Wake up with blood in nose
Nose Bleeds at Night: 5 Causes
We include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission Here’s our process.
Healthline only shows you brands and products that we stand behind.
Our team thoroughly researches and evaluates the recommendations we make on our site. To establish that the product manufacturers addressed safety and efficacy standards, we:
- Evaluate ingredients and composition: Do they have the potential to cause harm?
- Fact-check all health claims: Do they align with the current body of scientific evidence?
- Assess the brand: Does it operate with integrity and adhere to industry best practices?
We do the research so you can find trusted products for your health and wellness.
Read more about our vetting process.Was this helpful?
Is this cause for concern?
Waking up to find blood on your pillow or face can be a scary experience. But while nighttime nose bleeds may seem frightening, they’re rarely serious.
Just like any other part of your body, your nose bleeds when it’s cut or irritated. The lining of your nose is especially likely to bleed because it’s lined with many fragile blood vessels that lie very close to the surface. That’s why even minor injuries can cause a lot of bleeding.
Nose bleeds that happen once in a while are usually nothing to worry about. But if you get nose bleeds often, you might have a problem that your doctor needs to check out.
The causes of nighttime nose bleeds are the same as those of daytime nosebleeds. Here’s a rundown of factors that could make your nose bleed at night, and how to prevent them.
A number of things can dry out the lining of your nasal passages, including nutritional deficiencies.
Just like your skin gets cracked and bleeds when it’s dry, your nasal passages become irritated and bleed when they dry out, too.
What you can do:
- Turn on a humidifier in your bedroom at night — especially during the winter months.
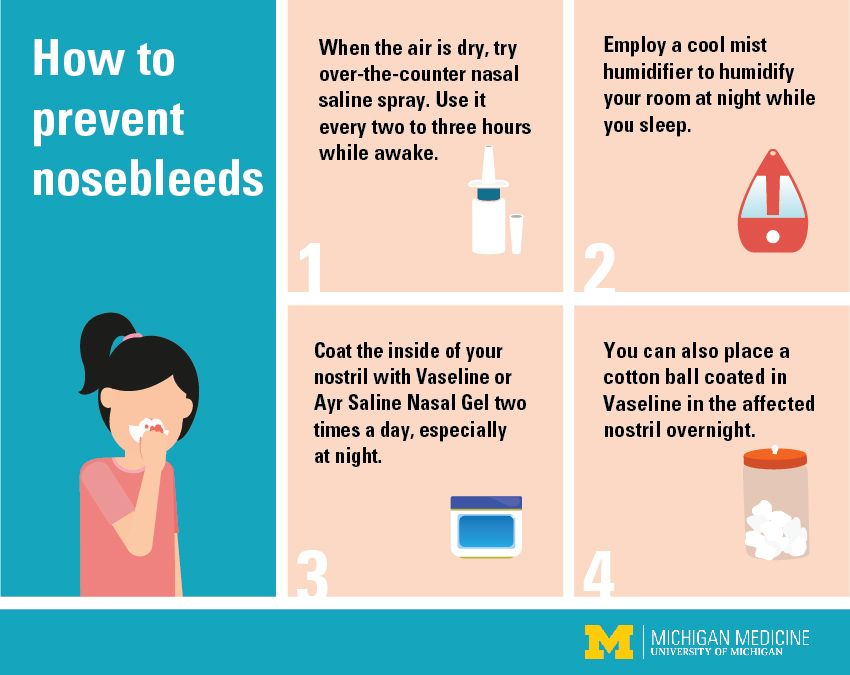 This will add moisture to the air.
This will add moisture to the air. - Use a saline (salt water) nasal spray before bed to keep your nasal passages moist.
- Apply a thin layer of petroleum jelly like Vaseline or an antibiotic ointment like Neosporin to the inside of your nose with a cotton swab.
Nose picking is one of the most common causes of nosebleeds. Whether you or your child do it as a force of habit or unconsciously while you sleep, you can damage your nose each time you insert your finger. The edge of your nail can tear the delicate blood vessels that lie just under the surface of your nose.
What you can do:
- To avoid picking, keep tissues close to your bed so you can blow your nose instead.
- If you pick while you sleep, wear gloves to bed so you can’t put your finger in your nose.
- Wash your hands every time you pick your nose. Having to get out of bed each time will force you to pay attention to the habit. Then if you do pick, your fingers will be clean and less likely to introduce bacteria to any wounds.

- You should cut your nails short so, if you do pick, you’ll be less likely to injure yourself.
You’re more likely to get nosebleeds during the cold winter months. Heating your home sucks moisture out of the air. Dry air dehydrates your nasal passages, leaving them cracked and bleeding. Living in a dry climate year-round has the same effect on your nose.
What you can do:
- Turn on a humidifier in your bedroom at night to add moisture to the air.
- Use a saline (salt water) nasal spray before bed to keep your nasal passages moist.
- Apply a thin layer of petroleum jelly or an antibiotic ointment to the inside of your nose with a cotton swab.
The same allergies that cause sniffling, sneezing, and watery eyes can also make your nose bleed.
Allergies cause nose bleeds in a few different ways:
- When your nose gets itchy, you scratch it, which can damage blood vessels.
- Blowing your nose repeatedly can rupture the blood vessels inside.
- Steroid nasal sprays and other medications you use to treat allergy symptoms dry out the inside of your nose.
What you can do:
- Try not to blow your nose too forcefully. Be gentle.
- Use tissues that contain moisturizer to soften the blow.
- Ask your allergist for an alternative to steroid nasal spray. Saline sprays can also help clear up congestion without drying out your nose.
- Talk to your doctor about allergy shots or other preventive medication.
- Try to avoid your allergy triggers, such as pollen, mold, or pet dander.
Sinus infections, colds, and other respiratory infections can damage the sensitive lining of the nose. Eventually, your nose can become irritated enough to break open and bleed. Blowing your nose too often when you have an infection can also cause nosebleeds.
Other signs that you have an infection include:
- stuffed, runny nose
- sneezing
- coughing
- sore throat
- fever
- aches
- chills
What you can do:
- Use a saline nasal spray or breathe in the steam from a hot shower to clear up congestion.

- Drink lots of fluids to loosen up mucus in your nose and chest.
- Get plenty of rest to help you feel better faster.
- If your doctor says you have a bacterial infection, you may need to take antibiotics to clear it up.
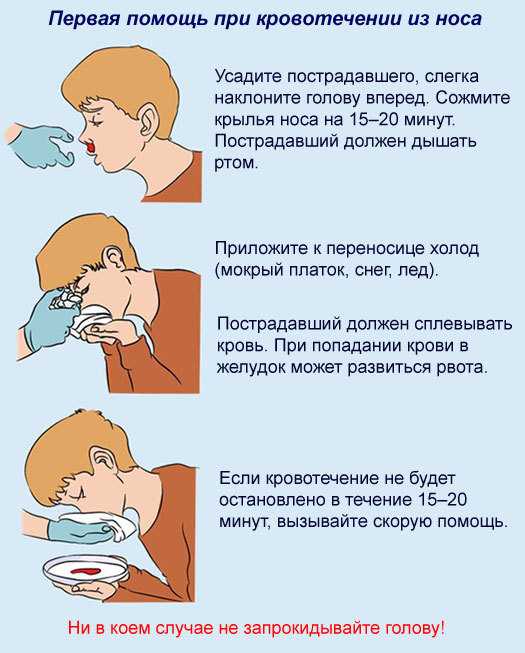
To stop bleeding
- Sit or stand up, tilting your head slightly forward. Don’t tilt your head back because it will cause the blood to run down your throat.
- Using a tissue or cloth, gently press your nostrils closed.
- Hold the pressure for 5 to 15 minutes.
- You can also place an ice pack on the bridge of your nose to constrict blood vessels and stop the bleeding faster.
- After 15 minutes, check to see if your nose is still bleeding. If it’s still bleeding, repeat these steps.
Was this helpful?
If your nose continues to bleed after 30 minutes — or if you’re unable to stop the bleeding — go to an emergency room or urgent care center.
If you have stopped the bleeding, it’s important to keep your head above the level of your heart for the next couple of hours.
You can also apply petroleum jelly or antibiotic ointment to the inside of your nose with a cotton swab to moisten the area and help it heal.
You don’t need to see your doctor for the occasional nose bleed. Do see your doctor if you get nose bleeds more than once a week or if they’re hard to stop.
Also call if:
- You bleed a lot, or you have trouble stopping the bleeding within 30 minutes.
- You get pale, dizzy, or tired during a nosebleed.
- The nosebleeds started after an injury or surgery.
- You have other symptoms, such as chest pain.
- It’s hard for you to breathe during a nosebleed.
Very rarely, nighttime nose bleeds are caused by a more serious condition called hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT). This inherited disease makes you bleed more easily. Frequent bloody noses are common with HHT.
People with HHT get a lot of nosebleeds and the bleeding can be heavy. Another sign of HHT is cherry-red spots on your face or hands. These are called telangiectasia. If you have these symptoms, see your doctor for a diagnosis.
These are called telangiectasia. If you have these symptoms, see your doctor for a diagnosis.
Is It Normal & Should You Be Worried
Nosebleeds
Nosebleeds occur when a blood vessel in your nose bursts. Bloody noses are common. Around 60 percent of Americans will experience a nosebleed some time in their life. About 6 percent will require medical attention.
Although there are many reasons that your nose bleeds, the two most common causes are direct impact injury and the temperature and humidity of your environment.
- Trauma. Fractures of the nose or the base of the skull can result in a bloody nose. If you’ve had a head injury that resulted in a bloody nose, see your doctor.
- Dry air. A dry outside environment or heated indoor air can irritate and dry out nasal membranes. This can cause crusts that may itch and bleed when picked or scratched. If you catch a cold in the winter, the combination of repeated nose blowing with exposure to cold, dry air, sets the stage for nosebleeds.

Picking your nose
If you have allergies, such as hay fever or any other condition that causes your nose to itch, it can lead to conscious and unconscious nose picking.
Blowing your nose
If you blow your nose hard, the pressure can rupture superficial blood vessels.
Clotting disorders
Hereditary clotting disorders, such as hemophilia and hemorrhagic telangiectasia, may cause recurring nosebleeds.
Medications
If you’re taking medication that thins your blood or acts as an anticoagulant — such as aspirin, clopidogrel (Plavix), or warfarin (Coumadin) — nosebleeds can be more difficult to stop.
Topical medications and nasal sprays
Topical nasal medications, such as corticosteroids and antihistamines, can sometimes lead to nosebleeds. If you often use a nasal spray, the repeated irritation caused by the tip of the bottle could cause nosebleeds.
Dietary supplements
Certain dietary supplements can thin your blood and prolong bleeding, causing nosebleeds that are difficult to stop. These include:
These include:
- ginger
- feverfew
- garlic
- ginkgo biloba
- ginseng
- vitamin E
Underlying conditions
If you have certain conditions such as kidney or liver disease, your blood’s ability to clot may be lower, making nosebleeds more difficult to stop.
Blood pressure
Conditions such as congestive heart failure or hypertension can make you more prone to nosebleeds.
Deformities
If you have a functional nasal deformity — congenital, cosmetic surgery, or injury related — it could lead to frequent nosebleeds.
Tumors
Tumors of the nose or sinuses — both malignant and nonmalignant — can lead to nosebleeds. This is more likely in older people and those who smoke.
Drug use
If you ingest cocaine or other drugs by snorting it into your nose, it can cause blood vessels in your nasal passages to rupture, leading to frequent nosebleeds.
Chemical irritants
If you’re exposed to chemical irritants — such as cigarette smoke, sulfuric acid, ammonia, gasoline — at work or elsewhere, it can lead to frequent and recurring nosebleeds.
While the majority of nosebleeds aren’t a cause for concern, some are. Get medical help right away if:
- your nose doesn’t stop bleeding after 20 minutes
- your nose is bleeding as the result of a head injury
- your nose has an odd shape or feels broken after an injury
Schedule an appointment with your doctor if you experience frequent and repeated nosebleeds that aren’t caused by minor irritation. Frequent nosebleeds that occur more than once a week may be a sign of a problem that should be evaluated.
You can help cut down on the frequency of your nosebleeds and perhaps prevent them by taking some simple actions:
- Avoid picking your nose and blow your nose gently.
- If you smoke, try to quit and avoid areas with secondhand smoke.
- Moisturize the inside of your nose with a nonprescription saline nasal spray.
- Use a humidifier during the winter months.
- Apply ointment, such as Bacitracin, A and D Ointment, Eucerin, Polysporin, or Vaseline, to the inside of each nostril at bedtime.
- Wear your seatbelt to protect from facial trauma in the event of an accident.
- Wear headgear that fits properly and protects your face when playing sports with a chance for face injury, such as karate, hockey, or lacrosse.
- Avoid breathing in irritating chemicals by using properly rated protective equipment.
If you have frequent and recurring nosebleeds, talk to your doctor about possible causes and to discuss steps you can take to avoid them.
Your doctor may refer you to an otolaryngologist — an ear, nose, and throat specialist, also called an ENT. If you’re on a blood thinner, they might recommend adjusting the dose.
Nosebleed: what to do?
Is your city Moscow?
- Pharmacies
- Catalog
- Discounts and promotions
- Loyalty program
- Jobs
- Help
- Rent
- Contacts
- COVID-19
September 1, 2021
Nosebleed, or epistaxis, is an unexpected and even frightening phenomenon.
Should one be alert when such an unpleasant symptom appears, what factors provoke it and how can one help in such a situation? Let's figure it out further.
Why does the nose bleed?
Bleeding from the nose is classified into "anterior" and "posterior". In the first case, the cause is damage to small blood vessels, this type is usually easy to stop. The second case is considered more dangerous, bleeding occurs due to injury to large vessels located deeper in the nose, so it cannot be dealt with at home. If the blood is "in full swing" - this is a reason for an urgent call for an ambulance.
Causes of nosebleeds include:
- nose injury;
- thinning of the mucous membrane;
- inflammatory processes in the nasal cavity;
- vascular fragility, diseases of the heart and blood;
- sudden increase in blood pressure;
- uncontrolled intake of certain drugs (anticoagulants, NSAIDs, vasoconstrictor drops for the common cold).

What should I do if my nose bleeds?
At the moment when the bleeding starts, it is important to try not to be nervous, because the excitement makes our heart beat faster, which leads to more blood loss.
The bleeding stop algorithm is as follows:
- Sit straight, tilt your head forward.
- You should be comfortable: loosen the belt and collar, if necessary, open the window.
- Place a cold, wet towel or ice on your nose and a warm heating pad on your feet. This will help constrict the vessels in your nose and dilate them in your legs, which will reduce bleeding.
- Clamp the bleeding vessel: squeeze the wings of the nose with your fingers for 3-5 minutes, the blood should stop. Also for this purpose, you can enter a gauze swab previously moistened with hydrogen peroxide into the nostril.
If you have completed all of the above and the blood continues to flow, call an ambulance immediately, as even a small loss of blood can lead to fainting.
What to remember about nosebleeds?
- Do not lie down and do not let your feet be above your head - this will increase bleeding;
- Do not tilt your head: a large amount of blood in the stomach can cause vomiting, and blood can flow into the windpipe and make breathing difficult.
- After the bleeding has stopped, refrain from eating and caffeinated drinks to avoid high blood pressure and new bleeding.
Prevention of nosebleeds
Remember, frequent nosebleeds are a reason to see a doctor. The specialist will identify the cause of the problem and prescribe treatment, which may include the use of hemostatic agents, as well as drugs that improve blood circulation.
To prevent rebleeding, your specialist may recommend:
- Taking medications and vitamins to strengthen blood vessels.
- Proper diet. Adding foods rich in vitamin K and C to the menu. Vitamin K is responsible for blood clotting, they are rich in parsley, spinach, basil, bananas, avocados, broccoli, bran, etc.
Vitamin C strengthens the walls of blood vessels, it is found in large quantities in rose hips, sweet peppers, currants, citrus fruits, etc.
- Activity and moderate physical activity: light exercise in the morning, daily walks in the fresh air, swimming pool, etc.
Be healthy!
- General
- Interesting
- Health
Popular
You may be interested
Disclaimer
This blog is not intended to provide diagnosis, treatment or medical advice. The information on this block is provided for informational purposes only. Please consult your physician for any medical and health-related diagnoses and treatments. The information on this blog should not be considered a substitute for consulting a physician.
Why dream of blood in a dream book: interpretation of dreams about blood
Blood in Miller's dream book
Only in one case, according to Miller's dream book, blood is interpreted positively: if it is spilled on the pavement. In this case, relatives will send you good news. In all other situations, you need to prepare for trouble. So, if you have stained your hands with blood, then the dream signals: urgently take care of yourself, rest, check your affairs. Otherwise, a black streak will come in your life.
Heavy bleeding is a harbinger of work and health problems. If you cooperate with foreign partners, it is the unsuccessful transactions with them that will create problems for you. Bloody clothing symbolizes enemies that can shake your career. If shortly before such a dream you have new acquaintances, be careful with them. A pool of blood on the ground speaks of your secret enemies who are just waiting for you to make a mistake.
Blood in Vanga's dream book
Blood is a symbol of kinship, so all dreams associated with blood will be related to your family or friends. Just to see blood in a dream - to conflicts and attempts at revenge in the environment. Your reputation will be in jeopardy due to the behavior of a friend if you dream of your clothes spattered with blood. If you are trying to stop the bleeding (whether it is weak or strong), this indicates your longing for one of the deceased loved ones.
The dream in which you defended yourself from the enemy, wounded him and got dirty with his blood, is a warning: it is better not to interfere in a quarrel between your loved ones, otherwise it will turn into serious consequences for you. Another warning dream is in which you drink pleasant cool water, and it turns into blood, and you smear yourself in it. Because of the generational curse, your fate will be unhappy until we pray for the forgiveness of the sins committed by your ancestors.
Because of the generational curse, your fate will be unhappy until we pray for the forgiveness of the sins committed by your ancestors.
Blood in the Islamic dream book
Mostly dreams about blood have a negative interpretation: to see blood on your clothes and not understand where it comes from - to fall under vain suspicions, to be slandered; stain clothes with blood - to "dirty" money; drinking blood - to receive some kind of wealth prohibited by Sharia; blood in a dream for a woman - to illness; going to the toilet with blood - to sinful intimate relationships.
Bleeding is interpreted depending on how you feel about it in a dream: if you think it is good, then you will benefit from people in power; if you think that it is bad, then this benefit will ultimately be to your detriment. Dreams are interpreted in a positive way in which you fall into a pool of blood (to wealth and success), and blood flows from your nose in a thin stream continuously (to a stable cash income). The usual bleeding from the nose personifies anxieties, problems, sorrows.
The usual bleeding from the nose personifies anxieties, problems, sorrows.
Blood in Freud's dream book
A person who sees blood in a dream takes his sexual relationships seriously. The more blood in a dream, the more partners.
Blood in Loff's dream book
Blood is interpreted negatively as a symbol of physical, material and moral exhaustion, even death. The only exception is the dreamed blood of your enemy, it promises you an unconditional victory.
Blood in the dream book of Nostradamus
Get bloodied in a dream - to news from relatives. To bleed - to temporary sorrows and loneliness. If blood flows in a dream from a wound of a person close to you, then your selfishness will cause discord in relationships.
Earth soaked in blood predicts serious difficulties, catastrophes and conflicts with human casualties. If you injured someone, then such a dream advises you to stop acting carelessly when solving a serious problem and take the initiative into your own hands.