Bright red blood early pregnancy
First Trimester Bleeding: Causes and Treatment
In the first trimester — the first three months of pregnancy — your body undergoes some pretty dramatic changes.
While you may still be able to fit into your regular pants, there’s a lot going on inside your body. This includes surging hormone levels and building a new blood flow system. With so much happening, first trimester bleeding is common.
According to one large 2009 study, 30 percent women have spotting or light bleeding in the first trimester. This can be a very normal part of early pregnancy. Many women experience some bleeding and go on to have healthy pregnancies.
There are several reasons why you might find vaginal spotting or bleeding in the first trimester. Let’s take a look at some of the common causes.
Spotting or light bleeding is usually not anything to worry about, especially if it lasts for a day or two. One dated research study showed that women who have spotting and light bleeding in the first trimester have similar pregnancies to women who don’t bleed.
On the other hand, heavy bleeding and other symptoms may be indicators of more serious conditions.
Implantation bleeding
Implanting means the fertilized egg is busy making use of the space and burrowing into the side of your womb (uterus). This happens about 6 to 12 days after you’ve conceived. The fertilized egg floats into its new home and must attach itself to the uterine lining to get oxygen and nutrition.
This settling in can cause light spotting or bleeding. Implantation bleeding usually happens just before you expect your period to begin. In fact, this kind of bleeding is often mistaken for a light period.
Distinguishing between implantation bleeding and your period can be challenging. It doesn’t help that other symptoms are similar to PMS:
- mild cramping
- lower backache
- headaches
- nausea
- tender breasts
But there are some clues that what you’re seeing isn’t a typical period. Implantation bleeding is usually lighter in color than a period — a light pink to a dull brown. It typically lasts from a few hours to a couple days and doesn’t involve heavy bleeding.
It typically lasts from a few hours to a couple days and doesn’t involve heavy bleeding.
Cervical polyp
About 2 to 5 percent of women have polyps — small, finger-like growths — on the cervix, the gateway from the vagina to the uterus.
Cervical polyps are usually benign — they don’t cause cancer. However, they can get inflamed or irritated and lead to bright red bleeding. Or you may not have any other symptoms at all, but they’re easy to diagnose during a routine pelvic exam.
Intercourse or a physical exam
Speaking of pelvic exams, keep in mind that anything that might poke at or near the cervix can also irritate it and cause bleeding. Yes, this includes sex! This happens because pregnancy hormones may make your cervix — along with many other things — more sensitive than normal.
You might see bright red blood on your underwear shortly after sex or a physical checkup. Don’t fret! The bleeding usually happens once and then goes away on its own.
Miscarriage
Sometimes what begins as spotting or lighter bleeding becomes heavy bleeding. It’s true that any heavy bleeding in the first trimester, especially if you also have pain, might be linked to a miscarriage. Most miscarriages happen in the first trimester of pregnancy.
Up to 20 percent of all pregnancies are miscarried. You can’t prevent most miscarriages, and they’re definitely not your fault or a sign that something’s wrong with you. Most women can and do go on to have a healthy pregnancy and baby.
If you’re going through a miscarriage, you might have symptoms like:
- heavy vaginal bleeding
- bleeding that is bright red to brown in color
- pain in the lower stomach
- dull or sharp pain in the lower back
- severe cramping
- passing clots of blood or tissue
If you have any of these symptoms, call your doctor. You can have bleeding and other symptoms of a miscarriage without having miscarried. This is called a threatened abortion (abortion is a medical term here).
Causes of threatened abortion include:
- a fall or trauma to the stomach area
- an infection
- exposure to certain medications
Carrying multiple babies
If you’re pregnant with twins (or another multiple of babies), you might have a greater chance of first trimester bleeding due to causes like implantation bleeding.
Miscarriages in the first trimester are also more common when you’re pregnant with more than one baby.
On the other hand, a 2016 study that followed more than 300 women who were pregnant with twins from in-vitro fertilization (IVF) found that they had a high chance of healthy pregnancies. Bleeding in the first trimester didn’t affect this.
Ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy happens when the fertilized egg mistakenly attaches somewhere outside the womb. Most ectopic pregnancies are in the fallopian tubes — the connections between the ovaries and the womb.
An ectopic pregnancy is less common than a miscarriage. It happens in up to 2.5 percent of all pregnancies. A baby can only grow and develop in the womb, so ectopic pregnancies have to be medically treated.
It happens in up to 2.5 percent of all pregnancies. A baby can only grow and develop in the womb, so ectopic pregnancies have to be medically treated.
Symptoms include:
- heavy or light bleeding
- sharp waves of pain
- severe cramping
- rectal pressure
If you have an ectopic pregnancy, know that there’s nothing you did to cause it.
Molar pregnancy
Another cause of bleeding in your first trimester is a molar pregnancy. This rare but serious complication happens in almost 1 in every 1,000 pregnancies.
A molar pregnancy or “mole” happens when the placental tissue grows abnormally due to a genetic error during fertilization. The fetus may not grow at all. A molar pregnancy can cause a miscarriage in the first trimester.
You might have:
- bright red to dark brown bleeding
- lower stomach pain or pressure
- nausea
- vomiting
Subchorionic hemorrhage
Subchorionic hemorrhage, or hematoma, is bleeding that happens when the placenta slightly detaches from the wall of the womb. A sac forms in the gap between the two.
A sac forms in the gap between the two.
Subchorionic hemorrhages vary in size. Smaller ones are the most common. Larger ones cause heavier bleeding. Many, many women have hematomas and go on to have healthy pregnancies. But a large subchorionic hemorrhage may also increase the risk of a miscarriage in the first 20 weeks of pregnancy.
Symptoms include:
- light to heavy bleeding
- bleeding may be pink to red or brown
- lower stomach pain
- cramping
Infection
Bleeding in the first trimester might have nothing to do with your pregnancy at all. An infection in your pelvic area or in the bladder or urinary tract can also cause spotting or bleeding. They may be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi.
A serious yeast infection or inflammation (vaginitis) can also cause bleeding. Infections typically cause spotting or light bleeding that is pink to red in color. You may have other symptoms like:
- itching
- lower stomach pain
- burning when urinating
- white discharge
- bumps or sores on the outer part of the vagina
Bleeding in the second or third trimester of your pregnancy is normally more serious than first trimester light bleeding.
Causes include:
- Cervix problems. Inflammation or growths on the cervix can cause light bleeding. This is usually not serious.
- Placental abruption.The placenta detaches from the womb wall before or during labor. This happens in just 1 percent of pregnant women.
- Placenta previa. The placenta is too low in the uterus and partly covers the cervix. Bleeding happens without pain.
- Vasa previa. Some of the placenta’s blood vessels go across the cervix.
- Premature labor: Bleeding may mean that you’re in labor too early.
- Missed abortion. A miscarriage may have happened earlier without any signs.
Let your doctor know if you experience any kind of bleeding during pregnancy. Get immediate medical care if you have any of these symptoms:
- heavy bleeding
- discharge with clots or tissue
- severe pain
- intense cramping
- severe nausea
- dizziness or fainting
- chills
- fever of 100.
 4°F (38°C) or higher
4°F (38°C) or higher
What your doctor will look for
A quick examination can usually tell your doctor what is causing your bleeding. You may need:
- physical exam
- ultrasound
- Doppler ultrasound exam
- blood test
Your doctor will likely also look at pregnancy markers. A blood test looks at your hormone levels. The main hormone in pregnancy — made by the placenta — is human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
Too much hCG can mean:
- twin or multiple pregnancy
- molar pregnancy
Low levels of hCG may mean:
- ectopic pregnancy
- possible miscarriage
- abnormal growth
Scans can show where the developing baby is and how it’s growing. The baby’s size can be measured on an ultrasound. The heartbeat can be checked with the ultrasound or Doppler scan as early as five and a half weeks of pregnancy. All these checks can reassure you and your doctor that everything is just fine.
Some issues that cause first trimester bleeding, like a cervical polyp, may be treated right in your doctor’s office. Other issues may need more treatment, medication, or surgery.
If the bleeding is a sign that your pregnancy can’t safely continue, your doctor may prescribe medications such as:
- Methotrexate is a drug that helps your body absorb harmful tissue like in an ectopic pregnancy.
- Misoprostol is used to end a dangerous pregnancy in the first 7 weeks.
You’ll need follow-up appointments to check on your health. Your doctor will make sure there is no leftover tissue or scarring in your womb. Your doctor can advise when it’s safe to try to conceive again if that’s what you want.
A miscarriage at any point in your pregnancy is a loss. Talking to a therapist or counselor can help you and your partner grieve in a healthy way.
Bleeding in your first trimester can be alarming. But in most cases, spotting and light bleeding are just a normal part of early pregnancy.
Heavy bleeding may be a sign of something more serious. You should always see your doctor if you have any questions or concerns regarding bleeding.
Causes of first trimester light bleeding and spotting that are usually not harmful to you and your baby include:
- implantation
- cervical polyps
- uterine infections
- yeast infection
- carrying multiple babies
More serious causes of bleeding in the first trimester are:
- miscarriage
- threatened abortion
- molar pregnancy
- ectopic pregnancy
- subchorionic hemorrhage (in many cases, women go on to have healthy pregnancies)
Pregnancy can be a roller coaster of emotions and symptoms. Above all, keep people you love and trust in the loop. Having someone to talk to about what you’re going through — even if your symptoms are completely normal — can make the experience much easier.
How Much Bleeding Is Normal In Early Pregnancy?
Light amounts of vaginal bleeding early in your pregnancy can occur. In most cases, it’s not serious. It can happen in the first 20 weeks for different reasons. It can be the result of something serious or non-serious. Continued bleeding throughout the pregnancy is not common. Call your doctor immediately if you are bleeding heavily. Go to the emergency room if you have severe pain.
In most cases, it’s not serious. It can happen in the first 20 weeks for different reasons. It can be the result of something serious or non-serious. Continued bleeding throughout the pregnancy is not common. Call your doctor immediately if you are bleeding heavily. Go to the emergency room if you have severe pain.
Path to improved health
Vaginal bleeding can happen from conception to delivery. Spotting is a type of light bleeding. You may see just a few drops of blood in your underwear. Heavy bleeding is more noticeable. It will require a sanitary pad to protect your clothing.
Call your doctor whenever you experience bleeding of any kind. Call your doctor if you have vaginal bleeding or spotting. This is important even if an ultrasound test confirms your pregnancy is normal. An ultrasound is where a technician moves a wand around your stomach to see an image of the baby.
Non-serious reasons for bleeding early in your pregnancy can include:
- Implantation (as the egg settles into your uterus the first 6-12 days)
- Sex
- Infection
- Hormones.
More serious causes of vaginal bleeding during the early part of pregnancy can include:
- An ectopic pregnancy (a pregnancy that starts outside the uterus and will not survive but can be life threatening).
- A miscarriage (losing the baby early in a pregnancy).
- A molar pregnancy (a fertilized egg that implants in the uterus that does not live).
In later pregnancy, the following serious medical conditions can cause vaginal bleeding:
- Placental abruption (the placenta detaches from the wall of the uterus before birth).
- Placenta previa (the placenta is lying too low in the uterus and nearly covers the cervix).
- Placenta accreta (when the placenta invades the uterus and doesn’t separate from the uterine wall).
- Preterm labor (labor that starts before completing 37 of 40 weeks of pregnancy).
Bleeding may be just one sign of preterm labor. Preterm labor also can include vaginal discharge, pressure in your pelvis or abdomen (lower stomach), a dull backache, cramps, contractions, and your water breaking.
If you are bleeding early in your pregnancy, your doctor will want to know how long and how much. If you have cramps and pain early in the pregnancy, he or she will order tests. This may include an ultrasound, blood, and urine tests.
If continued bleeding is not serious, your doctor may treat it by recommending that you rest, relax, stay off your feet, and not have sex. Keep your body healthy. Take a prenatal vitamin with folic acid daily while pregnant. Take it earlier if you plan to get pregnant. Avoid smoking, drinking alcohol, and taking illegal drugs. Talk to your doctor before taking prescription medicine. When you are pregnant, you should never douche (use vaginal cleansing products) or use tampons. Serious bleeding may need to be treated with a long-term bed rest, hospitalization, or surgery.
You cannot prevent a miscarriage after it has started. The exact cause is usually unknown. It’s rarely something the mother did wrong. Most women can have healthy pregnancies in the future. If you have lost more than 3 pregnancies, talk to your doctor.
If you have lost more than 3 pregnancies, talk to your doctor.
Things to consider
If you experience bleeding or spotting at any time during your pregnancy, your doctor will want to collect as much information as possible. That will include:
- How far along is your pregnancy?
- Have you had bleeding at any other time during your pregnancy?
- When did the bleeding start?
- Is the bleeding heavy or spotting?
- Does it start and stop?
- How much blood is there?
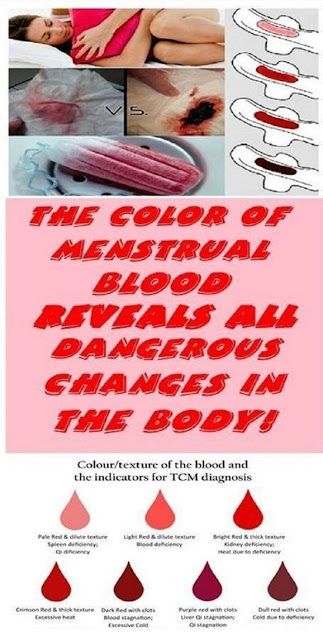
- What color is the blood (bright red or dark brown)?
- Does the blood have an odor?
- Do you have cramps or pain?
- Do you feel weak, tired, faint, or dizzy?
- Have you experienced vomiting, nausea, or diarrhea?
- Do you have a fever?
- Were you recently injured (such as a fall or car accident)?
- Have you engaged in any physical activity?
- Are you under extra stress?
- When did you last have sex? Did you bleed afterward?
- Do you have a bleeding disorder? Women with bleeding disorders are at risk of complications during and after pregnancy.
 This includes iron-deficiency anemia, bleeding during pregnancy, and serious bleeding after delivery (postpartum hemorrhage). Talk to your doctor before getting pregnant if you have a bleeding disorder. Also, bleeding disorders are genetic.
This includes iron-deficiency anemia, bleeding during pregnancy, and serious bleeding after delivery (postpartum hemorrhage). Talk to your doctor before getting pregnant if you have a bleeding disorder. Also, bleeding disorders are genetic. - What is your blood type? If your blood type is Rh negative, you will need treatment with a medicine called Rho(D) immune globulin. This prevents complications with future pregnancies.
Vaginal bleeding is usually blood without clots or tissue. If you see something other than blood, call your doctor immediately. Try to collect the discharge in a container and bring it with you when you see your doctor. It may mean you have miscarried. If that is the case, your doctor will provide additional care. If not all the tissue from the miscarriage has passed, your doctor may need to perform a procedure. This procedure is called a dilation and curettage (D and C). It involves opening (dilating) the cervix. Your doctor will gently suction out the remaining tissue from the miscarriage.
Questions to ask your doctor
- Can certain foods (such as spicy foods) cause bleeding?
- Is it best to avoid having sex throughout your entire pregnancy?
- Is spotting during later pregnancy normal?
- Is my life at risk?
- I feel sad. Is there someone I could talk to about my feelings? Is there a support group?
Resources
U.S. National Library of Medicine, Vaginal bleeding in early pregnancy
March of Dimes, Bleeding and Spotting From the Vagina During Pregnancy
Copyright © American Academy of Family Physicians
This information provides a general overview and may not apply to everyone. Talk to your family doctor to find out if this information applies to you and to get more information on this subject.
Pathological and physiological causes of bleeding during early pregnancy
The gestation period is a complex process that does not always go well. Every second woman has various complications. Most often, women go to the doctor with complaints of spotting. Why does bleeding occur during early pregnancy, how dangerous is it?
Most often, women go to the doctor with complaints of spotting. Why does bleeding occur during early pregnancy, how dangerous is it?
Causes of bleeding in pregnancy
Blood in the first trimester of pregnancy in the vaginal secretion is observed in 30% of expectant mothers. Bleeding can be weak, spotting, plentiful.
Most often, blood during early pregnancy is observed during implantation of the fetal egg. When the egg is attached, the vessels are often damaged, which leads to the appearance of blood secretions. They are similar to menstruation, last 1-2 days. This process is considered natural, does not indicate any pathologies.
Any bloody discharge during early pregnancy is a reason for an urgent appeal to a gynecologist. Even if there is no additional discomfort. At a remote consultation, our doctor will collect an anamnesis, draw up a clinical picture in order to identify the cause of bleeding. And he will select effective methods to eliminate the problem.
Blood during pregnancy - other common causes
In addition to the main ones, there are some other reasons why pathology can develop.
| No. | Cause |
| one | Excessive exercise, deep penetration during intercourse. If the cervix is damaged, slight red discharge occurs, which disappears within two hours. |
| 2 | Progesterone deficiency. With a low level of the hormone, the body starts the process of menstruation. Bloody discharge during pregnancy appears when the uterine mucosa is exfoliated. The situation may adversely affect the implantation of the fetal egg. |
| 3 | Miscarriage - occurs in 2-8% of pregnant women. It is characterized by pain in the lower abdomen, which is rapidly increasing, bloody discharge at the beginning of pregnancy. |
| four | Ectopic pregnancy. Dangerous condition, urgent hospitalization is required. |
| 5 | A failed miscarriage. Blood discharge during pregnancy, abdominal pain are the main manifestations of intrauterine development of the fetus. |
| 6 | Infections. To avoid dangerous complications, it is necessary to treat diseases. Parents of both sexes should be tested. |
| 7 | Full or partial hydatidiform mole. Pathology of the chorion, in which the size of the villi increases, bubble expansions form. The risk group includes women with ovarian dysfunction, inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system, and a history of cystic mole. |
| eight | Cervical cancer. Pregnant women are rarely diagnosed. The risk group includes women with a large number of abortions and childbirth, often changing sexual partners. |
| 9 | Subchorionic hematoma. Hemorrhage around the placenta most often resolves on its own. But it increases the risk of preterm birth and other complications. |
| ten | Cervical erosion. Detected in 50% of women. For pregnant women, the disease is not dangerous, but constant medical supervision is needed. |
Bleeding in the first trimester can be caused by causes that appear at any gestational age. These are fibroids, polyps in the uterus and cervical canal, cardiovascular pathologies that are associated with a weakening of the endothelium.
Physiological or pathological bleeding during gestation - differences
Clinical manifestations of bleeding in pregnant women depend on the causes. Physiological discharge of blood from the genital tract in the early stages of gestation proceeds without deterioration in well-being. With bleeding caused by erosion, fibroids and polyps, there are also no additional discomfort. In this case, only a few drops of blood are released, it bleeds for a short time.
Abundant bleeding, similar to menstruation, against the background of a general satisfactory condition, occurs with a deficiency of progesterone.
Bleeding with spontaneous interruption is accompanied by constant or periodic pain in the lumbar region, abdomen. Disturbed by nausea, bouts of dizziness, slightly increased body temperature. Bleeding can be weak or intense, and clots are often observed in the discharge.
When a fertilized egg is fixed outside the uterus, internal bleeding often occurs, and discharge from the genital tract may appear much later. Characteristic manifestations - acute pain in the abdomen radiates to the anal region, right or left side, blood pressure decreases, cold sweat appears, fainting is possible. Significant blood loss leads to the development of a state of shock with a high probability of death.
Characteristic manifestations - acute pain in the abdomen radiates to the anal region, right or left side, blood pressure decreases, cold sweat appears, fainting is possible. Significant blood loss leads to the development of a state of shock with a high probability of death.
Learn more about implantation bleeding
Why does it bleed at the initial stages of gestation? Most often, the appearance of spotting during pregnancy is associated with the implantation of the embryo. They occur 6-12 days after conception and are often one of the first signs of conception.
Usually, the appearance of spotting at the beginning of pregnancy coincides with the time of the onset of menstruation, if the cycle is regular. But discharge in pregnant women is not as abundant as menstrual bleeding. Duration - from several hours to three, with the first pregnancy up to 5 days.
How does implantation bleeding manifest?
- weak, pulling pain in the lower abdomen;
- headache, dizziness;
- sudden change of mood;
- bouts of nausea;
- increased sensitivity, swelling of the mammary glands;
- fatigue, drowsiness.
Important! When the embryo is implanted, little blood is released, usually these are small spots. The discharge may be pink, brown, orange, and there should be no clots.
Possible causes of early bleeding by week
The first months of pregnancy are the most difficult and dangerous. It is in the early stages that various pathologies and complications often appear.
Why blood may appear in the early stages during pregnancy:
- At the 4th week of pregnancy, discharge with an admixture of blood may appear - this is implantation bleeding. Heavy bleeding is a dangerous sign, most often indicates a miscarriage. Spontaneous abortion can be caused by exercise, fever, infections, drugs or alcohol. Such bleeding is profuse, painful, blood clots are present.
- The appearance of sanious discharge at the 5th week of pregnancy may be a sign of a missed pregnancy. The reasons are overwork, Rh conflict, bad habits, bacterial and viral diseases of the reproductive system, genetic disorders in the embryo.
 Symptoms - causeless fever, severe pain in the lower back and lower abdomen, the disappearance of signs of toxicosis.
Symptoms - causeless fever, severe pain in the lower back and lower abdomen, the disappearance of signs of toxicosis. - Blood in the discharge at the 6th week of pregnancy appears with an ectopic attachment of the fetal egg, fetal fading, Rhesus conflict. Discharge with blood at 6 weeks of pregnancy is a reason for an urgent visit to the gynecologist.
- At the 7th week of pregnancy, discharge with blood is not the norm. May indicate a miscarriage, missed or ectopic pregnancy.
- From the 8th week of pregnancy, one of the most dangerous periods of pregnancy begins. The formation of the placenta begins, the hormonal background changes. Bloody discharge appears with the threat of miscarriage or spontaneous abortion. Pregnancy is often not saved.
Pay attention! In the second trimester, bleeding occurs only in 5-10% of women. Most often this is due to late spontaneous abortion, isthmic-cervical insufficiency. The appearance of blood in the third trimester mainly occurs with presentation, placental abruption.
Early bleeding after IVF
The appearance of blood discharge during pregnancy on the 8-10th day after IVF is not considered a pathology, provided that the woman feels normal. After the introduction of the embryo into the uterine cavity, minor damage to the small uterine vessels often occurs. Brown, dark cream, pale pink, odorless discharge most often indicates a successful transplant, pregnancy.
If spotting after IVF is observed for 1-2 days, slight pulling pains in the lower abdomen are disturbing, this may be due to a progesterone deficiency. After the examination, the doctor will adjust the hormonal maintenance therapy.
Pink discharge on the 16th day after the transfer is a dangerous symptom. It may be a sign of detachment of the fetal egg, the threat of termination of pregnancy.
According to studies, uterine bleeding in the first trimester is a common occurrence in pregnancy after IVF. Discharge does not affect the incidence of adverse reproductive outcomes. The number of embryo rejections in women with and without uterine bleeding is approximately the same. Consult with our doctors by phone for more details.
The number of embryo rejections in women with and without uterine bleeding is approximately the same. Consult with our doctors by phone for more details.
Diagnostics
If blood has gone from the genitals of a pregnant woman, the doctor conducts an external and gynecological examination.
Analyzes and examinations:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- general urine analysis;
- tests for hCG, other hormones;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- CTG is performed to assess the vital activity of the fetus.
Treatment
Methods of treatment depend on the results of the examination.
Bloody discharge in the first trimester - causes and therapeutic measures:
| The reasons | Treatment |
| Miscarriage | Cleansing the uterus. |
| Ectopic pregnancy | Diagnostic laparoscopy, removal of residual fetal tissues, antibiotic therapy. |
| Risk of miscarriage | Hospitalization, bed rest, prescribing drugs to maintain pregnancy, sedatives and tocolytics to reduce uterine tone. |
| bubble skid | Curettage of the uterine cavity. |
| Cervical cancer | Operational intervention. |
| Polyp injury, cervical erosion | Expectant management, if the condition does not worsen, removal and cauterization is carried out after childbirth. |
| progesterone deficiency | hormone therapy. |
| Damage to the uterus | Complete bed rest. |
| Infectious pathologies | Depending on the type of pathogen - antibiotics, antiviral or antifungal drugs. |
Complications and consequences
It is impossible to ignore bloody impurities in vaginal discharge during pregnancy. Without proper and timely assistance, the following complications may occur:
- miscarriage;
- intrauterine fetal death;
- the development of an infectious process, sepsis due to the remainder of dead tissues in the uterine cavity;
- profuse blood loss can lead to death.
Important! Urgent medical attention is needed in case of heavy bleeding, discharge of bright scarlet blood, presence of blood clots in the discharge. In life-threatening and fetal conditions, severe pain in the abdomen, lower back, convulsions, profuse cold sweat, and loss of consciousness are disturbing.
Methods of prevention
If there is blood in the first trimester, it is important to remain calm. Stress and anxiety will only exacerbate the situation. But any health problem is easier to prevent than to treat.
But any health problem is easier to prevent than to treat.
How to avoid bleeding during childbearing - recommendations from a gynecologist:
- eat right and balanced, give up junk and junk food, eat more fresh vegetables and fruits;
- observe the drinking regime;
- in the absence of contraindications, moderate physical activity is indicated - yoga, swimming, special gymnastics for pregnant women;
- more time to walk in the fresh air;
- avoid stress, overwork, observe the daily routine, get enough sleep;
- give up bad habits, do not be in smoky rooms;
- timely visit a gynecologist;
- according to the doctor's prescription, take vitamin complexes for pregnant women;
- do not self-medicate.
The prognosis for bleeding during gestation depends on the causes and timely visit to the doctor. Properly provided medical care can save the life of the fetus and the woman.
FAQ
Why is there blood from the genital tract during gestation?
+
The causes of bleeding in early pregnancy are different. Most often, spotting appears when the fetal egg is fixed, progesterone deficiency, with erosion of the cervix and polyps. Dangerous causes - ectopic, molar, miscarriage, miscarriage.
What to do if there is bleeding during pregnancy?
+
Much depends on the amount of blood released, general well-being. If the bleeding is not strong, not for long, the general condition is normal, it is enough to lie down and rest. Write down the date of the attack, inform the doctor at the next visit. But if even slight spotting during early pregnancy lasts more than 72 hours, is accompanied by cramping or acute pain, fever, you should immediately visit a gynecologist or call an ambulance.
How can you recognize a miscarriage?
+
With the threat of interruption, spotting is scanty, pain in the lower abdomen is absent or may be dull, aching.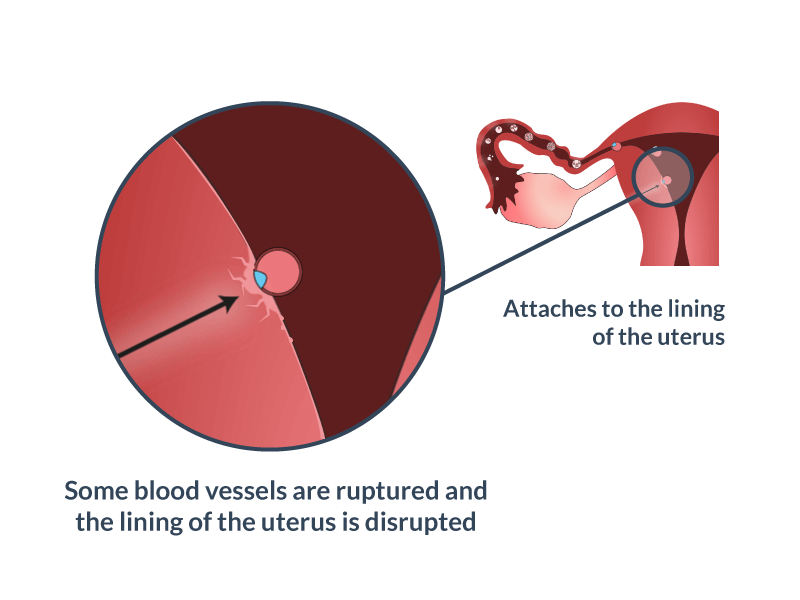 The condition is considered reversible, with timely treatment, pregnancy can be saved. If a miscarriage has begun, bleeding intensifies, cramping pain appears. The general condition is satisfactory. Urgent hospitalization is required, the probability of maintaining pregnancy is decided on an individual basis.
The condition is considered reversible, with timely treatment, pregnancy can be saved. If a miscarriage has begun, bleeding intensifies, cramping pain appears. The general condition is satisfactory. Urgent hospitalization is required, the probability of maintaining pregnancy is decided on an individual basis.
Expert opinion:
Bleeding during pregnancy is a dangerous symptom. Sometimes spotting can be caused by physiological reasons. But often such a symptom appears in life-threatening conditions for the woman and the fetus.
We publish only verified information
Article author
Menshikova Maria Viktorovna obstetrician-gynecologist
Experience 38 years
Consultations 1816
Articles 46
Specialist with extensive practical experience. He has a certificate of a mammologist, a certificate of professional certification. Participates in foreign business trips and individual training programs (Los Angeles).
He has a certificate of a mammologist, a certificate of professional certification. Participates in foreign business trips and individual training programs (Los Angeles).
- 1982 - 1986 NPO MONIIAG - obstetrician-gynecologist
- 1987 - 1989 VNITs OZMIR - obstetrician-gynecologist
- 1989 - 1992 departmental polyclinic st. Moscow - Kurskaya - obstetrician-gynecologist
- 1992 - 2001 NPO MONIIAG - obstetrician-gynecologist
- 2007 - 2008 NP KMIKM - doctor administrator
- 2009 - 2013 Pereslavl Central District Hospital, women's consultation - obstetrician-gynecologist
- 2020 to present Teledoctor24 LLC - doctor - consultant (gynecologist)
Bloody discharge during pregnancy ᐈ Blood during early pregnancy
Seeing bloody discharge, a pregnant woman is always frightened. They are considered a symptom of miscarriage and other equally serious pathologies. At the same time, in some cases, the appearance of a small amount of blood is considered the norm and does not pose a threat to the life and health of the fetus or the expectant mother.
In early pregnancy, bloody discharge occurs in 25% of women. In most cases, they are associated with the implantation of the fetal egg to the wall of the uterus. Also, scanty spotting may appear on the dates of the expected menstruation. If they end quickly, are not accompanied by pain, and the woman has not had miscarriages or pregnancy complications before, most likely she has nothing to worry about. However, it is necessary to consult an obstetrician-gynecologist and undergo an examination.
Why bloody discharge can appear and when it is dangerous, said Elena Petrovna Domnich, obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category, gynecologist-endocrinologist, ultrasound specialist of the ADONIS medical center.
Elena Nikolaevna, tell me, can a woman have periods during pregnancy?
- Sometimes during pregnancy, a woman may experience spotting, but this should not be interpreted as menstruation. Menstruation occurs at the end of the menstrual cycle, during which the endometrium changes, first proliferative, then secretory. During the cycle, the endometrium prepares for pregnancy, and if it does not occur, then menstruation begins.
During the cycle, the endometrium prepares for pregnancy, and if it does not occur, then menstruation begins.
In the event of pregnancy, menstruation is not possible, although bleeding may occur at the expected time. Because of this, some women do not immediately know that they are pregnant. However, when the obstetrician-gynecologist at the reception asks them about the nature of the discharge, it always turns out that they are different from menstrual. As a rule, they are more scarce, pass faster and are not accompanied by other symptoms. Sometimes a woman says that her period was very recent, but at the time of examination and examination, we find that she is already 8 or 12 weeks pregnant.
How often does this happen? Is spotting during pregnancy an exception or a fairly common occurrence?
- Bloody discharge is not common in pregnant women, but still it cannot be said that these are exceptional cases.
Tell me, if a woman is planning to conceive a child, and during the expected period she has unusual discharge, should she take a pregnancy test?
- Yes, but it's better to visit an obstetrician-gynecologist. There are cases when a woman is pregnant, but the test strip shows a negative result. To accurately determine whether there is a pregnancy, allows a blood test for the level of hCG.
There are cases when a woman is pregnant, but the test strip shows a negative result. To accurately determine whether there is a pregnancy, allows a blood test for the level of hCG.
So bleeding during pregnancy is not menstruation, but bleeding? Why can it appear and why is it dangerous?
- Yes, that's right. This is bleeding, not menstruation. It can be a symptom of a miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, or other pathology. For diagnosis, you must consult a doctor.
Tell me more, if a woman has a discharge and thinks she is menstruating, but a previous pregnancy test came back positive, could it be wrong?
- A pregnancy test is sometimes positive even if it is not. This happens if a woman has formed luteal cysts or developed a thyroid disease.
Bloody discharge during pregnancy requires contacting the antenatal clinic or the medical center where the woman was registered for pregnancy management.
 The causes of the pathological condition can be different - infectious diseases, fetal malformations that are incompatible with life, dehydration, abdominal trauma, taking certain drugs.
The causes of the pathological condition can be different - infectious diseases, fetal malformations that are incompatible with life, dehydration, abdominal trauma, taking certain drugs.  Bleeding is profuse and constant, characteristic blisters are present. The symptoms of early toxicosis are very pronounced, the size of the uterus, the hCG indicators do not correspond to the gestational age.
Bleeding is profuse and constant, characteristic blisters are present. The symptoms of early toxicosis are very pronounced, the size of the uterus, the hCG indicators do not correspond to the gestational age.