How to garnish wages for child support
Child Support Collection: Wage Garnishment & Property Seizure
The most common method of collecting a judgment for overdue child support is wage garnishment.
By Margaret Reiter, Attorney
If you owe unpaid child support, your child's other parent has a number of ways to collect the money from you.
- First, the other parent may go to court and ask a judge to issue a judgment (called a judgment for child support) for the amount of the arrears. Once the parent has a judgment, many collection methods become available, like wage garnishment and property seizure.
- Even without a judgment for past-due child support, other options for collection include automatic wage withholding.
- Finally, both the federal and state governments are also involved in enforcing child support orders—and they can use aggressive tactics to get the money for your kids.
If your child's other parent sues you and gets a judgment against you for unpaid child support, that parent has a whole host of collection methods available—more than without a judgment for child support arrears. And, even if the custodial parent got the judgment in one state and you have since moved to another state, that parent can register the judgment in the second state and enforce it there.
The most common method of collecting a judgment for overdue support is wage garnishment. The custodial parent can also seize your personal property, like your car, motorcycle, or boat.
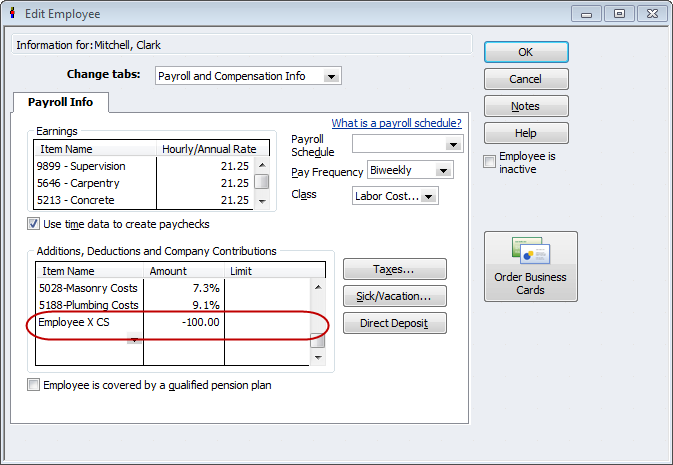
What Is Wage Garnishment?
A wage garnishment is similar to income withholding. A portion of your wages is removed from your paycheck and delivered to the custodial parent before you ever see it. In many states, the arrears need not be made into a judgment to be collected through wage garnishment.
Procedures for Wage Garnishment
To garnish your wages, the custodial parent obtains authorization from the court in a document usually called a writ of execution. Under this authorization, the custodial parent directs the sheriff to seize a portion of your wages. The sheriff in turn notifies you and your employer.
How Much Can the Court Take?
The amount garnished is a percentage of your paycheck. What you were once ordered to pay is irrelevant. The court simply wants to take money out of each of your paychecks—and leave you with a minimum to live on—until the unpaid support is made up.
Under federal law, if a court orders that your wages be garnished to satisfy any debt except child support or alimony, a maximum of roughly 25% of your net wages can be taken. For unpaid child support, however, up to 50% of your net wages can be garnished, and up to 60% if you're not currently supporting another dependent. If your check is already subject to wage withholding for your future payments or garnishment by a different creditor, the total amount taken from your paycheck can't exceed 50% (or 65% if you're not currently supporting another dependent and are more than 12 weeks in arrears).
How the Garnishment Is Initiated
To put a wage garnishment order into effect, the court, custodial parent, state agency, or county attorney must notify your employer. Once your employer is told to garnish your wages, your employer tells you of the garnishment.
Once your employer is told to garnish your wages, your employer tells you of the garnishment.
Requesting a Court Hearing
You can request a court hearing, which will take place shortly after the garnishment has begun. At the hearing, you can make only a few objections:
- The amount the court claims you owe is wrong.
- The amount will leave you with too little to live on.
- The custodial parent actively concealed your child, as opposed to merely frustrating or denying your visitation (not all states allow this objection).
- You had custody of the child at the time the support arrears accrued.
Seizing Your Property to Collect Child Support
If the wage garnishment doesn't cover the amount you owe, or you don't have wages or other income to be garnished, the custodial parent may try to get the unpaid support by going after other items of your property. Examples of the type of property that might be vulnerable include:
- cars
- motorcycles
- boats
- airplanes
- houses
- corporate stock
- horses
- rents payable to you, and
- accounts receivable.
In some cases, even spendthrift trusts and your interest in a partnership may be used for payment.
To learn about other ways the government or your child's other parent can collect child support from you, see our Enforcement of Child Support Obligations area.
Talk to a Lawyer
Need a lawyer? Start here.
Garnishment for Child Support and Alimony
Topics on this page
- How much of my earnings can be garnished for failure to pay child support or alimony?
- Can my bank account be garnished?
- What other sources of income can be taken if I don't make child support payments?
How much of my earnings can be garnished for failure to pay child support or alimony?
Maryland law follows the Federal Consumer Credit Protection Act. This Act allows more of your earnings to be taken for child support or alimony than for ordinary debts. For ordinary debts, the maximum that could be garnished would be approximately 20 to 25 percent of your earnings. For child support or alimony, the maximum that can be taken out of your check is either 50 or 60 percent, depending on whether you are in arrears and if you have another spouse or child to support:
For child support or alimony, the maximum that can be taken out of your check is either 50 or 60 percent, depending on whether you are in arrears and if you have another spouse or child to support:
- If you do not have another spouse or child to support, up to 60 percent of your after-tax earnings can be garnished, or 65 percent if you are more than 12 weeks behind when the earnings withholding order is issued.
- If you are supporting another spouse or child, the court can order 50 per cent of your earnings garnished, or 55 per cent if you are more than 12 weeks behind.
Read the Law: 15 U.S.C. § 1673 ; Md. Code, Family Law § 10-122
In Maryland, your employer is allowed to deduct an additional $2 for each deduction the employer is required to make under an earnings withholding order or earnings withholding notice.
Read the Law: Md. Code, Family Law § 10-128(a)(2)(iii)
Can my bank account be garnished?
In Maryland, a Writ of Garnishment can be issued for a bank account. Once the bank is served with the Writ, the bank freezes your bank account. This means that you will not be able to access money in the account (unless the amount in the account exceeds the amount of the garnishment). Learn more about bank garnishment.
Once the bank is served with the Writ, the bank freezes your bank account. This means that you will not be able to access money in the account (unless the amount in the account exceeds the amount of the garnishment). Learn more about bank garnishment.
Generally, for the bank garnishment, you may entitled to certain exemptions. However, for child support, you are considered to be an "obligor" rather than a "debtor." A "debtor" is someone who simply owes money to another. An "obligor" is someone who must pay money arising out of a separate legal duty. This distinction between a "debtor" and an "obligor" means that the exemptions provided to "debtors" are not available for "obligors."
Read the case: Kelly v. Montgomery County Office of Child Support Enforcement, 227 Md.App 106 (Court of Special Appeals 2016)
Read the law: Md. Code, Family Law § 10-101; § 10-108
What other sources of income can be taken if I don’t make child support payments?
If you fail to make child support or alimony payments, Maryland law allows the person you owe to ask the court for an earnings withholding order, which will take the payments you owe out of your paycheck, some pensions, unemployment benefits, Social Security or worker’s compensation payments.
Read the Law: Md. Code, Family Law §10-101
Source
Updated by PLL Contributors
Last Updated: Tue, 08/23/2022 - 8:16 am
Is this legal advice?
This site offers legal information, not legal advice. We make every effort to ensure the accuracy of the information and to clearly explain your options. However we do not provide legal advice - the application of the law to your individual circumstances. For legal advice, you should consult an attorney. The Maryland Thurgood Marshall State Law Library, a court-related agency of the Maryland Judiciary, sponsors this site. In the absence of file-specific attribution or copyright, the Maryland Thurgood Marshall State Law Library may hold the copyright to parts of this website. You are free to copy the information for your own use or for other non-commercial purposes with the following language “Source: Maryland's People’s Law Library – www.peoples-law.org. © Maryland Thurgood Marshall State Law Library, 2022. ”
”
How to recover child support from a working debtor? - Lawyer in Samara and Moscow
Legislation provides for a different procedure for paying and calculating child support.
1. On the payment of alimony by a parent on a voluntary basis
cash desks. The amount of alimony and the terms of payment are determined and indicated in the application by the parent paying the alimony. The administration will transfer alimony to the specified details or issue them when calculating wages. The payment of alimony in this manner does not apply to cases of deductions from wages for the purposes of labor legislation (clause 1, article 80 of the IC of the Russian Federation; article 137 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
2. On the payment of alimony on the basis of a notarial agreement
The amount of alimony is determined by agreement of the parties, however, it cannot be less than what would be relied on a child in the recovery of alimony in court (clause 1, article 80, art. Articles 99, 103 of the RF IC). The agreement may provide for a different procedure for the payment of alimony: as a percentage of earnings, in a fixed amount of money paid at a time or periodically, etc.
Articles 99, 103 of the RF IC). The agreement may provide for a different procedure for the payment of alimony: as a percentage of earnings, in a fixed amount of money paid at a time or periodically, etc.
on the basis of this agreement in accordance with the stipulated conditions for the timing and amount of payments (Article 109RF SC). Their size is calculated on the basis of wages and income (except for payments from which alimony is not withheld) minus tax payments. The types of income from which alimony for minor children is paid are defined in the List, approved. Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of July 18, 1996 N 841. Withholding by agreement cannot exceed 70% of earnings (Article 110 of the RF IC; Article 138 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The administration pays or transfers alimony to the beneficiary's account no later than within 3 days from the date of payment of wages to the alimony payer. The costs of paying alimony (for example, a bank commission or a postal order fee) are borne by their payer.
Such an agreement has the force of an executive document, and if the parent does not want to pay alimony voluntarily under a notary agreement, they can be collected forcibly through the bailiff service (clause 3, part 1, article 12, article 30 of the Law of 02.10.2007 N 229-FZ).
The bailiff will calculate the debt for the payment of alimony.
Alimony arrears for the past period can be collected on the basis of an agreement on the payment of alimony within the three-year period preceding the presentation for collection.
If non-payment of alimony was due to the fault of the debtor parent, they can be calculated for the entire past period.
The bailiff calculates the debt based on the terms of the agreement on the payment of alimony and earnings and other income of the person obliged to pay alimony, for the period during which the alimony was not collected (Article 113 of the RF IC).
In case of non-payment of alimony voluntarily and the absence of a notarized agreement on the payment of alimony, alimony can be collected in court.
3. Legal recovery of child support from a parent
There are two ways to recover child support through the courts: on the basis of an application for a court order or filing a claim for the recovery of alimony.
Issuance of a court order is a simplified procedure for the collection of alimony. The judge issues a court order within five days from the date of receipt of the application without a trial, summoning the debtor and the recoverer and hearing their explanations (Article 126 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
The judge sends a copy of the court order to the debtor, who, within ten days from the date of receipt of the order, has the right to file objections regarding its execution (Article 128 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
The judge cancels the court order if the debtor raises objections regarding its execution within the prescribed period. If no objections are received from the debtor within the prescribed period, the judge issues the second copy of the court order to the recoverer to present it for execution or, at the request of the recoverer, sends it to the bailiff for execution (Article 129, 130 Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
A court order cannot be issued in the case of an application for the payment of alimony in a fixed amount of money (clause 11 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation of October 25, 1996 N 9).
As a general rule, alimony will be assigned from the moment of applying to the court. In rare cases, if payment evasion is proven, they can be recovered for the past period, but not more than three years (clause 2, article 107 of the RF IC).
Alimony is assigned as a fixed amount or as a percentage of the parent's income.
Assignment of alimony as a percentage of the parent's income
If the parent has one job and a steady income, then alimony can be assigned as a percentage of income - for one child in the amount of one quarter, for two children - one third , for three or more children - half of the earnings and (or) other income of the parent (Article 81 of the RF IC). The court may increase or decrease the size of these shares depending on the financial or marital status of the parties and other circumstances of the case (for example, the disability of family members to whom the party is obliged by law to provide maintenance, the onset of disability or the presence of a disease that prevents the continuation of the previous work, the child's admission to work or engaging in entrepreneurial activity).
On assignment of alimony in a fixed amount of money
Alimony in a fixed amount of money is assigned if there is no agreement between the parents on the payment of alimony and the parent does not have a permanent income, or if there are several sources of income, or if the income is unstable, or if this parent receives earnings and (or) other income in whole or in part in kind or in foreign currency, and in other cases when it is impossible to collect alimony in percentage terms (Article 83 of the RF IC).
A fixed amount of maintenance is also determined taking into account the financial and marital status of the parties and other circumstances worthy of attention in order to maintain the child's previous level of support. Alimony must be set in a fixed amount of money corresponding to a certain number of minimum wages for further indexation (clause 2 of article 117 of the RF IC).
You can collect alimony in a fixed amount of money, for example, if the alimony payer hides his income.
Employer withholds child support based on a court order or court order in the same way as a child support agreement. If a court order or court decision is not executed voluntarily, then their enforcement through the bailiff service is possible. The bailiff will calculate the debt on the basis of a court order or decision in the manner indicated above.
Remember, at any stage of a family dispute, the Legal Center for Family Affairs of Attorney Anatoly Antonov is ready to provide you with legal support. Call us by phone in Samara + 7 (846) 212-99-71 right now and sign up for a consultation at a convenient time for you.
Legal Center for Family Affairs of Attorney Anatoly Antonov provides the following legal services on issues of paying alimony for minor children, as well as other family members:
- legal advice;
- drawing up an agreement on the payment of alimony;
- drawing up a statement of claim for the issuance of a court order;
- preparation of a statement of claim for the recovery of alimony and attachments to it, as well as filing it with the court;
- preparation of objections regarding claims for the recovery of alimony, for a reduction in the amount of alimony;
- familiarization with the materials of the case on the recovery of alimony, on the reduction of the amount of alimony;
- participation in court hearings (possibly without the presence of the principal) for the recovery of alimony;
- obtaining a court decision on the recovery of alimony;
- appeal against the decision of the court in a higher instance.

Original article taken from the website of the Electronic Journal "Azbuka Prava"
Relevance date of the material: 01/06/2016
To make an appointment for a consultation, call the round-the-clock number +7 (846) 212-99-71 or leave a request below
who can withhold and how much, sample application
If you work officially, then the employer withholds part of your salary and transfers it to the tax office.
Diana Shigapova
lawyer
In addition to tax payments, there are other situations when an employee receives less than what is required under an employment contract. I will tell you who and how can take part of the salary legally.
Regulatory framework for deductions
The basic rules for deductions from wages are set out in the Labor Code. Article 137 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation lists cases in which an employer can keep part of an employee's salary. Article 138 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation specifies the maximum amount of deductions: you cannot take all the income - something must remain for life.
The procedure for withholding personal income tax - personal income tax - is prescribed in chapter 23 of the tax code, and money from the earnings of a convicted person - in article 44 of the penitentiary code.
/prava-uchebnik/
Course: how to protect your rights at work
It happens that bailiffs take part of the debtor's salary. Articles 98 and 99 of the federal law "On Enforcement Proceedings" describe how this happens.
News that concerns everyone is in our telegram channel. Subscribe to keep abreast of what is happening: @tinkoffjournal.
Compulsory deductions
In some cases, the employer is required to withhold money from the salary - this does not depend on his will or the desire of the employee.
Personal income tax. People who are officially employed pay 13% of personal income tax from their labor income. Those who work "underhand" do not pay taxes and take a lot of risks.
Employees do not take the money to the tax office themselves - this is done for them by the employer, who acts as a tax agent. He calculates personal income tax, deducts it from the salary and transfers it to the tax office. And employees receive the amount already minus tax.
Art. 226 NK RF
Personal income tax is a priority payment: first, the state takes its part, and the rest of the deductions are calculated from the salary, minus the tax.
Part 1 99 of the Law "On Enforcement Proceedings"
You can read about personal income tax in a selection of articles:
- What is personal income tax, where does it go and how to pay it
- Everything you need to know about personal income tax and deductions
- How to calculate salary , if it is listed as gross
- I have been receiving a black salary for many years and now I thought about it
Retention of loans under writ of execution. For example, a person took a loan from a bank and did not repay it. The bank went to court, won the case and received a writ of execution.
For example, a person took a loan from a bank and did not repay it. The bank went to court, won the case and received a writ of execution.
/pristal/
What bailiffs can do
A writ of execution is a document that gives the right to enforce debt collection. There are other executive documents, for example, a court order and a notary's executive inscription. Read more about them in the article "How to get your money back if you lent it."
This does not only work with banks: the same thing happens if the debtor does not return the money to a microfinance organization or to a neighbor on receipt. Both the bank, the MFI, and the neighbor are the debtor's creditors. As soon as the creditor receives a writ of execution, he turns into a recoverer.
Art. 49 of the Law "On Enforcement Proceedings"
The creditor can take the writ of execution to the bailiffs - they will initiate enforcement proceedings and try to collect the debt. There are several ways to do this, one of the most effective is to send the debtor's employer a decision to foreclose on wages.
There are several ways to do this, one of the most effective is to send the debtor's employer a decision to foreclose on wages.
The resolution indicates the total amount of the debt and how many percent of the income must be withheld. The task of the employer is to fulfill what the bailiff wrote.
If the debt does not exceed 100,000 R, the claimant has the right to present a writ of execution to the employer directly - without the help of bailiffs.
Art. 9 of the Law "On Enforcement Proceedings"
The employer starts deductions from the day he received the writ of execution. On the day of the salary, the debtor will be paid the amount already minus the money that is intended for the claimant.
Art. 98 of the Law "On Enforcement Proceedings"
The employer sends the withheld money within three days according to the details from the resolution. As a rule, the money first goes to the bailiff service, and the bailiffs themselves transfer it to the claimant or distribute it among several claimants. If the creditor submitted the sheet directly to the employer, then he will receive money immediately from him.
If the creditor submitted the sheet directly to the employer, then he will receive money immediately from him.
Deductions continue until the debt is repaid or the employee quits. If the employee left the organization, then the employer returns the writ of execution to the person from whom he received it - the recoverer or bailiffs.
Maintenance withholding by agreement. For example, ex-spouses agreed on the amount of alimony and made a written agreement. This agreement must be certified by a notary - then it will have the power of a writ of execution.
Art. 100 SK RF
If the alimony payer violates the agreements, then the recipient has the right to recover the money forcibly. To do this, he needs to submit an agreement to the bailiffs or the employer of the alimony payer.
What to do? 07/25/18
How to pay child support if they are not required?
The employer withholds child support in the amount specified in the agreement, but not more than 70% of the salary.
Suppose the father of the child, by agreement, undertakes to pay alimony - 25,000 R per month. But this is the entire salary that he receives in his hands, minus personal income tax. If you take this money, then he will have nothing left - it's impossible.
Therefore, the employer will withhold only 17,500 R - this is exactly 70% of the salary. And the remaining 7500 R is a debt that the father of the child will pay from other income.
Art. 110 SK RF
Withholding of alimony under a writ of execution. It is not always possible to agree on the payment of alimony amicably - then the court is involved in the dispute.
As a general rule, the recipient of alimony will first apply to the Justice of the Peace for a writ. This is a simplified procedure: there are no meetings and debates of the parties. The judge simply checks the documents and issues an order within five days, if everything is done correctly. A court order is equal in strength to a writ of execution: it can also be submitted to the bailiffs or directly to the employer.
Art. 122 Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation
Some cases cannot be considered in writ proceedings, for example, when paternity must be established or if the payment of alimony affects the interests of other children. And it also happens that the debtor cancels the court order - this is not difficult. In such cases, the alimony recipient files a full-fledged claim, participates in court hearings and, if he wins, takes the writ of execution.
Art. 129 Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation
Both the court order and the writ of execution indicate the amount of alimony in the form of a share of income - ½, ⅓, ¼ - or a fixed amount, for example, 20,000 R per month.
We have something to read about the recovery of alimony:
- How to file for alimony
- How to recover alimony through a court
- How to calculate and pay alimony
- How to find out the arrears of alimony
The sequence of retention
11111111111111111111 accounted for by several creditors. For example, a person owes three banks, a management company's rent, and alimony to his ex-wife. This is how a queue of claimants is formed.
For example, a person owes three banks, a management company's rent, and alimony to his ex-wife. This is how a queue of claimants is formed.
Withholding based on two writ of execution. Not all debts are equal: some are considered more important than others and are closed earlier. The bailiffs distribute the money among the claimants, taking into account the priority.
Art. 111 of the Law "On Enforcement Proceedings"
Debts of the first stage: alimony, compensation for damage from a crime and various types of harm - moral, health, in connection with the death of a breadwinner.
Second line: obligations to employees. For example, a debtor - an individual entrepreneur - did not pay salaries to employees.
Third priority: debts to the state - taxes, contributions, fines.
And at the very end are the rest of the creditors.
The following principle works here: until the debts of one queue are closed, the money does not fall one step down.
For example, the debtor does not pay taxes to the state and the management company's utility bill. Both debts are trying to recover bailiffs.
His salary will go to taxes - this is a higher priority debt. And until this debt is closed, the management company will not receive a penny within the enforcement proceedings. This is how the sequence works.
Withholding amounts for several writ of execution of one turn. Debts within the same queue are also not equivalent: the bailiffs transfer the collected money in proportion to the size of the debt.
For example, a defaulter owes the bank 500,000 RUR, and an MFI owes 100,000 RUR. His salary is 50,000 RUR.
The total debt is 600,000 RUR. 16.67%. It is in such proportions that the creditors will divide the debtor's money.
First, the employer withholds personal income tax from the debtor's salary: 50,000 R × 13% = 6,500 R. Remaining: 50,000 R − 6,500 R = 43,500 R.
Another 50% is withheld from the balance in favor of creditors: 43,500 R × 50% = 21,750 R. 90,003 90,002 The bank will receive: 21,750 R × 83.33% = 18,124 R. 90,003 90,002
90,003 90,002 The bank will receive: 21,750 R × 83.33% = 18,124 R. 90,003 90,002
How to collect a debt through bailiffs
Are retroactive deductions possible? The employer starts deductions from the day he received the documents - retroactively is not allowed.
Here, the creditor sent a writ of execution to the debtor to work by mail. But for some reason, the documents arrived very late: the sheet was from January, and now it's already July. Then the debtor was lucky: he received a full salary for five months, and could be content with only half.
Employer-initiated deductions
I'll tell you in which cases an employer has the right to keep part of an employee's salary.
Art. 137 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
For the return of erroneously paid amounts - when, as a result of a counting error, the employee was transferred more than it should have been.
Rostrud believes that a counting error is a miscalculation when performing arithmetic operations. For example, a company has set hourly wages. The accountant incorrectly multiplied the cost of an hour by the time worked, and as a result, the employee was overpaid. In addition, the courts refer to counting errors as inaccuracies due to program failures.
For example, a company has set hourly wages. The accountant incorrectly multiplied the cost of an hour by the time worked, and as a result, the employee was overpaid. In addition, the courts refer to counting errors as inaccuracies due to program failures.
Letter of Rostrud No. 1286-6-1
To withhold erroneous transfers from wages, you must obtain the written consent of the employee. If there is no consent, the employer will have to go to court and prove that a counting error has occurred.
The employee left the company of his own free will. When he was fired, his salary was calculated incorrectly and he was given extra money. As it turned out later, the error happened due to a failure in the 1C program.
The ex-employee was sent a letter with a request to return the overpayment, which he ignored. Then the company went to court and proved that the reason for the overpayment was a counting error. The court confirmed that the former employee must return the money.
To pay off an advance payment issued under various circumstances. The employer can give the employee money for future service expenses. For example, an employee is sent on a business trip and a certain amount is allocated in advance to a sub-report - you need to report for it.
/ezda/
How to save on traveling work and business trips
Within three working days after returning from a business trip, the employee must draw up an advance report and attach documents to it that confirm his expenses - receipts from the hotel, printouts of electronic tickets by train or plane.
clause 26 of the regulation on the specifics of sending on business trips
The employer has the right to decide to withhold an advance from the salary for which the employee has not reported. But only if two conditions are met:
- The employee gave written consent to the deduction.
- A month has not yet passed since the day when it was necessary to submit an advance report or return the money.
If the employee does not agree with the deduction or the term has already expired, then the accountable amounts are collected in court.
Upon dismissal for unworked vacation days. An employer can provide employees with paid leave in advance.
Art. 122 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Let's say an employee has worked in a company for six months, for which 14 days of vacation are due. But he wants to rest longer, so he asks to be released for 24 days. The employer agrees: provides and pays the employee an additional 10 days in advance.
If an employee does not work for a full year and quits, there will be an overpayment for vacation pay. The employer has the right to withhold the overpayment from the calculation upon dismissal - and the consent of the employee is not required.
For damages. The employer has the right to recover compensation from the employee for the damage caused.
But this is a difficult procedure. First, the employer collects a commission and organizes an audit to calculate the amount of damage and find out who is to blame. An explanatory note is requested from the employee, and if he does not want to write it, then the commission draws up an act of refusal.
First, the employer collects a commission and organizes an audit to calculate the amount of damage and find out who is to blame. An explanatory note is requested from the employee, and if he does not want to write it, then the commission draws up an act of refusal.
Art. 247 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Based on the results of the audit, the employer establishes the exact amount of damage at market prices. For example, an employee broke a machine at a factory because he violated the operating instructions. Then you need to calculate the cost of repairing the equipment, and if it is no longer possible to restore it, then take the cost of a similar machine as damage.
Art. 246 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
The employer has the right to decide to withhold compensation for damage from the salary, even if the employee does not agree with this. But only if two conditions are met:
- The amount of damage does not exceed the average monthly salary of the employee.

- A month has not yet passed since the determination of the amount of damage.
st. 248 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
When the damage is more than the average monthly earnings, deduction is allowed only with the written consent of the employee or in court.
What to do? 09/07/18
What should I do if the employer wants to pin someone else's theft on me?
The Labor Code provides that an employee can negotiate with the employer and repay the damage in installments. And with the consent of the employer, the employee has the right to repair what he has broken, or to transfer to the company equivalent property for replacement.
Penalty deductions for non-fulfillment of the plan or misconduct. If an employee messed up or did not fulfill the plan, then money cannot be withheld from his salary. An employee receives a salary simply for coming to work and working there - it doesn’t matter if it’s bad or good.
For disciplinary offenses, such as being late or absenteeism, the Labor Code provides for special penalties: reprimand, reprimand, and dismissal. But it is impossible to reduce the salary part of the salary for this.
Art. 192 Labor Code of the Russian Federation
In many companies, employees receive not only a salary, but also a bonus. This is a variable part of the salary, which is paid for the achievement of certain results and compliance with the work schedule.
What to do? 06/19/18
Employer divides my salary into salary and bonus
The bonus rules are usually prescribed in the internal documents of the employer - regulations and regulations - or in the employment contract or annexes to it. The employer can indicate what he will encourage and what he will deprive of bonuses for.
For example, an organization has a regulation on bonuses. This document states that the employee will receive a bonus if he fulfills the sales plan - closes at least 10 deals per month - and does not receive disciplinary action. Then, if the employee does not cope with the plan or is late for work, he will be left without a bonus, but he will still receive a salary.
Then, if the employee does not cope with the plan or is late for work, he will be left without a bonus, but he will still receive a salary.
Withholding periods
| Types of retention | Term |
|---|---|
| Personal income tax from salary | On the day of salary. The withheld amounts are transferred to the tax office no later than the next day after payment |
| personal income tax from vacation and sickness benefits | On the day of payment. The withheld money is transferred to the tax office no later than the last day of the payment month |
| According to executive documents | On pay day. The dedicated amounts are sent to the creditor or bailiffs within three days from the date of payment of |
| Unprofitable vacation pay | on the day of dismissal |
| Reporting amounts | 9099, when the employee was supposed to provide an advance report by the advance report transferred due to an accounting errorMonth from the day the employee received the erroneous payment |
| Damage | Month from the day when the employer determined the amount of damage |
The terms of deduction can be different.
On the day of salary, personal income tax is withheld from wages, from vacation and sickness benefits. The withheld amounts are transferred to the tax office no later than the next day after payment. Also, on the day of the salary, there are deductions under executive documents. In this case, the withheld amounts are sent to the creditor or bailiffs within three days from the date of payment.
If deductions are unearned vacation pay, they are deducted on the day of dismissal.
If these are accountable amounts, then the deduction period is a month from the last day when the employee was supposed to submit an advance report.
If money transferred due to a counting error is withheld, then the period is a month from the day the employee received the erroneous payment.
If they are withheld on account of damages, then the period is one month from the day when the employer established the amount of damages.
Deductions at the request of the employee
Sometimes employees themselves ask to deduct money from their salary. For example, a forgetful employee has to pay monthly mortgage payments. In order not to delay payment, he writes a statement to the employer, where he asks to transfer part of the salary to pay off the mortgage loan.
For example, a forgetful employee has to pay monthly mortgage payments. In order not to delay payment, he writes a statement to the employer, where he asks to transfer part of the salary to pay off the mortgage loan.
The employer is not obliged to comply with such orders of the employee - he can agree or refuse. If he agrees, he must take into account: the legality of voluntary deductions is a confusing issue. It is possible that the labor inspectorate will not like such transfers, and the desire to meet the needs of the employee will turn into litigation for the company.
The Ministry of Labor believes that this should not be done: the Labor Code contains all the grounds for deduction and there is nothing there about statements from the employee. But Rostrud confirmed that the employer has the right to withhold money when the employee himself asked.
Yes, and the court said that this is possible: the employee has the right to dispose of his salary. If he wants the employer to transfer part of the money not to him, but somewhere else, then why not. And the norms of the labor code apply only to mandatory deductions and do not apply to voluntary ones.
And the norms of the labor code apply only to mandatory deductions and do not apply to voluntary ones.
Restrictions on deductions from wages
Different deductions have their own limitations.
In favor of the employer. An employer cannot take more than 20% for each payment of an employee's salary.
Here is an employee who received vacation pay "in advance" - for those days that he did not work. After the vacation, he wrote a letter of resignation - this is how an overpayment on vacation pay of 10,000 RUR was formed.
Calculation upon dismissal already minus tax - 30,000 RUR. The employer has the right to withhold from this money only 30,000 R × 20% = 6000 R.
The employee can pay the remaining 4000 R voluntarily, and if he refuses, the employer will have to forgive him the debt. This money is considered an overpayment of wages, but there is no counting error here, so it will not work to recover vacation pay in court.
Another example. The employee did not report for an advance in the amount of 30,000 R and did not return this money. He agreed to deductions from the salary, which is 50,000 R per month on hand.
The employee did not report for an advance in the amount of 30,000 R and did not return this money. He agreed to deductions from the salary, which is 50,000 R per month on hand.
The employer will withhold 20% for each payment of wages - this is exactly 10,000 R per month. It will take three months to return the entire accountable amount.
p. 5 of the review of judicial practice in civil cases of the Armed Forces for the third quarter of 2013PDF, 805 KB
personal income tax. The personal income tax rate is 13%. For non-residents, it is higher - 30%.
p. 1, 3 art. 224 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
According to executive documents , they can take up to 50% of the salary. Even if an employee has received several writ of execution, the employer is still obliged to keep at least half of his salary.
There are exceptions to this rule. In some cases, up to 70% is withheld - if this is a debt for alimony for minor children or for compensation:
- damage to health;
- crime damages;
- harm due to the death of the breadwinner.

Support agreement. The employer must withhold as much as specified in the agreement, but not more than 70% of the salary.
At the initiative of the employee. The amount of voluntary deductions is not limited: an employee can give at least the entire salary to where he decides.
How much can be withheld from salary
| Hold | Amount limitation |
|---|---|
| in favor of the employer | to 20% |
| personal income tax | 13%, 30% - non -residents |
| for executive documents | 9, to the general case, in general cases, in general cases. Up to 70% if it is alimony arrears, compensation for damages from a crime, harm due to the death of a breadwinner and harm to health|
| Under the agreement on alimony | Up to 70% |
| At the initiative of the employee | No restrictions |
- In favor of the employer - up to 20%.

- Personal income tax - 13% - residents, 30% - non-residents.
- According to executive documents - in the general case - up to 50% of the salary. Up to 70%, if it is alimony debt, compensation for damage from a crime, harm due to the death of a breadwinner and harm to health.
- Under the alimony agreement - up to 70%.
- At the initiative of the employee - no restrictions.
Non-deductible income
Not all payments from an employer are deductible. For example, a debt on executive documents cannot be withheld:
- With financial assistance at the birth of a child, marriage or death of relatives.
- Travel expenses reimbursement.
- Reimbursement of the cost of vouchers to Russian sanatoriums.
- Compensation for expenses for moving to another city.
p. 8, 15 h. 1 art. 101 of the Law "On Enforcement Proceedings"
Even the tax is not withheld from the entire salary if the employee has children. The more children, the less personal income tax: the first and second children reduce the tax base by 1400 R, each subsequent child by 3000 R. This is how the tax deduction for children works - we told in detail how to save with it.
The more children, the less personal income tax: the first and second children reduce the tax base by 1400 R, each subsequent child by 3000 R. This is how the tax deduction for children works - we told in detail how to save with it.
paras. 4 p. 1 art. 218 NK RF
For example, an employee received 50,000 R per month, but only 43,500 R in his hands, because 13% of the salary - 6,500 R - the employer withheld and transferred to the tax.
When a child was born to an employee, not the entire salary was taxed, but part of it: 50,000 R - 1400 R = 48,600 R. The employer began to withhold: 48,600 R × 13% = 6318 R.
Then the second child was born, and the taxable base decreased by another 1400 R. The budget began to receive even less: (48 600 R - 1400 R) x 13% = 6136 R.
In addition, personal income tax does not have to be paid from certain types of payments from the employer:
- From compensation of expenses for transport and rental housing on business trips, if there are supporting documents - checks and receipts.

- Daily allowance for business trips - no more than 700 R when traveling in Russia and up to 2500 R when traveling abroad.
- Material assistance for the birth of children - no more than 50,000 R per child, paid within a year from the date of birth.
- Financial assistance in case of death of relatives.
- Financial assistance in the amount of not more than 4000 R per year - for any purpose.
st. 217 NK RF
How to apply different types of deductions together
Deductions are easy to calculate if there are few of them. Everything is more complicated when a horde of applicants line up for a salary: the tax office is waiting for personal income tax, the former spouse is waiting for alimony, banks are paying off loans, and the employer wants to return the accountable amounts.
Then the algorithm for the employer is as follows:
- Withhold personal income tax from the entire amount.
- From what is left, withhold debts on writ of execution.

- Agree with the employee on the voluntary deposit of money - otherwise it will not come to the return of the accountable amounts.
I'll show you how it works using three examples:
Example 1. An employer collects 20% of an employee's salary every month for damage caused. But suddenly a writ of execution comes, according to which half of the salary now needs to be transferred to the bailiffs.
By law, after all deductions, the employee must have at least half of the salary left. This means that those 20% that used to go to the employer will now go to the bailiffs, and from them to the exactor.
Then the employer can sue the employee, get a writ of execution and join the line of claimants. Or, arrange for the employee to voluntarily pay money for damages. There is a third option - to forget and forgive.
Example 2. An employee took a loan from a microfinance organization and did not return it - now he gives half of the income to the recoverer on the writ of execution.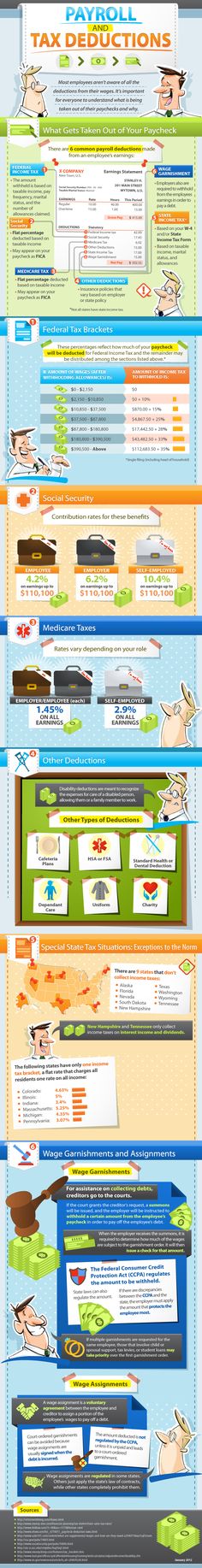 The ex-wife of the debtor brings the employer an agreement on the payment of alimony, according to which 70% of the salary is due to her.
The ex-wife of the debtor brings the employer an agreement on the payment of alimony, according to which 70% of the salary is due to her.
Alimony is the debts of the first priority, and loans are the fourth. First, the employer must withhold alimony, and then everything else. But after the alimony, the debtor will have only 30% of the salary - the MFI is not entitled to claim this part. It turns out that the creditor will not get anything from the salary.
Some debtors even make fictitious maintenance agreements to protect money from debt collectors. However, creditors may challenge such agreements.
Example 3. The employee has a debt - according to the executive document, the bailiffs take half of the earnings. He brings a statement to the boss, in which he asks to transfer the entire salary to a friend's bank card.
This is not possible: deduction under a writ of execution is mandatory, but not at the initiative of the employee. The employee is not entitled to dispose of the part of the salary that is intended for the claimant. If the employer fulfills such an order, he will violate the law. For this, administrative and even criminal liability is provided.
If the employer fulfills such an order, he will violate the law. For this, administrative and even criminal liability is provided.
Documentation
It all depends on the reason for the retention: in each case, the documents are executed differently.
Sample application for payroll deduction. Suppose an employee wants the employer not to pay his salary to the card, but transfer it to the bank to repay the employee's loan. Then he must write an application addressed to the head in a free form. The main thing is to indicate the amount of deductions and account details where to transfer the money.
It will not be possible to agree verbally. There is no way without a written statement - it is necessary for the employer to prove the legality of the deductions. The application will come in handy when the labor inspectorate comes up with the question: “Why are you transferring the salary to no one knows where, and not to the employee’s card?” Or if the employee suddenly decides that he did not ask for the money to be withheld and demands it back.
In addition, in this case, it is necessary to draw up an additional agreement to the employment contract.
part 5 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
The application is written in free form: make sure that the amount of deductions and details for transfers are indicated. The employer must accept the application, but it is not obliged to satisfy itSample consent to withholding. Here are the types of deductions that are impossible without the consent of the employee:
- Return of accountable amounts.
- Compensation for damage if it is more than the average monthly salary of an employee.
- Refund of money paid out due to an accounting error.
First, the employee gives consent in writing, and only after that the employer can issue an order and take part of his salary.
Consent to retention is written in any form, but the date and signature of the employee must be Sample order for retention. An order is needed to withhold money at the initiative of the employer or employee. But to withhold personal income tax or debt under an executive document, an order is not required.
An order is needed to withhold money at the initiative of the employer or employee. But to withhold personal income tax or debt under an executive document, an order is not required.
Sample provision for withholding unreturned accountable funds from wages. All rules for withholding accountable amounts are spelled out in the labor code, so no additional provision is required. But some employers are cunning and come up with documents to circumvent legal restrictions.
For example, by law, accountable amounts are allowed to be deducted from wages only with the written consent of the employee. Yes, and the amount of deduction is limited: no more than 20% from each salary.
The boss does not want to ask employees for permission and does not want to withhold the debt in installments of six months. Therefore, he invents a new provision, where he writes something like: “If the employee did not submit the advance report for the last month before the 5th day of the current month, then the employer has the right to withhold the accountable amounts in full from the employee’s salary. The consent of the employee is not required."
The consent of the employee is not required."
This is illegal: the labor code is more important than any internal regulations of the employer. The document is not valid if it worsens the position of employees in comparison with the requirements of the labor code.
Art. 8 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
You can complain about the illegal actions of the employer to the labor inspectorate and the prosecutor's office, and the deductions themselves can be challenged in court.
st. 391 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
How to reflect deductions in accounting
Skakunova Tatyana
Deputy Head of the Audit and Consulting Department for Residents GSL Law & Consulting
Accounting entries differ depending on the basis for deducting money from the employee's salary.
Withholding personal income tax.
Debit 70 credit 68, subaccount "Calculations for personal income tax" - personal income tax withheld from the amounts accrued to employees.
Withholding loans or alimony under a writ of execution.
Debit 70 credit 76, sub-account "Settlements under executive documents"
- money was withheld under the executive document from the employee's salary.
Maintenance withholding by agreement.
Debit 70 credit 76 - alimony was withheld from the employee's salary.
Withholding of accountable amounts.
Debit 94 credit 71 - accountable money not returned on time is reflected.
Debit 70 credit 94 - unreturned accountable amount withheld from salary.
Withholding overpaid vacation pay upon dismissal.
REVERSE Debit 20 (26, 44) credit 70 - the amount of vacation pay for unworked vacation days has been reversed.
Debit 70 credit 51 (50) - amounts paid upon dismissal minus unearned vacation pay.
The tax base for personal income tax when deducted for unworked vacation days is reduced by the amount of overpayment for vacation pay.
For example, holiday pay was overcharged - 19,000 R. Personal income tax from them:
19,000 R × 13% = 2470 R. 000 R) × 13% = 14,430 R.
Withholding personal income tax is reflected in the general order:
Debit 70 credit 68, subaccount "Calculations for personal income tax".
Withholding damages.
Debit 70 credit 73 - the cost of damage was deducted from the employee's salary by order of the manager.
Withholding at the request of the employee.
Debit 70 credit 76 - payments were withheld from the salary at the initiative of the employee.
What you need to know about deductions from wages
- The employer is obliged to withhold personal income tax and debt under executive documents from the salary. The consent of the employee is not required.
- The employer has the right to withhold damages from the employee. His consent is not needed if the amount of damage does not exceed the average monthly salary.