When to worry about morning sickness
Severe Morning Sickness (Hyperemesis Gravidarum) (for Parents)
What's Morning Sickness?
During the first trimester of pregnancy, many women have the bouts of nausea and vomiting known as morning sickness.
Despite its name, morning sickness can happen day or night. It usually starts around the 6th week of pregnancy, is at its worst around week 9, and stops by weeks 16 to 18. Although unpleasant, morning sickness is considered a normal part of a healthy pregnancy.
What’s Severe Morning Sickness?
Severe morning sickness is when nausea and vomiting get so serious that a pregnant woman vomits several times a day, loses weight, and gets dehydrated or is at risk for dehydration.
If this rare pregnancy-related condition isn’t treated, it can affect a woman's health and her baby's ability to thrive.
The medical term for severe morning sickness is "hyperemesis gravidarum" (hi-per-EM-eh-sis grav-ih-DARE-um), which means "excessive vomiting during pregnancy. " It usually follows a similar timeline to normal morning sickness. But it can go longer, sometimes lasting for the whole pregnancy. Often, the symptoms get less severe as the pregnancy continues.
Most cases of hyperemesis gravidarum affect a woman's first pregnancy. But women who have it in one pregnancy are more likely to have it in future pregnancies.
What Causes Severe Morning Sickness?
The cause of severe morning sickness isn’t known. But it might be related to the hormone changes of pregnancy. A hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin, or HCG, might be to blame because severe morning sickness most often happens when HCG levels are at their highest in a pregnant woman's body.
Severe morning sickness also might run in families. It’s more common in women whose close family members (such as mothers and sisters) have had it.
Other things that can increase a woman's chances of having severe morning sickness include:
- carrying multiples (twins, triplets, etc.
 )
) - history of motion sickness
- migraine headaches with nausea or vomiting
What Problems Can Happen?
The nausea and vomiting that happen in severe morning sickness are so extreme that they can harm the mother and the baby. Not being able to keep down food makes it hard for the mom to meet her nutritional needs. So she might lose weight. And a loss of fluids, combined with the loss of stomach acid from vomiting, can cause dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
If severe morning sickness isn’t treated, it can cause many problems, including organ failure and the early birth of her baby.
When Should I Call the Doctor?
Call the doctor right away if you’re pregnant and have any of these symptoms:
- nausea that lasts throughout the day, making it impossible to eat or drink
- vomiting three to four times per day or not being to keep anything in the stomach
- brownish vomit or vomit with blood or streaks of blood in it
- weight loss
- fainting or dizziness
- peeing less than usual
- a fast heart rate
- a lot of headaches
- unpleasant, fruity mouth or body odor
- extreme tiredness
- confusion
How Is Severe Morning Sickness Treated?
Treatments used for morning sickness, such as eating dry crackers in the morning or a bland diet, may be recommended for women with extreme morning sickness. But these might not help with severe symptoms.
But these might not help with severe symptoms.
Medical treatment can include:
- a short period of not eating to rest the gastrointestinal system
- intravenous (IV) fluids
- vitamin and nutritional supplements
Some women might get medicine to stop the vomiting, either by mouth or through an IV. The doctor might recommend eating foods with ginger or taking vitamin B6 supplements to help ease nausea. It can also help to:
- Eat a bland diet.
- Eat frequent small meals.
- Drink plenty of liquids when not feeling nauseated.
- Avoid spicy and fatty foods.
- Eat high-protein snacks.
- Avoid sensory stimuli that can act as triggers (like specific smells or noises).
If a woman feels anxious or depressed about her condition, talking to a therapist or counselor might help her cope with her feelings.
What Else Should I Know?
With treatment, women with severe morning sickness can feel better and get the nourishment they need so they and their babies thrive. And lifestyle changes can help ease nausea and vomiting and make the pregnancy more enjoyable.
And lifestyle changes can help ease nausea and vomiting and make the pregnancy more enjoyable.
With time, symptoms usually do improve. And, of course, they stop by the time a woman's next journey starts: parenthood.
Mayo Clinic Q and A: Morning sickness — should I be worried?
-
By
Liza Torborg
DEAR MAYO CLINIC: I’m 15 weeks pregnant and have had horrible morning sickness from the beginning of the pregnancy. I’ve lost weight and worry that will affect the baby's health. I didn't experience any morning sickness with my first pregnancy. Is this normal? What can I do to get back to eating while feeling nauseated all the time?
ANSWER: Nausea and vomiting during pregnancy — whether it happens only in the morning or lasts all day — can make you feel bad. It also can be worrisome, especially when it causes weight loss. For most pregnant women, though, morning sickness doesn’t pose a health threat.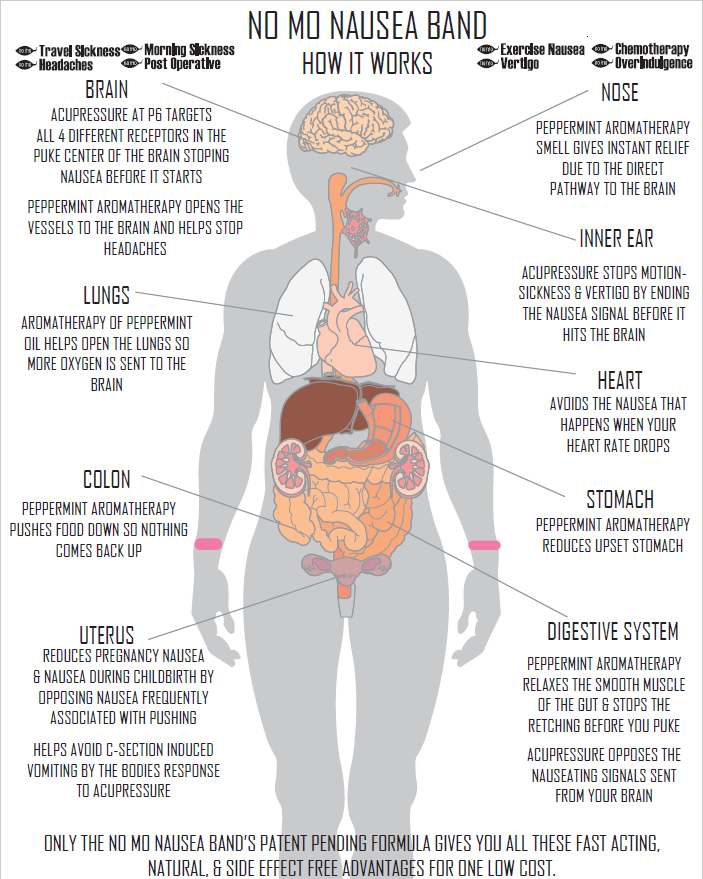 And it usually goes away as a pregnancy progresses. In the meantime, there are steps you can take to ease morning sickness.
And it usually goes away as a pregnancy progresses. In the meantime, there are steps you can take to ease morning sickness.
Morning sickness is most common during the first trimester, but it can linger throughout pregnancy. Exactly what causes morning sickness is unknown. It’s likely related to the hormones hCG and estrogen, which are high during pregnancy. As in your situation, it’s not unusual to have different levels of nausea with each pregnancy.
Women who have significant morning sickness often lose weight early in pregnancy. Only in rare circumstances does this cause problems. The nausea usually subsides over time. As that happens, most women are able to catch up and gain a healthy amount of weight by the end of the pregnancy.
Although morning sickness is hard to prevent, you may be able to make it less bothersome. Nausea tends to be worse when your stomach is completely full or empty. So rather than eating three large meals a day, eat smaller amounts more often. You can eat whatever foods appeal to you and don’t cause nausea. Some women find snacking on soda crackers or dry toast can quell feelings of queasiness. Ginger also can help. Try ginger ale, ginger tea or ginger lollipops.
You can eat whatever foods appeal to you and don’t cause nausea. Some women find snacking on soda crackers or dry toast can quell feelings of queasiness. Ginger also can help. Try ginger ale, ginger tea or ginger lollipops.
Drink plenty of fluids throughout the day, but don't drink too much at one time. Some women find drinking beverages with a meal makes nausea worse. If so, take in solid foods and liquids separately to see if that helps.
The smell of certain foods, especially during cooking, can be a problem. Avoid those foods if you are preparing meals, and ask someone to help make meals if cooking triggers nausea.
Pay attention to when and how you take your prenatal vitamins. Taking them in the morning can sometimes makes nausea worse. If that's the case for you, try taking them in the evening instead. Taking your vitamins with food also may help. If those changes don’t make a difference, try a vitamin that has low iron or is iron-free until you feel better.
Acupressure and acupuncture seem to reduce morning sickness for some women. Acupuncture involves inserting very fine needles into the skin at strategic points on the body. Acupressure wristbands are available without a prescription in most pharmacies.
Acupuncture involves inserting very fine needles into the skin at strategic points on the body. Acupressure wristbands are available without a prescription in most pharmacies.
If nausea continues, your doctor may suggest over-the-counter medications. Anti-nausea medications and medications to reduce acid production can be useful. A combination of doxylamine succinate, a sleep aid, and vitamin B6 may be recommended to decrease symptoms. If that doesn't work, a prescription medication may help.
A small percentage of women develop serious nausea and vomiting during pregnancy called hyperemesis gravidarum. Women with this disorder often become dehydrated and lose weight. If it isn't treated quickly, hyperemesis gravidarum may require hospitalization. Rarely, it can lead to premature birth or low birth weight.
If you notice symptoms in addition to nausea, such as lightheadedness, dizziness, faintness, a fast heartbeat, or inability to keep food or fluids down for more than 12 hours, contact your health care provider. You may need additional evaluation or treatment.
You may need additional evaluation or treatment.
Keep in mind that, although it’s certainly not a pleasant part of pregnancy, for most women, morning sickness resolves with a combination of self-care and time, and without any lasting problems. — Julie Lamppa, APRN, CNM, OB-GYN, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota
Related articles
Mayo Clinic Q and A: Cervical cancer and HPV screening
DEAR MAYO CLINIC: Since age 20, I have had annual visits with a gynecologist. I am now in my late 30s, and my physician recommended that [...]
By Cynthia Weiss • January 11, 2023
6 tips to keep your brain healthy
Changes to your body and brain are normal as you age. However, there are some things you can do to help slow any decline in [...]
By Mayo Clinic Staff • January 11, 2023
Why do you feel sick in the morning on an empty stomach
Nausea in the morning on an empty stomach is most common in pregnant women due to intoxication, but it is not uncommon for males or even children to have this problem
Do not worry too much if you have encountered such a problem once, it is likely that this is a banal poisoning. But, if nausea in the morning on an empty stomach does not go away, you should immediately consult a doctor. Some people are used to dealing with this problem with folk remedies and medicines and they really get better, but it is worth considering that most likely the disease or pathology itself continues to develop. And as a result, it will turn into a more serious form. That is why it is so important to consult a doctor who will find out the cause of morning sickness and prescribe the most effective treatment. nine0004
But, if nausea in the morning on an empty stomach does not go away, you should immediately consult a doctor. Some people are used to dealing with this problem with folk remedies and medicines and they really get better, but it is worth considering that most likely the disease or pathology itself continues to develop. And as a result, it will turn into a more serious form. That is why it is so important to consult a doctor who will find out the cause of morning sickness and prescribe the most effective treatment. nine0004
Possible diseases
Most often, morning sickness on an empty stomach may indicate the presence of the following diseases: unpleasant symptoms. This is due to inflammatory processes in the duodenum 12. The patient can also be tormented by: burning, bloating during and after eating, heartburn. nine0013 Inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis) - also characterized by nausea in the morning, as well as after eating fatty or fried foods. This disease is easily confused with gastritis due to the similarity of symptoms, but with pancreatitis, the patient begins to have problems with stools and an unpleasant, bitter taste in the mouth.
Other causes of nausea in the morning
After excluding the above diseases from the list of causes, the following causes can be considered:
- Pregnancy. Intoxication and nausea in the morning is often found in pregnant women, especially in the early stages. This is a normal reaction of the body to significant changes and hormonal changes. It is very important to completely exclude drugs for the treatment of the digestive tract during pregnancy. These funds can have an extremely negative impact on the health of the patient, the unborn child and the course of pregnancy. Therefore, you will have to endure this ailment and get by with folk remedies, but be sure to consult your doctor.
 nine0014
nine0014 - Migraine. Morning sickness on an empty stomach may precede a severe headache. You will most likely still feel a lot of noise and increased sensitivity to smells.
- High blood pressure (hypertension). The problem of morning sickness can be accompanied by headache and dizziness. If you do not pay attention to these symptoms in a timely manner, you risk starting this disease, which in turn can lead to a stroke.
- Cardiovascular disease - rarely, nausea on an empty stomach occurs with heart failure or developing myocardial infarction. If nausea is accompanied by pain, a feeling of heaviness and tightness behind the sternum, numbness or tingling in one half of the body, it is necessary to seek medical help as soon as possible, as this may be an incipient myocardial infarction. nine0014
- Increased intracranial pressure - Nausea and regurgitation in infants can occur when pressure increases inside the ventricles of the brain.
What to do if you feel sick in the morning
It is important to understand that regular morning sickness is a signal of the presence of a pathology or disease and it is highly undesirable to self-medicate. Be sure to consult a doctor for an examination, but if you don’t have such an opportunity at the moment, there are several effective ways that will help reduce or temporarily get rid of this problem:
Be sure to consult a doctor for an examination, but if you don’t have such an opportunity at the moment, there are several effective ways that will help reduce or temporarily get rid of this problem:
- Medicines. You need to be very careful and you must be sure that morning sickness is not the cause of pregnancy or an intestinal disease.
- Ginger root, mint and lemon drinks. You can make infusions of these products for maximum effect, simply by adding them to a glass and boiling water, after 15 minutes you will have a very effective and safe (in the absence of allergies) remedy for morning sickness. YOU can also just add them to hot tea. nine0014
- Medicinal collection - if nausea relentlessly torments you in the morning, you can try a collection of mint, oak bark and celandine. To prepare the drink, take 1 tsp of mint leaves, dried oak bark and chopped celandine, pour 0.5 l of boiling water and boil in a water bath for 10 minutes. After the broth is cooled and filtered, take 1 tablespoon 3-5 times a day before meals.

- During pregnancy. There are some little tricks you can use. For example, do not get out of bed quickly, drink plenty of fluids. Eliminate fatty and heavy foods from your diet. Eat small meals several times a day. nine0014
You might be interested
No morning sickness? You don't have to worry
For many women, one of the first signs of pregnancy (sometimes even without a period!) is the inability to stop eating.
Although this is commonly referred to as morning sickness, for most pregnant women this severe nausea has no time limit. Morning, noon and night, it's enough to confuse you.
One way some women can stay sane and ride the waves of morning sickness is to hope that this discomfort means their baby is growing. nine0004
What if you don't feel your stomach churning? Is your baby still growing and healthy? Does morning sickness mean anything about your child's health (or gender)?
Don't worry, we won't leave you hanging for 9 months waiting for an answer to these questions. Just keep reading on...
Just keep reading on...
What does it mean if you don't have morning sickness?
For a certain percentage of people, morning sickness is simply a pregnancy symptom that they never experience. By itself, the absence of nausea and vomiting does not mean that something is wrong. nine0004
An estimated 70 to 80 percent of pregnant women experience nausea and/or vomiting. So there are still 20 to 30 percent of people who don't get morning sickness at all!
If you find yourself pregnant without any nausea, you may feel happy, confused or even worried. Since morning sickness is such an often discussed symptom of the first trimester, it might seem odd that you don't have it.
Many people experience morning sickness in the first 4 months of pregnancy. Factors that contribute to nausea include elevated hormone levels and low blood sugar. If you're pregnant with twins or are tired from illness, stress, or travel, morning sickness may get worse. nine0004
Nausea during pregnancy can range from mild, infrequent nausea to extreme vomiting with frequent vomiting, which may require hospitalization for intravenous hydration and nutrition. A 2018 study found that hyperemesis could be a genetic component.
A 2018 study found that hyperemesis could be a genetic component.
If you have experienced severe nausea during previous pregnancies, please note that just because you have experienced morning sickness in the past, there is no guarantee that you will experience it again. (For better or worse, morning sickness can vary from pregnancy to pregnancy.)
Doesn't morning sickness mean you're having a boy (or girl)?
If you're trying to win at gender-guessing games, or just dying of impatience while waiting for the test results, you may want to know if you'll have a girl or a boy on the way.
You may have heard that a decrease in morning sickness means you are having a boy. This is based on the belief that hormone levels are higher when carrying a girl.
The logic behind this is that higher hormone levels can cause more nausea. So girls are rumored to be born with severe morning sickness, and boy pregnancies should go smoothly by comparison. nine0004
However, the science supporting this theory is limited. One 2019 study found that those who had a female fetus or twins were more likely to experience nausea and vomiting during pregnancy than those who had one male fetus.
One 2019 study found that those who had a female fetus or twins were more likely to experience nausea and vomiting during pregnancy than those who had one male fetus.
However, the researchers noted that other factors also affected the chances, including the mother's age, smoking status, and her pre-pregnancy BMI.
Ultimately, you can't tell your baby's gender by whether or not you have morning sickness. The only way to know if you will have a boy or a girl before delivery is through a chromosome analysis or ultrasound. nine0004
Does the absence of morning sickness mean a miscarriage?
Miscarriage is a real problem for many women (and their partners). Anything that indicates that the pregnancy is not proceeding as expected can be a wake-up call.
Because morning sickness is such a common symptom of pregnancy in the first trimester, not feeling well may give you some red flags. So should we praise nausea and vomiting as signs of a healthy pregnancy? nine0004
There are some studies showing that nausea and vomiting may indicate a reduced risk of pregnancy loss.
To better understand how nausea and vomiting can be associated with miscarriage, researchers in a 2016 study relied on hCG-confirmed pregnancy (think positive urinalysis) rather than ultrasound-confirmed pregnancy.
This allowed researchers to start testing for miscarriages earlier and detect more miscarriages. It also allowed them to track women's nausea more accurately during the first trimester. nine0004
No study is perfect, and this 2016 study was fairly homogeneous, making generalization difficult. However, this study represents a major step forward in the study of morning sickness and miscarriage.
A study found that in women who had had one or two miscarriages, morning sickness was very common during the first trimester and was associated with a 50-75 percent reduction in the chance of pregnancy loss. nine0004
There are many theories about why nausea and vomiting during pregnancy is associated with a reduced risk of miscarriage. One theory is that encouraging the consumption of carbohydrate-rich foods and ridding the body of any potential toxins that could be harmful to the baby is part of an evolutionary advantage.
Another theory is that vomiting is due to increased levels of hCG or markers of viable placental tissue in the body. More research on all of these theories will need to be done in the future as many questions remain. nine0004
While this means you can welcome nausea and vomiting as a reassuring sign, keep in mind that, as mentioned earlier, up to 80 percent of pregnant women are thought to experience morning sickness. This means there are many more healthy pregnancies that happen without morning sickness.
Conclusion
If you just got pregnant and don't feel morning sickness, you might start to worry.
But before you let the nightmare scenarios of pregnancy begin to fill your mind, consider taking a deep breath and pausing for a moment to think about other pregnancy symptoms you may be feeling. (Believe it or not, it can actually be comforting to think about all the other illnesses this pregnancy is causing you!)
Also remember that every pregnancy is different when it comes to morning sickness.