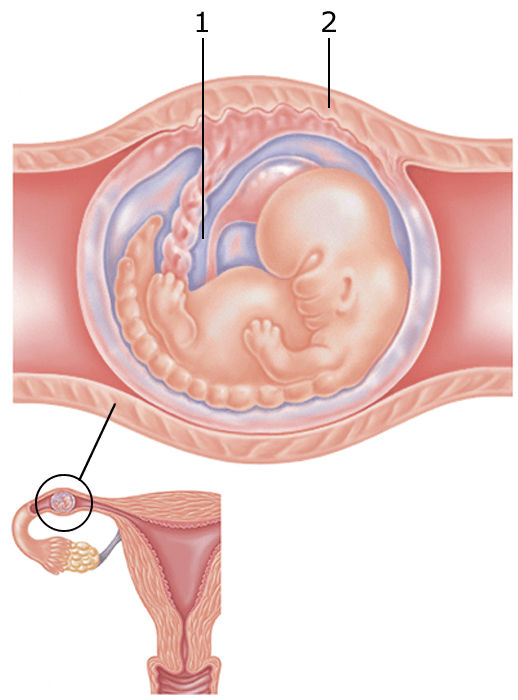
Baby position in 4th month of pregnancy
What Happens at 4 Months of Pregnancy?
In This Section
- Month by Month
- What happens in the second month?
- What happens in the third month?
- What happens in the fourth month?
- What happens in the fifth month?
- What happens in the sixth month?
- What happens in the seventh month?
- What happens in the eighth month?
- What happens in the ninth month?
- What happens in the tenth month?
Your 2nd trimester begins during your 4th month of pregnancy, starting on week 14.
What happens during week 13 - 14?
- The fetus has a CRL of about 3 inches (8 cm).
-
The biological sex of the fetus can sometimes be seen by looking at external sex organs on an ultrasound.
-
Hair begins to grow.
-
The prostate gland begins developing in biologically male fetuses.
-
Ovaries move down from the abdomen to the pelvic area in biologically female fetuses.
-
The roof of the mouth is formed.
What happens during week 15 - 16?
What are the symptoms of pregnancy in the fourth month?
Some of the early signs and symptoms of pregnancy go away when you’re 4 months pregnant. Nausea usually lessens. But other digestive problems — like heartburn and constipation — may be troublesome. Breast changes — growth, soreness, and darkening of the areola — usually continue. It’s common to have shortness of breath or to breathe faster. Increased blood flow may lead to unpleasant pregnancy symptoms, such as bleeding gums, nosebleeds, or nasal stuffiness. You also may feel dizzy or faint because of changes in your blood and blood vessels.
You also may feel dizzy or faint because of changes in your blood and blood vessels.
- Yes
- No
Help us improve - how could this information be more helpful?
How did this information help you?
Please answer below.
Are you human? (Sorry, we have to ask!)
Please don't check this box if you are a human.
You’re the best! Thanks for your feedback.
Thanks for your feedback.
We couldn't access your location, please search for a location.
Zip, City, or State
Please enter a valid 5-digit zip code or city or state.
Please fill out this field.
Service All Services Abortion Abortion Referrals Birth Control COVID-19 Vaccine HIV Services Men's Health Care Mental Health Morning-After Pill (Emergency Contraception) Pregnancy Testing & Services Primary Care STD Testing, Treatment & Vaccines Transgender Hormone Therapy Women's Health Care
Filter By All Telehealth In-person
Please enter your age and the first day of your last period for more accurate abortion options. Your information is private and anonymous.
I'm not sure This field is required.
AGE This field is required.
Or call 1-800-230-7526
Symptoms, Belly, Baby’s Development, More
You’re officially 4 months pregnant? Welcome to the second trimester! This is the fabled sweet spot of pregnancy, when you can put all the yuckiness of the first trimester behind you and coast for a little while.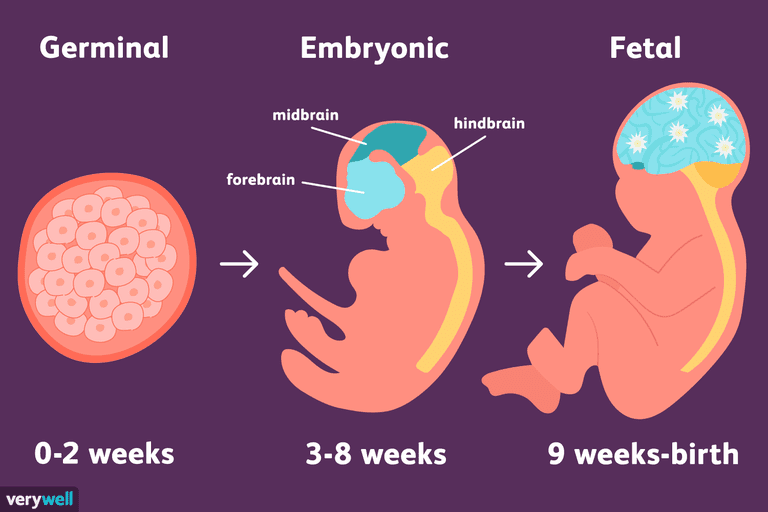 (But not too long, because months 6 and 7 are coming, and they’re a bit more uncomfortable, to put it mildly.)
(But not too long, because months 6 and 7 are coming, and they’re a bit more uncomfortable, to put it mildly.)
Four months is usually reason to celebrate: You’re feeling better, people know you’re pregnant and are asking you a million exciting questions, and you may even be seeing the beginnings of a bona fide baby bump. What else can you expect at 4 months? We’ll clue you in.
You may be starting to actually feel pregnant — not just bloated and cranky — around 4 months. After all, your uterus is growing by the day and things are getting just the slightest bit cramped in your midsection.
Here are some other symptoms you might notice:
- heartburn and indigestion
- backache
- stretch marks
- spider or varicose veins
- shortness of breath
- nasal swelling and congestion
- irritated or bleeding gums
- constipation
- round ligament pain
Many of these symptoms, like vein changes and nasal congestion, are because you have so much extra blood pumping through your veins. Your body ramps up production around 4 months and continues at this pace until about 35 weeks.
Your body ramps up production around 4 months and continues at this pace until about 35 weeks.
Other symptoms — like heartburn, constipation, and shortness of breath — are because your growing uterus is shifting your other organs around. We would tell you it gets better, but … these things tend to persist until delivery. Sorry! (The joys of pregnancy, right?)
Most people have started gaining some actual pregnancy weight at this point. You’re not throwing up all the time and are probably having some intense food cravings, so this is normal.
The amount of weight you’ll gain is totally individual. If you have concerns about whether you’re gaining too much or too little, run the numbers by your doctor — they know your medical history and your body size, so they should be able to give you a ballpark number for healthy weight gain in the second trimester of pregnancy.
Regardless of how much weight you have or haven’t gained, your baby belly is likely making an appearance. If this is your first pregnancy, it may still be super small or even non-existent (that’s normal, too!). But if this isn’t your first rodeo, you’re probably well-acquainted with your bump by now as it likely made an early showing.
If this is your first pregnancy, it may still be super small or even non-existent (that’s normal, too!). But if this isn’t your first rodeo, you’re probably well-acquainted with your bump by now as it likely made an early showing.
Hello, little avocado! At 4 months, your baby is between 4 and 5 inches long and may weigh up to 4 or 5 ounces. They don’t have as much fat as an avocado, though — they’re still pretty scrawny, and their skin is mostly translucent.
They may have some hair growing, their reproductive organs are developing quickly (if you wanted to find out your baby’s sex, you probably already know it!), and they’re gaining some muscle strength, too.
Most importantly, their eyes and ears have been developing, and baby can now hear you from inside the womb! You can start talking and singing to your little one so they get to know your voice. It’s also a great way to bond with your baby.
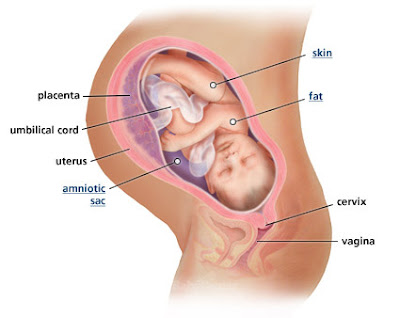
Depending on where your placenta is located, how your baby is positioned in your uterus, and how much body fat you have, you may or may not have started feeling your baby moving around in there. It’s normal if you’ve been noticing tiny kicks and flutters, but also fine if you haven’t felt much of anything yet.
It’s normal if you’ve been noticing tiny kicks and flutters, but also fine if you haven’t felt much of anything yet.
It’s also possible that you may notice some movement one day and then not feel much again for a little while. Again, baby is small enough to be nestling into different parts of your uterus where you may not sense much movement.
You don’t need to start officially counting kicks and keeping track of your baby’s movements until about 28 weeks, so at this point you shouldn’t worry if you’re not noticing any consistent pattern to baby’s bouncing.
Also? Appreciate those sweet little barely-there bumps and nudges. The muscles your baby is working hard to build are going to give them one heck of a right hook pretty soon, and your bladder will be baby’s prime target.
At 4 months pregnant with twins, you — and your babies — are actually very much aligned with a singleton pregnancy. Your twins are also avocado-sized, they’re developing along the same growth curve, and you may or may not be noticing your babies beginning to move around.
The only slight difference is that you may have gained more weight and your baby bump is probably pretty noticeable because there are two avocados in there, not one. (Hey, almost enough to make guacamole!) Otherwise, you’re not at a point yet where your twin pregnancy is going to distinguish you much from a singleton one.
You still have plenty of time to prepare for your baby’s arrival (and decorate the nursery … and take a childbirth class … and reject all of your partner’s name suggestions), but here are some things you can do at 4 months:
- Start building up your maternity wardrobe. The days of looping a hair elastic around the button on your pre-pregnancy jeans are numbered: You’ll have to give into the sweet, cozy embrace of a stretchy panel sooner or later, so you might as well look around for chic but comfortable pieces while you still have the energy.
- Settle on a birthing location. If you don’t know yet where you’ll be giving birth, this is a good time to commit.
 You want to make sure your insurance covers the location, that you’re comfortable with the staff there, and that you have enough time to schedule a tour before delivery.
You want to make sure your insurance covers the location, that you’re comfortable with the staff there, and that you have enough time to schedule a tour before delivery. - Enjoy healthy eats. Many women gain a lot of their pregnancy weight during the second trimester, because they don’t have morning sickness anymore but they’re not so cramped and swollen yet that they’ve lost their appetite. This is fine. You should eat about 300 extra calories per day during the second trimester! But there’s a healthy and a less-than-healthy way to gain pregnancy weight. Choose foods that are:
- rich in fiber, whole grains, vitamins, iron, and antioxidants
- full of healthy monounsaturated fats, like those found in nut butters and avocados (not the unhealthy kinds found in fast or fried foods)
- high in protein and calcium, for extra bone- and muscle-building power
- Stay hydrated. Your body’s working overtime and needs all the fluid it can get.
 It’s easy to become dehydrated during pregnancy, which can cause fatigue, headaches, and dizziness.
It’s easy to become dehydrated during pregnancy, which can cause fatigue, headaches, and dizziness.
Usually you’re feeling pretty good during the 4th month of pregnancy but, if you experience any of these symptoms, you should give your OB a call ASAP:
- any new spotting or a significant increase in spotting
- bleeding that soaks through a pad
- severe back or abdominal pain
- fever of 102 or higher
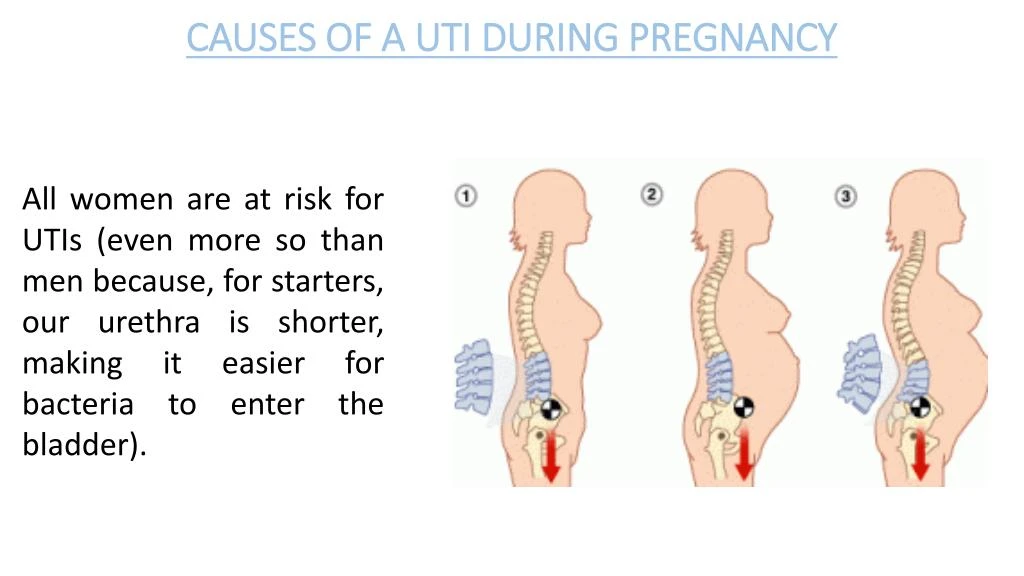
- pain with urination
- blurred vision or extreme dizziness
- watery vaginal discharge (as if your amniotic sac has broken)
- severe or persistent headache
- persistent vomiting or diarrhea
Having one of these symptoms may not be a sign that something is wrong with your pregnancy — you could have picked up a run of the mill virus, or simply be dehydrated. Still, your doctor will want to hear from you to rule out anything serious.
This is the time to sit back and soak up all the good stuff pregnancy has to offer: more energy, less nausea, tiny baby flutters, and dressing that cute little baby bump up in even cuter maternity clothes.
We’re not saying it’s all downhill from here, but when you’re struggling to bend over and put shoes on in a few months, you’re going to miss the 4-month milestone, we promise.
Fourth month of pregnancy
From the 13th week, the second trimester of pregnancy begins. It is believed that this is the most pleasant and safe period for mother and future baby. But even he requires certain rules to be observed...
With the increase in body weight and the growth of the tummy, the expectant mother may find that the underwear that she wore before no longer suits her. What you need to pay attention to, and how to choose new underwear? This is not such a simple process as it seems to many mothers...
4th month of pregnancy: the beginning of the second trimester
From the 13th week, the second trimester of pregnancy begins, which includes the 4th, 5th and 6th months of pregnancy. It is believed that this is the most pleasant and safe period for mom and baby. Nausea subsides, well-being improves, cheerfulness and activity appear. But even in this period there are worries and peculiarities.
- By the 13th week, my nausea and other discomfort disappeared. This is fine?
- This is normal, because by the 13th week, the level of progesterone, the main culprit of all discomfort, decreases. Nausea practically disappears, appetite improves.
Changes from the 13th week of pregnancy
- Tell me, what other changes can I expect in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy?
- From the 13th week, the uterus begins to actively increase. From the 14th week, you can feel it yourself. It has a rounded shape, its bottom is just below the womb. The uterus grows at the expense of the fetus and amniotic fluid. From the 16th week, the tummy in pregnant women is already noticeable, but so far it does not restrict movement.
From the 14th week, you can feel it yourself. It has a rounded shape, its bottom is just below the womb. The uterus grows at the expense of the fetus and amniotic fluid. From the 16th week, the tummy in pregnant women is already noticeable, but so far it does not restrict movement.
Tests and examinations in the 4th month of pregnancy
- What other tests and examinations do I need to undergo in the 4th month of pregnancy?
- Complete urinalysis, a clinical blood test that will allow you to see the risk of anemia, exclude inflammatory disorders, disorders in the endocrine system. And the most important study is perinatal screening in the second trimester of pregnancy - a triple or quadruple test.
- Why is it called triple or quadruple? Why is this test needed?
- Prenatal screening helps to detect fetal chromosomal pathologies, in particular, Down's syndrome and eliminate the risk of pregnancy gestosis. Perinatal screening is a combination of ultrasound findings at week 12 and blood tests in the first and second trimesters. In the first trimester, blood is donated for hCG and PAPP-A. In the second - b-hCG, AFP and free estriol ("triple test"), as an option, there is also a fourth indicator - inhibin A.
Perinatal screening is a combination of ultrasound findings at week 12 and blood tests in the first and second trimesters. In the first trimester, blood is donated for hCG and PAPP-A. In the second - b-hCG, AFP and free estriol ("triple test"), as an option, there is also a fourth indicator - inhibin A.
- I have a negative Rh factor. In the first trimester, I already donated blood for antibodies, when do I need to repeat the analysis?
- This test should be done every fourth week. If the result is negative, then on the 28th week, antiviral immunoglobulin is administered - prevention of the Rh conflict. The second dose of the drug is administered after childbirth.
Measurement of the pelvis, narrow pelvis during pregnancy
- Does the size of the pelvis matter for childbirth?
- Of course, the size of the pelvis is of great importance. The pelvis is measured with a special instrument - a pelvis. The distance between the most distant points is measured. If the pelvis is very narrow, then it is called anatomically narrow, and childbirth is possible only with the help of a caesarean section. Also, the pelvis is measured on an already mature pregnancy or during childbirth. If a discrepancy between the fetus and the size of the pelvis is detected, then the diagnosis is made: “clinically narrow pelvis”, and the birth is also completed promptly, with the help of a caesarean section.
The distance between the most distant points is measured. If the pelvis is very narrow, then it is called anatomically narrow, and childbirth is possible only with the help of a caesarean section. Also, the pelvis is measured on an already mature pregnancy or during childbirth. If a discrepancy between the fetus and the size of the pelvis is detected, then the diagnosis is made: “clinically narrow pelvis”, and the birth is also completed promptly, with the help of a caesarean section.
Infections during pregnancy
- If a genital infection is detected on smears, when should it be treated?
- Immunity decreases during pregnancy, which increases the risk of sexual infections. Usually smears are given for PCR diagnosis of genital infections - this allows you to identify the presence of a sexual infection. Additional tests are a bacterial culture from the vagina and a culture to identify the causative agents of a particular infection. If any infection is detected, then in the second trimester, somewhere in the 20th week, a full course of therapeutic treatment can be carried out. Antibacterial drugs are used, including antibiotics, vitamins, immunomodulators.
Antibacterial drugs are used, including antibiotics, vitamins, immunomodulators.
- What threatens an untreated infection, how can it harm my baby?
- Untreated infections can cause colpitis, inflammation of the uterus, and cervix. And provoke an abortion at any time. Damage to the internal organs of the fetus can also occur: liver, lungs, brain.
Thrush during pregnancy
- What is thrush during pregnancy, what are its symptoms?
- Thrush is caused by the yeast-like fungus Candida. The manifestation of the disease depends on the form of the course. In the acute form: itching, burning in the vagina, swelling, redness of the mucous membranes of the genital organs and abundant curd discharge. In the subacute form, these symptoms may be mild and not particularly disturbing. In carriers of thrush, signs of thrush are detected only with the help of tests.
- Is the treatment of thrush different during pregnancy?
- Treatment is divided into 2 groups: systemic and local preparations. Systemic: capsules, tablets - they are highly effective, but are contraindicated during pregnancy. During pregnancy, local methods of treatment are used: gels, creams, ointments, suppositories. After 20 weeks, the range of drugs allowed during pregnancy increases. This allows you to quickly cope with the disease.
Systemic: capsules, tablets - they are highly effective, but are contraindicated during pregnancy. During pregnancy, local methods of treatment are used: gels, creams, ointments, suppositories. After 20 weeks, the range of drugs allowed during pregnancy increases. This allows you to quickly cope with the disease.
4th month of pregnancy
- How does the baby develop?
- At the 4th month of pregnancy, the organs continue to develop, the brain system becomes more complex, the kidneys and the endocrine system begin to work more actively. Bones grow more actively. By the end of the fourth month, the baby is already 15 cm long. And the weight is 180 grams.
- What can he do during this period?
- The baby is actively moving. He already carries out reflex movements, extension and flexion of the fingers. Begins to carry out mimic movements, sucks a finger.
- Is it true that at this age there are already rudiments of milk teeth?
- Yes, by the 13th week the fetus has the rudiments of milk teeth.
- And who will I have?
- You are having a boy. By the 16th week, the genitals are already formed. The fetus has grown, and we can already accurately determine its gender.
- With weight gain and belly growth, the expectant mother may find that the underwear she used to wear no longer suits her. “Tell me, please, is it time for me to buy new underwear?”
- Yes, it's time. Many mothers in the 4th month of pregnancy feel discomfort from their usual clothing size: it presses, and pinches, and irritates the skin. Therefore, 4 months is the time when you need to choose the most comfortable underwear.
- What should I pay attention to? How to choose the right underwear?
- You should always pay attention to your needs. There are a lot of lingerie. Since the figures of expectant mothers are completely different and the demands are also different, then you need to approach the issue of choice, focusing only on yourself. First of all, pay attention to the naturalness of the fabrics. The fabric should be cotton or viscose, with the addition of elastane so that the fabric stretches well. Also, there should be no hard bones in the bra; there are special soft ones - they will not harm. The composition of the soft bones is unique: from the warmth of the body, they stretch and take the shape of the breast. Why should there be no bones? Because already from the first days, milk ducts form in the mother’s breast, and any clamping can harm the formation. Then there may be problems with lactation. Also, bras are seamless, made of micromodal material. This material is hygroscopic, air freely enters the body through this fabric. In such a bra it is very convenient to play sports, sleep. If you have very sensitive skin, then you can just walk in it every day. The only thing is that such a bra will not give much support to your breasts. The peculiarity of panties for pregnant women is that, firstly, the waist is lowered, so as not to press down on the stomach again, and secondly, the elastic band is weakened.
First of all, pay attention to the naturalness of the fabrics. The fabric should be cotton or viscose, with the addition of elastane so that the fabric stretches well. Also, there should be no hard bones in the bra; there are special soft ones - they will not harm. The composition of the soft bones is unique: from the warmth of the body, they stretch and take the shape of the breast. Why should there be no bones? Because already from the first days, milk ducts form in the mother’s breast, and any clamping can harm the formation. Then there may be problems with lactation. Also, bras are seamless, made of micromodal material. This material is hygroscopic, air freely enters the body through this fabric. In such a bra it is very convenient to play sports, sleep. If you have very sensitive skin, then you can just walk in it every day. The only thing is that such a bra will not give much support to your breasts. The peculiarity of panties for pregnant women is that, firstly, the waist is lowered, so as not to press down on the stomach again, and secondly, the elastic band is weakened. There is also a model with a high waist, this model is suitable for those mothers who have a tummy. Panties should be chosen according to the season: with a high waist it will be hot in summer. Also, according to the growth of your tummy, you select a model, and, of course, the one that you like best.
There is also a model with a high waist, this model is suitable for those mothers who have a tummy. Panties should be chosen according to the season: with a high waist it will be hot in summer. Also, according to the growth of your tummy, you select a model, and, of course, the one that you like best.
Dental care during pregnancy
- During pregnancy, mothers need to maintain their entire body and teeth are no exception.
- Why should you take care of your teeth during pregnancy? During this period, the hormonal background changes, which affects the condition of the teeth and gums of the expectant mother. Regular dental care is important for both the mother herself and the unborn baby. Any carious cavity, any inflamed gum can cause infection in the body. Many studies show that a disease such as periodontitis can cause premature birth or the birth of a child with low birth weight. Of course, you need to consult a dentist even during pregnancy planning: change old fillings, heal all new holes, and carry out a professional cleaning of the oral cavity. But usually women make an appointment with the dentist when they are already pregnant. It's not scary. Treating pregnant women's teeth is not only possible, but necessary.
But usually women make an appointment with the dentist when they are already pregnant. It's not scary. Treating pregnant women's teeth is not only possible, but necessary.
Anesthesia during pregnancy
- Can expectant mothers be given anesthesia?
- Many modern anesthetics are based on artecaine, which is safe for the fetus. Vasoconstrictor substances are not used for anesthesia. Also, by 14-16 weeks, the placenta is finally formed, and through it, anesthesia cannot harm the baby. Therefore, do not endure pain at the dentist, but make high-quality correct anesthesia.
- At what stage of pregnancy is dental treatment and anesthesia safest?
- The fact is that pregnancy is conditionally divided into three parts. In the first trimester, the baby is laying future organs, in the second trimester - their formation, and in the third - their independent functioning. The most dangerous are the first and third trimesters, the safest is the second.
So, by the end of the 4th lunar month, the baby already looks like an orange. All the systems laid down in the first trimester continue to develop. The baby is already moving, but mommy still does not feel him, because he is still very small.
Weekly development of the child | Regional Perinatal Center
Expectant mothers are always curious about how the fetus develops at a time when it is awaited with such impatience. Let's talk and look at the photos and pictures of how the fetus grows and develops week by week.
What does the puffer do for 9 whole months in mom's tummy? What does he feel, see and hear?
Let's start the story about the development of the fetus by weeks from the very beginning - from the moment of fertilization. A fetus up to 8 weeks old is called embryo , this occurs before the formation of all organ systems.
Embryo development: 1st week
The egg is fertilized and begins to actively split. The ovum travels to the uterus, getting rid of the membrane along the way.
The ovum travels to the uterus, getting rid of the membrane along the way.
On the 6th-8th days, implantation of eggs is carried out - implantation into the uterus. The egg settles on the surface of the uterine mucosa and, using the chorionic villi, attaches to the uterine mucosa.
Embryo development: 2-3 weeks
Picture of embryo development at 3 weeks.
The embryo is actively developing, starting to separate from the membranes. At this stage, the beginnings of the muscular, skeletal and nervous systems are formed. Therefore, this period of pregnancy is considered important.
Embryo development: 4–7 weeks
Fetal development by week in pictures: week 4
Fetal development by week photo: week 4
Photo of an embryo before the 6th week of pregnancy.
The heart, head, arms, legs and tail are formed in the embryo :) . Gill slit is defined. The length of the embryo at the fifth week reaches 6 mm.
Gill slit is defined. The length of the embryo at the fifth week reaches 6 mm.
Fetal development by week photo: week 5
At the 7th week, the rudiments of the eyes, stomach and chest are determined, and fingers appear on the handles. The baby already has a sense organ - the vestibular apparatus. The length of the embryo is up to 12 mm.
Fetal development: 8th week
Fetal development by weeks photo: weeks 7-8
The face of the fetus can be identified, you can distinguish the mouth, nose, auricles. The head of the embryo is large and its length corresponds to the length of the body; the fetal body is formed. All significant, but not yet fully formed, elements of the baby's body already exist. The nervous system, muscles, skeleton continue to improve.
Fetal development in the photo already sensitive arms and legs: week 8
The fetus developed skin sensitivity in the mouth (preparation for the sucking reflex), and later in the face and palms.
At this stage of pregnancy, the genitals are already visible. Gill slits die. The fruit reaches 20 mm in length.
Fetal development: 9–10 weeks
Fetal development by week photo: week 9
Fingers and toes already with nails. The fetus begins to move in the pregnant woman's stomach, but the mother does not feel it yet. With a special stethoscope, you can hear the baby's heartbeat. Muscles continue to develop.
Fetal development by week photo: week 10
The entire surface of the fetal body is sensitive and the baby develops tactile sensations with pleasure, touching his own body, the walls of the amniotic sac and the umbilical cord. It is very curious to observe this on ultrasound. By the way, the baby first moves away from the ultrasound sensor (of course, because it is cold and unusual!), And then puts his hands and heels trying to touch the sensor.
It's amazing when a mother puts her hand to her stomach, the baby tries to master the world and tries to touch with his pen "from the back".
Development of the fetus: 11–14 weeks
The development of the fetus in the photo of the legs: Week 11
The baby's arms, legs and eyelids are formed, and the genitals become distinguishable (you can find out the half child). The fetus begins to swallow, and if something is not to its taste, for example, if something bitter gets into the amniotic fluid (mother ate something), then the baby will begin to frown and stick out his tongue, making less swallowing movements.
Fruit skin looks translucent.
Fruit development: Week 12
Photo of the fetus 12 weeks per 3D Ultrasound
Week development photo: Week 14 5
urine. Blood forms inside the bones. And hairs begin to grow on the head. Moves more coordinated.
Fetal development: 15-18 weeks
Fetal development by week photo: week 15
The skin turns pink, the ears and other parts of the body, including the face, are already visible. Imagine, a child can already open his mouth and blink, as well as make grasping movements. The fetus begins to actively push in the mother's tummy. The sex of the fetus can be determined by ultrasound.
Imagine, a child can already open his mouth and blink, as well as make grasping movements. The fetus begins to actively push in the mother's tummy. The sex of the fetus can be determined by ultrasound.
Fetal development: 19-23 weeks
Fetal development by week photo: week 19
Baby sucks his thumb, becomes more energetic. Pseudo-feces are formed in the intestines of the fetus - meconium , kidneys begin to work. During this period, the brain develops very actively.
Fetal development by weeks photo: week 20
The auditory ossicles become stiff and now they are able to conduct sounds, the baby hears his mother - heartbeat, breathing, voice. The fetus intensively gains weight, fat deposits are formed. The weight of the fetus reaches 650 g, and the length is 300 mm.
The lungs at this stage of fetal development are so developed that the baby can survive in the artificial conditions of the intensive care unit.
Fetal development: 24-27 weeks
Lungs continue to develop. Now the baby is already falling asleep and waking up. Downy hairs appear on the skin, the skin becomes wrinkled and covered with grease. The cartilage of the ears and nose is still soft.
Fetal development by week photo: week 27
Lips and mouth become more sensitive. The eyes develop, open slightly and can perceive light and squint from direct sunlight. In girls, the labia majora do not yet cover the small ones, and in boys, the testicles have not yet descended into the scrotum. Fetal weight reaches 900–1200 g, and the length is 350 mm.
9 out of 10 children born at this term survive.
Fetal development: 28-32 weeks
The lungs are now adapted to breathe normal air. Breathing is rhythmic and body temperature is controlled by the CNS. The baby can cry and responds to external sounds.
Child opens eyes when awake and closes during sleep.
The skin becomes thicker, smoother and pinkish. Starting from this period, the fetus will actively gain weight and grow rapidly. Almost all babies born prematurely at this time are viable. The weight of the fetus reaches 2500 g, and the length is 450 mm.
Fetal development: 33–37 weeks
Fetal development by week photo: week 36
The fetus reacts to a light source. Muscle tone increases and the baby can turn and raise his head. On which, the hairs become silky. The child develops a grasping reflex. The lungs are fully developed.
Fetal development: 38-42 weeks
The fetus is quite developed, prepared for birth and considered mature. The baby has mastered over 70 different reflex movements. Due to the subcutaneous fatty tissue, the baby's skin is pale pink. The head is covered with hairs up to 3 cm.
Fetal development by weeks photo: week 40
The baby perfectly mastered the movements of his mother , knows when she is calm, excited, upset and reacts to this with her movements. During the intrauterine period, the fetus gets used to moving in space, which is why babies love it so much when they are carried in their arms or rolled in a stroller. For a baby, this is a completely natural state, so he will calm down and fall asleep when he is rocked.
During the intrauterine period, the fetus gets used to moving in space, which is why babies love it so much when they are carried in their arms or rolled in a stroller. For a baby, this is a completely natural state, so he will calm down and fall asleep when he is rocked.
The nails protrude beyond the tips of the fingers, the cartilages of the ears and nose are elastic. In boys, the testicles have descended into the scrotum, and in girls, the large labia cover the small ones. The weight of the fetus reaches 3200-3600 g, and the length is 480-520 mm.
After the birth, the baby yearns for touching his body, because at first he cannot feel himself - the arms and legs do not obey the child as confidently as it was in the amniotic fluid. Therefore, so that your baby does not feel lonely, it is advisable to carry him in your arms, press him to you while stroking his body.
And one more thing, the baby remembers the rhythm and sound of your heart very well .