights viruses that have already entered the body of a woman. nine0035
- Viferon - nasal ointment, which is prescribed for the prevention of influenza and respiratory infections during an epidemic. The ointment has protective and immunomodulatory effects, and also allows you to deal with disorders that are already occurring in the body at the time of use. Viferon in the form of a nasal ointment has no contraindications for use in pregnant women at any time, including the first trimester.
- Aquamaris is a natural drug in the form of a nasal spray that allows you to moisturize the nasal mucosa, thereby reducing the risk of influenza viruses entering the nasal cavity.
 nine0035
nine0035
I would like to say a few words about such a method of prevention as vaccination. Most often, the expectant mother may be at risk of infection due to the annual influenza epidemic. This disease is dangerous for a pregnant woman precisely because of its complications: pneumonia, bronchitis, otitis media. Influenza in a pregnant woman can also affect the health of the fetus. Most of all, it is dangerous in the early stages of pregnancy, when the tissues and organs of the human embryo are laid and formed. Viral intoxication or drug exposure can lead to pathology of the child's organs. In later pregnancy, there is a risk of infection of the fetus. nine0003
The most dangerous consequence of influenza in a pregnant woman is threatened miscarriage or premature birth!
It is quite natural that expectant mothers often wonder whether or not to vaccinate.
Studies have concluded that the use of inactivated ("killed") influenza vaccines does not have a teratogenic effect on the fetus and does not harm the health of a pregnant woman. After consulting with your doctor about such an inoculation, you can come to an optimal solution. nine0073 If an influenza epidemic is inevitable, and the pregnant woman has no contraindications, then the vaccine should be given. If a pregnant woman has a negligible risk of infection, she does not come into contact with a large number of people, or is opposed to vaccination, then you can not do it. According to research, it is known that vaccination of mothers reduces the risk of influenza infection of a born child by 63%. Seasonal influenza prevention is carried out in September, October. Vaccinations for pregnant women are recommended from the second trimester of pregnancy. nine0003
After consulting with your doctor about such an inoculation, you can come to an optimal solution. nine0073 If an influenza epidemic is inevitable, and the pregnant woman has no contraindications, then the vaccine should be given. If a pregnant woman has a negligible risk of infection, she does not come into contact with a large number of people, or is opposed to vaccination, then you can not do it. According to research, it is known that vaccination of mothers reduces the risk of influenza infection of a born child by 63%. Seasonal influenza prevention is carried out in September, October. Vaccinations for pregnant women are recommended from the second trimester of pregnancy. nine0003
In the period of a planned pregnancy, a flu shot is given 1 month before it: the formation of immunity occurs 2-4 weeks. Protection after vaccination lasts about a year.
If infection does occur, action should be taken immediately if at least one symptom of the disease is detected. The health of a pregnant woman and her unborn child depends entirely on her responsibility and respect for her own body.
Proven folk remedies will be used first. Since pregnant women cannot steam their legs, steam their hands, and this will facilitate nasal breathing. Bundle up, put on woolen socks and crawl under the covers: warmth, peace and sleep are good for colds. Do not forget to drink plenty of water - hot green tea with lemon and honey, lime blossom tea, cranberry juice, rosehip broth, dried fruit compote. Ginger in the form of tea also helps, not only with catarrhal symptoms, but with nausea in the morning. nine0003
Various hot milk drinks are also suitable. Honey can be added to milk, and it is best to boil it on onions. It must be emphasized right away that not all herbs for colds during pregnancy can be used. Here is a list of medicinal plants that are contraindicated: aloe, anise, barberry, elecampane (grass and root), sweet clover, oregano, St. John's wort, strawberries (leaves), viburnum (berries), raspberries (leaves), lemon balm, lovage, wormwood, licorice ( root), celandine, sage.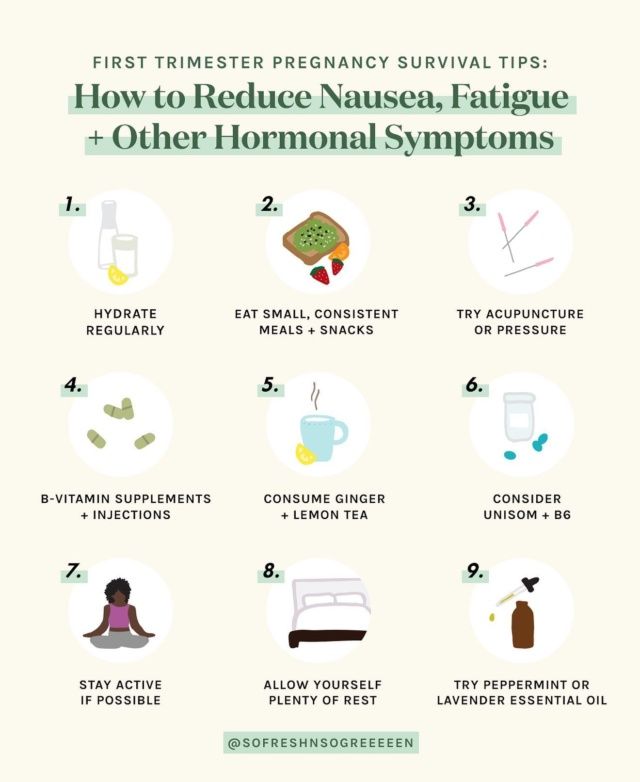 Accordingly, preparations containing these plants should not be taken. nine0003
Accordingly, preparations containing these plants should not be taken. nine0003
The use of medicines for colds during pregnancy must be treated with great care!
It is contraindicated to use the following drugs : Pertussin, Tussin plus, Joset, Glycodin, Ascoril, Travisil, Broncholitin, ACC, Grippeks, Codelac, Terpinkod. Do not use lozenges and lozenges for sore throat or cough are also undesirable due to the likelihood of allergic reactions.
Spray Pinosol, judging by the components indicated in the instructions, is not dangerous during pregnancy. However, the essential oils contained in the preparation - pine, peppermint, eucalyptus, thymol, guaiazulene (wormwood oil) - can lead to an allergic reaction with swelling of the nasal mucosa. nine0003
Viferon suppositories are allowed to be used only after 14 weeks from the start of conception. This drug contains recombinant human interferon alpha-2, ascorbic acid and alpha-tocopherol acetate and has antiviral, immunomodulatory and antiproliferative effects. It is used in the treatment of various infectious and inflammatory diseases in adults and children (including newborns). In the form of an ointment, Viferon is used to treat herpetic lesions of the skin and mucous membranes. The ointment is applied in a thin layer to the affected areas of the skin 3-4 times a day for 5-7 days. nine0003
It is used in the treatment of various infectious and inflammatory diseases in adults and children (including newborns). In the form of an ointment, Viferon is used to treat herpetic lesions of the skin and mucous membranes. The ointment is applied in a thin layer to the affected areas of the skin 3-4 times a day for 5-7 days. nine0003
The homeopathic preparation Stodal, which includes predominantly herbal ingredients, acts on various types of cough and has an expectorant and bronchodilator effect.
Viburkol - homeopathic suppositories - have analgesic, anti-inflammatory, sedative, antispasmodic action. They are prescribed in the complex therapy of acute respiratory viral infections and other uncomplicated infections (including in newborns), as well as in inflammatory processes of the upper respiratory tract and inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system. nine0003
So, you can try to eliminate a slight ailment on your own, but there are conditions under which you need to call a doctor at home:
- Prolonged fever;
- Myalgia, fatigue, fatigue, general malaise;
- Difficulty breathing, nasopharyngeal lumps and dry or wet barking cough;
- A pregnant woman is troubled by severe pressing headache.
 nine0035
nine0035
In conclusion, I would like to emphasize the importance of treating chronic diseases before pregnancy, a healthy lifestyle during childbearing and following all doctor's orders.
I wish expectant mothers and their loved ones to try to maintain a good mood: optimists live longer and happier, they are more productive. Remember your victories and pleasant moments more often and everything will be fine!
Colds ARI, SARS during pregnancy, consequences, treatment
Colds can suddenly take our wonderful future mothers by surprise.
What should I do if I get a cold (ARI/ARVI) during pregnancy?
Is it possible to protect yourself from SARS?
Which medicines are allowed and which are not?
Is it dangerous for the baby?
Pregnancy is a wonderful state, but, unfortunately, even this wonderful period in a woman’s life can be overshadowed by exacerbation of pre-existing chronic diseases of the respiratory system (almost 10% of the population suffers from one or another pathology of the respiratory organs and do not go to the doctor for treatment ).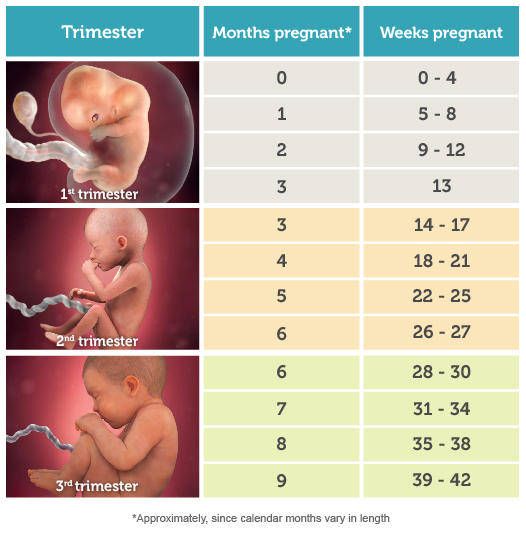 nine0003
nine0003
What is the danger of neglect in acute respiratory infections/ARVI during pregnancy
- The causative agents of viral and infectious diseases can contribute to miscarriage, increased blood loss during childbirth.
- Viruses can also activate existing in the body and other "dormant" infection, contribute to the development of inflammatory diseases of the internal genital organs.
- There is no particular predisposition to infection in pregnant women, but respiratory diseases of an infectious and viral nature in pregnant women are often more severe and give much more complications if treatment is not started on time. nine0035
- The most common diseases in pregnant women are SARS and influenza.
- Colds are dangerous during pregnancy, both in the 1st trimester, 2nd trimester, and 3rd trimester.
ARVI is an acute respiratory viral infection, i.e. The source of the disease is viruses that a sick person releases in large quantities when coughing, sneezing, talking. We are especially prone to viral infections during the cold season, as well as during the transitional periods of autumn and spring - when it is hot during the day, cold in the morning, and sometimes we dress completely inappropriate for the weather. nine0003
We are especially prone to viral infections during the cold season, as well as during the transitional periods of autumn and spring - when it is hot during the day, cold in the morning, and sometimes we dress completely inappropriate for the weather. nine0003
The onset of SARS is usually gradual with a general malaise, lethargy, slight fever, and a runny nose or sore throat.
Influenza, unlike SARS, is more severe and poses a great danger to both mother and fetus. Influenza epidemics recur almost every year, during which 30-40% of the population falls ill.
This is an acute viral disease transmitted by airborne droplets. The influenza virus penetrates through the respiratory tract, affects the mucous membrane, increases the permeability of the walls of blood vessels. The flu virus lowers the immune system, which can exacerbate chronic diseases. The onset of influenza is acute, sudden: 30 minutes ago everything seems to be fine, but now it’s temperature, chills, fever.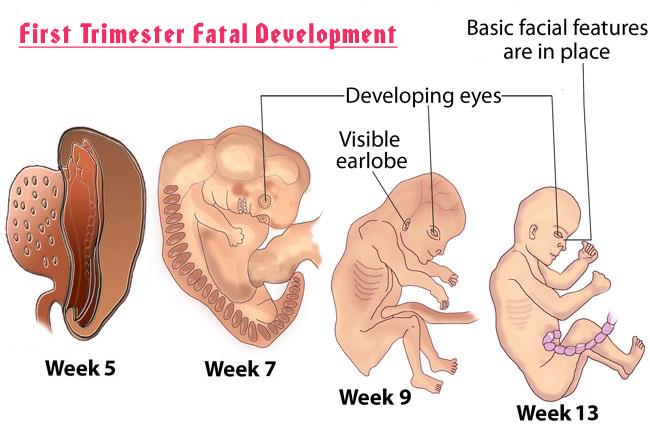 nine0003
nine0003
What to do if you get SARS during pregnancy?
Treat for sure!!!
Do not hope that it will go away on its own and somehow manage to lie down. Even with a slight malaise, the likelihood of complications in a pregnant woman is high.
Be sure to visit a doctor, a competent therapist or general practitioner will give you comprehensive recommendations on drug therapy, as well as the use of home remedies that will not harm you and your baby. nine0003
Do not self-medicate, antiviral drugs, herbs, lozenges, antibiotics and antibacterial drugs should not be taken without a doctor's prescription. Your body during pregnancy may react differently than in normal life.
Is it possible to protect yourself from SARS during pregnancy?
SARS prevention measures are simple and affordable:
- Pregnant women should limit their visits to crowded places with large crowds of people indoors, wash their hands more often (personal hygiene), beware of hypothermia, i.
 e. dress for the season and the weather. nine0035
e. dress for the season and the weather. nine0035 - Proper balanced nutrition, vitamin intake and more positive emotions are of great importance.
- After coming back from the street or working at home, it is a good idea to gargle with sea water and flush the nose.
- Before work, lubricate the nasal cavity with oxolin ointment or peach oil.
- At work and at home, take care of proper air humidification (ionizers, humidifiers)
- Important! Do not forget about regular walks in the fresh air, a full sexual life (if there are no contraindications) and sports (taking into account the physiological characteristics of the pregnant woman)
What medications can be taken during pregnancy if you have ARVI?
- Medications are prescribed individually, based on the situation, the doctor selects.
- You can bring down the temperature with Paracetamol (both tablets and suppositories).
- Absolutely everyone is shown a warm alkaline fortified drink.