Early miscarriage spotting
Signs of Early Miscarriage | Obstetrics & Gynecology
Skip to main content
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology
News | Careers | Giving | UC Davis Health
- UC Davis Health
- Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Miscarriage Management
- Signs of Early Miscarriage
Early miscarriage refers to loss of a pregnancy in the first trimester. The majority of early miscarriages occur before the pregnancy is 10 weeks gestation. Some miscarriages happen very early, even before a woman is sure she is pregnant. Still, miscarriage can be a hard and sad experience, no matter when it occurs.
Miscarriage is more common than many people realize. About 10 to 20% of women who learn they are pregnant will have an early miscarriage. The rates of early miscarriage are even higher when women are checking home pregnancy tests very close to the time of their period and are finding a positive test VERY early. By chance alone, 1% to 4% of women will have two miscarriages in a row. However, it is very rare to have 3 or more miscarriages in a row, which is recurrent miscarriage.
In medical terms, early miscarriage is called an early pregnancy failure. This means that the pregnancy failed to develop. Almost all early miscarriages are due to circumstances beyond anyone’s control, and were destined to happen before the woman even knows she is pregnant.
What are the symptoms of early miscarriage?
- Bleeding – light bleeding early in pregnancy is fairly common, and does not mean you will have a miscarriage.
- Brown discharge: This may look like coffee grounds. This “discharge” is actually old blood that has been in the uterus for a while and is just coming out slowly.
- Spotting, bright red bleeding or clots
- Passage of tissue through the vagina
- A gush of clear or pink vaginal fluid
- Abdominal pain or cramping
- Pregnancy symptoms, such as breast tenderness and nausea, begin to go away
- Dizziness, lightheadedness, or feeling faint
If you have any symptoms of a miscarriage, you should contact a doctor right away to have an evaluation. It will be important to have an ultrasound exam to look into the uterus to see if the pregnancy is normal or you are having a miscarriage. Even if you think you passed the entire pregnancy and are feeling better, you should see a doctor. Sometimes, passing tissue occurs with an ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy outside of the uterus) which can be life-threatening if not diagnosed early.
It will be important to have an ultrasound exam to look into the uterus to see if the pregnancy is normal or you are having a miscarriage. Even if you think you passed the entire pregnancy and are feeling better, you should see a doctor. Sometimes, passing tissue occurs with an ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy outside of the uterus) which can be life-threatening if not diagnosed early.
Types of early miscarriage
Early miscarriage is a non-medical term for lots of different types of events that might or might not actually result in pregnancy loss. The types of miscarriage include the following:
Spotting or bleeding in the first trimester in which the patient and the doctor are not yet sure if the pregnancy will miscarry or not. About 1/3 of all women will bleed in the first trimester, but only about half of those women will have a miscarriage.
The entire pregnancy is passed from the uterus, most commonly with bleeding and cramping, and no additional treatment or observation is needed.
The pregnancy is definitely miscarrying, but only some of the pregnancy tissue has passed. The tissue that is still in the uterus will eventually pass on its own. Some women may need emergency treatment if there is also heavy vaginal bleeding. Otherwise, women can use medicines to cause the rest of the tissue to pass or simply wait for the rest of the tissue to pass from the uterus.
With this type of miscarriage, the pregnancy implanted but the embryonic tissue (the part of the pregnancy that will develop into a fetus) never developed, or started to develop and then stopped.
With this type of miscarriage, the early embryo (or fetus once 10 weeks pregnant) stops developing and growing.
This is an uncommon type of miscarriage today. With a missed abortion, the pregnancy stops developing but the pregnancy tissue does not pass out of the uterus for at least 4 weeks. Sometimes, dark brown spotting or bleeding occurs, but there is no heavy bleeding.
Some miscarriages occur with an infection in the uterus. This is a serious condition that requires urgent treatment to prevent shock and death. With septic miscarriage, the patient usually develops fever and abdominal pain and may have bleeding and discharge with a foul odor. Antibiotics and suction evacuation of the uterus are important to start as quickly as possible.
This is a serious condition that requires urgent treatment to prevent shock and death. With septic miscarriage, the patient usually develops fever and abdominal pain and may have bleeding and discharge with a foul odor. Antibiotics and suction evacuation of the uterus are important to start as quickly as possible.
What causes early miscarriage?
Almost nothing you can do will cause an early miscarriage. Avoiding sex or heavy work will not impact an early pregnancy. There are a lot of changes that need to occur with the cells and genes in a developing pregnancy, and sometimes those changes do not happen perfectly. There are some health conditions or habits that can increase the chance that an early miscarriage will occur, including:
- Heavy smoking
- Use of illicit drugs, especially cocaine
- Poorly controlled diabetes
- Hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism
- Physical problems with the uterus, including fibroids or abnormalities of development of the uterus
Why see our specialists at UC Davis Health?
Our specialists can evaluate you quickly in an office setting. Any laboratory testing or ultrasound examinations that need to be done can be performed easily and conveniently. We perform our own ultrasound examination in the office and can share the results with you immediately.
Any laboratory testing or ultrasound examinations that need to be done can be performed easily and conveniently. We perform our own ultrasound examination in the office and can share the results with you immediately.
If we do confirm you have a miscarriage, we can discuss expectant management or treatment options with you immediately. Should you need blood testing to evaluate the pregnancy, the laboratory is in the same building as our office.
If you are having very heavy vaginal bleeding or are feeling very sick, you should go to the Emergency Room to see our physicians.
Treatment of early miscarriage
Not all miscarriages “need” treatment. The choice of whether to wait for the pregnancy to completely pass without any treatment is up to you. Our doctors are committed to providing options for all patients, including the pros and cons of all available options when miscarriage is diagnosed. All patients with Rh-negative blood, regardless of which option they choose, need treatment with Rh-immune globulin, an injection that prevents a woman from forming substances in her blood that may attack the baby during a future pregnancy.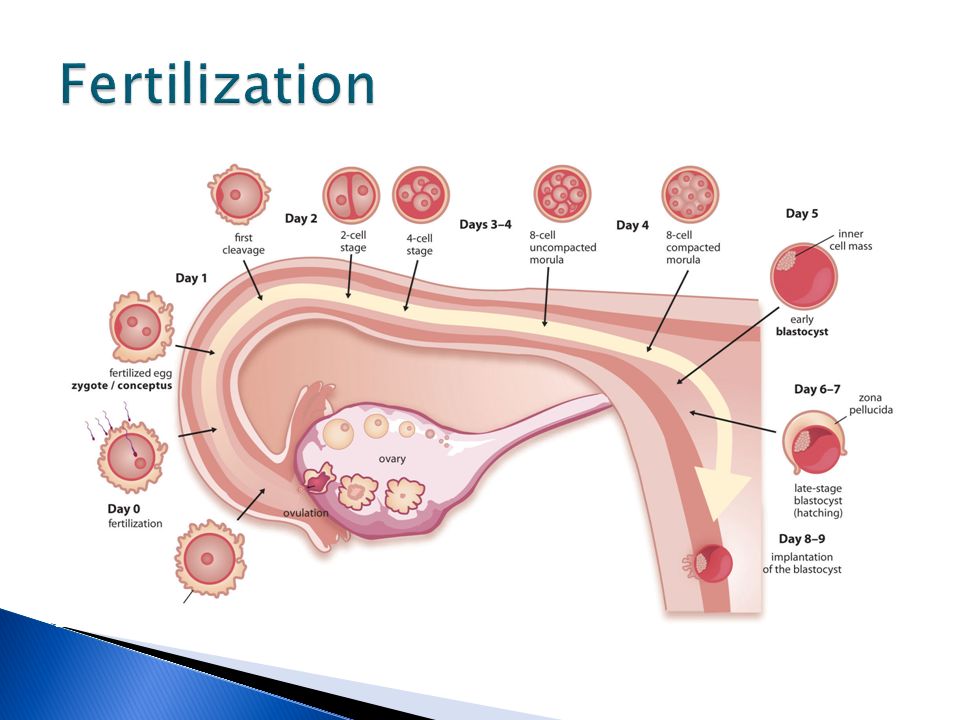
When a diagnosis of miscarriage is made, options include:
This means that you will not receive any treatment; just continued follow-up. In an early miscarriage, with time, most women will pass the pregnancy completely. The main issue is time – there is no way to predict exactly when this will occur. You will typically have heavy bleeding and severe abdominal cramping when the pregnancy does pass. Should you want this option, our doctors can review exactly what to expect, how much bleeding is too much bleeding, and what pain medications can be used once the pregnancy begins to pass from the uterus.
This treatment uses medicines to cause the pregnancy tissue to pass from the uterus. The medicines cause cramping and bleeding, just like what will occur with natural passing of the pregnancy tissue. Using the medicines is like expectant management, except that you know when the pregnancy is going to pass. Most women will pass the pregnancy within 24 hours of taking the medication. Similar to expectant management, our doctors can review exactly what to expect, how much bleeding is too much bleeding, and what pain medications to use during treatment. If the pregnancy does not pass, you can repeat the medical treatment, have a suction aspiration, or continue to wait.
Similar to expectant management, our doctors can review exactly what to expect, how much bleeding is too much bleeding, and what pain medications to use during treatment. If the pregnancy does not pass, you can repeat the medical treatment, have a suction aspiration, or continue to wait.
- This brief procedure can be done in the office or the operating room. The following steps occur regardless of the location:
- The woman is in the same position as during a regular pelvic exam, like when a Pap test is done.
- A speculum is placed in the vagina
- A cleansing antibacterial solution is applied to the cervix and vagina
- Numbing medicine is applied to the cervix to decrease cramping
- The cervix is dilated (opened) with thin rods; with early miscarriage, the cervix does not need to be opened much to complete the procedure
- A thin straw-like tube is placed through the open cervixThe pregnancy is removed using a mechanical suction pump attached to the tube
- Everything is removed from the vagina when the procedure is done
You may choose to have the procedure in the office or operating room based on your preferences – different women have different needs.
Office procedure:
- A spouse, partner, friend or relative can be in the room with you
- If desired, oral medications can be taken before the procedure to help you feel more relaxed
- You can eat or drink anything you want before the procedure
- The suction used in the office is most commonly a syringe that creates the suction so no noisy machine is used
- You will usually goes home 15-30 minutes after the procedure and can resume relatively normal activities
- Operating room procedure
- The procedure is done in an outpatient operating suite or in the main hospital
- You will be asleep during the procedure
- You cannot eat or drink anything after midnight on the night before the procedure because you will be receiving anesthesia
- You will feel sleepy for the whole day after the procedure and will need someone to be able to drive you home and be with you for the whole day after the procedure
- The operating room is more appropriate for women with certain medical conditions
After treatment for a miscarriage
Bleeding may continue for several weeks after a miscarriage but tends to be much lighter with a suction aspiration. Any bleeding may change in color from bright red to pink or brown. Lower abdominal cramping in the few days after treatment is also common. You should contact a doctor right away if the bleeding gets heavier after the miscarriage instead of lighter, if a fever develops, or if vaginal discharge or a strange or unpleasant vaginal odor occurs. Avoid intercourse, douching, or using tampons for one week. Regular activities can be resumed right away, based on how you feel. Importantly, if you want to delay getting pregnant after the miscarriage, it will be very important to start an effective method of contraception.
Any bleeding may change in color from bright red to pink or brown. Lower abdominal cramping in the few days after treatment is also common. You should contact a doctor right away if the bleeding gets heavier after the miscarriage instead of lighter, if a fever develops, or if vaginal discharge or a strange or unpleasant vaginal odor occurs. Avoid intercourse, douching, or using tampons for one week. Regular activities can be resumed right away, based on how you feel. Importantly, if you want to delay getting pregnant after the miscarriage, it will be very important to start an effective method of contraception.
Frequently asked questions about miscarriage
Having one miscarriage does not increase your chances of having another. If you have had only one prior miscarriage, the rate of miscarriage in the next pregnancy is similar to the overall rate in the general population.
No. Working, exercise and sexual activity do not increase the risk of miscarriage.
Patients were told years ago to wait one or two menstrual cycles to wait to get pregnant.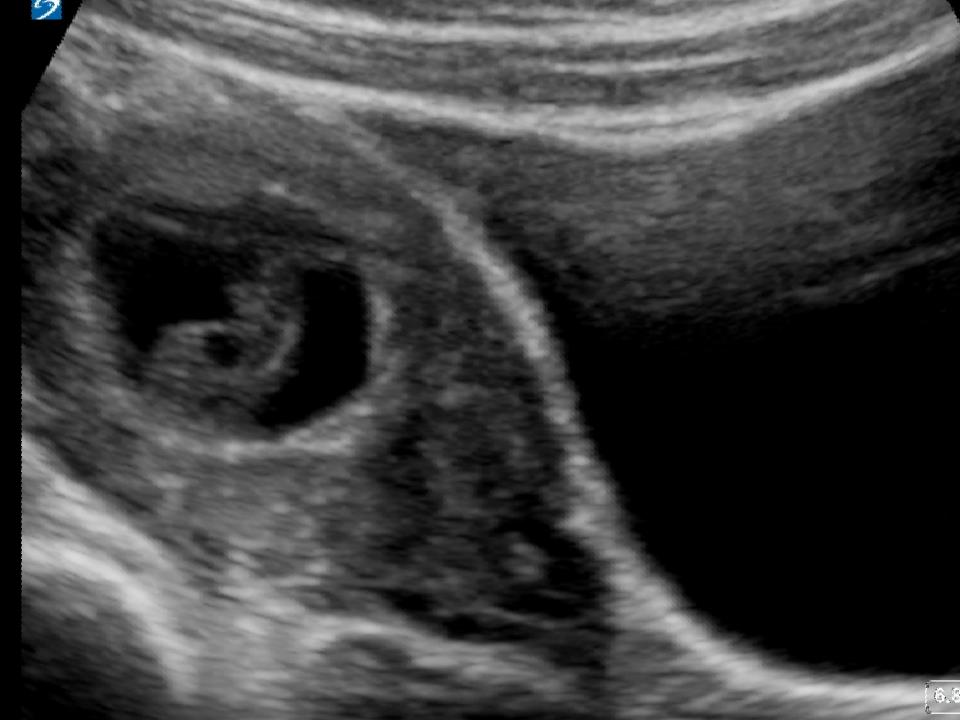 We know that it is highly unlikely that any problems occur with a next pregnancy if you get pregnant right away. How soon you decide to try again will depend on whether you want to be pregnant right away and if you feel you need time to recover emotionally from the miscarriage. Ovulation can resume as early as two weeks after a miscarriage, so if you do not want to get pregnant right away, you need effective contraception immediately.
We know that it is highly unlikely that any problems occur with a next pregnancy if you get pregnant right away. How soon you decide to try again will depend on whether you want to be pregnant right away and if you feel you need time to recover emotionally from the miscarriage. Ovulation can resume as early as two weeks after a miscarriage, so if you do not want to get pregnant right away, you need effective contraception immediately.
Since most early miscarriages are caused by problems specific to that fertilized egg, and miscarriage overall is relatively common, most experts do not recommend special testing until you have had three early miscarriages (or two miscarriages in women 40 years and older). At that point it is termed "recurrent" miscarriage and further testing may be needed. Studies have shown that even after a woman has experienced three consecutive miscarriages, her chance of the next pregnancy being normal is still about 70%. All women who have a pregnancy loss later in pregnancy should have further testing.
Tips to help support parents after pregnancy loss
UC Davis Health social worker Brenna Rizan, who works within the Department of Obstetrics/Gynecology provides supportive tips and advice for grieving parents, family and friends after pregnancy loss.
Related stories
Miscarriages are more common than people think - KCRA (Interview with Brenna Rizan)
Facebook Live: Discussing miscarriages with Dr. Mitch Creinin
UC Davis Early Pregnancy and Miscarriage Center
Vaginal bleeding - NHS
Bleeding during pregnancy is relatively common and does not always mean there's a problem – but it can be a dangerous sign.
Urgent advice: Call your midwife or GP immediately if:
- you have any bleeding from your vagina
Causes of bleeding in early pregnancy
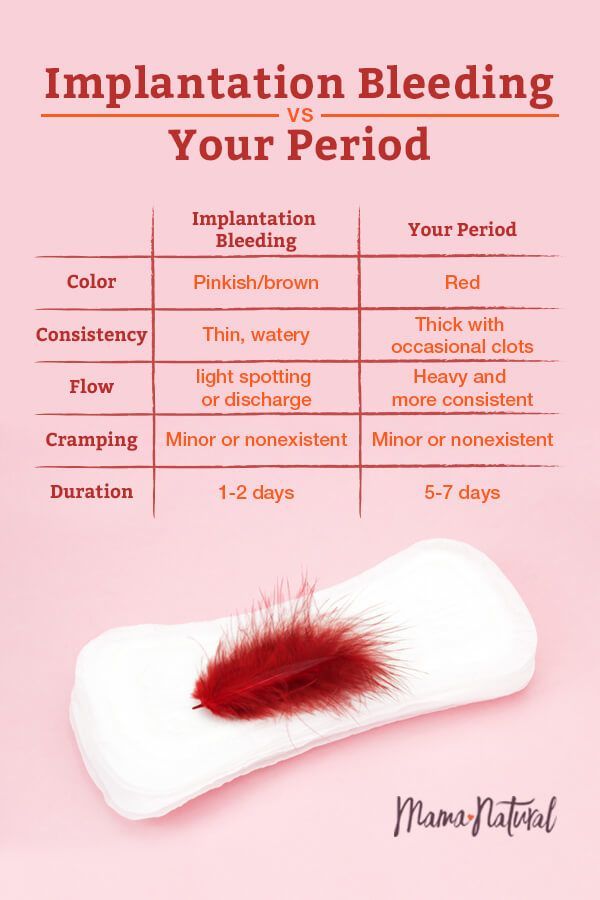
Implantation bleeding
In early pregnancy, you might get some harmless light bleeding, called "spotting". This is when the developing embryo plants itself in the wall of your womb. This type of bleeding often happens around the time your period would have been due.
This is when the developing embryo plants itself in the wall of your womb. This type of bleeding often happens around the time your period would have been due.
Cervical changes
Pregnancy can cause changes to the cervix, and this may sometimes cause bleeding – after sex, for example.
Miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy
During the first 12 weeks of pregnancy, vaginal bleeding can be a sign of miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy.
However, if you bleed at this stage of pregnancy it's likely you will go on to have normal and successful pregnancies.
Treating bleeding in early pregnancy
You may be offered a medicine called progesterone to stop bleeding in early pregnancy. This will only be recommended if you've had a scan to confirm you're pregnant and you've had a miscarriage before.
Your doctor may recommend you take the medicine twice a day until you're 16 weeks pregnant.
Miscarriage
If a pregnancy ends before the 24th week, it's called a miscarriage. Around 1 in 5 pregnancies ends this way.
Many early miscarriages (before 14 weeks) happen because there is something wrong with the baby. There can also be other causes of miscarriage, such as hormone or blood clotting problems.
Most miscarriages occur during the first 12 weeks (3 months) of pregnancy and, sadly, most cannot be prevented. Other symptoms of miscarriage include:
- cramping and pain in your lower abdomen
- a discharge or fluid from your vagina
- a discharge of tissue from your vagina
- no longer experiencing the symptoms of pregnancy, such as feeling sick
If you have bleeding or any of the symptoms above, contact your midwife or GP straightaway.
Ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is when a fertilised egg implants outside the womb – for example, in the fallopian tube.
It can cause bleeding and is dangerous because the fertilised egg cannot develop properly outside the womb. The egg has to be removed, which can be done through an operation or with medicines.
Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy tend to develop in the 6th week of pregnancy but can happen later.
Other signs of ectopic pregnancy can include:
- tummy pain low down which may be on one side
- vaginal bleeding or a brown, watery discharge
- pain in the tip of your shoulder
- discomfort when peeing or pooing
Call 111 if you have symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy.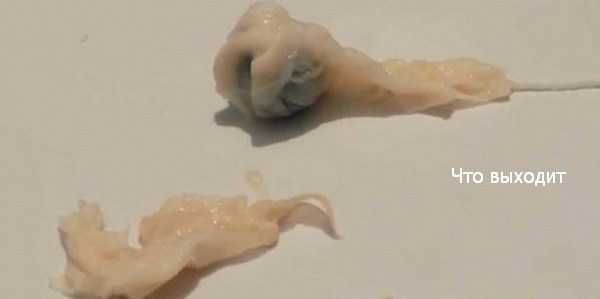
Causes of bleeding in later pregnancy
Cervical changes
These can lead to bleeding, particularly after sex.
Vaginal infections
Your midwife or doctor can discuss tests and treatment with you.
A 'show'
This is when the plug of mucus that has been in the cervix during pregnancy comes away, signalling that the cervix is getting ready for labour to start. It may happen a few days before contractions start or during labour itself.
Find out about the signs of labour and what happens in labour.
Placental abruption
This is a serious condition in which the placenta starts to come away from the womb wall. Placental abruption usually causes stomach pain, and this may occur even if there is no bleeding.
Low-lying placenta (placenta praevia)
This is when the placenta is attached in the lower part of the womb, near to or covering the cervix. Bleeding from a low-lying placenta can be very heavy, and put you and your baby at risk.
You may be advised to go into hospital for emergency treatment, and a caesarean section will usually be recommended. The Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists has more information on placenta praevia.
Vasa praevia
This is a rare condition where the baby's blood vessels run through the membranes covering the cervix.
When your waters break, these vessels may be torn and cause vaginal bleeding. The baby can lose a life-threatening amount of blood.
Finding out the cause of bleeding in pregnancy
To work out what is causing the bleeding, you may need to have a vaginal or pelvic examination, an ultrasound scan or blood tests to check your hormone levels.
Your doctor will also ask you about other symptoms, such as cramp, pain and dizziness. Sometimes it might not be possible to find out what caused the bleeding.
If your symptoms are not severe and your baby is not due for a while, you'll be monitored and, in some cases, kept in hospital for observation.
How long you need to stay in hospital depends on the cause of the bleeding and how many weeks pregnant you are.
Being in hospital allows staff to keep an eye on you and your baby, so they can act quickly if there are further problems.
Find the answers to common health problems in pregnancy
Video: What should I do if I start bleeding during early pregnancy?
In this video, a midwife tells you what to do if you start to bleed during early pregnancy.
Media last reviewed: 20 March 2020
Media review due: 20 March 2023
Early miscarriage.
 What is an early miscarriage?
What is an early miscarriage? IMPORTANT
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor.
Early miscarriage is a spontaneous termination of pregnancy for up to 12 obstetric weeks, often in the absence of cardiac activity in the fetus or an empty embryonic sac. Usually, an early miscarriage is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen or lower back of a different nature, bloody discharge from the vagina with a possible admixture of purulent masses or amniotic fluid. Diagnosis includes confirmation of pregnancy, physical examination of the patient, examination of the birth canal, and transvaginal ultrasound scanning. Treatment for an early miscarriage depends on its form and may include medical prolongation, termination of pregnancy, or vacuum aspiration.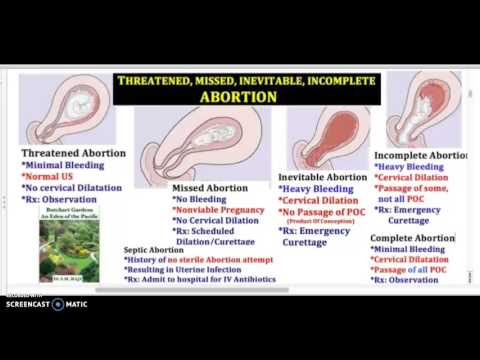
- Causes of early miscarriage
- Early miscarriage symptoms
- Diagnosis of early miscarriage
- Early miscarriage treatment
- Prognosis and prevention of early miscarriage
- Prices for treatment
General
Early miscarriage is a pathological condition in obstetrics and gynecology, which is characterized by spontaneous abortion for up to 12 weeks. According to official statistics, about 15-20% of all confirmed pregnancies end in spontaneous termination. Early miscarriage is the most common complication in obstetrics, it accounts for about 80% of all spontaneous abortions and in 70% of cases occurs before the clinical manifestation of pregnancy. About a third of all cases of early miscarriages occur before 8 obstetric weeks due to the absence of an embryo. This condition is most common among mothers over the age of 40. This is due to the high frequency of chromosomal abnormalities, which are responsible for over 50% of all early miscarriages.
early miscarriage
Causes of early miscarriage
More than half of early miscarriages are caused by fetal chromosomal mutations, in particular, autosomal trisomies, X-chromosome monosomies, and polyploidies. A minority of cases are provoked by factors that have a teratogenic effect on the fetus and create an unfavorable environment for its development. This includes the mother's use of alcohol, cigarettes, large amounts of caffeine (more than 4 cups per day) or drugs, infectious diseases (syphilis, chlamydia, toxoplasmosis), certain medications (NSAIDs, retinoids, antimycotics, antidepressants), occupational hazards (ionizing radiation, toxins, etc.).
Also, the cause of early miscarriage can be the mature age of the mother (after 40 years, the risk of spontaneous abortion is more than 40%), anomalies in the development of the genital organs, severe obesity, direct abdominal trauma, chronic diseases (antiphospholipid syndrome, polycystic ovaries, thyroid disease, etc. ).
).
Early miscarriage symptoms
There are several clinical variants of early miscarriage: threatening, incipient, septic and incomplete miscarriages, miscarriage in progress. A threatened miscarriage is manifested by pain in the suprapubic and lumbar regions of a pulling nature, scanty bloody discharge from the vagina. At the same time, hypertonicity of the uterus is observed, its dimensions correspond to the gestational age, and the internal pharynx is closed. An early miscarriage that has begun has the same symptoms, but they are more pronounced, and the cervical canal goes into an ajar state. A miscarriage in the course is characterized by recurring pains in the lower abdomen of a cramping nature, more pronounced bloody discharge, less often with an admixture of amniotic fluid. During the examination, the uterus is smaller than it should be for a given gestational age, the external and internal os are open. In the lumen of the vagina or cervix, elements of the fetal egg can be determined.
Incomplete early miscarriage (incomplete abortion) is a condition of a woman in which, after termination of pregnancy, elements of the fetal egg remain in the uterus. It is accompanied by moderate pain in the lumbar region and lower abdomen, massive bleeding, which can lead to hemorrhagic shock. Septic or infected early miscarriage - termination of pregnancy, characterized by signs of infection of the genital organs: a sharp increase in body temperature, general weakness, pain in the pelvic area, purulent discharge from the vagina, increased heart rate and respiratory rate, muscular defense of the anterior abdominal wall.
Diagnosis of early miscarriage
Diagnosis of early miscarriages is based on the collection of anamnestic data and patient complaints, an objective examination, data from laboratory and instrumental research methods. When interviewing a woman, an obstetrician-gynecologist pays attention to the date of the last menstruation, bad habits, occupational hazards, chronic diseases present, recent infections, medications and the results of past pregnancies. Collecting complaints, the specialist specifies the amount of bleeding from the vagina, the presence of pus or amniotic fluid, the nature and localization of the pain syndrome. At the baseline examination of a woman with suspected early miscarriage, the general condition, body temperature, heart rate, respiratory rate and blood pressure are assessed. Next, an examination of the abdomen is performed, followed by a vaginal examination using speculums and a bimanual examination to assess the size and consistency of the uterus. Among the laboratory tests, in addition to basic tests, the level of progesterone and β-human chorionic gonadotropin (β-hCG) is measured to determine a possible ectopic pregnancy.
Collecting complaints, the specialist specifies the amount of bleeding from the vagina, the presence of pus or amniotic fluid, the nature and localization of the pain syndrome. At the baseline examination of a woman with suspected early miscarriage, the general condition, body temperature, heart rate, respiratory rate and blood pressure are assessed. Next, an examination of the abdomen is performed, followed by a vaginal examination using speculums and a bimanual examination to assess the size and consistency of the uterus. Among the laboratory tests, in addition to basic tests, the level of progesterone and β-human chorionic gonadotropin (β-hCG) is measured to determine a possible ectopic pregnancy.
The leading place in the diagnosis of early miscarriage is occupied by ultrasound (ultrasound). Currently, transvaginal ultrasound (TVS) is the "gold standard" in the diagnosis of pregnancies in the early stages. Only if it is impossible to carry out a transabdominal scan (TAS) is used. Signs of early miscarriage include an average internal diameter of the fetal egg over 20 mm on the TVS and 25 mm on the TAS, respectively, the absence of cardiac activity or the complete absence of its visualization. Differential diagnosis of early miscarriage is carried out with benign and malignant neoplasms of the cervix and vagina, chorionepithelioma and ectopic pregnancy.
Signs of early miscarriage include an average internal diameter of the fetal egg over 20 mm on the TVS and 25 mm on the TAS, respectively, the absence of cardiac activity or the complete absence of its visualization. Differential diagnosis of early miscarriage is carried out with benign and malignant neoplasms of the cervix and vagina, chorionepithelioma and ectopic pregnancy.
Early miscarriage treatment
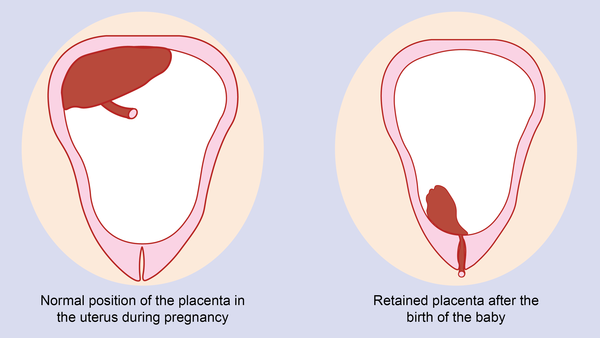
The treatment regimen for early miscarriage directly depends on the clinical form of the pathology and the decision of the mother. With a threatened or incipient miscarriage, prolongation of pregnancy is possible, with intrauterine death of the fetus, medical abortion is indicated. In order to maintain pregnancy and prevent early miscarriage, gestagens are used. Tranexamic acid is also used for hemostatic purposes, and drotaverine is used to relieve pain. If it is impossible to prolong the pregnancy, medical curettage is indicated. There are various options for its implementation, in which prostaglandin analogues can be combined with an antiprogestin.
Surgical treatment is indicated in cases of infected and incomplete early miscarriage, as well as massive bleeding caused by the latter. The essence of the surgical intervention is to remove the remaining tissues of the chorion or placenta and complete hemostasis. As a rule, such interventions are performed using a vacuum aspirator or other sources of vacuum, less often they resort to instrumental curettage. According to modern research, before surgery for early miscarriage, it is effective to preliminarily (1-1.5 hours) use of NVPS and drugs from the benzodiazepine group.
Prediction and prevention of early miscarriage
The prognosis for early miscarriage is favorable in most cases. The risk of repeated miscarriage increases slightly and is 19-20% compared to the average of 15%. Among couples in whom it was not possible to identify the cause of early miscarriage, in more than 65% of cases, re-pregnancy goes well.
There is no specific prevention of early miscarriage. Non-specific preventive measures involve the exclusion of etiological factors through full antenatal protection of the fetus and rational pregnancy planning. If a couple wants to have a child, it is recommended to visit specialized centers and consult a geneticist. After confirming the fact of pregnancy, in order to prevent early miscarriage, a woman should exclude all teratogenic factors, completely abandon bad habits and undergo all control examinations according to the recommendations of an obstetrician-gynecologist.
Non-specific preventive measures involve the exclusion of etiological factors through full antenatal protection of the fetus and rational pregnancy planning. If a couple wants to have a child, it is recommended to visit specialized centers and consult a geneticist. After confirming the fact of pregnancy, in order to prevent early miscarriage, a woman should exclude all teratogenic factors, completely abandon bad habits and undergo all control examinations according to the recommendations of an obstetrician-gynecologist.
Sources
- In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor.
Early miscarriage - symptoms and how to prevent it
The term "early miscarriage" refers to a spontaneous abortion that occurs in the first 6-8 weeks of pregnancy. It can occur before 20 weeks of pregnancy for reasons related to the natural states of the fair sex.
 According to statistics, the logical outcome of every fifth pregnancy is a miscarriage. However, quite often a woman does not even know that she was pregnant by the time the fetus is rejected by the body.
According to statistics, the logical outcome of every fifth pregnancy is a miscarriage. However, quite often a woman does not even know that she was pregnant by the time the fetus is rejected by the body. In addition, a curious pattern was revealed: more often than a natural one, a pregnancy induced artificially ends in a miscarriage. For example, in vitro fertilization, unfortunately, does not always lead to a successful pregnancy and the birth of a baby on time.
Why can I have an early miscarriage?
Here are the most common causes, each of which significantly increases the risk of miscarriage:
- the future mother has certain infectious diseases, as well as STDs;
- intoxication of a woman's body for various reasons, including as a result of her living in an ecologically unfavorable region;
- all kinds of metabolic disorders in the body;
- hormonal disruptions, including those caused by a malfunction of the thyroid gland;
- various neoplasms in the uterus and others, as well as the cervix, pathologies;
- future mother leading a life far from a healthy lifestyle.
 May include drinking alcohol, smoking, taking psychotropic and narcotic drugs, as well as malnutrition;
May include drinking alcohol, smoking, taking psychotropic and narcotic drugs, as well as malnutrition; - obesity;
- immune status disorders;
- cardiac diseases;
- diabetes mellitus;
- too early for pregnancy or, conversely, the patient's overly mature age at times increases the risk of miscarriage;
- all kinds of pathologies of chromosomes and genes;
- prolonged exposure to stress or severe psycho-emotional trauma in a woman.
The timing of a miscarriage may depend, among other things, on the patient's genetic predisposition to miscarriage. Finally, often its specific cause remains unexplained to the end.
Symptoms of miscarriage
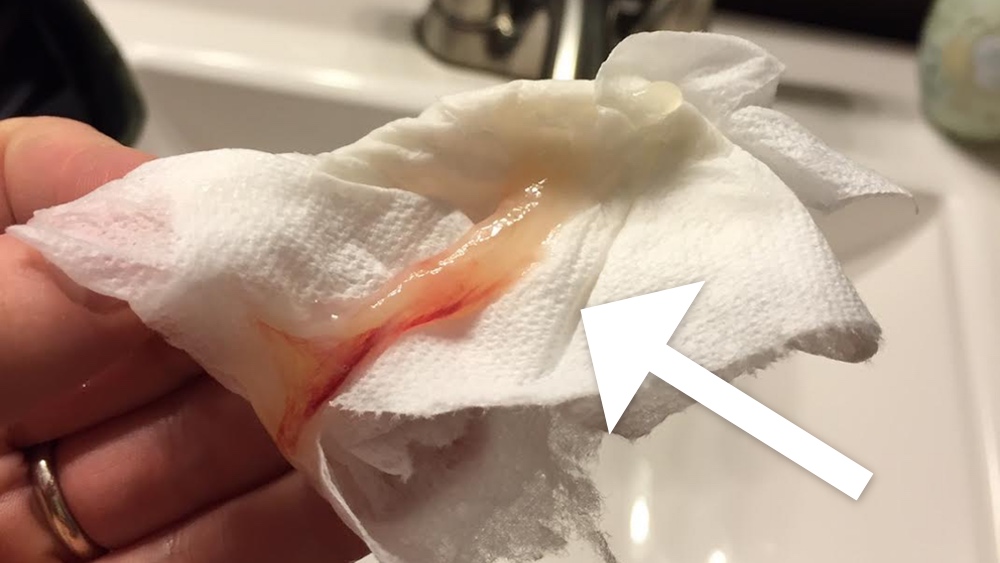
A pregnant woman should urgently seek medical help if she has the following warning signs:
- bleeding from the vagina;
- spotting discharge from the genital tract. They can have both light pink and intense red or brownish tint;
- convulsions;
- severe pain in the lumbar region;
- abdominal pain, etc.
All of the above signs can be symptoms of a miscarriage. Timely provision of qualified medical care is the key to maintaining pregnancy.
Life after miscarriage
If a woman could not bear the pregnancy - an early miscarriage crossed out all her plans - then she needs to calm down and take all measures to prevent such complications in the future. Usually obstetricians-gynecologists recommend planning a new pregnancy no earlier than six months after a miscarriage. During this time, a woman needs to be examined and find out if she has any pathology in her body that could lead to an abortion. It can be various STDs and infectious diseases. In the presence of chronic diseases that can provoke spontaneous abortion, it is necessary to throw all your efforts into their treatment.
Gynecologists of the corresponding department of our private clinic in Ryazan will help you find out what could have caused the miscarriage, as well as make recommendations on how to prepare for pregnancy.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/hemorrhage-in-miscarriage-meaning-2371523-FINAL-f2ab04cab1cc491e964a45e682f93da5.png)
Learn more