Are braxton hicks contractions
Definition, What They Feel Like, and Triggers
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
In this Article
- What Are Braxton Hicks Contractions?
- What Do Braxton Hicks Contractions Feel Like?
- Triggers of Braxton Hicks Contractions
- How Do Braxton Hicks Contractions Compare With True Labor Contractions?
- Other Abdominal Pain During Pregnancy
- When to Call Your Doctor
- Treatment of Braxton Hicks Contractions
What Are Braxton Hicks Contractions?
Braxton Hicks contractions are the "false" labor pains that a pregnant woman might have before “true” labor. They’re your body's way of getting ready for the real thing. But they don’t mean labor has started or is about to begin.
What Do Braxton Hicks Contractions Feel Like?
Some women describe Braxton Hicks contractions as tightening in their belly that comes and goes. Many say they feel like mild menstrual cramps. Braxton Hicks contractions may be uncomfortable, but they don’t cause labor or open your cervix.
Unlike true labor, Braxton Hicks contractions:
- Usually aren’t painful
- Don’t have a regular pattern
- Don’t get closer together
- Don’t last longer as they go on
- Don’t get stronger over time
- May stop when you change activities or positions
- Are felt only in your belly
- Taper off and disappear
You may have Braxton Hicks contractions during your third trimester of pregnancy or as early as your second trimester. They’re normal and nothing to worry about.
Triggers of Braxton Hicks Contractions
Dehydration is the most common cause of Braxton Hicks contractions. Other triggers include:
- Illness that causes nausea or vomiting
- The fetus’s movement
- The mother’s activity, especially lifting something or having sex
How Do Braxton Hicks Contractions Compare With True Labor Contractions?
To figure out whether your contractions are the real thing and you're going into labor, ask yourself these questions.
How often do the contractions happen?
- False labor: Contractions are often irregular and don’t get closer together.
- True labor: Contractions come at regular intervals and last about 30 to 70 seconds. As time goes on, they get stronger and closer together.
Do they change when you move?
- False labor: Contractions may stop when you walk or rest. They may go away if you change positions.
- True labor: Contractions continue even after you move, change positions, or try to rest.
How strong are they?
- False labor: Contractions are usually weak and don't get much stronger. Or they may be strong at first and then get weaker.
- True labor: Contractions get stronger at a steady pace.
Where do you feel the pain?
- False labor: You usually feel it only in the front of your belly or pelvis.

- True labor: Contractions may start in your lower back and move to the front of your abdomen. Or they may start in your abdomen and move to your back.
Other Abdominal Pain During Pregnancy
Sharp, shooting pains on the sides of your belly are called round ligament pain. This happens because the ligaments that support your uterus and attach to your pelvis get stretched as your uterus grows.
Round ligament pain tends to happen with movement, like standing up, rolling over, coughing, sneezing, or even urinating. The pain may also move into your groin. It typically lasts only a few seconds or minutes.
To ease round ligament pain:
- Change your position or activity. It might help to lie on your opposite side.
- Support your belly when you stand or roll over. Move more slowly.
- Try to rest. A hot bath or heating pad may help.
When to Call Your Doctor
Early in your pregnancy, talk to your doctor about what may or may not be expected and when you might need to call them.
If you're not sure that what you're feeling may be labor, call your doctor or midwife. They should be available at any time to answer questions and discuss your concerns.
Call your doctor or midwife right away if you have:
- Any vaginal bleeding
- Constant fluid leaks, or if your water breaks (this can be gushing or trickling fluid)
- Strong contractions every 5 minutes for an hour
- Contractions that you can’t "walk through"
- A distinct change in your baby's movement, or if you feel fewer than 10 movements every 2 hours
- Any signs of true labor before 37 weeks of pregnancy
Treatment of Braxton Hicks Contractions
You don't have to do anything for these contractions. If they’re making you uncomfortable, try one of these tips:
- Drink water.
- Take a walk. False labor contractions often stop when you change position or get up and move.
- If you've been active, take a nap or rest.
- Relax by taking a warm bath or listening to music.

- Get a massage.
Health & Pregnancy Guide
- Getting Pregnant
- First Trimester
- Second Trimester
- Third Trimester
- Labor and Delivery
- Pregnancy Complications
- All Guide Topics
Definition, What They Feel Like, and Triggers
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
In this Article
- What Are Braxton Hicks Contractions?
- What Do Braxton Hicks Contractions Feel Like?
- Triggers of Braxton Hicks Contractions
- How Do Braxton Hicks Contractions Compare With True Labor Contractions?
- Other Abdominal Pain During Pregnancy
- When to Call Your Doctor
- Treatment of Braxton Hicks Contractions
What Are Braxton Hicks Contractions?
Braxton Hicks contractions are the "false" labor pains that a pregnant woman might have before “true” labor. They’re your body's way of getting ready for the real thing.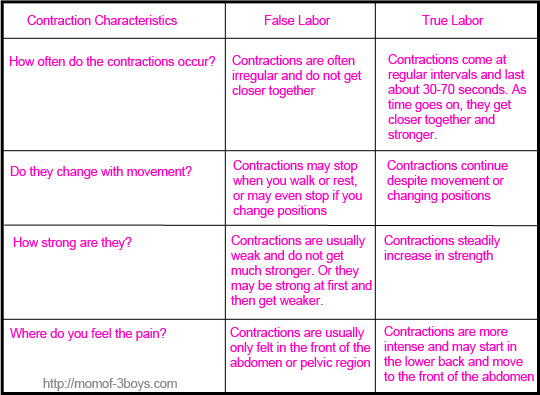 But they don’t mean labor has started or is about to begin.
But they don’t mean labor has started or is about to begin.
What Do Braxton Hicks Contractions Feel Like?
Some women describe Braxton Hicks contractions as tightening in their belly that comes and goes. Many say they feel like mild menstrual cramps. Braxton Hicks contractions may be uncomfortable, but they don’t cause labor or open your cervix.
Unlike true labor, Braxton Hicks contractions:
- Usually aren’t painful
- Don’t have a regular pattern
- Don’t get closer together
- Don’t last longer as they go on
- Don’t get stronger over time
- May stop when you change activities or positions
- Are felt only in your belly
- Taper off and disappear
You may have Braxton Hicks contractions during your third trimester of pregnancy or as early as your second trimester. They’re normal and nothing to worry about.
Triggers of Braxton Hicks Contractions
Dehydration is the most common cause of Braxton Hicks contractions. Other triggers include:
Other triggers include:
- Illness that causes nausea or vomiting
- The fetus’s movement
- The mother’s activity, especially lifting something or having sex
How Do Braxton Hicks Contractions Compare With True Labor Contractions?
To figure out whether your contractions are the real thing and you're going into labor, ask yourself these questions.
How often do the contractions happen?
- False labor: Contractions are often irregular and don’t get closer together.
- True labor: Contractions come at regular intervals and last about 30 to 70 seconds. As time goes on, they get stronger and closer together.
Do they change when you move?
- False labor: Contractions may stop when you walk or rest. They may go away if you change positions.
- True labor: Contractions continue even after you move, change positions, or try to rest.

How strong are they?
- False labor: Contractions are usually weak and don't get much stronger. Or they may be strong at first and then get weaker.
- True labor: Contractions get stronger at a steady pace.
Where do you feel the pain?
- False labor: You usually feel it only in the front of your belly or pelvis.
- True labor: Contractions may start in your lower back and move to the front of your abdomen. Or they may start in your abdomen and move to your back.
Other Abdominal Pain During Pregnancy
Sharp, shooting pains on the sides of your belly are called round ligament pain. This happens because the ligaments that support your uterus and attach to your pelvis get stretched as your uterus grows.
Round ligament pain tends to happen with movement, like standing up, rolling over, coughing, sneezing, or even urinating. The pain may also move into your groin. It typically lasts only a few seconds or minutes.
The pain may also move into your groin. It typically lasts only a few seconds or minutes.
To ease round ligament pain:
- Change your position or activity. It might help to lie on your opposite side.
- Support your belly when you stand or roll over. Move more slowly.
- Try to rest. A hot bath or heating pad may help.
When to Call Your Doctor
Early in your pregnancy, talk to your doctor about what may or may not be expected and when you might need to call them.
If you're not sure that what you're feeling may be labor, call your doctor or midwife. They should be available at any time to answer questions and discuss your concerns.
Call your doctor or midwife right away if you have:
- Any vaginal bleeding
- Constant fluid leaks, or if your water breaks (this can be gushing or trickling fluid)
- Strong contractions every 5 minutes for an hour
- Contractions that you can’t "walk through"
- A distinct change in your baby's movement, or if you feel fewer than 10 movements every 2 hours
- Any signs of true labor before 37 weeks of pregnancy
Treatment of Braxton Hicks Contractions
You don't have to do anything for these contractions. If they’re making you uncomfortable, try one of these tips:
If they’re making you uncomfortable, try one of these tips:
- Drink water.
- Take a walk. False labor contractions often stop when you change position or get up and move.
- If you've been active, take a nap or rest.
- Relax by taking a warm bath or listening to music.
- Get a massage.
Health & Pregnancy Guide
- Getting Pregnant
- First Trimester
- Second Trimester
- Third Trimester
- Labor and Delivery
- Pregnancy Complications
- All Guide Topics
false or real / “Waiting for a baby”
February
Shortly before the birth, the expectant mother may be disturbed by training contractions, rhythmic contractions of the uterus, which quickly pass and appear occasionally. How to distinguish them from real contractions, and why they are needed, we will try to find out.
For the first time, the phenomenon of temporary contractions was described by the English doctor John Braxton Hicks. That is why they are called - Braxton Hicks contractions or false, training contractions, precursor contractions. In his scientific work of 1872, he argued that these contractions are short-term (from half a minute to 2 minutes) contractions of the muscles of the uterus, which are felt by a pregnant woman as an increase in the tone of the uterus. They appear after the 20th week of pregnancy. And during the day they happen often, but the expectant mother in the daytime may not even notice them. However, as time goes on, they intensify, becoming more and more obvious.
WHAT DO YOU NEED FALSE BROUGHT
The uterus is a muscular organ. And like any muscle that has to perform the work allotted to it in the body, it needs training. After all, if she hangs for all forty weeks like a bag, she will not cope with the load in childbirth. Thus, the purpose of training or false contractions is to prepare the uterus and cervix for childbirth. That is why one of the names of training bouts is contractions harbingers - harbingers of an approaching birth.
That is why one of the names of training bouts is contractions harbingers - harbingers of an approaching birth.
ARE FALSE PARTS PAINFUL?
As a rule, false contractions are painless, but with increasing duration they become more noticeable and bring more discomfort. However, in all women, they manifest themselves in different ways, someone does not feel them at all, and someone does not sleep at night, tossing and turning and trying to find a comfortable position for sleeping. It all depends on the pain threshold. The main thing in this situation is to stop being nervous about this and calm yourself with the thought that such training is necessary for the most important upcoming event - the birth of your crumbs. And to calm down a little and sleep better, ask your doctor to prescribe a sedative for you and get a special pillow for expectant and nursing mothers. With her, falling asleep and experiencing the discomfort of the last weeks of pregnancy will be much easier!
HOW TO LIVE WITH FREQUENT PARTS
Some expectant mothers complain that their Braxton Hicks contractions are frequent and cause significant discomfort, even when they are doing housework or other light physical activity. In such a situation, obstetricians are advised to lie down or vice versa, take an easy walk, in any case, change the type of activity. If training contractions bother you a lot, it is recommended to drink a glass of water, juice or herbal tea, calm down and get some rest. Ask someone close to give you a massage. Lie in silence. And to also benefit from training fights, try doing breathing exercises: practice breathing techniques in childbirth in practice.
In such a situation, obstetricians are advised to lie down or vice versa, take an easy walk, in any case, change the type of activity. If training contractions bother you a lot, it is recommended to drink a glass of water, juice or herbal tea, calm down and get some rest. Ask someone close to give you a massage. Lie in silence. And to also benefit from training fights, try doing breathing exercises: practice breathing techniques in childbirth in practice.
HOW TO DIFFERENTIATE TRAINING FROM LIVING
The most important thing to understand is that real contractions are much more painful than Braxton Hicks contractions. You will understand it right away. In addition, the contractions that bring you closer to childbirth are more regular. The contractions begin in the lower back, spread to the front of the abdomen, and occur every 10 minutes (or more than 5 contractions per hour). Then they occur with an interval of about 30-70 seconds and over time the intervals between them are reduced. Some women describe the sensations of labor pains as severe menstrual cramps, or sensations during diarrhea, when the pain rolls in waves in the abdomen. These contractions, unlike false ones, continue even after a change in position and when walking, constantly intensifying. As soon as you feel all these symptoms, call your ob-gyn - hour X has arrived. If in doubt, also do not be afraid to disturb the doctor. The doctor will ask you a few questions that will help him determine the type of contractions and eliminate all your doubts and worries. After all, it is always better to consult a doctor and trust his professional experience.
Some women describe the sensations of labor pains as severe menstrual cramps, or sensations during diarrhea, when the pain rolls in waves in the abdomen. These contractions, unlike false ones, continue even after a change in position and when walking, constantly intensifying. As soon as you feel all these symptoms, call your ob-gyn - hour X has arrived. If in doubt, also do not be afraid to disturb the doctor. The doctor will ask you a few questions that will help him determine the type of contractions and eliminate all your doubts and worries. After all, it is always better to consult a doctor and trust his professional experience.
You should seek help if:
• you have more than four contractions an hour and they happen regularly
• contractions are accompanied by pain in the lower spine
• contractions are accompanied by watery or bloody vaginal discharge
• the contractions are so strong that it is very difficult for you to endure them
• there is a marked change in the child's movement, or less than 10 movements every 2 hours
• you think your waters have started to break
Alla Misyutina, Consultant Physician, Independent Laboratory INVITRO
Dear women, during labor, the body needs a lot of oxygen, so proper breathing is very important. A large influx of oxygen into the blood of mother and baby alleviates the condition of the crumbs, which during childbirth experiences oxygen starvation. Special breathing techniques help to properly open the birth canal and make contractions and attempts as effective as possible.
A large influx of oxygen into the blood of mother and baby alleviates the condition of the crumbs, which during childbirth experiences oxygen starvation. Special breathing techniques help to properly open the birth canal and make contractions and attempts as effective as possible.
Different types of breathing should be used at different stages of labor.
• During "false" contractions, breathing should be deep and slow. During the period when the contractions become more intense, it is necessary to use "pain-relieving breathing". This breathing is slow, deep, the inhalation is done through the nose, it should be longer than the exhalation through the mouth. More details: inhale is done at the expense of 1-2-3-4, and exhale - at the expense of 1-2-3-4-5-6. With the help of such breathing: mom relaxes, distracts from pain, focuses on the score; the baby receives as much as possible, so he needs oxygen.
• In breaks from contractions, you need to rest and breathe evenly without any effort, so that you can then easily follow the doctor's recommendations.
• During attempts, you need to exhale all the air from the lungs, then take a deep breath and push for up to 6-9 seconds. Quickly exhale all the air, quickly take a deep breath and again hold your breath for 6-9 seconds, and so on - about three times per attempt.
• In breaks from attempts to rest and breathe deeply, evenly and relaxed.
• It is very important to only push on the perineum and never push on the head. In this case, all efforts are wasted and will appear in the form of burst vessels in the eyes and on the face.
• In the period after the birth of the head, it is necessary to stop pushing and breathing shallowly, some call this breathing “dog-like”, deep breathing can harm both mom and baby. Then everything goes on as usual, the main thing is to obey the doctor.
• After the baby was born, within half an hour the last stage of labor begins - the birth of the placenta. Special breathing is no longer required, at the doctor's command, push a little into the perineum and EVERYTHING! Dear women, pain during childbirth is good, it means that your baby will be born soon. There is no need to resist the pain, this is a mistake that brings a woman and a child nothing but fatigue. On the contrary, it is necessary to concentrate and help in every possible way to give birth to a healthy baby.
There is no need to resist the pain, this is a mistake that brings a woman and a child nothing but fatigue. On the contrary, it is necessary to concentrate and help in every possible way to give birth to a healthy baby.
BIRTH AGAIN
So, you have decided that this is no longer a “teaching”, but the beginning of childbirth. In addition to contractions, the onset of labor can be indicated by the outflow of amniotic fluid and the passage of a mucous plug that closes the lumen of the cervix. The mucous plug can also come off 2-3 days before delivery. However, her departure does not always mean that it is time to go to the hospital. During pregnancy, the cervix is tightly closed. With the onset of labor pains, its opening begins: the cervix of the uterus gradually expands to 10-12 cm in diameter (full disclosure). The birth canal is preparing to "release" the child from the womb. Intrauterine pressure increases during contractions as the uterus shrinks. And in the end, this leads to rupture of the fetal bladder and the outflow of part of the amniotic fluid.
The first, preparatory, period of labor for women giving birth for the first time takes an average of 12 hours, and 2-4 hours less for those who have second births. At the beginning of the second stage of labor, contractions join the contractions - contractions of the muscles of the abdominal wall and diaphragm. In addition to the fact that different muscle groups are involved in contractions and attempts, they have one more important difference: contractions are an involuntary and uncontrollable phenomenon, neither their strength nor frequency depend on the woman in labor, while attempts to a certain extent obey her will , it can delay or strengthen them. Therefore, at this stage of childbirth, a lot depends on the expectant mother and her ability to quickly and correctly follow the commands of the obstetrician taking delivery. And most importantly - to tune in correctly and not allow panic and thoughts about something bad. Obstetricians and gynecologists recommend that mothers perceive childbirth as a holiday, a baby's birthday. Then it will be easier to concentrate on the fact that now your main task is to help the baby be born. If, during childbirth, the expectant mother panics, the concentration of adrenaline in her blood will increase significantly. Which will not have a very good effect on the process of childbirth. Adrenaline affects the synthesis of oxytocin, which significantly weakens contractions and slows down the process of childbirth. In addition, adrenaline completely blocks the production of endorphins, which will increase the feeling of pain during contractions and attempts. That is why it is so important to properly tune in, concentrate and help the baby to be born as soon as possible.
Then it will be easier to concentrate on the fact that now your main task is to help the baby be born. If, during childbirth, the expectant mother panics, the concentration of adrenaline in her blood will increase significantly. Which will not have a very good effect on the process of childbirth. Adrenaline affects the synthesis of oxytocin, which significantly weakens contractions and slows down the process of childbirth. In addition, adrenaline completely blocks the production of endorphins, which will increase the feeling of pain during contractions and attempts. That is why it is so important to properly tune in, concentrate and help the baby to be born as soon as possible.
Lilia Egorova
How to distinguish real contractions from training ones?
Shemyakina Natalya Nikolaevna, head of the obstetric department of the maternity hospital "Leleka" will help you figure it out.
Training contractions, or as they are also called, fake, or Braxton-Hicks contractions, are irregular contractions that do not have increasing intensity. The uterus may tone up, but normally, it should pass quickly.
The uterus may tone up, but normally, it should pass quickly.
For example, the tone appeared once in half an hour and the uterus relaxed rather quickly. Then the tone reappeared only after two hours and again passed. These are training contractions, they do not increase in intensity and do not become more frequent.
Training bouts are physiologically provided by our body. So the uterus is preparing to do the hard work in the process of childbirth. Normally, training contractions appear in terms of pregnancy close to childbirth - from the 37th week of pregnancy.
The appearance of training contractions in the early stages of pregnancy is not the norm
The uterus can tone up with an active lifestyle, physical activity, with a change in body position, but this tone should quickly pass. Normally, the uterus should not often come into tone. And even more so, contractions, as such, should not be until the 37th week of pregnancy.
Braxton Hicks contractions in the early stages are a threat of preterm labor. If a woman has contractions periodically during the day: after an hour, after 2, then again after an hour, (even if they are not regular), for periods up to 37 weeks, such a tone should alert the expectant mother.
If a woman has contractions periodically during the day: after an hour, after 2, then again after an hour, (even if they are not regular), for periods up to 37 weeks, such a tone should alert the expectant mother.
Because this is not the norm, but the threat of premature birth. This is an occasion to contact a specialist and change your rhythm of life, put on a bandage. The causes of premature birth are most often internal, caused by hormonal disorders and a violation of the physical health of a woman. But significant physical activity and stress can also cause premature birth.
Labor pains
Unlike training pains, labor pains are regular. The uterus comes to tone first once every 15 minutes, and after a while - once every 7-10 minutes. Contractions gradually become more frequent, longer and stronger. And already occur every 5 minutes, then 3 and finally every 2 minutes.
True labor pains are contractions every 2 minutes, 40 seconds. If within an hour or two the contractions intensify - pains that begin in the lower abdomen or in the lower back and spread to the stomach - most likely, these are real labor pains.
Training contractions are NOT so much painful as unusual for a woman. When the expectant mother sees how the stomach comes into tone, its shape changes and it becomes dense, like an inflated ball. This might scare you a little. But a woman must understand that in real, labor pains, there must be a clear periodicity, intensification and acceleration over a certain period of time. Real fights never stop, but practice fights do. The uterus then comes to tone, then relaxes.
Women often confuse contractions with tone, which is caused by other physiological processes in the body. For example, increased intestinal peristalsis, intestinal infections, colic, etc.
What else should alert a woman?! If within an hour or two the uterus periodically comes into tone and mucous, bloody (streaked with blood or brown) discharge appears, then most likely there are structural changes in the cervix - it opens. Also an important sign to seek help is the discharge of the mucous plug long before childbirth. Her departure in terms of childbirth, a week or two before childbirth is normal.
Her departure in terms of childbirth, a week or two before childbirth is normal.
Tracking labor pains
There are several methods for determining the types of contractions. A woman can do this herself, writing down the frequency and duration of contractions on paper or tracking them using special programs for a computer and phone. Or you can contact a doctor at antenatal clinic or at the maternity hospital, where a specialist will conduct fetal monitoring (fetal CTG). With the help of 2 sensors, the fetal heartbeat, uterine contractions are monitored and it is determined whether these are training contractions or labor.
When should I go to the maternity hospital?
If within an hour or two there is an increase and intensification of pain, its intensity increases, the frequency of contractions is clear and regular, you can go to the maternity hospital. A woman can make a mistake, but it’s better to come and make sure for sure whether these are labor or training contractions.