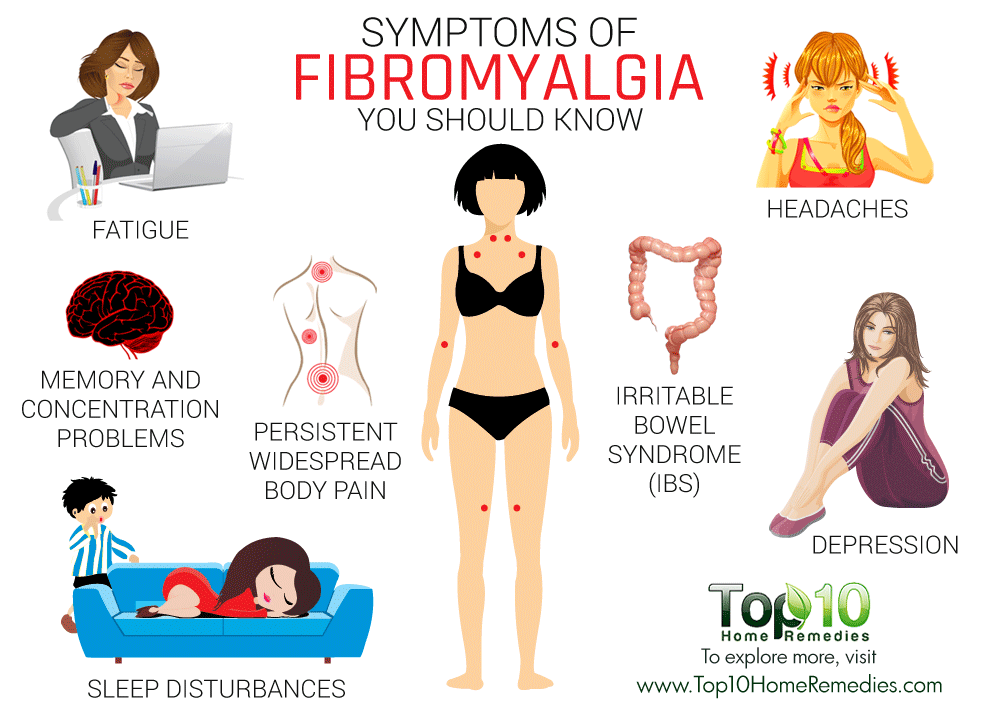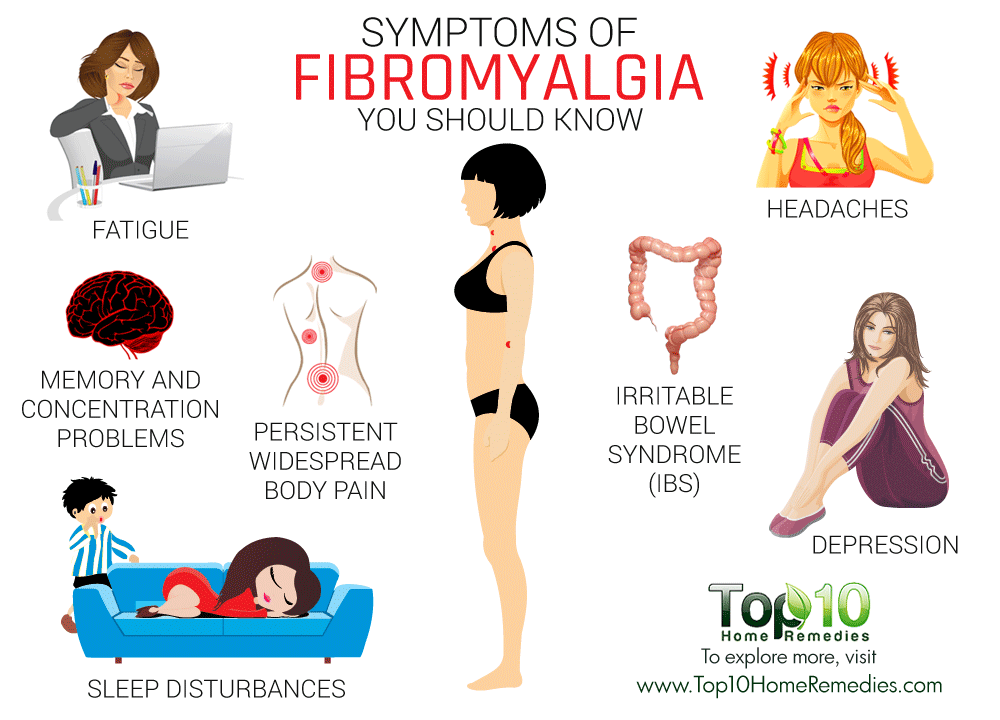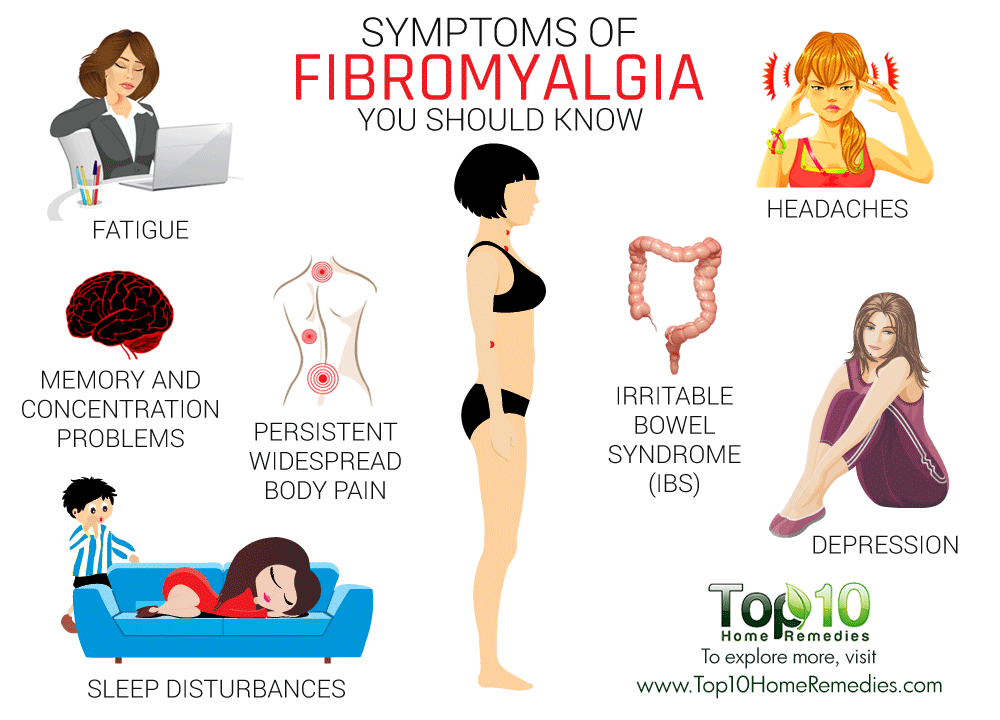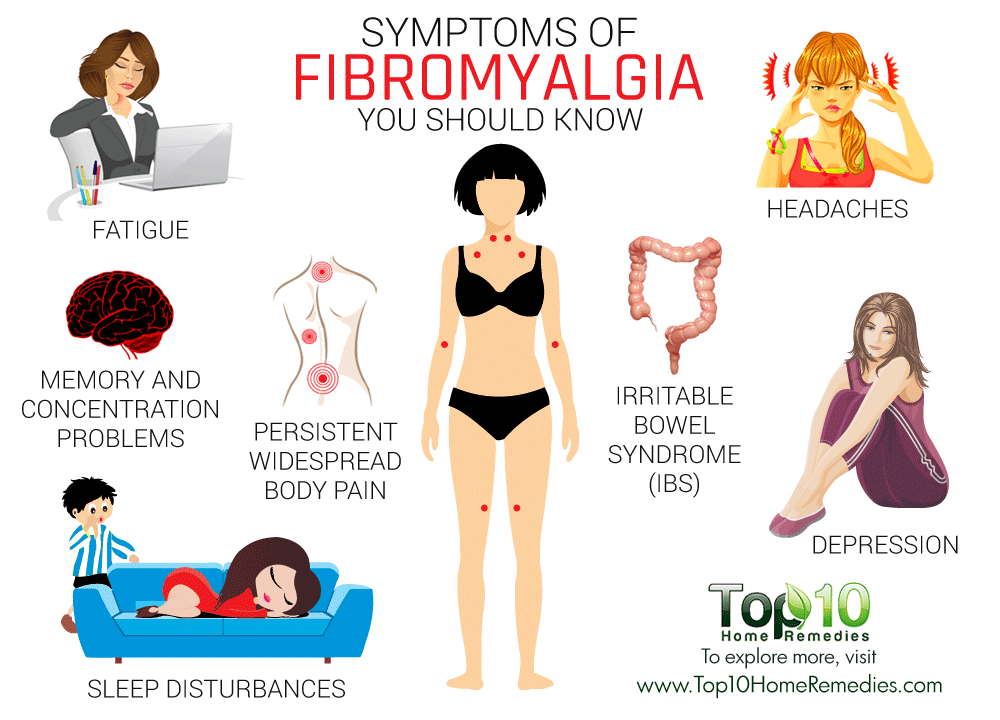
Symptom of pregnancy headache
When To Take, Types & Accuracy
Overview
How Does a Pregnancy Test Work?What is a pregnancy test?
A pregnancy test is a way to determine if you’re pregnant. If your pregnancy test is positive, it means you’re pregnant. If the test is negative, it means you aren’t pregnant. Pregnancy tests work by detecting human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), a hormone your body makes when you’re pregnant.
From the very beginning of pregnancy, your body starts to go through changes to support the cells that will develop into your baby. One thing that happens very quickly is the production of HCG. If you’re pregnant, your body starts to produce more HCG. Your HCG levels start to build up once the fertilized egg implants in your uterus — about six to 10 days after conception.
There are two main types of pregnancy tests — urine tests and blood tests. Often, you’ll take a urine test at home with a home pregnancy test. This type of test is available over the counter (you don’t need a prescription from your healthcare provider) and in a variety of price ranges. Blood tests to check for pregnancy happen in your healthcare provider’s office and involve giving a sample of your blood. The other way to confirm a pregnancy is by using an ultrasound. Your provider performs an ultrasound in their office.
There are several reasons why you might take a pregnancy test. You could be trying to get pregnant and hoping for a positive result. You might have experienced an issue with your birth control. You might even be about to have a medical procedure or start a new medication that could be complicated by pregnancy. No matter what the reason, if you ever have any questions about your test results, the best thing to do is reach out to your healthcare provider.
What hormone levels are checked for a pregnancy test?
Pregnancy tests look for an elevated amount of HCG. Levels of HCG rise quickly – doubling every few days in the first weeks of pregnancy. The placenta produces HCG. Only pregnant people have a placenta, which develops shortly after a fertilized egg attaches to your uterine wall.
When should I take a pregnancy test?
If you think you could be pregnant, it’s a good idea to take a test and make sure. Home pregnancy tests can differ in how early they’ll detect a pregnancy. In many cases, you might get a positive result from an at-home test as early as 10 days after conception. For a more accurate result, wait until after you’ve missed your period to take a test. Remember, if you take a test too soon, it could be negative even if you’re pregnant. If you get a negative test and then miss your period, take another test.
What time should I take a pregnancy test?
In general, the best time is when you have your first morning pee. However, some pregnancy tests are sensitive enough to detect HCG no matter what time of day you take the test. When possible, try to wait until it’s been three hours since your last pee before you take the test. You could also take two pregnancy tests to confirm you get the same result.
Test Details
How do pregnancy tests work?
When you take a pregnancy test, it’s looking for the amount of human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) in your body. You can find HCG in your pee or blood. HCG needs time to build up in your body. Each day of early pregnancy, your body will create more HCG. As the weeks go on, you’ll have more and more HCG in your body, which will make it more likely that a pregnancy test will show as positive. This means if you take a test too soon, it will come back negative.
You can find HCG in your pee or blood. HCG needs time to build up in your body. Each day of early pregnancy, your body will create more HCG. As the weeks go on, you’ll have more and more HCG in your body, which will make it more likely that a pregnancy test will show as positive. This means if you take a test too soon, it will come back negative.
Pregnancy tests work by reacting to the amount of HCG in either your pee or blood. In a urine test, a piece of reactive paper detects the HCG. This test might show a plus sign, double vertical lines or even the word “pregnant.” Different tests will show a positive result in unique ways. Read the directions that come with the test to know what a positive result will look like. For example, most tests have a control window that shows up first. Seeing a symbol in this window will tell you that the test is working. Keep in mind that different brands of tests will take different amounts of time to show a result.
If you take a blood test, your provider will take a sample of your blood and send it to a lab. The lab will determine the amount of HCG in your blood. Your provider will contact you with your results.
The lab will determine the amount of HCG in your blood. Your provider will contact you with your results.
What are the different types of pregnancy tests?
There are two main types of pregnancy tests: urine and blood tests.
Urine tests are typically done at home — though you can have a urine test done at your healthcare provider’s office — while your provider performs a blood test.
At-home pregnancy test
An at-home test uses your pee to look for HCG. They contain special strips that detect HCG. Most at-home pregnancy tests are about 99% effective when used correctly. That’s about the same accuracy rate as pregnancy tests done in your healthcare provider’s office. These tests are available in most drug or grocery stores. They’re easy to use and inexpensive. It’s important to read the instructions on these tests before taking them.
There are three ways to take an at-home pregnancy test:
- Pee in a clean cup. Then, place one to several drops of your pee on a chemical strip.

- Place the pregnancy test strip in your urine stream while you pee.
- Pee in a clean cup and then dip the test strip in the pee while it’s still in the cup.
For many of these tests, HCG can be detected in your urine about 10 days after conception. However, taking it after you miss your period reduces the chance of getting a false-negative result. A missed period typically happens around 14 days after conception.
There are a few things to keep in mind when you take a home pregnancy test, including:
- Use your first morning pee if you can. This is the time of day when your HCG levels will be the most concentrated and easily detected. If you do it at another time of day, try to make sure your pee has been in your bladder for at least three hours.
- Don’t drink excessive amounts of fluids before you take a pregnancy test. This can dilute (thin out) your HCG levels.
- Check the expiration date on the package.
- Read the directions that come with the test thoroughly before starting the test, and follow every step exactly.
Blood test
Another type of pregnancy test is a blood test. Blood tests are rarely done because they’re expensive and tend to have the same result as a urine test. This type of pregnancy test is done using a small sample of blood from a vein in your arm. This blood test not only detects whether the pregnancy hormone is in your body, but can also determine how much of the hormone is present. This is helpful for when your provider needs to know the exact amount of HCG in your blood, not just if there’s HCG in your blood.
A blood test for pregnancy might be done in special circumstances, such as for people who are having fertility treatments or when the healthcare provider thinks there might be a problem.
These blood tests are slightly more sensitive than urine tests because they can detect very small levels of HCG. That means they can provide a more accurate answer very early on in pregnancy — within seven to 10 days after conception. For this test, your blood sample is taken at your provider’s office or the hospital, then sent to a lab for analysis.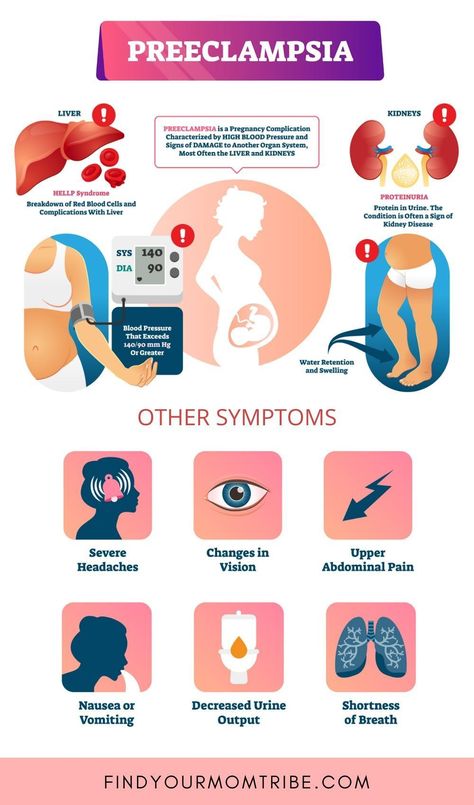 Results might take anywhere from a few hours to two days.
Results might take anywhere from a few hours to two days.
Your provider might also choose to use a blood test to compare HCG levels during the pregnancy. Your HCG levels usually double about every two days during the first few weeks of pregnancy. If the levels don’t rise, it might suggest a problem with the pregnancy. Extremely high HCG levels might mean that you’re carrying twins or that there’s an issue with the pregnancy.
Are all home pregnancy testing methods the same?
Most brands of at-home pregnancy tests are reliable. Although the exact testing method of different pregnancy tests can differ from one type to the other, they all look for HCG in your body. If you’re using an at-home test, most will give you the same result. The difference with your at-home tests will be the sensitivity of the test. Some might be more sensitive than others and produce a positive result (detect HCG in your urine) sooner than others. For the most accurate reading, it’s still recommended that you wait until you’ve missed your period. At that point, all tests should be accurate.
At that point, all tests should be accurate.
What are the advantages of using a home pregnancy test?
There are quite a few advantages to using a home pregnancy test, including:
- Pregnancy tests are inexpensive.
- They’re easy to use.
- Home tests provide results quickly.
According to pregnancy kit manufacturers, most at-home pregnancy tests are 98% to 99% accurate when you use them exactly as instructed. Positive results can be trusted, but you can get a false negative result if you take the test too soon.
Blood tests tend to be more expensive and inconvenient. However, blood tests can detect pregnancy sooner and are the only tests to show specific amounts of HCG in your body.
Is there anything you shouldn’t do before a pregnancy test?
Most pregnancy tests don’t ask you to avoid activities or change your lifestyle. The only medication that may interfere with your results is fertility medication containing HCG.
Here are some helpful tips you should follow for the best results:
- Read the instructions carefully before doing anything.
- Wait until you miss your period to take the test.
- Use your first pee or pee from a full bladder. Chugging water before your test in order to pee may affect your results.
Results and Follow-Up
How long does it take to get results of a pregnancy test?
Each home pregnancy test is different. Read the instruction manual carefully. It will tell you how many minutes to wait for your result. In most cases, you can expect to wait three minutes for your result. Keep in mind that if you wait too long to check your result, it may be inaccurate.
Even a faint line on a pregnancy test could mean you’re pregnant. Your test will also have a control window that indicates that you took the test correctly. The instructions with your test will outline all of this. If you have any questions or remain unsure of your result after several tests, please contact your healthcare provider.
A faint line is different than an evaporation line. An evaporation line may appear if you wait too long to check your results — meaning your pee is dry. Most tests ask you to read your results before 10 minutes. This ensures the pee doesn’t dry up and you don’t get an evaporation line.
Most tests ask you to read your results before 10 minutes. This ensures the pee doesn’t dry up and you don’t get an evaporation line.
How soon will a pregnancy test be positive?
It depends on which type of test you use. Some at-home pregnancy tests may be able to detect pregnancy before you miss your period. However, if you want the most accurate result, it’s best to wait until you have missed your period.
How accurate are pregnancy tests?
Pregnancy tests are about 99% accurate when you use them correctly.
How common are false results on pregnancy tests?
False results — either a false negative or a false positive — mainly happen due to using the test incorrectly. The main reason for a false-negative is testing too early. You might also get a false-negative if you use a home test incorrectly, such as using too much or too little pee. It’s important to follow the directions on your test kit to make sure you get an accurate result.
Can a positive test be wrong?
A false positive is rare, but it can happen. This may be the case if you experience a chemical pregnancy or lose the pregnancy shortly after the fertilized egg attaches to your uterine wall.
This may be the case if you experience a chemical pregnancy or lose the pregnancy shortly after the fertilized egg attaches to your uterine wall.
What type of pregnancy test confirms pregnancy first?
A blood test confirms pregnancy first because it can detect a smaller amount of HCG as compared to a test that uses your pee.
Are there any medications that can change the result of my pregnancy test?
For the most part, medications don’t change your pregnancy test results. Antibiotics, pain relievers and alcohol don’t impact your test results.
However, fertility drugs are one exception. These medications can sometimes cause a false-positive on your pregnancy test. If you’re taking fertility medications, reach out to your healthcare provider about your results to make sure they’re accurate.
What should I do after getting a positive pregnancy test?
If you take a pregnancy test at home and it’s positive, there are a few things you should do, including:
- Take your prenatal vitamins.
 Pick a vitamin with folic acid included in the ingredient list. Start taking these while you’re trying to conceive, if possible. This is because the folic acid can help prevent complications during fetal development.
Pick a vitamin with folic acid included in the ingredient list. Start taking these while you’re trying to conceive, if possible. This is because the folic acid can help prevent complications during fetal development. - Call your healthcare provider for an appointment. This appointment might not happen for several weeks — but it’s a good idea to call your provider and make an appointment.
- Make sure to pursue healthy habits like not drinking alcohol or smoking during pregnancy. You may also want to limit the amount of caffeine you consume each day during pregnancy.
Additional Details
Will an ectopic pregnancy show up on a pregnancy test?
Yes, you’ll still have a positive result on a pregnancy test if you have an ectopic pregnancy.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Pregnancy tests are how a person finds out if they’re pregnant. Most people take a pregnancy test at home using their pee. However, you can also take a pregnancy test at your provider’s office using a blood sample or pee. For the most accurate results, wait until you miss your period to take a home pregnancy test. If you use pregnancy tests correctly, the results are 99% accurate. Contact your healthcare provider if you have questions about the results of your pregnancy test.
For the most accurate results, wait until you miss your period to take a home pregnancy test. If you use pregnancy tests correctly, the results are 99% accurate. Contact your healthcare provider if you have questions about the results of your pregnancy test.
Fertilization, Process & When It Happens
How does conception occur?
Conception (or fertilization) is when sperm and an egg join together. It’s one of the many steps that happen to create a pregnancy.
Conception is closely related to a person’s menstrual cycle. A menstrual cycle describes the sequence of events that occur within your body as it prepares for the possibility of pregnancy each month. Women or people assigned female at birth (AFAB) ovulate during their menstrual cycle. Ovulation is when your ovary releases an egg for fertilization. Tiny finger-like structures called fimbriae help guide the egg through your fallopian tubes towards your uterus. During this journey through your fallopian tubes, an egg can be fertilized by sperm.
Sperm production begins in the testicles of men or people assigned male at birth (AMAB). During ejaculation, millions of sperm cells are set free with the sole purpose of finding an egg to fertilize. When you have unprotected sex, sperm cells swim up through your vagina and into your fallopian tubes. Millions of sperm battle to reach and penetrate the egg, but only one breaks through the egg's outer layer to fertilize it. If sperm doesn't fertilize an egg, the egg dissolves.
If a sperm is successful on its quest to fertilize an egg, the now fertilized egg (called a zygote) continues to move down your fallopian tube, dividing into two cells, then four cells, then more cells. About a week after the sperm has fertilized the egg, the zygote has traveled to your uterus. It's now a growing cluster of about 100 cells called a blastocyst.
The blastocyst then attaches itself to the lining of your uterus (the endometrium). This attachment process is called implantation. However, just because conception occurs doesn't mean implantation will. Sometimes implantation doesn't happen, and you pass the fertilized egg in your next menstrual period.
Sometimes implantation doesn't happen, and you pass the fertilized egg in your next menstrual period.
If implantation happens, the cells continue to divide — some cells develop into your baby and others form the placenta. You begin to release hormones that tell your body a baby is growing inside your uterus. These hormones also signal the uterus to maintain its lining rather than shed it. This means you won't get your menstrual period, which may be the first way you know you’re pregnant.
Timeline of getting pregnant
You calculate your menstrual cycle from the first day of menstrual bleeding to the start of the next first day of menstrual bleeding. Most menstrual cycles are around 28 days long. The exact time you ovulate varies depending on how long your menstrual cycle is.
The process of getting pregnant in a 28-day menstrual cycle is:
- Day one: First day of your period.
- Around day 14: Ovulation occurs.
- Within 24 hours of ovulation: Sperm fertilizes an egg (conception occurs).
- About six days after fertilization: The fertilized egg implants into your uterine lining.
- Around day 21: If conception and implantation occurred during this menstrual cycle, you're pregnant. However, getting a positive pregnancy test may take another five to seven days.
Conception and a positive pregnancy test
After conception, a fertilized egg travels through your fallopian tubes to your uterus. The fertilized egg (called an embryo) implants (attaches) into the wall of your uterus. This triggers the placenta to form. Your placenta begins producing and releasing human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) into your blood and pee. HCG can be found in a person’s blood around 11 days after conception. It takes slightly longer for hCG to show up on at-home pregnancy tests (that measure hCG in pee).
What are my chances of conceiving?
Just because an egg and sperm are near each other doesn't mean conception will happen. In general, conception only happens 25% to 30% of the time. This percentage decreases once you reach age 35.
In general, conception only happens 25% to 30% of the time. This percentage decreases once you reach age 35.
How does conception work with IVF?
Conception still works the same way — sperm must fertilize an egg. However, with in vitro fertilization (IVF), sperm fertilizes an egg in a lab. An egg, either from the intended parent or a donor, is mixed with sperm from a parent or donor. Conception happens when sperm fertilizes the egg.
Once conception occurs, your provider places the created embryo inside the uterus that will carry the pregnancy for implantation.
When does conception happen?
Conception occurs between 12 and 24 hours after ovulation. It’s sometimes hard to pinpoint ovulation, so using ovulation predictor kits or tracking your menstrual cycle on a calendar may be helpful. The two biggest factors in conception are:
- The timing of sexual intercourse with ovulation.
- Egg and sperm health.
When should I have sex to conceive?
Conception can happen after unprotected sex as early as five days before ovulation. This is because some sperm can live that long inside female reproductive organs.
This is because some sperm can live that long inside female reproductive organs.
If you’re trying to conceive, the best times to have sex are:
- In the three days before ovulation: In this scenario, sperm will be “waiting” for the egg to come down the fallopian tube.
- At ovulation or within 24 hours of ovulating: Your egg lives for only 24 hours, so if you have unprotected sex during this time, your egg may end up “waiting” for sperm to reach it, or they may run into each other in your fallopian tubes.
Where does conception happen?
Conception typically happens in your fallopian tubes. This is where an egg goes after it leaves your ovary and where sperm wait for an egg. In some cases, fertilization can happen in your uterus once your egg has left your fallopian tubes.
What things prevent conception from happening?
Certain health conditions may affect your ability to conceive. Just because the sperm and egg meet doesn't mean fertilization will occur.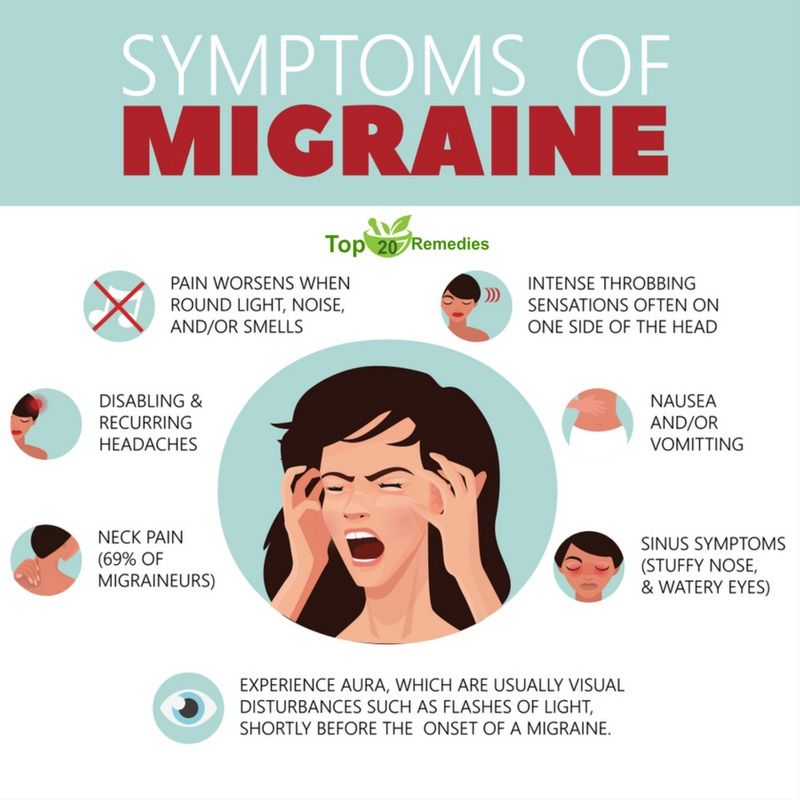 Some of the most common factors are:
Some of the most common factors are:
- Anovulation (you’re not ovulating).
- Low sperm count or issues with sperm motility (how sperm move).
- A blockage in the testicles, ovaries or fallopian tubes.
- Decreasing amount of quality eggs and quality sperm (usually related to aging).
Can you feel conception?
Not usually. You may notice signs that you've ovulated, such as changes in your cervical mucus or basal body temperature. However, most people don't feel fertilization. You may feel a dull ache or experience light spotting several days after conception. This could be from the fertilized egg implanting in your uterus.
When do you start feeling pregnant?
How long it takes to “feel” pregnant varies. Some people may start to feel pregnant shortly after conception, while others don’t have any pregnancy symptoms for weeks after a positive test.
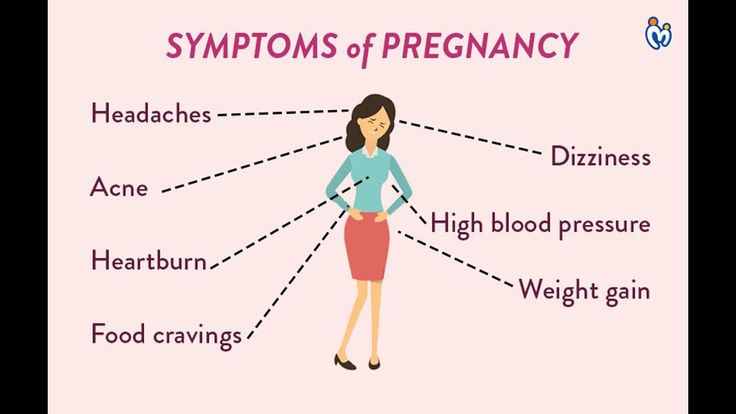
Common signs of pregnancy are:
- A missed period.
- Frequent urination.

- Feeling tired.
- Nausea.
- Sore or swollen breasts.
- Spotting (light vaginal bleeding).
- Headaches.
- Mood swings.
Take a home pregnancy test if you have any of the above symptoms and think there’s a chance you’re pregnant. Your healthcare provider can order a blood test to confirm pregnancy.
Are conception and fertilization the same?
Conception and fertilization are two different parts (or steps) of the same process. Conception is the first step, where an egg and sperm join. Fertilization is another step, where the joined sperm and egg plant like a seed into your uterine lining.
How long after conception will my pregnancy test be positive?
It can take between 11 and 14 days after conception to get a positive pregnancy test. At-home pregnancy tests check for human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone released by the placenta. Your pee must have enough hCG to get a positive pregnancy test. However, your healthcare provider can check for hCG in your blood sooner — around 10 days after conception.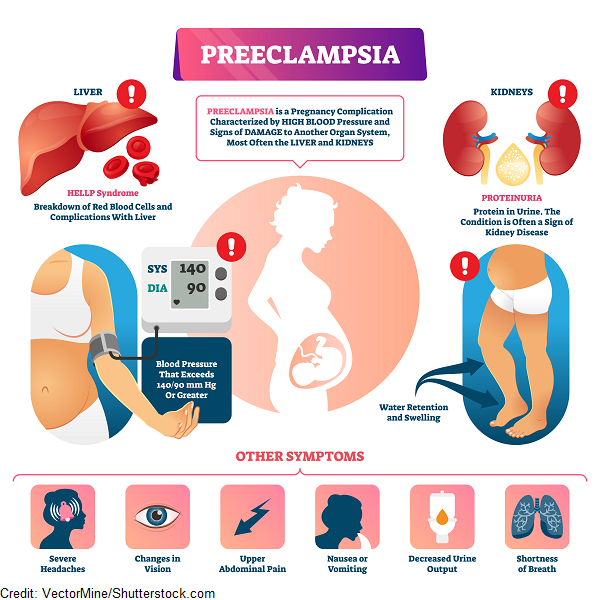
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Conception is when sperm fertilizes an egg. It’s one of the many critical steps in getting pregnant. Conceiving a child is a complex process dependent on lots of factors. Being unable to conceive is a common problem, and there are lots of resources available to help you. Contact your healthcare provider if you’re struggling with conceiving. They can explain the process and identify any issues preventing conception and pregnancy.
Headache during pregnancy: where does it come from and how to get rid of it
November 14, 2020 Likbez Health
Sometimes you just need to get some sleep, and sometimes you need to call an ambulance immediately.
When to call an ambulance
Call 103 or 112 urgently if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- sudden and severe headache;
- consciousness becomes confused or completely lost;
- pain worsens over 5 minutes; nine0012
- flies, spots flash in the eyes;
- throbbing and noisy in the ears;
- speech has become slurred, words are drawn out;
- arms and legs weaken, convulsions set in;
- the muscles of the neck are very stiff, it is impossible to reach the chest with the chin;
- fever of 39 °C or more;
- increased heart rate at rest;
- severe shortness of breath;
- the child pushes without stopping or stops abruptly;
- leaking water or blood; nine0012
- lower abdomen hurts, as if contractions had started.

Why pregnant women can get headaches
Pregnancy headaches are not always life threatening. But the doctor needs to be told about it in any case. If the symptom appeared for the first time and does not hurt much, postpone the conversation until a scheduled visit. If your headache is recurring or gets worse, it's best to make an appointment as soon as possible. The gynecologist will decide what needs to be done or refer you to another doctor.
There are many causes of headaches. Scientists have found that in pregnant women in 57% of cases it is primary, that is, not associated with other diseases. The most common are migraines and tension headaches. nine0003
Everything else is a secondary headache caused by various pathologies. Usually it is high blood pressure and infections. But there are also more dangerous reasons.
1. Stress and fatigue
A pregnant woman's body experiences increased stress, because it has to work for two. If at the same time the expectant mother is exposed to stress, strong feelings or sleeps little, she develops a tension headache.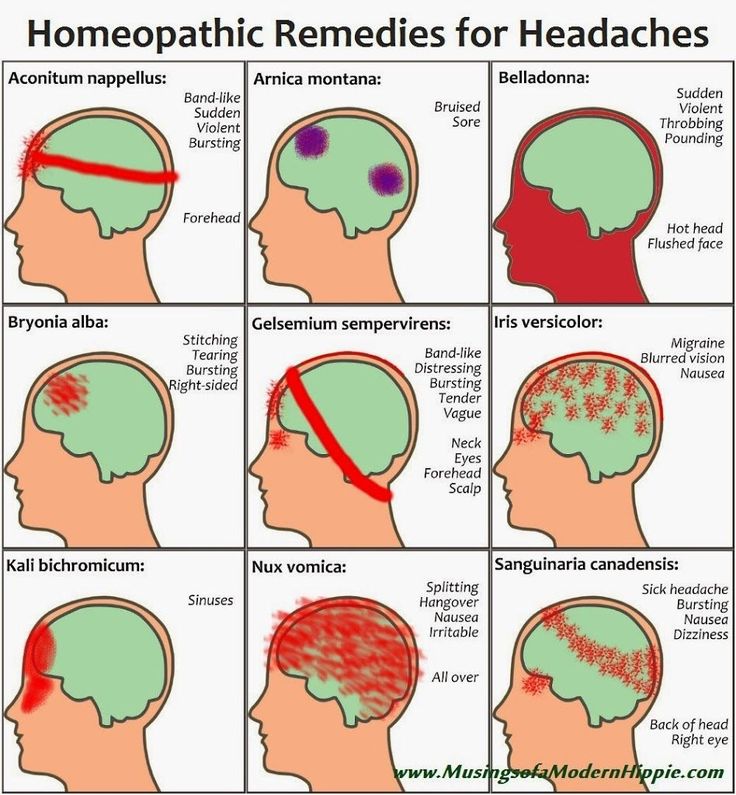
Discomfort lasts from 30 minutes to several days. The head hurts in the forehead, occiput, both temples. But there is no feeling that they put on a tight hoop or helmet. The pain does not get worse when bending over, walking, or climbing stairs, bright lights, or sounds. nine0003
What to do
Tension headache can go away on its own: just get some fresh air or sleep. Sometimes pleasant emotions help, which distract from experiences.
If the pain persists for 2-3 consecutive days, see a doctor. He will select painkillers that are safe for the child.
2. Medications
Any medicine that enters the stomach or bloodstream can cause headaches even if the dosage is correct. In pregnant women, this often occurs due to drugs for high blood pressure, heart disease, antibiotics, anticonvulsants. nine0003
Long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for headaches may cause the opposite effect: the pills do not remove, but provoke symptoms.
What to do
If your head hurts a few hours after taking the medicine, you need to see a doctor to change the medicine. Do not drink non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for more than 3-5 days. If they do not help, you need to tell the doctor about it.
3. Love for coffee or rejection of it
Coffee can cause headaches during pregnancy. Unpleasant symptoms occur if you drink more than 3-4 cups a day.
Abrupt refusal of coffee is also harmful. It is worth finding out about pregnancy and stopping brewing a fragrant drink, and after 1-2 days, aching pain will appear in the temples and the back of the head.
What to do
Coffee is best avoided during pregnancy. If a headache occurs a day after this, you can drink a small cup of the drink and wait a day again. Gradually, the dependence on coffee will pass. nine0003
Coffee drinkers can reduce their drink intake to 1-2 cups per day.
4. Infection with fever
Acute viral (usually ARVI) or bacterial (eg, streptococcal tonsillitis) infections cause fever and headache. This is a normal reaction to foreign microorganisms.
This is a normal reaction to foreign microorganisms.
But any infection is dangerous for pregnant women. It can cause fetal defects, growth retardation and even miscarriage. And with meningitis, especially listeriosis, there is a threat to the life of the mother. nine0003
What to do
If you have a headache with fever, call your doctor. He will prescribe safe medications or give you a referral to the hospital if a severe infection is suspected. In this case, you need strong antibiotics, droppers to maintain the body and sometimes hormones.
5. Preeclampsia and preeclampsia
After 20 weeks, preeclampsia may develop in pregnant women. This is a disease in which one of three symptoms or a combination of them may appear: high blood pressure, edema, and protein in the urine. nine0003
Without proper treatment, preeclampsia turns into preeclampsia. The pressure rises sharply, the head and lower abdomen hurt unbearably, the baby pushes unusually hard or, on the contrary, suddenly calms down. Preeclampsia can lead to placental abruption, damage to the liver and other organs, bleeding, and even seizures. Without urgent medical care, the fetus and mother die.
Preeclampsia can lead to placental abruption, damage to the liver and other organs, bleeding, and even seizures. Without urgent medical care, the fetus and mother die.
What to do
When the first signs of preeclampsia appear, the pregnant woman is hospitalized to find treatment. After that, she is discharged home under the supervision of her gynecologist. nine0003
But if her health worsens, the doctor again sends the woman to the hospital, where she is prescribed medication to reduce pressure, special drips to keep her body functioning. If improvement does not occur within a day, a caesarean section is performed.
6. Migraine
One of the causes of migraine is a change in estrogen levels. But the disease very rarely appears due to pregnancy. On the contrary, in 70% of women, the symptoms subside dramatically after conception. Nevertheless, migraines torment many. nine0003
It may begin with an aura: flashes of light, spots before the eyes, tingling in the hands or numbness of half of the face, sometimes tinnitus. Each symptom can last from 20 minutes to an hour.
Each symptom can last from 20 minutes to an hour.
A migraine attack develops after the aura. In this case, one side of the head hurts and throbs, nausea or vomiting appears. A woman is irritated by bright lights, loud noises, smells. They make the pain worse.
Seizures last from a few hours to a week or more. After a migraine, there is a feeling of severe fatigue, exhaustion, and an awkward turn of the head can return the pain. nine0003
What to do
Any medication for migraine during pregnancy must be prescribed by a doctor. In some cases, drugs from the group of beta-blockers are used.
Studies have shown that frequent migraine in pregnancy is associated with a lack of magnesium. The doctor will help you choose the appropriate type of vitamin and mineral complex and its dosage.
7. Cerebral vascular disease
Hormone problems in some pregnant women increase blood clotting, which increases the risk of thrombosis, stroke or bleeding in the meninges. These conditions are very dangerous: a woman can die within a few minutes or remain disabled. nine0003
These conditions are very dangerous: a woman can die within a few minutes or remain disabled. nine0003
Vascular involvement is always accompanied by several symptoms:
- severe headache on one side;
- nausea and vomiting;
- blurred vision;
- loss of consciousness;
- convulsions.
What to do
Urgently call an ambulance. The pregnant woman must be laid or seated so that she does not hit when she falls. You can't give medicine! You can only open the window so that there is more air in the room.
Which treatment the doctor prescribes depends on the specific disease. These can be drugs that reduce blood clotting and dissolve blood clots. In some cases, urgent surgery is needed. nine0003
8. Brain tumors
Studies show that progesterone and estrogens during pregnancy can trigger or accelerate the growth of tumors in the brain. Symptoms of the disease appear slowly, over several months, and depend on the size and location of the tumor.
The headache may gradually increase, then vision, speech, hearing deteriorate, limbs go numb and convulsions appear. Sometimes it is difficult for a woman to keep her balance.
What to do
If a pregnant woman often has a headache or she forgets what she wanted to buy in the store and how to cook her favorite borscht, confuses her way home, you need to go to a neurologist. First, he will prescribe standard treatment, simple and safe medicines, rest, good sleep.
If this does not help, the symptoms persist or worsen, a deep examination is needed. The pregnant woman will be sent for an MRI of the brain. This procedure is safe for the fetus. If the diagnosis is confirmed, surgery may be required. nine0003
What to do if the doctor cannot find the cause of the pain
If you have been examined and the doctor cannot tell you why your head hurts and diagnoses you with vascular dystonia, this is cause for concern. There is no such disease.
Seek another doctor. Perhaps he uses new diagnostic methods that will help to deal with the problem and choose a treatment.
Perhaps he uses new diagnostic methods that will help to deal with the problem and choose a treatment.
How to avoid pregnancy headaches
Experts recommend:
- Avoid triggers. For example, if you notice that certain foods, smells, or situations cause headaches, try not to encounter them.
- Protect yourself from stress, do not worry about trifles.
- Move more. During pregnancy, walk every day in the fresh air and do special exercises for expectant mothers.
- Eat right. Try to eat a lot of vegetables and fruits, dairy products, drink at least 2.4 liters of liquid. Every day, the menu should include fish, poultry or lean meat. And it is better not to buy sweet, fast food and other junk food. nine0012
- Follow the daily routine. You need to sleep at least 8 hours a day and go to bed no later than 22-23 hours in order for melatonin to be produced normally.
- Learn to relax. Learn simple meditation techniques or breathing exercises.
Read also 🧐
- How pregnancy develops by week
- How to calculate the duration of pregnancy
- What rights does a pregnant woman have at work
- 7 best sex positions for pregnant women
- How to recognize a miscarriage and what to do next
Migraine during pregnancy: what to do
Migraine is a benign disease, it does not affect the course of pregnancy and fetal development. However, migraine and pregnancy is a combination that requires a responsible attitude. Especially with frequent migraines (more than 2 times a week) and migraines with aura, since:
-
medicines approved for use, few,
-
and the approach to the treatment and prevention of migraine during this period is extremely individual: it depends on the frequency, severity and duration of headache, the degree of impact on life.
Our neurologist Daria Korobkova conducted a live broadcast on the clinic's Instagram account, where she told how migraine and pregnancy are connected, why attacks become more frequent or disappear, and answered subscribers' questions.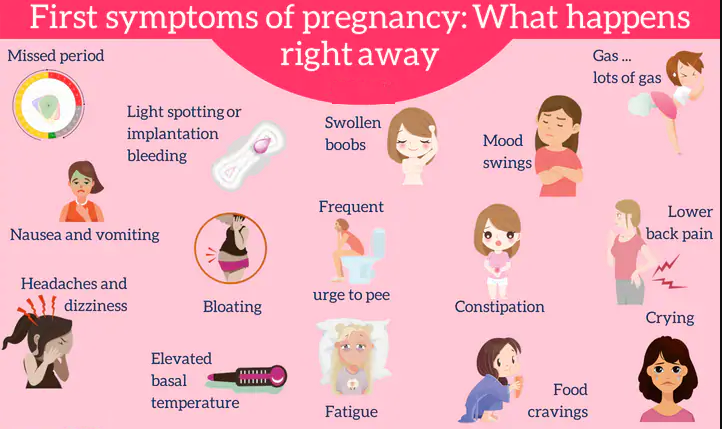 The ether was saved, see “Air recording: migraine during pregnancy and GV. nine0003
The ether was saved, see “Air recording: migraine during pregnancy and GV. nine0003
We will tell about migraine during breastfeeding separately.
The statistics of clinical observations of migraine during pregnancy looks like this:
In 60-70% of pregnant women with migraine, headache attacks become less frequent, milder, or even completely disappear in the second and third trimesters. This is due to the stabilization of estrogen levels. By the beginning of the second trimester, it rises 6 times and its fluctuations stop.
In other women, migraine during pregnancy either remains unchanged or worsens. But as the duration of pregnancy increases, the proportion of such women gradually decreases:
If at the end of the first trimester the frequency and intensity of attacks persist, then it is most likely that migraine will disturb the woman during the entire period of pregnancy and after childbirth too.
How to manage migraine during pregnancy?
The main thing here is to learn how to control seizures and, if necessary, seek medical help.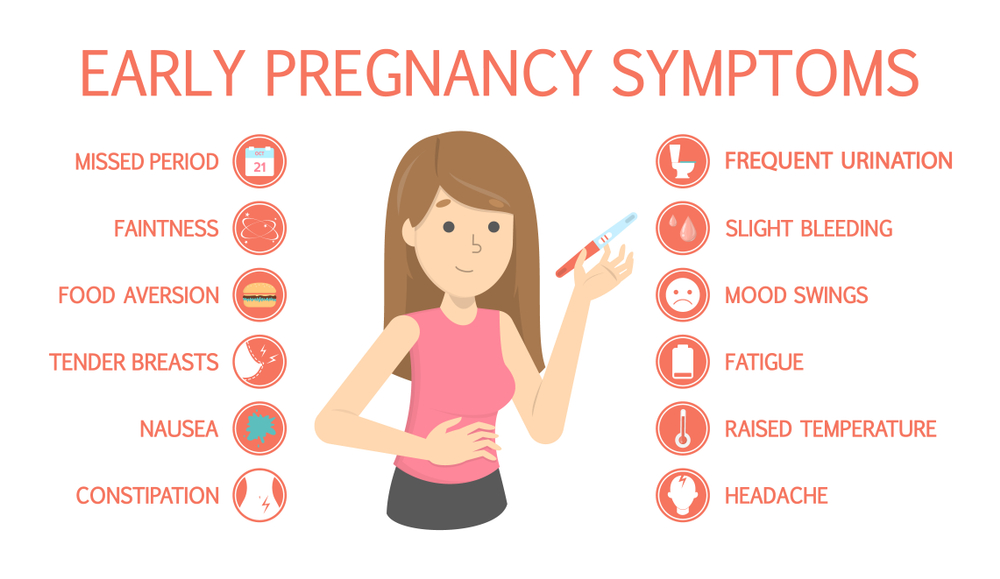
-
Follow lifestyle advice:
-
get enough sleep; nine0003
-
drink plenty of fluids;
-
eat fractionally and without long breaks;
-
rest;
-
avoid stressful situations. This is one of the main provocateurs of migraine. Psychotherapy, relaxation and stress management are here to help you.
-
Keep a headache diary. This will help you take control of migraine triggers.
nine0012
Yes, yes, following these simple recommendations is sometimes enough to make seizures less frequent! Pregnancy is a special state of a woman. If in other periods of life we do not take such recommendations so seriously, then in this situation it is worth trying to change the philosophy of life and attitude towards ourselves =)
How to relieve an attack?
-
Favor non-drug methods.
 Sometimes, in order to relieve an attack, it is enough to eliminate an unfavorable factor:
Sometimes, in order to relieve an attack, it is enough to eliminate an unfavorable factor:
-
dry biscuits, ginger, or applesauce may help with nausea;
-
for dehydration - diluted juice or other liquid;
-
sleep, walking or breathing exercises can also help to cope;
-
If the attacks are severe, interfere with your life, then under the supervision of a specialist, you can resort to drug therapy.
PARACETAMOL is considered the safest and can be taken throughout pregnancy. nine0003
All other drugs have nuances. For example:
-
ibuprofen can be taken in the second trimester, and in the first trimester it is better to limit, in the third trimester the drug is contraindicated for use;
-
aspirin is prohibited in the 3rd trimester and is undesirable for taking in the first two, as it can cause extremely undesirable consequences;
-
It is strictly forbidden to use ergotamine and opioid analgesics;
nine0011
triptans are not officially approved for use during pregnancy as no controlled studies have been conducted.