Rhinitis during pregnancy
Relief for Ongoing Nasal Congestion Is Possible
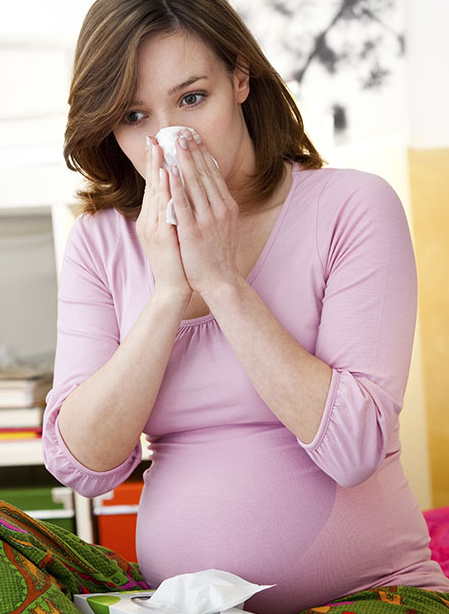
If you're expecting a baby, you may be dealing with a stuffy nose that doesn’t seem to go away. This hassle is called pregnancy rhinitis. The cause of this condition isn’t really clear. However, it may be caused by hormonal changes.Having a history of allergies or asthma does not raise your risk of getting pregnancy rhinitis.
More than just a stuffy nose
Pregnancy rhinitis is an inflammation of the mucous membranes lining the nose. This causes nasal congestion. Increased blood flow to the nasal passages and enlargement of the nasal veins also play a role.
Symptoms occur during pregnancy. They can last for several weeks. On top of feeling uncomfortable, your sleep may be disrupted. This is because the congestion gets worse when you lie down. This may make you to feel more tired during the day. Long-lasting congestion also can lead to complications. These can include sinusitis and ear infections.
Be cautious when seeking treatment
Many women use non-prescription, over-the-counter (OTC) decongestant sprays to open up their nasal passages. Know that these medicines don’t work for pregnancy rhinitis. These medicines may give you temporary relief. However, they may actually make your symptoms worse and lead to a complete nasal blockage.
How can you get relief from pregnancy rhinitis? Experts say you can breathe easy with these measures:
-
Don’t use OTC nasal decongestants.
-
Drink plenty of fluids.
-
Increase the humidity levels in your home. Use a humidifier.
-
Don’t use nasal irritants, such as cigarette smoke.
-
Get moving. Regular, moderate-intensity exercise can reduce congestion. It can also help you sleep better. But first, check with your healthcare provider to see what exercises are safe for you.
-
When you go to sleep, raise the head of your bed. For instance, use an extra pillow or a wedge.

-
Ask your healthcare provider about using OTC nasal strips and saline sprays or drops.
The good news? Even if you don’t do anything, you can expect your stuffy nose to clear up soon after your baby is born. It often goes away within two weeks of childbirth.
Online Medical Reviewer: Bowers, Nancy, RN, BSN, MPH Foley, Maryann, RN, BSN
Date Last Reviewed: 4/12/2016
© 2000-2019 The StayWell Company, LLC. 800 Township Line Road, Yardley, PA 19067. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.
© 2000-2019 The StayWell Company, LLC. 800 Township Line Road, Yardley, PA 19067. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.
Pregnancy rhinitis | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Pregnancy rhinitis | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content5-minute read
Listen
If you have unexplained breathing problems, see your doctor as soon as possible. If your breathing problems are very bad and come on quickly, call triple zero (000) for an ambulance.
If your breathing problems are very bad and come on quickly, call triple zero (000) for an ambulance.
What is pregnancy rhinitis?
Pregnancy rhinitis usually involves a stuffy nose, itchy eyes, and post-nasal drip. These symptoms seem to come out of nowhere during pregnancy. While it's not a life-threatening medical condition, pregnancy rhinitis can be bothersome. There are things you can do to find some relief.
What are the symptoms pregnancy rhinitis?
Symptoms of pregnancy rhinitis are like those of allergic rhinitis (hay fever). These include:
- a runny or congested nose
- sneezing
- itchy eyes
- watery eyes
While it might feel like you are getting a cold, pregnancy rhinitis is not associated with bacterial or viral infection. This means it is not contagious.
CHECK YOUR SYMPTOMS — If you are feeling unwell and not sure what to do next, check your symptoms using the healthdirect Symptom Checker tool.
What causes pregnancy rhinitis?
Rhinitis is an inflammation of the lining of your nose.
People who are affected by allergies may also experience similar symptoms during pregnancy. In these circumstances, symptoms are triggered by one or more allergens. These allergens may be seasonal, such as:
- pollens
- fungi
- moulds
Or they can be perennial (year-round) such as:
- dust mites
- pets
- cockroaches
Rhinitis in pregnancy may also have a non-allergic origin. It's not known exactly why rhinitis occurs more frequently in pregnancy. Some research suggests that factors such as hormones increase the likelihood of rhinitis during pregnancy.
Smoking is also associated with pregnancy rhinitis. It's never too late for future parents to quit smoking.
How is pregnancy rhinitis diagnosed?
Pregnancy rhinitis should be distinguished from other conditions such as infections. Your doctor can do this during a routine visit.
Your doctor can do this during a routine visit.
You may have a breathing problem if:
- you feel you can't get enough air through both your nose and mouth
- you are breathless
- you feel like you're being suffocated
- your chest feels very tight
- you are needing more of your usual asthma or lung medications
If you have unexplained breathing problems, see your doctor as soon as possible. If your breathing problems are very bad and come on quickly, call triple zero (000) for an ambulance.
FIND A HEALTH SERVICE — The Service Finder can help you find doctors, pharmacies, hospitals and other health services.
How long will my symptoms last?
While pregnancy rhinitis can occur at any time during your pregnancy, it is most common during the first trimester.
Symptoms may last for at least 6 weeks. The good news is they usually disappear within 2 weeks of your baby's birth.
How is pregnancy rhinitis treated?
Your pregnancy rhinitis may be triggered by a known allergen. If this is the case, you can try and avoid or limit your exposure to the allergen.
Nasal irrigation is a drug-free technique to clear out air-borne allergens and mucus from blocked nostrils.
Using salt water (saline) nasal sprays can provide relief and is a good solution during pregnancy.
Persistent symptoms are managed individually. If you have itchy-watery eyes, there are certain eye drops that are approved for use during pregnancy. Similarly, specific medicated nasal sprays and antihistamines can be used.
However, always check with your doctor or pharmacist before taking any medicine while pregnant.
Is there an impact on my unborn baby?
There are insufficient studies to fully understand the impact of pregnancy rhinitis on the growth and development of unborn babies.
However, any condition that reduces your quality of life has the potential to affect your baby. This includes the quality of your sleep during pregnancy.
This includes the quality of your sleep during pregnancy.
If you are concerned about your sleep or breathing during pregnancy, speak to your doctor. They can help you find the best way to clear your breathing passages and improve your sleep.
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Sources:
Auris Nasus Larynx (Medical Management of rhinitis in pregnancy), American Journal of Rhinology & Allergy (Redefining Pregnancy-induced Rhinitis), International Journal of Chemistry, Mathematics and Physics (Chronic Rhinosinusitis and Its Impact on Pregnancy), South Eastern Sydney Local health District/The Royal Hospital for Women (Hay Fever in Pregnancy and Breastfeeding), The Royal Women’s Hospital (Medicines in Pregnancy), Australasian Society of Clinical Immunology and Allergy (ASCIA) (Allergic Rhinitis Clinical Update)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: July 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Medicines during pregnancy
- Cold and flu during pregnancy and breastfeeding
- Allergies: controlling your environment
- Airborne allergies
- Allergies and hay fever during pregnancy
Need more information?
Allergic rhinitis - symptoms, causes and treatment - MyDr.com.au
Rhinitis means inflammation of the lining of the nose. Allergic rhinitis means that this inflammation is caused by an allergy.
Read more on myDr website
Allergic rhinitis (hay fever)? - Australasian Society of Clinical Immunology and Allergy (ASCIA)
Allergic rhinitis (commonly known as hay fever) affects around 18% of people in Australia and New Zealand. It can affect children and adults.
It can affect children and adults.
Read more on ASCIA – Australasian Society of Clinical Immunology and Allergy website
Allergic Rhinitis (hayfever) - Allergy & Anaphylaxis Australia
Allergic rhinitis (hay fever) is one of the most common allergic conditions affecting 1 in 5 people in Australia. It is caused by the body’s immune system reacting to common allergens in the environment such as pollen, house dust mite, moulds and animal danders (skin cells and fur).
Read more on Allergy and Anaphylaxis Australia website
Hay Fever (Allergic Rhinitis) - Australasian Society of Clinical Immunology and Allergy (ASCIA)
The Australasian Society of Clinical Immunology and Allergy (ASCIA) is the peak professional body of clinical immunology and allergy in Australia and New Zealand. ASCIA promotes and advances the study and knowledge of immune and allergic diseases, including asthma.
ASCIA promotes and advances the study and knowledge of immune and allergic diseases, including asthma.
Read more on ASCIA – Australasian Society of Clinical Immunology and Allergy website
Immunotherapy for Allergic Rhinitis (Hay Fever) - Allergy & Anaphylaxis Australia
Allergen Immunotherapy (AIT) has been used for over 100 years and is a proven treatment providing long-term relief for hay fever. The aim of AIT is to help people react less to their trigger allergen/s that cause symptoms (such as grass pollen/house dust mite). This means having no/less symptoms and a better quality of life.
Read more on Allergy and Anaphylaxis Australia website
Pollen - a trigger for hay fever - National Asthma Council Australia
Plant pollen is well known as a trigger for seasonal allergic rhinitis (hay fever) and seasonal allergic conjunctivitis.
Read more on National Asthma Council Australia website
Hay Fever & Asthma | Hay Fever-related Asthma Causes & Symptoms - Asthma Australia
Hay fever is a common allergy, also known as allergic rhinitis, that can also trigger asthma flare-ups. Learn more about hay fever-related asthma & symptoms here.
Read more on Asthma Australia website
Other Allergic Conditions - Allergy & Anaphylaxis Australia
Other Allergic Conditions included: Urticaria (Hives), Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis), Allergic Conjunctivitis, Allergic Rhinitis (hayfever), Sinusitis
Read more on Allergy and Anaphylaxis Australia website
Thunderstorm asthma - Australasian Society of Clinical Immunology and Allergy (ASCIA)
It seems reasonable to think that rain would relieve allergic rhinitis (hay fever) and asthma triggered by pollen, by washing pollen out of the air. However, rain from some thunderstorms can make some people's symptoms worse. Epidemics of thunderstorm asthma in Australia have occurred in Melbourne and Wagga Wagga.
However, rain from some thunderstorms can make some people's symptoms worse. Epidemics of thunderstorm asthma in Australia have occurred in Melbourne and Wagga Wagga.
Read more on ASCIA – Australasian Society of Clinical Immunology and Allergy website
Allergy Treatments - Australasian Society of Clinical Immunology and Allergy (ASCIA)
The Australasian Society of Clinical Immunology and Allergy (ASCIA) is the peak professional body of clinical immunology and allergy in Australia and New Zealand. ASCIA promotes and advances the study and knowledge of immune and allergic diseases, including asthma.
Read more on ASCIA – Australasian Society of Clinical Immunology and Allergy website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
Need further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Pregnancy rhinitis - why does it occur and how to treat it?
Rhinitis of pregnant women is not dangerous, but worsens the quality of life of a woman during pregnancy.Article rating
3.26 (Votes: 34)
Contents
- How long does pregnancy rhinitis occur and how long does it last?
- Symptoms of pregnancy rhinitis
- Causes of pregnancy rhinitis
- How to distinguish the symptoms of rhinitis during pregnancy from other pathologies?
- Treatment of rhinitis of pregnant women
- General recommendations for pregnant women who have symptoms of rhinitis
- Drugs for the treatment of rhinitis
Rhinitis of pregnancy (nasal obstruction) is a common pathology that occurs in about 30% of expectant mothers. Manifested by a typical triad of symptoms: nasal congestion, difficulty breathing, the presence of mucous secretions. By itself, it is not dangerous, but worsens the quality of life of a woman during pregnancy. The difficulty of stopping the pathology and relieving symptoms lies in the fact that during pregnancy there are restrictions on the use of a number of physiotherapeutic methods and drugs.
Manifested by a typical triad of symptoms: nasal congestion, difficulty breathing, the presence of mucous secretions. By itself, it is not dangerous, but worsens the quality of life of a woman during pregnancy. The difficulty of stopping the pathology and relieving symptoms lies in the fact that during pregnancy there are restrictions on the use of a number of physiotherapeutic methods and drugs.
When does pregnancy rhinitis occur and how long does it last?
Most often, pathology occurs:
- up to and including the 20th week of pregnancy - in this case, rhinitis usually resolves on its own (after about a month or two) and does not manifest itself in the later stages;
- after the 20th week of pregnancy - this condition can continue until childbirth and after them (after 2-3 weeks).
If the symptoms last longer than two months and are not relieved by any independent action (vasoconstrictor sprays are prohibited!), then the cause may be hiding in a chronic disease.
Symptoms of pregnancy rhinitis
- Difficult nasal breathing, nasal congestion;
- Nasal discomfort, sneezing;
- Presence of clear mucous discharge;
- Feeling of constriction in the region of the nose and sinuses;
- Mild headaches.
Difficulty in nasal breathing in the mother leads to sleep disturbance and hypoxia, which is also felt by the fetus.
Causes of pregnancy rhinitis
The pathogenesis of the disease is still a controversial issue. Most doctors are inclined to believe that it is of a hormonal nature and is associated with an increased level of estrogen and acetylcholine in the blood serum (as a result), which leads to hyperemia of the nasal mucosa and swelling. The concentration of estradiol, estrone, estriol in the bloodstream of pregnant women increases, in some future mothers, for this reason, the shape of the nose may change, it may increase in size.
There is evidence that pregnant women with symptoms of vasomotor rhinitis have elevated serum placental hormone levels. Another reason that can cause long-term nasal obstruction is the tone of smooth muscle cells under the influence of the inhibitory action of the steroid hormone progesterone. It causes fluid retention in the body and has such a side effect on the nasal mucosa.
Another reason that can cause long-term nasal obstruction is the tone of smooth muscle cells under the influence of the inhibitory action of the steroid hormone progesterone. It causes fluid retention in the body and has such a side effect on the nasal mucosa.
Histochemical studies have shown that nasal congestion may occur due to plethora due to hyperactivity of the parasympathetic nervous system in pregnant women.
How to distinguish the symptoms of pregnancy rhinitis from other pathologies?
Symptoms of rhinitis during pregnancy are really similar to manifestations of other diseases, for example, viral infections, sinusitis. It is difficult for a future mother to distinguish a pathology by external signs, therefore a doctor's consultation is necessary. Our clinic employs specialists with extensive experience who will quickly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
If the symptoms are accompanied by a sore throat, fever, then this indicates the presence of a bacterial and/or viral infection or other inflammatory process.
With sinusitis, mucous discharge may have a yellowish or greenish tint. When pressing in the area of the maxillary and frontal sinuses, there are painful sensations, when the head is tilted, the pain may intensify. Also, sinusitis often causes an increase in temperature, while with nasal obstruction, such symptoms are not observed.
Sometimes rhinitis of pregnancy is confused with allergic rhinitis, which may worsen, there may be sensitization to allergens to which patients have not previously reported sensitivity.
Treatment of pregnancy rhinitis
In our clinic, a thorough diagnosis is carried out in order to exclude diseases similar to rhinitis in terms of symptoms. After the examination, individual treatment is prescribed depending on the severity, severity and indications.
Treatment is complicated by the fact that many drugs can cause contraction of the myometrium and fetal circulation or vasoconstriction with impaired placental function. Therefore, a doctor should prescribe drug therapy, you can not use drugs on your own - they can cause a violation of the development of the fetus.
Therefore, a doctor should prescribe drug therapy, you can not use drugs on your own - they can cause a violation of the development of the fetus.
General advice for pregnant women with symptoms of rhinitis
- Washing the nose with mild saline solution (2 teaspoons of sea salt per glass of water). Salt solution improves the discharge of nasal mucus and reduces the feeling of congestion.
- Nasal douches (nose washers) are very helpful. You can use regular saline for them.
- Ventilate the room before going to bed, use humidifiers. Dry air can exacerbate unpleasant symptoms.
- Use a high pillow (or multiple pillows) to sleep with your head well above your torso.
- Walking in the fresh air before going to bed is useful.
- Do morning exercises and breathing exercises several times a day to reduce the symptoms of hypoxia.
- Do not wear perfume and stay away from smokers.
Do not use vasoconstrictor nasal drops during pregnancy as they may cause vasomotor rhinitis.
Preparations for the treatment of rhinitis
Preparations for use during pregnancy are selected with great care and individually. Pregnant women are not given oral systemic corticosteroids, although their effect on the fetus is not fully understood. In some cases, the doctor prescribes corticosteroids in the form of aerosols. Oral antihistamines are also not prescribed due to the increased risk of embryopathies. The choice of physiotherapy is also limited, because most methods negatively affect the development of the fetus.
If you suffer from rhinitis, headaches or other unpleasant symptoms, we advise you to see a doctor immediately. Timely treatment is the key to the quality of life of the mother, which is very important for bearing the fetus. And also allows you not to miss other more serious diseases that can adversely affect the health of the mother and child.
Important! Do not use drugs that were prescribed to you by a doctor before pregnancy, or drugs prescribed to someone else.
Rhinitis during pregnancy usually does not pose a threat to either the fetus or the mother, but improper treatment can lead to unpredictable consequences.
Seeing a doctor early can help keep you healthy.
Don't delay treatment, call now. We work around the clock in Moscow.
tel.: 8 (499) 501-15-53 (24 hours)
Rhinitis in pregnancy
Otorhinolaryngologist, surgeon at GMS Clinic Oleg Abramov talks in his article about rhinitis of pregnancy (hereinafter referred to as RH).
It was no coincidence that I chose this topic after a series of publications on the social network about allergic rhinitis (hereinafter referred to as AR), as recent studies note that although the cause of RB is not completely clear, the combination of AR, which is especially poorly controlled together with RB, can lead to severe nasal congestion, to insufficient oxygen supply, and, as a result, to increased fatigue, irritability, frequent SARS, sleep disturbance, which can certainly affect the development of the fetus. Moreover, the presence of AR is associated with snoring in women during pregnancy, and together they can provoke the development of sleep apnea syndrome (stopping breathing during sleep), which leads to arterial hypertension, preeclampsia, slowed fetal growth and low Apgar scores. Therefore, the relevance of this problem is only growing.
Moreover, the presence of AR is associated with snoring in women during pregnancy, and together they can provoke the development of sleep apnea syndrome (stopping breathing during sleep), which leads to arterial hypertension, preeclampsia, slowed fetal growth and low Apgar scores. Therefore, the relevance of this problem is only growing.
Definition and concept
Rhinitis of pregnancy is a disease accompanied by nasal congestion and discharge, periodic sneezing without signs of inflammation, allergies, or other causes. This condition can occur in any trimester of pregnancy and usually resolves within two weeks after delivery.
Occurrence
Nasal congestion is a very common problem during pregnancy (occurs in about 65% of cases), which can occur due to various reasons. RB, according to various sources, occurs in 9-40% of cases, and in one of the last observations there is an increasing incidence, that is, most of all RB is observed in the 3rd trimester - 38. 9%, including those who did not have problems in the 1st and 2nd trimesters.
9%, including those who did not have problems in the 1st and 2nd trimesters.
Causes and mechanism of occurrence
The mechanism of occurrence is not fully understood, and it is believed that RB occurs due to hormonal changes, in particular, under the influence of progesterone, estrogen, hCG and other hormones, the concentration of which gradually increases during pregnancy. Some authors believe that the occurrence of RB is associated with the worsening of concomitant AR. Some studies show that hormonal action leads to relaxation of the smooth muscles that make up the vessel wall of the nasal mucosa, resulting in nasal congestion. Such findings are supported by other studies that show that oral contraceptives cause similar effects in the nasal cavity (but not in everyone). Other studies show that elevated body mass index, overweight, multiple pregnancies provoke or aggravate RB.
Progression and potential risks
RB, in the absence of adequate treatment, has an adverse effect on the course of pregnancy and can lead to the development of rhinosinusitis, which is especially difficult to tolerate in the 3rd trimester. On the other hand, pregnancy is a special period in a woman's life, during which a large number of drugs are prohibited, and ENT pathologies, these restrictions have not been spared either. Very often I hear at the reception: "Doctor, I'm pregnant and I've been suffering with my nose all this time, but the doctors tell me - there's nothing to be done, I need to endure it." On the other hand, the opposite situation is often observed: “Doctor, I am pregnant and I cannot live without vasoconstrictor drops.” These situations, of course, are not correct, since on the one hand there is a way out and optimal treatment, and on the other hand, constant exposure to vasoconstrictor drugs is not a way out of the situation at all.
On the other hand, pregnancy is a special period in a woman's life, during which a large number of drugs are prohibited, and ENT pathologies, these restrictions have not been spared either. Very often I hear at the reception: "Doctor, I'm pregnant and I've been suffering with my nose all this time, but the doctors tell me - there's nothing to be done, I need to endure it." On the other hand, the opposite situation is often observed: “Doctor, I am pregnant and I cannot live without vasoconstrictor drops.” These situations, of course, are not correct, since on the one hand there is a way out and optimal treatment, and on the other hand, constant exposure to vasoconstrictor drugs is not a way out of the situation at all.
Diagnostics
At the moment, there is no specific test to confirm or exclude RB. The diagnosis is made on the basis of the patient's complaints and the exclusion of other pathologies of the nasal cavity.
Choice of therapeutic tactics
Saline solutions
Before considering more serious medications, we should start with our favorite saline solutions. It should be noted that we are not talking about ordinary saline solutions, but hypertonic saline solutions (with an increased salt content, approximately 19-23 g/l). Such sprays are sold in all pharmacies, but they will not be sold to you right away (you need to ask). Several studies have noted significant efficacy in reducing congestion when used in AR, chronic rhinosinusitis. Also, comparative studies show their greater effectiveness compared to conventional isotonic solutions. Examples: Physiomer - hypertonic solution (my favorite), Aqualor-congestion, or Aqualor-severe runny nose, Aquamaris Strong.
It should be noted that we are not talking about ordinary saline solutions, but hypertonic saline solutions (with an increased salt content, approximately 19-23 g/l). Such sprays are sold in all pharmacies, but they will not be sold to you right away (you need to ask). Several studies have noted significant efficacy in reducing congestion when used in AR, chronic rhinosinusitis. Also, comparative studies show their greater effectiveness compared to conventional isotonic solutions. Examples: Physiomer - hypertonic solution (my favorite), Aqualor-congestion, or Aqualor-severe runny nose, Aquamaris Strong.
Doctor, not helping...
As is known from past publications, intranasal glucocorticosteroids (iGCS) are the most effective in the treatment of AR today. They have proven efficacy in reducing nasal congestion, as well as nasal itching and watery eyes, and allow adequate control of symptoms. But, given their hormonal effect and possible harmful effects on the fetus, there are certain risks in their use. It should also be noted that at the moment there are no studies that provide reliable data confirming the danger of their use. Modern ICS — mometasone (nasonex, desrinit) and fluticasone (avamys, flixonase) has a very low systemic bioavailability, less than 1% and proven efficacy, thus can be considered as initial therapy for RB. The studies did not reveal a statistically significant relationship between the development of fetal defects and the use of these drugs.
It should also be noted that at the moment there are no studies that provide reliable data confirming the danger of their use. Modern ICS — mometasone (nasonex, desrinit) and fluticasone (avamys, flixonase) has a very low systemic bioavailability, less than 1% and proven efficacy, thus can be considered as initial therapy for RB. The studies did not reveal a statistically significant relationship between the development of fetal defects and the use of these drugs.
Who are the FDA in the US and why is everyone listening to them?
Everything is very simple (it’s a pity that everything is not so simple with us). I copy the explanation from Wikipedia: “An agency of the US Department of Health and Human Services, one of the federal executive departments. The department is engaged in quality control of food products, medicines, cosmetics, tobacco products and some other categories of goods, and also monitors compliance with legislation and standards in this area.
Budesonide (Tafen Nasal) is classified as category B according to the FDA's classification for drug effects on the fetus, which means that there is evidence that the drug is safe to use during pregnancy. The bioavailability of budesonide is 33%. This drug has moved from group C to group B, thanks to several high-quality studies in Sweden since the beginning of the 21st century, proving its safety.
The bioavailability of budesonide is 33%. This drug has moved from group C to group B, thanks to several high-quality studies in Sweden since the beginning of the 21st century, proving its safety.
Also, according to the current recommendations of the American Academy of Allergology and Immunology (AAAAI), ICS are considered safe and effective in the treatment of rhinitis and rhinosinusitis during pregnancy. But at the same time, there is no indication of specific drugs. Other competent medical associations also do not give any recommendations in terms of choosing a drug. Therefore, summing up all of the above, and also according to the latest review, mometasone, fluticasone, budesonide can be considered as safe and effective agents in the treatment of RB. It should also be noted that an experienced ENT doctor should be involved in prescribing the drug and managing the patient, since these drugs are sold without a prescription in the Russian Federation; we strongly recommend not to self-medicate.