Infant red eyelid
Pink Eye (Conjunctivitis) in Newborns
Newborns with symptoms of conjunctivitis (pink eye) should see a doctor right away.
Neonatal conjunctivitis is a red eye in a newborn caused by infection, irritation, or a blocked tear duct. When caused by an infection, neonatal conjunctivitis can be very serious.
Symptoms and Causes of Conjunctivitis in Newborns
Newborns with conjunctivitis develop drainage from the eyes within a few days to several weeks after birth. Their eyelids become puffy, red, and tender. The cause of neonatal conjunctivitis is often difficult to determine because, in many instances, the symptoms don’t vary by cause.
Conjunctivitis in a newborn may be caused by a blocked tear duct, irritation produced by the topical antimicrobials given at birth, or infection with a virus or bacterium passed from the mother to her baby during childbirth. Even mothers without symptoms (asymptomatic) at the time of delivery can carry and pass bacteria or viruses to babies during birth.
The most common types of neonatal conjunctivitis include the following:
- Inclusion (chlamydial) conjunctivitis
Chlamydia trachomatis can cause inclusion conjunctivitis and genital infections (chlamydia). A woman with untreated chlamydia can pass the bacteria to her baby during childbirth. Symptoms of inclusion conjunctivitis include redness of the eye(s), swelling of the eyelids, and discharge of pus. Symptoms are likely to appear 5 to 12 days after birth. Symptoms can develop earlier if the amniotic sac is ruptured during delivery. Some newborns with chlamydial conjunctivitis can have the infection in other parts of their bodies. The bacteria can infect the lungs and nasopharynx (where the back of the nose connects to the mouth). - Gonococcal conjunctivitis
Neisseria gonorrhoeae can cause gonococcal conjunctivitis, as well as the sexually transmitted infection called gonorrhea. A woman with untreated gonorrhea can pass the bacteria to her baby during childbirth.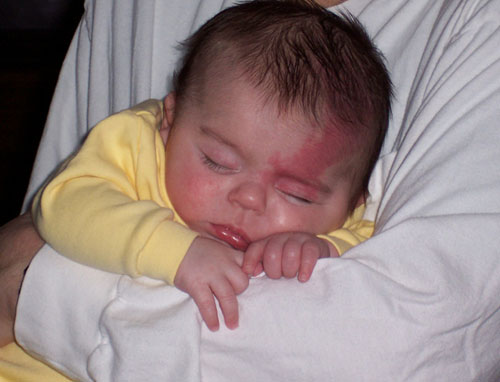 Symptoms usually include red eyes, thick pus in the eyes, and swelling of the eyelids. This type of conjunctivitis usually begins in the first 2-5 days of life. It can also progress to serious infections of the bloodstream (bacteremia) and lining of the brain and spinal cord (meningitis) in newborns.
Symptoms usually include red eyes, thick pus in the eyes, and swelling of the eyelids. This type of conjunctivitis usually begins in the first 2-5 days of life. It can also progress to serious infections of the bloodstream (bacteremia) and lining of the brain and spinal cord (meningitis) in newborns. - Chemical conjunctivitis
When eye drops are given to newborns to help prevent a bacterial infection, the newborn’s eye(s) may become irritated. This may be diagnosed as chemical conjunctivitis. Symptoms of chemical conjunctivitis usually include mildly red eye(s) and some swelling of the eyelids. Symptoms are likely to last for only 24 to 36 hours. - Other neonatal conjunctivitis
Viruses and bacteria other than Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae can cause conjunctivitis. For example, bacteria that normally live in a woman’s vagina and are not sexually transmitted can cause conjunctivitis. Additionally, the viruses that cause genital and oral herpes can cause neonatal conjunctivitis and severe eye damage. The mother may pass such viruses to her baby during childbirth. However, herpes conjunctivitis is less common than conjunctivitis caused by gonorrhea and chlamydia. Symptoms usually include red eye(s) and swollen eyelids with some pus.
The mother may pass such viruses to her baby during childbirth. However, herpes conjunctivitis is less common than conjunctivitis caused by gonorrhea and chlamydia. Symptoms usually include red eye(s) and swollen eyelids with some pus.
Prevention and Treatment of Conjunctivitis in Newborns
To prevent neonatal conjunctivitis, most states have laws requiring providers to put drops or ointment in a newborn’s eyes, typically within 2-3 hours of birth. In the past, hospitals used silver nitrate; now hospitals mostly use antibiotic eye drops, typically erythromycin. During pregnancy and prior to giving birth, women with genital herpes should consult with their physician about ways to minimize the chances of spread to their newborn baby.
Doctors may treat neonatal conjunctivitis caused by a bacterial infection with antibiotics. It will depend on the severity of the infection and the bacteria that caused it. Some antibiotics are applied as an eye drop or ointment in the eye (topical). Other antibiotics are given by mouth (orally), through a vein (intravenous), or as a shot (intramuscular). Doctors may treat a newborn’s conjunctivitis with a combination of topical, and either oral, intravenous, or intramuscular antibiotics. Rinsing the newborn’s infected eye with a saline solution will remove any debris that may develop in response to the infection.
Other antibiotics are given by mouth (orally), through a vein (intravenous), or as a shot (intramuscular). Doctors may treat a newborn’s conjunctivitis with a combination of topical, and either oral, intravenous, or intramuscular antibiotics. Rinsing the newborn’s infected eye with a saline solution will remove any debris that may develop in response to the infection.
If a blocked tear duct causes conjunctivitis, a gentle, warm massage between the eye and nasal area may help. If the blocked tear duct does not clear by 1 year of age, the newborn may require surgery.
Treatments for the common causes of neonatal conjunctivitis are as follows:
- Inclusion (chlamydial) conjunctivitis
Doctors usually use oral antibiotics to treat inclusion conjunctivitis. - Gonococcal conjunctivitis
Doctors give intravenous (IV) or intramuscular (IM) antibiotics to treat gonococcal conjunctivitis. If untreated, the newborn could develop corneal ulcerations (open sores in the cornea) and blindness.
- Chemical conjunctivitis
Since this type of conjunctivitis is caused by chemical irritation, treatment is usually not required. The newborn will usually get better in 24 to 36 hours. - Other bacterial and viral conjunctivitis
Doctors usually give antibiotic drops or ointments to treat conjunctivitis caused by other bacteria For both bacterial and viral conjunctivitis, a warm compress to the eye may relieve swelling and irritation. Be sure to wash hands before and after touching the infected eyes.
Baby Red Around Eyes: Causes and Treatments
If your sweet baby has redness around their eyes but they haven’t been crying, you’re probably wondering what’s causing it — and how much you should worry.
Let’s look at what could be going on.
Rubbing
Skin around the eyes is probably the most delicate skin of the body. (Yes, this is the first place we’ll notice fine wrinkles later in life for that very reason.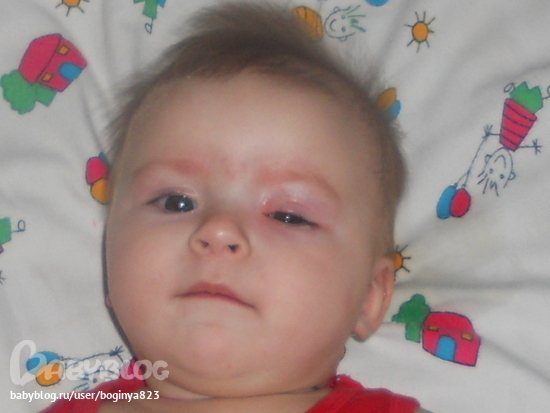 ) If your child has been rubbing their eyes, the area will easily turn red.
) If your child has been rubbing their eyes, the area will easily turn red.
Rubbing — in and of itself — isn’t really cause for concern, unless what’s making your baby rub is more serious. (Do keep in mind that fingers + eyes = recipe for infections.)
But if it’s just a sleepy behavior your newborn’s picked up, you can try hand covers to prevent it, or wait for it to resolve on its own.
Irritants
Irritants are substances that injure the eyes, skin, or airways in some way. You can divide irritants into indoor and outdoor. Indoor irritants include:
- cigarette smoke
- perfumes
- sunscreen
- soaps
Outdoor irritants include:
- smoke
- fumes
- chemical vapors
- chlorine in pool water
- smog
Irritants usually cause localized redness that resolves once your baby is removed from the area where the irritant exists, or the irritant is removed from your home.
Allergies
Allergies happen when our eyes (or another part of our body) react to an allergen. An allergen is usually a harmless substance that triggers an immune response in people who are sensitive to the allergen.
An allergen is usually a harmless substance that triggers an immune response in people who are sensitive to the allergen.
Common allergens include:
- dust mites
- mold
- perfume in cosmetics and lotions
- medications
- foods
- dander from pets
- pollen from trees, plants, grasses, and weeds
- insect venom
If your child has a sensitivity and encounters an allergen, their eyes may produce histamine to fight the allergen. As a result, their eyelids and conjunctiva (the tissue that covers the white part of your eye and the inside of the eyelids) becomes red, swollen, and itchy.
You’ll probably also notice that your child’s eyes are watery with excess tears. A vicious cycle can set in: They rub their eyes to relieve the itching and burning, but the rubbing action irritates their eyes further and the redness increases.
While some of these allergens (like dust mites and pet dander) are around all year long, others are seasonal. If your child is allergic to pollen, you’ll notice their red eyes when pollen counts are high.
If your child is allergic to pollen, you’ll notice their red eyes when pollen counts are high.
Children with eye allergies often have nasal allergies as well. Yes, it’s double the trouble. If you suspect that the redness around your child’s eyes is an allergic reaction, check if they’re sneezing excessively or have a stuffy nose.
Sometimes, if an allergic reaction happens often enough, your child’s mast cells can become oversensitive.
Think of mast cells as your body’s first line of defense against invaders. When mast cells in the eye become oversensitive, they release histamine even if the allergen doesn’t come into direct contact with the eye.
Eye allergies are also called allergic conjunctivitis.
Infections
An eye infection happens when viruses or bacteria enter the eye area. It’s important to know the difference, because bacterial conjunctivitis needs antibiotic treatment.
Viral conjunctivitis
This is also called pink eye, although pink eye can be viral or bacterial. Children with colds commonly develop viral eye infections. Symptoms include:
Children with colds commonly develop viral eye infections. Symptoms include:
- red, puffy eyelids
- red in the white part of the eye
- watery eyes
Bacterial conjunctivitis
This is more serious than viral conjunctivitis. You’ll notice the same symptoms as those that you notice in a viral eye infection. Symptoms also include:
- a sticky, yellow discharge from the eye
- eyelashes and eyelids that may get stuck together from the discharge
Newborn conjunctivitis
Redness in the eye area of a newborn can be caused by a blocked tear duct, irritation, or infection. Newborn conjunctivitis can be serious, so talk with your pediatrician right away.
Stye
A stye (also called a hordeolum) is a painful, red bump on the eyelid. A stye happens when a hair follicle, oil gland, or sweat gland becomes infected. Symptoms include:
- painful, red bump on the eyelid
- redness on the eyelid
- tenderness and swelling around the eye
Periorbital cellulitis
If the area around your child’s eye is injured or if your child has a sinus infection, they may develop periorbital cellulitis. This is a bacterial infection of the eyelids and skin around them. You’ll notice that your child’s eyelids are very red and swollen.
This is a bacterial infection of the eyelids and skin around them. You’ll notice that your child’s eyelids are very red and swollen.
This is a serious condition and needs immediate treatment.
If your child has redness around their eyes, you can start treatment at home. However, if your child is a newborn or you suspect cellulitis, get immediate medical treatment.
Irritants
If you can, pin down which irritant is affecting your child. Try a different brand of soap, shampoo, and laundry detergent.
Allergies
Eye allergies usually come with a wider range of symptoms that also affect the nasal and airway passages. Keep a journal to track what could be causing the allergic reaction.
Here are some areas to examine:
- What’s on your baby’s daily menu?
- Is the allergic reaction related to the season?
- Does it happen at day care? Or every time you visit a specific family member or friend?
- Is the allergy related to animals?
- Do food allergies, like those to milk, wheat, or eggs, run in your family?
Eye infections
Viral conjunctivitis
Take care of viral conjunctivitis by rinsing the eyes often with warm water.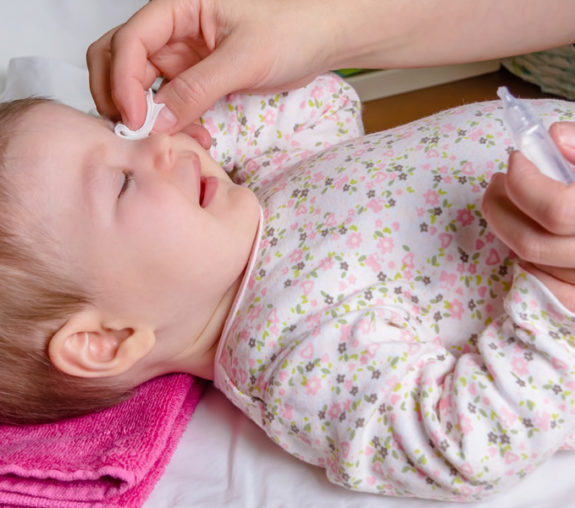 Use a clean cotton ball for each eye. Wash your hands before and after each cleaning.
Use a clean cotton ball for each eye. Wash your hands before and after each cleaning.
If you’re nursing, you can try dripping some of your milk into the corner of the eye. Human milk contains many healing properties.
Antibiotics won’t help a viral eye infection. Expect the redness to last between 4 and 7 days.
Bacterial conjunctivitis
A sticky, yellow discharge indicates a bacterial infection. You can use warm water and your milk to keep the area clean and to provide some relief, but you’ll need to talk with a doctor about antibiotic eye drops or eye cream to fight the infection.
Newborn conjunctivitis
Newborns with redness in or around the eye need immediate medical attention.
If the redness is from a blocked tear duct, you can gently massage the opening of the duct and below the lower eyelid to help it open up.
Sometimes, the antimicrobial eye drops that your baby is given right after birth can irritate the eyes. This mild redness should clear up within 24 to 36 hours.
Infection can happen when viruses or bacteria in the birth canal pass from the mother to the baby.
Stye
Use a warm compress three to four times a day to ease discomfort and reduce redness. If you’re nursing, use a few drops of your milk, too.
Take your baby to a pediatrician if you don’t see any improvement despite the home treatments. Take your journal with you so that the doctor can help track any possible causes.
Remember to tell your pediatrician about any milk, egg, or gluten allergies that run in your family.
If your newborn has a bacterial infection, depending on the severity, your pediatrician will prescribe:
- topical treatment, such as eye drops or ointment (most often)
- oral antibiotics (less commonly)
- intravenous antibiotics (very rarely)
If your baby’s tear duct is blocked, your pediatrician can show you how to massage the duct area to help it open.
Tear ducts usually open by themselves. However, if the duct doesn’t open by the time your child reaches age 1, they may need simple surgery.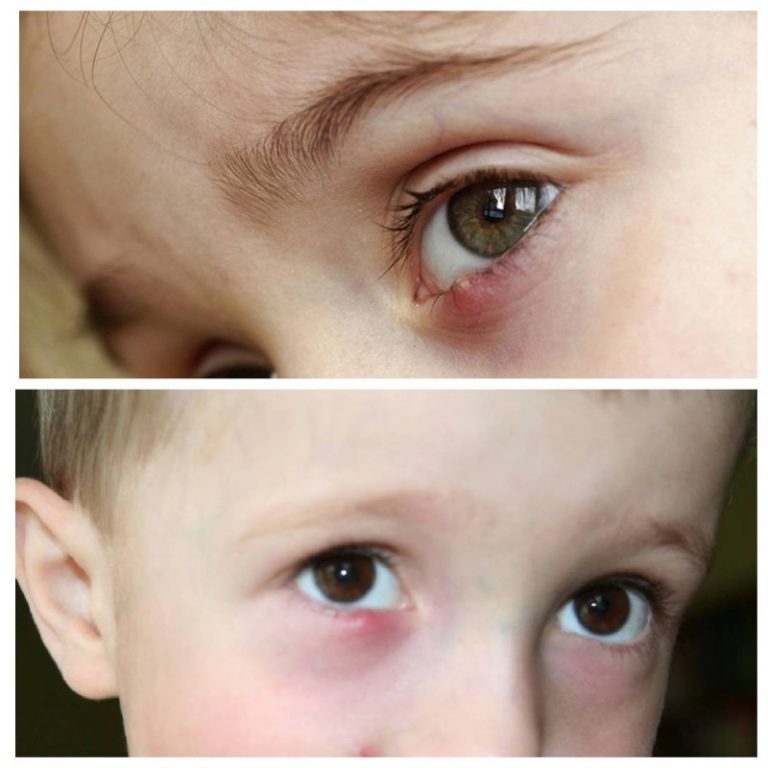
If your toddler has bacterial conjunctivitis, your pediatrician will prescribe antibiotics.
Any time your little one has something going on, you may worry. But while redness around the eyes may bother you and your baby, it’s usually a simple thing to deal with.
Just be sure to call the doctor if there’s discharge, or if the issue hasn’t gotten better after a few days.
possible causes and treatments
Redness of the eyelids in a newborn is quite common. There can be many reasons for this phenomenon. In some cases, eyelids with slight redness are considered normal. Sometimes such a cosmetic defect can signal a serious illness and require immediate medical attention. Why can infants change the color of the skin on the eyelids? Does it always require treatment? When should you see a doctor? All answers are in the article. nine0003
Possible causes
Red eyelids in a newborn may be due to various reasons. One of the most common is that the baby has a very thin skin on the eyelids, through which blood vessels are visible.
Another cause is infantile hemangioma, in which there is also a red eyelid in newborns after childbirth. Why does this phenomenon occur? During delivery, the baby passes through the birth canal and is compressed by the internal organs of the mother. As a result, the blood vessels in the baby burst, possibly hemorrhage. Redness may spread throughout the eyelid, appearing as a spot above the eye. nine0003
Very often, hemangioma disappears by itself by about a year, without the intervention of specialists. If this does not happen, and redness covers all large areas of the baby's skin, you need to contact a pediatrician. In such situations, laser treatment may be required.
Rubs the baby's eyes: possible causes, consultation...
From the first days of life, the baby is under constant control of the parents. Behavioral reactions,...
Another common cause of eyelid redness is blepharitis. Most often, this disease occurs in newborns with low body weight and weakened immunity. Babies who have appeared before the due date are subject to this phenomenon. The disease is infectious. The causative agents of blepharitis are staphylococci. Redness of the eyelids and swelling (of varying degrees) persist for a long time. The disease can affect the entire area of the eye or focus only in its corner. In addition to redness, blepharitis is accompanied by swelling, peeling and purulent discharge from the organ of vision. The baby squints in bright light. nine0003
Babies who have appeared before the due date are subject to this phenomenon. The disease is infectious. The causative agents of blepharitis are staphylococci. Redness of the eyelids and swelling (of varying degrees) persist for a long time. The disease can affect the entire area of the eye or focus only in its corner. In addition to redness, blepharitis is accompanied by swelling, peeling and purulent discharge from the organ of vision. The baby squints in bright light. nine0003
Redness that occurs suddenly may indicate an allergic reaction in the body of the newborn. In such cases, the pediatrician prescribes the necessary tests to identify the allergen. In most cases, the reason lies in the products that the nursing mother consumes. In such situations, she needs to review her diet and exclude from it foods that could cause an undesirable reaction in a child.
Purulent inflammation of the eyelash bulb can also cause redness. The common and most common name for this phenomenon is barley. Pathology is accompanied by swelling and pain in the localization area. A few days later, a purulent core ripens in the area of inflammation, which in no case should be squeezed out on its own. After the release of the purulent mass, the pain subsides, the swelling subsides. nine0003
Pathology is accompanied by swelling and pain in the localization area. A few days later, a purulent core ripens in the area of inflammation, which in no case should be squeezed out on its own. After the release of the purulent mass, the pain subsides, the swelling subsides. nine0003
Rubbing the baby's eyes: possible causes, consultation...
From the first days of life, the baby is under the constant control of the parents. Behavioral reactions,...
Phlegmon is a serious disease that requires immediate medical attention. This is an inflammation that completely affects the upper or lower eyelid of the baby. Pathology in most cases is accompanied by a strong compaction and swelling. Sometimes there is an increase in body temperature, redness of the sclera. If left untreated, phlegmon will quickly spread to a healthy eye. nine0003
Another condition that can cause swollen red eyelids in a newborn is uevitis, or inflammation of the choroid. It requires immediate medical attention.
Redness of the eyelids may indicate acute viral infections that occur in the body of the newborn.
Conjunctivitis
Redness can be caused by a purulent inflammatory process - conjunctivitis, which is caused by bacteria and other harmful microorganisms. The disease is characterized by swelling of varying degrees, discharge of pus from the eyes, and photophobia. Treatment should be prescribed only by a doctor after examining the baby and confirming the diagnosis. Often, conjunctivitis is one of the manifestations of an allergic reaction. This disease can be combined with blepharitis and keratitis (inflammation of the cornea). nine0003
Souring eyes in newborns: possible causes and...
Souring eyes in a newborn baby is a very common problem. But parents don't...
In each case, the pediatrician prescribes specific drugs that can cope with the pathogen. From conjunctivitis in a child in a pharmacy, you can buy prescription drugs in the form of drops and ointments. For allergic conjunctivitis, antihistamines are used. The effect of such therapy comes quickly enough. Within a day, the child's condition improves. Also, from conjunctivitis, the child will be helped by regular rubbing of the eyelids with a decoction of chamomile. For its preparation 1 tsp. raw materials are poured into a glass of water, put on fire, allowed to boil, cooled, filtered. nine0003
For allergic conjunctivitis, antihistamines are used. The effect of such therapy comes quickly enough. Within a day, the child's condition improves. Also, from conjunctivitis, the child will be helped by regular rubbing of the eyelids with a decoction of chamomile. For its preparation 1 tsp. raw materials are poured into a glass of water, put on fire, allowed to boil, cooled, filtered. nine0003
When not to sound the alarm
In some cases, redness of the eyelids is not the result of serious diseases, so parents do not need to worry. However, it is important to remember that only a qualified pediatrician can determine the cause of the phenomenon.
Thin skin, through which blood vessels are visible - this is considered the norm for babies. Over time, this flaw will disappear. Do not worry if the redness is not accompanied by peeling, itching, and an increase in basal temperature. nine0003
Changes in the color of the eyelids can be caused by mechanical damage to the mucous membrane of the eye. In the first time after birth, the child randomly moves his arms and may accidentally hit himself or rub his eyes with a blouse sleeve.
In the first time after birth, the child randomly moves his arms and may accidentally hit himself or rub his eyes with a blouse sleeve.
Insect bites can also cause swelling. In such situations, special gels will come to the aid of parents, the use of which is allowed for children from the first months of life.
Treatment
Sometimes topical treatment - drops and ointments - is enough to completely eliminate the problem. However, more often complex therapy is needed. In case of blockage of the lacrimal canal, massage and antibacterial drops may be indicated. Allergic reactions are removed only with the help of antihistamines and washing. nine0003
Blepharitis is a serious disease that requires long-term therapy. It should include ointments, drops, washing, lotions. In some cases, you may need the help of other specialists - an ophthalmologist, dermatologist, gastroenterologist. With conjunctivitis, topical preparations are usually sufficient. Comprehensive treatment is needed for uveitis. Glucocorticosteroids, immunosuppressive therapy will be required.
Glucocorticosteroids, immunosuppressive therapy will be required.
What parents should do
Immediate contact with a pediatrician can prevent serious consequences. If a foreign body has got into the eye of a newborn, it is necessary to carefully remove it. If parents are afraid to carry out manipulations on their own or doubt the outcome, it is better to seek help from a specialist. nine0003
Rubbing the baby's eyes: possible causes, consultation...
From the first days of life, the baby is under the constant control of the parents. Behavioral reactions,...
Mom and dad of a newborn need to carefully monitor his condition, regularly examine the baby's body, pay attention to the slightest changes. In addition, in the first months of life, it is necessary to regularly wash the baby's eyes with a solution of chamomile or plain clean water. Before carrying out the procedure, parents must thoroughly wash their hands. nine0003
To prevent injuries, injuries and bruises, parents should securely fix the position of the baby in the stroller and crib. Under no circumstances should a newborn baby be left unattended. As a prevention of mechanical injuries, it is advisable to wear special gloves on the baby's hands.
Under no circumstances should a newborn baby be left unattended. As a prevention of mechanical injuries, it is advisable to wear special gloves on the baby's hands.
What to avoid
It is strictly forbidden to self-medicate and resort to the use of any medicines without the advice of a specialist. In no case, in the presence of pustules, attempts should be made to squeeze out the contents. This can greatly aggravate the situation. Suspecting barley, it is strictly forbidden to use bandages and make compresses. If the baby has reddened eyelids or eyes, call a doctor. This will help prevent many possible troubles. nine0003
Folk remedies
Recipes of traditional healers can be used as a prophylactic. They are also used as part of complex therapy and for daily care of the baby.
A weak chamomile decoction, the preparation of which is discussed above, is suitable for wiping a child's eye. Cornflower is also suitable for preparing a hygiene product. The decoction is prepared according to the same principle as chamomile. It is necessary to carry out hygiene procedures 5-6 times a day. nine0003
It is necessary to carry out hygiene procedures 5-6 times a day. nine0003
Conclusion
Parents often notice that their newborn has red eyelids. If this happens, you first need to carefully examine the face of the child. Perhaps he accidentally scratched himself. If no injury is found, contact your pediatrician. He will establish why the newborn has red eyelids and prescribe the necessary treatment.
causes and should the baby be shown to the doctor?
Redness of the eyelids in a newborn can put parents on their guard. In some cases, this is considered normal, as the baby's skin is very thin and delicate. But sometimes redness is a sign of serious illness, so it is recommended to consult a pediatrician. nine0012
Do not self-medicate! Be sure to consult a qualified physician. The information is for informational purposes only and does not replace medical advice.
- Why this symptom occurs in babies
- Blood vessels in an infant
- If reddened after childbirth
- Red circles on the skin under the eyes and around them
- What to do for parents
- precautions8
Why does this symptom occur in infants
It is impossible to unequivocally name the cause, which leads to reddening of the eye . Sometimes this is an anatomical feature of thin skin, and over time it disappears.
Sometimes this is an anatomical feature of thin skin, and over time it disappears.
But it is important to be alert if the skin is reddened, flaky, accompanied by itching - this may indicate a disease.
Blood vessels in a newborn
Blood vessels are visible through the thin skin of a newborn, especially in the most vulnerable places. This is not a pathology: the reason is the thinness of the skin, through which you can easily see the capillaries filled with blood. nine0003
However, if the vessels are visible not only on the eyelids, but also on the whites of the eyes, it is worth sounding the alarm. This may indicate pathologies of the vascular system of the visual organs of an inflammatory nature. A similar phenomenon signals uveitis, iridocyclitis, iritis and a number of other eye pathologies.
If reddened after childbirth
Red eyelids in a newborn (baby) from birth can be the result of various reasons. Hemangioma is quite common.
During childbirth, the baby passes through the birth canal and is compressed by the mother's internal organs. Because of this, blood vessels burst, possibly bleeding.
Because of this, blood vessels burst, possibly bleeding.
Redness may spread all over the eyelid, appearing as a spot above the eye. In some cases, the hemangioma goes away on its own.
But if this does not happen, and its size increases, swelling occurs, surgery or laser treatment may be required.
Common cause of eyelid redness and swelling - blepharitis. Weak, premature babies, whose immunity is reduced, are more susceptible to it.
Infectious disease, provoked by staphylococci. The eyelids with this disease remain red and swollen for a long time. Pathology can spread throughout their territory or be located only in the corner of the eye.
The sudden appearance of redness may indicate an allergy, inflammation of the eye. If an infection enters the organs of vision, then both the eyelids and the proteins around the pupils turn red. nine0003
It is important to prevent the risk of foreign body entry. All treatment must be prescribed by a doctor.
If you have a small child, you may find it helpful to read about eye problems in newborns:
Red circles on the skin under and around the eyes
failures in the infant's body. Red circles may have a yellow or blue tint depending on the cause. nine0003
To determine it, you need to take into account the accompanying symptoms : swelling, itching, fever, sleep problems.
Circles may occur under one or two eyes. If they occur under only one, the cause may be a hemangioma (the spot will be bluish-red, with jagged edges) or a papilloma.
Perhaps it is a mechanical effect - skin friction or impact.
Redness under both eyes is a common consequence of various infections. They appear with purulent tonsillitis, diseases of the oral cavity, with adenoids that block the nasopharynx and disrupt breathing. nine0003
If both the upper and lower eyelids turn red, the cause may be hidden in dacryocystitis, allergies, dry keratoconjunctivitis, acute viral infections, bacterial diseases of the organs of vision, uveitis, trauma. In more rare cases, the cause is helminths (worms).
In more rare cases, the cause is helminths (worms).
Circles are also a symptom of fatigue. In any case, it is important to consult a specialist who will determine the cause of this phenomenon.
What to do for parents
If you notice redness in your baby, immediately show it to the pediatrician. Consultation with other specialists may be required. nine0003
If you suspect an allergy, you should visit an allergist in order to carry out the necessary tests and analyses.
If there is a suspicion of inflammation of the organs of vision , an ophthalmologist's consultation is required . He will conduct an examination, collect an anamnesis. In some cases, the help of a neurologist is required.
Treatment will depend on the problem causing the redness. If a foreign body gets into the eye, you need to carefully get it out. The baby needs healthy sleep.
Make the light in the room where it is located more subdued. The doctor may recommend rinsing the affected eyes with Furacilin several times a day.
Sometimes topical treatment - drops and ointments - is enough. More often complex therapy is needed. In case of blockage of the tear duct, massage and antibacterial drops for children may be indicated. For allergies - antihistamines, washings.
Blepharitis requires a long and complex therapy: ointments, drops, washes, lotions. You may have to work with an ophthalmologist, dermatologist, gastroenterologist, as the disease is often associated with disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. nine0003
Comprehensive treatment is also needed for uveitis. Glucocorticosteroids, immunosuppressive therapy will be required. With conjunctivitis, topical preparations are usually sufficient.
Do Not Recommend: Precautions
First of all, do not self-medicate , because the delicate skin and body of the baby is very easy to injure. Consult your doctor and follow the advice he gives.
It is important to avoid exposure to ultraviolet rays of the sun, as they are harmful to the child's eyes.