How to calculate syrup dose for child
Pediatric Dose Calculator
Created by Łucja Zaborowska, MD, PhD candidate
Reviewed by Bogna Szyk and Steven Wooding
Based on research by
Pan SD, Zhu LL, Chen M, Xia P, Zhou Q. “Weight-based dosing in medication use: what should we know?“ Patient Prefer Adherence (2016)
Last updated: Jan 04, 2023
Table of contents:- How to use the pediatric dose calculator?
- Dose frequency abbreviations
- How do you calculate pediatric doses?
- Child dose calculations examples
The pediatric dose calculator is a simple tool for computing the pediatric dosage for a child of a given weight. 👶
Our calculator allows you to convert values in mg or μg to a precise volume of the medication, using a wide range of units.
The article below is an essential part of our peds dosing calculator - keep on reading to discover all the necessary medical abbreviations, information on pediatric medication dosing, and tips on how to calculate the pediatric dose on your own.
Disclaimer: We try our best to make our Omni Calculators as precise and reliable as possible. However, this tool can never replace professional medical advice.
How to use the pediatric dose calculator?
Pediatric dosage is a complicated matter - we can't deny it. We decided to make things easier for you and explain step-by-step all the actions you need to take to receive the most accurate results.
| 💡 Our mg per kg dosage calculator works both ways; you may convert medication's weight to volume and the other way around. |
-
Decide whether your dose is given in mg or μg.
Milligrams (mg) are 1000 times greater unit than micrograms (μg) - 1 mg = 1000 μg.
-
Find out your type of dosage.
Your dose in mg/μg might be given:
-
per kilogram per day (e.
 g., mg/kg/day) - the most popular option
g., mg/kg/day) - the most popular option -
per kilogram per dose (e.g., mg/kg/dose)
-
per day (e.g., mg/day)
-
per dose (e.g., mg/dose)
The calculator will display the chosen dosage type underneath.
Dosage type has a crucial impact on the value of the dosage!
Only the first two types use the dosage calculator by weight; two latter ones rely on a predetermined amount of medication.
-
Finally, enter your dose amount in mg or μg.
Double-check all the settings - you want to make sure that the pediatric drug dose calculator is computing exactly what you want it to calculate.
-
Choose the frequency. - check the section below.
-
Choose the weight of your child and a proper unit.
-
Enter your drug concentration.
Choose the mass of the drug per given volume of the medication.
The calculator will display the chosen concentration underneath.
| 💡 Our calculator can also compute the number of tablets needed. To calculate that, enter 1 into the volume field. 💊 |
- Yay! Your results are here - it wasn't that hard, was it? 🎉
If you've already found out everything you need to know, you may as well try and discover our other child dose calculations:
- Ibuprofen dosage
- Paracetamol dosage calculator
- Simple dosage calculator
- Epinephrine dose for kids
Dose frequency abbreviations
Dose frequency might be quite misleading since all the abbreviations originate from the Latin language. Here we present a short, useful medical dictionary:
- dQ - once per day
- BID - twice per day
- TID - three times per day
- QID - four times per day
- q4 hr - once every four hours (6 times per day)
- q3 hr - once every three hours (8 times per day)
- q2 hr - once every two hours (12 times per day)
- q1 hr - once every hour (24 times per day)
How do you calculate pediatric doses?
There's one primary dose calculation formula for children:
▪️ mg/μg per kilogram per day
dose (volume) = (dose (mg/μg) * child's weight) / (concentration * frequency)
where:
concentrationis usually given in mg/mLchild's weightis given in kgfrequencymeans the number of times a chosen medication is given per day. E.g., q1 hr frequency has a value of 24.
E.g., q1 hr frequency has a value of 24.
However, this equation still has to be modified for every other type of dosage! Below, we enumerated all the available pediatric dosage calculations formulas:
▪️ mg/μg per kilogram per dose
dose (volume) = (dose (mg/μg) * child's weight) / concentration
▪️ mg/μg per day
dose (volume) = dose (mg/μg) / (concentration * frequency)
▪️ mg/μg per day
dose (volume) = dose (mg/μg) / concentration
Hey, how about discovering our other professional pediatric tools:
- Maintenance fluids 🚰
- Blood volume 💉
- Blood transfusion 💉
- Growth charts 📈
Child dose calculations examples
Our baby has a fever! 🤒🌡️👶
Still not sure how to calculate pediatric doses? We're going to focus on an mg/kg/day formula since it's the most complex one. Carefully follow the example below:
Carefully follow the example below:
- We bought some paracetamol to lower the fever - its container states that this syrup's concentration is equal to 120 mg /5 mL. Our prescribed peds dose is 10 mg/kg. Our kid's 4.5 years old and weights 20 kg. We need two doses of paracetamol per day.
How much mL of paracetamol syrup do we need per day?
Let's use the following formula:
dose (volume) = (dose (mg/μg) * child's weight) / (concentration * frequency)
First, let's boil down the concentration:
120 mg/5 mL / 5 = 24 mg / 1 mL = 24 mg/mL
Then come back to the equation itself:
dose (volume) = (10 mg/kg * 10 kg) / (24 mg/mL * 2)
dose (volume) = 100 mg / 48 mg/mL
dose (volume) = 2.083 ≈ 2.1 mL - we need 2. 1 mL of paracetamol per dose, twice per day.
1 mL of paracetamol per dose, twice per day.
Yay, we got it! You're becoming the true pediatric dose master.
Łucja Zaborowska, MD, PhD candidate
Dosage (weight)
Dosage type
Frequency
Weight
Drug concentration
Dosage (volume)
Dosage
per dose
per 24h
Check out 5 similar pediatric dosage calculators 👶💊
Amoxicillin pediatric dosageIbuprofen dosageInfant Tylenol dosage… 2 more
Pediatric Dose Calculation | Step by Step + Examples
Pediatric drug dosages can be a real challenge. Especially if the process for its correct calculation is not known. In this article I will explain how to calculate the pediatric dose of the main medications in Pediatrics.
Contenido a revisar
- 1 Dosage in Pediatrics.
- 1.1 General aspects for the calculation of Pediatric Dose
- 2 Video of how to calculate Pediatric Dose
- 3 How to calculate the Dosage of Medicines in Pediatrics
- 3.
 1 Pediatric dose calculation according to weight in kg
1 Pediatric dose calculation according to weight in kg- 3.1.1 Calculate the Dose of Paracetamol.
- 3.2 Calculate Pediatric Antibiotics Dose
- 3.3 Pediatric Dose Calculation in Special Situations
- 3.4 Pediatric doses of drugs in drops.
- 3.5 Adjust Dosage of Medications.
- 3.
- 4 Calculate Pediatric Dose of Intramuscular and Endovenous drugs.
- 4.1 Simple drug calculation.
- 4.2 Drug calculation with Reconstitution
- 4.2.1 What is the Reconstitution of a Medication?
- 4.2.2 Reconstitution of the Drug.
- 5 Calculate Pediatric Dose based on mg or mL administered.
- 5.1 Formula to calculate Pediatric Dose based on mg administered
- 5.2 Formula to calculate Pediatric Dose based on mL administered
- 6 Dosage of drugs most used in Pediatrics
- 6.1 Medications most used in Pediatrics
- 7 Examples of How to Calculate Pediatric Dose.
- 7.
 0.1 Example 1
0.1 Example 1 - 7.0.2 Example 2
- 7.0.3 Example 2.1
- 7.
Dosage in Pediatrics.
Unlike adults, in which most medications already have a set dose. In Pediatrics, it is necessary to calculate the dose to be administered according to the weight in Kilograms (Kg) or the Body Surface.
The most used Pediatric Medication Dose Calculation is based on the patient’s weight in Kg. However, the most exact method is the one that uses the Body Surface.
General aspects for the calculation of Pediatric Dose
To calculate the Pediatric Dose of a drug, you need to know 3 essential data:
- Patient weight (Kg).
- Drug dosage.
- Presentation of the drug.
It is preferred to work with the Weight in Kilograms. Most of the literature and doses are expressed in Kg. Therefore, if the patient’s weight is in pounds, it will be necessary to convert it into Kg.
It is also important to pay attention to the Dosage of the medicine.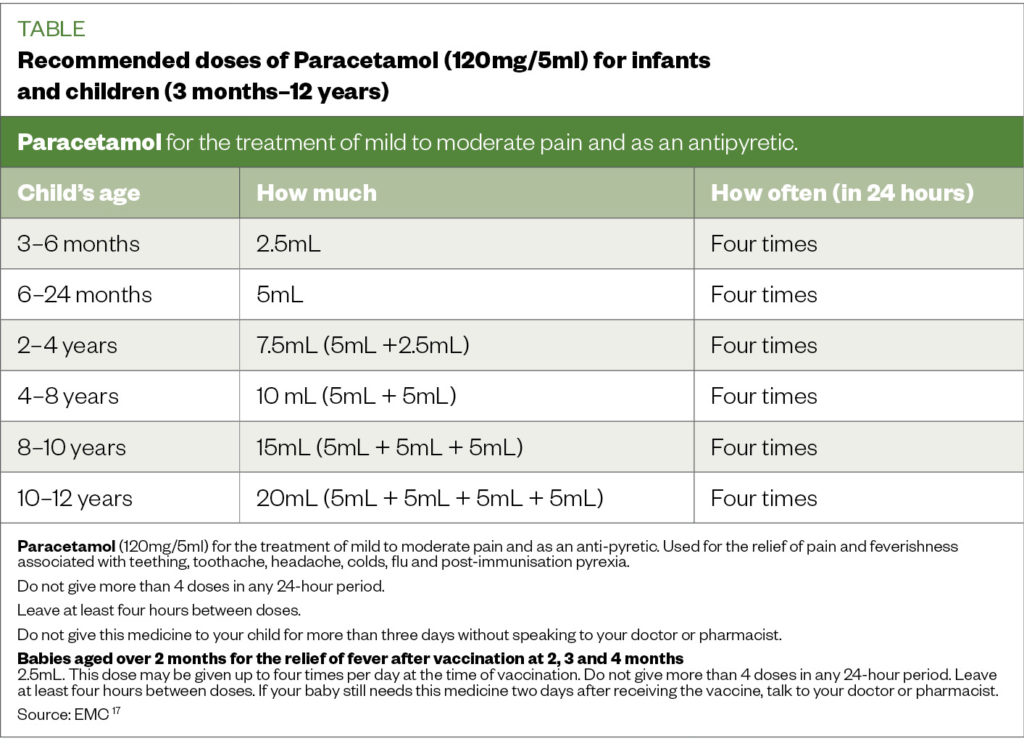 Some medications bring their dose expressed in a total to be administered during the day. While others express it in doses to be administered every certain number of hours.
Some medications bring their dose expressed in a total to be administered during the day. While others express it in doses to be administered every certain number of hours.
For example: the Paracetamol Dose is 10-15 mg / Kg / dose every 6h. This means that this dose can be repeated every 6 hours. But the Cefixime Dose is 8mg / Kg / Day.
Video of how to calculate Pediatric Dose
How to calculate the Dosage of Medicines in Pediatrics
To calculate the Pediatric Dose of a drug, the Weight in Kg or the Body Surface can be used. However, the most used method is based on Weight in Kg. In this article I will explain you step by step how to do it.
Pediatric dose calculation according to weight in kg
The first thing we must do is Calculate the total Dose to be administered of the Medication. Which we obtain by multiplying the Dose by the Weight of the Patient. (So it is imperative to know the patient’s weight)
If for some reason it is not possible to weigh the patient, their weight can be determined using the Ideal Weight Formulas.
Calculate the Dose of Paracetamol.
For example the Dose of Paracetamol is 10-15 mg / Kg / dose. This means that we can use a dose of at least 10 and a maximum of 15 mg. In this example we will use a 15 mg dose in a child weighing 12 kg. Therefore, the total dose to be administered is:
Total dose = (Weight of the patient in kg) x (dose of Drug)
Total dose ⇒ (12 Kg) x (15mg) = 180 mg
In this example 180 mg is the total to be given. But “NO” is what we will give the patient. Before giving the indication we must know the presentation and concentration of the drug.
Paracetamol for example can be found in various presentations. As a tablet, as a suppository or as a Syrup. In Pediatrics, most of the medications that are administered orally are preferred in Syrup. Therefore, it is necessary to know the concentration in milliliters (mL) of the drug.
Acetaminophen in presentation of 120mg / 5mLDepending on the brand and manufacture, concentrations may vary. In the case of Paracetamol Syrup, the most common concentration is 120mg / 5ml.
So continuing with the example, How many mL should we give to our patient?
For this we must apply a rule of three.
Or just remember that the total Dose to be administered must be divided by the mg of the medication presentation and the result multiplied by the mL of the medication presentation.
mL to be administered = (Total Medication Dose) / (mg of presentation) x (ml of presentation)
mL to be administered = (180 mg) / (120 mg) x (5ml) ⇒ (1. 25) x (5ml) = 7.5ml every 4-6 hours
25) x (5ml) = 7.5ml every 4-6 hours
Calculate Pediatric Antibiotics Dose
The process is the same as with most Medications. We must know the patient’s Weight in Kg and calculate the total dose to be administered.
The majority of Antibiotics administered by Oral Route come in the form of Syrup. The classic example is Amoxicillin. Which has a dose of 80 mg / Kg / day divided into doses every 8 or 12 hours.
The dose of Amoxicillin is expressed as a total to be administered every 24 hours. Therefore, this dose should be divided by 3 (if it is given every 8 hours) or by 2 (if it is given every 12 hours)
If we put it into practice with the patient in the previous example. Which we remember that weighs 12 Kg, then we will have:
Total dose = (12 Kg) x (80 mg) = 960 mg.
Now we must know the presentation and concentration of the drug. The most common presentations of Amoxicillin are 250mg / 5mL and 125mg / 5mL.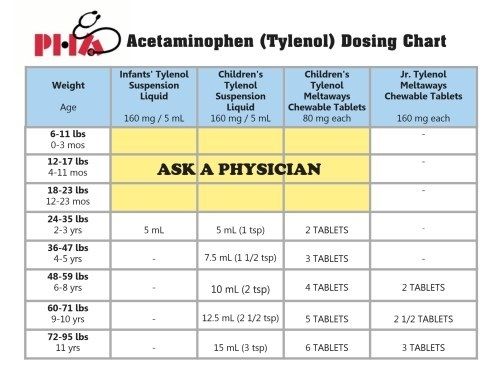 In this example we will use the 250mg / 5mL presentation.
In this example we will use the 250mg / 5mL presentation.
mL to be administered = (960mg) / (250mg) x (5mL) ⇒ (3.84) x (5mL) = 19.2 mL
Remember that 19.2 mL are equivalent to 960 mg of Amoxicillin. The dose to be administered each day. However this should be divided into 2 or 3 takes. So if we indicate it every 8 hours it would remain:
mL to be administered every 8 hours = (19.2 mL) / 3 = 6.4 mL every 8 h.
Why between 3? the reason is simple. Since we want to administer this drug every 8 hours, we must divide the 24 hours a day by that interval. So 24/8 = 3. If it were every 12 hours it would be ⇒ 24/12 = 2.
Pediatric Dose Calculation in Special Situations
Certain Medications may seem a bit more complicated. Trimethoprim / sulfamethoxazole is an antibiotic whose dose is 8mg / Kg / day divided into doses every 12 hours.
But its presentation in syrup is (40mg / 200mg / 5mL) which essentially says that it has 40 mg of Trimethoprim and 200 mg of sulfamethoxazole every 5 mL. But when calculating the Pediatric Dose, it is based on Trimethoprim.
But when calculating the Pediatric Dose, it is based on Trimethoprim.
If we use the same patient from the previous example, then the calculation would be:
Total dose = (12 Kg) x (8 mg) = 96 mg.
mL to be administered = (96 mg) / (40 mg) x (5mL) ⇒ (2.4) x (5mL) = 12mL
mL to be administered every 12 hours = (12mL) / 2 = 6mL every 12 hours.
Pediatric doses of drugs in drops.
On occasion it may be necessary to indicate the number of drops to administer of a medicine. Especially in those whose doses are usually low or for the convenience of the patient’s parents.
An example of this is Cefixime. It has a dose of 8 mg / Kg / day. In this case the dose is every 24 hours. The presentation is usually in syrup with a concentration of 100mg / 1mL. If we calculate the dose to be administered in a child weighing 10 kg, it would be:
Total dose = (10 Kg) x (8mg) = 80 mg
mL to be administered = (80mg) / (100mg) x (1mL) ⇒ (0.8) x (1mL) = 0. 8mL every day
8mL every day
It is impractical for the patient’s parents to calculate the 0.8 mL. In these cases it is preferred to indicate the medicine in drops. In addition, many medications such as Cefixime usually bring a dropper for the administration of the medication.
So how many drops should we give the patient?
To calculate the Dose of medicines in pediatrics in drops, we only have to multiply the amount of mL to be administered by 20. (Remember that 20 drops make 1 mL)
Drops to administer = (mL to administer) x 20.
Drops to be administered = (0.8 mL) x 20 = 16 drops every day.
Adjust Dosage of Medications.
Occasionally we will have to adjust the dose of a medication. For reasons of comfort for the parents and the patient or for the convenience of the personnel who will give the medicine.
The important thing in these cases is to always take into account the dose range of the drug.
For example, a 7-year-old child who weighs 21.2 Kg and who should be given Paracetamol would have a total dose of 318 mg (calculated at 15mg / Kg / dose) and we should give him 13.25 mL every 6 hours.
However, it is impractical. Especially for inexperienced staff like parents. Calculate the 13.25 mL. Therefore, it is perfectly valid to adjust the dose and give the patient 13 mL of Paracetamol every 6 hours.
The same can happen when administering the drug in tablets or pills. Sometimes it may be necessary to adjust the dose of the medicine.
For example, if in the same previous case we had to give Prednisone (5 mg tablets) to treat a recurrent Bronchospasm crisis, then how many tablets should we give the patient?
#Pills = (Total Dose) / (Concentration of the pills)
So the first thing is to calculate the total Dose of Prednisone, which has a Dose of 1-2 mg / Kg / dose. Which can be repeated every 24 or 12 hours. In this example we will calculate it at 1 mg / Kg / every 12 hours.
Total dose = (1) x (21.2Kg) = 21.2 mg
Then we must give:
#Pills = (21.2mg) / (5mg) = 4.24 pills
#Pills every 12 hours = (4.24) / 2 = 2.12 pills every 12h
We cannot expect even the most meticulous parent to try to cut each pill to exactly give the 4.24 pills. So it is necessary to adjust the dose to 2 pills of Prednisone every 12 hours.
Calculate Pediatric Dose of Intramuscular and Endovenous drugs.
Medications administered intramuscularly (IM) or endovenously (EV) are calculated in the same way as those administered orally (PO). The difference is usually when they are indicated and whether or not they require dilution or reconstitution.
Simple drug calculation.
The calculation of the dose of medications administered by IM or EV is basically the same as those administered by PO.
For example Diclofenac. It has a dose of 0.5 to 1 mg / Kg / dose which can be repeated every 8 hours. The most common presentation of Diclofenac is 75mg / 3mL.
The most common presentation of Diclofenac is 75mg / 3mL.
If we calculate the dose to be administered to a 6-year-old patient whose weight is 20 kg then we will have:
Total dose = (20 Kg) x (1mg) = 20 mg.
The indication would be valid as: Diclofenac 20 mg I.M C / 8 hours. However, remember that the medication will be administered in mL. Therefore, it is necessary to determine how many mL should be administered via IM to the patient?
Process that is identical to the one used in the previous examples:
mL to be administered = (20 mg) / (75 mg) x (3mL) ⇒ (0.26) x (3mL) = 0.8 mL every 8 hours.
Drug calculation with Reconstitution
Certain medications essentially only require the calculation of the Total Dose. An example of this is usually Benzathine Penicillin. Which usually has a dose of 50,000 units (u) in a single dose. So to indicate it, it would be enough to calculate the total dose.
For example, in a child who weighs 14 kg and has Acute Pharyngotonsillitis, the dose would be:
Total dose = (14 Kg) x (50,000 u) = 700,000 u / single dose.
The indication could be as: Benzathine Penicillin 700,000 units I.M # 1.
However, it is vital to remember that Penicillin is usually presented in powder and requires Reconstitution before it can be administered.
Reconstitution is a process that is essentially delegated to the Nursing staff. However, it is imperative that all health professionals have full knowledge of how it is done and also be able to explain it to parents if required.
What is the Reconstitution of a Medication?
It is the process of adding a solvent to a drug in the form and quantity necessary for proper administration by the indicated route.
In simple terms it is to convert a drug, usually in powdered form in a mixture which can be administered orally, intravenous or intramuscular.
Reconstitution of the Drug.
The Presentation of Penicillin is usually 1.2 or 2.4 million units with 5 mL of sterile water. So how many mL should be given to the patient?
The first thing is to do the Reconstitution of the medicine. For this, the 5mL of water or solution is placed in the Penicillin powder. The mixture is stirred to obtain a homogeneous, lump-free solution. Now it is necessary to determine the Concentration
It is important to clarify that the Reconstitution can be done with any amount of mL of water or dextrose solution or Saline Solution. Always taking into account the properties of the medicine and the concentration to be obtained.
In the case of Benzathine Penicillin whose presentation is 1.2 million units when diluted in 5 mL we obtain a Concentration of 240,000 units / 1 mL
Drug concentration = (Presentation) / (amount of mL for Reconstitution).
Drug concentration = (1,200,000 units) / 5mL = 240,000 units per 1 mL
As we will give our patient 700,000 units, the amount in mL to be administered will be:
mL to be administered = (700,000u) / (240,000u) x (1mL) = 2. 9 mL.
9 mL.
The calculation of drug doses in pediatrics always follows the same pattern.
In some cases it may be necessary to indicate the drug in an intravenous infusion. What you can read here. (we are writing the article :)).
Calculate Pediatric Dose based on mg or mL administered.
Occasionally we will have to know the Dose at which a drug already prescribed or indicated is calculated. Whether you’re receiving a referral patient or are in medical guard. In Pediatrics, the ideal is always to verify the Doses of the medications.
Formula to calculate Pediatric Dose based on mg administered
Then to calculate the Pediatric Dose of a drug based on the mg administered we will apply the following formula:
Medication dose = (mg administered) / (Weight in Kg)
For example, if we have a 3-year-old child weighing 14 kg with an indication from the previous medical guard that says “Gentamicin 70 mg EV every 24 hours”. What dose did they use to calculate Gentamicin?
Medication dose = (70 mg) / (14 Kg) = 5 mg / Kg / every 24 hours.
Which is correct, because Gentamicin has a dose of 5-7.5 mg / Kg / day.
It is important to bear in mind that the formula tells us the dose of the medicine in the same interval of hours that is indicated. So sometimes we will have to verify if your dose is correct in a range of 24 hours.
Formula to calculate Pediatric Dose based on mL administered
The procedure is similar to the previous one. With the only detail that it is necessary to first calculate the Dose in mg based on the mL administered. Therefore, it is also imperative to know the presentation and concentration of the administered drug.
Then the Formula would be:
Step 1: mg administered = (mL administered) / (mL of Presentation) x (mg of Presentation)
Step 2: Medication dose = (mg administered) / (Weight in Kg)
For example, suppose we receive a 1-year-old child weighing 10 kg and we see that it has as Indication: “Paracetamol (120mg / 5mL) 6 mL vo every 4-6 hours due to Fever”. So how many mg are being given to the patient in total? and What dose did they use to calculate it?
So how many mg are being given to the patient in total? and What dose did they use to calculate it?
The first thing will be to determine what is the total dose in mg administered to the patient based on the mL of Paracetamol:
mg administered = (6 mL) / (5 mL) x (120 mg) ⇒ (1.2) x (120mg) = 144 mg
Now that we have the total mg administered, we can find the Dose at which it has been calculated:
Medication dose = (144 mg) / (10 Kg) = 14.4 mg / Kg / dose
Which is correct because the dose of Paracetamol is between 10 – 15 mg / Kg / dose. Also in this example the dose of Paracetamol has been adjusted. If it is calculated at 15mg / Kg / dose, it would touch 6.25mL every 4-6 hours. Which was impractical.
Dosage of drugs most used in Pediatrics
Here is a list of the most commonly used medications in Pediatrics with their most common doses and presentations / concentrations.
Medications most used in Pediatrics
List of drugs most used in Pediatrics and their usual presentation
Examples of How to Calculate Pediatric Dose.
For practical purposes, below you can find a couple of examples of how to calculate the dose of medicines in Pediatrics.
Example 1
A 3-year-old boy weighing 10Kg consulted with a 7-hour history of Febrile Process. The temperature is measured at 39 ° C, so it is decided to administer Paracetamol. What dose and how many mL should be administered?
See Procedure
Step 1: Calculate Total Dose
Total dose = (10) x (15) = 150mg
Step 2: Calculate the mL to be administered
mL to be administered = (150mg) / (120mg) x (5mL) = 6.25 mL every 6 hours
See Answer
Answer: the total dose is 150 mg and 6.25 mL of Paracetaml should be administered every 6 hours.
Answer 2: Dose can be adjusted to 6 mL every 6 hours
Example 2
An 8-year-old boy weighing 23 kg already known for Bronchial Asthma will be discharged from the Pediatric service after having completed 3 days of Methylprednisolone E. V due to a Bronchospasm Crisis. For discharge, it is decided to overlap Prednisolone, which must be met every 12 hours for 4 days. What dose and how many mL should be administered?
V due to a Bronchospasm Crisis. For discharge, it is decided to overlap Prednisolone, which must be met every 12 hours for 4 days. What dose and how many mL should be administered?
See Procedure
Step 1: Calculate Total Dose
Total dose = (23) x (2) = 46mg
Step 2: Calculate the mL to be administered
mL to be administered = (46mg) / (15mg) x (5mL) = 15.3 mL
mL to be administered every 12 hours = 15.3 mL / 2 = 7.65mL every 12h
See Answer
Answer: The total dose is 46 mg and 7.65 mL of Prednisolone should be given every 12 hours. Which can be adjusted without problem to 7.5 mL every 12h.
Example 2.1
Continuing with the same example. Pharmacy informs us that they do not have Prednisolone and that they only have Prednisone in tablets with a concentration of 5mg. How many tablets should our patient take?
See Explanation
Prednisone and Prednisolone have the same dose (1-2 mg / Kg / day every 24 or 12 hours).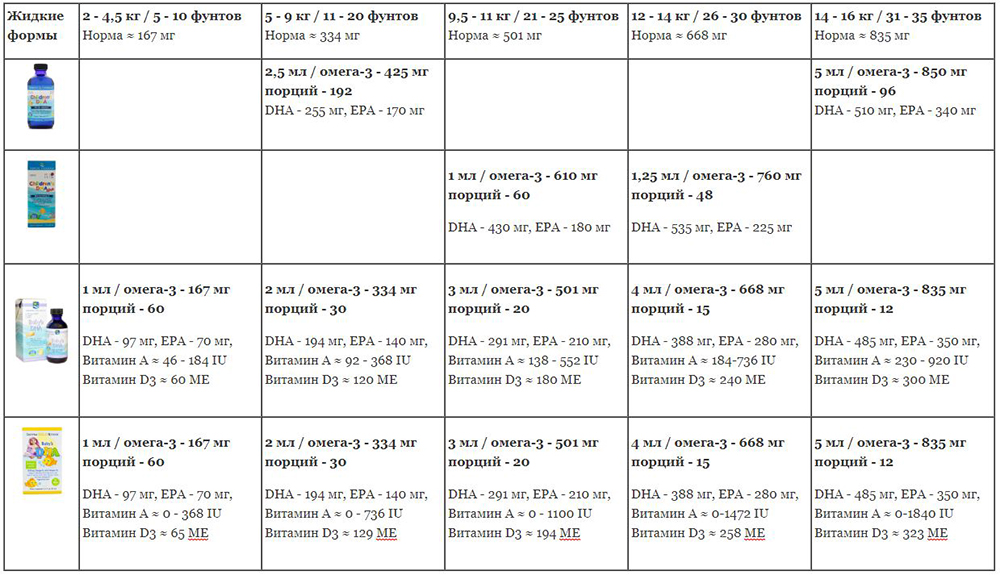 So the total dose to achieve is always 46 mg. So our patient should take:
So the total dose to achieve is always 46 mg. So our patient should take:
#Pills = (Total Dose) / (Concentration of the pills)
#Pills to take = (46mg) / (5mg) = 9.2 pills
#every 12 hours = 9.2 / 2 = 4.6 pills every 12 hours
As it is impractical to take 4.6 pills, the dosage can be adjusted. So we could indicate to take 4 pills and half of another (4.5) or only 4 tablets every 12 hours. What follows is within the dose range of Prednisone.
👨🏻⚕️ Key points to calculate the dose of a medicine in Pediatrics 🔑
- You must know the Weight in Kg.
- The dose should be calculated and adjusted if necessary
- The most accurate way to calculate a drug is based on the Body Surface ⚕️
- Although the indication can be expressed only in mg, it is important to know how many mL should be administered Oral, intramuscular or endovenous route of a drug
- Reconstitution of a drug must be explained to parents and their correct understanding must be verified
References consulted
Ver refernecias
- Engorn Branden, Flerlage Jamie (2015).
 Dosis Farmacologicas. En Manual Harriet Lane de Padiatria (págs. 640-800). España: ElSeiver.
Dosis Farmacologicas. En Manual Harriet Lane de Padiatria (págs. 640-800). España: ElSeiver. - Dusenbery M. Susan, White J. Andrew (2009). Medicina del adolescente. En Manual Washington de Pediatría (págs. 154-165). España: Wolters Kluwer Health España.
- Kathleen A. Neville, Leeder J. Steven (2016). Farmacoterapia Pediatrica. En Nelson Tratado de Pediatría (págs. 411-423). España: ElSeiver.
- Lonnie K. Zeltzer, Elliot J. Krane, Tonya M. Palermo (2016). Tratamiento del dolor en los niños. En Nelson Tratado de Pediatría (págs. 450-465). España: ElSeiver.
Don’t leave without rating the article.
4.6/5 (119 Reviews)
Hugo Parrales M.D
MD. University teacher. Passionate about internal medicine. Biochemistry and Pathophysiology are my favorite subjects. I have created this website as a portal to help understand certain topics and as a source of review.
ComentariosNurofen syrup dosage for a child by weight + calculator
When a child has a high temperature, we usually take Nurofen or Paracetamol from the first-aid kit and do not think about the fact that there should be some special dosage of Nurofen syrup for a child by weight (well, or the dosage of Paracetamol).
We simply look at the instructions for these drugs and give the child the exact amount of suspension indicated in it, based on his age.
You may be interested in reading: If your child is often sick: 3 ways to improve immunity
However, this approach is not always effective. As an example, after taking the syrup, the baby's temperature drops badly and soon rises again. Which forces us to give the child an antipyretic again.
About why this happens and how it can be avoided, and will be discussed in this article.
Before using the medicines listed in this article, you should consult with your pediatrician. nine0010
Let me remind you that I am not a doctor. And just a mother who shares her observations and experiences. Therefore, this text can be considered only as another source of information on this topic, and not as a guide to action. Well, I think we understood each other)
Contents of the article:
Prehistory
Alice was 9 or 10 months old (I don't remember exactly), when she had a high fever for several days. Which didn't crash.
Which didn't crash.
More precisely, after taking the antipyretic, the temperature dropped slightly, but then quickly rose again. nine0003 I, on the advice of our local pediatrician, alternated Nurofen and Paracetamol syrups, as well as suppositories.
But, one night, we even had to call an ambulance. in the evening, despite taking antipyretics, Alice's temperature remained at the same level.
I remember she was sleeping, and I measured her sleeping temperature probably every 20 minutes. It is good that a non-contact thermometer was used for this purpose. I can’t imagine how it is possible to monitor the temperature of a sleeping child with an ordinary thermometer ...
In general, if you still use a mercury thermometer, I strongly advise you to take a closer look at its non-contact counterpart. Yes, I know, some mothers are wary of this device. And some of the owners, perhaps, even had time to be disappointed. But, I'll tell you - this is not a reason to refuse such a necessary and very convenient device) You can read about why an infrared thermometer often lies and how to measure their temperature correctly, you can read in my article:
Non-contact thermometer for a child - handy device that lies? nine0007
So, back to our story.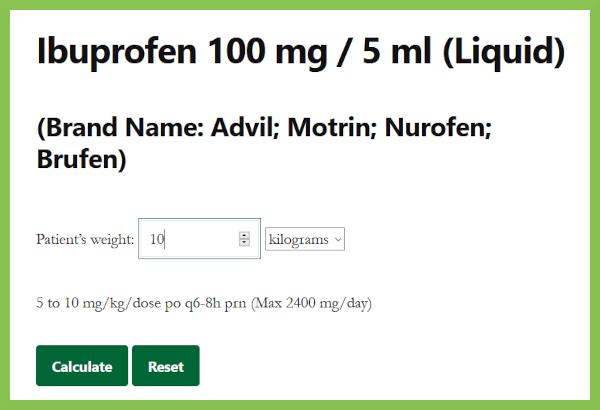 The ambulance arrived only 2 hours after the call. And just by that time, thank God, my daughter's temperature dropped to 38.
The ambulance arrived only 2 hours after the call. And just by that time, thank God, my daughter's temperature dropped to 38.
Of course, the ambulance doctor did not give any injections, because the temperature has already dropped.
In response to the doctor's question about our complaints, I told him about a badly fluctuating temperature.
“How do you calculate the dose of antipyretic?” the doctor asked me.
“I give according to the instructions, of course. According to our age,” I replied. nine0003 “Didn't you know that the instructions contain general recommendations, average doses are indicated? The specific dose must be calculated individually according to the weight of your child. If you gave 2.5 ml, then this is not enough for your weight, ”the ambulance doctor said and left.
No, I didn't know that. For me, the words of the ambulance doctor became news. How is it to calculate the antipyretic according to the weight of the child? And I climbed to enlighten on this topic on the Internet.
Why you need to calculate the dose of antipyretic syrups for a child according to his weight
So what's going on?
And the fact that, according to pediatricians, in the vast majority of cases, the reason for the high " " temperature is the WRONG dosage of the antipyretic drug.
Indeed, the calculation of the dose of antipyretics should be made depending on the weight of the child, and not his age.
Take, for example, the instructions for Nurofen syrup. nine0007
And, we see that for a child aged 3 months. up to 12 months a single dose of syrup is 2.5 ml.
Only, up to 6 months. this syrup can be given only three times a day.
A from 6 months. up to 12 months - It is permissible to give already 4 times a day.
As a result, nevertheless, it turns out that the SINGLE dose for a three-month-old baby and a ten-month-old baby is the SAME.
But, after all, the weight of a three-month-old and a ten-month-old child can differ by half!
And it becomes completely unsurprising that a single dose of 2.5 ml. Nurofen, which is enough to reduce the temperature of a three-month-old baby weighing 5 kg, for a 10-month-old baby weighing 9kg. - is no longer sufficient.
It is also worth mentioning the fact that children of the same age may have different weights. Some kids are overweight and some are underweight. One child weighs 5 kg at 3 months, and the other, of the same age, 8 kg.
Therefore, it is so important to calculate the dose of antipyretic syrups for a child precisely by his weight, and not by age.
Nurofen Syrup dosage for a child by weight
How to calculate the maximum allowable single dose of Nurofen syrup
In order for the syrup to work effectively, we need to calculate its maximum allowable SINGLE dose.
Carefully read the instructions for the Nurofen preparation:
"The maximum DAILY dose should not exceed 30 mg/kg of the child's body weight with intervals between doses of the drug 6-8 hours.
"
From this it follows that the maximum SINGLE dose of Nurofen syrup is 10 mg/kg of the child's weight.
Now, we need to know the baby's weight. nine0004
How to find out the weight of a child
Usually, children under one year of age are weighed every month at the clinic for preventive examinations.
Also, many houses have floor scales. A small child can also be weighed on them)
For example, I do it this way. I take the child in my arms, I stand with him on the scales. For an accurate measurement, the child must be calm at this moment. I write down our total weight with the child.
Next, I let the child play and stand on the scales alone. nine0003 Weighed - wrote down.
Then I simply subtract my weight from our total weight with the child. We get a net child's weight)
Of course, there is always an error on such scales (however, as on any scales), so it is better to round the result down a little.
Especially if the child was weighed in clothes and in a diaper (here you can safely subtract 200-300 gr).
If, say, the weight of a child in clothes and in a diaper when weighed on floor scales turned out to be 8,750, it is better to take the figure 8,500 (8.5) for calculations. nine0004
An example of calculating a single dose of Nurofen syrup
Now, let's solve a mathematical problem.
Let's take a child weighing 8.5 kg as an example.
Look at the instructions for Nurofen: 5 ml. the drug contains 100 mg. the active ingredient is ibuprofen.
The maximum single dose of syrup, as we have already found out, is 10 mg/kg of the child's weight. It is necessary to calculate a single dose of Nurofen syrup in milliliters for a child weighing 8.5 kg.
Let us first calculate a single dose of Nurofen in mg:
8.5 x 10 mg/kg = 85 mg - a single dose of suspension.
In 5 ml - 100 mg of ibuprofen, and in x? ml - 85 mg.
Using the proportion method, we derive a single dose of Nurofen syrup: (5*85/100) = 4.25 ml. Round up to 4.3 ml.
That's it, we have calculated the maximum single dose of Nurofen. We do not exceed this single dose, i.e. we give it no more than 3 times a day.
Why am I describing all this here? But because on a decree from such a seemingly easy example, the brain can melt even for mothers-mathematicians)
I'm already silent about the humanities moms, to which I also belong.
Maybe my children rarely get sick (pah-pah-pah!!!), so I don't remember by heart all these milliliters, milligrams and proportions. I will say one thing - when my daughters get sick, I have no time for calculations. But, it has to.
Therefore, swearing, when once again I had to surf the Internet and remember these damned proportions, I gave my word to alleviate my fate.
And I made an online calculator, where I entered the formula for calculating the SINGLE dosage of Nurofen syrup for a child by weight. nine0003 If you, like me, are too lazy to remember and calculate the dosage of antipyretic syrup every time, you can also use it.
nine0003 If you, like me, are too lazy to remember and calculate the dosage of antipyretic syrup every time, you can also use it.
So, you just need to enter the weight of the child in kg. in the specified field.
If the number is not round, enter through a comma or a dot, for example, 8.5 (or 8.5) and see the result in the lower right corner (syrup 100 mg/5 ml) for a child by weight
Enter the child's weight in kg.
A single dose of syrup will be:
0 ml.
Cool, right? ))) And no problems with calculations)
ATTENTION!!! IMPORTANT!
Sometimes, for technical reasons and due to high traffic to this page, calculators may be temporarily unavailable for calculations.
If you plan to repeatedly use calculators and want to have quick access to them, I recommend subscribing to my blog
Subscribe to the blog "MamaNastya" by e-mail :
Email address
Dosage of paracetamol syrup for a child by weight 9
syrups - different dosages
I want to warn - on sale there are several types of antipyretic syrups with active substance paracetamol. For example, there are syrups with the same name Paracetamol, there is Panadol syrup and there is Efferalgan. Maybe some more Yes, I just know these. nine0004
For example, there are syrups with the same name Paracetamol, there is Panadol syrup and there is Efferalgan. Maybe some more Yes, I just know these. nine0004
The dosages of these syrups may vary! Be careful! Be sure to check the instructions for how much active ingredient (paracetamol) your syrup contains.
For example, in 1 ml syrup "Efferalgan" contains 30 mg of paracetamol. I warn you right away if you have Efferalgan, the calculations below and the calculator are NOT for this suspension. count dosage yourself.
The instructions for Panadol syrup indicate that in 5 ml. The drug contains 120 mg. paracetamol. nine0003 We also had a syrup with the same name "Paracetamol", with the same amount of active ingredient as "Panadol". That is, there is also 5 ml. syrup contains 120 mg. paracetamol.
This ratio is exactly 5 ml/120 mg. in syrups with the active ingredient "Paracetamol" is considered the most popular.
But, I repeat once again - be sure to check the composition of the suspension!
Personally, I don't want to get confused and now I always buy Panadol Baby syrup. A syrup with this name is popular; it is on sale in any pharmacy. And, importantly, it comes with a measuring syringe. nine0003 I remember the cheaper syrup called Paracetamol only came with a scoop. I can’t and don’t like to give syrup from a spoon. It seems to me that only a syringe can measure the exact amount of suspension. That's why I prefer Panadol.
A syrup with this name is popular; it is on sale in any pharmacy. And, importantly, it comes with a measuring syringe. nine0003 I remember the cheaper syrup called Paracetamol only came with a scoop. I can’t and don’t like to give syrup from a spoon. It seems to me that only a syringe can measure the exact amount of suspension. That's why I prefer Panadol.
By the way, I prefer to buy antipyretic syrups, as well as other important preparations for a child's first aid kit, in advance. And the Internet service zdravcity.ru
helps me in this. If you are not familiar with this very convenient and profitable service, you can read my review article:
Why do we choose the Zdravcity service
An example of calculating a single dose of Paracetamol syrup
So, I have Panadol syrup, 5 ml. which contains 120 mg. the active substance is paracetamol.
For calculating one-time dosages, we read the instructions, which already indicate the maximum SINGLE dose - 15 mg/kg. child's weight.
child's weight.
For example, let's take the same weight of a child - 8.5 kg.
Let us first calculate a single dose of "Panadol" in mg:
8.5 x 15 mg / kg = 127.5 mg - a single dose of Panadol.
But, we need a single dose in milliliters.
In 5 ml - 120 mg of paracetamol, and in x? ml - 127.5 mg.
Using the proportion method, we derive a single dose of Panadol syrup:
(5 * 127.5 / 120) = 5.3 ml. - this is the maximum single dose of Panadol syrup, which can be given up to 4 times a day, not more than . So that the daily dose does not exceed the figure indicated in the instructions of 60 mg / kg. child's weight.
I painted everything tediously again, didn't I? ))) nine0003 And why))) When you can just enter the weight of the child here and the calculator will calculate everything for us:
Calculator "Paracetamol syrup dosage for a child by weight"
child by weight
Enter the child's weight in kg.
A single dose of syrup will be:
0 ml.
Well, that's all) I hope the information was useful to you!
In order not to lose this page, you can save a link to it on your wall in social networks. To do this, scroll a little lower to the phrase "Share a link to the article" and click on the button of your social network. nine0003 By the way, I will be pleased)
P.S.: And yet, I wish you to use these calculations as little as possible) Be healthy and don't get sick!
dose tablets for children from 2-5 to 7-9 years old
Paracetamol is one of the most famous antipyretic and analgesic medicines. It belongs to the group of non-narcotic aniline analgesics. Adults take it themselves and often give it to babies when they need to bring down the temperature. There is nothing wrong with this, if you follow the dosage appropriate for age and choose a convenient dosage form. nine0004
Can paracetamol be given to children under one year old?
In some sources you can read that childhood is a contraindication for the use of this medicine. It's a delusion. The drug is produced in the form of syrups and suspensions especially for the smallest. They do not contain alcohol, dyes and other harmful substances.
It's a delusion. The drug is produced in the form of syrups and suspensions especially for the smallest. They do not contain alcohol, dyes and other harmful substances.
According to the instructions, you can drink it from the second month of life. The main indications for this are:
- fever after vaccination; nine0301
- fever in infectious and inflammatory diseases;
- painful sensations that are difficult to endure.
Special dosages are available for patients under one year of age. It is important for parents to keep track of how much medication the child has taken. If you do not exceed the permissible limit, there will be no undesirable consequences. Even allergic reactions to paracetamol occur infrequently.
Paracetamol for children from 1 to 3 months
In the first month after birth Paracetamol is prohibited. As a rule, the baby does not need it due to the strong immunity received from the mother. In the next two months, the need may appear - the pediatrician will indicate it. It is not recommended to give the baby the drug on its own. The doctor will tell you how to take it correctly and in what doses. nine0004
It is not recommended to give the baby the drug on its own. The doctor will tell you how to take it correctly and in what doses. nine0004
Usually the indication is a reaction to vaccination - just at this time the first vaccinations are given (not counting those given in the maternity hospital).
According to the instructions, a single dose is prescribed at the age of two to three months. Its volume does not exceed 2.5 ml. The optimal form is suspension. However, in case the baby refuses to drink the medicine, there are rectal suppositories.
Paracetamol for children from 3 months to 1 year
After reaching the age of three months, the use of paracetamol becomes more free. Most often it is given to babies to reduce temperature at:
- SARS;
- influenza;
- chickenpox;
- scarlet fever;
- measles;
- pig.
The remedy will also help with pain. Babies may have pain in their ears and throat, muscles and joints, they are worried about colic and teething.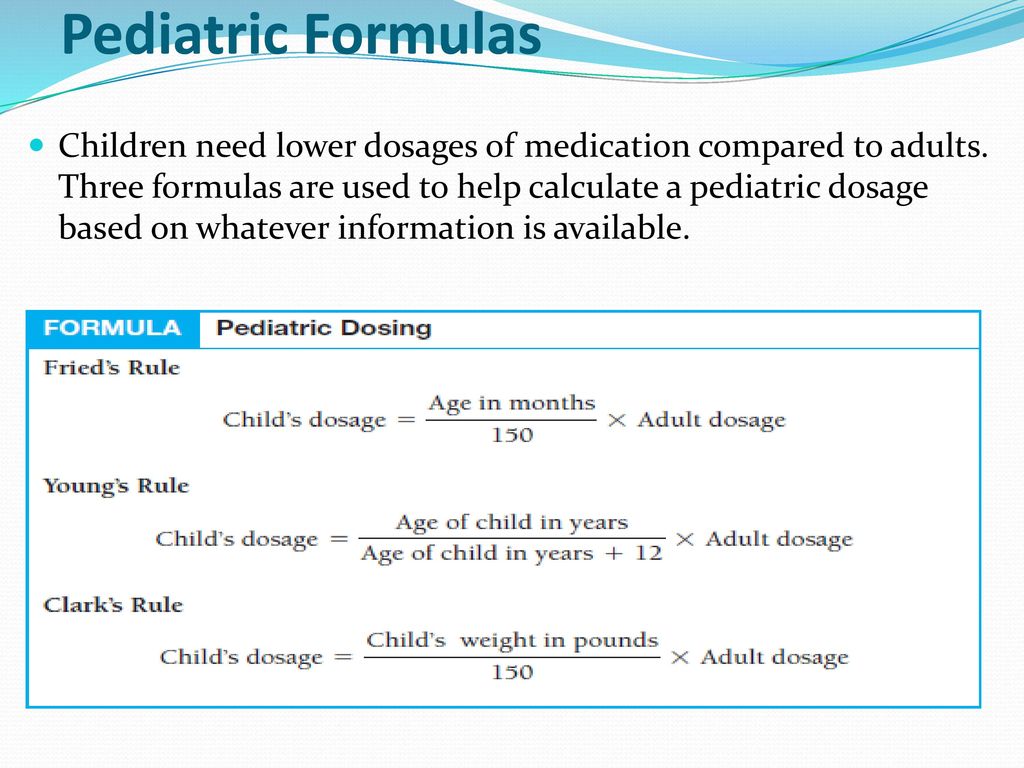 Sometimes you can get by with breast milk containing natural analgesics. But if it does not help, medicines come to the rescue.
Sometimes you can get by with breast milk containing natural analgesics. But if it does not help, medicines come to the rescue.
The allowable dosage is calculated based on the body weight of the child. Up to a year, the limit is 60 mg per kg of body weight per day, a single dose is from 10 to 15 mg per kg. Correctly determine how much medicine in a single dose, measuring spoons or syringes provided by the manufacturer help. nine0004
Paracetamol for children in syrups
Syrup or suspension is the most convenient form of children's antipyretics for this age group. This is an aqueous solution in which the active substance is mixed with sugar. It has a pleasant taste and smell, thanks to which the kids take it quite willingly.
Paracetamol syrup is usually a yellowish thick liquid. It has a fruity aroma, and there are two flavors: orange and strawberry. For 5 ml of solution there are 120 mg of analgesic. nine0004
The dosage of paracetamol for children is determined according to the instructions. It states that the 100 ml bottle is designed for 16 doses. This is easy to check. Based on the proportion "120 mg per 5 ml", 100 ml contains 2400 mg of the substance.
It states that the 100 ml bottle is designed for 16 doses. This is easy to check. Based on the proportion "120 mg per 5 ml", 100 ml contains 2400 mg of the substance.
Divide by 12 mg (average single dose) to get 200 mg. Dividing 200mg by the claimed 16 doses results in 12.5kg, which is the average weight of a 3-year-old child.
At what age can children take paracetamol tablets? nine0294
The transition time from suspensions to tablets depends on the degree of development of the swallowing reflex. It’s impossible to say for sure how long to wait, but it’s definitely better not to experiment until three years.
In the case of paracetamol directly, the dosage must also be taken into account. The standard tablet of the drug of the same name contains 0.5 g of the active substance. It is necessary to compare this figure with the permissible children's dosage - 60 mg per kg of body weight. Knowing how much a person weighs on average at a certain age, it’s easy to figure it out. nine0004
nine0004
Divide 500 mg (=0.5 g) by 60 mg to get 8.3 kg. This is the minimum weight at which a small patient can drink a whole tablet. It corresponds to 7-9 months. So by the age of three, such a dosage form is quite acceptable.
The main thing is to correctly calculate how many tablets you can give. At four years old, a child weighs about 16 kg. He can be given 16 kg * 120 mg = 1920 mg of paracetamol per day (that's a little less than 4 pieces).[1]
When paracetamol is contraindicated
Do not take the medication in question if you are hypersensitive to it. This applies not only to children, but also to adults. Take it with great care if:
- low levels of the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase;
- violation of bilirubin metabolism;
- kidney and liver diseases;
- pathologies of the hematopoietic system;
- diabetes mellitus (the syrup contains sugar).
It is important to balance the need to lower the temperature against the possible risks. If there are contraindications, it is better to consult a doctor so that he can choose a more suitable remedy. nine0004
If there are contraindications, it is better to consult a doctor so that he can choose a more suitable remedy. nine0004
Without special prescriptions, antipyretics can be drunk for no longer than three days. Under normal conditions, the desired result is achieved during this time. If it is not, the reception should be stopped and consulted with a pediatrician.
Possible side effects
Although paracetamol is a fairly common medicine, it is being phased out worldwide due to side effects. Its metabolites adversely affect the liver. In the presence of a disease of this organ, which is asymptomatic, the pathological process under the influence of metabolites will only intensify. nine0004
Other side effects:
- renal colic;
- decrease in the level of platelets, which leads to blood thinning;
- decrease in the level of leukocytes, which weakens the protective functions of the body;
- anemia leading to oxygen starvation of tissues;
- reduction in blood sugar concentration.

Allergic reactions are possible: itching, rashes, Quincke's edema. In the presence of diseases of the liver, hematopoietic or endocrine system, it is better to choose another medicine. nine0004
Poisoning possible
Cases of paracetamol poisoning are not uncommon. In adults, the most common causes are overdose, interaction with alcohol and anticonvulsants. In children, only the first reason is possible - due to incorrect calculation by parents or uncontrolled self-administration.
Intoxication is manifested by nausea, vomiting, pain in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen. With adequate and timely medical care, complications do not occur. nine0004
Acute poisoning rarely leads to death, but can cause serious disturbances in the body if it is impossible to:
- stabilize the acid-base balance;
- reduce serum creatinine;
- optimize blood clotting.
Risks increase with hepatic encephalopathy, when the liver is unable to remove harmful substances from the body and they enter the brain.