Acid reflux sign of early pregnancy
Is Heartburn a Sign of Early Pregnancy?| TUMS
There are so many noticeable changes going on in your body when you’re pregnant. But there are also subtle symptoms of pregnancy you may have before you know you're pregnant. You might be wondering, is heartburn an early pregnancy sign?
Let’s take a look at heartburn and how it might relate to pregnancy symptoms, as well as how to manage some discomfort you might be experiencing.
So, Is Heartburn an Early Sign of Pregnancy?It is—for some women.
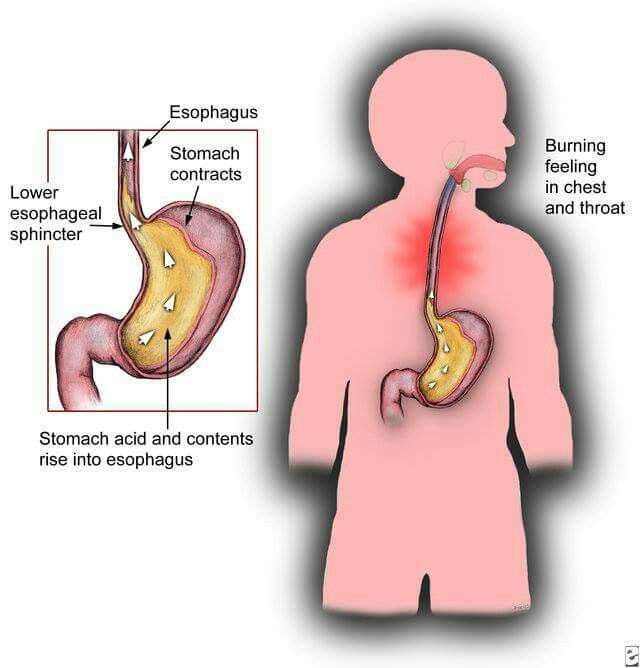
Let’s back up a second and define “heartburn” because, for some women, it might be the first time they’ve experienced this digestive symptom. Heartburn is a term that describes a burning sensation in your chest. You feel heartburn when stomach acid refluxes, or seeps back up, into your esophagus, the part of the digestive track that connects your mouth to your stomach.
While every woman’s body is different, and you can certainly experience heartburn and indigestion without being pregnant, heartburn can occur at any point in a pregnancy1. So, a woman may experience heartburn as an early pregnancy symptom—even before she knows she’s pregnant.
If you have recently been experiencing symptoms of heartburn and indigestion and think you might be pregnant, see your doctor.
Will I experience heartburn while I am pregnant?Possibly—and likely. Many women experience heartburn beyond their first trimester of pregnancy2. There are a few reasons why:
Hormones relax muscles…During pregnancy, a rising level of the hormone progesterone relaxes the valve (known as the lower esophageal sphincter) that separate the stomach and esophagus. As a result, stomach acids can flow back into your esophagus2 and lead to some of the classic uncomfortable heartburn feelings that come with acid indigestion.
…and slow digestionAdditional hormones slow digestion, which mean food may stay in your stomach longer2 and lead to a higher likelihood of acid indigestion.
Later, as a pregnancy progresses and the uterus expands, it puts pressure on other organs in the abdomen3—including the stomach.
So, a stomach getting pushed out of place, with the food in it lingering longer, and a valve to the throat that’s a bit looser. The result? Heartburn.
A baby with lots of hair?You might have heard the old wives’ tale that having heartburn while pregnant means you’ll deliver a baby with a more hair on its head. One small scientific study years ago did find a correlation4! Make of that what you will.
Treatment for Heartburn and Acid Indigestion During Early PregnancyBefore jumping into the possible treatment options for pesky heartburn, confirm you are indeed pregnant with your trusted health care provider. They can help you better understand how to approach your symptoms and decide next steps.
If you are indeed pregnant and experiencing heartburn, we recommend taking the following measures to keep your heartburn symptoms at bay. 3
3
- Avoid foods that flare up your symptoms. These might include spicy foods, fried foods or meals, caffeine such as coffee or soda. Create a journal of foods that you’ve noticed might cause upset stomach.
- Stay away from large meals just before bedtime. This can trigger acid reflux due to your sleeping position.
- Sleep with a pillow wedge that raises your head to deter acid reflux.
- Consult with your doctor to determine whether an antacid, like TUMS, would be right for you.
While it’s no fun to experience heartburn and acid indigestion, talk to your care provider about the many tools and resources to help you manage. Whether together you decide you should use TUMS to help manage your symptoms or find comfort in pairing antacids with other preventative measures, you have options.
Read more about heartburn and pregnancy and other heartburn and indigestion-related issues.
Sources
- Simerpal Kaur Gill, Caroline Maltepe and Gideon Koren. The effect of heartburn and acid reflux on the severity of nausea and vomiting of pregnancy. Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology, April 2009. 23(4):270-272. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2711677/
- Juan C Vazquez. Heartburn in pregnancy. BMJ (British Medical Journal) Clinic Evidence, 2015; 2015: 1411. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4562453/
- Pregnancy – signs and symptoms. Department of Health, State Government of Victoria, Australia. https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/HealthyLiving/pregnancy-signs-and-symptoms.
- Kathleen A. Costigan, Heather L. Sipsma and Janet A. DiPietro. Pregnancy Folklore Revisited: The Case of Heartburn and Hair. Birth: Issues in Perinatal Care, November 2006. Volume 33, Issue 4 p. 311-314. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1523-536X.
 2006.00128.x
2006.00128.x
7 early pregnancy signs: Heartburn, gas, tender breasts, and more
Photo: iStockphoto
When you’re hoping to be pregnant and you haven’t missed your period yet—or it’s a day or two late—it’s pretty easy to interpret nearly any physical symptom as a sign of pregnancy. It’s not uncommon to feel symptoms in the first week or two of your pregnancy—or even earlier. “Some women experience pregnancy symptoms from the moment of conception,” says Karen Nordahl, a general practitioner and obstetrician in Vancouver and co-author of Fit to Deliver. “Usually, this is second- or third-time moms who remember a particular sensation, such as increased gas.” But many first-time moms miss these early pregnancy signs because the very first symptoms aren’t necessarily the ones we associate with having a baby on the way. So, yes, while some women experience nausea or hypersensitivity to smells, these seven symptoms are among the most common during the first few weeks of pregnancy.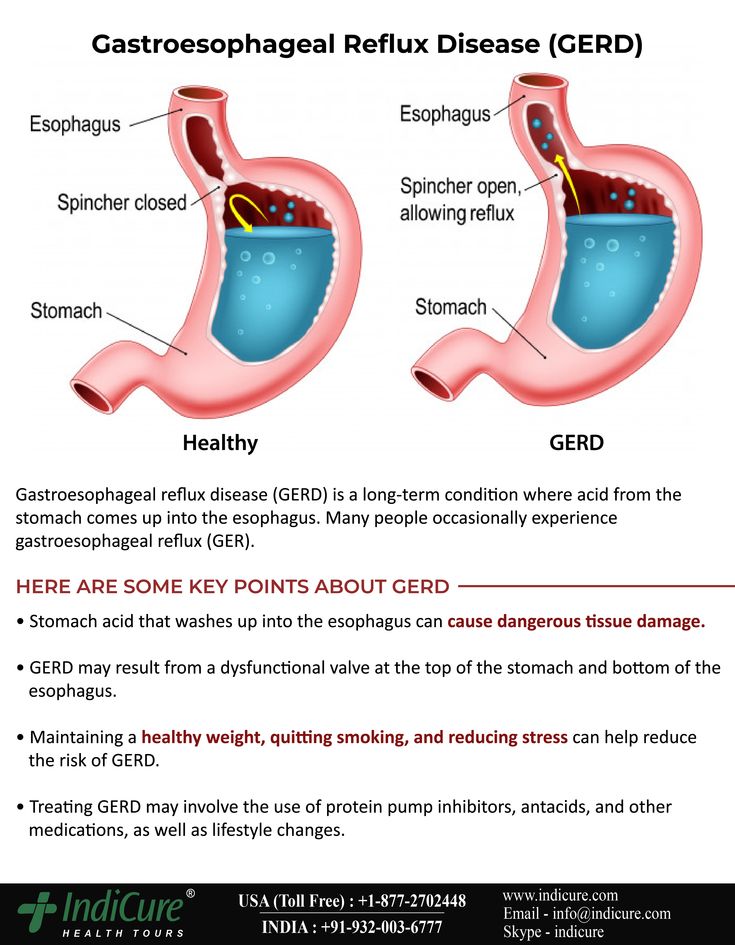
Digestive changes are one of the most common early pregnancy signs, says Nordahl. If you feel a burning sensation in your chest after scarfing down your usual black coffee and egg-salad sandwich from the deli near your office, it might not be that the deli changed the recipe to include green onions or switched coffee brands; it could actually be pregnancy-related heartburn. One telltale sign of heartburn is that the burning sensation can feel worse when you bend over or lie down. It’s safe to reach for an antacid to relieve the burning, but also try to avoid certain foods, such as citrus fruits.
2. Pregnancy sign: Sore breasts Before you start cursing your bra for suddenly feeling more like a contraption from the hardware store than the lacy lingerie that took a serious chunk out of your paycheque, consider that your newly sore boobs could be a sign that you’re pregnant.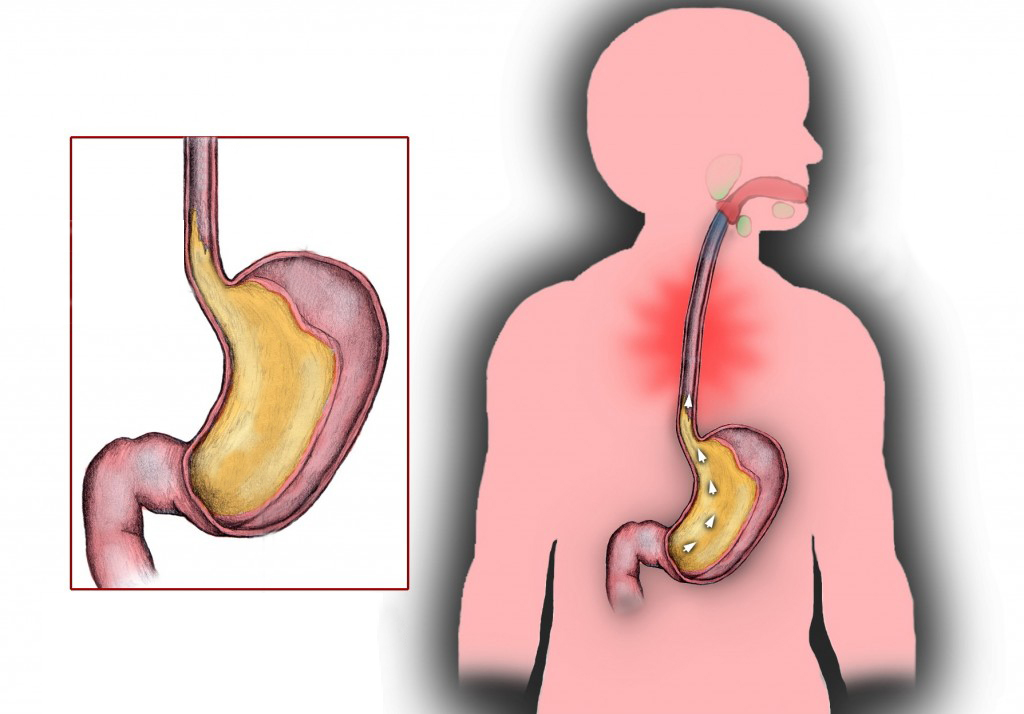 Breast tenderness is another common early pregnancy sign, according to Nordahl. For many women, what can make this symptom particularly confusing is that breast soreness is also a very common sign of your period. But early on in your pregnancy, your breasts may hurt because they’re expanding in preparation for producing milk.
Breast tenderness is another common early pregnancy sign, according to Nordahl. For many women, what can make this symptom particularly confusing is that breast soreness is also a very common sign of your period. But early on in your pregnancy, your breasts may hurt because they’re expanding in preparation for producing milk.
Being gassy—or, less eloquently, “farty”—is no problem when you’re chillaxing alone in your threadbare sweatpants, but it’s next-level horrifying when you’re out and about anywhere else. Unfortunately, it’s one of the more common early pregnancy signs. Expect flatulence during not only the first few weeks of pregnancy but also the next nine months. Inevitably, your unruly gas will strike right in the middle of a work meeting or during a cool-down in your silent yoga class.
4. Pregnancy sign: Bloating Can’t zip up those light-wash jeans that fit like a glove a few weeks ago? It could be that extra-large soda and popcorn you inhaled while transfixed on the onscreen hunk at the cinema last night, but it could also be a sign that you’re expecting.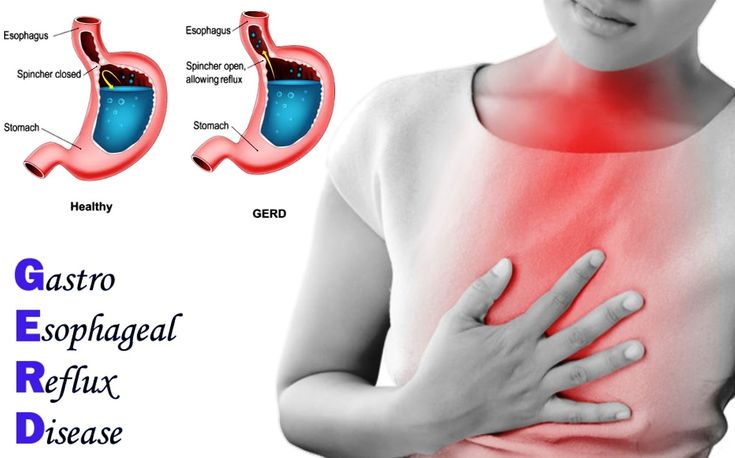 Like breast tenderness, abdominal bloating is a symptom that’s common before your period, making it hard to tell apart from monthly premenstrual symptoms. The usual tactic to fight extra bloating and constipation is to ease up on excess salt and stay hydrated with water, both of which are good habits, whether you’re pregnant or not. But you might also want to buy a pregnancy test.
Like breast tenderness, abdominal bloating is a symptom that’s common before your period, making it hard to tell apart from monthly premenstrual symptoms. The usual tactic to fight extra bloating and constipation is to ease up on excess salt and stay hydrated with water, both of which are good habits, whether you’re pregnant or not. But you might also want to buy a pregnancy test.
Pelvic cramping as an early pregnancy sign? Yep, it can be, according to Nordahl. That might seem counterintuitive, as cramps are super-typical symptoms of Aunt Flow. You were probably hoping that being pregnant meant you could kiss cramps goodbye, but sadly that’s not the case. Light cramps can be caused by early pregnancy hormonal shifts and implantation of the fertilized egg on your uterine lining.
6. Pregnancy sign: Fullness The unusual sensation of feeling “full” is yet another early symptom of pregnancy. “Fullness can be experienced before a period is missed, but a first-time mom may miss it,” says Nordahl. “A second- or third-time mom may pick up on it right away, especially if she is actively trying to conceive.” If you’re getting a feeling of déjà vu from previous pregnancies that you’re experiencing at the gut level (literally), congrats, you could be preggo!
“Fullness can be experienced before a period is missed, but a first-time mom may miss it,” says Nordahl. “A second- or third-time mom may pick up on it right away, especially if she is actively trying to conceive.” If you’re getting a feeling of déjà vu from previous pregnancies that you’re experiencing at the gut level (literally), congrats, you could be preggo!
Well, duh, of course a missed period is the most common of early pregnancy signs. For many women who haven’t been pregnant before, this is usually the first symptom they notice, explains Nordahl. But hindsight is often 20/20. “A first-time mom usually thinks back and realizes that a few things were different but wasn’t sure what they meant,” she says.
90,000 GERD during pregnancy. What is GERD during pregnancy? IMPORTANT
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor.
GERD during pregnancy is an acid-dependent disease of the esophagus caused by damage to the mucosa during the reflux of stomach contents, which has arisen or worsened under the influence of gestational factors. Manifested by heartburn, sour eructation, odynophagia, less often - nausea, vomiting, dysphagia, epigastric pain, cough, dysphonia, hypersalivation in sleep, taste perversions, depressed mood. It is diagnosed using alkaline and omeprazole tests, esophagoscopy, pH-metry, manometry. For treatment, alginates, antacids, selective histamine blockers, drugs that inhibit the proton pump, prokinetics are used. nine0006
ICD-10
K21 Gastroesophageal reflux
- Causes
- Pathogenesis
- Classification
- Symptoms of GERD during pregnancy
- Complications
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of GERD during pregnancy
- Prognosis and prevention
- Prices for treatment
General
GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastroesophageal reflux) is one of the most common diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, contributing to such a common symptom as pregnancy heartburn.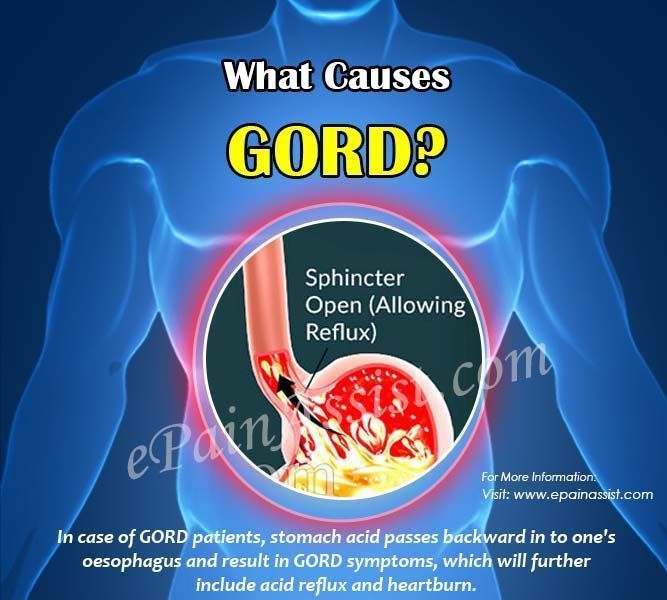 According to the observations of specialists in the field of obstetrics and gynecology, from 30 to 95% of patients during the period of bearing a child experience heartburn, which some experts even consider a natural manifestation of pregnancy. In 21-80% of patients suffering from GERD, the disease debuted precisely in connection with gestation.
According to the observations of specialists in the field of obstetrics and gynecology, from 30 to 95% of patients during the period of bearing a child experience heartburn, which some experts even consider a natural manifestation of pregnancy. In 21-80% of patients suffering from GERD, the disease debuted precisely in connection with gestation.
Women who have given birth multiple times are more susceptible to the disease. The relevance of timely detection of gastroesophageal reflux is due to a significant deterioration in the quality of life of a pregnant woman and the need to prescribe pharmacotherapy to almost half of the patients.
GERD during pregnancy
Causes
Gastroesophageal reflux of acidic gastric contents develops with a weakening of the cardiac sphincter, impaired motility of the esophagus and stomach, increased gastric secretion, and a decrease in the protective properties of the esophageal mucosa. The occurrence of GERD is promoted by congenital and acquired hernia of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm with displacement into the posterior mediastinum of the abdominal esophagus, part or all of the stomach, smoking, dietary errors, and obesity. nine0006
The occurrence of GERD is promoted by congenital and acquired hernia of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm with displacement into the posterior mediastinum of the abdominal esophagus, part or all of the stomach, smoking, dietary errors, and obesity. nine0006
A certain role is played by the intake of nitrates, antidepressants, progestins, anticholinergics, calcium channel blockers and other drugs that cause transient relaxation of the esophageal sphincter. Specialists in the field of modern gastroenterology consider pregnancy as a separate prerequisite for the development of gastroesophageal reflux disease. The high incidence of GERD during gestation is associated with the action of factors such as:
- Increased progesterone levels. Under the action of progestins, the lower esophageal sphincter relaxes, the tone of which is restored only in the postpartum period. By reducing the tone of smooth muscle fibers and reducing the sensitivity of intestinal receptors to histamine and serotonin, physiological hyperprogesteronemia slows down gastrointestinal motility and impairs gastric emptying.
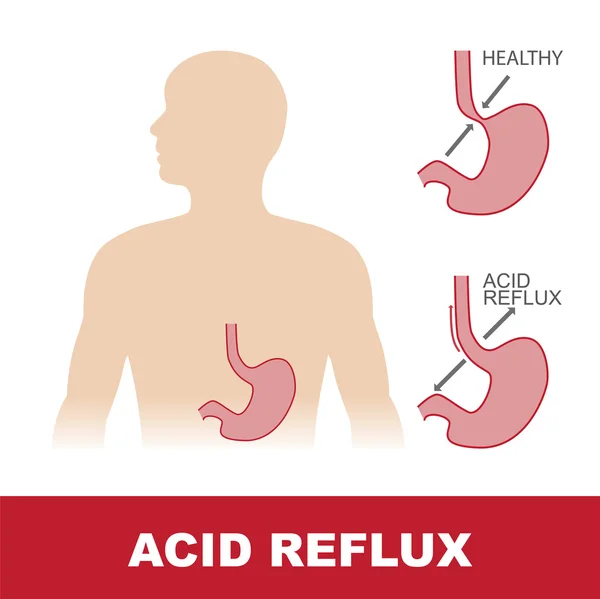 As a result, reflux occurs more frequently.
As a result, reflux occurs more frequently. - Increased intra-abdominal pressure. During pregnancy, the relative position of the internal organs of the abdominal cavity is disturbed, which is associated with the development of the fetus and the growth of the uterus. When the stomach is displaced towards the diaphragm, evacuation stagnation of its contents is formed faster and the risk of diaphragmatic hernia formation increases. The factor of increasing intra-abdominal pressure is most significant in carrying multiple pregnancies and large fetuses. nine0016
Pathogenesis
The mechanism of development of GERD during pregnancy is based on the reflux of aggressive stomach contents into the lower esophagus. Gastroesophageal reflux usually occurs when the pressure of the cardiac sphincter is less than 2 mm Hg. Art. or an increase in intragastric pressure of more than 5 mm Hg. Art. Both of these factors are found in pregnant women. Refluxate containing hydrochloric acid, pepsin, and in some cases bile acids, has an irritating effect on the epithelium of the esophagus, causes a local inflammatory reaction, and in some patients provokes the onset of erosive processes. nine0006
nine0006
Classification
When systematizing the forms of GERD in pregnant women, the same criteria are taken into account as outside the gestational period - the nature of the course of the disease and the condition of the esophageal mucosa. This approach makes it possible to develop optimal medical tactics aimed at eliminating clinical symptoms and the morphological basis of their occurrence without the risk of negative effects on the fetus. Depending on the time of existence of the disorder, acute gastroesophageal reflux disease is distinguished, lasting up to 3 months, and a chronic process that exists for 3 months or more. Taking into account the characteristics of damage to the esophageal mucosa, such forms of GERD are distinguished as: nine0006
- Gastroesophageal reflux without esophagitis. With a non-erosive variant of the disorder, detected in 55-70% of patients, there are no endoscopic signs of damage to the epithelium. Although the likelihood of complications in this case is lower, the patient's quality of life deteriorates in the same way as in the presence of erosions.

- Reflux esophagitis. In 30-45% of pregnant women with GERD during endoscopy, visible signs of esophagitis caused by the aggressive action of the contents of the stomach are determined. In the erosive form of gastroesophageal reflux, acute and long-term consequences of the disease are more often observed. nine0016
When predicting the outcome of GERD in a pregnant woman, the severity of the endoscopically positive variant of the disease according to the Los Angeles classification is also taken into account. The most favorable during pregnancy is reflux esophagitis A and B degrees, in which the defects extend to 1-2 folds of the mucosa, and their sizes, respectively, are up to or more than 5 mm. With C degree of GERD, less than 75% of the esophageal circumference is affected, and with D - 75% or more, which significantly increases the likelihood of a complicated course. nine0006
Symptoms of GERD during pregnancy
75% of patients with gastroesophageal reflux complain of heartburn, which gradually increases as labor approaches.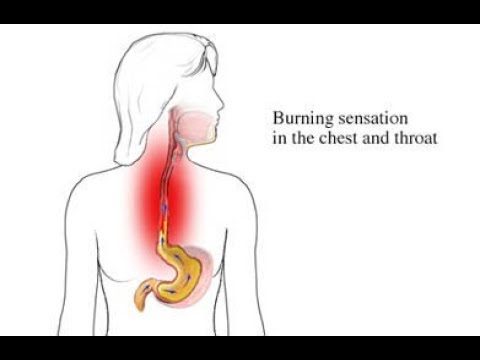 Discomfort and burning behind the sternum often occur after eating spicy, fatty, fried foods, overeating, exercise, lying down and bending over. Heartburn attacks can recur several times a day and last from minutes to several hours. Pregnant women suffering from GERD may experience sour or bitter belching, sensation of a lump in the throat, retrosternal pain when swallowing with irradiation to the precordial region, neck, lower jaw, interscapular space. nine0006
Discomfort and burning behind the sternum often occur after eating spicy, fatty, fried foods, overeating, exercise, lying down and bending over. Heartburn attacks can recur several times a day and last from minutes to several hours. Pregnant women suffering from GERD may experience sour or bitter belching, sensation of a lump in the throat, retrosternal pain when swallowing with irradiation to the precordial region, neck, lower jaw, interscapular space. nine0006
Sometimes in the II-III trimesters, nausea and vomiting are noted, it is extremely rare that swallowing solid and then liquid food is difficult. Extra-esophageal manifestations of reflux disease during pregnancy are a feeling of fullness in the epigastrium, rapid satiety, repeated attacks of coughing and suffocation, a hoarse voice, sore throat, increased salivation during sleep, burning cheeks and tongue, taste perversion, bad breath. Often, pregnant women experience a sad, depressed mood. Rarely, GERD is asymptomatic. nine0006
nine0006
Complications
Usually, gastroesophageal reflux does not contribute to the occurrence of any obstetric complications, however, with extensive erosive damage to the esophagus, a more pronounced anemia of pregnant women may develop. In two thirds of patients, GERD worsens during pregnancy: in 10-11% of cases, a relapse occurs in the 1st trimester, aggravated by early toxicosis, in 33-34% - in the 2nd trimester, and in more than half of pregnant women - in the 3rd.
Rare specific complications that occur against the background of physiological immunodeficiency during pregnancy are acute esophagitis caused by candidal and herpes infections. There is a risk of ulceration of the mucosa with the development of esophageal bleeding. Long-term consequences of reflux disease are narrowing (strictures) of the esophagus, dysplasia and metaplasia of the epithelium (Barrett's esophagus) and esophageal adenocarcinoma. nine0006
Diagnostics
In pregnancy, the diagnosis of GERD is usually made on the basis of typical clinical symptoms with daily occurrence of heartburn. An obstetrician-gynecologist and a gastroenterologist are involved in the diagnosis. Instrumental methods traditionally used in the diagnosis of the disease are used to a limited extent in pregnant women due to the possible provocation of preterm labor and the aggravation of other complications (nephropathy, early toxicosis, preeclampsia, eclampsia). Recommended for diagnostic purposes: nine0006
An obstetrician-gynecologist and a gastroenterologist are involved in the diagnosis. Instrumental methods traditionally used in the diagnosis of the disease are used to a limited extent in pregnant women due to the possible provocation of preterm labor and the aggravation of other complications (nephropathy, early toxicosis, preeclampsia, eclampsia). Recommended for diagnostic purposes: nine0006
- Alkaline test. Reception of absorbable antacids quickly stops an attack of heartburn. The positive effect of alkaline preparations is associated with the neutralization of hydrochloric acid coming from the stomach into the esophagus. In the presence of extraesophageal manifestations, the study is supplemented with an omeprazole test aimed at eliminating symptoms by inhibiting gastric secretion.
- Endoscopy of the esophagus. Esophagoscopy is performed if extensive erosion, ulceration, esophageal bleeding, strictures are suspected, and neoplasia can be ruled out. In endoscopic examination, GERD is manifested by swelling and slight vulnerability of the esophageal mucosa, it is possible to identify areas of damaged epithelium.
 In some cases, it is possible to visualize the reflux of gastric juice. nine0016
In some cases, it is possible to visualize the reflux of gastric juice. nine0016 - Intraesophageal pH-metry. The method is effective in non-erosive forms of gastroesophageal reflux. Electrometric determination of the acidity of the contents of the esophagus is carried out using a flexible intraesophageal probe attached to an acidogastrometer. pH-metry allows you to identify episodes of reflux of gastric juice and determine the conditions for their occurrence.
- Manometry. Registration of pressure in different parts of the gastrointestinal tract using special catheters with strain gauges verifies the weakening of the cardiac sphincter and dysmotility. A manometric study also provides an objective assessment of elasticity, tone, contractile activity of the esophageal wall, and pressure profiling in the esophagus. nine0016
If necessary, the examination is supplemented with gastrocardiomonitoring, gastrointestinal impedancemetry, bilemetry. X-ray studies of the esophagus during pregnancy are not performed. GERD is differentiated from functional dyspepsia, gastric and duodenal ulcers, acute infectious esophagitis, benign tumors and esophageal cancer. If extraesophageal symptoms are detected, differential diagnosis with angina pectoris, bronchial asthma may be required.
GERD is differentiated from functional dyspepsia, gastric and duodenal ulcers, acute infectious esophagitis, benign tumors and esophageal cancer. If extraesophageal symptoms are detected, differential diagnosis with angina pectoris, bronchial asthma may be required.
Treatment of GERD during pregnancy
Therapeutic tactics are aimed at the rapid elimination of clinical symptoms, restoration of the esophageal mucosa, prevention of complications and relapses. In 25% of cases, the condition can be improved by non-drug methods. Pregnant women with mild GERD are recommended to stop smoking, correct diet and diet with frequent small meals, reduce the amount of high-protein and low-lipid foods, and exclude citrus juices, chocolate, caffeine-containing drinks, spices, mint, and alcohol. nine0006
Care must be taken when using drugs that transiently reduce the tone of the cardia. Efficient sleep with a raised headboard, chewing chewing gum with calcium carbonate. Identification of severe clinical symptoms requires the appointment of special drug therapy. During pregnancy, some of the drugs used in standard treatment regimens for gastroesophageal reflux are used with caution due to possible effects on the fetus or the occurrence of obstetric complications. Patients with severe GERD are shown: nine0006
Identification of severe clinical symptoms requires the appointment of special drug therapy. During pregnancy, some of the drugs used in standard treatment regimens for gastroesophageal reflux are used with caution due to possible effects on the fetus or the occurrence of obstetric complications. Patients with severe GERD are shown: nine0006
- Nonabsorbable antacids and alginates. Considered 1st line drugs for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease in pregnant women. By neutralizing hydrochloric acid, reducing the digestive capacity of pepsin, adsorbing lysolecithin, bile acids, improving the evacuation of stomach contents, stimulating the secretion of prostaglandins, antacids reduce the damaging effect of refluxate. Alginates have a protective effect on the esophageal mucosa.
- Histamine h3 receptor blockers. They are used when antacid therapy for GERD is ineffective. The antisecretory activity of selective histamine blockers is due to the action on the receptors of the parietal cells of the stomach.
 Due to inhibition of secretion, the acidity and volume of gastric contents decrease, which helps to reduce its aggressiveness and pressure on the cardiac sphincter. The effect of h3-histamine blockers on the fetus is not well understood, which limits their use. nine0016
Due to inhibition of secretion, the acidity and volume of gastric contents decrease, which helps to reduce its aggressiveness and pressure on the cardiac sphincter. The effect of h3-histamine blockers on the fetus is not well understood, which limits their use. nine0016 - Proton pump inhibitors. High efficiency and rapid achievement of therapeutic results in the appointment of PPIs are based on blocking the secretion of hydrochloric acid at the level of the secretory tubules of parietal cells. The limited use of pump inhibitors is due to a decrease in the bactericidal properties of gastric juice, which, against the background of natural suppression of immunity, contributes to the development of food infections and impaired calcium absorption, which is necessary for the normal course of gestation. nine0016
As additional means, prokinetics that improve gastrointestinal motility and herbal enveloping preparations can be used. During gestation, surgical treatment of severe and complicated forms of GERD is not performed. Pregnancy is recommended to be completed by natural childbirth at a physiological time. Caesarean section is performed when obstetric indications are identified.
Pregnancy is recommended to be completed by natural childbirth at a physiological time. Caesarean section is performed when obstetric indications are identified.
Prognosis and prevention
With the appointment of adequate treatment, the damaged mucosa of the esophagus usually fully recovers after 4-12 weeks, with non-erosive variants of the disease, improvement occurs within 4-10 days. Prevention of gastroesophageal reflux involves the normalization of diet and lifestyle: giving up bad habits, adequate rest and sleep, controlling weight gain with a tendency to obesity, eliminating foods that irritate the esophageal mucosa or stimulate gastric hypersecretion, taking drugs that can disrupt gastrointestinal motility, only as directed and under medical supervision. To prevent recurrence of GERD in a pregnant woman, a 1-3-day intake of alginates and antacids "on demand" is recommended when symptoms appear. nine0006
You can share your medical history, what helped you in the treatment of GERD in pregnancy.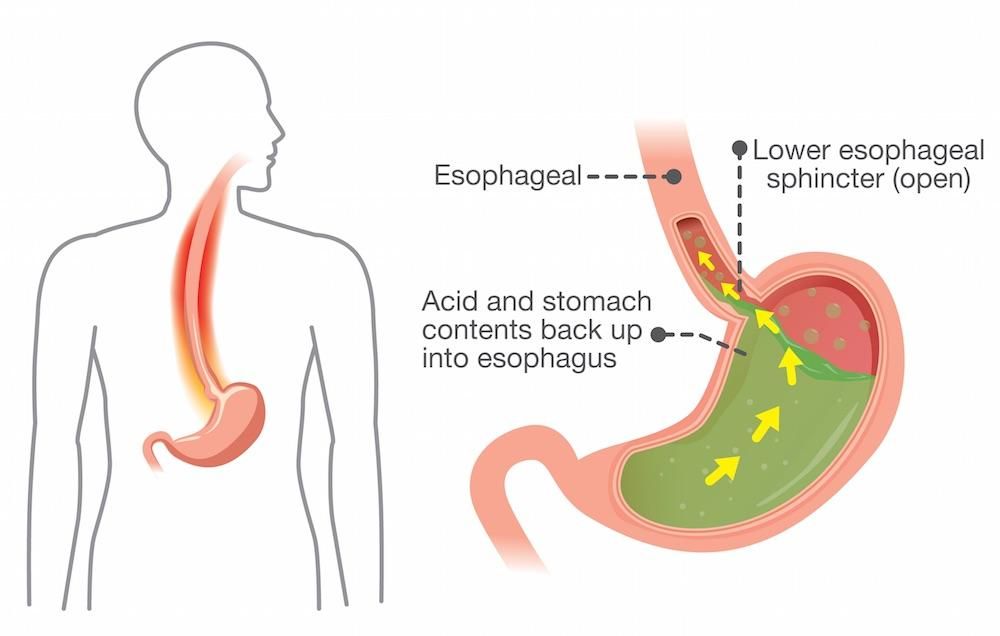
Sources
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease during pregnancy/ Elohina TB, Tyutyunnik VL// Experimental and clinical gastroenterology. - 2009 - No. 3.
- Pregnancy heartburn: an everyday trifle that must be endured, or gastroesophageal reflux disease that should be stopped? / Argunova IA// Gastroenterology. - 2015 - No. 3. nine0016
- Features of the course of gastroesophageal reflux disease in pregnant women/ Grishechkina IA, Kusakina AA, Miermanova MK// Young scientist. - 2015. - No. 13.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease / Babak O.Ya., Fadeenko G.D. – 2000.
- This article was prepared based on the materials of the site: https://www.krasotaimedicina.ru/
IMPORTANT
Information from this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor. nine0006
nine0006
Toxemia, Intestinal Problems & Heartburn
Find out how pregnancy affects the digestive tract, which trimesters are more likely to cause indigestion and nausea, and what to do to manage them.
During pregnancy, the burden on the mother's body increases. The body needs more nutrients, the body produces additional hormones. And the growing fetus puts pressure on neighboring organs, including the stomach and intestines. We tell you what symptoms are observed in each trimester, how to cope with toxicosis and get rid of heartburn. nine0006
Contents:
- 2. Toxicosis and pregnancy
- 3. Causes, risks and treatment of diarrhea during pregnancy
- 4. Heartburn and stomach pain during pregnancy
- 5. Bloating, constipation and microbiota during pregnancy
- 6. Note
Changes in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract by trimesters of pregnancy
The average duration of pregnancy is 40 weeks, which are usually divided into trimesters in accordance with the stages of intrauterine development of the child. nine0006
nine0006
Each trimester is accompanied by a number of changes in the body, including in the gastrointestinal tract:
| The first trimester 26 weeks | Third trimester of pregnancy 27–40 weeks |
| Morning sickness Morning sickness 9 |
The Atlas Genetic Test will help you find out how your genes affect the level of female sex hormones necessary for fertility and pregnancy.
Causes of gastrointestinal problems during pregnancy
Every pregnancy is accompanied by inevitable changes in the functioning of the digestive system. They are most often caused by hormonal changes and increased stress on the organs, but they can also be associated with lifestyle and health conditions, for example:
- Sedentary lifestyle and unbalanced diet; nine0016
- Certain drugs, including calcium or aluminum antacids;
- Viral and bacterial infections;
- Intolerance to certain nutrients and allergic reactions;
- Stress;
- Diseases of the thyroid gland.
If you have chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and you are planning a pregnancy, try to consult your doctor in advance. Symptoms of conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or acid reflux are more likely to get worse during pregnancy. Your doctor will help prepare your body and create a prevention plan to help relieve symptoms during this time. nine0006
Irritable bowel syndrome, or IBS, is a functional bowel disease that causes frequent abdominal pain, impaired peristalsis, bloating, constipation, or diarrhea.
Morning sickness, vomiting and general malaise during pregnancy
Morning sickness and morning sickness during early pregnancy are common, because the body undergoes important changes necessary for the development of the child.
up to 90%
women experience nausea during pregnancy
Doctors find it difficult to say with certainty why pregnant women feel sick in the morning. The main theory is hormonal changes. But there are some patterns associated with an increased risk of morning sickness:
The main theory is hormonal changes. But there are some patterns associated with an increased risk of morning sickness:
- Multiple pregnancy;
- Toxicosis during a previous pregnancy;
- History of morning sickness during pregnancy in close relatives;
- Tendency to motion sickness in transport;
- Use of oral contraceptives containing estrogen before pregnancy; nine0016
- Frequent migraines;
- BMI 30 and above;
- Increased levels of stress hormones
Risks of severe morning sickness and how to reduce nausea
Nausea and vomiting are usually not associated with a risk for mother and child and will pass by 16-20 weeks of pregnancy, but it is not necessary to wait so long - there are ways that can help reduce nausea and enjoy the process of waiting for a new person:
- Get plenty of rest - fatigue increases toxicosis; nine0016
- Avoid smells and foods that cause nausea;
- Eat something right after waking up.
 A toast or a slice of bread will help reduce nausea;
A toast or a slice of bread will help reduce nausea; - Avoid hunger - empty stomach increases nausea. Eat small meals often, prefer low-fat, high-carbohydrate foods;
- Try ginger - studies show it helps with nausea;
- Sip as often as possible and prefer still water. nine0016
In rare cases, pregnant women may develop hyperemesis gestationis or excessive vomiting. This is a serious condition that can lead to dehydration, kidney damage, seizures, abnormal heart rhythms, and even death.
Signs of dehydration include dry mouth, dizziness, dark urine, infrequent urination and/or dizziness.
Symptoms of excessive pregnancy vomiting:
- frequent nausea for a long time and regular vomiting after meals;
- dry skin and lips;
- sudden weight loss;
- low blood pressure (below 90/60).
If symptoms of excessive pregnancy vomiting occur, do not wait until the condition resolves on its own. It is necessary to seek medical help as soon as possible - the doctor will prescribe treatment, help adjust the diet and lifestyle of the expectant mother.
It is necessary to seek medical help as soon as possible - the doctor will prescribe treatment, help adjust the diet and lifestyle of the expectant mother.
0.5–2%
pregnant women experience excessive vomiting
Diarrhea during pregnancy
The word "diarrhea" comes from the Greek language and literally means "to flow through". This is a condition during which bowel movements or bowel movements occur three times a day or more often. This phenomenon is especially typical for the third trimester of pregnancy, but it can also occur earlier.
Symptoms of diarrhea:
- Three or more bowel movements per day
- Urgent urge to have a bowel movement
- Abdominal pain and cramps
- Bloating
Causes of diarrhea during pregnancy poisoning, dysbacteriosis, bacterial and viral infections:
| Gastroenteritis | Lactose and gluten use for those intolerant to these nutrients |
| Bacterial infections: listeriosis or salmonella | Chronic gastrointestinal diseases: Crohn's disease, IBS, ulcerative colitis |
| Some antibiotics and antacids to reduce acidity | Laxatives |
| Sugar substitutes such as sorbitol | Overconsumption of certain foods |
Tip: If you have recently returned from a holiday in an exotic country with nausea and diarrhea and find out you are pregnant, see your doctor as soon as possible. nine0267
nine0267
Gastroenteritis
One common cause of diarrhea during pregnancy is gastroenteritis, or stomach flu. It is caused by bacterial or viral infections: norovirus, rotavirus, E. coli, salmonella, which enter the body through contact with contaminated surfaces, dishes, food and water.
Gastroenteritis usually lasts about three days. However, severe illness is a health hazard, especially during pregnancy, as it can cause dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and lead to preterm labor. nine0006
The main symptoms of gastroenteritis include diarrhea without blood, nausea and vomiting, stomach cramps and pain, slight fever, headache and muscle pain.
Take extra precautions to reduce your risk of getting sick: frequent handwashing and surface disinfection. If the expectant mother has small children, they are not recommended to use the same cutlery.
Risks of diarrhea during pregnancy
Usually diarrhea during pregnancy is not a cause for concern. However, you should consult a doctor if the following symptoms occur during this period:
However, you should consult a doctor if the following symptoms occur during this period:
- Diarrhea for more than two days;
- Stools with blood or mucus;
- Sudden weight loss;
- Abdominal pain;
- Dehydration.
How to treat diarrhea during pregnancy
If you have diarrhea during pregnancy, drink plenty of fluids, avoid foods high in fat and sugar, avoid dairy products, and caffeinated drinks.
Dehydration is a serious risk, especially during pregnancy, so electrolyte balance should be restored first with fluids and simple foods:
| Moderate fruit juices | Drinks without alcohol and caffeine |
| Bananas | Potato |
| Rice | Toast |
| Rusks | Light soups and broths |
| Pasta | Applesauce |
Find out about your body's ability to break down lactose and gluten with the Atlas Microbiota Test. nine0267
nine0267
Stomach pain and heartburn during pregnancy
Many women experience stomach pain during pregnancy, especially the upper part of the stomach, as well as heartburn - a burning sensation in the chest and esophagus.
This is more common in the third trimester, after about 27 weeks. This is an unpleasant but natural phenomenon during pregnancy: the baby grows inside the uterus and presses on other organs, including the stomach. And hormones cause the muscles to relax, which causes acid from the stomach to enter the esophagus and irritate it. In addition, pain can be caused by problems with certain organs such as the gallbladder, or inflammation of the pancreas. nine0006
Symptoms of heartburn during pregnancy:
- Burning in chest and esophagus;
- Feeling of overeating, heaviness or bloating;
- Belching, including with acid and/or food particles;
- Nausea.
Avoid cramps and heartburn during pregnancy is unlikely.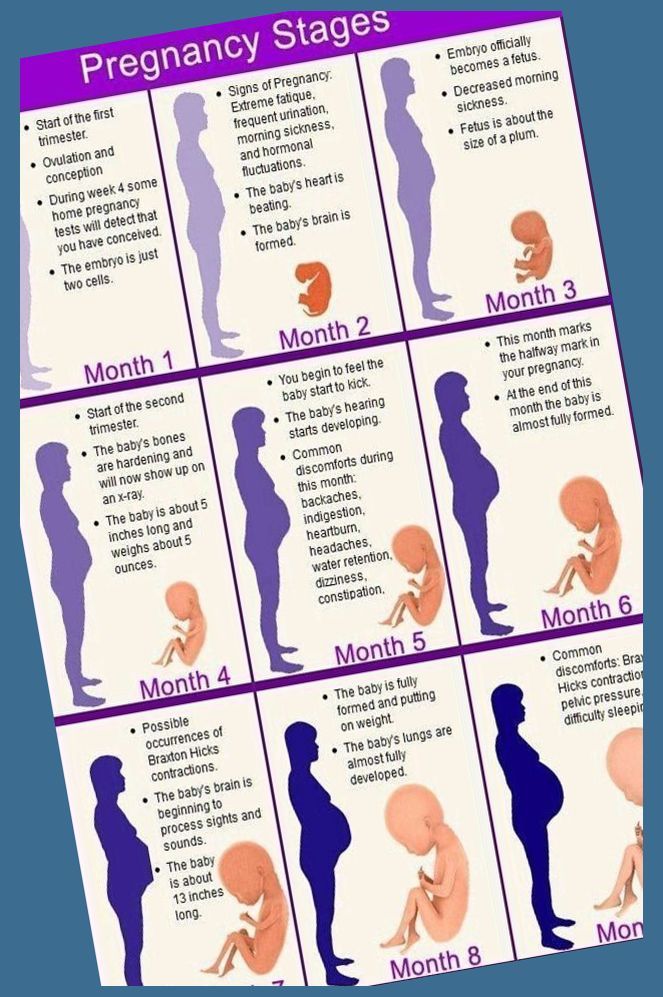 However, some tips can help reduce their frequency:
However, some tips can help reduce their frequency:
Nutrition : try to avoid overeating - eat easily digestible food in small portions; do not eat three hours before bedtime; watch your posture while eating - so the pressure on your stomach will be less. nine0006
Smoking and alcohol: In addition to known harms to mothers and babies, tobacco smoke also relaxes the muscles in the lower esophagus, allowing acid to enter the esophagus. And alcohol provokes heartburn and acid reflux.
Although stomach pain and heartburn often accompany pregnancy, abdominal pain, especially in the third trimester, should be taken seriously. It can be a sign of preterm labor or placental abruption, and puts mother and baby at risk. nine0006
If you experience severe abdominal pain during pregnancy that is accompanied by the following symptoms, seek medical attention as soon as possible:
| Abdominal pain and fever | Bleeding |
| Regular seizures | Unusual vaginal discharge / spotting |
| Vomiting | Low back pain |
| Pain or burning when urinating | Severe pain that lasts 30-60 minutes |
Bloating, constipation and microbiota during pregnancy
Excessive gas and constipation during pregnancy can be caused by hormonal changes, such as increased production of progesterone.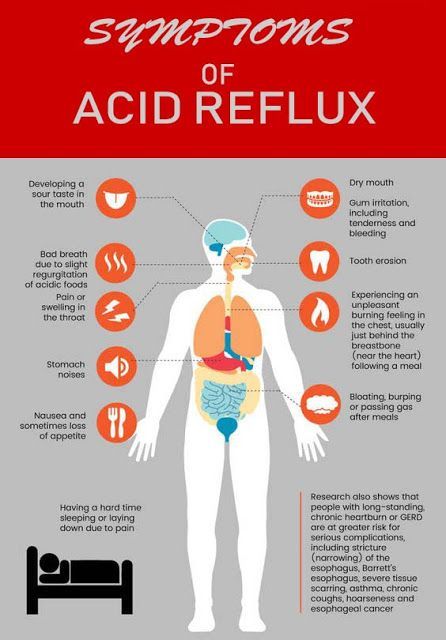 This hormone, essential for nourishing the uterus and fetus, relaxes the muscles of the body, including the muscles in the intestines, which slows down digestion and increases flatulence. A similar reaction of the body can be observed before each menstruation, when the production of progesterone increases. nine0006
This hormone, essential for nourishing the uterus and fetus, relaxes the muscles of the body, including the muscles in the intestines, which slows down digestion and increases flatulence. A similar reaction of the body can be observed before each menstruation, when the production of progesterone increases. nine0006
Flatulence - bloating of the abdomen due to the accumulation of gases.
Here are a few simple rules that will help improve intestinal motility and avoid constipation and bloating:
- If you don't usually eat a lot of fiber and indigestible foods like legumes, try to gradually introduce them into your diet;
- Avoid carbonated drinks and fatty foods;
- Move more;
- Drink plenty of fluids.
If bloating and constipation are accompanied by severe pain that lasts more than 30 minutes, or if you have been constipated for two or more weeks, see your doctor. nine0006
Gut microbiota and bacteria during pregnancy
A woman's body goes through many changes during pregnancy, and this can affect the microbiota, the bacterial ecosystem that lives in the gut.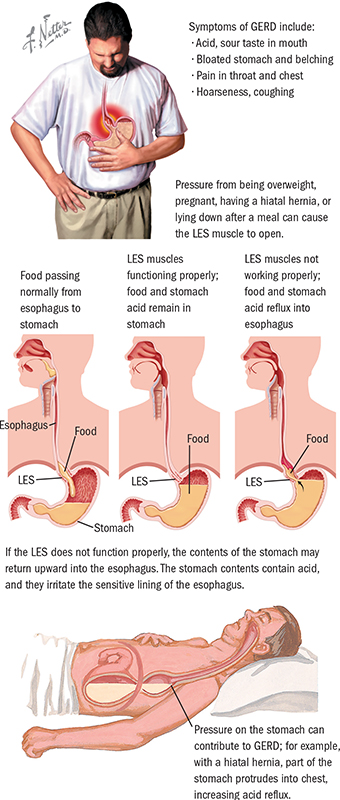 Trillions of microorganisms do important work for the whole body: they synthesize vitamins and essential acids, keep your intestines working and protect it from disease and inflammation.
Trillions of microorganisms do important work for the whole body: they synthesize vitamins and essential acids, keep your intestines working and protect it from disease and inflammation.
The additional influx of female hormones that accompanies pregnancy alters gut function and affects the microbiota. This is good, because the bacterial community is constantly adjusting to external and internal conditions in order to keep up with the needs of the body. nine0006
To keep your gut bacteria running smoothly, they need your help. Provide them with healthy foods and plant fibers. Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and seeds contain prebiotics, special substances that beneficial bacteria feed on. When properly balanced, the bacteria even increase your body's defenses against harmful microorganisms that can cause gastroenteritis during pregnancy.
The Atlas Microbiota Test will help you understand how to prepare your intestines for future pregnancy and reduce the risk of digestive problems.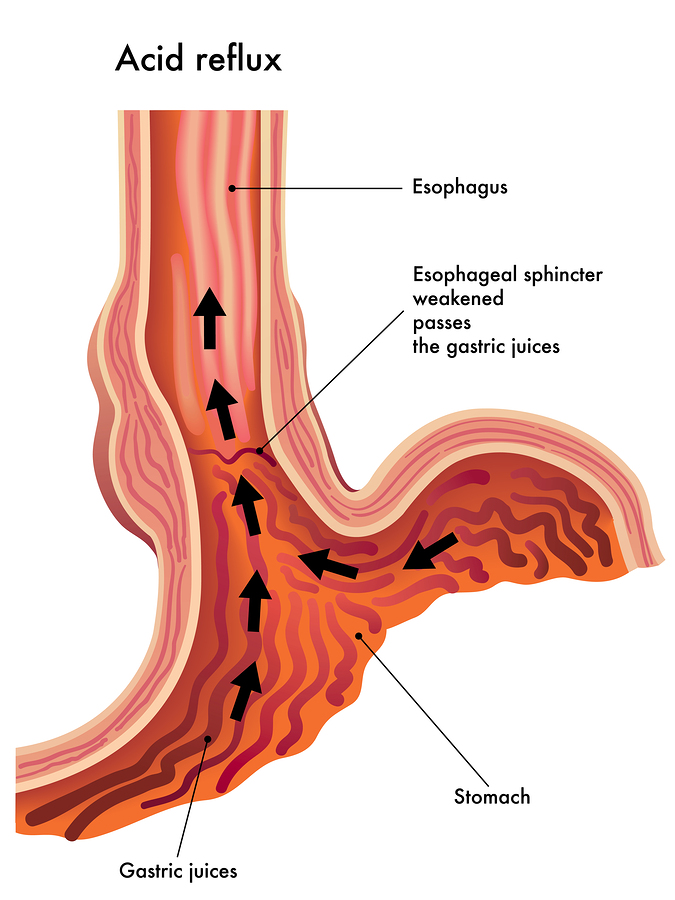 nine0267
nine0267
☝️ Take note
Now you have all the necessary knowledge and tools to help you cope with digestive problems during pregnancy. They are quite varied and quite natural, but in some cases it is necessary to immediately seek medical help:
- Vomiting blood;
- Blood in stool;
- Diarrhea for more than two days;
- Constipation for more than two weeks;
- Sudden weight loss;
- Severe pain interfering with daily activities; nine0016
- Difficulty breathing;
- Pain when swallowing or difficulty swallowing;
- Excessive fatigue.
More articles on the causes of digestive problems on the blog:
- 7 foods that cause gas and bloating
- Lindsey J Wegrzyniak, Treatment of Hyperemesis Gravidarum, 2012 nine0015 Edwards A. et al., The Maternal Gut Microbiome During Pregnancy, 2018
- National Health and Safety (NHS), Vomiting and morning sickness in pregnancy
- Kudzai Kanhutu, Travel and pregnancy: an infectious diseases perspective, 2011
- CDC, Pregnant travelers
- U.