Breech position 36 weeks
What happens if your baby is breech?
Babies often twist and turn during pregnancy, but most will have moved into the head-down (also known as head-first) position by the time labour begins. However, that does not always happen, and a baby may be:
- bottom first or feet first (breech position)
- lying sideways (transverse position)
Bottom first or feet first (breech baby)
If your baby is lying bottom or feet first, they are in the breech position. If they're still breech at around 36 weeks' gestation, the obstetrician and midwife will discuss your options for a safe delivery.
Turning a breech baby
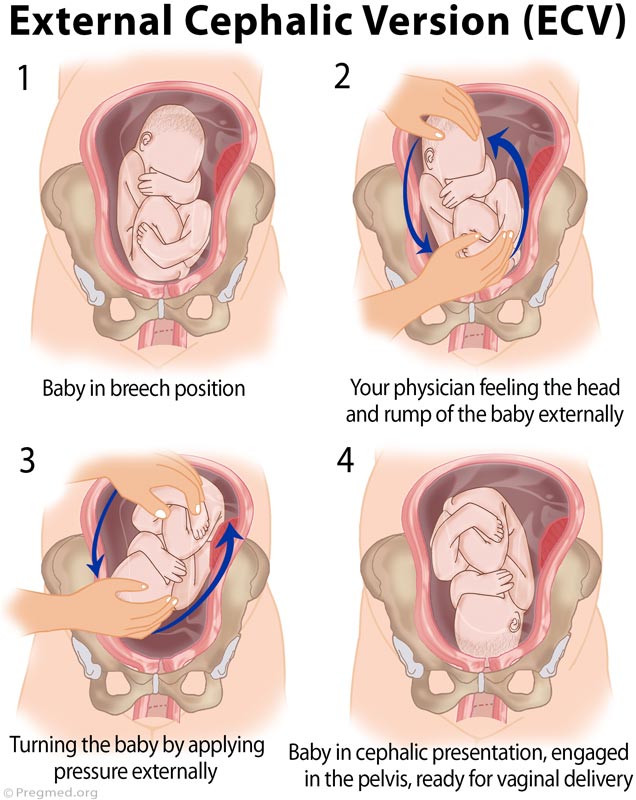
If your baby is in a breech position at 36 weeks, you'll usually be offered an external cephalic version (ECV). This is when a healthcare professional, such as an obstetrician, tries to turn the baby into a head-down position by applying pressure on your abdomen. It's a safe procedure, although it can be a bit uncomfortable. Around 50% of breech babies can be turned using ECV, allowing a vaginal birth.
Giving birth to a breech baby
If an ECV does not work, you'll need to discuss your options for a vaginal birth or caesarean section with your midwife and obstetrician.
If you plan a caesarean and then go into labour before the operation, your obstetrician will assess whether it's safe to proceed with the caesarean delivery. If the baby is close to being born, it may be safer for you to have a vaginal breech birth.
The Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RCOG) website has more information on what to expect if your baby is still breech at the end of pregnancy.
The RCOG advises against a vaginal breech delivery if:
- your baby's feet are below its bottom – known as a "footling breech"
- your baby is larger or smaller than average – your healthcare team will discuss this with you
- your baby is in a certain position – for example, their neck is very tilted back, which can make delivery of the head more difficult
- you have a low-lying placenta (placenta praevia)
- you have pre-eclampsia
Lying sideways (transverse baby)
If your baby is lying sideways across the womb, they are in the transverse position. Although many babies lie sideways early on in pregnancy, most turn themselves into the head-down position by the final trimester.
Although many babies lie sideways early on in pregnancy, most turn themselves into the head-down position by the final trimester.
Giving birth to a transverse baby
Depending on how many weeks pregnant you are when your baby is in a transverse position, you may be admitted to hospital. This is because of the very small risk of the umbilical cord coming out of your womb before your baby is born (cord prolapse). If this happens, it's a medical emergency and the baby must be delivered very quickly.
Sometimes, it's possible to manually turn the baby to a head-down position, and you may be offered this.
But, if your baby is still in the transverse position when you approach your due date or by the time labour begins, you'll most likely be advised to have a caesarean section.
Video: My baby is breech. What help will I get?
In this video, a midwife describes what a breech position is and what can be done if your baby is breech.
Media last reviewed: 7 February 2020
Media review due: 7 February 2023
Page last reviewed: 12 November 2020
Next review due: 12 November 2023
Causes, Complications, Turning & Delivery
Overview
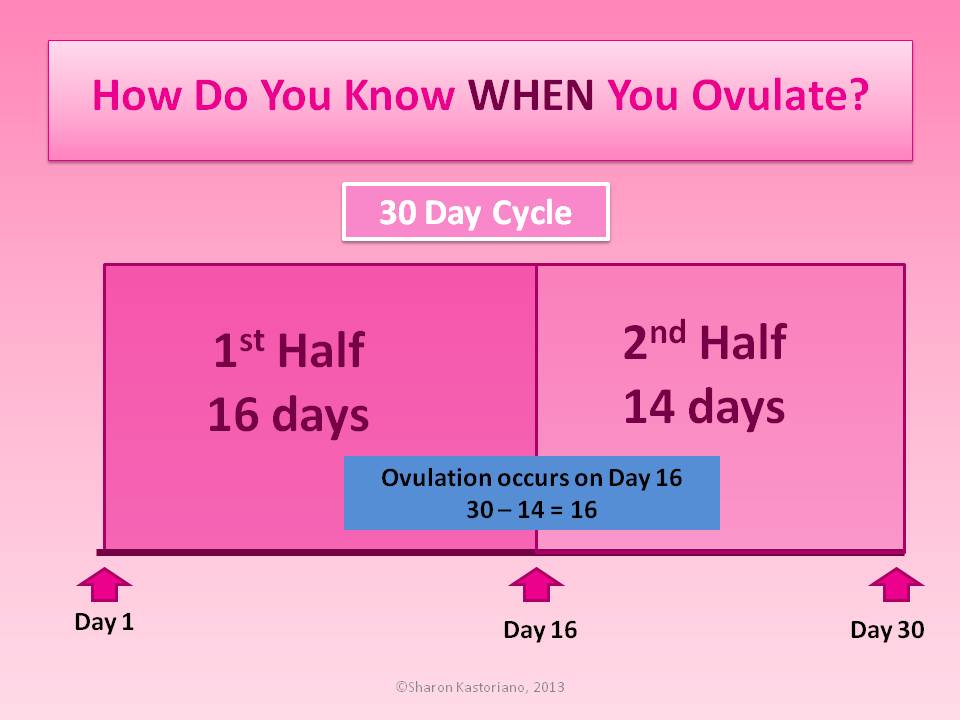
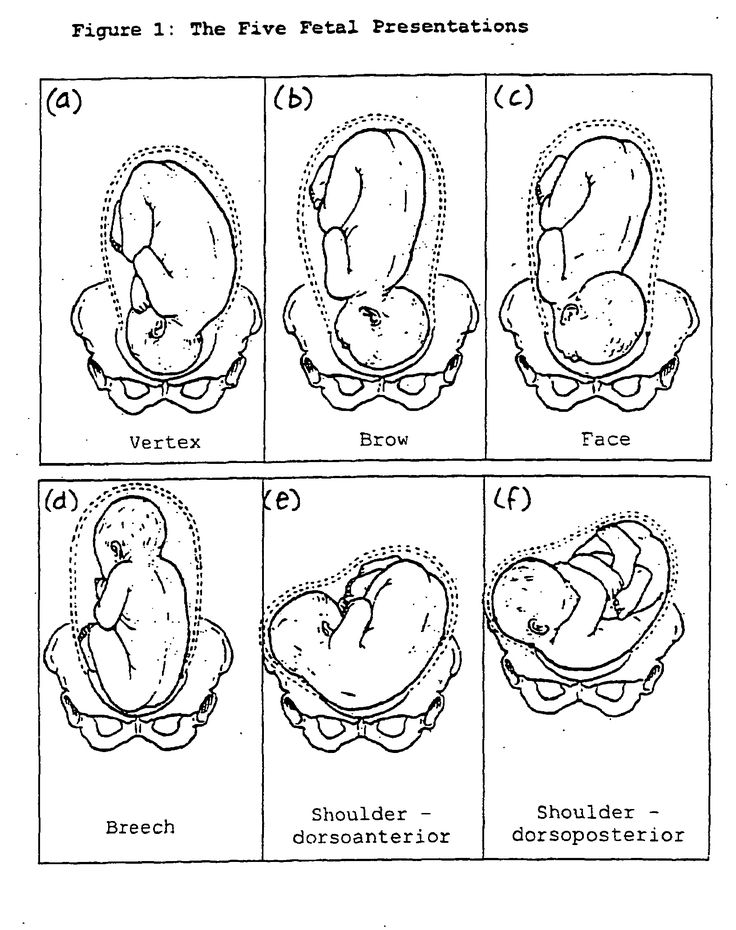
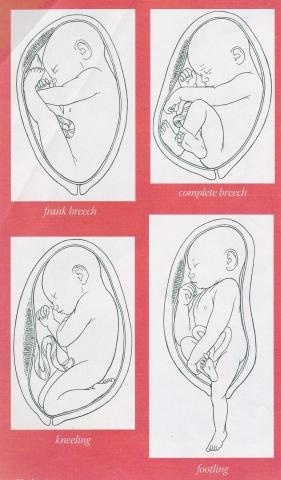
Types of breech positions during pregnancy.What is a breech baby?
A breech baby, or breech birth, is when your baby’s feet or buttocks are positioned to come out of your vagina first. Your baby’s head is up closest to your chest and its bottom is closest to your vagina. Most babies will naturally move so their head is positioned to come out of the vagina first during birth. Breech is common in early pregnancy and most babies will move to a head-first position by 36 weeks of pregnancy. This head-first position is called vertex presentation and is the safest position for birth.
How common is a breech baby?
There is a small chance that your baby will not move into a head-first position before 37 weeks of pregnancy.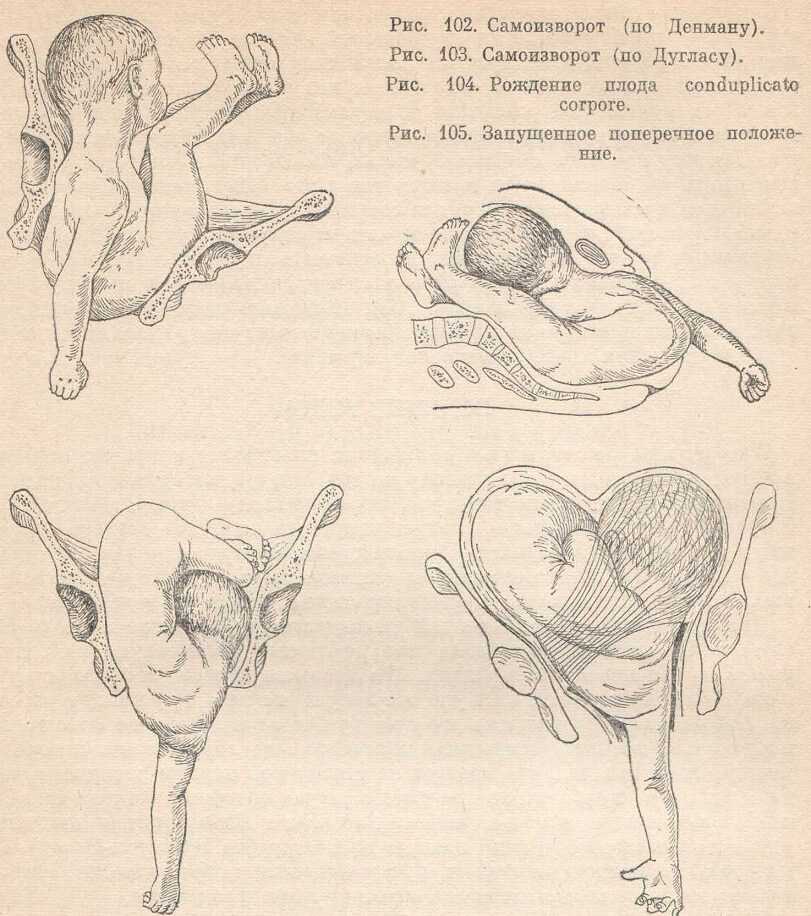 Breech babies account for about 3% to 4% of all full-term pregnancies.
Breech babies account for about 3% to 4% of all full-term pregnancies.
What are the types of breech position a baby can be in?
There are several fetal positions your baby may present in. Ideally, your baby is positioned head-down, facing your back, with their chin tucked to their chest.
Breech babies can be in a few different positions:
- Frank breech: The baby’s buttocks are aimed at the vaginal canal with its legs sticking straight up in front of their body and the feet near their head.
- Complete breech: The baby’s buttocks are pointing downward and both the hips and the knees are flexed (folded under themselves).
- Footling breech: One or both of the baby’s feet point downward and will deliver before the rest of their body.
- Transverse lie: This is a form of breech presentation where your baby is positioned horizontally across your uterus instead of vertically. This would make their shoulder enter the vagina first.
How does a breech baby affect pregnancy?
Your pregnancy is usually not affected. Most breech babies are born healthy, although there is a slightly elevated risk for certain birth defects. Your baby’s movements may feel a little different. You will feel your baby’s kicks lower in your belly. You may feel a hard lump closer to your ribs. This is your baby’s head.
If you planned a vaginal delivery, a breech baby could change these plans. When your baby is breech, a vaginal delivery can be complicated and dangerous. Your healthcare provider may feel comfortable attempting a vaginal breech delivery, but in most cases, they will recommend a Cesarean birth (C-section).
How does a breech baby affect delivery?
If your baby presents in a breech position after 36 weeks of pregnancy, your birthing plan will likely change. It's usually unsafe for a breech baby to be born vaginally due to risks of injury. In most cases, a planned C-section is the safest way to deliver your baby. Some healthcare providers may be comfortable with a vaginal breech birth. In some cases, turning your baby to a head-down position while they are still inside your uterus is an option. Your baby is then born head first.
Some healthcare providers may be comfortable with a vaginal breech birth. In some cases, turning your baby to a head-down position while they are still inside your uterus is an option. Your baby is then born head first.
Symptoms and Causes
How can you tell if your baby is breech?
You may be able to tell if your baby is breech, especially if you have had past pregnancies where your baby was head-first. The places where you feel lumps and kicks might indicate that your baby is breech. Let your healthcare provider know where you feel movement. They will feel your belly or do an ultrasound to confirm that your baby is breech.
What causes a baby to be breech?
It’s not always known why a baby is breech. Some factors that may contribute to this position are:
- You are expecting multiples (twins or more). This makes it harder for each baby to get into the right position.
- There is too much or too little amniotic fluid.
- The uterus is not normal in shape or has abnormal growths such as fibroids.
 Most of the time, the uterus is shaped like an upside-down pear. If it's shaped differently, there might not be enough room for a full-grown baby to move into position.
Most of the time, the uterus is shaped like an upside-down pear. If it's shaped differently, there might not be enough room for a full-grown baby to move into position. - The placenta covers all or part of the cervix (a condition called placenta previa).
- The baby is preterm. This means they are less than 37 weeks gestation and may not have turned to a head-first position.
- Your baby has a birth defect that causes them to not turn head-down.
Diagnosis and Tests
How is a breech baby diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider may be able to tell which way your baby is facing by placing their hands at certain places on your abdomen. By feeling where the baby’s head, back and buttocks are, it’s usually possible to find out what part of the baby is positioned to come out of the vagina first. An ultrasound may be used to confirm the baby’s position.
When is a breech baby diagnosed?
Almost all babies are breech at some point. As your pregnancy progresses, your baby will naturally move to a head-down position — probably between 32 and 36 weeks.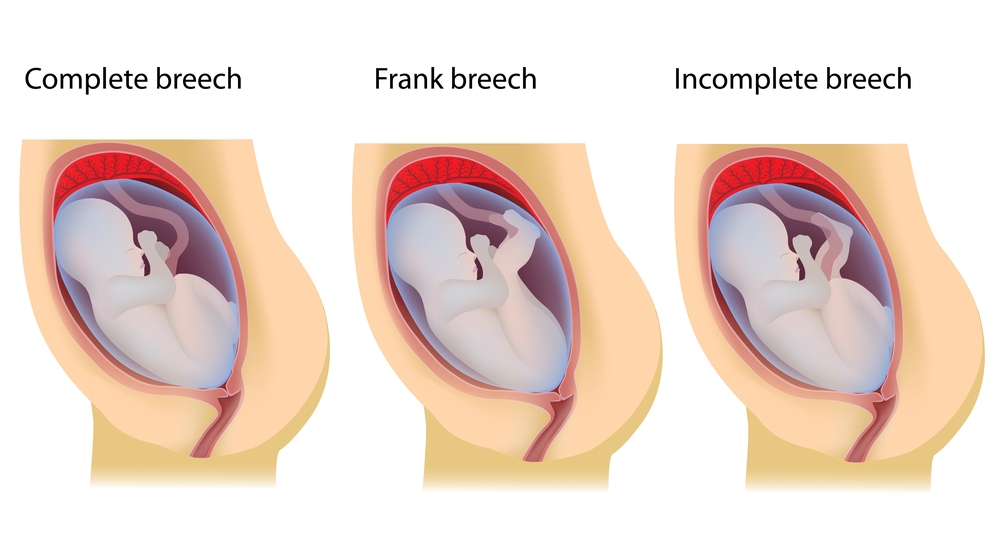 Your healthcare provider will feel your belly and determine where your baby is positioned. This will happen during most of your appointments in the third trimester. After 37 weeks, a breech baby usually does not turn on their own. Your healthcare provider will discuss delivery options with you.
Your healthcare provider will feel your belly and determine where your baby is positioned. This will happen during most of your appointments in the third trimester. After 37 weeks, a breech baby usually does not turn on their own. Your healthcare provider will discuss delivery options with you.
Management and Treatment
What are the options for treating a breech baby?
If your baby is breech at 37 weeks of pregnancy, your healthcare provider may:
- Try turning your baby in your uterus into the head-first position.
- Plan a C-section birth.
- Plan a vaginal breech birth.
What are some complications of having a breech baby?
The complications of having a breech baby usually do not occur until it's time to deliver. Some breech babies can be safely delivered through the vagina.
The risks of attempting a vaginal breech birth are:
- Injuries to your baby’s legs or arms such as dislocated or broken bones.
- Umbilical cord problems.
 The umbilical cord can be flattened or twisted during delivery. This can cause nerve or brain damage due to a lack of oxygen.
The umbilical cord can be flattened or twisted during delivery. This can cause nerve or brain damage due to a lack of oxygen.
Will my doctor try to flip my baby if it's breech?
If your baby is breech, your healthcare provider may consider turning your baby so that you can have a vaginal delivery. In some cases, trying to turn your baby may not be safe or the risks outweigh the benefits.
Flipping your baby may not be safe if you have any of the following:
- Bleeding from your vagina.
- Placenta previa. This is when your placenta covers all or part of your cervix.
- A nonreactive nonstress test.
- An abnormally small baby.
- Low level of amniotic fluid.
- Low or high fetal heart rate.
- Premature rupture of the membranes.
- Twins or multiples.
The most common method used to turn a breech baby is called external cephalic version (ECV). It's performed by your healthcare provider around 37 weeks of pregnancy.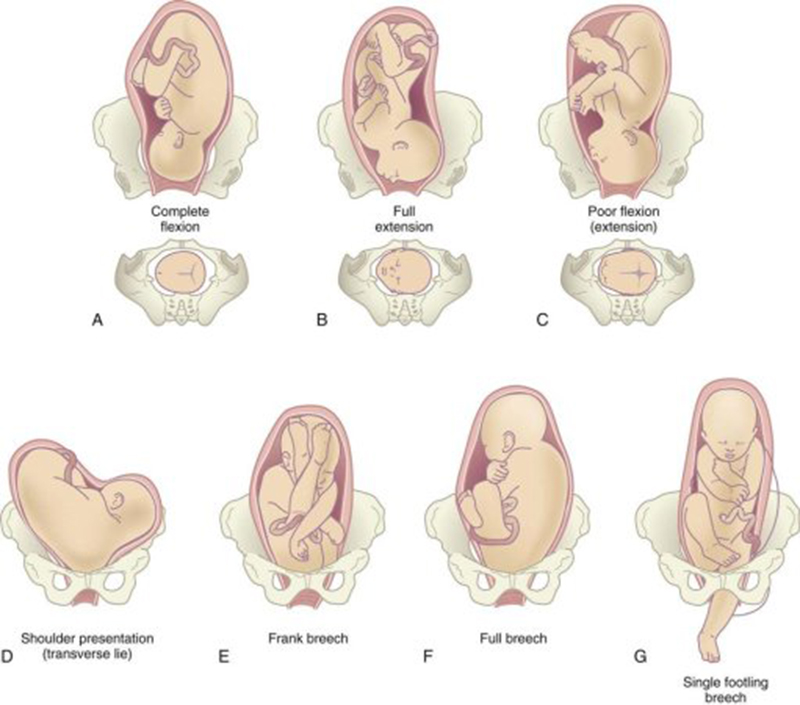 This procedure is performed in the hospital just in case an emergency occurs. It involves placing hands on your abdomen and applying firm pressure to turn your baby to a head-down position while your baby is still in your uterus. It is about 65% effective and carries some risks.
This procedure is performed in the hospital just in case an emergency occurs. It involves placing hands on your abdomen and applying firm pressure to turn your baby to a head-down position while your baby is still in your uterus. It is about 65% effective and carries some risks.
What are the risks of turning my breech baby?
The risks of ECV include the following:
- Premature labor.
- Premature rupture of the amniotic sac.
- Blood loss for either you or your baby.
- Emergency C-section.
- Your baby might turn back to the breech position.
Although the risk of having these complications is small, some healthcare providers prefer not to try to flip a breech baby.
Will my breech baby flip on their own?
Most babies will flip to a head-down position before they reach full term (37 weeks). If your baby is still in a breech position at this time, your healthcare provider will determine if you can deliver vaginally or if you will need a C-section.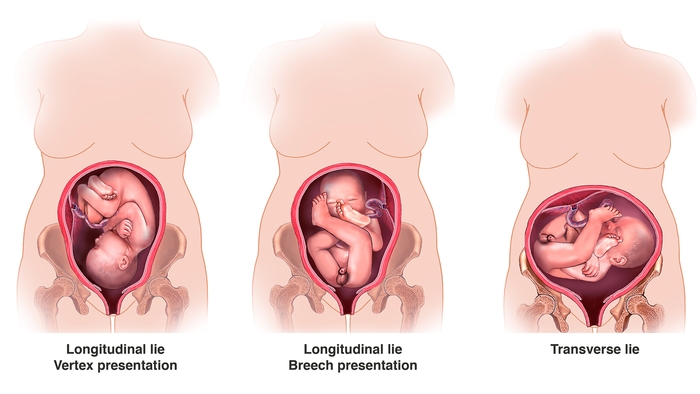
How can I flip my baby if it's breech?
Some women will try at-home methods to flip their baby to a head-first position. They may help, but there is no scientific evidence that they work.
- Bridge position: Lie on the floor with your legs bent and your feet flat on the ground. Raise your hips and pelvis into a bridge position. Hold this position for 10 or 15 minutes several times a day.
- Child’s pose: Rest in the child’s pose for 10 to 15 minutes. It can help relax your pelvic muscles and uterus. You can also rock back and forth on your hands and knees or make circles with your pelvis to promote activity.
- Music: Place headphones or a speaker at the bottom of your uterus to encourage your baby to turn.
- Temperature: Try placing something cold at the top of your stomach where your baby’s head is. Then, place something warm at the bottom of your stomach.
A chiropractic technique, called the Webster technique, can also help your uterus relax.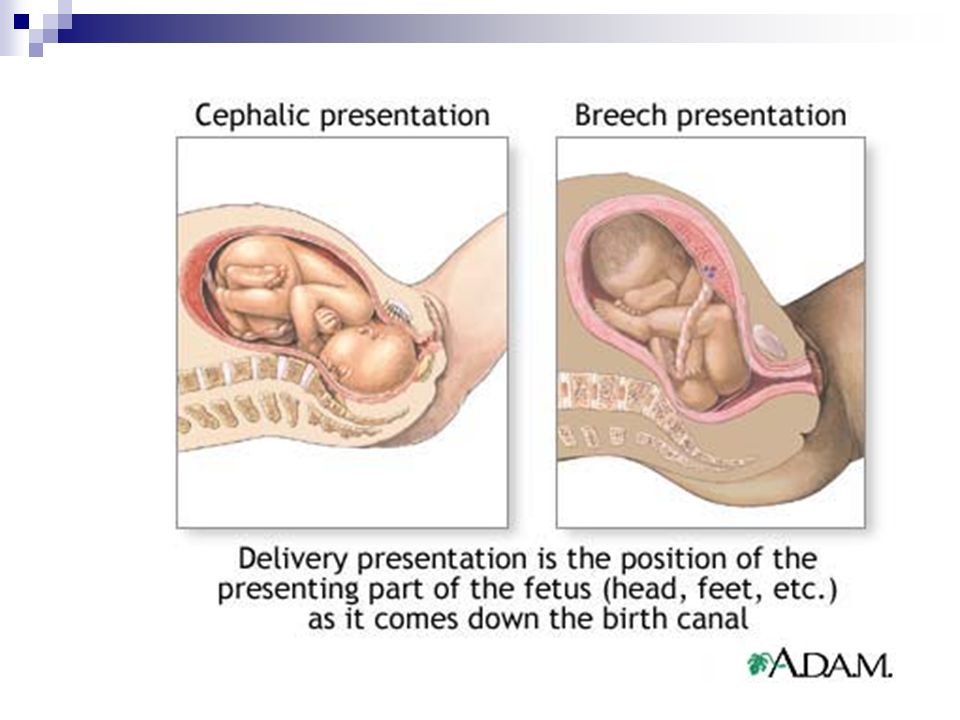 Some providers even recommend acupuncture. Both of these techniques need to be done by a professional that your healthcare provider has recommended.
Some providers even recommend acupuncture. Both of these techniques need to be done by a professional that your healthcare provider has recommended.
Prevention
How can I reduce my risk of having a breech baby?
There is nothing you can do to prevent your baby from being in a breech position. If your baby is in a breech position, it’s not because you did anything wrong.
Outlook / Prognosis
Can you deliver vaginally with a baby breech?
It's possible to deliver a breech baby vaginally. It can be more dangerous for the baby and the risk of injury is much higher. If the umbilical cord is compressed during birth, the baby could be deprived of oxygen and this could harm their brain and nerves. The cord could also slip around the baby’s neck or arms, causing injury. Healthcare providers have various levels of comfort with vaginal deliveries of breech babies. Talk to your provider about the risks and benefits of different types of birth for a breech baby.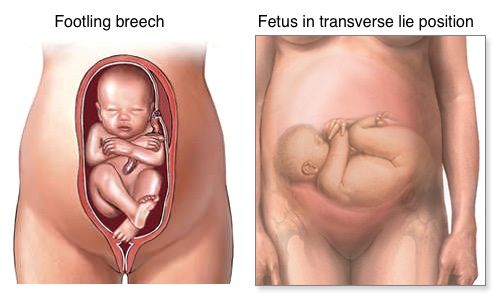
Living With
When should I see my healthcare provider?
Contact your healthcare provider if you experience any of the following symptoms during pregnancy:
- Severe cramping or contractions.
- Vaginal bleeding.
What questions should I ask my doctor?
Learning your baby is breech may give you concerns about your delivery. It’s completely natural to have questions. Some questions to ask your doctor can include:
- How can I tell if my baby is breech?
- Is my baby OK?
- What are the benefits and risks of turning my baby?
- What are my options for delivery if my baby remains in the breech position?
- What are the health risks to my baby and me if they are born breech?
Frequently Asked Questions
Do birth defects cause breech position?
Birth defects are slightly more common in breech babies. It might be the reason that the baby didn’t move to the head-down position. Most babies who are breech at delivery are born without any health complications.
Will I need a C-section if my baby is breech?
Most of the time, a C-section is the safest way to deliver a breech baby. Your risks of developing complications are much higher if you try to deliver a breech baby through the vagina. However, some healthcare providers may feel comfortable performing a vaginal breech birth.
How does labor start if your baby is breech?
Having a breech baby doesn’t change some of the first signs of labor like contractions or rupturing of your membranes. In most cases, your healthcare provider will recommend a planned C-section. If your delivery is planned, you may not have any labor symptoms.
If you are in labor and go to the hospital for delivery, your provider will confirm your baby’s position a final time. Your provider could attempt a vaginal delivery, but it's more likely they will proceed with a C-section to be safe.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Having a breech baby can be unexpected and change the vision you had for childbirth.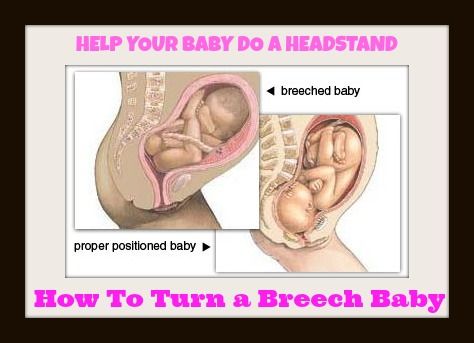 Talk to your healthcare provider about what to expect during a breech delivery. They can help you understand the risks and benefits of a breech birth so that you and your baby are kept safe.
Talk to your healthcare provider about what to expect during a breech delivery. They can help you understand the risks and benefits of a breech birth so that you and your baby are kept safe.
Breech presentation - how to turn the baby
Vatagina Maria Alexandrovna
Obstetrician-gynecologist, Oncogynecologist
Clinical Hospital Lapino-1 "Mother and Child", Clinic "Mother and Child" Mytishchi
Do not worry and worry if a child under 36 weeks is "ass forward": this is completely normal and the baby still has time to roll over. By the way, it happens that the baby turns upside down and immediately before the birth, and even in the birth itself
Try to get the baby to turn into the desired position. Tell everything in detail: why he should turn around, what it will give both mother and child in childbirth. You can talk out loud, or you can talk to yourself, the main thing is to talk to the baby about it all the time
In the water, the mother’s body relaxes, which means that the muscles of the uterus relax, its volume increases somewhat, and as a result, the child has a little more space “for maneuvers ".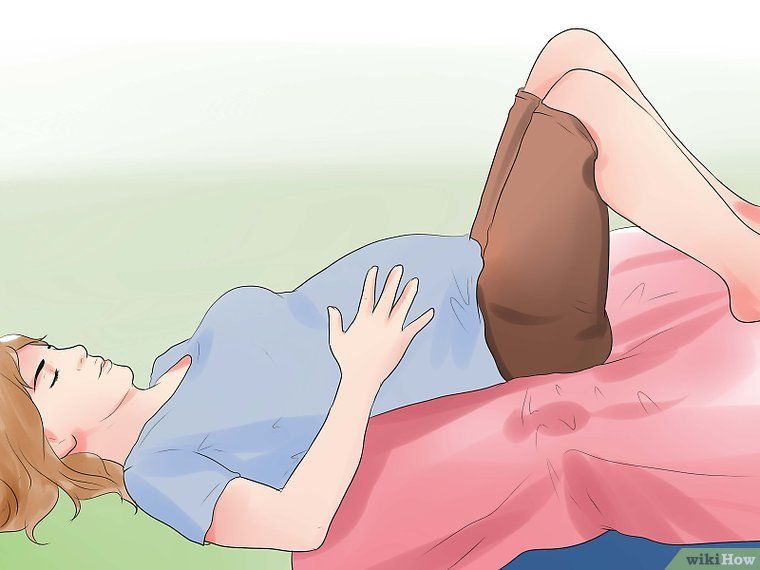
Talk to him
There is always a connection between a child and a mother. And mother is the first person whom the baby believes and obeys. Therefore, try to persuade the baby to turn into the desired position. Tell everything in detail: why he should turn around, what it will give both mother and child in childbirth. You can talk out loud, or you can talk to yourself, the main thing is to talk to your baby about it all the time. Be gentle and at the same time persistent. Be sure to connect the future dad to the conversation, children obey men even more. When you persuade the baby, additionally stroke the stomach, as if instructing the child how to turn around. Great option: dad talks and strokes his stomach with you. nine0003
Imagine
Visualization is a way in which a person imagines a picture he needs. So the expectant mother just needs to imagine the baby in the right position. If you don't know what it looks like or you just can't imagine a baby in your belly - find a beautiful photo from a magazine, book, Internet.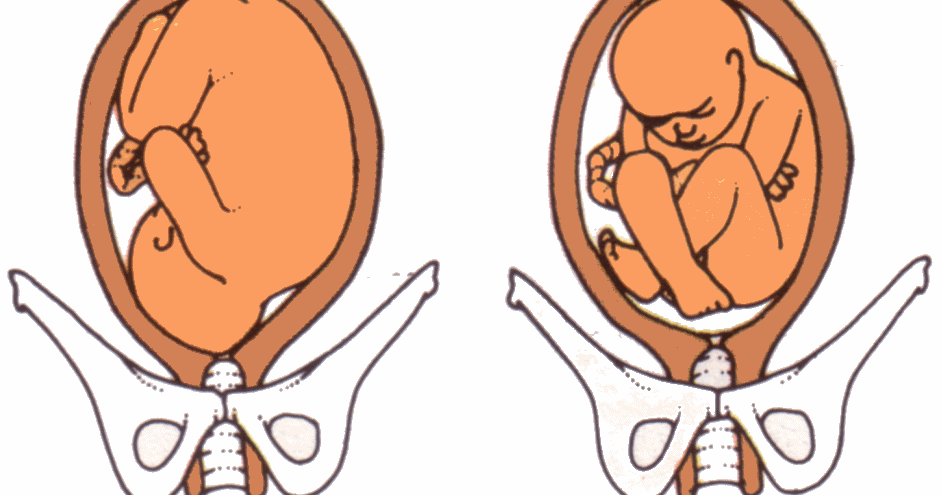 Some kind of anatomical accuracy is not important here, just a pleasant and understandable picture is enough: the baby lies upside down inside the mother's belly. Look at the illustration more often and imagine that inside you the baby is also in the correct position. But you must not only look at someone else's photo, but imagine yourself and your child. nine0003
Some kind of anatomical accuracy is not important here, just a pleasant and understandable picture is enough: the baby lies upside down inside the mother's belly. Look at the illustration more often and imagine that inside you the baby is also in the correct position. But you must not only look at someone else's photo, but imagine yourself and your child. nine0003
Lure him
Another way is to lure the baby. Children, especially small ones, are very curious, so make the baby turn around by showing him something interesting. But the baby is still in the stomach, how can he see something? We do not know exactly how the baby reacts to the world outside the mother's stomach, but it is believed that he, for example, can hear sounds. Place headphones with pleasant music in the lower abdomen, this can also encourage the child to turn towards the sound. Music should be calm, melodic and not loud so that the baby is not scared. nine0003
You can also turn on the flashlight and put it against the mother's stomach in the place where the baby's head is, and then, while talking, slowly move the flashlight to the side and down, dragging the baby along with you.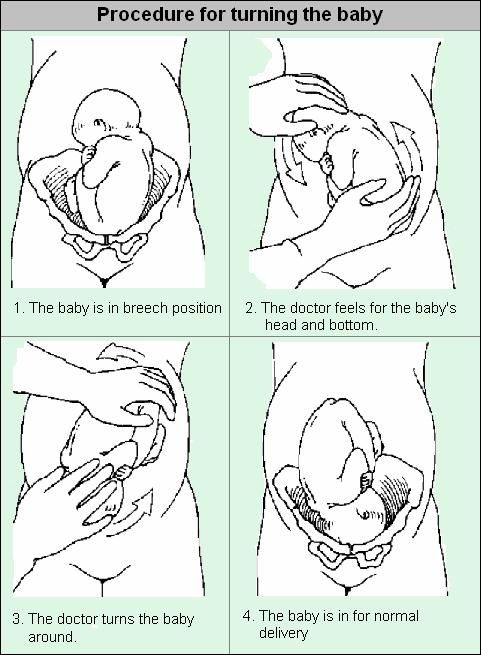
Swim and relax
Swimming also helps your baby get into head presentation. In the water, the mother’s body relaxes, which means that the muscles of the uterus also relax, its volume increases somewhat, and as a result, the child has a little more space “for maneuvers”. But swimming should be pleasant for mom, if a woman is afraid of water or she is not warm enough, then there will be no relaxation. Therefore, you must want to swim, plus the water must be at a comfortable temperature. nine0003
Do the exercises
There are very simple exercises , that will help the baby to fit correctly. But first, check with your doctor if you can do such exercises. Gymnastics to turn the baby into head presentation is not carried out if there is gestosis, the threat of termination of pregnancy, a scar on the uterus after a previous cesarean section, placenta previa.
Turns. Lying on the couch, turn from side to side 3-4 times in 10 minutes. Perform 3 times a day. The turn usually occurs within the first week. nine0003
Perform 3 times a day. The turn usually occurs within the first week. nine0003
Force of attraction. Lie on your back with a large pillow under your lower back and a small one under your head. Bend your knees, placing your feet on the floor. Lie like this for 10 minutes.
Knee-elbow position. Stand on your knees and elbows, at this time the pelvis is located above the head. Stay in this position for 15 minutes several times a day.
Consult a specialist
If exercises and psychological methods do not work, there is another way – prophylactic external rotation performed by an experienced obstetrician-gynecologist in the maternity hospital. First, the mother is injected with drugs that relax the uterus, then the doctor tries to turn the child with certain hand movements, acting on his head and pelvis through the belly of the expectant mother. All this takes place under the control of ultrasound, and usually a woman does not experience any discomfort during this manipulation.
True, external rotation is now rarely performed: firstly, not all obstetricians and gynecologists can do it, and not all doctors believe that it is needed; secondly, not every woman is psychologically tuned in to him, and, besides, there are not always indications for him. nine0003
Psychological methods may seem questionable, but they often help. And if you add gymnastics and swimming, then the likelihood that the baby will turn into the correct position only increases. So if you don’t want to do a cesarean section with a breech presentation or give birth “ass first”, then you should try all the methods that are suitable and allowed for you.
Make an appointment
to the doctor - Vatagina Maria Aleksandrovna
Clinical Hospital Lapino-1 "Mother and Child" Clinic "Mother and Child" Mytishchi
Gynecology
By clicking on the send button, I consent to the processing of personal data
The problem of breech presentation of the fetus.
 External obstetric rotation of the fetus on the head.
External obstetric rotation of the fetus on the head. Breech presentation of the fetus occurs in 3% -5% of cases at full-term pregnancy. Vaginal delivery with breech presentation is associated with high risks both on the mother's side and on the fetus's side. Thus, breech presentation is currently considered pathological, even if the conditions necessary for childbirth through the birth canal are ideally met, and the fetus is relatively small relative to the size of the mother's pelvis. During vaginal delivery, the arms and head of the fetus may tilt back, which can lead to injury. nine0003
Currently the most common method of delivery in breech presentation is a caesarean section (90%). Among the indications for the use of caesarean section, breech presentation ranks third among others in the world. However, this the operation does not make it possible to completely eliminate the risk of trauma to the fetus, since when it is removed, it is also possible to tilt the arms and head of the fetus, and their release requires the use of complex manipulations. nine0003
nine0003
To correct breech presentation today, the world is using EXTERNAL OBTETAL HEAD TURN proposed at the end the century before last by the Russian obstetrician Arkhangelsky B.A.
External obstetric cephalic rotation (EFRT) is a procedure during which the doctor turns the fetus from the outside through the wall of the uterus breech presentation in the head. A successful attempt at NAPP allows women to give birth on their own, avoiding a caesarean section. nine0003
What is required for external cephalic fetal rotation?
External obstetric rotation of the fetus on the head is performed before the onset of labor, usually starting from 36 weeks of pregnancy.
It is necessary to consult a doctor and conduct an ultrasound examination to confirm the fact breech presentation of the fetus and determine the conditions for NAPP, starting from 34-35 weeks of pregnancy.
| The operation of external rotation of the fetus on the head in breech presentation |
When NAPP is possible:
- From 36 to 37 weeks, since with earlier use, it is likely that it will return to the breech presentation.

- In the presence of a singleton pregnancy.
- Subject to the mobility of the buttocks of the fetus (if they are tightly pressed against the entrance to the mother's pelvis, it will be extremely difficult to change the position of the fetus). nine0122
- Sufficient amount of amniotic fluid. With oligohydramnios, this manipulation can be traumatic for the fetus, while with polyhydramnios there is a high probability of a reverse rotation of the fetus in a breech presentation.
- Sufficient amount of amniotic fluid. With oligohydramnios, this manipulation can be traumatic for the fetus, while with polyhydramnios there is a high probability of a reverse rotation of the fetus in a breech presentation.
- Fetal head flexed
When NAPP is not possible:
- With the outflow of amniotic fluid.
- If the patient has contraindications to the use of drugs used to relax the uterus (tocolysis).
- In the presence of obstetric indications or indications from the health of the mother for delivery by caesarean section.
- With the extensor position of the fetal head.
- If the fetus has congenital developmental features. nine0122
- With multiple pregnancy.
- In the presence of structural features of the uterus in a pregnant woman
However, in addition to this, there are a number of factors that may favor or, on the contrary, serve as a contraindication to external obstetric turning the fetus on the head, and which can only be determined by a doctor during a direct examination of a pregnant woman.
How NAPP is conducted
For manipulation, hospitalization in the maternity hospital is necessary. Preliminarily, an additional examination of the pregnant woman is carried out in the required volume, including ultrasound. nine0003
When conducting an NAPP:
Immediately before the start of the manipulation, a CTG is recorded to assess the condition of the fetus.
Drugs are administered to prevent uterine contractions (tocolytics).
Further, under constant ultrasound and KGT control, as well as the continued administration of drugs that relax the uterus, the doctor performs a turn.
Holding both hands on the surface of the pregnant woman's abdomen, one on the head of the fetus, and the other on the buttocks of the fetus, the doctor pushes and rotates the fetus to the upside down position. A pregnant woman may feel some discomfort during the procedure. The degree of discomfort depends on the individual sensitivity of each patient. nine0003
After the procedure is successfully completed, the CTG is recorded again, to make sure that the fetus feels well and has successfully undergone the procedure. Usually during the day, the condition of the mother and fetus is monitored, after which the patient is discharged and continues the pregnancy until spontaneous delivery occurs.
If the doctor notices a deterioration in the condition of the fetus according to the monitoring data, then the procedure is immediately stopped.
If the first attempt was not successful, your doctor may suggest another attempt if the fetus is in good health. nine0003
APP is performed ONLY in a maternity ward where there is an opportunity for an emergency delivery, if necessary.
Risks associated with NAPP
Subject to constant monitoring of the condition of the fetus, constant tocolysis (administration of drugs that relax the uterus) The risks associated with this procedure are minimal. Complications from its use occur in less than 1-2% of cases.
Complications of NAPP include: nine0197 - compression or "twisting" of the umbilical cord. In this case, constant monitoring of the condition of the fetus allows you to immediately fix its deterioration and stop the procedure.
- discharge of amniotic fluid or the development of labor.