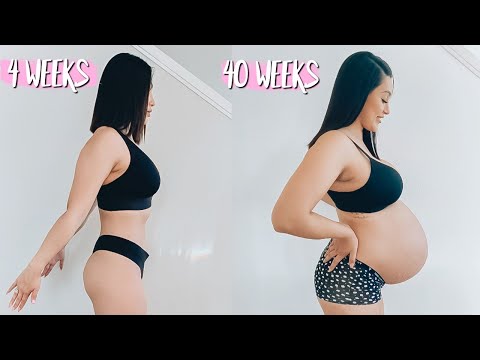
Can you leak urine while pregnant
Pregnancy & Bladder Control: Causes, Diagnosis & Treatment
What is incontinence?
Urinary incontinence is the inability to control the passage of urine. If you experience incontinence, you might feel an urgent need to urinate or leak urine between trips to the bathroom. You also might find that you have to make frequent trips to a toilet if you have incontinence. This can happen for many reasons, including pregnancy, childbirth and age.
How does the bladder work?
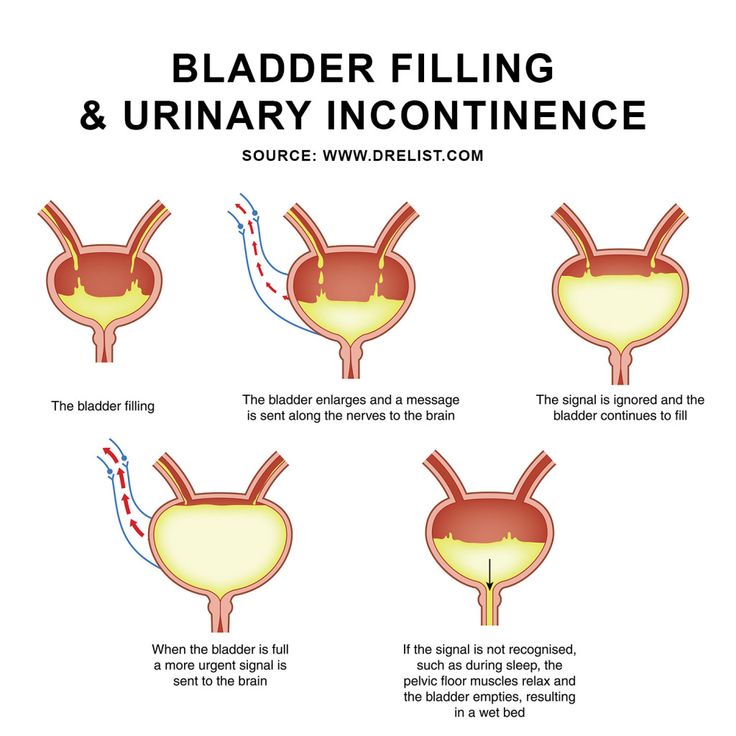
Your bladder is a round, muscular organ that’s located above the pelvic bone. It’s held in place by the pelvic muscles. A tube called the urethra allows urine to flow out of the bladder. The bladder muscle relaxes as your bladder fill with urine, while the sphincter muscles help to keep the bladder closed until you’re ready to urinate.
Other systems of your body also help to control the bladder. Nerves from the bladder send signals to the brain when the bladder is full and then nerves from the brain signal the bladder when it’s ready to be emptied. All of these nerves and muscles must work together so that your bladder can function normally.
How do pregnancy and childbirth affect bladder control?
During pregnancy, you might leak urine between trips to the bathroom. This is called incontinence. One type of incontinence that can affect pregnant women is stress incontinence. If you’re experiencing stress incontinence, you might leak urine when you:
- Cough.
- Laugh.
- Do physical activity.
Your bladder rests under the uterus. As your growing baby expands, the bladder gets compressed (flattened), making less space for urine. This extra pressure can make you feel the urge to urinate more often than normal. Usually, this is temporary and goes away within a few weeks of your baby’s birth.
However, the risk of experiencing incontinence after pregnancy often depends on your particular pregnancy, the type of delivery and the number of children you have. Women who have given birth — by vaginal delivery or C-section — are at a much higher risk of stress incontinence than women who have never had a baby.
Loss of bladder control can be caused by pelvic organ prolapse (slipping down) that can sometimes happen after childbirth. Your pelvic muscles can stretch and become weaker during pregnancy or a vaginal delivery. If the pelvic muscles do not provide enough support, your bladder might sag or droop. This condition is called cystocele. When the bladder sags, it can cause the urethra’s opening to stretch.
What causes bladder control loss in women after pregnancy and childbirth?
There are several things that can cause you to experience a loss of bladder control after having a baby, including:
- Pelvic organ prolapse: If the muscles around your bladder become weak, the organ can actually slip out of position. This condition is called cystocele.
- Pelvic nerve damage: The pelvic nerves that control your bladder function can get injured during a long or difficult vaginal delivery.
- Injury during delivery: Sometimes, delivery with forceps can result in injuries to the pelvic floor muscles and anal sphincter muscles.
- Injury because of prolonged pushing: Prolonged pushing during a vaginal delivery can also increase the likelihood of injury to the pelvic nerves.
Is it common to leak urine during pregnancy?
For many women, urine leakage (incontinence) is a common during pregnancy or after giving birth. As your body changes throughout pregnancy to accommodate a growing baby, the bladder can be placed under pressure. This is normal for many women during pregnancy.
How are bladder control problems during or after pregnancy diagnosed?
Although most problems with bladder control during or after a pregnancy disappear over time, you should talk to your healthcare provider if the problem continues for six weeks or more after birth. It’s a good idea to keep a diary that records your trips to the bathroom. In this diary, you’ll want to make sure to keep track of how often your have urine leakage and when it occurs.
During an appointment, your healthcare provider will perform a physical examination to rule out various medical conditions and see how well your bladder is functioning. Your provider may also order various tests, including:
Your provider may also order various tests, including:
- Urinalysis: During this test, you will be asked to provide a urine sample. This sample will be analyzed for possible infections that could cause incontinence.
- Ultrasound: Images produced by ultrasound waves can make sure that your bladder is emptying completely.
- Bladder stress test: During this test, your provider will check for signs of urine leakage when you cough forcefully or bear down.
- Cystoscopy: This test involves a thin tube with a miniature camera at one end being inserted into your urethra. Your provider will be able to look inside your bladder and urethra during this test.
- Urodynamics: A thin tube is inserted into your bladder during this test. Water flows through this tube to fill the bladder, so that the pressure inside the bladder can be measured.
How are bladder control problems treated?
There are several techniques for treating bladder control problems. Kegel exercises may help to improve bladder control and reduce urine leakage. In addition, changing your diet, losing weight, and timing your trips to the bathroom may help.
Kegel exercises may help to improve bladder control and reduce urine leakage. In addition, changing your diet, losing weight, and timing your trips to the bathroom may help.
Some suggestions to help with bladder control problems include:
- Switching to decaffeinated beverages or water to help prevent urine leakage. Drinking beverages such as carbonated drinks, coffee and tea might make you feel like you need to urinate more often.
- Limiting the amount of fluids you drink after dinner to reduce the number of trips to the bathroom you need to make during the night.
- Eating foods that are high in fiber to avoid being constipated, since constipation can also cause urine leakage.
- Maintaining a healthy body weight. Extra body weight can put additional pressure on the bladder. Losing weight after your baby is born can help to relieve some of the pressure on your bladder.
- Keeping a record of when you experience urine leakage. It’s a good idea to keep track of what times during the day you have urine leakage.
 If you can see a pattern, you might be able to avoid leakage by planning trips to the bathroom ahead of time.
If you can see a pattern, you might be able to avoid leakage by planning trips to the bathroom ahead of time.
After you’ve established a regular pattern, you might be able to stretch out the time between trips to the bathroom. By making yourself hold on longer, you’ll strengthen your pelvic muscles and increase control over your bladder.
How can loss of bladder control due to pregnancy or childbirth be prevented?
Labor and vaginal delivery have an impact on the pelvic floor muscles and nerves that affect bladder control, so you should discuss your options with your healthcare provider.
Cesarean sections (C-sections) are associated with a lower risk of incontinence or pelvic prolapse than vaginal deliveries, but they may present other risks. Large babies who weigh more than 9 pounds at birth may increase the risk of nerve damage during delivery.
Exercising pelvic floor muscles with Kegel exercises can help prevent bladder control problems.
Bladder control problems might show up months to years after childbirth.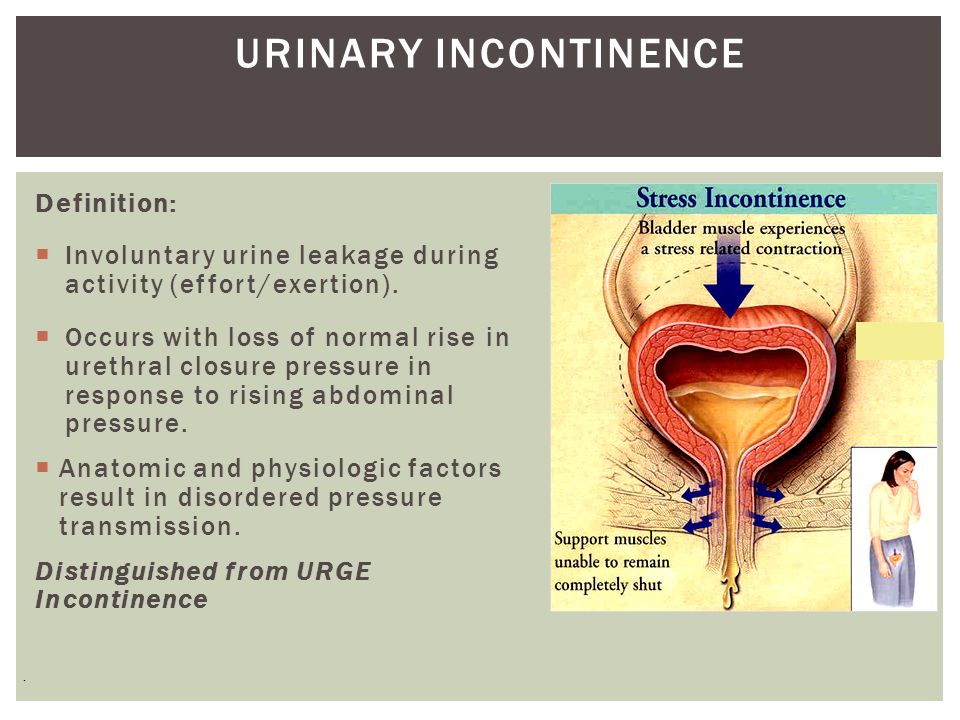 Talk to your healthcare team if this happens to you.
Talk to your healthcare team if this happens to you.
How do I do Kegel exercises?
Kegel exercises, also called pelvic floor exercises, help strengthen the muscles that support the bladder, uterus and bowels. By strengthening these muscles during pregnancy, you can develop the ability to relax and control the muscles in preparation for labor and birth.
Kegel exercises are highly recommended during the postpartum period (after you give birth) to promote the healing of perineal tissues, increase the strength of the pelvic floor muscles and help these muscles return to a healthy state (including better urinary control).
To do Kegel exercises, imagine you are trying to stop the flow of urine or trying not to pass gas. When you do this, you are contracting (tightening) the muscles of the pelvic floor, and are practicing Kegel exercises. While doing these exercises, try not to move your leg, buttock or abdominal muscles. In fact, no one should be able to tell that you are doing Kegel exercises.
Kegel exercises should be done every day. Doing five sets of Kegel exercises a day is recommended. Each time you contract the muscles of the pelvic floor, hold for a slow count of 10 seconds and then relax. Repeat this 15 times for one set of Kegels.
Tips to prevent involuntary urine leakage (incontinence) during and after pregnancy | Women's Health | Your Pregnancy Matters
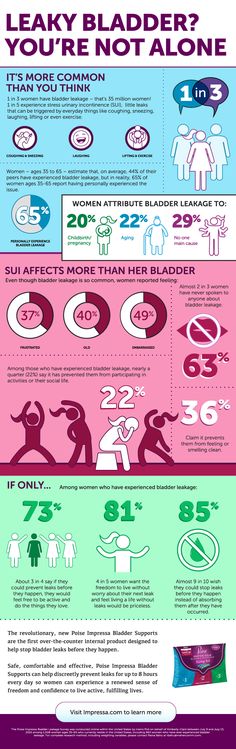
Instructions on how to locate pelvic muscles and exercises to strengthen them can help prevent incontinence during and after pregnancy.Friends and family describe stress urinary incontinence (SUI) to pregnant women as if it’s just a fact of life: "After you have a baby, you won't be able to cough, sneeze, or exercise without peeing a little."
SUI is the most common type of urinary incontinence associated with pregnancy. More than a third of pregnant women experience involuntary urine leakage during the second and third trimesters, and a third leak during the first three months after delivery.
But you don’t have to just live with urinary incontinence. There are steps you can take to prevent and reduce leakage before, during, and after pregnancy. Interventions can include lifestyle modifications and strengthening your pelvic floor muscles through Kegel exercises.
Unfortunately, not all health care providers make such recommendations. Or they might suggest performing Kegels, but they don't show patients how to do them correctly. There's a lot going on in the pelvic region during pregnancy, and many women don't know how to locate or engage their pelvic floor muscles.
UT Southwestern has one of the largest Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery divisions in the country. We help patients at all stages of life with strategies and therapies to prevent or treat urinary incontinence.
The first step in prevention is education.
Why does urinary incontinence occur with pregnancy?
Pregnancy and childbirth can cause incontinence in several ways:
- Your growing baby takes up a lot of room.
 As the uterus expands, it puts increased pressure on the bladder, urethra, and pelvic floor muscles. This can lead to leakage.
As the uterus expands, it puts increased pressure on the bladder, urethra, and pelvic floor muscles. This can lead to leakage. - Changing progesterone levels during pregnancy can weaken the pelvic floor. Increases in this hormone loosen up your ligaments and joints so the belly can expand and so you can deliver. But it can also loosen ligaments in the pelvis that help you hold in urine.
- Childbirth, particularly vaginal delivery, can stretch and weaken the pelvic floor muscles. This can lead to pelvic organ prolapse, in which your bladder, uterus, or rectum droops into the vaginal canal. Prolapse can be associated with urinary incontinence.
- Vaginal delivery also can result in pelvic muscle and nerve injury, which can result in bladder control problems.
If you experience urinary incontinence during pregnancy, you are at higher risk of having a persistent problem after birth. Tell your health care provider about urinary incontinence symptoms as soon as you notice them during pregnancy or at your first postnatal visit.
More than 80% of postpartum women who experience SUI symptoms during pregnancy may continue to experience stress incontinence without treatment.
Related reading: Body after birth: Treating post-pregnancy problems
Where are the pelvic floor muscles?
During initial exam, I often use a clock visual to help women know where their pelvic floor muscles can be palpated. If you lie on your back, imagine the top of the opening of your vagina is 12 o’clock and the bottom of the opening is 6 o’clock.
The pelvic floor muscles are easiest to palpate at the 5 o’clock and 7 o’clock positions– about even with where your legs meet your hips and approximately 3 to 4 centimeters above the vaginal opening.
These are the same muscles you contract when you try to stop the flow of urine midstream or if you were to tighten your vagina around a tampon. And these are the muscles you contract to do Kegel exercises. These pelvic floor muscle exercises were named after Dr. Arnold Kegel, who described them in the 1940s to help patients strengthen their pelvic floor muscles to treat urinary incontinence.
Arnold Kegel, who described them in the 1940s to help patients strengthen their pelvic floor muscles to treat urinary incontinence.
The proper way to Kegel
Verbal or written instructions alone don't necessarily help patients know whether they're doing Kegel exercises properly.
When we see patients for urinary incontinence, we provide education and instruction. We often recommend one to six sessions of supervised Kegel exercises with a female pelvic medicine and reconstructive surgery doctor, a pelvic floor physical therapist, or another provider who has expertise in pelvic floor disorders. While physical therapy or other medical visits usually are not covered by insurance for preventive purposes, they usually are once a problem develops.
In these appointments, your provider will describe how to locate and engage the pelvic floor muscles. The provider will gently press on the pelvic floor muscles with a gloved exam finger inside your vagina and ask you to squeeze the muscles. The muscles will be identified as described. Make sure you’re not squeezing your stomach, legs, or gluteal muscles at the same time, and don’t hold your breath.
The muscles will be identified as described. Make sure you’re not squeezing your stomach, legs, or gluteal muscles at the same time, and don’t hold your breath.
Some patients benefit from holding a mirror between the legs to visualize the external anatomy during the exercise. When done properly, you should see the area between your vagina and anus lift toward your upper body.
Doing Kegel exercises regularly is key to strengthening the pelvic floor. We recommend women do 10 repetitions, holding each squeeze for 5 to 10 seconds, three times each day.
You can do the exercises while lying down, sitting, or standing. Many patients find it easier to remember to do Kegels if the exercises become part of a daily routine. Maybe do a set while lying in bed right after you wake up, another as you eat lunch, and another at bedtime.
Most women see less frequent urine leakage within a few weeks or months after maintaining a Kegel exercise routine.
Before your big day arrives, get a preview of the accommodations for new moms at UT Southwestern's Clements University Hospital. From the chef-prepared meals to the roomy, high-tech labor and delivery suites, we want to make sure that you, your baby, and your family have the opportunity to bond in a safe and soothing environment.
Lifestyle changes to reduce urinary incontinence
Along with Kegel exercises, there are a few other noninvasive methods to eliminate or reduce the risk of urinary incontinence:
- Lose weight. Excess body weight puts pressure on the bladder. Even a 10% reduction in weight can significantly help with urinary incontinence. Work with your doctor to manage your weight gain during pregnancy, and after the birth of your little one, returning to your pre-pregnancy weight will help relieve the pressure on your bladder and pelvic floor.

- Quit smoking. Smoking has been shown to increase the risk of urinary incontinence as it leads to bladder irritation and chronic coughing.
- Make dietary changes. Some foods and beverages can make incontinence worse. These include caffeine, alcohol, and spicy and acidic foods. This is especially important if you experience urinary frequency and urgency and have trouble making it to the bathroom once you have the urge to urinate. Constipation can worsen symptoms of urine leakage. Stool in the rectum can put pressure on the bladder, urethra, and pelvic floor, so include plenty of higher-fiber foods and fluids in your daily diet.
Other treatments for urinary incontinence
Your doctor may recommend alternative treatment options, such as:
- Electrical stimulation: This therapy can help rehabilitate weak pelvic floor muscles and can be done in conjunction with Kegel exercises.
- Medications: Certain drugs can be used to treat urgency urinary incontinence (UUI) that does not respond to diet and behavioral modification, such as timed voiding to avoid overfilling of the bladder.
 UUI is associated with a sudden, intense urge to urinate followed by involuntary loss of urine. It is often associated with urinary frequency and urgency. Medications to treat UUI allow the bladder to fill up with more urine before giving the body a signal that it needs to use the bathroom.
UUI is associated with a sudden, intense urge to urinate followed by involuntary loss of urine. It is often associated with urinary frequency and urgency. Medications to treat UUI allow the bladder to fill up with more urine before giving the body a signal that it needs to use the bathroom. - Pessary: This is a plastic insert that supports the vaginal walls. It can be removed, replaced, and cleaned at home.
- Surgical procedures: There are several surgical procedures that can be performed for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence that does not respond to the conservative measures described above. One of the most common and effective surgeries involves placing a synthetic mesh sling between the vagina and the middle portion of the urethra. This supports the urethra like a hammock and helps control urine leakage during activities such as coughing, sneezing, laughing, exercise. Other effective surgeries for SUI that do not involve mesh include the Burch colposuspension and the traditional pubovaginal sling with graft material procured from the patient’s own body.
 Urethral bulking injection is an office procedure that may provide relieve of symptoms in patients who have contraindications for surgery.
Urethral bulking injection is an office procedure that may provide relieve of symptoms in patients who have contraindications for surgery.
If you are experiencing urinary incontinence during or after pregnancy, know that you’re not alone. Talk with your doctor – we can help you get back to exercising, laughing, and sneezing without worrying about a accidental urine leakage.
To visit with an incontinence expert, call 214-645-8300 or request an appointment online.
Frequent urination during pregnancy - Juno
Article content
When is considered frequent
Urges are frequent if they occur more than 9 times a day. Usually only a small amount of urine is passed at a time. Pregnant women may have about 20 visits to the toilet per day, while the daily amount of urine can also increase to 2 liters.
Is it an early sign of pregnancy?
HCG slightly increases the volume of urine excreted, so frequent urination begins already in the first weeks of pregnancy. The symptom does not 100% indicate the onset of fertilization - it should be considered in conjunction with other manifestations - primarily with a positive test. nine0008
The symptom does not 100% indicate the onset of fertilization - it should be considered in conjunction with other manifestations - primarily with a positive test. nine0008
However, keep in mind that with an increase in the daily volume of urine at a very early date, a false negative result is possible. Also, the symptom is less pronounced in ectopic pregnancy due to lower hCG levels, so an examination is required in any case.
If you began to frequent the toilet and there is a delay, then pregnancy is very likely.
Physiological causes of frequent urination in pregnant women
In healthy women, this phenomenon is associated with the body getting used to carrying a baby, as well as with other physiological reasons. nine0008
In the first half of pregnancy
The main causes of frequent urination during early pregnancy:
- Increased progesterone production. This hormone relaxes muscle tissue, helping to maintain pregnancy.
 As a result, urine is retained worse, the urge to void becomes more frequent due to the reduced tone of the bladder.
As a result, urine is retained worse, the urge to void becomes more frequent due to the reduced tone of the bladder. - Increased blood supply in the pelvis. Due to the proximity of the bladder to the uterus, its increased sensitivity occurs - filling receptors react more strongly. nine0027
- Active work of the kidneys. During the bearing of a child, the renal blood flow increases 1.5 times for the constant renewal of amniotic fluid and the timely removal of metabolic products. Accordingly, more urine begins to be produced.
Physiological increase in urination does not cause pain and discomfort, itching and burning. In the presence of negative symptoms, you need to consult a doctor to rule out pathologies.
Second half of pregnancy
The main reason for frequent urge to urinate in the second and third trimester is the increased pressure of the uterus on the bladder. However, diseases can also be the cause:
- Infections. Changes in the pelvis in pregnant women and a decrease in protective forces increase the risk of developing urethritis, cystitis, pyelonephritis.
 Such pathologies are accompanied not only by frequent urination, but also by pain, discomfort in the area of inflammation, and a burning sensation. The woman's health is deteriorating; nine0027
Such pathologies are accompanied not only by frequent urination, but also by pain, discomfort in the area of inflammation, and a burning sensation. The woman's health is deteriorating; nine0027 - Gestational diabetes. An increase in blood glucose in violation of carbohydrate metabolism. The amount of urine separated increases significantly.
Other pathologies include neoplasms in the small pelvis, endocrine and neurological disorders.
Soreness with frequent urination in pregnant women - is it normal or not?
Painful urination is not normal. Unpleasant sensations indicate the development of a pathological process. Pain and discomfort are a sign of urinary tract irritation. Cystitis is very likely if a woman has severely reduced immunity or has chronic diseases of the pelvic organs. Sometimes it can be accompanied by a temperature and requires a mandatory visit to the doctor. nine0008
Calls at night
Pregnant women often complain about how tired they are at night "hiking". The situation is explained by the fact that the work of the kidneys depends on the position of the body. In the later stages, the female body is prone to fluid retention and edema, especially when in an upright position. When the expectant mother lies down, the renal blood flow and the outflow of fluid from the tissues increase. As a result, the kidneys excrete more urine.
The situation is explained by the fact that the work of the kidneys depends on the position of the body. In the later stages, the female body is prone to fluid retention and edema, especially when in an upright position. When the expectant mother lies down, the renal blood flow and the outflow of fluid from the tissues increase. As a result, the kidneys excrete more urine.
What is the duration of frequent urination during pregnancy? nine0003
The phenomenon begins already from the first days of pregnancy and is especially pronounced up to about 12 weeks. Later, the number of emptyings gradually decreases, because by 4-5 months the body adapts to new conditions. The diaphragm rises, creating more space for the growing uterus and "unloading" the pelvic organs.
Frequent urination during pregnancy in the second trimester may indicate the addition of an infection or the development of inflammation, but it is also possible as a manifestation of the individual characteristics of the organism. You can find out more precisely this moment from your doctor, who is involved in pregnancy management. nine0008
You can find out more precisely this moment from your doctor, who is involved in pregnancy management. nine0008
In the third trimester, the opposite phenomenon is possible - fluid retention. However, the closer the birth, the more often the urge to urinate becomes. In the last month of gestation, the uterus descends and puts pressure on the organs of the urinary system.
How likely is miscarriage in the absence of frequent urination?
A woman does not always immediately find out about a missed pregnancy. Fetal movements are not felt in the early stages, so pregnant women "listen" to other signs. In the first weeks, the abrupt cessation of toxicosis and frequent urge to urinate are alarming. These symptoms can indeed indicate the death or developmental delay of the fetus, as well as an ectopic pregnancy, but not always. Toward the end of the first trimester, the kidneys excrete less urine, in some this has been observed since 9‒10 weeks.
How to deal with frequent urination during pregnancy: tips
In the absence of pathologies, the discomfort caused by physiological frequent urination can be reduced as follows:
- Stay hydrated.
 Drink enough, but don't overdo it. Give preference to water over sugary drinks like coffee.
Drink enough, but don't overdo it. Give preference to water over sugary drinks like coffee. - Eat rationally. Eliminate diuretic foods (citrus fruits, spicy foods), as well as things that cause constipation. nine0027
- Exercise. Strengthen your pelvic muscles by training your vaginal and anus sphincters.
- Get more rest. Sleep during the day is very useful, especially in the later stages - after being in a horizontal position, the bladder empties faster, as a result, the load on the kidneys during night rest is reduced.
- Maintain immunity. Avoid hypothermia, take vitamin complexes as prescribed by the doctor.
- Empty your bladder as much as possible. Do not hold back the urge and try to make sure that all the urine comes out completely. In this regard, it is easier to urinate in the shower. nine0027
Control your condition. If other symptoms (pain, fever, burning sensation) appear in addition to frequent urination, tell your doctor immediately.
1st trimester of pregnancy: what happens to the fetus
1st trimester of pregnancy: what happens to the fetus - Private maternity hospital Ekaterininskaya Clinics1st trimester: 1st to 12th weeks
The gestational age is calculated from the first day of the last menstruation, since it is difficult to determine the exact day of conception. Since conception usually occurs in the middle of the menstrual cycle, you are not actually pregnant during the first two weeks, but this period is counted as the beginning of pregnancy. nine0008
As soon as the fertilization of the egg takes place around the 3rd week, the hormones begin to produce changes in your body little by little. As a result, you may experience some of the following symptoms:
- Morning sickness. As a result of rising levels of hormones characteristic of pregnancy, up to 80% of women in the 1st trimester experience morning sickness with symptoms such as nausea and vomiting.
 The idea that such malaise is observed only in the morning is a common misconception. In fact, symptoms can appear at any time of the day or night. Up to 1 in 5 women experience morning sickness in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy and can sometimes persist throughout pregnancy. nine0007 If you experience morning sickness, avoid foods that make you sick, eat little and often, avoid fatty and spicy foods, drink more water. If you experience severe symptoms or symptoms that bother you, see your doctor.
The idea that such malaise is observed only in the morning is a common misconception. In fact, symptoms can appear at any time of the day or night. Up to 1 in 5 women experience morning sickness in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy and can sometimes persist throughout pregnancy. nine0007 If you experience morning sickness, avoid foods that make you sick, eat little and often, avoid fatty and spicy foods, drink more water. If you experience severe symptoms or symptoms that bother you, see your doctor. - Breast changes. The mammary glands will begin to increase in size, soreness may appear. The nipples will increase in size, become darker and more protruding.
- Fatigue. High levels of the hormone progesterone can make you feel tired and sleepy. Rest as often as possible in a horizontal position with your legs up and eat as well as possible, which is not easy if you are experiencing morning sickness!
- Increased emotionality.
 A higher level of emotionality, manifested as a result of an increase in hormone levels, is a normal phenomenon. Understanding and patience on the part of your partner and loved ones is very important here. nine0027
A higher level of emotionality, manifested as a result of an increase in hormone levels, is a normal phenomenon. Understanding and patience on the part of your partner and loved ones is very important here. nine0027 - Food likes and dislikes. You may find yourself intolerant of one food and addicted to another. This is usually not a problem, unless you feel like eating weird foods like chalk. If you are concerned about the situation, contact your doctor.
- Frequent urination. As your body fluid levels increase and your uterus presses on your bladder, you will become more likely to visit the toilet. Go to the toilet as soon as you feel the need - this minimizes the pressure on the bladder. nine0027
- Feeling of dizziness. Sometimes you may feel a little dizzy (this is due to hormonal changes). Try not to stay on your feet for a long time and slowly rise from a sitting or lying position. If you experience severe dizziness, contact your doctor immediately.
- Heartburn and constipation. Your digestive system will slow down to give you more time to digest your food. This can lead to heartburn and constipation. To help manage heartburn, try to eat small meals at regular intervals and avoid fried or spicy foods and carbonated drinks. Constipation is helped by eating a diet rich in fiber, maintaining physical activity and drinking plenty of water. nine0027
1st trimester milestones
- Approximately 7 days after fertilization, the embryo implants in the uterine wall. The placenta, umbilical cord, and amniotic sac will begin to form to provide nourishment and protection to the embryo.
- By the end of the first 12 weeks of pregnancy, the uterus is palpable through the wall of the abdomen, the abdomen will begin to grow.
Child development in the 1st trimester of pregnancy
By the end of the 1st trimester:
- All the main organs of the baby are formed, the circulatory system works.

Learn more