Can i give birth at 30 weeks
FAQs About Babies Born at 30 Weeks
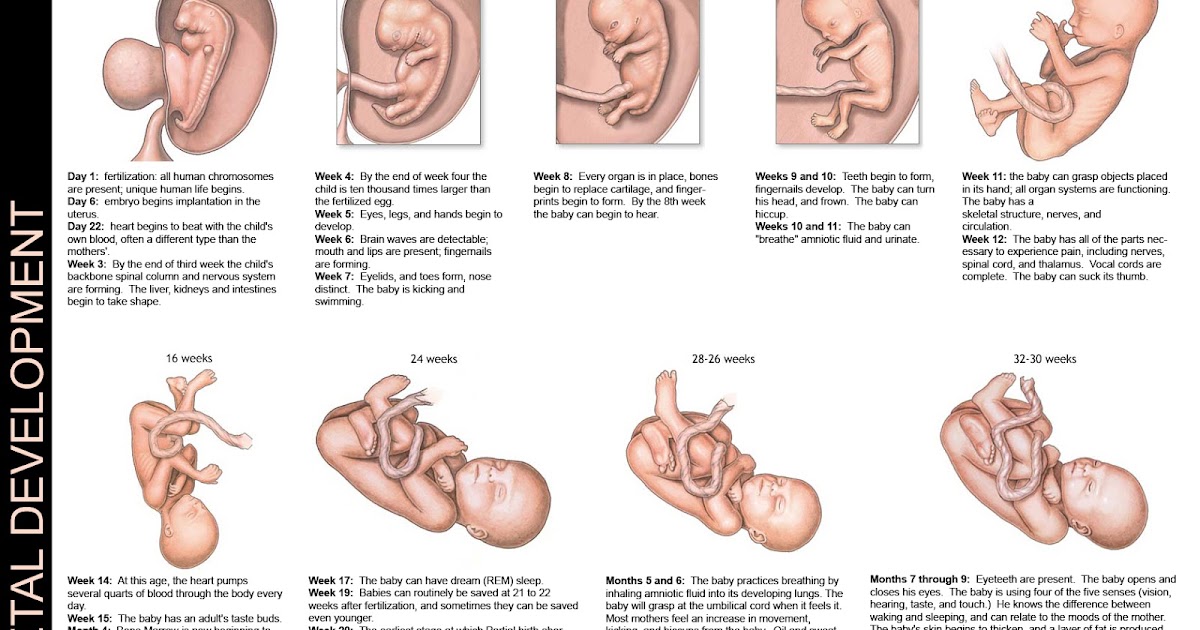
What does a baby born at 30 weeks look like?
Doctors and medical specialists consider a premature baby born at 30 weeks to be “very preterm.” This means that once they’re born, they’ll likely require immediate medical attention to help them breathe, eat, and reach developmental milestones.
A baby born at 30 weeks will look significantly smaller than babies born closer to their due date. Premature babies’ heads will appear disproportionately larger than the rest of their bodies, and they may weigh as little as 3 pounds.
At 30 weeks, preterm babies may also have:
- Fuzzy bodies, as they may still be covered in fine hair (called lanugo)
- Angular features because their fat stores haven’t developed yet
- Slightly translucent or wrinkled skin, with veins visible under their skin
What are the reasons for giving birth at 30 weeks?
Premature births can happen to anyone. While there may not always be a specific cause for a baby being born at 30 weeks, there are some factors that can increase the risk of preterm birth.
Some possible reasons for giving birth at 30 weeks include:
- A genetic predisposition to preterm birth
- Previously giving birth to a preterm baby or having miscarriages or abortions
- Getting pregnant again less than six months after giving birth
- Issues with your reproductive organs
- Having diabetes or high blood pressure
- Lifestyle factors such as smoking or drug use
- Experiencing a highly stressful event while pregnant
Other possible risk factors for preterm birth include experiencing physical injury or trauma, getting pregnant through in-vitro fertilization, and being over or underweight before getting pregnant.
Speak with your doctor if you have any of these known risk factors. Remember that even if you don’t have these risk factors, preterm labor and delivery is still possible, so monitor your pregnancy symptoms and report any abnormal changes to your doctor.
What are the possible complications?
Having a premature baby can come with a higher risk of complications compared to full-term babies. Some preterm health issues resolve over time, while others can have long-term effects.
Some preterm health issues resolve over time, while others can have long-term effects.
Your baby’s specific needs or issues will determine the type of medical treatment or intervention they may require.
Some more immediate health complications that a baby born at 30 weeks of gestation might experience include:
- Heart issues such as an abnormal opening between the aorta and pulmonary artery, which can cause your baby to develop a heart murmur or heart failure
- Breathing issues or respiratory distress caused by underdeveloped lungs. Your baby may have apnea (long pauses in their breathing) or develop a disorder called bronchopulmonary dysplasia.
- Brain hemorrhage, which can be mild and have little to no immediate impact. More severe bleeding can cause permanent brain injury.
- Low core body temperature, which can lead to hypothermia
- Gastrointestinal issues caused by underdeveloped digestive tracts
- Blood issues including anemia (caused by low red blood cell count) or jaundice, which causes yellowing of the skin and eyes
- Weakened immune systems, which can increase their risk of developing rapidly spreading infections
- Sudden infant death syndrome
If you’re wondering how long you and the baby might stay in the hospital, the answer depends on the severity of any health issues.
Even if a premature baby receives medical care, there is still a risk that they may experience long-term complications. These can include:
- Disorders of movements, muscle tone, and posture, such as cerebral palsy
- Learning disabilities or developmental delays
- Issues with their vision, hearing, or dental development
- Chronic health challenges like asthma
- Behavioral or psychological challenges
Remember that not all babies born at 30 weeks will experience serious or long-term health complications. Once your baby is born, their medical team will diligently monitor their health and do everything they can to treat your baby.
What is the survival rate?
Despite the possible health complications, the survival rate for babies born at 30 weeks is quite high. In areas that can quickly provide high-quality health care to newborns, the survival rate for babies born at 30 weeks is approximately 90–95 percent.
How can a baby born at 30 weeks be managed?
A baby born at 30 weeks will typically spend some time in the neonatal intensive care unit until they’re more fully developed.
The level of care that your newborn needs will determine the kind of treatments they need to receive. These can include:
- Placing them in an incubator to keep them warm until they can better regulate their core body temperature
- Monitoring their vital signs like heart rate or blood pressure
- Feeding them through a tube if their swallowing and sucking reflexes haven’t fully developed
- Giving them fluids intravenously to make sure their levels stay on target
- Exposing them to bilirubin lights to treat jaundice
- Giving them medication to help regulate bodily functions or treat infections
- Admitting them for surgery to treat any serious defects or complications
These are just some of the possible ways in which your baby’s care team will help provide for their needs.
Once your baby reaches certain milestones, like gaining weight and being able to breathe and eat on their own, they’ll be ready to leave the hospital. Doctors and nurses will make sure you have everything you need to confidently care for your newborn from the comfort of your own home.
Doctors and nurses will make sure you have everything you need to confidently care for your newborn from the comfort of your own home.
A final note about babies born at 30 weeks
Delivering a baby at 30 weeks can be an overwhelming experience. But with the right health care support in place, your baby can survive and thrive. You and your doctor will continue to monitor your baby’s health as they develop to identify if there are any related long-term complications.
Preterm labor and premature birth: Are you at risk?
Preterm labor and premature birth happen too early, before 37 weeks of pregnancy.
Babies born prematurely are more likely to have health problems than babies born on time.
Learn the signs and symptoms of preterm labor so you can get help quickly if they happen to you.
We don’t always know what causes preterm labor and premature birth. We do know certain risk factors may make you more likely to give birth early.

Talk to your provider about what you can do to help reduce your risk for preterm labor and premature birth.
Download our English and Spanish health action sheets on preterm labor.
What are preterm labor and premature birth?
Preterm and premature mean the same thing — early. Preterm labor is labor that begins early, before 37 weeks of pregnancy. Labor is the process your body goes through to give birth to your baby. Preterm labor can lead to premature birth. Premature birth is when your baby is born early, before 37 weeks of pregnancy. Your baby needs about 40 weeks in the womb to grow and develop before birth.
Babies born before 37 weeks of pregnancy are called premature. Premature babies can have serious health problems at birth and later in life. About 1 in 10 babies is born prematurely each year in the United States.
What are the signs and symptoms of preterm labor?
Signs of a condition are things someone else can see or know about you, like you have a rash or you’re coughing. Symptoms are things you feel yourself that others can’t see, like having a sore throat or feeling dizzy. Learn the signs and symptoms of preterm labor so you can get help quickly if they happen to you.
Symptoms are things you feel yourself that others can’t see, like having a sore throat or feeling dizzy. Learn the signs and symptoms of preterm labor so you can get help quickly if they happen to you.
If you have even one of these signs and symptoms of preterm labor, call your provider right away:
- Change in your vaginal discharge (watery, mucus or bloody) or more vaginal discharge than usual
- Pressure in your pelvis or lower belly, like your baby is pushing down
- Constant low, dull backache
- Belly cramps with or without diarrhea
- Regular or frequent contractions that make your belly tighten like a fist. The contractions may or may not be painful.
- Your water breaks
When you see your provider, he may do a pelvic exam or a transvaginal ultrasound to see if your cervix has started to thin out and open for labor. Your cervix is the opening to the uterus (womb) that sits at the top of the vagina (birth canal). A transvaginal ultrasound is done in the vagina instead of on the outside of your belly. Like a regular ultrasound, it uses sound waves and a computer to make a picture of your baby. If you’re having contractions, your provider monitors them to see how strong and far apart they are. You may get other tests to help your provider find out if you really are in labor.
Like a regular ultrasound, it uses sound waves and a computer to make a picture of your baby. If you’re having contractions, your provider monitors them to see how strong and far apart they are. You may get other tests to help your provider find out if you really are in labor.
If you’re having preterm labor, your provider may give you treatment to help stop it. Or you may get treatment to help improve your baby’s health before birth. Talk to your provider about which treatments may be right for you.
Are you at risk for preterm labor and premature birth?
We don’t always know for sure what causes preterm labor and premature birth. Sometimes labor starts on its own without warning. Even if you do everything right during pregnancy, you can still give birth early.
We do know some things may make you more likely than others to have preterm labor and premature birth. These are called risk factors. Having a risk factor doesn’t mean for sure that you’ll have preterm labor or give birth early. But it may increase your chances. Talk to your health care provider about what you can do to help reduce your risk.
But it may increase your chances. Talk to your health care provider about what you can do to help reduce your risk.
Because many premature babies are born with low birthweight, many risk factors for preterm labor and premature birth are the same as for having a low-birthweight baby. Low birthweight is when a baby is born weighing less than 5 pounds, 8 ounces.
These three risk factors make you most likely to have preterm labor and give birth early:
- You’ve had a premature baby in the past.
- You’re pregnant with multiples (twins, triplets or more).
- You have problems with your uterus or cervix now or you’ve had them in the past. Your uterus (also called the womb) is where your baby grows inside you.
Medical risk factors before pregnancy for preterm labor and premature birth
- Being underweight or overweight before pregnancy. This can include having an eating disorder, like anorexia or bulimia.

- Having a family history of premature birth. This means someone in your family (like your mother, grandmother or sister) has had a premature baby. If you were born prematurely, you’re more likely than others to give birth early.
- Getting pregnant again too soon after having a baby. For most women it’s best to wait at least 18 months before getting pregnant again. Talk to your provider about the right amount of time for you.
Medical risk factors during pregnancy for preterm labor and premature birth
Having certain health conditions during pregnancy can increase your risk for preterm labor and premature birth, including:
- Connective tissue disorders, like Ehlers-Danlos syndromes (also called EDS) and vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (also called vEDS). Connective tissue is tissue that surrounds and supports other tissues and organs. EDS can cause joints to be loose and easy to dislocate; skin to be thin and easily stretched and bruised; and blood vessels to be fragile and small.
 It also can affect your uterus and intestines. vEDS is the most serious kind of EDS because it can cause arteries and organs (like the uterus) to rupture (burst). EDS and vEDS are genetic conditions that can be passed from parent to child through genes.
It also can affect your uterus and intestines. vEDS is the most serious kind of EDS because it can cause arteries and organs (like the uterus) to rupture (burst). EDS and vEDS are genetic conditions that can be passed from parent to child through genes. - Diabetes. Diabetes is when your body has too much sugar (called glucose) in your blood.
- High blood pressure and preeclampsia. High blood pressure (also called hypertension) is when the force of blood against the walls of the blood vessels is too high. This can stress your heart and cause problems during pregnancy. Preeclampsia is a kind of high blood pressure some women during or right after pregnancy. If not treated, it can cause serious problems and even death.
- Infections, including sexually transmitted infections (also called STIs) and infections of the uterus, urinary tract or vagina
- Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (also called ICP).
 ICP is the most common liver condition that happens during pregnancy.
ICP is the most common liver condition that happens during pregnancy. - Thrombophilias. These are conditions that increase your risk of making abnormal blood clots.
Other medical risk factors during pregnancy include:
- Getting late or no prenatal care. Prenatal care is medical care you get during pregnancy.
- Not gaining enough weight during pregnancy. This can include having an eating disorder, like anorexia or bulimia.
- Bleeding from the vagina in the second or third trimester
- Preterm premature rupture of the membranes (also called PPROM). Premature rupture of membranes (also called PROM) is when the amniotic sac around your baby breaks (your water breaks) before labor starts. PPROM is when this happens before 37 weeks of pregnancy. If you have any fluid leaking from your vagina, call your provider and go to the hospital.
- Being pregnant after in vitro fertilization (also called IVF). IVF is a fertility treatment used to help women get pregnant.
- Being pregnant with a baby who has certain birth defects, like heart defects or spina bifida. Birth defects are health conditions that are present at birth. They change the shape or function of one or more parts of the body. Birth defects can cause problems in overall health, how the body develops or how the body works. Spina bifida is a birth defect of the spine.
Risk factors in your everyday life for preterm labor and premature birth
- Smoking, drinking alcohol, using street drugs or abusing prescription drugs.
- Having a lot of stress in your life.
- Low socioeconomic status (also called SES). SES is a combination of things like your education, your job and your income (how much money you make).
- Domestic violence. This is when your partner hurts or abuses you. It includes physical, sexual and emotional abuse.
- Working long hours or having to stand a lot
- Exposure to air pollution, lead, radiation and chemicals in things like paint, plastics and secondhand smoke.
 Secondhand smoke is smoke from someone else’s cigarette, cigar or pipe.
Secondhand smoke is smoke from someone else’s cigarette, cigar or pipe.
Age and race as risk factors for preterm labor and premature birth
Being younger than 17 or older than 35 makes you more likely than other women to give birth early. In the United States, black women are more likely to give birth early. Almost 17 percent of black babies are born prematurely each year. Just more than 10 percent of American Indian/Alaska Native and Hispanic babies are born early, and less than 10 percent of white and Asian babies. We don’t know why race plays a role in premature birth; researchers are working to learn more about it.
Can you reduce your risk for preterm labor and premature birth?
Yes, you may be able to reduce your risk for early labor and birth. Some risk factors are things you can’t change, like having a premature birth in a previous pregnancy. Others are things you can do something about, like quitting smoking.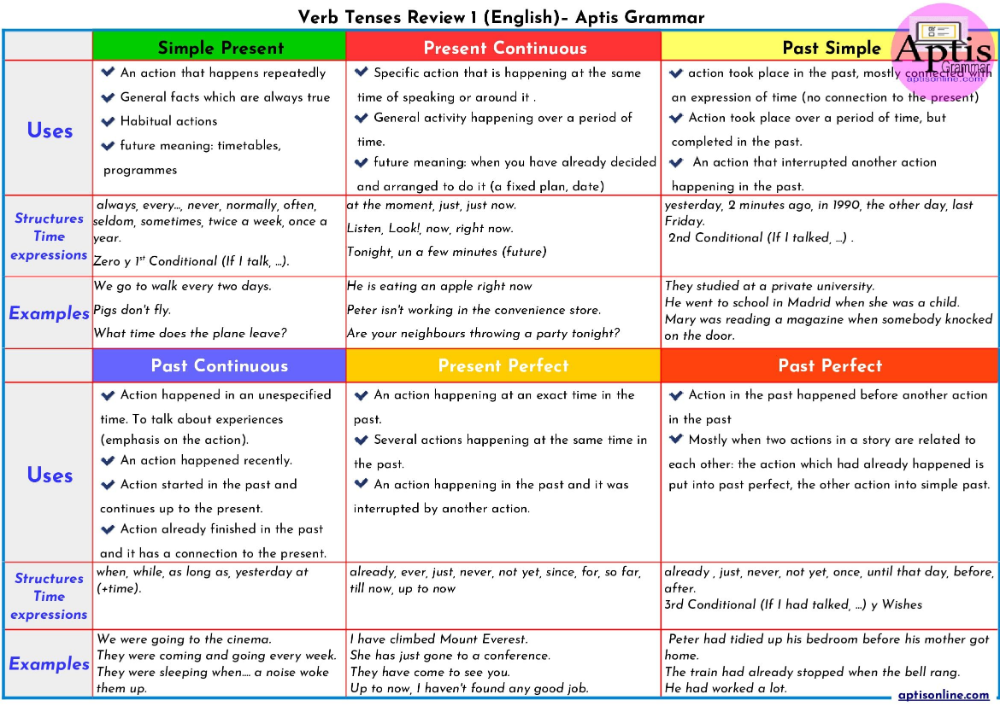
Here’s what you can do to reduce your risk for preterm labor and premature birth:
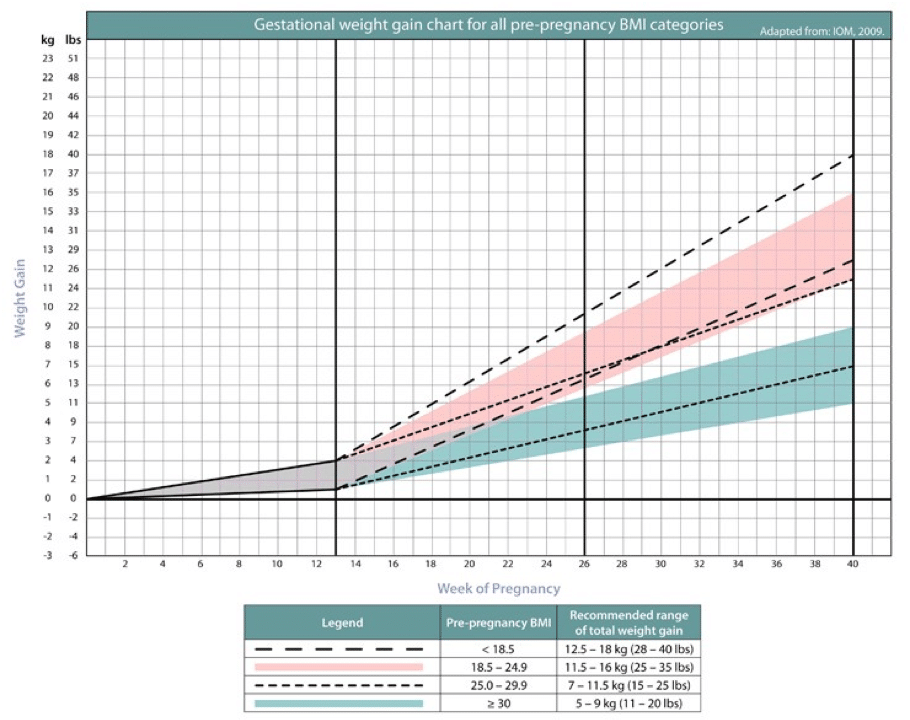
- Get to a healthy weight before pregnancy and gain the right amount of weight during pregnancy. Talk to your provider about the right amount of weight for you before and during pregnancy.
- Don’t smoke, drink alcohol, use street drugs or abuse prescription drugs. Ask your provider about programs that can help you quit.
- Go to your first prenatal care checkup as soon as you think you’re pregnant. During pregnancy, go to all your prenatal care checkups, even if you’re feeling fine. Prenatal care helps your provider make sure you and your baby are healthy.
- Get treated for chronic health conditions, like high blood pressure, diabetes, depression and thyroid problems. Depression is a medical condition in which strong feelings of sadness last for a long time and interfere with your daily life.
 It needs treatment to get better. The thyroid is a gland in your neck that makes hormones that help your body store and use energy from food.
It needs treatment to get better. The thyroid is a gland in your neck that makes hormones that help your body store and use energy from food. - Protect yourself from infections. Talk to your provider about vaccinations that can help protect you from certain infections. Wash your hands with soap and water after using the bathroom or blowing your nose. Don’t eat raw meat, fish or eggs. Have safe sex. Don’t touch cat poop.
- Reduce your stress. Eat healthy foods and do something active every day. Ask family and friends for help around the house or taking care of other children. Get help if your partner abuses you. Talk to your boss about how to lower your stress at work.
- Wait at least 18 months between giving birth and getting pregnant again. Use birth control until you’re ready to get pregnant again. If you’re older than 35 or you’ve had a miscarriage or stillbirth, talk to your provider about how long to wait between pregnancies.
 Miscarriage is the death of a baby in the womb before 20 weeks of pregnancy. Stillbirth is the death of a baby in the womb after 20 weeks of pregnancy.
Miscarriage is the death of a baby in the womb before 20 weeks of pregnancy. Stillbirth is the death of a baby in the womb after 20 weeks of pregnancy.
Last reviewed: March, 2018
See also: Signs and symptoms of preterm labor infographic
Premature birth - Juno
Premature birth: content of the article
What is preterm birth
The birth of a baby weighing more than 0.5 kg from 22 to 37 weeks is considered early. According to statistics, 15 million babies are born prematurely around the world.
In our country, until 2012, babies were registered who were born at 28 weeks, and all those born earlier - a week later. The development of obstetrics made it possible to nurse critically premature babies and increased their survival statistics.
Who is at risk
Any pregnant woman can give birth prematurely. Some expectant mothers have a higher chance of preterm birth. The risk zone includes pregnant women:
- under 17 and over 35;
- have more than one fetus;
- have structural features of the uterus or its cervix;
- use harmful substances - drugs, alcohol, smoke;
- have heavy physical activity;
- have a history of preterm birth;
- work in hazardous production;
- are subjected to sexual, emotional abuse, stress, mental stress.

At risk are expectant mothers who are not registered during the gestation period or ignore ultrasound, screenings, laboratory tests.
The threat of early preterm birth is more common with diagnoses: diabetes mellitus, anemia, hypertension, genitourinary infections, hypothyroidism, problems with weight before conception (deficiency or obesity), thrombophilia, vaginal bleeding. There is also a risk when conceiving through IVF, with congenital malformations of the fetus.
If a woman has previously given birth to a child ahead of schedule, the chances of premature birth remain in subsequent pregnancies. The same applies to the weight of the crumbs: if the firstborn was born with a lack of body weight, then his brother or sister may be underweight.
Risk factors
Doctors point to a number of factors that take place long before the conception of a child. These include:
- Gynecological diseases suffered in childhood or adolescence;
- Early initiation of intimate life;
- Hereditary factor;
- Pathologies of previous pregnancy: preeclampsia, fetoplacental insufficiency, premature birth;
- Excessive uterine distension in multiple pregnancies, polyhydramnios;
- Threat of early miscarriage.
Another risk factor is surgery or trauma to the abdominal organs during the gestation period.
Risk of preterm birth at different terms
The birth of a child prematurely has many negative consequences for him. It depends on the trimester in which the pregnancy ended.
The most severe consequence is the death of the infant. With early preterm birth in the period of 22-24 weeks, the threat is the highest - up to 80% of babies die. This occurs against the background of intracranial hemorrhage of 3-4 degrees, cardiopulmonary insufficiency, intrauterine infection of the fetus.
Among those born in the period of 25 - 26 weeks, 40% of babies die, in 27 - 28 - about 20%, in 29 - 32 - no more than 10%, and in 33 - 34 - 2% of newborns are at risk.
Modern medicine is able to provide care for a premature baby and save his life. But no one can guarantee a full healthy life. Such a child can subsequently be given disappointing diagnoses: cerebral palsy, mental retardation, retinopathy of prematurity. He may suffer all his life from problems with the digestive and respiratory systems, impaired vision, hearing, delayed mental and physical development. Diagnosis implies disability.
He may suffer all his life from problems with the digestive and respiratory systems, impaired vision, hearing, delayed mental and physical development. Diagnosis implies disability.
For a woman in labor, preterm labor is usually not dangerous. Without concomitant pathologies, the mother's body does not care how long the child is born. There are only psychological problems: stress, fear and worries about the baby. It is better for a mother to tune in that her child, in case of severe prematurity, will be taken to the intensive care unit for nursing, so she will not see him immediately.
A newly minted mother needs rehabilitation. Therapy is prescribed, depending on the cause of the pathology: a complex of vitamins, antioxidants, hormones.
Why preterm birth is dangerous
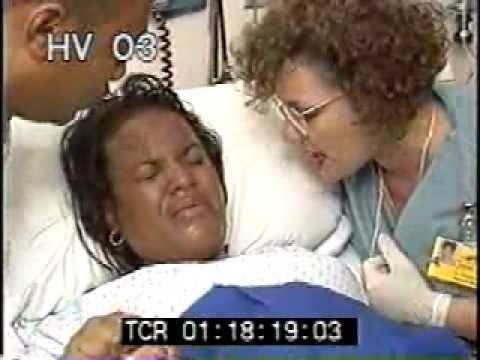
Infants are immature: their body is covered with a large amount of cheese-like lubricant, there is a deficiency of subcutaneous fatty tissue, few hairs on the head and fluff on the body, cartilage on the ears and nose are soft, the nails do not go beyond the fingertips, the navel is located closer to the pubis.
Babies are underweight. Depending on the weight of the crumbs, 4 degrees of prematurity are distinguished: at the 1st degree, the baby weighs from 2500 to 2001 g, the 2nd - from 2000 to 1500 g, the 3rd - from 1500 to 1001 g, the 4th - 1000 g and below .
The development of the genital organs has not been completed: the testicles in boys are not lowered into the scrotum, and in girls the large labia do not cover the small and clitoris.
Children have immature lungs. They cannot breathe adequately - often they need help. The cry is weak. There are also problems with digestion. The body cannot absorb all the components from mother's milk.
Extrauterine life for children becomes a strong stress. It's hard to deal with him. They poorly resist infections, quickly lose heat, thermoregulation is impaired. They are subject to hemorrhages against the background of fragile vessels. Especially dangerous are hemorrhages in the cervical spinal cord and ventricles of the brain.
Among the complications of preterm birth are intracranial hemorrhages, asphyxia, intrauterine growth retardation.
Types of preterm birth
Several classifications have been adopted. Let's consider them.
- By term: critically early - up to 28 weeks, significantly early - from 28 to 32 weeks, moderately early or late - from 32 to 37 weeks;
- By the mechanism of attack: induced and spontaneous. Induced cause artificially for medical reasons. Occurs in 40% of cases. Spontaneous in 60% of cases begin with contractions, in 40% - with a rupture of the membranes;
- By the nature of the course: spontaneous, with regular labor activity, without it and artificially provoked. In 80% of cases, preterm labor begins spontaneously. At the same time, the fetal bladder can be intact - and then the contractions are regular, growing. Or amniotic fluid may pour out, labor activity is chaotic. For medical reasons, early delivery can be artificially induced.
 For example, in case of danger to the life of the mother, intrauterine death of the fetus, or defects that are incompatible with life;
For example, in case of danger to the life of the mother, intrauterine death of the fetus, or defects that are incompatible with life; - According to symptoms: threatening, incipient and incipient. With threatening early premature birth, the lower abdomen and lower back hurt, the tone rises. Her neck remains unchanged, the external os is closed. When the process begins, pains appear in the lower abdomen. Regular contractions may begin. The neck is flattened or shortened. The main symptom of the onset of preterm labor is regular labor activity. The cervix opens by 2 - 3 cm, it happens quickly.
In 40% of women in labor, water breaks, 35% gave birth quickly and quickly. The active phase lasts less than when the baby appears on time. The contractions are monotonous, long and painful, the pauses between them are small.
Causes of preterm birth
Doctors indicate the main causes of the pathology:
- Early activity of the fetal endocrine system;
- Infections and inflammatory processes - ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis, pyelonephritis, bacterial vaginosis.
 They stimulate the production of prostaglandins. Hormones affect the uterine muscles - cause contractions and premature birth;
They stimulate the production of prostaglandins. Hormones affect the uterine muscles - cause contractions and premature birth; - Placental bleeding. They occur with incorrect presentation or detachment. The situation is serious, there is a threat to the life of the mother. Therefore, with presentation, hospitalization is indicated;
- Neck weakness. In 20% of cases, it leads to preterm birth. This also includes such factors: the interval between the current and previous gestation is less than 2 years, the woman is expecting 4 children or more;
- Isthmic-cervical insufficiency. The cervix opens itself - a miscarriage or premature birth occurs. It is possible to open mechanically - when scraping after a miscarriage, IVF, abortion;
- Pathologies on the part of the baby - intrauterine infection, malformations of internal organs.
Chronic ailments, dental problems, angina, health status during gestation, genetic factors are all common reasons for early delivery. Sometimes it is impossible to determine. Although this is important for the development of effective means of preventing pathology.
Sometimes it is impossible to determine. Although this is important for the development of effective means of preventing pathology.
Symptoms of preterm labor
We list the signs by which you may suspect that the baby is in a hurry to be born ahead of time.
Spasms over the pubis. They are similar to pain during menstruation.
Pain, pressure and discomfort in the genitals, thighs, pelvis. There is a dull pain in the lumbar region.
Feeling of pressure, pressure in the back.
Diarrhea, spasms and pain in the intestines.
Vaginal discharge - they get worse. May be watery, pink, brown, bloody.
Contractions of varying intensity. Touch your stomach with your fingertips - you will feel the contraction and relaxation of the uterus. Counted more than 4 contractions in 60 minutes? Call an ambulance - you need an urgent examination by an obstetrician.
The following symptoms are also dangerous: sudden blurred vision, flashes and “flies” before the eyes, incessant migraine, swelling of the face or hands, temperature of 38º C and above, painful urination, abdominal trauma, decreased fetal activity in the 3rd trimester (less than 10 movements in 12 hours).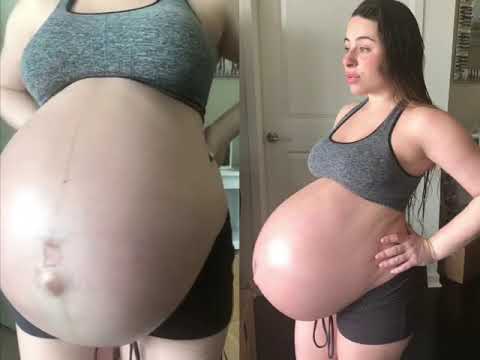
Any of the above symptoms indicate the risk of preterm birth. Seek medical attention.
Diagnosis of preterm birth
Includes several stages.
Transvaginal ultrasound. The length of the cervix is measured, fetal fibronectin is determined - a kind of "biological glue" that binds the fetal sac to the uterine mucosa.
Gynecological examination. Allows you to assess the degree of opening of the neck, its length.
Rapid test for the determination of phosphorylated protein-1. The test determines the possibility of preterm birth. In the future, this helps prevent iatrogenic complications.
When diagnosing, 2 parameters are evaluated:
- Regularity of contractions;
- Neck changes - shortening and smoothing. informative method. For example, with a neck length of 3 cm, the risk of preterm birth in the next week is 1%. The patient is not admitted to the hospital, there is no danger to her and the fetus.

Differential diagnosis
Its goal is to correctly diagnose. The early birth of a baby is accompanied by cramps in the lower abdomen, diarrhea, pain in the lumbar region. These same symptoms are characteristic of other conditions: appendicitis, colitis, cystitis, pyelonephritis.
When complaining of pain in the lower abdomen, the patient is examined for the consistency of the scar after the previous cesarean section, for example. When the temperature rises, flu, sore throat, viral infection are excluded.
Diagnosis
Preterm birth is stated based on the clinical picture. Doctors are guided by such markers.
The first is the length of the neck - less than 2 - 2.5 cm.
The second is the determination of phosphorylated protein-1.
The third is the regularity of contractions. There should be at least 4 in 20 minutes.
Fourth - neck changes in dynamics.
Fifth - assessment of the degree of maturity of the neck. Determined by the level of PSIFR-1 in the cervical canal.
Determined by the level of PSIFR-1 in the cervical canal.
Usually the process begins rapidly, suddenly and intensely.
Treatment for preterm birth
The goal is to reduce the tone of the myometrium, reduce uterine contractions. This is achieved by blocking oxytocin receptors - it is the hormone oxytocin that triggers the birth process.
Such antagonists of oxytocin receptors are tocolytics. One of the modern representatives of this group of drugs is atosiban.
The remedy is effective, but has contraindications. It is forbidden to treat pregnant women for less than 24 and more than 33 weeks, with uterine bleeding, growth retardation, distress or fetal death, severe preeclampsia, with rupture of the fetal membrane after 30 weeks, placenta previa or its detachment.
5 stages of preterm labor
The first stage is forecasting their onset. Depends on the situation: the process is starting, has begun, or it is a threat.
Stage two - prevention of respiratory distress syndrome in a child. Doctors stimulate the maturation of the lungs. Apply funds from the group of glucocorticoids.
Stage three - prolongation of pregnancy. Doctors try to delay preterm labor by giving the baby's lungs and placenta time to mature. For this, tocolytics are used - they inhibit the contractile activity of the uterus. Usually prophylaxis is carried out - tocolysis is carried out before contractions. When started, therapy is ineffective. The duration of treatment is a maximum of 48 hours.
Stage four - preparation for the birth of a premature baby. The woman in labor is transferred to a higher-level hospital. The physiology of preterm labor does not differ from the birth of a child at term. But close attention is required from doctors to minimize complications for mom and baby.
The fifth stage is the prevention of infections and their complications. At risk are women in labor whose waters have broken. If the patient gives birth before 34 weeks, she can be pierced with a course of dexamethasone. It accelerates the maturation of the placenta and internal organs of the baby, reduces the risk of complications.
If the patient gives birth before 34 weeks, she can be pierced with a course of dexamethasone. It accelerates the maturation of the placenta and internal organs of the baby, reduces the risk of complications.
OB sequence
When registering a patient with preterm birth, the doctor gets acquainted with the exchange card, studies the general, gynecological and infectious anamnesis, and the results of examinations. Clarifies complaints and evaluates the condition of the woman in labor. He examines her, measures the pulse and respiration rate, temperature, pressure, abdominal circumference and the height of the uterus.
Clarifies data on the fetus: movements, measures heart rate by auscultation - listening to the heart through the mother's stomach through the device. To assess the condition of the crumbs, the doctor performs cardiotocography. The device records the heart rate.
Ultrasound is performed to assess the condition of the child and mother's organs.
A gynecological examination is carried out: with intact membranes - external, with their rupture - internal. This is necessary to determine the position and position of the child, to assess the degree of disclosure.
Conduct a laboratory examination. They take a smear from the vagina: culture for β-hemolytic streptococcus, bacteriological culture, take blood and urine for a general analysis.
According to the results of the examination, the obstetrician confirms or refutes preterm birth, their stage.
The expectant mother is informed about her condition, forecasts for the child. At the slightest opportunity, they try to prolong the pregnancy. If the child is ready to be born in the near future, the doctor determines the tactics of assistance, coordinates the issue of anesthesia with the woman in labor.
In the absence of indications for a caesarean section, they give birth naturally. This is the best way - it is less traumatic for the baby. A gentle approach is what a weak newborn needs.
A gentle approach is what a weak newborn needs.
Preterm birth care policy
The woman in labor is provided with continuous psychological support. Describe the current obstetric situation.
With head presentation, they give birth naturally.
With pelvic - take into account clinical indications. Caesarean section is not the only effective method in this case. The operation does not improve the prognosis for a premature baby, but it puts an additional burden on the mother's body: it increases infection, morbidity, and complications.
With foot presentation, only a caesarean section is done.
Anesthesia is carefully selected. Avoid opiates - they depress the respiratory center, which is dangerous for premature babies.
At the birth of a baby before 34 weeks, vacuum aspiration is prohibited. It increases the risk of neonatal morbidity. Dosed episiotomy, exit forceps for the birth of the head and epidural anesthesia are performed.
The umbilical cord is clamped at least 1 minute after the baby is born. This tactic reduces the frequency of intraventricular hemorrhage in preterm pregnancies up to 37 weeks of gestation.
Control the state of the crumbs. CTG is done every hour for 40 minutes, auscultation - periodically.
General recommendations for prevention
You need to think about it from the first trimester. If you want to inform the baby, follow the advice of gynecologists.
- Take care of yourself. Rest, avoid nervous overload. Sleep at least 7 hours;
- Eat well. Eat foods rich in vitamins, exclude fast food, fatty, fried, spicy and salty foods from the diet. Give up coffee and strong tea;
- Observe the drinking regimen. Try not to feel thirsty - drink water every 2 hours. If you don't want to - don't force yourself;
- Avoid physical activity. Active training, hard work, general cleaning alone are taboo for a pregnant woman.
 Try not to go outside on ice - you may fall, you will strain your muscles - this can increase your tone and provoke premature birth;
Try not to go outside on ice - you may fall, you will strain your muscles - this can increase your tone and provoke premature birth; - Maintain personal hygiene. Wash your face after a bowel movement. Always wash and dry from front to back. This way you will not bring bacteria from the intestine into the vagina. Infections are provocateurs of premature birth;
- Lead a healthy lifestyle. Alcohol and cigarettes are taboo. Smoking pregnant women are predisposed to preterm labor. If you take medications on a regular basis, tell your gynecologist about it. Walk outdoors. Cancel active workouts in favor of leisurely walks in the park;
- Register at the antenatal clinic in the first trimester - at 6 ‒ 8 weeks. Visit a gynecologist, listen to him, take tests, undergo ultrasound, screenings;
- Be careful with sex. In the first trimester, it is better to limit or abstain from it as much as possible - the embryo must be fixed. With placenta previa and other pathologies, the gynecologist may forbid you to have intimate contacts - listen to him;
- Learn to understand your body.
 In the 2nd trimester, start listening to the baby: his movements, activity. Fix any changes, strange and unpleasant sensations - and talk about them to the doctor. In case of acute pain, contractions, spasms, blood, urgently call an ambulance - this may be a premature birth;
In the 2nd trimester, start listening to the baby: his movements, activity. Fix any changes, strange and unpleasant sensations - and talk about them to the doctor. In case of acute pain, contractions, spasms, blood, urgently call an ambulance - this may be a premature birth; - Maintain bed rest. A gynecologist can advise you to rest. For example, with increased uterine contractions, tone;
- Rest every hour. Sit in a chair, lift your legs up. This will relax the muscles, eliminate swelling;
- Be aware of the signs of preterm labor. In case of their threat, you will not miss a moment and consult a doctor. Perhaps the process can be stopped with the help of drugs. Treatment minimizes complications in the premature baby.
Preterm birth prevention
It is divided into 2 stages: before conception and after.
Preventive measures before conception
It is advisable to carry them out to mothers from the risk zone. The gynecologist limits intrauterine manipulations, such as curettage. During IVF, the number of embryos for transfer is regulated taking into account the age of the expectant mother and her health. Inform about the possibility of premature birth at conception through reproductive technologies.
The gynecologist limits intrauterine manipulations, such as curettage. During IVF, the number of embryos for transfer is regulated taking into account the age of the expectant mother and her health. Inform about the possibility of premature birth at conception through reproductive technologies.
Hydration is shown - enhanced drinking regimen. It improves fetoplacental blood flow and reduces the risk of preterm birth.
Eliminate infections. It is advisable to do this at the planning stage, since antibiotic treatment during gestation harms the fetus.
It is recommended to postpone the conception of a child soon after the birth of an older brother or sister. Mommy's body needs to recover from the previous pregnancy. It takes him at least 2 years to do this. During this time, the uterus will return to its previous state, strength, vitamin reserves and body reserves will be restored.
Vitamin complexes are prescribed for predisposition to preterm birth for planning and expectant mothers. Protein-rich dietary supplements are helpful. They strengthen the immune system, improve blood circulation, protect the pregnant woman from infections - and hence the child.
Protein-rich dietary supplements are helpful. They strengthen the immune system, improve blood circulation, protect the pregnant woman from infections - and hence the child.
Secondary prevention of early delivery
With the threat of premature birth, the condition of the pregnant woman is monitored at critical periods: from 2 to 12 and from 18 to 22 weeks. During these periods, it is better to stay in the hospital of the perinatal center. Doctors prescribe drugs to maintain and prolong pregnancy.
Therapy is selected on an individual basis.
With a short neck from 1 to 2.5 cm, progesterone suppositories are prescribed vaginally. The hormone is also shown in previous preterm births. This tactic reduces their risk by 35%. This is a natural hormone. It is efficient and safe. It is prescribed in the first trimester. Synthetic hormone is harmful: it can provoke gestational diabetes.
If there is a threat of early birth of the crumbs, sutures are placed on the neck. The expectant mother is out of the risk zone in this situation, stitches may not be applied.
The expectant mother is out of the risk zone in this situation, stitches may not be applied.
Another option is to install a pessary on the neck.
These methods reduce the statistics of premature births. But the mortality rate of newborns is not affected.
When carrying twins, circular or U-shaped sutures can be applied. In most cases, such tactics with a short neck in multiple pregnancies can provoke preterm labor. Vaginal progesterone is not prescribed.
For infections (for example, bacteriuria, gonococcus, syphilis, β-hemolytic streptococcus, bacterial vaginosis, chlamydia), antibiotic prophylaxis is prescribed. Depending on the diagnosis, penicillin, ampicillin, metronidazole, erythromycin, ceftriaxone, josamycin may be prescribed.
Terminals
Premature birth is one of the fears of many expectant mothers. Nobody is immune from this. But you can minimize the risks. Follow the recommendations of the gynecologist, take care of yourself, listen to your body, do not refuse to stay in the perinatal center.
Don't think bad. Modern medicine successfully nurses premature babies, reduces the risks of complications and consequences.
Obstetrician-gynecologist of the first qualification category -
Panasenko Irina Gennadievna
Childbirth after 30 - articles from the specialists of the clinic "Mother and Child"
Broitman Evgeniya Viktorovna
Reproductologist
Clinical Hospital "AVICENNA" GC "Mother and Child"
According to psychologists, the birth of a child at a more mature age is more favorable than in youth. As a rule, in a couple where parents are over 30, they prepare in advance for the appearance of the first child, and the child is born desired.
In addition, life experience, wisdom, and psychological maturity appear exactly at the age of 30. All these qualities allow you to calmly relate to your condition, make informed decisions. Psychological comfort for the baby in such a family is provided.
The medical aspects of late pregnancy and childbirth have also improved in recent years.
Previously, there was an opinion that with increasing age, the number of possible complications of both pregnancy and childbirth increases in direct proportion.
However, in recent years this view has been refuted by most studies. The frequency of occurrence of such pathology of pregnancy as fetoplacental insufficiency (and as a result, intrauterine hypoxia and fetal growth retardation), as well as nephropathy of pregnant women occurs among women over 30 years of age with the same frequency as among younger pregnant women. Moreover, patients after 30 years of age, as a rule, are more disciplined and responsible, better follow the doctor's recommendations. This contributes to the prevention and timely treatment of emerging complications of pregnancy.
It is widely known that the incidence of diseases of internal organs, such as arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, obesity, metabolic syndrome, unfortunately increases after 30 years. However, the level of development of modern medicine allows timely diagnosis and treatment of such conditions at the stage of preparation for pregnancy and during it.
However, the level of development of modern medicine allows timely diagnosis and treatment of such conditions at the stage of preparation for pregnancy and during it.
A necessary condition in such a situation is careful monitoring of the course of pregnancy, the state of internal organs. If necessary, the doctor prescribes treatment (both drug and non-drug), which does not adversely affect the baby's condition, and at the same time contributes to the normalization of the functions of the expectant mother's organs.
Women aged 35 and older have a significantly increased risk of having children with a genetic disorder (eg Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, Patau syndrome, etc.). However, at the present stage of development of medical genetics, most of these diseases can be diagnosed even in the early stages of pregnancy.
As early as 11-12 weeks of gestation, ultrasound examination can reveal some malformations and reveal changes that may indicate the presence of a fetal chromosomal pathology.
So, the presence of a thickening of the collar zone in the fetus at 11 - 12 weeks of pregnancy in most cases reveals Down's syndrome. The second ultrasound examination is performed at 20-22 weeks of pregnancy. During these periods, it is possible to determine the anatomy of all organs of the fetus, to identify deviations in development.
Another important method for diagnosing genetic diseases are biochemical markers of chromosomal pathology. They are determined in the blood of the expectant mother at 11-12 weeks and at 16-20 weeks of pregnancy.
In the 1st trimester, the concentration in the blood of a protein associated with pregnancy and chorionic gonadotropin is monitored, in the second trimester - a combination of alphafetoprotein and human chorionic gonadotropin. To make sure that the suspicions are correct, so-called invasive diagnostic methods are used.
This is a chorion biopsy (obtaining cells from the future placenta), which is performed at 8-12 weeks of pregnancy, amniocentesis (aspiration of amniotic fluid at 16-24 weeks), cordocentesis - puncture of the umbilical cord of the fetus (performed at 22-25 weeks of pregnancy).
These methods allow you to accurately determine the chromosome set of an unborn child and speak with confidence about the presence or absence of genetic diseases in him. All studies are carried out under ultrasound control, which allows you to minimize the degree of complications.
It was previously believed that the first childbirth over the age of 30 was an indication for caesarean section. Now this position is hopelessly outdated. Most women of mature age give birth on their own. Of course, it should be remembered that in patients of this age category, such complications of childbirth as the development of weakness in labor, acute fetal hypoxia are somewhat more common than in the general population.
In such situations, the doctor in charge of the birth may decide to have an emergency operation. But almost all women who give birth to their first child after 30 years have a chance to give birth on their own.
For a successful course of pregnancy and childbirth, it is more important than for young mothers to monitor their health, carefully follow all the doctor's recommendations.