Acid in pregnancy
Indigestion and heartburn in pregnancy
Indigestion, also called heartburn or acid reflux, is common in pregnancy. It can be caused by hormonal changes and the growing baby pressing against your stomach.
You can help ease indigestion and heartburn by making changes to your diet and lifestyle, and there are medicines that are safe to take in pregnancy.
Symptoms of indigestion and heartburn
Symptoms of indigestion and heartburn include:
- a burning sensation or pain in the chest
- feeling full, heavy or bloated
- burping or belching
- feeling or being sick
- bringing up food
Symptoms usually come on soon after eating or drinking, but there can sometimes be a delay between eating and developing indigestion.
You can get symptoms at any point during your pregnancy, but they are more common from 27 weeks onwards.
Things you can do to help with indigestion and heartburn
Changes to your diet and lifestyle may be enough to control your symptoms, particularly if they are mild.
Eat healthily
You're more likely to get indigestion if you're very full.
If you're pregnant, it may be tempting to eat more than you would normally, but this may not be good for you or your baby.
Find out more about a healthy diet in pregnancy and foods to avoid.
Change your eating and drinking habits
You may be able to control your indigestion with changes to your eating habits.
It can help to eat small meals often, rather than larger meals 3 times a day, and to not eat within 3 hours of going to bed at night.
Cutting down on drinks containing caffeine, and foods that are rich, spicy or fatty, can also ease symptoms.
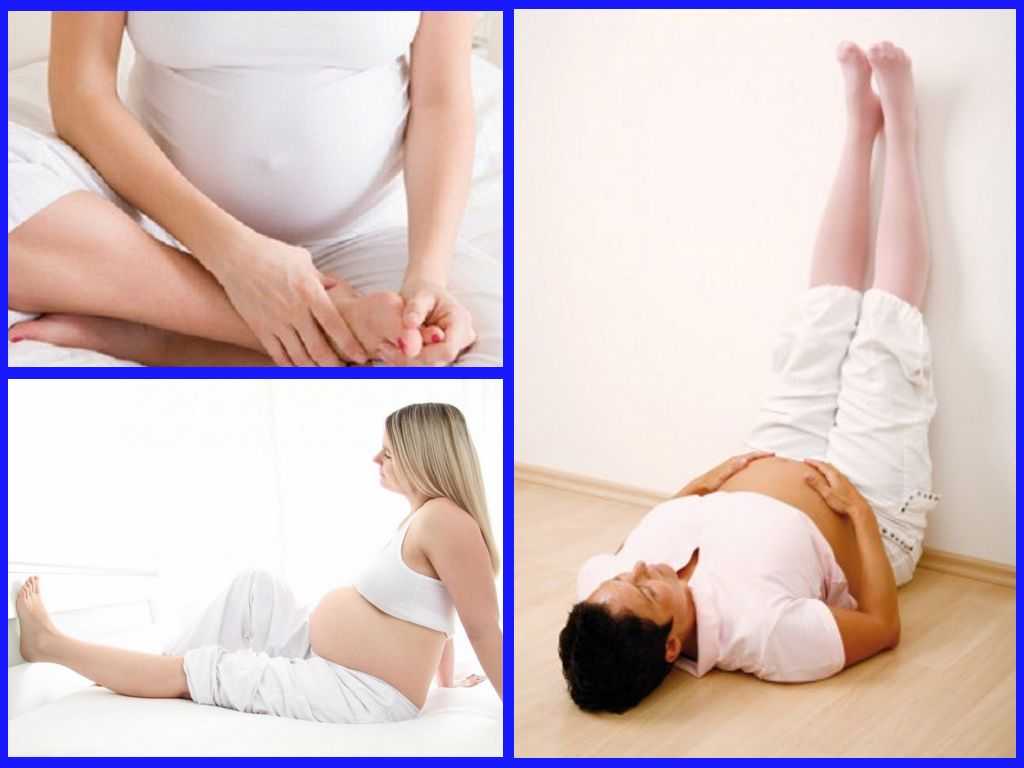
Keep upright
Sit up straight when you eat. This will take the pressure off your stomach. Propping your head and shoulders up when you go to bed can stop stomach acid coming up while you sleep.
Stop smoking
Smoking when pregnant can cause indigestion, and can seriously affect the health of you and your unborn baby.
When you smoke, the chemicals you inhale can contribute to your indigestion. These chemicals can cause the ring of muscle at the lower end of your gullet to relax, which allows stomach acid to come back up more easily. This is known as acid reflux.
Smoking also increases the risk of:
- your baby being born prematurely (before week 37 of your pregnancy)
- your baby being born with a low birthweight
- sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), or "cot death"
There's lots of help available to stop smoking.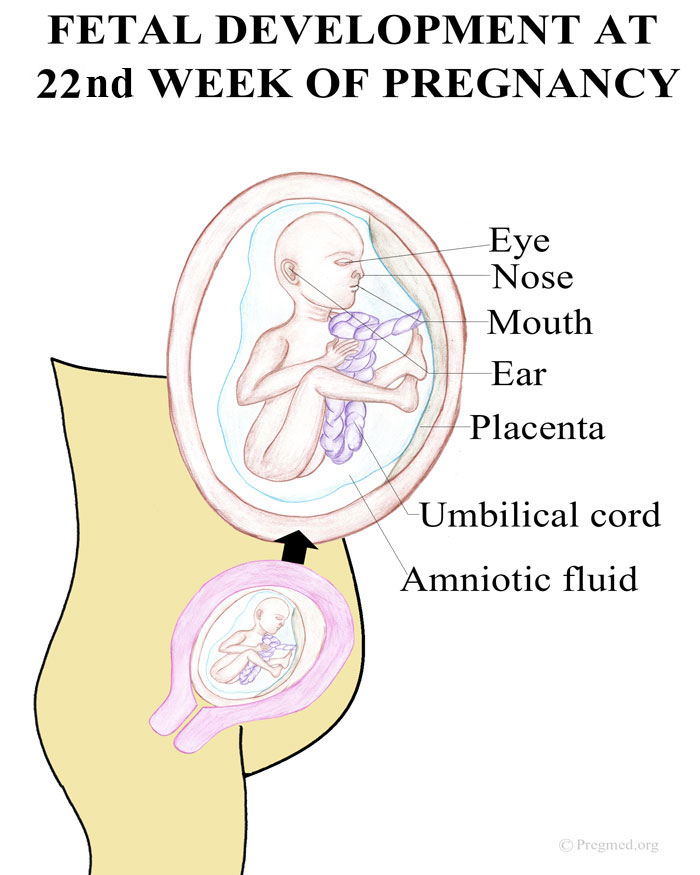 Talk to your midwife or call the NHS Smokefree helpline on 0300 123 1044. Find out more about stopping smoking in pregnancy.
Talk to your midwife or call the NHS Smokefree helpline on 0300 123 1044. Find out more about stopping smoking in pregnancy.
Avoid alcohol
Drinking alcohol can cause indigestion. During pregnancy, it can also lead to long-term harm to the baby. It's safest to not drink alcohol at all in pregnancy.
Find out more about alcohol and pregnancy
When to get medical help
See your midwife or GP if you need help managing your symptoms or if changes to your diet and lifestyle do not work. They may recommend medicine to ease your symptoms.
You should also see your midwife or GP if you have any of the following:
- difficulty eating or keeping food down
- weight loss
- stomach pains
Your midwife or GP may ask about your symptoms and examine you by pressing gently on different areas of your chest and stomach to see whether it's painful.
If you're taking prescription medicines
Speak to your GP if you're taking medicine for another condition, such as antidepressants, and you think it may be making your indigestion worse. They may be able to prescribe an alternative medicine.
Never stop taking a prescribed medicine unless you're advised to do so by your GP or another qualified healthcare professional who's responsible for your care.
Medicines for indigestion and heartburn
Medicines for indigestion and heartburn during pregnancy include:
- antacids – to neutralise the acid in your stomach (some are available over the counter from a pharmacist)
- alginates – to relieve indigestion caused by acid reflux by stopping the acid in your stomach coming back up your gullet
You may only need to take antacids and alginates when you start getting symptoms. However, your GP may recommend taking them before symptoms come on – for example, before a meal or before bed.
However, your GP may recommend taking them before symptoms come on – for example, before a meal or before bed.
If you're taking iron supplements as well as antacids, do not take them at the same time. Antacids can stop iron from being absorbed by your body.
If antacids and alginates do not improve your symptoms, your GP may prescribe a medicine to reduce the amount of acid in your stomach. 2 that are widely used in pregnancy and not known to be harmful to an unborn baby are:
- ranitidine – a tablet you take twice a day
- omeprazole – a tablet you take once a day
Causes of indigestion in pregnancy
Symptoms of indigestion come when the acid in your stomach irritates your stomach lining or your gullet. This causes pain and a burning feeling.
When you're pregnant, you're more likely to have indigestion because of:
- hormonal changes
- the growing baby pressing on your stomach
- the muscles between your stomach and gullet relaxing, allowing stomach acid to come back up
You may be more likely to get indigestion in pregnancy if:
- you had indigestion before you were pregnant
- you've been pregnant before
- you're in the later stages of pregnancy
Video: Eating well on a budget
In this video, a dietitian gives advice on how to eat healthily on a budget.
Media last reviewed: 13 January 2021
Media review due: 13 January 2024
Pregnancy Heartburn? 7 Ways to Get Relief
Keywords
Kathryn Walker, MD
Women and Newborn
Learn more about women and newborn services we offer.
Expectant mothers everywhere are aching to know one thing: “How can I get some relief from this awful pregnancy heartburn?”
To help ease your pain, here are some answers to your “burning” questions. (Pardon the pun.)
(Pardon the pun.)
When you’re growing a human being, you don’t have time for that yucky acid reflux. But your usual go-to methods for treating it may not be safe for your unborn baby. (Remember Pepto Bismol? That’s on the No Fly List for moms-to-be, according to FDA recommendations.)
Instead, here are some of the safest and best ways to get rid of heartburn when you’re pregnant:
- Dip into some yogurt. Its probiotics and soothing texture make yogurt a great option for extinguishing heartburn – or at least dousing the flames a little.
- Drink milk with honey. According to the American Pregnancy Association, a tablespoon of honey mixed in a glass of warm milk may be just what you need to neutralize heartburn-causing acid.
- Snack on almonds. Munching on a handful of almonds may provide heartburn relief since these nuts have a lower acidity level than others.
- Eat pineapple or papaya.
 For some women, the digestive enzymes in pineapple and papaya have helped ease symptoms. Eating these fruits after your meals can aid digestion and reduce your chances of heartburn.
For some women, the digestive enzymes in pineapple and papaya have helped ease symptoms. Eating these fruits after your meals can aid digestion and reduce your chances of heartburn. - Try a little ginger. You probably knew ginger was a good remedy for an upset stomach. Well, that makes it a helpful candidate for fighting off heartburn, too. Among ginger’s many benefits, it can reduce inflammation and prevent stomach acid from traveling up the esophagus.
- Chew sugar-free gum. Another effective method for taming the burn is to chew some sugar-free gum. One study found that chewing sugar-free gum for 30 minutes after a meal can reduce acid reflux.
- Take (doctor-approved) medication. When all else fails, certain medications are considered safe to use for pregnancy heartburn relief. Just make sure you speak to your doctor or OB-GYN first. If your heartburn is severe, they may prescribe special medication to help control it.

While not every tip mentioned above may work to ease your symptoms, you’ve got nine months to try them all and figure out what works.
It’s important to be extremely careful about the medications you take when pregnant.
For heartburn relief, over-the-counter antacids (such as Tums, Mylanta, Rolaids, and Maalox) are all considered safe medications to use during pregnancy.
As always, consult with your provider about any medications you’re taking – even if they’re considered safe. (This is especially true for high-risk pregnancies.)
If you experience any unusual symptoms while taking an over-the-counter medication, call your doctor immediately.
They say prevention is the best medicine, so knowing common heartburn triggers can help you keep the acid at bay.
Of course, pregnancy itself is a major trigger for heartburn. As your growing uterus puts pressure on your stomach, this pushes stomach acid up your throat.
Those lovely hormones are no help either. They tend to relax the valve between your stomach and esophagus, which makes it easier for acid to make its way upward.
They tend to relax the valve between your stomach and esophagus, which makes it easier for acid to make its way upward.
While there’s nothing you can do to stop this entirely, there are a few things that can help prevent heartburn from flaring up during pregnancy:
- Avoid lying down after eating. It may be tempting to take a post-meal nap, but if you want to prevent heartburn, don’t lie down after eating. Consider napping in an upright recliner instead.
- Prop yourself up at night. It’s hard enough to sleep well while pregnant without throwing acid reflux on top of everything. To prevent nighttime heartburn, try propping yourself up when you go to sleep to counteract the acid.
- Don’t eat before bedtime. In addition to propping yourself up at night, try not to eat anything within three hours of hitting the sack.
- Skip spicy, acidic, or fried foods. Ask yourself: Are those greasy chips worth being doubled over in pain later? (Probably not.
 ) If you want to avoid the risk, steer clear of any and all rich, fatty foods. Not only will this help prevent heartburn, but making more nutritious choices helps ensure that you your baby is getting the important vitamins and minerals that they need to stay healthy in utero.
) If you want to avoid the risk, steer clear of any and all rich, fatty foods. Not only will this help prevent heartburn, but making more nutritious choices helps ensure that you your baby is getting the important vitamins and minerals that they need to stay healthy in utero. - Eat small meals, but more frequently. Your pregnant tummy doesn’t love to be hit with large amounts of food to digest in one go. Make things easier on your gut by eating several small meals throughout the day instead of three large ones.
- Eat slowly. Wolfing down those small meals will defeat the purpose of spreading them out. Eating quickly increases the risk of acid reflux, so slow down and enjoy your food.
- Wear loose clothing. Tight-fitting clothes are not your stomach’s best friend when you’re trying to prevent heartburn – particularly during pregnancy. Wear clothing that offers support without being restrictive.
- Drink your liquids between meals.
 If you’re the type of person who likes to take a swig of their drink between each bite, it’s time to change course. Drinking liquids during meals can exacerbate heartburn symptoms, so take little sips if you’re thirsty at mealtime.
If you’re the type of person who likes to take a swig of their drink between each bite, it’s time to change course. Drinking liquids during meals can exacerbate heartburn symptoms, so take little sips if you’re thirsty at mealtime.
Someday, scientists may very well invent a miracle medication that promises permanent pregnancy heartburn relief. Unfortunately, that hasn’t happened yet.
So, if you’re wondering how long you can expect to deal with heartburn while you’re pregnant, it will probably be throughout your entire pregnancy. (Now may be a good time to remind yourself that you get a cute little baby out of this when you’re done.)
However, just because there’s no cure, that doesn’t mean you can’t find some relief in the meantime.
If severe pregnancy heartburn is getting in the way of everyday life, it’s time to see a doctor.
Intermountain Healthcare offers individualized and compassionate pregnancy care for women of all ages and health needs.
To get the care you need, search for a provider or find an Intermountain Healthcare location near you.
Intermountain Moms Women's Health, Baby Your Baby, Pregnancy, Women and Newborn
Last Updated: 5/21/2021
-
Intermountain Moms
-
Intermountain Moms
Copyright ©2022, Intermountain Healthcare, All rights reserved.
what you need to know, why you need it during pregnancy
In 1931, the English physician and scientist Lucy Wills decided to prescribe brewer's yeast extract to pregnant women with anemia. After a short time, the condition of the patients improved markedly. Scientists have long tried to understand what kind of healing component helped them.
Thanks to the improvement of technologies for extraction and isolation of substances in the form of crystals, it was possible to identify the secret component. In 1941, a team of scientists led by Professor Mitchell managed to get what they were looking for from spinach leaves. It turned out that this is an organic acid, which was called folic acid (from the Latin folium - "leaf").
What you need to know about folic acid
Folic acid (or vitamin B9) is a water-soluble vitamin that is essential for many vital processes. Bacteria synthesize it in small amounts in the body, but most of it comes from food. These are leafy vegetables, seaweed, nuts, sunflower seeds, etc.
These are leafy vegetables, seaweed, nuts, sunflower seeds, etc.
Among the main functions of folic acid are:
- participation in the processes of cell division during the period of active growth and development in childhood and adolescence;
- participation in DNA synthesis;
- stimulation of hematopoiesis;
- participation in metabolic processes.
Help: what are water-soluble and fat-soluble vitamins
Water-soluble vitamins are eliminated from the body naturally within a few hours. Therefore, you need to use them regularly. As for fat-soluble ones, they can be deposited, for example, in the liver. Among these are vitamins A, E, K, D.
Benefits of folic acid for women
For a woman, folic acid is one of the essential components to maintain youth. Sufficient consumption of this vitamin promotes tissue regeneration, maintaining skin firmness and elasticity.
B9 is also essential for successful conception. He takes part in the maturation of female germ cells (oocytes), implantation and the formation of the placenta.
He takes part in the maturation of female germ cells (oocytes), implantation and the formation of the placenta.
Important! Folic acid isn't just for women. Vitamin B9takes an active part in spermatogenesis - the formation of male germ cells (spermatozoa). Therefore, for successful conception, both partners need a sufficient level of its consumption. It's over 200 micrograms. per day.
Why folic acid is so important during pregnancy
Pregnant women need more vitamin B9. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends taking at least 400 micrograms of folic acid per day during pregnancy. This is most important in the first trimester, when the organs of the future baby are laid. For their development, it is necessary to ensure intensive cell division, which requires a large amount of folate. This is especially true of the neural tube of the fetus, from which the brain and spinal cord are then formed.
Lack of vitamin B9 in the diet can lead to serious adverse effects on the fetus, including:
- malformations of the nervous system;
- heart defects;
- increased risk of developing Down syndrome;
- vascular disorders.

Taking folic acid (and other vitamins and minerals) in the first half of pregnancy is also justified by the woman's relatively poor appetite. This happens against the background of toxicosis. Due to malnutrition, there is a shortage of biologically active substances necessary for mother and fetus.
Note that a pregnant woman needs not only folic acid, but also other B vitamins (B1, B2, B6, B12), vitamins A, D, E, C, biotin and minerals. Therefore, expectant mothers are often prescribed special complexes, for example, Elevit *, Complivit, Multi-tabs and others. Such preparations contain several vitamins and minerals at once, which are necessary for maintaining a healthy pregnancy. Folic acid is also available separately, mainly in the form of tablets - Foliber, Folacin and others.
Folic acid intake during pregnancy and lactation is important to coordinate with your doctor, who will determine the need for prescribing the drug and dosage. The drug is contraindicated in the absence of an established deficiency of vitamin B9, individual intolerance, malignant tumors, as well as pernicious anemia without additional intake of vitamin B12.
*dietary supplement. Not a drug
Folic acid for pregnancy planning
Our services
Surrogate mothers are urgently needed.
Requirements: physical and mental health, presence of own children is obligatory, age up to 35 years. For all questions, please contact:
8(495)2235324, 8(926)0423057
home » About clinic » Folic acid when planning a pregnancy
Any woman who plans to soon become pregnant and become a mother should consciously and carefully prepare for this new status. And if everyone knows about a healthy lifestyle, parting with bad habits and walking in the fresh air, then expectant mothers often ignore the intake of certain vitamins and medicines before pregnancy. One such remedy is folic acid.
What is folic acid?
Folic acid is vitamin B9. Often you can hear the generalized name - folates, they are derivatives of this vitamin. We must understand that we get them from food, and folic acid tablets are a synthetic agent that is already converted into folates inside the body.
Often you can hear the generalized name - folates, they are derivatives of this vitamin. We must understand that we get them from food, and folic acid tablets are a synthetic agent that is already converted into folates inside the body.
All derivatives of vitamin B9 play an important role in hematopoiesis, that is, the formation of new blood cells. Therefore, the lack of these substances leads to anemia - a condition in which there are not enough red blood cells, or they are irregular in shape and do not perform their functions. Folates have another very important feature: they stimulate the formation of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), which are the basis of all body cells. Therefore, it is folic acid that is necessary for all rapidly dividing human tissues, including embryonic tissues.
The role of folic acid:
- is involved in the formation of DNA in all cells, that is, the source of hereditary information;
- stimulates hematopoiesis;
- indirectly blocks the formation of cancer cells;
- restores muscle tissue;
- during pregnancy: plays a role in the formation and development of the nervous tissue of the fetus, participates in the formation of placental vessels.

Why do you need folate during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, especially in the early stages, the consumption of folate increases dramatically. All cells of the embryo are intensively dividing in order to eventually form full-fledged tissues. The nervous tissue of the future man is transformed especially quickly and difficultly. And it is she who requires a large amount of folic acid.
Folic acid deficiency during pregnancy can occur due to the following reasons:
- Inadequate dietary folate intake.
- Folate malabsorption (in chronic inflammatory diseases of the stomach and intestines).
- Genetic disorders of the folate cycle. In rare cases, a woman's body lacks the necessary enzymes (MTHFR). As a result, folic acid is not converted to folates, and they do not perform the necessary functions. Intermediate metabolic products accumulate in the body, which can lead to cardiovascular diseases, tumor processes, infertility and miscarriage.
 In the presence of such a mutation, it is recommended to take folic acid derivatives, for example, Metafolin. It is absorbed faster and in greater volume.
In the presence of such a mutation, it is recommended to take folic acid derivatives, for example, Metafolin. It is absorbed faster and in greater volume. - Certain anti-epilepsy and hormonal drugs dramatically lower blood folate levels:
- oral contraceptives;
- barbiturates, diphenylhydantoin;
- sulfa drugs (for example, biseptol), which inhibit the synthesis of vitamin B9 by the intestinal microflora;
- drinking alcohol also lowers their levels.
At what stage of pregnancy should I take folic acid supplements?
Folic acid intake to prevent fetal malformations should be started already at the stage of preparation for pregnancy, at least three months before the intended conception. That is why pregnancy should be planned. If conception occurred unexpectedly, then you need to start taking the drug as soon as it became known.
Reasons for taking folates at the stage of pregnancy planning:
- With an unbalanced diet, a woman can have a low level of folic acid, so it takes time to replenish her reserves.
 It usually takes three to four months.
It usually takes three to four months. - The neural tube of the fetus is laid at such an early stage that a woman may not yet be aware of the pregnancy, especially with a long menstrual cycle.
- Folate deficiency can make pregnancy difficult.
Doctors at the Intime Family Planning Clinic give the following recommendations for taking folic acid: in most cases, three months before conception and throughout pregnancy, you need to take 400 micrograms of folic acid per day. In some cases, the dosage is advised to increase: up to 1 mg per day for epilepsy and diabetes; up to 4 mg per day if there have been children with neural tube defects in the past Increased doses of folates can only be prescribed by a doctor after a thorough examination. The dose of folic acid during pregnancy remains the same.
We wish you an easy pregnancy and healthy babies!
×
Send a request for a free consultation
We provide the first free consultation for new patients.