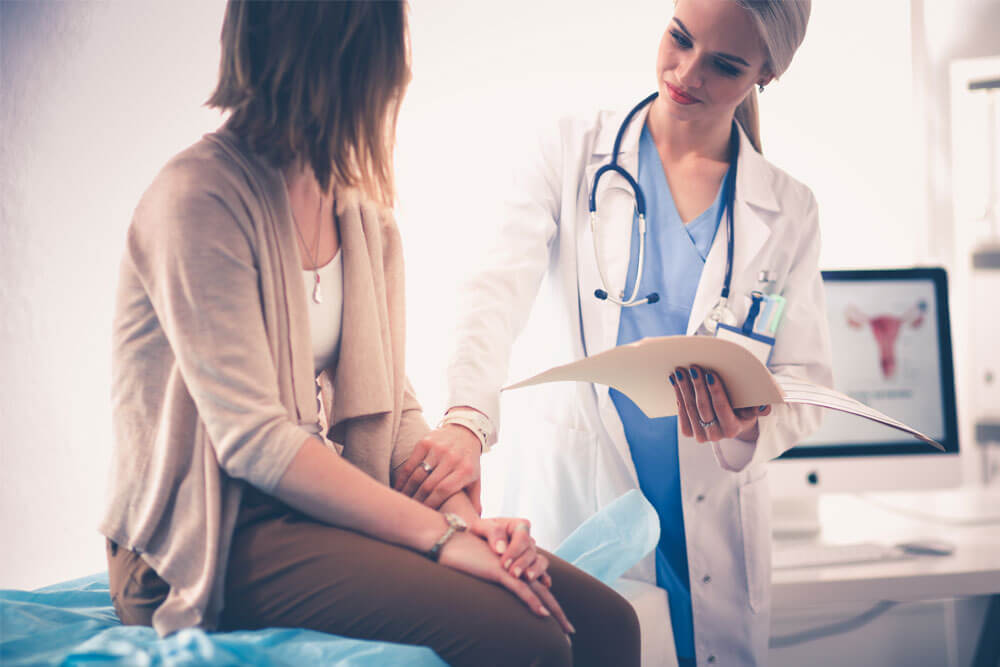
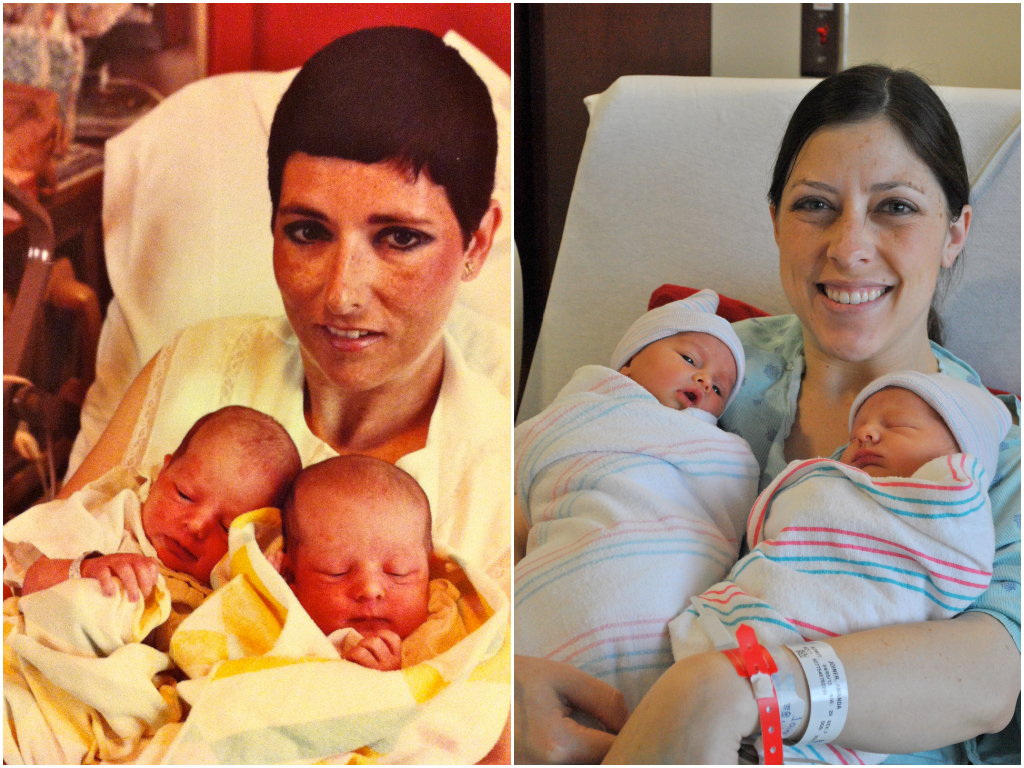
Can you have a natural birth with twins
Giving birth to twins or more
It's important to understand your birth options if you're expecting more than 1 baby.
Twins and triplets are more likely to be born early and need special care after birth than single babies.
Your birth choices with twins
It's a good idea to discuss your birth options with your midwife or consultant early on in your pregnancy.
You'll normally be advised to give birth in a hospital, as there's a higher chance of complications with twins.
There are usually more health professionals at a multiple birth – for example, there may be 2 midwives, an obstetrician and 2 paediatricians (1 for each baby).
You'll already have met your obstetrician and midwives to discuss your baby's birth beforehand, so they will not all be strangers.
For more information on who's who, read about the antenatal team.
The process of labour is more or less the same as for 1 baby, but your maternity team will usually advise you to have your babies electronically monitored because of the higher risk of complications.
This means attaching belts with sensors (1 for each twin) to your bump. You'll still be able to move around into different positions.
Once your waters have broken, your midwife may ask your permission to attach a clip attached to a wire to the first baby's head to get a more accurate measure of their heartbeat.
You'll be offered a drip in case it's needed later – for example, to restart contractions after your first baby is born.
Triplets or more babies are almost always delivered by a planned caesarean section.
Can you have a natural birth with twins?
Lots of women think they have to have a caesarean section with twins. In fact, more than 40% of twin births are vaginal.
If you're planning a vaginal delivery, it's usually recommended that you have an epidural for pain relief, but you can discuss this with your midwife.
If there are any problems, it's easier for your antenatal team to deliver your babies quickly if you have already got an epidural in place.
Find out more about the signs and stages of labour
You're more likely to have a vaginal birth if the first twin is in a head-down position.
But there may be medical reasons why a vaginal birth is not recommended.
If you have had a caesarean section before, for example, it's not usually recommended that you have a vaginal birth with twins.
As with any vaginal birth, you may need an assisted birth. This is where forceps or vacuum delivery are used to help deliver your babies.
Once the first baby is born, your midwife or doctor can check the position of the second baby by feeling your tummy and doing a vaginal examination. They may also use an ultrasound scan.
If the second baby is in a good position, it should be born soon after the first, as your cervix is already fully dilated.
If your contractions stop after the first baby is born, the doctor or midwife may discuss giving you hormones via a drip to restart them.
Caesarean section and twins
In the UK, more than half of twins and almost all triplets are delivered by caesarean.
You may choose to have a planned caesarean, or your doctor may recommend a caesarean, if:
- the first baby is lying feet, knees or buttocks first (breech)
- 1 twin is lying sideways (transverse)
- you have a low-lying placenta
- your twins share a placenta
- you have had a difficult delivery with a single baby before
As with any pregnancy, if you plan a vaginal birth, you may still end up needing an emergency caesarean.
In very rare cases, some women deliver 1 twin vaginally and then need a caesarean section to deliver the second twin. This happens in less than 5% of twin births.
Finding out if your twins are identical
After the birth, your midwife will examine the placenta to check that it's all there and look at the membranes.
If your babies have a single placenta with 1 outer membrane (chorion) and 2 inner membranes (amnion), they must be identical (monozygotic).
Otherwise, the only way to tell if they're identical is through DNA testing. This is not available on the NHS.
This is not available on the NHS.
For advice on how to find out if your twins are identical, you can phone the Multiple Births Foundation on 020 3313 3519 or email them at [email protected].
Video: how can my twin or multiple births be managed?
In this video, a midwife explains what can happen when giving birth to more than 1 baby.
Media last reviewed: 1 November 2019
Media review due: 2 November 2022
Page last reviewed: 13 May 2019
Next review due: 13 May 2022
Giving birth to twins | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Twins are more likely to be born early, often before 38 weeks, so it's important to understand your birth options. Less than half of all twin pregnancies last beyond 37 weeks.
Because of the likelihood that your babies will be born early, there is a good chance one or both of them will spend some time in special care.
As twins are often born prematurely, it's a good idea to discuss birth options with your midwife or doctor early in your pregnancy.
You should also discuss where you would like to give birth. You will most likely be advised to give birth in a hospital because there's a higher chance of complications with a twin birth.
It's common for more medical staff to be involved in the birth of twins, such as a midwife, an obstetrician and two paediatricians - one for each baby.
While the process of labour is the same as when single babies are born, twin babies are more closely monitored. To do this, an electronic monitor and a scalp clip might be fitted on the first baby once your waters have broken. You will be given a drip in case it is needed later.
Vaginal birth
About one third of all twins are born vaginally and the process is similar to that of giving birth to a single baby. If you're planning a vaginal delivery, it's usually recommended that you have an epidural for pain relief. This is because, if there are problems, it's easier and quicker to assist the delivery when the mother already has good pain relief.
If the first twin is in a head down position (cephalic), it's usual to consider having a vaginal birth. However, there may be other medical reasons why this would not be possible. If you have had a previous caesarean section, it's usually not recommended you have a vaginal birth with twins.
If you have a vaginal birth, you may need an assisted birth, which is when a suction cup (ventouse) or forceps are used to help deliver the babies.
Once the first baby is born, the midwife or doctor will check the position of the second baby by feeling your abdomen and doing a vaginal examination. If the second baby is in a good position, the waters will be broken and this baby should be born soon after the first as the cervix is already fully dilated. If contractions stop after the first birth, hormones will be added to the drip to restart them.
Caesarean section
You may choose to have an elective caesarean from the outset of your pregnancy, or your doctor may recommend a caesarean section later in the pregnancy as a result of potential complications. You’re nearly twice as likely to have a caesarean if you’re giving birth to twins than if you’re giving birth to a single baby.
You’re nearly twice as likely to have a caesarean if you’re giving birth to twins than if you’re giving birth to a single baby.
The babies' position may determine whether they need to be delivered by caesarean section or not. If the presenting baby - the one that will be born first - is in a breech position (feet, knees or buttocks first), or if one twin is lying in a transverse position (with its body lying sideways), you will need to have a caesarean section.
Some conditions also mean you will need a caesarean section; for example if you have placenta praevia (a low-lying placenta) or if your twins share a placenta.
If you have previously had a very difficult delivery with a single baby, you may be advised to have a caesarean section with twins. Even if you plan a vaginal birth, you may end up having an emergency caesarean section.
This could be because:
- one or both babies become distressed
- the umbilical cord prolapses (falls into the birth canal ahead of the baby)
- your blood pressure is going up
- the labour is progressing too slowly
- assisted delivery doesn't work
In very rare cases, you may deliver one twin vaginally and then require a caesarean section to deliver the second twin if it becomes distressed.
After the birth
After the birth, your midwife will examine the placenta to determine what type of twins you have. Twins can either be fraternal or identical.
If your babies need special care
Depending on where you plan to give birth, you may need to go to another hospital with appropriate facilities if complications in your pregnancy indicate you're likely to have an early delivery. This may not be near to home, so make sure to check there are enough beds for both your babies in the neonatal unit.
Ask if your chosen hospital has a transitional care unit or a special care nursery. These are places that allow mothers to care for their babies if they need special care but not intensive care. These hospitals are more likely to be able to keep you and your babies in the same place.
You might also want to ask if your hospital has cots that allow co-bedding (where your babies sleep in a single cot), if this is appropriate and if you want your babies to sleep together.
If you have one baby in the hospital and one at home, you will need to think about splitting your time between the two. When you visit your baby in hospital, ask if you can bring their twin and if co-bedding is allowed during visits.
If you want to breastfeed and only one twin can feed effectively, you may need to express milk to feed the twin who is having trouble feeding. You may then need to put the twin who can feed on the breast to encourage milk production in order to get enough milk to feed both babies.
Check if your hospital offers support from a community neonatal nurse, which would allow for you and your babies to leave hospital earlier, for example if your baby is still tube-fed.
When you go to clinics for follow-up appointments, it's a good idea to ask not to be booked into early morning appointments. Getting out of the house with two babies, particularly if one is unwell, can be difficult.
For more information and support, visit Twins Research Australia.
Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Twin birth without caesarean section
Pregnancy with many children requires special efforts and patience. Preparation for the natural birth of twins has been going on for 9 months, because this process is a huge burden on the woman's body. So, future "polymoms" will perform ultrasound and visit a specialist more often than others.
Important!
As early as 32–33 weeks, you should expect the onset of childbirth, since a multiple pregnancy may not be carried until the end of the term.
Natural birth of twins is not always possible. But even if the process of bearing the fetus proceeds smoothly, in the last trimester you need to be prepared for the occurrence of an unplanned situation that will require an emergency delivery, possibly with the help of an operation.
What do you need to know about natural birth of twins?
In some cases, there is no difference between the birth of one and two babies. But still, more often, the natural birth of twins is more difficult than in the case of the birth of one baby. No wonder: after all, a woman does double work.
But still, more often, the natural birth of twins is more difficult than in the case of the birth of one baby. No wonder: after all, a woman does double work.
Important!
If the pregnancy is successful, the babies and mother are doing great, and if both babies are upside down, the chances of a natural birth of twins are very high.
The process will take place in classical stages. The first stage is the opening of the cervix, which is manifested by contractions. Then comes the second stage, when the babies are born. And, finally, at the third stage, the afterbirth is born. The second period will be longer in this case, because two babies are born. Depending on whether the fetuses have a common placenta, or each has its own placenta, one or two children's places will be born in the third period.
But if one baby is in the cephalic presentation, and the other in the breech, then one child appears on its own, and the second is often removed by surgical methods. In this case, the natural birth of twins is impossible.
In this case, the natural birth of twins is impossible.
Approaching natural birth of twins
During pregnancy, the uterine muscles are overstretched by two fetuses. Therefore, contractions may be weak, and the natural birth of twins themselves will be long.
In terms of sensations and signs, double births are no different from standard ones. If a woman notes the appearance of the following signs, then the birth of twins in a natural way is just around the corner.
- The stomach dropped, and breathing became much easier.
- Urination became even more frequent, as the uterus presses harder on the bladder.
- Pain appeared in the lumbar region.
- The gait has become sedate and measured.
Features of the process of giving birth to twins in a natural way
Any process of the birth of a child is divided into periods - the opening of the cervix, the expulsion of the fetus and the appearance of a child's place. Natural birth of twins is no exception.
Natural birth of twins is no exception.
Cervical dilatation
In the first stage of labor, a woman notes the onset of contractions in the form of severe discomfort in the perineum, lower abdomen, and lumbar region. At the same time, at first they may be irregular, but over time they become periodic, and the time between contractions becomes shorter and shorter.
Usually, at the end of the first period, the bladder opens and the amniotic fluid is poured out. Together with them, the mucous-blood plug also leaves.
Exile period
As soon as the cervix opens 10 cm, there is a contraction period during which babies are born. When giving birth to twins in a natural way, this stage lasts twice as long, because not one, but successively two crumbs have to go through the birth canal.
It is very important for a woman to follow all the recommendations of experts on proper breathing and behavior in attempts. This will help speed up the process.
So the first child was born. The newborn is examined and his condition is assessed. At the same time, specialists evaluate the position and heartbeat of the second baby, determining whether it will be possible to complete the birth of twins in a natural way. If necessary, the doctor opens the second amniotic sac. As a rule, the interval between the birth of the first and second baby is no more than 15 minutes.
The newborn is examined and his condition is assessed. At the same time, specialists evaluate the position and heartbeat of the second baby, determining whether it will be possible to complete the birth of twins in a natural way. If necessary, the doctor opens the second amniotic sac. As a rule, the interval between the birth of the first and second baby is no more than 15 minutes.
Birth of the placenta
At the final stage, the placenta or baby place comes out. With twins, the placenta can be either one for two, and each child has its own. This means that one or two placentas will be born. It is important to make sure that the placenta was born entirely and nothing was left in the uterine cavity. To this end, it is carefully examined.
If necessary, the woman is stitched, after which the newly-born mother rests.
It is desirable that the natural birth of twins takes place in specialized perinatal centers. There are specially trained personnel in such institutions, and the center itself has all the necessary conditions in order to quickly carry out an operation and get the kids out if necessary. However, in the absence of such a center in the region of residence of a mother who is expecting twins, there is no need to worry. If the pregnancy is going well, the birth of twins in an ordinary maternity hospital will also be successful.
However, in the absence of such a center in the region of residence of a mother who is expecting twins, there is no need to worry. If the pregnancy is going well, the birth of twins in an ordinary maternity hospital will also be successful.
Twin birth: natural or cesarean section
PreviousNext
- Why do multiple pregnancies and twin births happen?
- Fraternal twins
- Identical twins
- Features of pregnancy by identical twins depending on the time of separation of the zygote.
- Can a woman have twins in her first birth?
- How often do twin births occur?
- How long does a twin birth take?
- When is the due date for multiple pregnancies?
- Which is better for twins - caesarean section or natural childbirth?
Contents:
The human reproductive system is very economical, and usually a woman becomes the mother of one baby. However, occasionally we come across parents walking with a double stroller or trying to fit two identical toddlers into a car. Why is this happening? What is the probability of becoming a mother of twins? What awaits a woman when the time comes for twins to be born - caesarean section or natural childbirth? We answer your questions.
However, occasionally we come across parents walking with a double stroller or trying to fit two identical toddlers into a car. Why is this happening? What is the probability of becoming a mother of twins? What awaits a woman when the time comes for twins to be born - caesarean section or natural childbirth? We answer your questions.
Why do multiple pregnancies and twin births happen?
Sometimes two or even more babies begin to grow in the womb of a future mother at once. If you do not consider unique and very rare cases, then twins can be homozygous (identical, emerging from the same egg) and heterozygous (fraternal, grown from different eggs).
Fraternal twins
Heterozygous twins appear when several eggs mature in a woman at the same time. Babies are always isolated - each of them has an individual placenta and fetal (amniotic) bladder. They may have different sexes, and, in general, they usually resemble each other no more than the children of this couple, born several years apart from different pregnancies. At the same time, eggs can be fertilized both as a result of one sexual intercourse, and different - with an interval of several hours or days.
At the same time, eggs can be fertilized both as a result of one sexual intercourse, and different - with an interval of several hours or days.
If a woman has a very active sex life, it is even possible that one egg is fertilized by the sperm of one partner, and the second by the other. Then, during the birth of twins, babies are born, each of which has its own father, which in scientific language is called the term "superfecundation". The exact frequency of this phenomenon is unknown, but in cases where DNA examinations were performed when paternity was disputed (in other words, when potential dads suspected in advance that the matter was unclean), superfecundation was confirmed in 2.4% of twin pairs 1 .
Identical twins
Monozygotic twins are a different story. At first, everything happens as usual: one egg comes out of the follicle during ovulation, it is fertilized by one sperm, it becomes one zygote (a cell with the combined genetic material of the parents), from which one embryo should develop. But after a while, it suddenly splits into two identical copies. One of them can divide again, and then instead of giving birth to twins, the mother will give birth to triplets, if both zygotes do this, there will be four twins.
But after a while, it suddenly splits into two identical copies. One of them can divide again, and then instead of giving birth to twins, the mother will give birth to triplets, if both zygotes do this, there will be four twins.
Features of pregnancy by identical twins depending on the time of separation of the zygote.
If fraternal twins always have separate "apartments" - each has its own placenta and amniotic bladder, in identical twins it depends on the time of separation 2 .
| Day of separation of the zygote | Percentage of cases | Features |
|---|---|---|
| 1–3 | 18–36% | Each baby has its own placenta and amniotic sac, just like fraternal ones. |
| 4-8 | 60-70% | Twins share a common placenta but amniotic sacs are separated. |
| 8–13 | 1-2% | Twins share one amniotic sac and feed on a common placenta. |
| 13–15 | 0.5% | Siamese twins appear late in separation. Contrary to the common misconception, they do not grow together, but, on the contrary, do not have time to separate. |
Can a woman have twins in her first birth?
Everything is possible. Do you remember that multiple pregnancies can be identical and heterozygous? The likelihood of developing identical twins is the same for all women. In both first and subsequent births, twins of identical babies are born in about 4 out of 1000 pregnancies 3 .
Do you remember that multiple pregnancies can be identical and heterozygous? The likelihood of developing identical twins is the same for all women. In both first and subsequent births, twins of identical babies are born in about 4 out of 1000 pregnancies 3 .
Fraternal twins appear for a different reason - due to hyperovulation, i.e. maturation of two or more eggs in one cycle. This is influenced by the following factors 4 :
-
Use of fertility drugs.
-
Recent withdrawal of hormonal contraceptives or irregular use of contraceptives.
-
Obesity, i.e. body mass index above 305.
-
Genetic predisposition. If you yourself have a twin, if your mother or your sister gave birth to twins, your chances are higher than the average natural probability of giving birth to twins 6 .
-
Rost.
 Tall women are more likely to become mothers of fraternal twins.
Tall women are more likely to become mothers of fraternal twins. -
Woman's age. The likelihood of multiple pregnancy increases after age 35 7 .
How often do twins occur?
In obstetrics, there is the so-called Hellin's law 8 , which says that the probability of having twins, triplets, etc. obeys the following formula: 1/89N-1, where N is the number of twins.
| Number of fruits | Probability | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 1 out of 89 genera | 1.1% |
| 3 | 1 out of 7,921 births | 0. |
| 4 | 1 out of more than 700 thousand births | 0.00014% |
Hellin's Law is just a curious observation made by a late 19th century physician, and modern science offers much more complex formulas. However, sometimes it works amazingly. For example, in 2016 in Russia there were 1,876,646 births, in which 22,144 twins and 408 triplets were born 9 , which is 1.18% and 0.021% as a percentage. Not bad accuracy!
In general, the statistics of twin births in our country looks like this:
Percentage of twin births among all births in Russia from 1996 to 2016 9 .
It is easy to see that in the late 90s and early 2000s, the statistics were almost constant, and then unexpectedly, but surely, they crept up. The answer is simple: medicinal and other assisted reproductive technologies have been actively developing lately, and they often lead to multiple pregnancies 10 . So the last numbers are naturally occurring twins plus the contribution of infertility treatments.
The answer is simple: medicinal and other assisted reproductive technologies have been actively developing lately, and they often lead to multiple pregnancies 10 . So the last numbers are naturally occurring twins plus the contribution of infertility treatments.
How long does it take to give birth to twins?
Doctors distinguish three stages in childbirth - the period of disclosure, the period of exile and the subsequent period. The first period begins with contractions and ends with the full opening of the cervix, the third starts after the birth of the baby and ends with the appearance of the afterbirth - the placenta and the remains of the membranes. The duration of these periods depends more on the individual characteristics of the body than on how many babies the woman bore.
Of greatest interest is the period of exile - the very one when babies from a cozy mother's womb are "expelled" into our difficult world. They come out sequentially, which means that we can assume that the birth of twins is longer for this particular interval between the appearance of the first and second child. So how much does he make?
So how much does he make?
Thanks to doctors from the Hesse region in Germany, this question has a very precise answer. For 15 years, they carefully researched information about natural births of twins in local hospitals. As a result, an impressive amount of data was collected - more than 4,000 cases of multiple pregnancies, as a result of which more than 8,000 babies were born. The analysis of this array made it possible to calculate the most probable interval that passes between the birth of babies in twin births in a natural way. For 3 out of 4 mothers, this takes no more than 15 minutes, and on average, one twin is only 13.5 minutes older than the other 11 .
| Interval between births of twins, minutes | Birth rate |
|---|---|
| Up to 15 | 75. |
| 16-30 | 16.4% |
| 31-45 | 4.3% |
| 46-60 | 1.7% |
| Over 60 | 1.8% |
Rarely in obstetric practice, surprising cases are noted when a much longer time elapses between the birth of twins. Apparently, the first position among the record holders for the duration of the birth of twins is occupied by a resident of the German city of Cologne named Oksana (we will not say, but the name suggests that she may be our former compatriot).
On November 17, 2018, at the 26th week of pregnancy, a woman went into premature labor. She gave birth to a live premature baby girl weighing 900 grams, after which the cervix closed and the contractions stopped. The doctors decided to give the second child the opportunity to stay in the mother's womb as long as possible. As a result, another girl was born four days after the planned date - 97 days later than her sister and already in 2019 12 . By the way, don't worry about the older baby: the doctors took her out, and after a three-month separation, the twins met again.
When is the due date for multiple pregnancies?
Pregnancy in a woman expecting several babies at once is usually shorter. Twins can be expected as early as week 35, triplets at week 33, and four twins starting at week 29 13 . After the birth of twins, doctors surround newborns with special care. And the birth of three or more babies requires the closest attention, because such twins in the vast majority of cases are born prematurely.
A woman who has several children has a significantly higher chance of becoming a mother ahead of schedule. Doctors will try to do everything to prolong the pregnancy as much as possible, but the woman herself should not risk the future of her babies either. At the very least, she needs to monitor her diet and health, breathe fresh air, avoid psychological stress and excessive physical exertion.
What is better for twins - caesarean section or vaginal delivery?
The final decision on the tactics of childbirth is made by the specialists of the maternity hospital, guided by all the information available to them about the pregnancy. However, practice shows that if everything goes on the whole normally (the gestational age at the time of delivery exceeds 32 weeks, and the first twin is settled in head presentation, that is, it is going to go head first), there is no significant difference between the natural birth of twins and caesarean section 14 .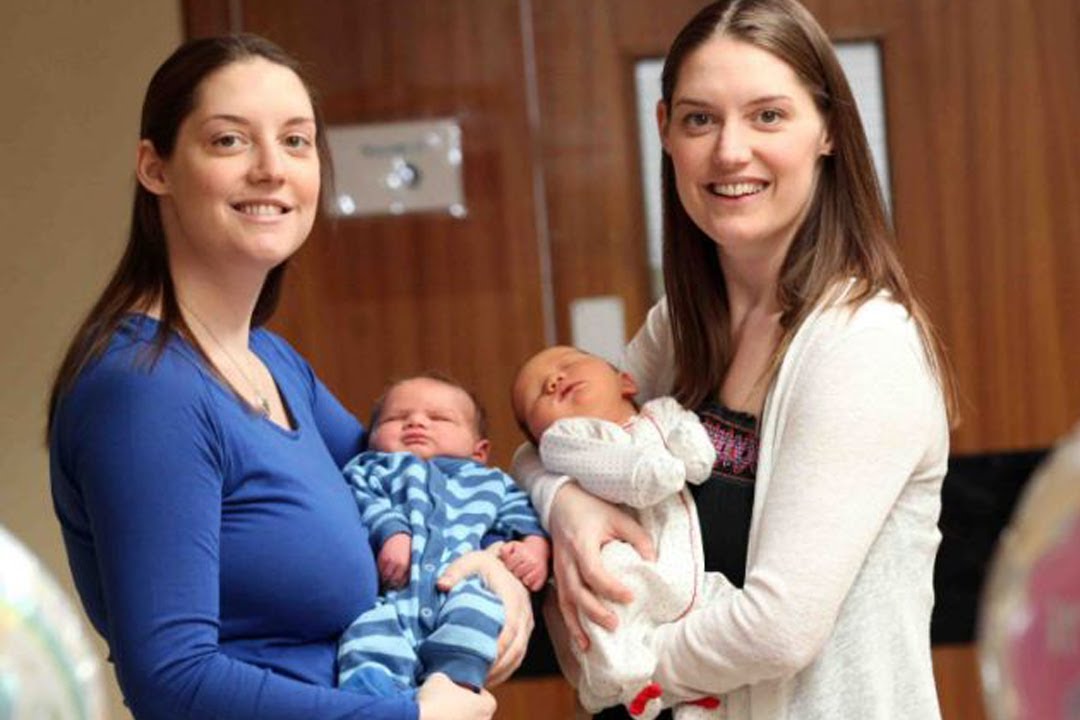 A large study involving 106 medical centers in 25 countries showed that the risk to babies remains the same with both modes of delivery.
A large study involving 106 medical centers in 25 countries showed that the risk to babies remains the same with both modes of delivery.
Cesarean section is indicated for breech presentation of the first twin in twin birth. However, in this situation, the operation is recommended even during pregnancy with one baby. If the twins are growing up in a common amniotic sac, doctors also usually opt for a caesarean section. In other cases, you should not be afraid of giving birth to twins in a natural way - they are no more dangerous than surgery 14 .
Sources:
-
Wenk, R. E.; Houtz, T; Brooks, M; Chiafari, F. A. (1992). How frequent is heteropaternal superfecundation? Acta geneticae medicae et gemellologiae. 41(1):43–7.
-
Curran, Mark (2005-11-02). twinning. Focus Information Technology.
-
Professor Hanan Hamamy. GFMER. Monozygotic twinning.
-
Joel Forman, MD.
 Causes of Identical and Fraternal Twins.
Causes of Identical and Fraternal Twins. -
WebMD. Moms' Obesity Makes Twins More Likely.
-
U.S. National Library of Medicine. Is the probability of having twins determined by genetics?
-
ACOG. Multiple Pregnancy.
-
Johan Fellman (November 5th 2018). Historical Studies of Hellin's Law, Multiple Pregnancy - New Challenges, Julio Elito Jr., IntechOpen.
-
Federal State Statistics Service (Rosstat). Demographic Yearbook of Russia. 2017: Stat. Sat / Rosstat. - M., 2017. - 263 p. ISBN 978-5-89476-447-4.
-
Kulkarni AD, Jamieson DJ, Jones HW, Kissin DM, Gallo MF, Macaluso M, Adashi EY (2013). Fertility Treatments and Multiple Births in the United States. New England Journal of Medicine. 369(23): 2218–2225.
-
Stein W, Misselwitz B, Schmidt S (2008).

 013%
013%  8%
8%