Baby ready to be born
How Does A Baby Know When To Be Born?
Many parents-to-be wonders how does a baby knows when to be born? It’s fascinating to ponder the mystery of it.
In the last few decades, researchers have been doing their best to answer questions about how and why babies are born.
Let’s find out how women’s and babies’ bodies work around the time of birth and what exactly triggers labor.
Does your body or your baby decide when labor starts?
We know the birth process is a team effort. Mother and baby are perfectly ‘in tune’, from the time conception occurs.
Research has beautifully explained how the placenta works.
It acts as the baby’s lungs, filling the blood cells with oxygen, and also works as the baby’s liver, filtering out and getting rid of any waste products. These are the best-known functions of fetal circulation.
The placenta, with the help of the attached umbilical cord, is also in charge of providing all the communication between a woman’s brain and her baby.
It’s a complex mechanism. Hormones, cell markers, enzymes, and DNA all travel through the blood system from one to the other.
The baby sends the mother the information about what is needed and the mother provides it.
As one of nature’s best-connected teams, mother and baby work together, almost as one, to achieve the baby’s complete development and, when the time comes, a successful birth.
The due date
Your due date is mathematically calculated to mark the time when your pregnancy reaches 40 weeks. Basically, it involves adding 280 days to the first day of your last period.
If only it were that easy to know the exact date your baby was going to be born!
This method is not an individualized way of calculating each pregnancy. It’s a general one, based on average statistics. For example, it doesn’t take into account the different lengths of women’s menstrual cycles.
Human pregnancy is considered full-term between 37 and 42 weeks. This means babies are fully formed and ready to be born at any time during this five-week period.
In fact, only 3-5% of babies are born on their given due date.
You can learn more about the due dates here.
You might also like to try BellyBelly’s Due Date Calculator.
What determines when a baby is ready to be born?
If a baby can be born at any time between 37 and 42 weeks, you might be wondering how the process starts up. How does a baby know when to be born?
What is it that sends labor signals to pregnant women, and tells the baby it’s time to be born and get ready to go through the birth canal?
Let’s look at the leading research in this area.
Research from the UT Southwestern Medical Center discovered certain cell markers that appear just before labor.
A cell marker is a molecule with a very specific role: to identify specific cells and bind with them so they can work together.
When these cell markers enter the amniotic fluid, the baby releases a combination of hormones that travel to the mother’s brain. This triggers a response in the mother’s uterus and cervix, basically saying, ‘Let’s take action. The changes we were waiting for are finally here.
This triggers a response in the mother’s uterus and cervix, basically saying, ‘Let’s take action. The changes we were waiting for are finally here.
The researchers also found there was another very important internal factor that tells the baby it’s time to come out: the baby’s lungs.
Are You Getting BellyBelly’s Pregnancy Week By Week Emails?
We think they’re the best on the internet!
Click to get the FREE weekly updates our fans are RAVING about.
Their study found two special proteins (SRC-1 and SRC-2) are released from the baby’s lungs into the amniotic fluid just before the beginning of labor. This causes an inflammatory response in the uterus that sends labor signals to the mother’s brain.
These two proteins also start the release of surfactants, which are substances that help a baby’s lungs to work effectively after birth.
The baby must have surfactant in her lungs. It’s essential for breathing after a baby is born. Surfactant is so important that if there’s a high risk of preterm labor, doctors will give the mother steroid injections. This is to speed up the production and release of surfactant to help the baby’s lungs develop faster.
Surfactant is so important that if there’s a high risk of preterm labor, doctors will give the mother steroid injections. This is to speed up the production and release of surfactant to help the baby’s lungs develop faster.
In these cases, the obstetric team will try to stop labor from happening for at least 24 hours. That’s how long it takes for the injections to help with the production of surfactant in the baby’s lungs.
You might like to read What Causes Labor To Start for more information.
How does your body know when to go into labor?
As we’ve just seen, Mother Nature always knows best.
Helped by the delivery of certain markers, enzymes, hormones, and surfactants, you and your baby work together. This teamwork starts up the body systems that will put an end to the pregnancy, and lead to the birth of your baby.
What are some signs that labor is near?
At the end of pregnancy, when the time to give birth is getting closer, the cervix starts to change. It becomes shorter and thinner (effaces) and opens up (dilates) in order to allow the baby’s body to pass through the vagina.
It becomes shorter and thinner (effaces) and opens up (dilates) in order to allow the baby’s body to pass through the vagina.
The release of the mucus plug often follows these changes, as the cervix is no longer tightly closed. You might notice some backache that in hindsight pointed to the mild uterine contractions acting on the cervix.
When the first labor signals start, you might experience the feeling that your pelvis feels full or heavy. This is your baby moving lower into the pelvis.
For more information be sure to read Signs Of Labor – 7 Signs You Might Be In Labor.
How does a baby know when to turn head down?
This is a common question many parents ask after learning the theory behind the triggers for labor.
The baby has been growing in your uterus, guided by nature and with very little conscious brain input from you.
So how does a baby know how to get into the optimal head-down position for birth?
As you might have guessed, the answer might be less complicated than surfactant components, lung development, and complex hormonal activity.
The reason a baby turns into the head down or vertex position is simply a matter of space. As the baby gets bigger, there is less room in the womb, and the baby looks for the most comfortable position.
In most cases, this is the one where the head of the baby is close to your pelvis and the rest of the body is higher up.
Here is some useful information if your baby is in the breech position after 36 weeks.
Are babies awake during labor?
This is also a common question. Many parents want to know whether babies are asleep or awake during labor.
During pregnancy, a baby spends most of the time sleeping, particularly in the last trimester. This deep need for REM sleep is important for brain and nervous system development.
However, during labor, the baby spends more time awake.
Understandably, during labour the baby can feel that something quite different is happening. It’s important that the baby is awake, especially when a birth is close.
The theory behind this is babies need to be alert when they are born so the correct bonding and attachment can happen.
Labor is a lengthy process and a baby who has spent most of her life sleeping requires a bit of rest every now and then.
During labor women rest between contractions; some might even nod off. But because the baby doesn’t feel the contractions the same way the mother does, she can sleep for much longer than the time between two contractions. It’s normal for a baby to sleep up to 30 minutes every couple of hours.
Birth From Your Baby’s Point Of View is a fascinating look at what babies sense and feel as they’re being born.
Do babies feel pain during birth?
A woman can communicate with care providers and tell them how much pain she experiences during labor.
She can express not only its intensity but where she feels pain – in her body, vagina, back, or belly.
But do babies experience pain during labor?
There are no solid ways to measure the perception of pain in utero, but evidence suggests a baby can perceive pain. This is seen in changes to fetal heart rate during a medical procedure, or the mother’s perceptions of the baby’s reactions when a blood sample is taken during labor to check the baby’s pH.
This is seen in changes to fetal heart rate during a medical procedure, or the mother’s perceptions of the baby’s reactions when a blood sample is taken during labor to check the baby’s pH.
Mighty hormones
Natural endorphins and oxytocin are released during labor and they cross the placental barrier so the baby also benefits from their effect.
We must bear in mind that when a woman is given synthetic oxytocin during labor, her own natural production stops. The placenta works so well to control what passes to the baby that it doesn’t allow artificial hormones to enter the baby’s circulation.
When the woman has an epidural, the production of endorphins stops as she is no longer in pain, and the baby has to navigate labor without these natural pain relief hormones.
It’s believed the main reason a newborn baby sleeps so much is to recover fully from birth.
Good attachment and lots of nurturing and love will get those healing hormones flowing in no time.
4 ways your body gets ready for labour
1. You have Braxton Hicks contractions
During your pregnancy, you may feel your tummy tighten for a few seconds, then relax again. This can happen from the middle of your pregnancy and are thought of as 'practice' contractions. They do not mean you are in labour and are nothing to worry about.
As the end of pregnancy approaches, Braxton Hicks contractions may become more powerful, so it's easy to mistake them for the start of labour. Braxton Hicks contractions are irregular and don't last very long. Although they can be uncomfortable, they aren’t painful.
Find out more about the difference between Braxton Hicks and labour contractions.
Contact your midwife, birth centre or labour ward for advice if you're worried that the tightenings you're feeling might be the start of labour.
2. Your baby settles into position
Babies move around a lot in your womb during pregnancy but at some point in late pregnancy your baby will get into position for birth. If this is your first baby, you may find he or she is already in position by 35 weeks.
If this is your first baby, you may find he or she is already in position by 35 weeks.
Remember, you should continue to feel your baby move right up to the time you go into labour and during labour. If you think your baby’s movements have slowed down, stopped or changed, contact your midwife or maternity unit immediately. Find out more about your baby’s movements.
The most common position for birth is head down with your baby's back facing outwards, which is called an anterior position. The is the ideal position for giving birth, because your baby may fit through your pelvis more easily.
If your baby is head-down but facing your tummy, this is called the posterior position. Some midwives and antenatal teachers believe that spending time leaning forwards (for example, being on your hands and knees or leaning forward over a beanbag or birth ball) can help encourage them to turn.
Whether your baby turns or not, you may find it comfortable to be in this during late pregnancy and labour, so it's worth a try.
Find out more about getting your baby in the best position for birth.
Breech position
Your baby is in breech position if they are sitting bottom or feet down in the womb. If your baby is in a breech position at 36 weeks, you may be offered an external cephalic version (ECV). This is when a doctor tries to turn the baby into a head-down position by putting pressure on your stomach.
This is a safe procedure that will be done at the hospital. Around 50% of breech babies can be turned using ECV.
Find out more about what happens when your baby is breech.
Engaging
If this is your first baby, they will usually may move down into your pelvis before the birth. This is called 'engaging' and when it happens any breathlessness you've been feeling will probably ease. Second or later babies may also do this, but it may not happen as early.
Multiple pregnancy
If you're having twins or triplets, your babies may be in different positions. All the babies’ positions are important, but your healthcare team will be more interested in the position of the first baby when considering how you will give birth.
3. You have a 'show'
When you are pregnant, a small plug of mucus blocks the entrance to your cervix (the neck of your womb).
As your cervix begins to stretch and get ready for the birth, this mucus plug starts to come away and you may notice it on your underwear. This is called a ‘show’, although not everyone will experience this.
The show is pink because it’s bloodstained. It’s normal to lose a small amount of blood with the mucus, but if you’re losing more blood it may be a sign something is wrong. Call your hospital or midwife straight away if you’re concerned.
Your labour may not start for hours or even days after you lose the mucus plug. Or you could already be in early labour. If you're full term when the mucus plug comes out, you may have other signs that labour has started.
If you think the mucus plug has come out before you're 37 weeks pregnant, call your midwife. You may not be in labour, but it’s best to get checked out.
4. Your waters break
Your baby develops inside a bag of fluid called the amniotic sac. When your baby is ready to be born the sac breaks and the fluid comes out through your vagina. This is your waters breaking. Your waters may break at any time during labour. Some babies are even born in their waters.
When your baby is ready to be born the sac breaks and the fluid comes out through your vagina. This is your waters breaking. Your waters may break at any time during labour. Some babies are even born in their waters.
You may have a big gush of water or just a trickle, so you may not be sure whether your waters have broken or you've just wet yourself. If you think your waters have broken, contact your midwife or hospital straight away as they may want to give you a check-up.
It is a good idea to make a note of when your waters broke so you can tell the midwife.
Tell your midwife straight away if:
- the waters are smelly or coloured
- you’re losing blood.
This could mean you and your baby need urgent attention. It may help to wear a sanitary pad (not a tampon) so you can show the midwife what’s happening.
If your waters break before you go into labour
Sometimes your waters may break before you go into labour. Most women go into labour on their own within 24 hours. If this doesn’t happen your midwife will offer to induce labour and you’ll be advised to give birth in hospital, if you’re not there already.
If this doesn’t happen your midwife will offer to induce labour and you’ll be advised to give birth in hospital, if you’re not there already.
This is because your waters breaking before labour starts increases your baby’s risk of infection.
Find out more about what to expect when your waters break.
37-40 weeks of pregnancy
37th week of pregnancy for a baby
At 37 weeks of gestation, the baby is approximately 48 cm tall and weighs 2,600 g. facial features, pronounced cartilage tissue. The accumulation of subcutaneous fat at this stage of pregnancy makes the outline of the body softer and more rounded. The skin of the child is gradually smoothed out, it is no longer as pink as in the previous weeks of intrauterine development, the integument gradually brightens. The body of the baby is still abundantly covered with grease, but the amount of fluff is noticeably reduced, fluff hair remains only on the shoulders and back, in some babies they disappear almost completely.
Fat accumulation continues this week. It reaches a maximum of 15% of the total body weight of the child. It is difficult to overestimate the importance of adipose tissue for newborns, it is it that protects the child from overheating or hypothermia, since the baby's thermoregulation system after childbirth is still not sufficiently formed and continues to develop in the first months of a small person's life.
At this time, not only the volume of subcutaneous fat increases, but muscles and skeleton also develop intensively. The child constantly moves arms and legs. These unique workouts help increase muscle mass. Also, the baby makes rhythmic respiratory movements that strengthen the intercostal muscles and the diaphragm, and prepare the respiratory organs for childbirth.
Pregnant woman at 37 weeks
As the due date approaches, pregnant women begin to notice the appearance of their precursors, that is, certain signs, changes that occur under the influence of hormones. The body of a woman is preparing to give birth to a child, progesterone gives way to the dominant role of the birth hormone estrogen, the state of health of a pregnant woman changes.
The body of a woman is preparing to give birth to a child, progesterone gives way to the dominant role of the birth hormone estrogen, the state of health of a pregnant woman changes.
From the 37th week, expectant mothers can observe the following changes:
- slight weight loss;
- abdominal shrinkage;
- the appearance of training or "false" contractions and the increase in their intensity;
- discharge of mucus from the cervix.
The nature of the stool changes, it becomes looser, aching pains in the lower back of varying intensity may appear, the fundus of the uterus descends. A woman notes some signs on her own, others are observed by a gynecologist during a routine examination.
Harbingers do not appear in all women. Some expectant mothers notice only some of the above symptoms, while others observe signs of an impending birth not two or three weeks before their date, but just a few hours. Both the appearance of precursors at the 37th week and their absence are a variant of the norm and depend on the individual characteristics of the woman's body.
This week the woman's body is intensified preparation for the birth of a child. If the fetus is located correctly, head down, it gradually descends, goes to the lower part of the uterus, presses to the body and bends the limbs, intuitively taking the most comfortable position for passing the birth canal. The consequence of the movement of the fetus is the omission of the bottom of the uterus. The abdomen drops, the pressure on the diaphragm significantly decreases, the pregnant woman can breathe easily, the shortness of breath that haunted her in previous weeks disappears. The pressure on the stomach also decreases, heartburn disappears, a feeling of heaviness after eating and other unpleasant sensations. Moving the baby can put pressure on the bowels and bladder. A pregnant woman at this time often experiences the urge to urinate, may suffer from frequent loose stools. The reason for frequent bowel movements is not only the mechanical effect of the uterus on it, but also an increase in the content of estrogens in the body, hormones that contribute to the excretion of fluid. At the 37th week, the expectant mother can empty her intestines up to 3-4 times a day and at the same time observe a significant liquefaction of feces.
At the 37th week, the expectant mother can empty her intestines up to 3-4 times a day and at the same time observe a significant liquefaction of feces.
38th week of pregnancy: the development of the future baby
At the 38th week, the fetus is fully formed, so childbirth at this time is no longer dangerous for both the mother and the baby. The weight of the fetus is about 3 kg, but this indicator can vary significantly for different babies, the weight depends on the individual characteristics of the mother and child, the structural features of the body and other factors. The body length of a newborn is approximately 50 cm.
All organs and systems at 38 weeks of age are characterized by physiological and morphological maturity, they are fully ready for work. At this time, the child prepares for childbirth, makes respiratory movements and prepares the intercostal muscles for breathing. The tissues of the lungs are bathed in amniotic fluid, which helps maintain the right level of surfactant that coats the baby's lungs from the inside. All elements of the respiratory system are ready for use. With the first breath after birth, the alveoli begin to transfer oxygen from the air to the blood, gas exchange occurs, the respiratory and circulatory systems begin to work intensively.
All elements of the respiratory system are ready for use. With the first breath after birth, the alveoli begin to transfer oxygen from the air to the blood, gas exchange occurs, the respiratory and circulatory systems begin to work intensively.
Pregnant woman
The body of a pregnant woman continues to actively prepare for the birth of a baby, the estrogen content rapidly increases, and the progesterone level decreases significantly. A change in the hormonal background contributes to the softening of the tissues of the birth canal and cervix. Throughout pregnancy, the lumen of the cervical canal is closed by a plug of thick mucus, which protects the baby from infection, and the uterine cavity protects against the penetration of microorganisms dangerous to health. In the last weeks of pregnancy, the consistency of the mucus changes, it becomes more liquid and begins to gradually flow out. In some women, mucus leaves gradually, while in other women in labor at the same time. The discharge resembles colorless egg white in its consistency and appearance. Sometimes the mucus is colored pinkish, brown or yellow. The discharge of the cork is painless, a woman may experience a slight feeling of discomfort in the lower abdomen. More abundant vaginal discharge than during the entire pregnancy can signal the passage of the cork.
The discharge resembles colorless egg white in its consistency and appearance. Sometimes the mucus is colored pinkish, brown or yellow. The discharge of the cork is painless, a woman may experience a slight feeling of discomfort in the lower abdomen. More abundant vaginal discharge than during the entire pregnancy can signal the passage of the cork.
A woman should carefully monitor the color and volume of discharge, since too much colorless discharge may indicate not only the cork has come off, but also be one of the symptoms of amniotic fluid leakage. Indicator pads and amnio tests or test strips will help determine the cause of the discharge. Pads are sold in many pharmacies and can be easily used at home. If amniotic fluid leakage is confirmed, you should immediately consult a doctor.
After the mucus plug has passed, you should stop visiting the pool and swimming in open water, as the risk of infection of the child increases significantly. It is also necessary to exclude sexual contact.
39th week of pregnancy: what happens to the fetus?
At 39 weeks, the baby weighs 3100-3500 g and is 50-52 cm tall. Height and weight are very relative and can vary significantly. The baby is rapidly preparing for the most important test of his life - birth, which requires endurance and considerable effort. During this period of pregnancy, the size and weight of the child's adrenal glands, that is, the glands of the endocrine system, which are responsible for the reaction of the human body to stress factors, increase. It is the hormones adrenaline and norepinephrine produced by the adrenal glands that help the child quickly adapt to new temperature conditions, tactile, sound and light impulses.
All the senses of the baby are developed at 39 weeks. Within a few moments after birth, the baby can focus his eyes, he reacts to bright light and moving objects, many scientists claim that newborns distinguish colors, see the faces of parents and doctors. The hearing of the baby in the last weeks of fetal life is also fully developed; after birth, he reacts to loud sounds and noise. A newborn baby is able to determine the main shades of taste, recognize sour, bitter, sweet and salty.
A newborn baby is able to determine the main shades of taste, recognize sour, bitter, sweet and salty.
In the womb, the baby is in an aquatic environment that minimizes contact. Immediately after birth, the baby experiences many tactile sensations, unlike intrauterine life, he feels the touch of his mother's hands and diapers, towels, dressings and other materials. Babies especially like the touch of skin to skin, so in a modern maternity hospital, newborns must be laid out on their mother's stomach even before cutting the umbilical cord. The child adapts to the new environment more easily, feels protected. Laying out a child has not only a psychological aspect, since it contributes to the colonization of microorganisms from the mother's skin to the skin and mucous membranes of the baby, and increases its immunity.
Pregnant woman
In the last weeks of pregnancy, the expectant mother strives to prepare her apartment or house as much as possible for the arrival of a new family member. Scientists call this sign of impending birth the nesting syndrome. Many women observe signs of the syndrome from the thirtieth week of pregnancy, however, nesting reaches its maximum point at the 39-40th week. Pregnant women tend to do general cleaning and repairs, re-paste the wallpaper and purchase a lot of new things that, in their opinion, are simply necessary in the house. After giving birth, many purchases are puzzling. The reason for this behavior is an increase in the level of adrenaline and norepinephrine in the body. These hormones are produced by the adrenal glands, they are necessary not only for the woman, but also for the baby to prepare for the upcoming birth.
Scientists call this sign of impending birth the nesting syndrome. Many women observe signs of the syndrome from the thirtieth week of pregnancy, however, nesting reaches its maximum point at the 39-40th week. Pregnant women tend to do general cleaning and repairs, re-paste the wallpaper and purchase a lot of new things that, in their opinion, are simply necessary in the house. After giving birth, many purchases are puzzling. The reason for this behavior is an increase in the level of adrenaline and norepinephrine in the body. These hormones are produced by the adrenal glands, they are necessary not only for the woman, but also for the baby to prepare for the upcoming birth.
40th week of pregnancy: how does the baby develop?
40 weeks - term pregnancy. The weight of a child who was born at such a period ranges from 2,600 g to 4,400 g, and his body length is 48-53 cm. These indicators are very arbitrary, since miniature babies weighing 2,600 g and real heroes are born at 40 weeks, whose body weight approaches 5,000 g. The length of the newborns can also vary from 45 to 55 cm.
The length of the newborns can also vary from 45 to 55 cm.
Most women give birth exactly at 40 weeks. At this time, the baby is completely ready for birth, it meets all the parameters of a full-term baby. Before childbirth, the child closely presses the arms and legs to the body, bends the head as much as possible and presses against the exit from the uterus. This position allows you to make it possible to pass the birth canal with the narrowest part of the skull. In the course of labor, with each contraction, the child gradually moves down, he does not move in a straight line, but makes helical-translational movements, as if screwing into the mother's birth canal. During the progress of the newborn, the complete descent of his head, the cervix fully opens. This is followed by attempts, that is, contractions of the uterus, which advance the child through the birth canal. Gradually, the head of the baby is shown, and after it - his torso. Childbirth is a complex mechanism that is aimed not only at the safe passage of the birth canal by the child, protecting him from accidental injuries due to increased pressure, but also at preventing ruptures of the woman's soft tissues.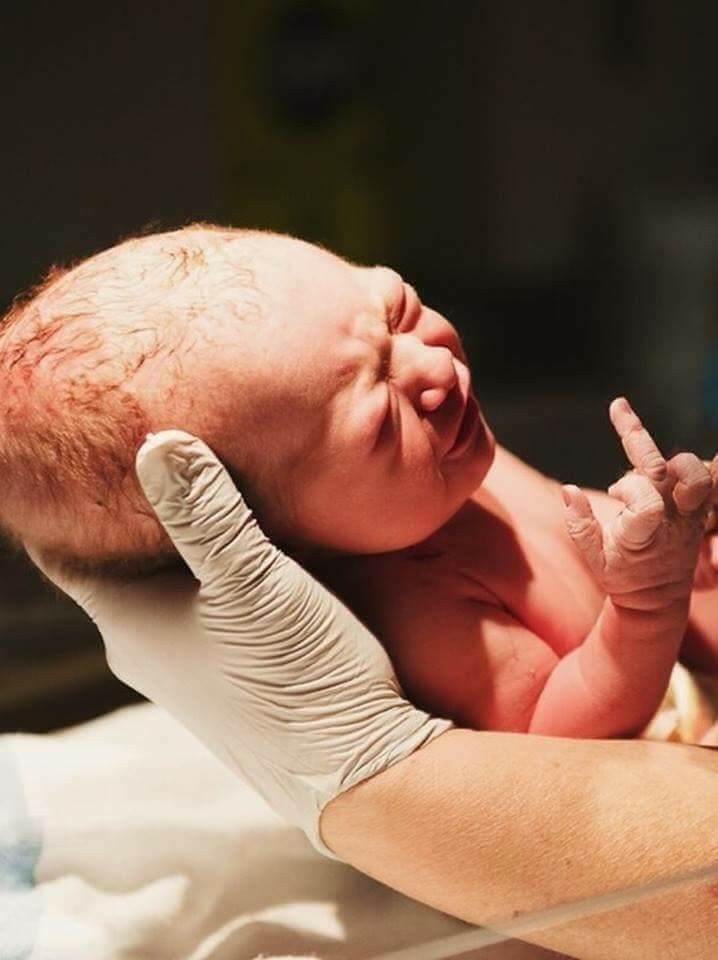
Pregnant woman
The long wait for meeting her unborn child is coming to an end, and the 40th week of pregnancy is the last for most women. Every day, the anxiety of the expectant mother increases, a long wait affects the mood and well-being. Women strive to have a baby as soon as possible so that pregnancy and painful contractions are a thing of the past. Every pregnant woman dreams of meeting a baby, wants to hug him to her chest and stroke the delicate head.
Many women, especially primiparas, are afraid that labor will begin unnoticed, but such cases are extremely rare. A woman feels the onset of childbirth, feels regular contractions, which are repeated at regular intervals and gradually increase, the time interval between them is reduced.
Labor may be preceded by prenatal rupture of amniotic fluid, which occurs in a certain percentage of women in labor. After the waters break, contractions may be quite weak or completely absent. Regardless of the intensity of contractions, the outpouring of water is one of the signs of the onset of labor and requires immediate contact with specialists, hospitalization of a woman in a maternity hospital or hospital, since when the water breaks, the integrity of the bladder is violated and the risk of penetration of microorganisms dangerous to the health of the child increases into the uterine cavity. It is important that after the water breaks, the baby is born in a maximum of 10-12 hours.
It is important that after the water breaks, the baby is born in a maximum of 10-12 hours.
A pregnant woman should properly tune in to childbirth, concentrate on the desired result and believe in her own strength, fulfill the task assigned to her by nature. The right psychological attitude and theoretical knowledge will help a woman become a mother, successfully go through all the stages of childbirth and press the long-awaited child to her heart.
Harbingers - childbirth is coming soon!
Wrestler Maria Vladimirovna
Obstetrician-gynecologist
Clinical Hospital MD GROUP, Clinic "Mother and Child" Savelovskaya
False contractions
They may appear after the 38th week of pregnancy. False contractions are similar to Braxton-Hicks contractions, which a woman could already feel starting from the second trimester of pregnancy (the uterus seems to stiffen for a few seconds - a couple of minutes, then the tension in it subsides). False contractions train the uterus before childbirth, they are irregular and painless, the intervals between them are not reduced. Real labor pains, on the contrary, are regular, their strength gradually increases, they become longer and more painful, and the intervals between them are reduced. That's when you can already say that the birth began for real. In the meantime, false contractions are going on, it is not necessary to go to the maternity hospital - you can easily survive them at home.
False contractions train the uterus before childbirth, they are irregular and painless, the intervals between them are not reduced. Real labor pains, on the contrary, are regular, their strength gradually increases, they become longer and more painful, and the intervals between them are reduced. That's when you can already say that the birth began for real. In the meantime, false contractions are going on, it is not necessary to go to the maternity hospital - you can easily survive them at home.
Abdominal prolapse
Approximately two to three weeks before birth, the baby, in preparation for birth, presses the presenting part (usually the head) against the lower part of the uterus and pulls it down. As a result, the uterus moves lower into the pelvic region, its upper part ceases to put pressure on the internal organs of the chest and abdominal cavity. In the people it is called - the stomach dropped. As soon as the stomach drops, the expectant mother notices that it has become easier for her to breathe, but, on the contrary, it becomes more difficult to sit and walk. Heartburn and belching also disappear (after all, the uterus no longer presses on the diaphragm and stomach). But, having dropped down, the uterus begins to put pressure on the bladder - naturally, urination becomes more frequent.
Heartburn and belching also disappear (after all, the uterus no longer presses on the diaphragm and stomach). But, having dropped down, the uterus begins to put pressure on the bladder - naturally, urination becomes more frequent.
For some, uterine prolapse causes a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen and even slight pain in the area of the inguinal ligaments. These sensations arise due to the fact that the child's head, moving down, irritates the nerve endings of the pelvic organs.
During the second and subsequent births, the belly drops later - right before the birth. It happens that this harbinger of childbirth is not at all.
Removal of the mucous plug
This is one of the main and obvious harbingers of childbirth. During pregnancy, the glands in the cervix produce a secret (it looks like a thick jelly and forms the so-called cork), which prevents various microorganisms from entering the uterine cavity. Before childbirth, under the influence of estrogens, the cervix softens, the cervical canal opens slightly and the cork can come out - the woman will see that there are mucus clots on the linen that look like jelly. Cork can be of different colors - white, transparent, yellowish-brown or pink-red. Often it is stained with blood - this is completely normal and may indicate that childbirth will occur within the next day. The mucus plug can come out all at once (at once) or come out piecemeal throughout the day.
Cork can be of different colors - white, transparent, yellowish-brown or pink-red. Often it is stained with blood - this is completely normal and may indicate that childbirth will occur within the next day. The mucus plug can come out all at once (at once) or come out piecemeal throughout the day.
Weight loss
Approximately two weeks before delivery, weight loss may occur, usually by 0.5–2 kg. This happens because excess fluid is removed from the body and swelling decreases. If earlier during pregnancy, under the influence of the hormone progesterone, fluid in the body of a pregnant woman accumulated, now, before childbirth, the effect of progesterone decreases, but other female sex hormones - estrogens - begin to work hard, they remove excess fluid from the body of the expectant mother.
In addition, the expectant mother often notices that at the end of pregnancy it became easier for her to put on rings, gloves, shoes - this means that swelling on the hands and feet has decreased.
Change of stool
Right before childbirth, hormones often act on the intestines - they relax its muscles, as a result, stool disorder begins. Sometimes such frequent (up to 2-3 times a day) and even loose stools are mistaken for an intestinal infection. But if there is no nausea, vomiting, discoloration and smell of feces, or any other symptoms of intoxication, you should not worry: this is one of the harbingers of the upcoming birth.
On the eve of childbirth, you often don't feel like eating at all. All this is also the preparation of the body for natural childbirth.
Mood changes
Many women experience mood changes a few days before giving birth. The expectant mother gets tired quickly, she wants to have more rest, sleep, even some kind of apathy appears. This state is quite understandable - you need to gather strength to prepare for childbirth. Often, just before giving birth, a woman wants to retire, looking for a secluded place where you can hide and focus on yourself and your experiences.







:strip_icc():format(jpeg)/kly-media-production/medias/2785562/original/028627600_1556001360-shutterstock_1019963743.jpg)