Back of thigh itching
Most Common Causes and Treatment Options
We’re all probably familiar with having itchy skin. It’s often an irritating sensation, and you have to fight the urge to scratch.
Sometimes, but not always, other symptoms can accompany itchy skin, like a rash, redness, or raised bumps. Itchy skin can also occur all over your body or only in specific areas, such as the arms or legs.
If you have itchy thighs and are wondering what could possibly be causing it, we may be able to shed some light on the matter, along with possible treatment options and home remedies.
There are a wide variety of conditions that can cause itchy thighs. Below, we’ll explore some of the potential causes and the treatments that may help.
Sometimes there’s a simple reason for itchy skin: having skin that’s too dry. Dry skin can occur anywhere on the body, even on the thighs. In addition to being very itchy, you may notice that your skin feels rough or scaly to the touch.
A variety of factors can contribute to dry skin, including:
- low humidity
- cold weather
- age
- poor skin care
- overuse of certain irritating products, like some soaps
To soothe dry skin, apply a moisturizing cream or ointment to the area, and avoid hot water.
Chafing happens when your skin is injured from friction, such as rubbing against clothing or another body part.
The thighs, particularly the inner thigh, are often affected by chafing. The symptoms of chafing can include:
- redness
- a burning sensation
- itching
Thigh chafing can often happen when you’re being physically active. It tends to happen most often when you’re walking, running, or cycling.
Factors that contribute to chafing include:
- having excess thigh muscle or fat
- sweating
- wearing clothing that doesn’t fit well
Applying a lubricating ointment like petroleum jelly may help relieve symptoms and prevent further chafing.
Dermatitis is inflammation of the skin. You may have heard of two common types of dermatitis, atopic and contact.
Atopic dermatitis is also called eczema. Eczema causes patches of itchy, dry skin. It can occur on many areas of the body. It’s unknown what causes eczema, although genetics may play a role.
Allergic contact dermatitis, a type of contact dermatitis, happens when you have a skin reaction to something you’ve come in contact with. Things like poison ivy or nickel can cause it. Symptoms can include intensely itchy skin, rash, and sometimes fluid-filled blisters.
For example, you could develop contact dermatitis on your thighs if you come into contact with poison ivy while walking in shorts. Some people have even developed it from sitting in a chair with nickel components.
You can treat mild atopic dermatitis with topical steroid creams. Severe cases may call for immunosuppressive therapies or light therapy.
For allergic contact dermatitis, avoiding the allergen and using topical steroids can bring relief and reduce inflammation.
Heat rash happens when your sweat ducts get clogged. This leads to sweat becoming trapped under your skin. Symptoms can include:
- redness
- bumps or tiny blisters
- itching
Like chafing, heat rash often happens in areas where the skin can rub together, like the:
- groin
- thigh area
- armpits
- chest
- neck
The rash often clears up as you cool down.
Jock itch is a fungal infection. A group of fungi called dermatophytes causes it. These fungi thrive in moist sweaty areas where they can multiply quickly, resulting in jock itch.
Jock itch affects the skin of the inner thigh, buttocks, and genital area. The rash from jock itch can have an itchy or burning sensation. It often appears red, dry, and flaky.
The infection can spread from person to person through the sharing of things like clothing or towels.
Using an over-the-counter antifungal cream can help clear the infection. In more severe cases, prescription antifungal creams or pills may be necessary.
Swimmer’s itch is a reaction to certain microscopic parasites. These parasites are often found in freshwater. If they come into contact with you while you’re in the water, they may burrow under your skin, causing an uncomfortable itchy rash.
Symptoms of swimmer’s itch can include sensations of itching or burning as well as small red bumps or blisters. It can occur on any area of skin that’s directly exposed to water, including the thighs.
It can occur on any area of skin that’s directly exposed to water, including the thighs.
The itchy rash typically appears while you’re still in the water, then disappears after a few hours. However, about 10 to 15 hours after the initial rash, the redness and itch return.
The symptoms of swimmer’s itch typically go away in about 1 to 2 weeks without prescription treatments. You can use anti-itch lotions or corticosteroid cream to help ease the redness and itching in the meantime.
Pityriasis rosea, also called Christmas tree rash, is a skin rash that can affect people of all ages. However, it seems to happen more often between the ages of 10 and 35.
What causes it isn’t fully understood, but a virus may be the culprit. In some people, the rash may itch. For others, it may not.
Symptoms like fever, fatigue, and headache may come before the rash. Then, the “herald patch,” a large oval-shaped red spot, appears on the skin. More patches then develop on the torso, arms, and legs.
Although it’s a relatively common rash, pityriasis rosea isn’t always easy to diagnose since it can look like other types of red, itchy skin conditions, such as:
- eczema
- psoriasis
- ringworm
Pityriasis rosea often goes away in 1 or 2 months, although it can persist. If you have pityriasis rosea and it’s itchy, see a dermatologist for treatment suggestions.
Meralgia paresthetica is a condition that affects the outer thigh. It includes symptoms such as:
- burning or aching pain
- itching
- numbness
- tingling
In most cases, the symptoms only occur on one side of the body. However, some people develop symptoms on both sides. The symptoms may get worse after walking or standing.
Meralgia paresthetica develops from pressure on the nerve that supplies sensation to the front and side of your thigh. This pressure may occur from:
- clothing that’s too tight
- scar tissue after surgery or an injury
- excess weight
- pregnancy
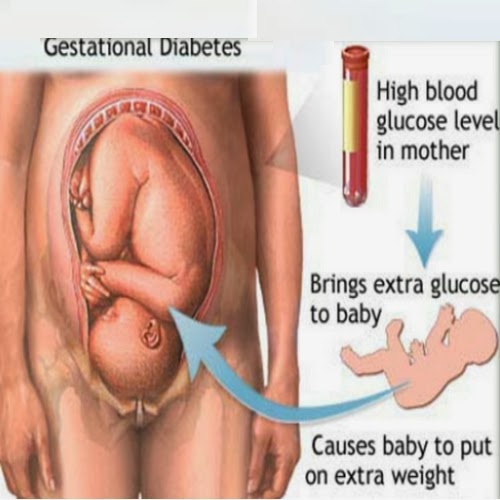
You may be more likely to develop this condition if you have diabetes.
In many cases, you can get relief from these symptoms by:
- wearing looser clothing
- losing weight
- taking an over-the-counter pain medication like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin)
- using a topical anti-itch lotion
In more severe cases, you may need:
- prescription medication
- physical therapy
- pulsed radio-frequency treatment
Pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy (PUPPP), also known as polymorphic eruption of pregnancy, is one of the most common skin conditions that occur during pregnancy.
It most often develops in the third trimester. PUPPP can sometimes also happen following delivery.
PUPPP is characterized as an itchy rash that’s raised and red, but it can take on many forms. It initially develops on the abdomen, often in stretch marks that have appeared during pregnancy. The rash can then spread to other areas of the body, including the thighs.
The condition isn’t serious. It disappears within a couple weeks of delivery. You can treat symptoms with antihistamines and topical corticosteroids.
It disappears within a couple weeks of delivery. You can treat symptoms with antihistamines and topical corticosteroids.
Make an appointment with your doctor about your itchy thighs if:
- the itching is interfering with your day-to-day activities or disrupting your sleep
- an itchy rash appears suddenly or affects a large area
- symptoms don’t clear up or get worse with at-home care
Seek emergency medical care if you:
- have symptoms of a skin infection, including:
- drainage of pus from the affected area
- fever
- chills
- are experiencing a severe form of allergic reaction called anaphylaxis
The treatment of itchy thighs will depend on what’s causing the itching. In some cases, you may be able to effectively treat your condition at home. But if the itching doesn’t go away or worsens, it’s important to see your doctor. If you don’t already have a primary care provider, you can browse doctors in your area through the Healthline FindCare tool.
Depending on the cause, your doctor may prescribe one or more of the following to help ease your symptoms. Treatments may include:
- topical corticosteroids for inflammation
- antibiotics to help treat complications like a bacterial skin infection
- prescription antifungal creams or pills for conditions like jock itch
- light therapy to help with inflammatory skin conditions like eczema or pityriasis rosea
- other prescription medications to help manage specific conditions like eczema
There are several things you can do at home to help with itch relief or before you see a doctor. You could:
- Use a moisturizer. Moisturizing products can help ease dry, itchy skin. Try to use moisturizers that contain hyaluronic acid, glycerin, or petroleum jelly, which can help trap moisture in your skin.
- Take a bath. Make sure the water is lukewarm, not hot. You can also add baking soda or oatmeal to your bathwater for extra relief.
 Moisturize your skin after getting out of the tub. Don’t bathe excessively, though. Aim for once daily for around 5 to 10 minutes max.
Moisturize your skin after getting out of the tub. Don’t bathe excessively, though. Aim for once daily for around 5 to 10 minutes max. - Use OTC medications. These medications, like oral antihistamines and topical corticosteroid creams, can help ease the discomfort associated with itching, depending on the cause.
- Avoid tight or poorly fitting clothes. Clothing that doesn’t allow your skin to breathe can trap sweat. Ill-fitting shorts, pants, or shirts can cause your skin to chafe.
- Use unscented soaps and deodorants. Try to avoid perfumed products, as these may irritate your skin.
- Avoid scratching. This can break the skin and increase the risk of infection. Instead, gently tap or pat the affected area.
- Avoid irritating products. Use only moisturizers or products recommended by your doctor, like Vanicream or CeraVe.
There are many possible conditions that can cause itching on your thighs. Some of the more common causes include dry skin, eczema, chafing, and jock itch.
Some of the more common causes include dry skin, eczema, chafing, and jock itch.
The treatment for itchy thighs depends on what’s triggered the itching. Often, you can treat itching at home with moisturizers, good skin care, and OTC medications.
If the itching on your thighs is disrupting your daily life, or if it isn’t getting better or gets worse, make an appointment with your doctor. You may need a prescription medication to treat your condition.
Itchy Upper Leg | 8 Itchy Thighs Causes
Upper leg itch quiz
Take a quiz to find out what's causing your itch.
Take upper leg itch quiz
Environmental
Environmental causes of an upper leg itch can be related to lifestyle habits or certain exposures.
- Allergens The skin works primarily as a protective barrier and is very sensitive to environmental factors that cause irritation or allergic reactions. Allergens can include drugs, topical treatments such as soaps or lotions, certain fabrics or metals, plants, foods and a variety of other substances.
 Itching that results acts as a warning or deterrent from using these irritants.
Itching that results acts as a warning or deterrent from using these irritants. - Insect bites A bite from any insect mosquito, spider, flea, etc. can easily stimulate the nerve cells on the skin that results in itchiness.
- Stress Some people scratch when they are stressed, or scratch their skin as a habit in certain neurologic or psychiatric conditions.
This list does not constitute medical advice and may not accurately represent what you have.
Insect bite from a chigger
Chiggers are mites that feed on humans and animals only while they are larvae, or their infant form. People can contract chiggers when they contact infected grass. Chiggers feed for three to four days on a piece of skin, and secrete a fluid that causes intense itching.
Rarity: Rare
Top Symptoms: lower leg itch, lower leg redness, knee itch, ankle itch, ankle redness
Urgency: Phone call or in-person visit
Mosquito bite
Mosquito bites are bites from flying insects that feed on the blood of animals, including humans. Mosquito bites are more common during the summer or in warmer climates, at dawn or dusk, and near bodies of water.
Mosquito bites are more common during the summer or in warmer climates, at dawn or dusk, and near bodies of water.
In most cases, mosquito bites will cause a local skin reaction that gets better on ...
Upper leg itch quiz
Take a quiz to find out what's causing your itch.
Take upper leg itch quiz
Restless legs syndrome (RLS)
Restless Legs Syndrome, also called RLS or Willis-Ekbom Disease, is a neurologic and sensory disorder. It causes uncomfortable sensations in the legs that are only relieved by walking or by moving the legs.
The cause is not in the legs but in the brain. One theory is low levels of iron in the brain.
RLS may be hereditary. It is more common in women than in men, especially in middle age. It may get more severe as the person gets older.
Symptoms may happen only a few times a week and are usually worse at night.
There will be an irresistible urge to move the legs in order to relieve the uncomfortable sensations; difficulty sleeping, with daytime exhaustion and inability to concentrate; and sometimes depression and anxiety due to the effect on quality of life.
Diagnosis is made through patient history and physical examination. Blood tests and sleep studies may be done.
Treatment involves first addressing any underlying medical condition, such as iron deficiency. In some cases, anti-seizure medications can be helpful.
Normal episode of itchy skin
Itchy skin is also called pruritis. There are a number of "normal" causes for itching, meaning the cause is not disease-related and does not result in seriously damaged skin.
The most common causes are:
- Dry skin, due to bathing in soap or bubble bath that may be too harsh and is stripping the natural oils from the skin.
- Mild allergies, which may be caused by dust; certain plants and flowers; nickel-containing jewelry; and any sort of soap, detergent, lotion, or perfume.
- Pregnancy, due to stretching of skin or to a condition called prurigo. Prurigo causes small, itchy bumps which may be due to an autoimmune system dysfunction during pregnancy.

- Menopause, due to hormonal changes that may leave the skin overly dry.
Diagnosis is made through physical examination and sometimes allergy tests.
Treatment involves bathing only with mild, hypoallergenic soap; regular moisturizing with unscented lotion; wearing soft, loose, non-synthetic clothing; avoiding any substances that seem to provoke the itching; and sometimes prescription medicated creams.
Rarity: Common
Top Symptoms: feeling itchy or tingling all over
Symptoms that always occur with normal episode of itchy skin: feeling itchy or tingling all over
Urgency: Self-treatment
Non-specific insect bite
Insect bites are very common. They often cause itchiness, redness, and some swelling. Most insect bites can be treated at home.
Rarity: Common
Top Symptoms:
Urgency: Self-treatment
Eczema (atopic dermatitis)
Atopic dermatitis, also called eczema, dermatitis, atopic eczema, or AD, is a chronic skin condition with an itchy rash.
AD is not contagious. It is caused by a genetic condition that affects the skin's ability to protect itself from bacteria and allergens.
AD is most often seen in infants and young children. Most susceptible are those with a family history of AD, asthma, or hay fever.
Infants will have a dry, scaly, itchy rash on the scalp, forehead, and cheeks. Older children will have the rash in the creases of elbows, knees, and buttocks.
Without treatment, a child may have trouble sleeping due to the intense itching. Constant scratching may cause skin infections and the skin may turn thickened and leathery.
Diagnosis is made through physical examination, patient history, and allergen skin tests.
AD cannot be cured, but can be controlled through prescribed medications, skin care, stress management, and treatment of food allergies. Those with AD often have allergies to milk, nuts, and shellfish. Keeping the skin clean and moisturized helps prevent flareups.
Dermatofibroma
A dermatofibroma is a fairly common skin growth that usually appears on the lower legs, but may appear anywhere on the body. These mole-like growths are benign (noncancerous.)
These mole-like growths are benign (noncancerous.)
The cause is not known, though a dermatofibroma may appear after a minor injury. The growths are not contagious.
Dermatofibromas are most common in adults and are rarely found in children.
Symptoms include a hard, raised growth that is red, pink, or brown and less than half an inch across. They are usually painless but may be tender or itchy, and may appear alone or in groups.
Any new growth on the skin should be seen by a medical provider, especially if the growth is very dark in color or changes its shape or appearance quickly.
Diagnosis is made through physical examination and sometimes biopsy.
A dermatofibroma does not require treatment unless it is interfering with clothing or is unsightly. They can be surgically removed, though this will leave a scar and the growth may eventually return.
Allergic contact dermatitis of the thigh
Allergic contact dermatitis means the skin has touched something that provoked an allergic reaction, causing inflammation and irritation.
"Contact" means the allergic reaction came from touching something, not from consuming something. The first exposure to the substance sensitizes the immune system, and then the second exposure actually causes the symptoms.
The most common causes of allergic contact dermatitis are:
- Nickel, a metal often used in belt buckles, the buttons on pants, and jewelry, including piercing jewelry.
- Poison ivy.
- Various types of perfumes, including those founds in soaps, fabric softeners, and detergents.
- Of course, there are many more.
Symptoms include red, itching, scaling, flaking skin that may be painful due to the irritation and inflammation.
Diagnosis is made through first avoiding contact with any suspected substance, to see if the dermatitis clears. Patch testing can be done if the results are not certain.
Treatment involves fully avoiding the allergy-provoking substance and using topical steroid cream as prescribed. Cool compresses and calamine lotion can help to ease the discomfort.
Rarity: Common
Top Symptoms: upper leg itch, upper leg redness, scabbed area of the upper leg
Symptoms that always occur with allergic contact dermatitis of the thigh: upper leg redness
Urgency: Self-treatment
Upper leg itch quiz
Take a quiz to find out what's causing your itch.
Take upper leg itch quiz
What is atopic dermatitis? - Bratsk Regional Dermatovenerological Dispensary
Atopic dermatitis is a common disease that occurs in all countries, in adults and children, boys and girls.
Atopic dermatitis may manifest itself in different ways, but there are basic symptoms: dry, flaky skin, redness, severe itching, rash.
This condition is often referred to as eczema in toddlers, and in adolescents and adults - neurodermatitis. Foreign doctors often use the term eczema, although international the common name is atopic dermatitis.
Today the world suffers from this disease 5% to 20% of children, and 2% to 10% of adults
Term ATOPIA comes from the Greek word which means "something unusual, weirdness".
In fact, this means an unusual hypersensitivity of the body to environmental factors, incorrect, excessive reaction to stimuli, which leads to inflammation of the skin.
So, atopic dermatitis is chronic
recurrent allergic skin inflammation
Why chronic? Atopic dermatitis usually appears in early childhood, during first 6 months of life. There is no cure for atopic dermatitis. Although about 60% of children outgrow it. But most ex-atopics keep dry, irritated skin for life.
Why recurrent? Recurrent - recurring with a certain frequency. Symptoms of atopic dermatitis - itching, rash, irritated skin - appear in periods. Sometimes they disappear, and the skin looks almost healthy, and sometimes they reappear or intensify, flare up.
Period subsidence is called "remission", and outbreaks - "exacerbation".
What about allergies? In the early With age, the skin becomes the main "target" for irritants that cause allergic reactions. reaction. The atopic baby's immune system overreacts to the invasion, and an exacerbation develops - the skin becomes inflamed.
reaction. The atopic baby's immune system overreacts to the invasion, and an exacerbation develops - the skin becomes inflamed.
During an exacerbation of atopic dermatitis, not only the condition worsens skin, but also general well-being. The quality of life decreases.
Constant itching depresses the child, interferes with sleep. He can shut himself up become sullen, socially inactive. Therefore, parents should help their child both with the help of proper care, and psychologically.
To indicate the causes of exacerbation of atopic dermatitis, often use the English term "trigger". It translates as "trigger" or "let go".
Trigger is any factor that provokes an exacerbation of atopic dermatitis
A diagnosis of Atopic Dermatitis can put only a doctor!
He will prescribe the correct treatment regimen, explain the principles of atopic skin care.
The main goal of treatment is to prolong remission and prevent new outbreaks. The task of parents is to be allies of the doctor, strictly follow his appointments and provide the child with an appropriate image life.
The task of parents is to be allies of the doctor, strictly follow his appointments and provide the child with an appropriate image life.
2. Why does atopic dermatitis?
An important role in the development of atopic dermatitis in a child is played by heredity. According to one study, if one of the parents was sick or suffers from atopic dermatitis, then with a probability of 56% in a child he will develop too.
If both parents are ill, the probability rises to 81%. Moreover, if parents suffer from allergic rhinitis or bronchial asthma, then the risk development of atopic dermatitis in a child also increases.
But heredity alone is not enough for the development of the disease.
Atopic dermatitis occurs when there is a genetic predisposition environmental factors that weaken the child's immune system are connected.
How does the environment influence?
Disease triggers can become:
- Food or inhalation allergens (e.
 g. dust, pollen)
g. dust, pollen) - Skin chemicals (soaps, detergents)
- Climate. As a rule, the aggravation of the disease occurs in the cold season, and a significant improvement in the summer
Physical causes:
irritation from clothing, sweating, itchy and scratchy
May also trigger become:
- Frequent viral diseases of the nasopharynx and upper respiratory tract (ARVI).
- Foci of chronic infection in the oral cavity.
Need them on time treat so that the process does not go into a chronic stage.
- Tobacco smoke.
- Passive smoking.
- Stress and drinking during pregnancy also increase the risk of atopic dermatitis in children.
Therefore, the future mother it is important to lead a healthy lifestyle and worry less.
3. How does atopic dermatitis manifest itself?
Atopic dermatitis can be recognized by several early signs.
1. itching varies in intensity.
2. dry, flaky skin.
3. redness and swelling.
4. eruptions in the form of nodules
5. greasy scales, yellowish crusts on the face and under the hair. Over time these the symptoms spread almost all over the body.
Depending on age, atopic dermatitis manifests itself in different ways,
therefore it is distinguished by different age stages, as well as severity course of the disease
Infant stage
In the infant stage, blisters form on the skin, from which oozes transparent liquid. This is called the exudative (weeping) form. atopic dermatitis. Doctors used to use the term "baby eczema". More often the face, trunk, less often the thighs and lower legs suffer. Skin in inflamed areas it becomes painful, itches, a burning sensation is felt. In "dry form" atopic dermatitis skin flakes and cracks appear.
It is easy to infect these wounds, therefore, when caring for inflamed skin, hygiene is important.
Childhood
Weeping form is less common in childhood. The skin becomes dry flaky and itchy. Skin folds thicken, areas of keratinized skin - hyperkeratosis. Skin color becomes uneven. Peel off the skin of the eyelids, eyebrows. Severe itching especially torments at night. At this stage, rashes appear in elbow and popliteal folds, gluteal folds, on the elbows, wrists, on back of the neck, hands and feet.
Adolescence
Adolescence dryness and scaling covering the entire upper part body, hands and feet. On the face, the rash often appears around the eyes and mouth. Periods of exacerbation occur more often.
The disease is severe, often pustules form on the skin, sometimes associated with a fungal infection.
If the disease has not receded during adolescence, there is a risk that it will accompany a person throughout his life.
And now about gravity. In addition to age stages, course of atopic dermatitis
is divided into mild, moderate and severe.
Light degree of atopic dermatitis
Redness of the skin in separate small areas, slight itching during the day, aggravated at night - signs of a mild course of atopic dermatitis. Exacerbations are rare - 1-2 per year.
Medium degree of atopic dermatitis
skin areas (from 10 to 50%), severe redness, thickened skin, in places weeping, moderate or severe itching. This is already moderate. Exacerbations occur often - 3-4 times a year.
Heavy degree of atopic dermatitis
In severe atopic dermatitis, more than half of the skin affected, dry and thickened areas are adjacent to weeping, itching is very strong. There are practically no periods of improvement.
Depends on the stage and severity a treatment prescribed by a doctor, the observance of which will definitely help
cope with the unpleasant manifestations of atopic dermatitis.
4. This is really serious. disease?
Atopic dermatitis significantly reduces the quality of life. First turn - because of the painful itching. It prevents the child from resting at night and negatively affects the state of the nervous system. systems.
First turn - because of the painful itching. It prevents the child from resting at night and negatively affects the state of the nervous system. systems.
But the severity of atopic dermatitis is not only in this. Atopic dermatitis is a systemic allergic disease. Word “Systemic” in this case means that the child suffers not only from the skin. IN To varying degrees, the disease affects the entire body.
Atopic march is a typical sequence in the development of allergic diseases
Often atopic dermatitis can be the beginning of a whole complex of diseases - so called Atopic March .
Atopic march is a term that refers to the typical sequence of development of allergic diseases. As the child grows older, some manifestations of allergies subside, while others become more pronounced.
Atopic march starts in infancy as atopic dermatitis and allergies to certain foods.
When the baby becomes older, with a probability of 50-60%, the next stage occurs, which manifests itself in allergic rhinitis and conjunctivitis.
At the same time or a little later, 30-40% of atopic patients may develop The most dangerous manifestation of the "atopic march" is bronchial asthma.
One of the most important tasks of parents - from early childhood to correctly and consistently solve problems with the child's skin condition. After all, care and proper treatment of atopic dermatitis will help not only relieve the child from itching, but also reduce the likelihood development of the atopic march.
6. Treatment of atopic dermatitis in
If you suspect signs of atopic dermatitis in your child or yourself, contact a dermatovenereologist at BroKVD. The doctor will clarify the diagnosis, offer a comprehensive examination according to the standard, prescribe complex treatment, recommend examination of narrow specialists, teach how to care for the skin, learn how to carry out prevention, to prevent frequent exacerbation.
Patients come to us on their own or with referrals from doctors allergists, pediatricians, therapists. You may be offered treatment in inpatient or outpatient settings. Patients with a similar diagnosis are dispensary observation.
You may be offered treatment in inpatient or outpatient settings. Patients with a similar diagnosis are dispensary observation.
SCHOOL OF ATOPIC DERMATITIS", on which the doctor a dermatovenereologist will convey information to you in an accessible form, present presentation, talk about disease prevention, proper skin care.
We are waiting for you at SCHOOL "ATOPIC DERMATITIS" at the addresses:
KDO No. 1 per. Dubyninskiy 20, 1st floor, office №7, fourth Tuesday every month at 12:30 pm.
For more information tel. registry office: 37-17-00 (Padunsky and Pravoberezhny district)
KDO No. 2 st. Ryabikov 5, 3rd floor, office No. 305, second, Fourth Monday of each month at 15:30
For more information tel. reception: 41-70-78 (Central District),
We care about your health!
why spots and irritation occur, fungus
It is not uncommon for doctors to be treated with such a complaint as itching on the inside of the thigh. It occurs as a single manifestation or accompanied by other symptoms. There are many reasons for the itching sensation. What can provoke its appearance?
It occurs as a single manifestation or accompanied by other symptoms. There are many reasons for the itching sensation. What can provoke its appearance?
Causes of itching on the inside of the thigh
Itching is usually a symptom of some disease. But the sign may also indicate the impact of the external environment, which is not dangerous for human health.
Allergy
The most common cause of itching on the inside of the thigh is an allergic reaction. Often, food, dust, pollen, animal hair act as provoking factors.
In case of allergy, in addition to itching, a reddish rash occurs. It looks like blisters or spots on the inside of the thigh in women or men.
Insect bites
Itching on the buttocks occurs in a person when he is bitten by mosquitoes, bees, gadflies, etc. Together with it, puffiness forms on the skin, the site of the lesion swells. Symptoms persist for several days, then disappear without a trace.
A big mistake is scratching the bite area.
This threatens with the penetration of the infection into the thigh cover, which will cause more vivid signs and increase the healing time.
Infection
There are infectious diseases, one of the manifestations of which is itching in the groin, legs and other parts of the body. Such pathologies include fungal skin lesions. It causes redness on the inner side of the thigh, which is flaky, itchy. The cover becomes dry, cracks form.
You can become infected with the fungus through contact with a sick person or animal, through objects of common use. Infectious pathology affects those people who have a weakened immune system.
Another cause of itchy skin is scabies. This is an infection caused by the scabies mite. When it penetrates the skin, its waste products cause severe itching. Also, infectious diseases that can cause the symptom in question include chickenpox, rubella, measles.
Vascular pathologies
Diseases of the blood vessels often cause itching in the lower extremities. It causes an increase in the concentration of platelets in the patient's blood. Capillaries break, small hematomas appear. Usually, people who are diagnosed with varicose veins or vasculitis suffer from an itchy symptom.
It causes an increase in the concentration of platelets in the patient's blood. Capillaries break, small hematomas appear. Usually, people who are diagnosed with varicose veins or vasculitis suffer from an itchy symptom.
Diseases of the internal organs
Itching and burning of the thigh skin can be caused by diabetes mellitus. The disease provokes a narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels and unpleasant skin symptoms. It can also itch if there is a malfunction in the functioning of the kidneys, liver, gallbladder.
Skin problems
Skin conditions are common causes of itching. Many diseases are accompanied by this symptom. People complain that the outer or inner part of the thigh itches, with ailments such as dermatitis and psoriasis.
Mental disorders
Skin irritation often occurs after depression, anxiety. Conflicts, stressful situations can provoke a symptom. An unpleasant symptom is formed in a certain area of \u200b\u200bthe skin or spreads to the entire area of \u200b\u200bthe body.
Diagnosis
To eliminate itching on the skin of the thighs, you need to know its cause. It is impossible to determine it on your own. Therefore, it is necessary to visit a doctor and undergo a comprehensive examination.
To find out why the skin of the thighs itch, prescribe different methods, depending on the presence of concomitant symptoms. Allergies, fungus, skin pathologies are detected already at the stage of an external examination by a doctor. For confirmation, only a laboratory study of scrapings, blood, and allergen tests is required.
If there is a malfunction of the internal organs, blood vessels or the psyche, then the diagnosis is carried out using instrumental methods. These include ultrasound, computed or magnetic resonance imaging, angiography.
Which doctor should I contact?
If there is an itching sensation on the inner side of the thigh without obvious reasons, then it is worth visiting a therapist. He will conduct a skin examination and determine which doctor will continue to see the patient. If the itchy symptom is accompanied by red spots on the inside of the thighs, peeling, then you can go straight to the dermatologist.
If the itchy symptom is accompanied by red spots on the inside of the thighs, peeling, then you can go straight to the dermatologist.
Ways to deal with itching
Skin irritation on the legs is treated differently depending on what caused it. If the matter is an allergic reaction, then it is required to eliminate all allergens from the patient's life and undergo therapy with antihistamines and agents containing glucocorticoids.
Antifungal drugs are used in case of fungal infection of the thigh, antibiotics are used in case of infectious pathologies.
Such diseases are treated with courses, which cannot be stopped even after feeling better.
If the cause of itching on the skin of the thighs lies in vascular diseases, pathologies of internal organs, mental disorders, then the therapy is carried out according to an individual scheme, depending on the specific disease.
Prevention
To avoid irritation on the inside of the thighs, you need to take your diet seriously.