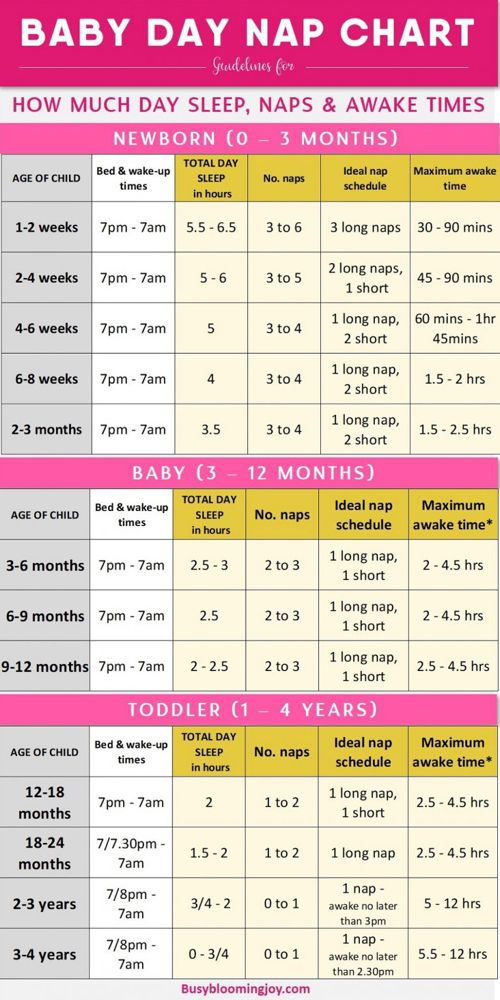
Can babies be born at 6 months
Premature baby | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Premature baby | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content10-minute read
Listen
What is a premature baby?
Most pregnancies last 40 weeks. A baby born before the 37th week is known as a premature or pre-term baby. Medical advances have meant that more than 9 out of 10 premature babies survive, and most go on to develop normally.
In Australia, almost 1 in every 10 babies is born prematurely. Most Australian premature babies are born between 32 and 36 weeks and don't have any serious long-term problems.
Very premature babies are at a higher risk of developmental problems. It is possible for babies born at 23 to 24 weeks to survive, but it is risky.
Most babies born before 32 weeks, and those weighing 2. 5 kg or less, may need help breathing and may be cared for in a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) until they have developed enough to survive on their own. Babies born between 32 and 37 weeks may need care in a special care nursery (SCN)
Why are babies born prematurely?
The cause of premature birth is unknown in about half of all cases. However, some of the reasons babies are born prematurely include:
- problems with the cervix, when it is too weak to hold the weight of the baby and uterus so it starts to open prematurely (called cervical incompetence)
- multiple pregnancy (twins or more)
- the mother gets an infection
- the mother has a medical condition that means the baby must be delivered early, such as pre-eclampsia
- problems with the placenta such as placental insufficiency, placenta praevia, placenta accreta or placental abruption
- preterm premature rupture of membranes, when the amniotic sac spontaneously ruptures
- the mother has a health condition like diabetes
- a history of premature birth
If you are less than 37 weeks pregnant and you experience any of the signs of premature labour, such as contractions, your waters breaking, bleeding, a 'show' of mucus from your vagina or a sudden decrease in your baby's movements, contact your doctor or nearest delivery suite immediately. It may be possible to slow down or stop the labour. But each day the baby stays inside your womb, the greater their chance of survival.
It may be possible to slow down or stop the labour. But each day the baby stays inside your womb, the greater their chance of survival.
In most cases labour starts by itself, and the signs will usually be the same as labour that starts at full term.
The signs of premature labour include:
- pressure in the pelvis, as if the baby is pushing down
- cramping in the lower part of the belly
- diarrhoea, nausea or vomiting
- constant lower back pain
- a change in your vaginal discharge, or more discharge than normal
- mucous, blood or fluid leaking from your vagina
- waters breaking
- regular contractions, or contractions that come more than 4 times an hour
- baby’s movements slowing down or stopping
Find out more about the signs of labour and what happens.
What should I do if I experience the signs of premature labour?
If you have any of the signs listed above, contact your midwife or doctor straight away. If you are going to have your baby early, it’s important to get help as soon as possible.
If you are going to have your baby early, it’s important to get help as soon as possible.
You should also contact your midwife or doctor if you experience swelling in your face, hands or feet, or double vision, blurred vision or other eye disturbances. These are signs of pre-eclampsia, which is a common cause of pre-term deliveries.
If you go into labour prematurely, you will need to be treated in a hospital that has facilities for the newborn, such as a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) or special care nursery (SCN).
You can find your nearest suitable hospital on the Miracle Babies Foundation website.
How is a premature labour managed?
At the hospital, you will probably have a pelvic examination or an ultrasound. The medical team will check whether your cervix has started to open for labour and monitor the baby.
It is best for very premature babies to be born at a hospital that has an NICU. If the hospital where the baby is born does not have an NICU, you and your baby may be transferred to another hospital.
When you are in labour, you may be given medicines to stop the contractions for a while. This allows you to be transferred to another hospital if necessary. You may also receive injections of corticosteroids 12 to 24 hours before the birth. Steroids will reduce the risk of the baby suffering from the complications of being born very early (particularly breathing difficulties and bleeding).
Premature babies can be born very quickly. They will usually be born through the vagina. However, in some cases the doctor may decide it is safest to deliver the baby via caesarean. Your doctor will discuss this decision with you.
A medical team from the neonatal (newborn) unit will be there for the birth. As soon as your baby is born, they will care for the baby in your room, possibly using a neonatal (baby) resuscitation bed. The team will keep your baby warm and help them to breathe with an oxygen mask or breathing tube, and possibly medicine. Some babies need help to keep their heart beating with cardio-pulmonary resuscitation (CPR) or an injection of adrenalin.
Once your baby is stable, they may be transferred to the NICU or SCN.
Will I be able to hold my baby?
How soon you are able to hold your baby will depend on their medical condition. You may be able to hold them on the day they are born, but you might need to wait a few days or weeks until they are stable enough.
Holding you baby, known as kangaroo care, is important part of your baby’s health and wellbeing, and the maternity staff will support you as soon as you are able.
Will I be able to feed my baby?
After your baby is born, you’ll be asked to start expressing breastmilk. Maternity staff, lactation consultants and Australian Breastfeeding Association counsellors will help you. Breastmilk is full of antibodies and nutrients that will be very important for your baby’s health and growth.
What will my premature baby look like?
Babies born at 36 to 37 weeks usually look like small full-term babies. Very premature babies will be small (perhaps fitting in your hand) and look very fragile.
- Skin: it might not be fully developed, and may appear shiny, translucent, dry or flaky. The baby may not have any fat under the skin to keep them warm.
- Eyes: the eyelids of very premature babies may be fused shut at first. By 30 weeks they should be able to respond to different sights.
- Immature development: your baby might not be able to regulate its body temperature, breathing or heart rate. They may twitch, become stiff or limp or be unable to stay alert.
- Hair: your baby may have little hair on its head, but lots of soft body hair (called 'lanugo').
- Genitals: the baby's genitals may be small and underdeveloped.
Will my premature baby's development be delayed?
Some common issues for premature babies include:
- breathing problems
- heart problems
- problems in their digestive tract
- jaundice
- anaemia
- infections
Most premature babies will develop normally, but they are at higher risk of developmental problems so will need regular health and development checks at the hospital or with a paediatrician. If you are worried about your child's development, talk to your doctor.
If you are worried about your child's development, talk to your doctor.
Problems that may occur later in children who were born prematurely include:
- language delays
- growth and movement problems
- problems with teeth
- problems with vision or hearing
- thinking and learning difficulties
- social and emotional problems
How do I calculate my baby's correct age?
When you're judging whether your premature baby is developing normally, it is important to understand their 'corrected age'.
The corrected age is your baby's chronological age minus the number of weeks or months they were born early. For example, a 6-month-old baby who was born 2 months early would have a corrected age of 4 months. That means they may only be doing the things that other 4-month-olds do. Most paediatricians recommend correcting age when assessing growth and development until your child is 2 years old.
When will my baby be able to come home?
The hospital will not send your baby home until they are confident both the baby and you are ready. Staff will make sure you understand how to care for your baby at home. They will also show you how to use any equipment you may need.
Staff will make sure you understand how to care for your baby at home. They will also show you how to use any equipment you may need.
You will need appointments to see a neonatologist (newborn baby doctor) or paediatrician. Your local child health nurse will also see you regularly.
It is normal to feel a little worried when you are looking after your baby yourself after so long in hospital. Take it slowly in a calm and quiet environment until you both get used to being at home.
Who can I talk to for advice and support?
If you need support, contact the Miracle Babies Foundation's 24-hour support line on 1300 622 243.
The Australian Breastfeeding Association can provide advice and support on feeding your baby on 1800 686 268.
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Sources:
Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (AIHW) (Mothers and babies), Raising Children Network (Premature labour, birth and babies), Raising Children Network (Your premature baby's appearance), Raising Children Network (Premature baby development concerns), Raising Children Network (Going home with your premature baby), Women’s and Children’s Health Network (Premature babies), NSW Pregnancy and Newborn Services Network (Birth before 32 weeks), Miracle Babies (What is prematurity?), Miracle Babies (Treatment of preterm labour), Queensland Government (Queensland Clinical Guidelines; Preterm labour and birth)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: March 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- Neonatal intensive care unit (NICU)
- Special care nursery (SCN)
- What is kangaroo care?
Need more information?
Premature birth & premature babies | Raising Children Network
This essential guide for parents of premature babies covers gestational age, premature birth risk factors, premature labour and premature development.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Premature babies and birth | Raising Children Network
Premature babies are born before 37 weeks of pregnancy. Our essential guide covers premature birth, babies, development, NICU and more.
Read more on raisingchildren. net.au website
net.au website
Dads: premature birth and premature babies | Raising Children Network
After a premature birth, it can be hard for dads. Our dads guide to premature babies and birth covers feelings, bonding, and getting involved with your baby.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Premature birth: questions & checklist | Raising Children Network
Our checklist has answers to questions about premature birth and labour, covering where and how premature babies are born, and things to ask medical staff.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Bonding with premature babies in the NICU | Raising Children Network
For parents with premature babies in the NICU, bonding might seem hard. This guide explains how to use touch, song, play and daily care to bond with baby.
This guide explains how to use touch, song, play and daily care to bond with baby.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Premature birth: coping with your feelings | Raising Children Network
After a premature birth and while caring for a premature baby, it’s normal to have powerful and mixed feelings. Here’s how to cope with your feelings.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Breastfeeding your premature baby | Australian Breastfeeding Association
This article is based on our booklet 'Breastfeeding Your Premature Baby'. The booklet contains valuable information from research on breastfeeding premature infants, as well as experiences of other parents of premature babies to inform, reassure and encourage you. If your baby has been, or is about to be born prematurely, we recommend that you purchase the booklet, which will provide much more information to help you deal with the challenges of breastfeeding and parenting your baby.
Read more on Australian Breastfeeding Association website
NICU: sleep & noise for premature babies | Raising Children Network
Noise in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) can affect how premature babies sleep. Here’s how you and staff can help your premature baby sleep better.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Sleeping - Miracle Babies
A premature baby’s success at sleeping is vitally important to their health and growth
Read more on Miracle Babies Foundation website
What is Prematurity? - Miracle Babies
Prematurity is the term used to describe when a baby is born early
Read more on Miracle Babies Foundation website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
Need further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
the long-term impacts of being born extremely early
Scientists are watching out for the health of adults born extremely premature, such as these people who took part in a photography project.Credit: Red Méthot
They told Marcelle Girard her baby was dead.
Back in 1992, Girard, a dentist in Gatineau, Canada, was 26 weeks pregnant and on her honeymoon in the Dominican Republic.
When she started bleeding, physicians at the local clinic assumed the baby had died. But Girard and her husband felt a kick. Only then did the doctors check for a fetal heartbeat and realize the baby was alive.
The couple was medically evacuated by air to Montreal, Canada, then taken to the Sainte-Justine University Hospital Center. Five hours later, Camille Girard-Bock was born, weighing just 920 grams (2 pounds).
Five hours later, Camille Girard-Bock was born, weighing just 920 grams (2 pounds).
Babies born so early are fragile and underdeveloped. Their lungs are particularly delicate: the organs lack the slippery substance, called surfactant, that prevents the airways from collapsing upon exhalation. Fortunately for Girard and her family, Sainte-Justine had recently started giving surfactant, a new treatment at the time, to premature babies.
After three months of intensive care, Girard took her baby home.
Today, Camille Girard-Bock is 27 years old and studying for a PhD in biomedical sciences at the University of Montreal. Working with researchers at Sainte-Justine, she’s addressing the long-term consequences of being born extremely premature — defined, variously, as less than 25–28 weeks in gestational age.
Families often assume they will have grasped the major issues arising from a premature birth once the child reaches school age, by which time any neurodevelopmental problems will have appeared, Girard-Bock says. But that’s not necessarily the case. Her PhD advisers have found that young adults of this population exhibit risk factors for cardiovascular disease — and it may be that more chronic health conditions will show up with time.
But that’s not necessarily the case. Her PhD advisers have found that young adults of this population exhibit risk factors for cardiovascular disease — and it may be that more chronic health conditions will show up with time.
Camille Girard-Bock, born at 26 weeks of gestation, is now studying the effects of prematurity for a PhD.Credit: Red Méthot
Girard-Bock doesn’t let these risks preoccupy her. “As a survivor of preterm birth, you beat so many odds,” she says. “I guess I have some kind of sense that I’m going to beat those odds also.”
She and other against-the-odds babies are part of a population which is larger now than at any time in history: young adults who are survivors of extreme prematurity. For the first time, researchers can start to understand the long-term consequences of being born so early. Results are pouring out of cohort studies that have been tracking kids since birth, providing data on possible long-term outcomes; other studies are trialling ways to minimize the consequences for health.
These data can help parents make difficult decisions about whether to keep fighting for a baby’s survival. Although many extremely premature infants grow up to lead healthy lives, disability is still a major concern, particularly cognitive deficits and cerebral palsy.
Researchers are working on novel interventions to boost survival and reduce disability in extremely premature newborns. Several compounds aimed at improving lung, brain and eye function are in clinical trials, and researchers are exploring parent-support programmes, too.
Researchers are also investigating ways to help adults who were born extremely prematurely to cope with some of the long-term health impacts they might face: trialling exercise regimes to minimize the newly identified risk of cardiovascular disease, for example.
“We are really at the stage of seeing this cohort becoming older,” says neonatologist Jeanie Cheong at the Royal Women’s Hospital in Melbourne, Australia. Cheong is the director of the Victorian Infant Collaborative Study (VICS), which has been following survivors for four decades. “This is an exciting time for us to really make a difference to their health.”
“This is an exciting time for us to really make a difference to their health.”
The late twentieth century brought huge changes to neonatal medicine. Lex Doyle, a paediatrician and previous director of VICS, recalls that when he started caring for preterm infants in 1975, very few survived if they were born at under 1,000 grams — a birthweight that corresponds to about 28 weeks’ gestation. The introduction of ventilators, in the 1970s in Australia, helped, but also caused lung injuries, says Doyle, now associate director of research at the Royal Women’s Hospital. In the following decades, doctors began to give corticosteroids to mothers due to deliver early, to help mature the baby’s lungs just before birth. But the biggest difference to survival came in the early 1990s, with surfactant treatment.
“I remember when it arrived,” says Anne Monique Nuyt, a neonatologist at Sainte-Justine and one of Girard-Bock’s advisers. “It was a miracle.” Risk of death for premature infants dropped to 60–73% of what it was before1,2.
Marcelle Girard looks in at baby Camille, born weighing just 920 grams (2 pounds).Credit: Camille Girard-Bock
Today, many hospitals regularly treat, and often save, babies born as early as 22–24 weeks. Survival rates vary depending on location and the kinds of interventions a hospital is able to provide. In the United Kingdom, for example, among babies who are alive at birth and receiving care, 35% born at 22 weeks survive, 38% at 23 weeks, and 60% at 24 weeks3.
For babies who survive, the earlier they are born, the higher the risk of complications or ongoing disability (see ‘The effects of being early’). There is a long list of potential problems — including asthma, anxiety, autism spectrum disorder, cerebral palsy, epilepsy and cognitive impairment — and about one-third of children born extremely prematurely have one condition on the list, says Mike O’Shea, a neonatologist at the University of North Carolina School of Medicine in Chapel Hill, who co-runs a study tracking children born between 2002 and 2004. In this cohort, another one-third have multiple disabilities, he says, and the rest have none.
In this cohort, another one-third have multiple disabilities, he says, and the rest have none.
“Preterm birth should be thought of as a chronic condition that requires long-term follow-up,” says Casey Crump, a family physician and epidemiologist at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, who notes that when these babies become older children or adults, they don’t usually get special medical attention. “Doctors are not used to seeing them, but they increasingly will.”
Outlooks for earliesWhat should doctors expect? For a report in the Journal of the American Medical Association last year4, Crump and his colleagues scraped data from the Swedish birth registry. They looked at more than 2.5 million people born from 1973 to 1997, and checked their records for health issues up until the end of 2015.
Source: Ref. 4
Of the 5,391 people born extremely preterm, 78% had at least one condition that manifested in adolescence or early adulthood, such as a psychiatric disorder, compared with 37% of those born full-term. When the researchers looked at predictors of early mortality, such as heart disease, 68% of people born extremely prematurely had at least one such predictor, compared with 18% for full-term births — although these data include people born before surfactant and corticosteroid use were widespread, so it’s unclear if these data reflect outcomes for babies born today. Researchers have found similar trends in a UK cohort study of extremely premature births. In results published earlier this year5, the EPICure study team, led by neonatologist Neil Marlow at University College London, found that 60% of 19-year-olds who were extremely premature were impaired in at least one neuropsychological area, often cognition.
When the researchers looked at predictors of early mortality, such as heart disease, 68% of people born extremely prematurely had at least one such predictor, compared with 18% for full-term births — although these data include people born before surfactant and corticosteroid use were widespread, so it’s unclear if these data reflect outcomes for babies born today. Researchers have found similar trends in a UK cohort study of extremely premature births. In results published earlier this year5, the EPICure study team, led by neonatologist Neil Marlow at University College London, found that 60% of 19-year-olds who were extremely premature were impaired in at least one neuropsychological area, often cognition.
Such disabilities can impact education as well as quality of life. Craig Garfield, a paediatrician at the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine and the Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago, Illinois, addressed a basic question about the first formal year of schooling in the United States: “Is your kid ready for kindergarten, or not?”
To answer it, Garfield and his colleagues analysed standardized test scores and teacher assessments on children born in Florida between 1992 and 2002. Of those born at 23 or 24 weeks, 65% were considered ready to start kindergarten at the standard age, 5–6 years old, with the age adjusted to take into account their earlier birth. In comparison, 85.3% of children born full term were kindergarten-ready6.
Of those born at 23 or 24 weeks, 65% were considered ready to start kindergarten at the standard age, 5–6 years old, with the age adjusted to take into account their earlier birth. In comparison, 85.3% of children born full term were kindergarten-ready6.
Despite their tricky start, by the time they reach adolescence, many people born prematurely have a positive outlook. In a 2006 paper7, researchers studying individuals born weighing 1,000 grams or less compared these young adults’ perceptions of their own quality of life with those of peers of normal birthweight — and, to their surprise, found that the scores were comparable. Conversely, a 2018 study8 found that children born at less than 28 weeks did report having a significantly lower quality of life. The children, who did not have major disabilities, scored themselves 6 points lower, out of 100, than a reference population.
As Marlow spent time with his participants and their families, his worries about severe neurological issues diminished. Even when such issues are present, they don’t greatly limit most children and young adults. “They want to know that they are going to live a long life, a happy life,” he says. Most are on track to do so. “The truth is, if you survive at 22 weeks, the majority of survivors do not have a severe, life-limiting disability.”
Even when such issues are present, they don’t greatly limit most children and young adults. “They want to know that they are going to live a long life, a happy life,” he says. Most are on track to do so. “The truth is, if you survive at 22 weeks, the majority of survivors do not have a severe, life-limiting disability.”
A nurse uses electroencephalography (EEG) to carry out a check of brain development on a baby born at 25 weeks.Credit: BSIP/Universal Images Group via Getty
BreathlessBut scientists have only just begun to follow people born extremely prematurely into adulthood and then middle age and beyond, where health issues may yet lurk. “I’d like scientists to focus on improving the long-term outcomes as much as the short-term outcomes,” says Tala Alsadik, a 16-year-old high-school student in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
When Alsadik’s mother was 25 weeks pregnant and her waters broke, doctors went so far as to hand funeral paperwork to the family before consenting to perform a caesarean section. As a newborn, Alsadik spent three months in the neonatal-intensive-care unit (NICU) with kidney failure, sepsis and respiratory distress.
As a newborn, Alsadik spent three months in the neonatal-intensive-care unit (NICU) with kidney failure, sepsis and respiratory distress.
The complications didn’t end when she went home. The consequences of her prematurity are on display every time she speaks, her voice high and breathy because the ventilator she was put on damaged her vocal cords. When she was 15, her navel unexpectedly began leaking yellow discharge, and she required surgery. It turned out to be caused by materials leftover from when she received nutrients through a navel tube.
The brain, interrupted
That certainly wasn’t something her physicians knew to check for. In fact, doctors don’t often ask if an adolescent or adult patient was born prematurely — but doing so can be revealing.
Charlotte Bolton is a respiratory physician at the University of Nottingham, UK, where she specializes in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). People coming into her practice tend to be in their 40s or older, often current or former smokers. But in around 2008, she began to notice a new type of patient being referred to her owing to breathlessness and COPD-like symptoms: 20-something non-smokers.
But in around 2008, she began to notice a new type of patient being referred to her owing to breathlessness and COPD-like symptoms: 20-something non-smokers.
Quizzing them, Bolton discovered that many had been born before 32 weeks. For more insight, she got in touch with Marlow, who had also become concerned about lung function as the EPICure participants aged. Alterations in lung function are a key predictor of cardiovascular disease, the leading cause of death around the world. Clinicians already knew that after extremely premature birth, the lungs often don’t grow to full size. Ventilators, high oxygen levels, inflammation and infection can further damage the immature lungs, leading to low lung function and long-term breathing problems, as Bolton, Marlow and their colleagues showed in a study of 11-year-olds9.
Treatments for premature babies have improved in recent decades, but survival rates vary by age and country.Credit: Mohammed Hamoud/Getty
VICS research backs up the cardiovascular concerns: researchers have observed diminished airflow in 8-year-olds, worsening as they aged10, as well as high blood pressure in young adults11. “We really haven’t found the reason yet,” says Cheong. “That opens up a whole new research area.”
“We really haven’t found the reason yet,” says Cheong. “That opens up a whole new research area.”
At Sainte-Justine, researchers have also noticed that young adults who were born at 28 weeks or less are at nearly three times the usual risk of having high blood pressure12. The researchers figured they would try medications to control it. But their patient advisory board members had other ideas — they wanted to try lifestyle interventions first.
The scientists were pessimistic as they began a pilot study of a 14-week exercise programme. They thought that the cardiovascular risk factors would be unchangeable. Preliminary results indicate that they were wrong; the young adults are improving with exercise.
Girard-Bock says the data motivate her to eat healthily and stay active. “I’ve been given the chance to stay alive,” she says. “I need to be careful.”
From the startFor babies born prematurely, the first weeks and months of life are still the most treacherous. Dozens of clinical trials are in progress for prematurity and associated complications, some testing different nutritional formulas or improving parental support, and others targeting specific issues that lead to disability later on: underdeveloped lungs, brain bleeds and altered eye development.
Dozens of clinical trials are in progress for prematurity and associated complications, some testing different nutritional formulas or improving parental support, and others targeting specific issues that lead to disability later on: underdeveloped lungs, brain bleeds and altered eye development.
For instance, researchers hoping to protect babies’ lungs gave a growth factor called IGF-1 — which the fetus usually gets from its mother during the first two trimesters of pregnancy — to premature babies in a phase II clinical trial reported13 in 2016. Rates of a chronic lung condition that often affects premature babies halved, and babies were somewhat less likely to have a severe brain haemorrhage in their earliest months.
Could baby’s first bacteria take root before birth?
Another concern is visual impairment. Retina development halts prematurely when babies born early begin breathing oxygen. Later it restarts, but preterm babies might then make too much of a growth factor called VEGF, causing over-proliferation of blood vessels in the eye, a disorder known as retinopathy. In a phase III trial announced in 2018, researchers successfully treated 80% of these retinopathy cases with a VEGF-blocking drug called ranibizumab14, and in 2019 the drug was approved in the European Union for use in premature babies.
In a phase III trial announced in 2018, researchers successfully treated 80% of these retinopathy cases with a VEGF-blocking drug called ranibizumab14, and in 2019 the drug was approved in the European Union for use in premature babies.
Some common drugs might also be of use: paracetamol (acetaminophen), for example, lowers levels of biomolecules called prostaglandins, and this seems to encourage a key fetal vein in the lungs to close, preventing fluid from entering the lungs15.
But among the most promising treatment programmes, some neonatologists say, are social interventions to help families after they leave the hospital. For parents, it can be nerve-racking to go it alone after depending on a team of specialists for months, and lack of parental confidence has been linked to parental depression and difficulties with behaviour and social development in their growing children.
At Women & Infants Hospital of Rhode Island in Providence, Betty Vohr is director of the Neonatal Follow-Up Program. There, families are placed in private rooms, instead of sharing a large bay as happens in many NICUs. Once they are ready to leave, a programme called Transition Home Plus helps them to prepare and provides assistance such as regular check-ins by phone and in person in the first few days at home, and a 24/7 helpline. For mothers with postnatal depression, the hospital offers care from psychologists and specialist nurses.
There, families are placed in private rooms, instead of sharing a large bay as happens in many NICUs. Once they are ready to leave, a programme called Transition Home Plus helps them to prepare and provides assistance such as regular check-ins by phone and in person in the first few days at home, and a 24/7 helpline. For mothers with postnatal depression, the hospital offers care from psychologists and specialist nurses.
The results have been significant, says Vohr. The single-family rooms resulted in higher milk production by mothers: 30% more at four weeks than for families in more open spaces. At 2 years old, children from the single-family rooms scored higher on cognitive and language tests16. After Transition Home Plus began, babies discharged from the NICU had lower health-care costs and fewer hospital visits — issues that are of great concern for premature infants17. Other NICUs are developing similar programmes, Vohr says.
With these types of novel intervention, and the long-term data that continue to pour out of studies, doctors can make better predictions than ever before about how extremely premature infants will fare. Although these individuals face complications, many will thrive.
Although these individuals face complications, many will thrive.
Alsadik, for one, intends to be a success story. Despite her difficult start in life, she does well academically, and plans to become a neonatologist. “I, also, want to improve the long-term outcomes of premature birth for other people.”
Scientists have found out at what age is best to give birth
If a woman wants to become a mother of three children in the future, she should give birth to her first child at the age of no more than 23 years, scientists have found out. The science department of Gazeta.Ru tells about the ideal age for childbirth and how breast milk affects the child's ability to perceive emotions.
Over the past few decades, the age at which women first become mothers has steadily increased. First of all, this trend concerns economically developed countries: according to Report of the Statistical Office of the European Union (Eurostat) published in 2015,
Pregnancy was postponed for 14 years
For the first time in the world, a woman gave birth to a healthy child as a result of transplantation of ovarian tissues into the body, which were . ..
..
June 10 17:31
In 2013, 51.2% of women living in the EU had their first child between the ages of 20 and 29, and 40.6% between the ages of 30 and 39. At the same time, the average age of the birth of the first child is 28.7 years.
The earliest first child is born in Bulgaria (on average at 25.7 years), Romania (25.8 years), Latvia (26.1 years), Estonia (26.5 years), Poland and Lithuania (26. 7 years) and Slovakia (26.9 years). The later mothers are in Greece (29.9 years), Luxembourg (30.0 years), Spain (30.4 years) and Italy (30.6 years). These countries also have the largest number of women who have given birth to their first child after 40 years of age. In Russia, the age of birth of the first child is also steadily growing, but has not yet exceeded the thirty-year mark, currently amounting to 27.2 years (for comparison, at 1980 this figure was 23 years). Meanwhile, doctors do not get tired of repeating: with age, the quality and quantity of eggs that the female body produces are steadily declining. The pace of this process is purely individual, but on average it begins at the age of 30.
The pace of this process is purely individual, but on average it begins at the age of 30.
A group of researchers from the University. Erasmus of Rotterdam analyzed data on pregnancies and childbirth of more than 58 thousand women. The time period covered by the data is 300 years, up until the 1970s. As the authors said in an interview with the scientific portal New Scientist , some scientists "accused" the studied material of being outdated and not reflecting the current situation. However, Dick Habbema, one of the authors of the article, states: “We needed information about those generations that aspired to have as many children as possible and did not use contraceptives.” As a result of the work, scientists managed to compile a so-called fertility calculator - a table that shows at what age a woman is recommended to give birth to the first and subsequent child, provided that she wants to become the mother of one, two or three children.
During the work, the scientists obtained the following data:
The lower the height, the earlier the birth
The height of a woman directly affects how long her pregnancy will last, scientists have found. Department of Science...
Department of Science...
August 19 12:54
If a woman wants to give birth to three children, she must give birth to her first child no later than 23 years old, if she wants to become a mother of two children, she should start no later than 27 years old, and the first and only child can be born at 32 years old.
In all of the above cases, the probability of successful development of the situation and the birth of all planned children will be more than 90%.
The chances of a favorable outcome will decrease to 75% if a woman starts having children at the age of 31 (if she wants to have three), 34 years and 37 years for two and one child, respectively. If pregnancy is postponed to 35, 38 and 41 years, respectively, the probability of happy motherhood will decrease even more - up to 50%.
According to the calculations of specialists, if a woman, for medical reasons, is going to give birth using in vitro fertilization (about the pitfalls of this procedure science department already told a few months ago), she has more time to think. To give birth to three children with a more than 90 percent success rate, you can start at 28, twins at 31, and with one child you can wait until 35 at all.
To give birth to three children with a more than 90 percent success rate, you can start at 28, twins at 31, and with one child you can wait until 35 at all.
If you are not afraid of the 75% success rate, then the age brackets are raised to 33, 35 and 39 years respectively.
If a lady is ready to take a risk and try to carry a child conceived with the help of IVF with a 50% chance of a positive outcome, then you can start at 36, 39and 42 years respectively.
Alcohol will not spoil the baby
Breastfeeding women may well consume alcoholic beverages, scientists have found. Department of Science...
September 12 17:21
Alan Pacey, study participant and professor at the University of Sheffield, comments: “Everyone thinks that having children can wait, our research shows that it can't. Our table should be printed out and hung on the walls in clinics. We need to focus on informing high school and college girls so they can start planning their lives in advance. ” In addition, researchers focus on the following fact: the media quite often report that a certain singer or actress became a mother at a very late age, including through IVF. According to scientists, in no case should one be guided by this information, thinking that "if she could do it, I can do it too." Spanish researcher Martha Devesa says we don't know how many failed IVF attempts these women went through, or what treatment they needed to make the pregnancy uncomplicated.
” In addition, researchers focus on the following fact: the media quite often report that a certain singer or actress became a mother at a very late age, including through IVF. According to scientists, in no case should one be guided by this information, thinking that "if she could do it, I can do it too." Spanish researcher Martha Devesa says we don't know how many failed IVF attempts these women went through, or what treatment they needed to make the pregnancy uncomplicated.
But for those women who have already become mothers, there is another reason not to neglect the advice of doctors and breastfeed the baby. A paper on the discovery by a research team led by Kathleen Krol and Tobias Grossmann of the Max Planck Society's Institute for Brain Research was published in the latest issue of PNAS . Scientists have found:
how well young children respond to the emotions of those around them depends on two factors - the presence of a specific variation of the CD38 gene and the duration of breastfeeding.
The results of an experiment in which 98 seven-month-old children and their mothers took part showed that children who were fed breast milk in the first months of life preferred to look at faces showing happy emotions and showed less interest in angry or sad faces. Mother's milk was even able to level the results of the work of a special variation of the CD38 gene, which reduces the level of the hormone oxytocin in the child's body. As a result, he does not see the difference between happy, sad or angry faces and looks at them for the same length of time. In addition, the same version of CD38 makes a child predisposed to autism. The authors of the work assure: they were able to prove that breast milk increases the level of oxytocin so much that it can cope with a genetic predisposition to poor emotion recognition and autism.
Late children bring back youth - articles from specialists of the clinic "Mother and Child"
The number of women who gave birth to their first child between 30 and 40 years has almost tripled in the last 20 years. In addition, the number of first-time mothers after 40 years has increased by almost 50%. And physicians are forced to reckon with it. Gradually, the offensive word “old-timer” disappeared from their vocabulary, and childbirth in adulthood is no longer considered something out of the ordinary.
In addition, the number of first-time mothers after 40 years has increased by almost 50%. And physicians are forced to reckon with it. Gradually, the offensive word “old-timer” disappeared from their vocabulary, and childbirth in adulthood is no longer considered something out of the ordinary.
Increasingly, women are postponing childbirth while studying or moving up the career ladder. The number of early births (up to 20 years old) in all civilized countries is steadily falling (Russia, however, is an exception).
Numerous studies have shown that pregnancy and childbirth after 35 do not pose such a serious danger as previously thought. The average portrait of a woman in her thirties who is preparing to become a mother has changed a lot lately. As a rule, she belongs to the middle class, is well educated, takes care of her health. Her body is not worn out by numerous births.
It has always been believed that later children are more likely to be born prematurely, gain less weight and get sick more in early childhood. Recent research has cast doubt on this.
Recent research has cast doubt on this.
American doctors who observed 4 thousand women in labor in one of the hospitals in New York came to the conclusion that a woman over 35 years old, if she is physically healthy and has not had miscarriages, has a chance to give birth to a normal healthy child (even if this is the first birth) almost the same as a 20-year-old.
For a middle-aged woman who has devoted all her young years to a career, pregnancy is an opportunity to try herself in a completely new way. In addition, she is more likely to find support from her husband, since a mature man is psychologically more prepared for the role of a father than a young one.
As you know, psychological readiness for motherhood comes much later than biological. According to psychologists, pregnancy in adulthood is much more favorable than in early youth. A woman perceives her condition more calmly, less prone to stress, less likely to experience internal conflicts. She is more disciplined and lives in harmony with herself. Many consider the birth of a child a gift of fate or a blessing from God.
She is more disciplined and lives in harmony with herself. Many consider the birth of a child a gift of fate or a blessing from God.
Older women, most of whom married late, as a rule, stand firmly on their feet, have reached a certain level in their professional activities, and are confident that they will return to work some time after giving birth. All this allows them to look to the future with great calmness and optimism. A middle-aged woman who has devoted all her young years to a career may look at pregnancy as an opportunity to try herself in a completely new capacity. In addition, she is more likely to find support from her husband, since a mature man is psychologically more prepared for the role of a father than a young one. As a rule, middle-aged parents, unlike young ones, devote more time to raising a child. As a result, many "late" children are ahead of their peers in their intellectual and physical development. The secret here is in the atmosphere of love and mutual understanding in the family where the long-awaited baby appeared.
American psychologists conducted a survey among women who became mothers before the age of 20 and between 30 and 40 years. Both were asked to answer the question of whether they would give birth at the same age if they could make a new decision. More than half of those whose children were born before the age of 20 answered “no”, and the majority of older mothers expressed confidence that they had chosen the optimal time for the birth of a child.
Hollywood star Kim Basinger first became a mother when she was already over 40. Actress Beverly D * Angelo, a friend of Al Pacino, gave birth to his charming twins when she was 49. The famous actress Marina Neelova had a daughter when she was 41 years old. And there are many such examples.
Doctors today can help even those women whose reproductive period has ended. Various methods are used for this: hormone therapy, implantation of a donor egg in the uterus. Muscovite Natalya Alekseevna Surkova got into the Guinness Book of Records, becoming a mother at the age of 57.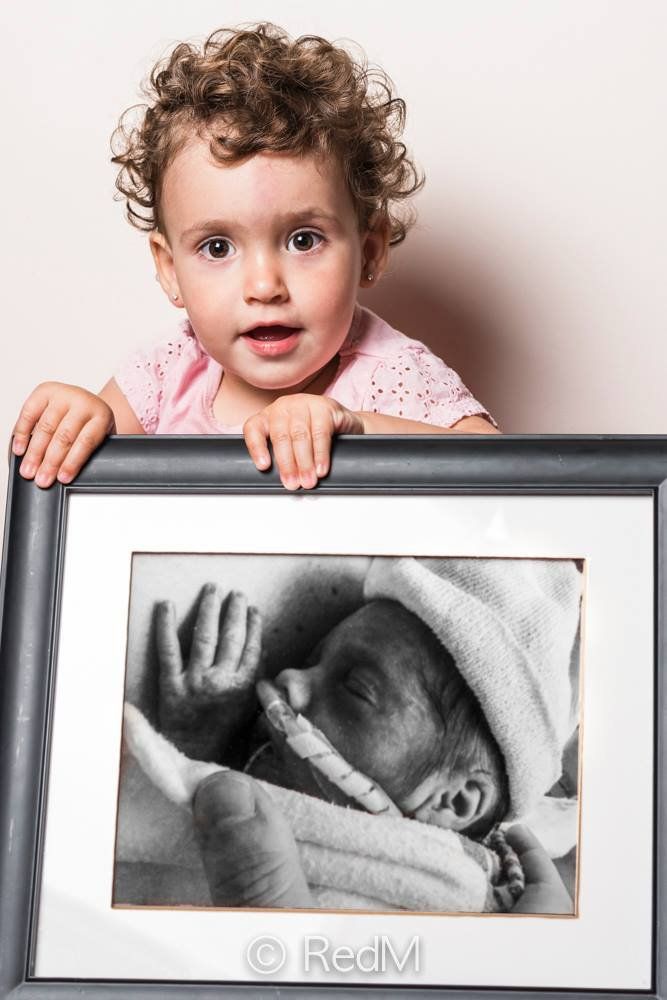 She already had two adult children. Recently, a 66-year-old woman from Romania gave birth to a child. For many years she taught at the University and wrote books for children, but she had no babies of her own before. True, doctors are not particularly enthusiastic about the increase in the number of mothers-grandmothers: the risk of complications and the responsibility of the doctor who “leads” such a woman in labor are too high.
She already had two adult children. Recently, a 66-year-old woman from Romania gave birth to a child. For many years she taught at the University and wrote books for children, but she had no babies of her own before. True, doctors are not particularly enthusiastic about the increase in the number of mothers-grandmothers: the risk of complications and the responsibility of the doctor who “leads” such a woman in labor are too high.
Of course, late motherhood has its problems. Women over 35 are more likely to experience health complications during pregnancy, especially diabetes and high blood pressure. These complications occur in approximately 6% of women over 35 years of age compared to 1.3% in younger women.
Another problem: the "solid" age of the parents increases the risk of developing anomalies in the fetus, the birth of children with severe hereditary diseases. Therefore, all primiparas over 35 years of age are usually offered an amniocentesis in the second trimester of pregnancy - an analysis of amniotic fluid. This allows you to identify about 200 hereditary diseases associated with a violation of the chromosome set.
This allows you to identify about 200 hereditary diseases associated with a violation of the chromosome set.
You can also find out the degree of risk of such diseases using the "triple" test - it is done around the 16th week of pregnancy. For analysis, blood is taken from a vein. Women of older reproductive age do not recover from childbirth as quickly as younger women. For some of them, after decades of taking care of themselves, it can be difficult to get used to the fact that the baby, especially in the first months, requires constant care and attention.
Another disadvantage of late childbirth is that parents have to limit themselves to one child or have a second one when the first one is still very small - after all, the time allotted by nature for acquiring offspring is not unlimited.
Should I do a Caesarean section?
In women over 30-40 years of age, childbirth can be more difficult and protracted than in younger women - this is the generally accepted opinion. In fact, any experienced obstetrician can testify that in many cases, older mothers do an excellent job with minimal medical help. Often and, by the way, not always justified, at this age they offer a caesarean section. This does not raise questions if there are medical indications for surgery or a woman managed to get pregnant only with the help of doctors. Then, trying to eliminate any risk to the baby and taking into account the aggravating factors, the doctor makes such a decision.
In fact, any experienced obstetrician can testify that in many cases, older mothers do an excellent job with minimal medical help. Often and, by the way, not always justified, at this age they offer a caesarean section. This does not raise questions if there are medical indications for surgery or a woman managed to get pregnant only with the help of doctors. Then, trying to eliminate any risk to the baby and taking into account the aggravating factors, the doctor makes such a decision.
Recent studies have shown that, on average, the duration of labor for older mothers exceeds the duration of labor for young mothers by only 45 minutes. And at 40, you can not be afraid of difficult childbirth if you are well prepared for them physically and psychologically.
Where to start?
If for some reason you put off the birth of your child, you should prepare in advance for his possible birth.
Try to get rid of bad habits if you have them. By the age of 35, we have time to experience a stronger impact of adverse environmental factors than by the age of 20.
Should we add to them the harm from smoking and alcohol? Watch your health, do not start even trifling, at first glance, diseases. If you treat a cold rather than endure it on your feet, you are much more likely to keep your kidneys and heart healthy, organs that take a lot of stress during pregnancy.
Control your weight and maintain muscle tone. Go in for sports or exercise. Excess weight creates additional problems during gestation.
It should be borne in mind that after 35 years, the ability to bear children gradually decreases. Experts believe that at this age it may take 6-12 months to conceive instead of four. Before you decide it's time to start procreation, visit a therapist. Sometimes a woman is being treated for infertility for years, during which time she develops various ailments. These diseases may not cause much concern, but they can interfere with the normal course of pregnancy.
During pregnancy, you will need to be more attentive to yourself than younger women, to strictly monitor your diet and regimen.
It is worth taking seriously the choice of a doctor and a maternity hospital. It is desirable that the clinic be equipped with everything necessary in case you need urgent help for a newborn.
"If you want to preserve beauty, have a child at forty," say the French. If a woman is healthy, during pregnancy she blossoms. In this magical way, estrogens act - female sex hormones, the production of which increases several times. In addition, the eggs of a pregnant woman are not "spent", so aging seems to be suspended. Menopause in women who have become mothers in adulthood may come later. Raising a baby provides a unique opportunity to turn from a middle-aged woman into a young mother.
Such parents usually go through the so-called midlife crisis painlessly - they just don't have time to delve into their problems. Not soon they will have another test, which psychologists call the "empty nest" syndrome - when children grow up and leave their father's house.