Bleeding in the 3rd trimester
Vaginal bleeding in late pregnancy: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia
One out of 10 women will have vaginal bleeding during their 3rd trimester. At times, it may be a sign of a more serious problem. In the last few months of pregnancy, you should always report bleeding to your health care provider right away.
You should understand the difference between spotting and bleeding:
- Spotting is when you notice a few drops of blood every now and then on your underwear. It is not enough to cover a panty liner.
- Bleeding is a heavier flow of blood. With bleeding, you will need a liner or pad to keep the blood from soaking your clothes.
When labor begins, the cervix starts to open up more, or dilate. You may notice a small amount of blood mixed in with normal vaginal discharge, or mucus.
Mid- or late-term bleeding may also be caused by:
- Having sex (most often just spotting)
- An internal exam by your provider (most often just spotting)
- Diseases or infections of the vagina or cervix
- Uterine fibroids or cervical growths or polyps
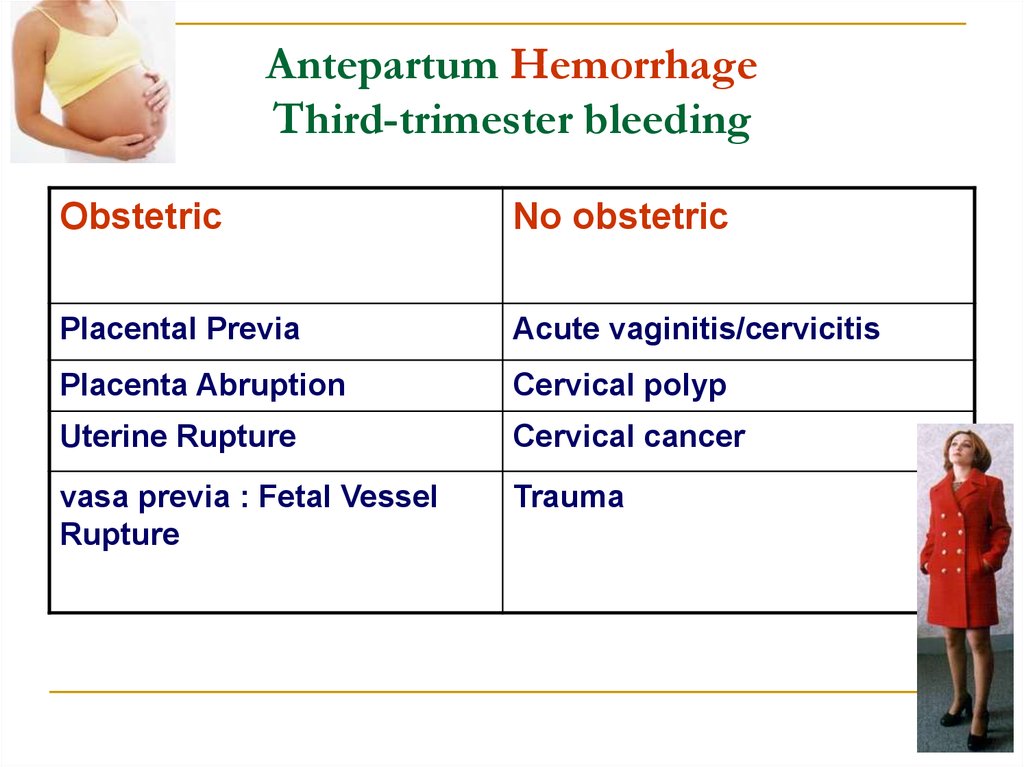
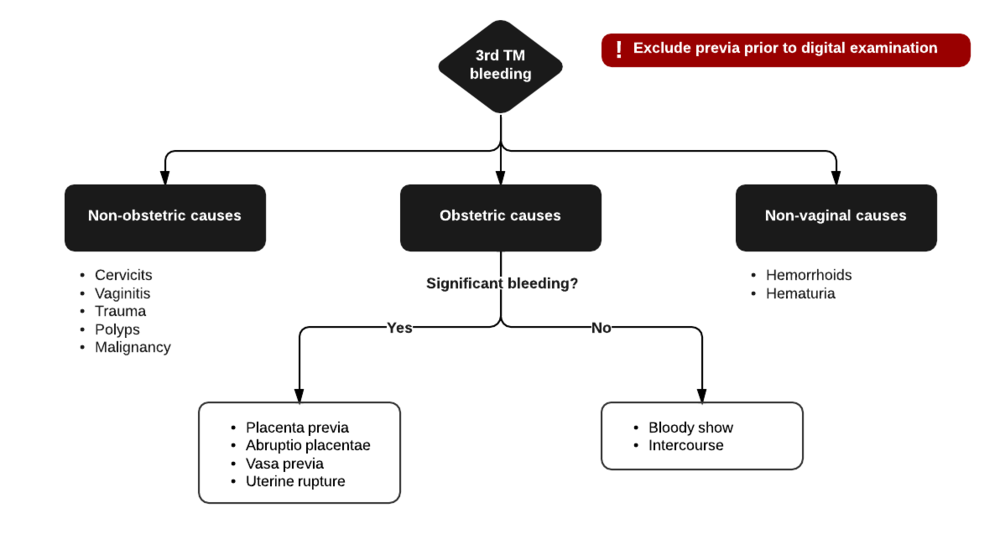
More serious causes of late-term bleeding may include:
- Placenta previa is a problem of pregnancy in which the placenta grows in the lowest part of the womb (uterus) and covers all or part of the opening to the cervix.
- Placenta abruptio (abruption) occurs when the placenta separates from the inner wall of the uterus before the baby is born.
To find the cause of your vaginal bleeding, your provider may need to know:
- If you have cramping, pain, or contractions
- If you have had any other bleeding during this pregnancy
- When the bleeding began and whether it comes and goes or is constant
- How much bleeding is present, and whether it is spotting or a heavier flow
- The color of the blood (dark or bright red)
- If there is an odor to the blood
- If you have fainted, felt dizzy or nauseated, vomited, or had diarrhea or a fever
- If you have had recent injuries or falls
- When you last had sex and if you bled afterward
A small amount of spotting without any other symptoms that occurs after having sex or an exam by your provider can be watched at home. To do this:
- Put on a clean pad and recheck it every 30 to 60 minutes for a few hours.

- If spotting or bleeding continues, call your provider.
- If the bleeding is heavy, your belly feels stiff and painful, or you are having strong and frequent contractions, you may need to call 911 or your local emergency number.
For any other bleeding, call your provider right away.
- You will be told whether to go to the emergency room or to the labor and delivery area in your hospital.
- Your provider will also tell you whether you can drive yourself or you should call an ambulance.
Baeseman ZJ. Vaginal bleeding in pregnancy. In: Kellerman RD, Rakel DP, eds. Conn's Current Therapy 2021. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier 2021:1227-1229.
Francois KE, Foley MR. Antepartum and postpartum hemorrhage. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 18.
Hull AD, Resnik R, Silver RM. Placenta previa and accreta, vasa previa, subchorionic hemorrhage, and abruptio placentae. In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore TR, Greene MF, Copel JA, Silver RM, eds. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 46.
In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore TR, Greene MF, Copel JA, Silver RM, eds. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 46.
Salhi BA, Nagrani S. Acute complications of pregnancy. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 178.
Updated by: John D. Jacobson, MD, Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda Center for Fertility, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Browse the Encyclopedia
Vaginal bleeding in late pregnancy Information | Mount Sinai
What Causes Bleeding Later in Pregnancy?
When labor begins, the cervix starts to open up more, or dilate. You may notice a small amount of blood mixed in with normal vaginal discharge, or mucus.
You may notice a small amount of blood mixed in with normal vaginal discharge, or mucus.
Mid- or late-term bleeding may also be caused by:
- Having sex (most often just spotting)
- An internal exam by your provider (most often just spotting)
- Diseases or infections of the vagina or cervix
- Uterine fibroids or cervical growths or polyps
More serious causes of late-term bleeding may include:
- Placenta previa is a problem of pregnancy in which the placenta grows in the lowest part of the womb (uterus) and covers all or part of the opening to the cervix.
- Placenta abruptio (abruption) occurs when the placenta separates from the inner wall of the uterus before the baby is born.
What to Tell Your Health Care Provider
To find the cause of your vaginal bleeding, your provider may need to know:
- If you have cramping, pain, or contractions
- If you have had any other bleeding during this pregnancy
- When the bleeding began and whether it comes and goes or is constant
- How much bleeding is present, and whether it is spotting or a heavier flow
- The color of the blood (dark or bright red)
- If there is an odor to the blood
- If you have fainted, felt dizzy or nauseated, vomited, or had diarrhea or a fever
- If you have had recent injuries or falls
- When you last had sex and if you bled afterward
What Should Happen Next?
A small amount of spotting without any other symptoms that occurs after having sex or an exam by your provider can be watched at home. To do this:
To do this:
- Put on a clean pad and recheck it every 30 to 60 minutes for a few hours.
- If spotting or bleeding continues, call your provider.
- If the bleeding is heavy, your belly feels stiff and painful, or you are having strong and frequent contractions, you may need to call 911 or your local emergency number.
For any other bleeding, call your provider right away.
- You will be told whether to go to the emergency room or to the labor and delivery area in your hospital.
- Your provider will also tell you whether you can drive yourself or you should call an ambulance.
Baeseman ZJ. Vaginal bleeding in pregnancy. In: Kellerman RD, Rakel DP, eds. Conn's Current Therapy 2021. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier 2021:1227-1229.
Francois KE, Foley MR. Antepartum and postpartum hemorrhage.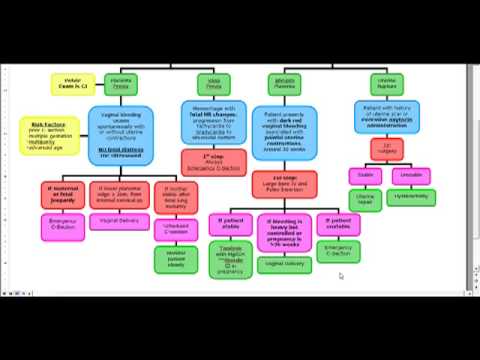 In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 18.
In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 18.
Hull AD, Resnik R, Silver RM. Placenta previa and accreta, vasa previa, subchorionic hemorrhage, and abruptio placentae. In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore TR, Greene MF, Copel JA, Silver RM, eds. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 46.
Salhi BA, Nagrani S. Acute complications of pregnancy. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 178.
Last reviewed on: 10/5/2020
Reviewed by: John D. Jacobson, MD, Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda Center for Fertility, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A. D.A.M. Editorial team.
D.A.M. Editorial team.
Medical advice for doctors | Remedium.ru
10/14/2022
Dental anomalies: classification, causes and treatment
The close relationship between oral health, systemic and psychological health requires careful assessment of oral health as part of health maintenance surveillance. Understanding the normal sequence and patterns of teething is the basis for identifying and treating children...
More
10/13/2022
Painful sexual disorder
N.N. Stenyaev; NMITs AGP them. IN AND. Kulakova
Painful sexual disorder, which combines the concepts of dyspareunia, vaginismus, pelvic pain, penetration disorder, is widespread in women of reproductive and postmenopausal age in the world (up to 34–45%) and more often manifests itself as a coming . ..
..
More
10/11/2022
Diagnosis of disorders in the coagulation system, assessment of the risk of hemorrhagic complications in severe cirrhosis/liver diseases according to global screening tests of the hemostasis system and principles for their correction: guidelines
M.V. Mayevskaya 1 * , M.S. Zharkova 1 , V.T. Ivashkin 1 , E.N. Bessonova 2 , N.I. Geyvandova 3 , E.A. Kitsenko 4 , N.V. Korochanskaya 5.6 , I.A. Kurkina 1 , A.L. Melikyan 7 , V.G. Morozov 8 , Yu.V. Horonko 9 ; 1 First Moscow State Medical University named after I. M. Sechenov (Sechenov University), 2...
M. Sechenov (Sechenov University), 2...
More
10.10.2022
Features of eating behavior in women: risk assessment of complications
T.P. Shevlyukova, E.A. Mateikovich, P.A. Ermakova, A.A. Ermakova, Tyumen State Medical University
Introduction. Studies show that up to 8% of pregnant women suffer from eating disorders. Such problems are found everywhere, most often women do not even realize that...
More
09/29/2022
How to treat sinusitis in adults?
Sinusitis, like rhinosinusitis, refers to inflammation in the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. Acute sinusitis lasts less than four weeks.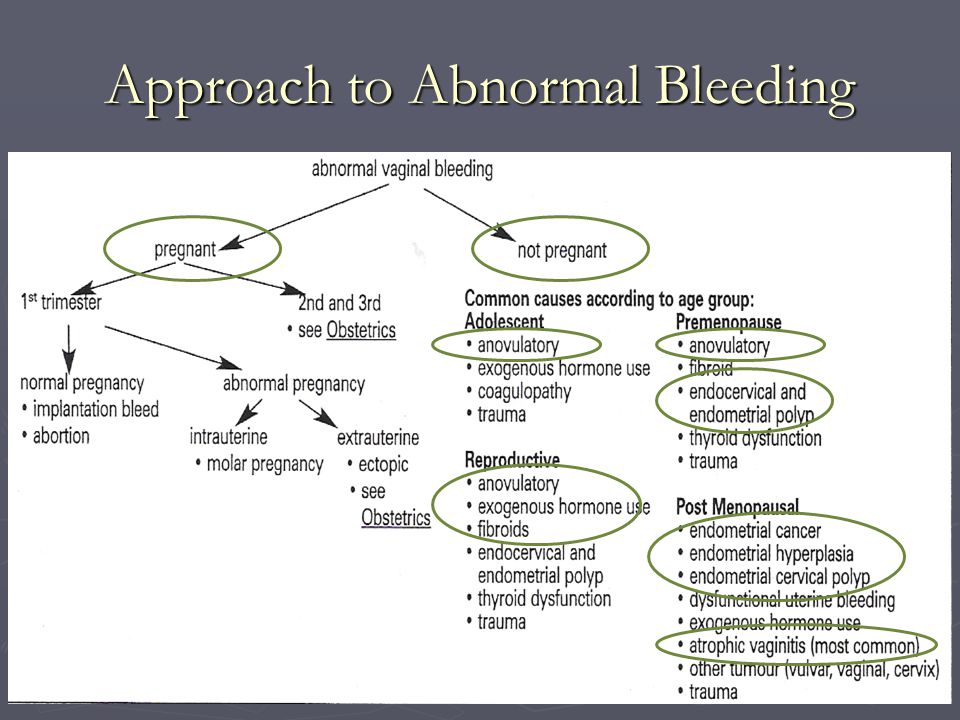 The most common etiology is a viral infection associated with the common cold. Distinguish acute viral sinusitis associated with colds and flu-like...
The most common etiology is a viral infection associated with the common cold. Distinguish acute viral sinusitis associated with colds and flu-like...
More
09/28/2022
Symptoms of perforation of the tympanic membrane
Violation of the integrity of the tympanic membrane - various variants of its perforation - can occur with acute otitis media, blunt or penetrating ear trauma (with or without a foreign body), as well as with barotrauma. Clinical manifestations are generally similar, but management tactics may vary...
More
09/27/2022
Choan atresia
Choanal atresia is a congenital condition in which the posterior choanae in the nasal cavity are blocked by bone, soft tissue, or both.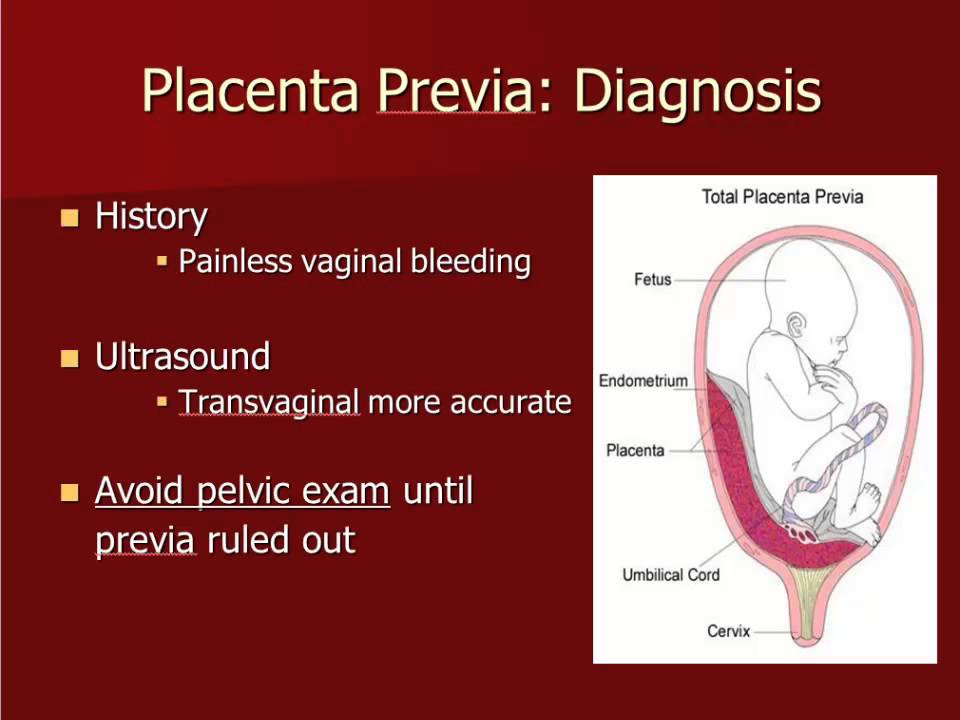 Complete nasal congestion in a newborn can lead to death from asphyxia. When you try to inhale, the tongue is pulled up to the palate, which leads to obstruction of the mouth ...
Complete nasal congestion in a newborn can lead to death from asphyxia. When you try to inhale, the tongue is pulled up to the palate, which leads to obstruction of the mouth ...
More
09/26/2022
How to treat SARS?
Acute respiratory viral infections (ARVI) are a group of benign, self-limiting viral diseases. SARS is the most common acute infectious disease in the world. Sometimes the terms "cold" and acute respiratory infections are used, which may imply other pathogens, in addition to viruses. Precise...
More
09/22/2022
How to protect yourself from the flu?
Influenza (influenza - obsolete) is a seasonal respiratory disease caused by influenza viruses that has pandemic potential and is associated with the death of 350-650 thousand people worldwide annually. Influenza caused the largest pandemic in the 20th century, known as the "Spanish flu" (1918–1920), date...
Influenza caused the largest pandemic in the 20th century, known as the "Spanish flu" (1918–1920), date...
More
09/21/2022
Psychiatric comorbidity and psychoemotional status of patients with acne
E.V. Dvoryankova 1.2* , N.A. Shevchenko 3 , O.V. Zhukov a 4.5 ; 1 Center for theoretical problems of physico-chemical pharmacology of the Russian Academy of Sciences, 2 Medical family center Pangea, 3 Center for the complex rehabilitation of the disabled "Butovo", 9003. Russian...
More
Load more
Pregnancy and bleeding in early and late periods
Get test results
- Home
- How to recognize the disease
- Pregnancy and childbirth
- Bleeding during pregnancy
More about the doctor
Bleeding during early and late pregnancy
Bleeding at various stages of pregnancy is a pathological symptom. Its appearance requires additional research methods aimed at clarifying the cause and selecting therapy.
Its appearance requires additional research methods aimed at clarifying the cause and selecting therapy.
Causes of bleeding during pregnancy
The only physiological cause of bleeding in the early stages may be the manifestation of implantation of the fetal egg in the uterine cavity. Pathological causes will depend on the gestational age.
In the early stages bleeding can be caused by:
- Complete or partial detachment of the ovum.
- Placenta previa.
- Fetal death.
- Pathology of hemostasis or Rhesus conflict.
Second trimester bleeding is rare. The reasons may be:
- Placenta previa.
- Spontaneous fetal death.
- Isthmic-cervical insufficiency.
In the third trimester bleeding occurs as a result of:
- Premature detachment of a normally located placenta.

- Offers placenta.
Diagnosis
To clarify the cause of bleeding during pregnancy, it is necessary to find out the patient's complaints, the conditions for their occurrence, as well as possible provoking factors. The doctor evaluates the nature of menstrual and reproductive function.
After vaginal examination, additional examination methods are prescribed, which include:
- Examination of the hormonal profile with the determination of the level of human chorionic gonadotropin, as well as progesterone. A discrepancy between the level of v-hCG and the term may indicate fetal death or an ectopic pregnancy.
- Blood test for Rh factor, as well as the determination of antibodies. With a negative Rh mother, a threat may develop due to increasing antibodies against the fetal organism.
- Coagulogram. The evaluation of the coagulation system is carried out in order to exclude pathologies of hemostasis.
- Ultrasound . A non-invasive method is used to visualize the placenta, fetus, and determine the blood flow between the mother and fetus. With the help of ultrasound, it is possible to set the exact date, as well as exclude fetal growth retardation or malformations, and calculate the heart rate.
- Cardiotocography. A non-invasive study is ordered to evaluate the vital signs of the fetus by recording the heart rate.
Treatment
If the disease is caused by fetal death, curettage of the uterine cavity or induction of labor is performed.
In case of partial detachment of membranes, hemostatic and hormonal treatment is prescribed.
Isthmic-cervical insufficiency involves surgical intervention with suturing of the cervix, as well as hormonal treatment with progesterone drugs.
Premature abruption of a normally located placenta, as well as uterine rupture, is an indication for emergency operative delivery.