When does ovulation occur after birth
Pregnancy possible soon after giving birth
By Genevra Pittman, Reuters Health
4 Min Read
NEW YORK (Reuters Health) -- Just had a baby, and not ready for another one quite yet?
To be safe, you should consider using contraception as soon as 3 weeks after birth, according to a new review published in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Women who are breastfeeding are very unlikely to conceive, and most women who aren’t breastfeeding won’t start ovulating again until 6 weeks after giving birth. Still, it’s possible in less time, say the authors.
“For women with a new baby, contraception may not be at the top of their list of concerns,” Dr. Emily Jackson, one of the study’s authors, from the World Health Organization (WHO), told Reuters Health in an email.
“It is really important that people who provide care to postpartum women bring up the subject of contraceptives, alert women to the fact that they may become fertile soon after having a baby, and make sure that women have their chosen method before they become fertile again,” said Jackson, also a family doctor in Los Angeles.
Using some kinds of contraceptive pills right after pregnancy is dangerous because both the estrogen in pills and post-pregnancy hormones increase a woman’s risk of blood clots. That risk drops off over time.
The aim of the current study was to help determine at what point after a woman gives birth the benefits of using contraceptive pills again begin to outweigh the risks.
Jackson and her colleague Dr. Anna Glasier reviewed four studies that have examined when non-breastfeeding women begin to ovulate again after giving birth, and whether women had a good chance of getting pregnant during those first ovulations.
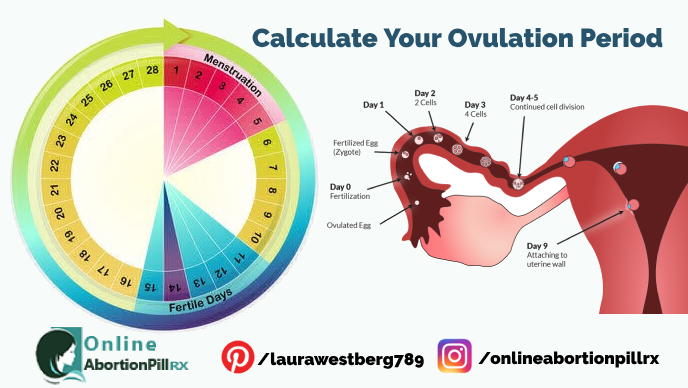
In all of the studies combined, ovulation started, on average, between 45 and 94 days after a woman gave birth. However, in two studies women started ovulating as early as 25 and 27 days after giving birth.
The studies also found that most of those first ovulations probably wouldn’t result in pregnancy.
Based on these results, and on data regarding the likelihood of blood clots, the WHO determined that the benefits of starting contraceptive pills containing both estrogen and progestin probably outweigh any risks starting at 3 weeks after birth.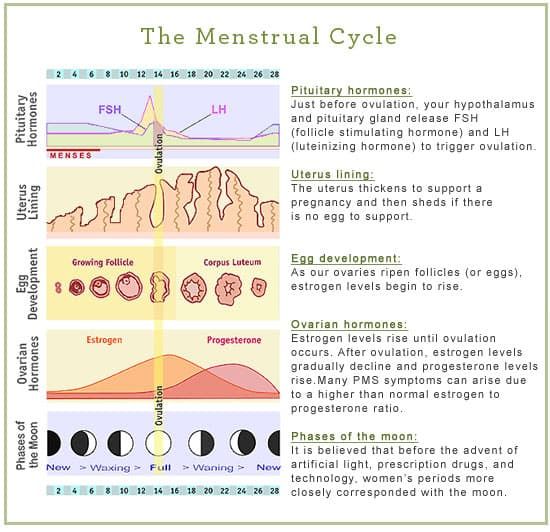
After 6 weeks, WHO researchers said that there should be no restrictions on new mothers taking contraceptive pills.
Contraceptive pills that contain progestin only are thought to be safe right away after a woman gives birth, and so these could be an option for women, said Dr. Kavita Nanda, a researcher at Family Health International who was not involved in the current study.
The study’s recommendations only apply to women who are not regularly breastfeeding.
In addition, doctors don’t recommend that mothers who are breastfeeding take contraceptive pills with estrogen, because of a controversial potential risk that those could slow infants’ growth.
Jackson also said it’s important that doctors speak to all women, including women who are breastfeeding, about their options for contraception.
“Breastfeeding can be a lot of work, and women may have a break in breastfeeding that they don’t plan for or stop breastfeeding earlier than they thought they would, potentially putting them at higher risk for pregnancy unexpectedly,” Jackson said.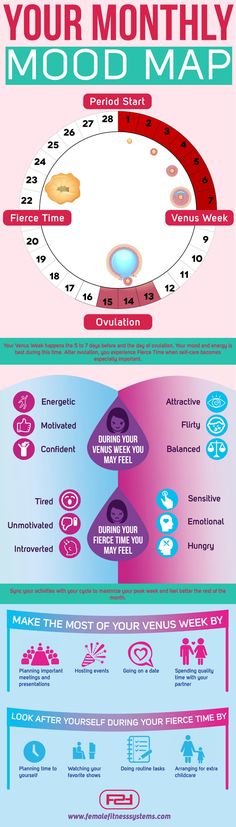
“It would be great if we could make sure that all women were prepared in advance to address their return to fertility postpartum.”
SOURCE: bit.ly/hqlHLT Obstetrics & Gynecology, March 2011.
How soon can you get pregnant after having a baby?
Myths about postpartum fertility are widespread. From rumors that it is impossible to get pregnant while breastfeeding to beliefs that the body will not get pregnant until it is “ready,” it can be hard to get the facts.
While unlikely, it is possible to get pregnant less than 6 weeks after having a baby. However, it is impossible until a woman ovulates again. The point at which ovulation happens varies from person to person, which means some women could get pregnant earlier than others.
Sometimes, ovulation happens before a period, so it is also possible for a woman to get pregnant before having the first postpartum period.
In this article, learn more about how soon a woman can get pregnant after having a baby, as well as how long to wait, and the possible risks of pregnancies that are too close together.
Ovulation occurs when an ovary releases an egg for fertilization. If the egg is unfertilized, the body expels the egg, the uterine lining, and blood in a menstrual period. Ovulation must occur for a woman to get pregnant, and regular periods are a sign that a woman has ovulated.
A 2011 review of previous studies found that women ovulate for the first time between 45 to 94 days after giving birth. Most women did not begin ovulating until at least 6 weeks after childbirth, but a few ovulated sooner.
Usually, women who are not breastfeeding ovulate sooner after giving birth than women who do breastfeed.
However, a woman’s first ovulation cycle might occur before she gets her first postpartum period. This means that it is possible for a woman to get pregnant before menstruation begins again.
Pregnancy causes many hormonal shifts, and it takes the body time to get back to normal.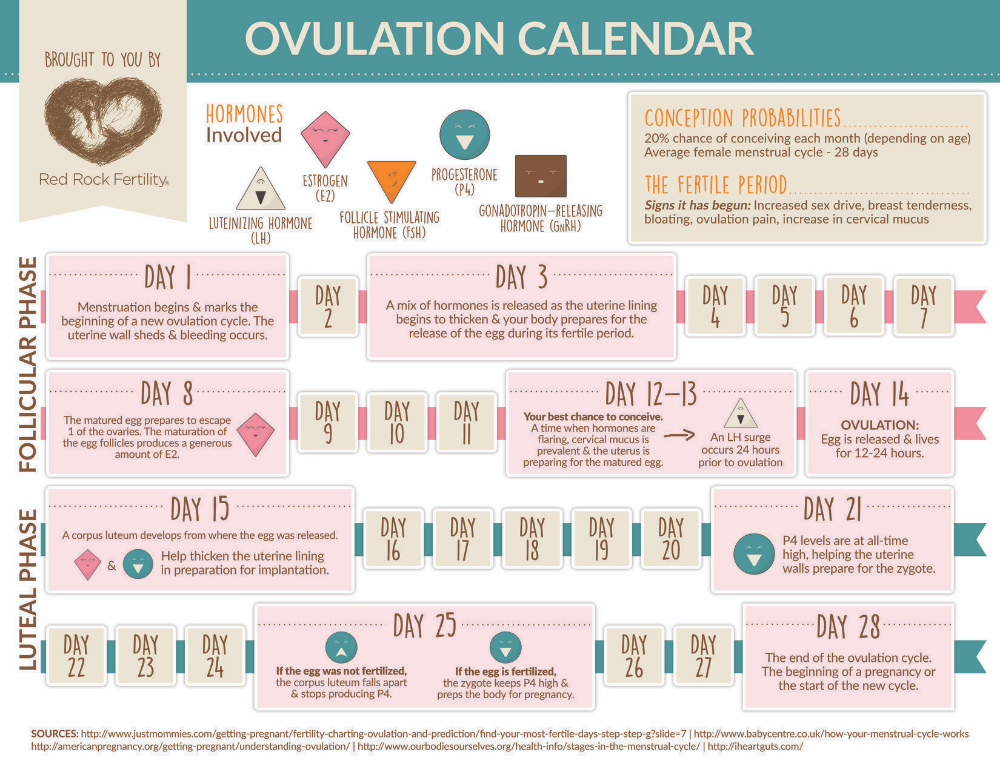 For many women, their first few postpartum periods are irregular.
For many women, their first few postpartum periods are irregular.
Breastfeeding often prevents ovulation, but this is not always the case. However, women who breastfeed their infants exclusively for 6 months are less likely to ovulate during this time than women who do not breastfeed.
Some women use breastfeeding as a birth control method. Doctors call this the lactational amenorrhea method (LAM). Amenorrhea means a lack of menstruation.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the following three factors must be present for LAM to have the best chance at preventing pregnancy:
- The baby must be younger than 6 months old. After 6 months, breastfeeding often becomes less frequent, increasing the risk that ovulation will return.
- The mother must be exclusively or almost exclusively breastfeeding. Giving formula or other foods to the baby increases the time between breastfeeding sessions. Breastfeeding on demand with intervals of no more than 4–6 hours between feedings is the most effective strategy.

- The woman’s period must not have returned. While not all menstruating women are fertile, the return of a woman’s period suggests the body is preparing to ovulate.
Research on the effectiveness of the LAM is mixed. One major challenge of this method is that it is difficult to use correctly. Traveling away from the baby overnight or spending long days at work can create gaps in breastfeeding that make this method less effective.
According to Planned Parenthood, LAM is about 98 percent effective when people use this method in the first 6 months after the baby is born.
After 6 months postpartum, LAM is less effective. Women who are not considering another pregnancy might think about starting to use another contraceptive method.
Share on PinterestThe World Health Organization advise waiting 24 months before trying for another baby.
Getting pregnant again too soon after giving birth increases the risk of adverse outcomes for both the woman and baby.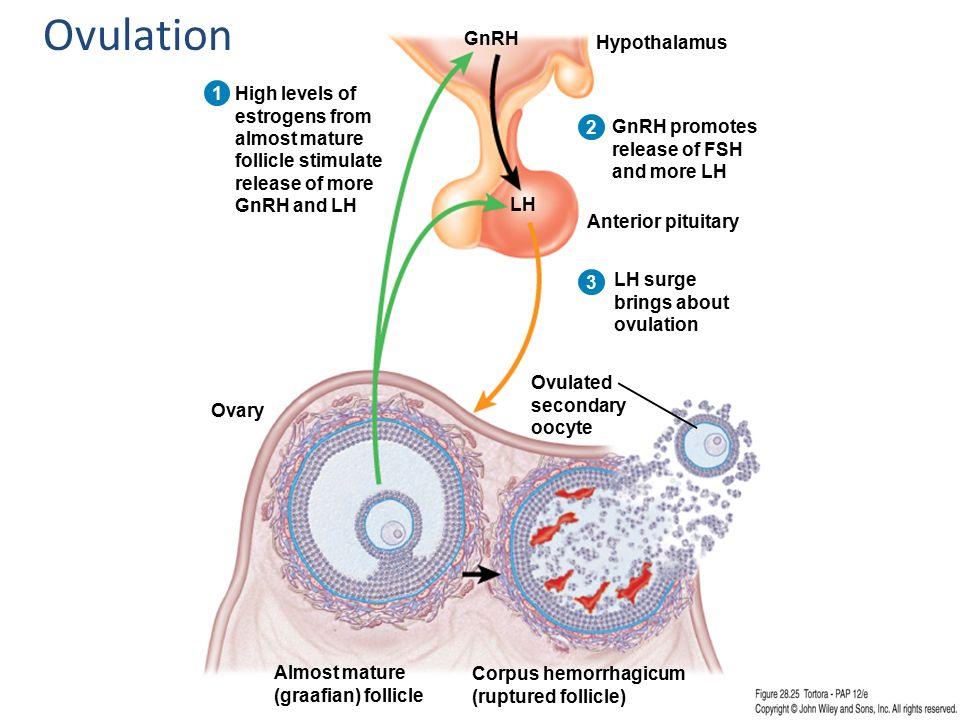 Recovering from birth takes time, especially if there were complications.
Recovering from birth takes time, especially if there were complications.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the safest option is to wait 24 months before trying for another baby. The charity March of Dimes suggests waiting at least 18 months.
Women who have had a pregnancy loss, stillbirth, hemorrhage, or surgical birth may need to wait longer. Talk to a midwife or doctor for help timing the next pregnancy.
Some women cannot imagine having another baby after giving birth, while others cannot wait to start planning for another.
There is no right or wrong way to feel about getting pregnant after childbirth. But practical considerations — including whether pregnancy might disrupt breastfeeding, and the safety of a pregnancy soon after birth — should play a role in the decision.
Also, recommendations for when it is safe to have sex after giving birth vary. In general, it is best to wait until postpartum bleeding has stopped, pain has disappeared, and a woman wants to have sex.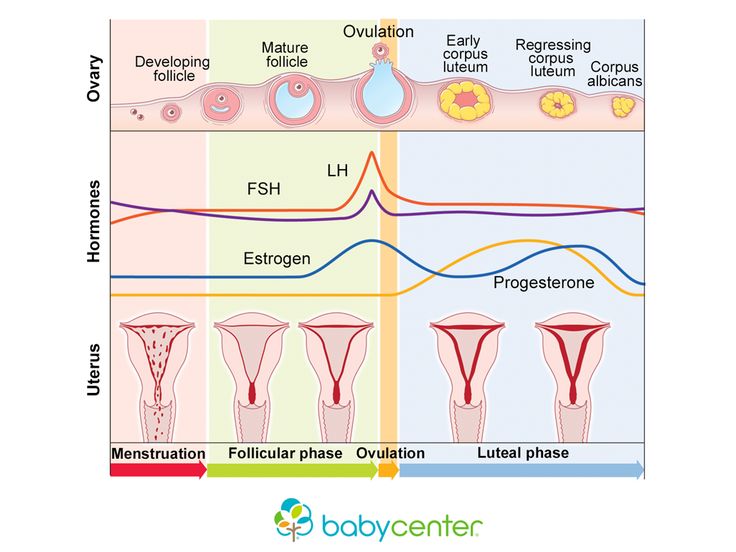
Consider using the final postpartum doctor’s visit as a chance to discuss birth control options and ask questions about fertility, as well as any concerns about having sex.
Women have many options for preventing pregnancy, including condoms and hormonal contraceptives that are safe to use while breastfeeding. In many cases, the LAM method will be effective for the first 6 months postpartum.
About menstruation after childbirth | Clinic.kg
Menstruation after childbirth
30 June 2019
A healthy pregnancy and delivery of a healthy baby is a reason for a woman to be proud of herself and her health. An important topic that worries many women after childbirth is menstruation: when to expect it, why the cycle is irregular, is it possible to get pregnant while breastfeeding, and much more. We will analyze the main issues in our article.
Postpartum discharge
Postpartum profuse discharge in a woman has nothing to do with menstruation - these are lochia, which from bloody become sanious, and then transparent, completely disappearing. After about two months, the uterus and ovaries return to their physiological state and size, which means that the onset of menstrual cycles with the maturation of eggs and menstruation is quite possible. Thus, a woman can expect her first menstruation from the 2-3rd month after childbirth.
After about two months, the uterus and ovaries return to their physiological state and size, which means that the onset of menstrual cycles with the maturation of eggs and menstruation is quite possible. Thus, a woman can expect her first menstruation from the 2-3rd month after childbirth.
When should my period start after childbirth?
This period depends on the type of feeding of the child: natural or artificial. Breast milk is produced under the influence of the pituitary hormone prolactin. The level of estrogen does not increase, therefore, when breastfeeding, menstruation begins, on average, 2 months after childbirth, more often when feeding “by the hour”. But there are times when some nursing women do not have periods for a year, and for some, they can recover in a month and a half after childbirth. On average, the onset of menstruation with breastfeeding varies from 3 months to six months.
How long do periods last after childbirth?
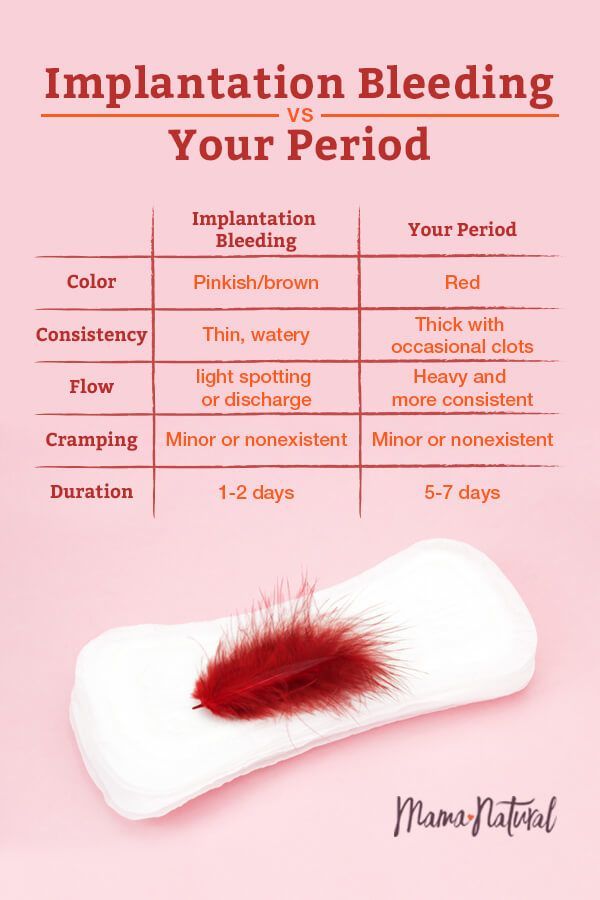
Often the first menstruation is quite heavy. There may be strong discharge, menstruation with blood clots. If you have to change the pad every hour, you should seek help from a doctor: this may be a symptom of bleeding that has begun. Subsequent periods usually become normal. In other cases, in the first months, women have irregular spotting. This is typical for breastfeeding, when prolactin synthesis gradually decreases.
There may be strong discharge, menstruation with blood clots. If you have to change the pad every hour, you should seek help from a doctor: this may be a symptom of bleeding that has begun. Subsequent periods usually become normal. In other cases, in the first months, women have irregular spotting. This is typical for breastfeeding, when prolactin synthesis gradually decreases.
Reasons for the slow recovery of the regular cycle
Each woman has her own individual period for the restoration of the menstrual cycle. This is determined by the activity of the production of hormones of the sex glands, the pituitary gland, the state of the immune and reproductive systems as a whole. There are a number of reasons for this that affect the body in the postpartum period:
- features of the individual hormonal background;
- hereditary factors;
- the nature of the birth process;
- features of the restoration of the uterus.
What to do if the menstrual cycle has become irregular:
- In the first months of the postpartum recovery period, do not panic. In most cases, this is the norm. For each woman, the normalization of the cycle occurs individually, usually during the first months of the resumption of menstrual bleeding. Irregularity is more common in nursing mothers.
- It takes about 2 months to restore the normal function of all organs and systems. Balance in the endocrine system comes later, especially if breastfeeding is used. Therefore, a woman can feel completely healthy, but she will not have a period.
- Notice the irregular cycle only after 3 cycles. This may be due to an inflammatory process, endometriosis or a tumor of the genital organs. A delay in the second period is not dangerous, unless it is associated with a second pregnancy.
Menstruation after caesarean section
Menstruation after caesarean section is restored in the same way as after normal delivery. During lactation, periods do not come for six months. Against the background of artificial feeding from the maternity hospital due to the lack of nipple stimulation (which activates the synthesis of oxytocin, which contracts the uterus), recovery may be somewhat slower, plus there is still a scar on the uterus. Therefore, the restoration of menstrual function may occur a little later, for several weeks.
During lactation, periods do not come for six months. Against the background of artificial feeding from the maternity hospital due to the lack of nipple stimulation (which activates the synthesis of oxytocin, which contracts the uterus), recovery may be somewhat slower, plus there is still a scar on the uterus. Therefore, the restoration of menstrual function may occur a little later, for several weeks.
Cycle after a pathological course of pregnancy or childbirth
After termination of a miscarriage or abortion, the first menstruation occurs within 45 days. If this does not happen, the woman should seek help from a gynecologist. To exclude such causes of amenorrhea as the remaining part of the fetal egg in the uterus or inflammation, 10 days after the termination of a frozen or normal pregnancy, an ultrasound scan is necessary.
Pathologies of menstruation, what to pay attention to and immediately contact a specialist:
- Sudden cessation of postpartum discharge is a sign of a bending of the uterus or endometritis, accumulation of lochia in the uterine cavity - lochiometers.
- Scanty periods for 3 or more cycles. Perhaps they are a symptom of hormonal disorders, Sheehan's syndrome or endometritis.
- Irregularity of menstruation six months after its restoration, a break between bloody discharge for more than 3 months. Most often associated with ovarian pathology.
- Excessive bleeding for 2 or more cycles, especially after a surgical delivery or abortion. They are often caused by the tissues of the membranes remaining on the walls of the uterus.
- The duration of menstruation is more than a week, which is accompanied by weakness, dizziness.
- Abdominal pain, fever, foul smell, discoloration of vaginal discharge - a sign of a tumor or infection.
- Spotting before and after menstruation is a likely symptom of endometriosis or an inflammatory disease.
- Itching in the vagina, an admixture of curdled discharge is a sign of thrush.
- Bleeding twice a month for more than 3 cycles.
Is it possible to get pregnant?
The most common myth is that a woman cannot get pregnant if she is breastfeeding a baby.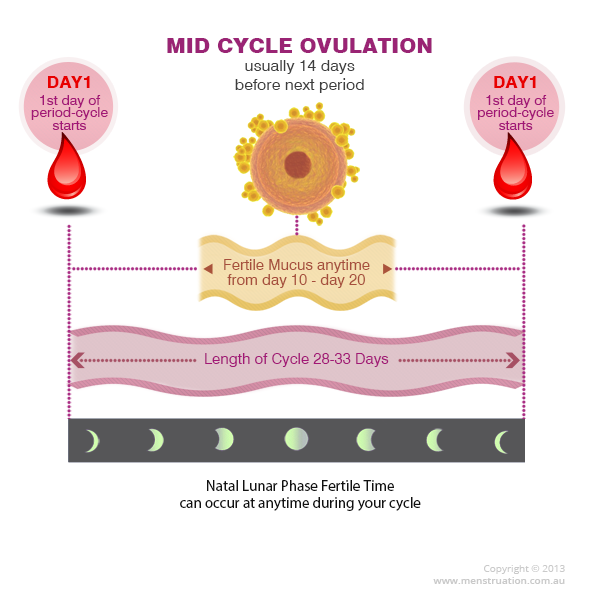 The fact is that the process of ovulation, the first after childbirth, is formed before the onset of the first spotting, and it is she who, with unprotected intercourse, can lead to an unplanned pregnancy, and a woman will give birth to the weather. If a woman does not feed, it is necessary to think about protection after childbirth immediately, from the very first sexual contact, since the dynamics of the restoration of reproductive functions is different for everyone, after 6-8 weeks from the moment of birth, the first ovulation is already possible.
The fact is that the process of ovulation, the first after childbirth, is formed before the onset of the first spotting, and it is she who, with unprotected intercourse, can lead to an unplanned pregnancy, and a woman will give birth to the weather. If a woman does not feed, it is necessary to think about protection after childbirth immediately, from the very first sexual contact, since the dynamics of the restoration of reproductive functions is different for everyone, after 6-8 weeks from the moment of birth, the first ovulation is already possible.
Remember that a long delay in menstruation after childbirth or a cycle failure are not always symptoms of dangerous disorders, but in any case it is undesirable to self-medicate. For any questions and problems that arise with the reproductive system, please contact our specialists for advice.
Ovulation after childbirth during breastfeeding
Ovulation is one of the most important physiological processes in a woman's body, associated with her ability to endure and give birth to offspring. At this time, under the influence of hormones in the reproductive organs, the maturation and preparation of the egg for fertilization occurs. 9Ovulation duration of ovulation depends on several factors that are directly related to the state of women's health and may change in the following cases:
At this time, under the influence of hormones in the reproductive organs, the maturation and preparation of the egg for fertilization occurs. 9Ovulation duration of ovulation depends on several factors that are directly related to the state of women's health and may change in the following cases:
- beginning menopause;
- had an abortion;
- the next 6-12 months after the birth of the child.
The process of development of the egg stops during the period of childbearing, as well as at the time of the onset of menopausal symptoms, when the processes preceding age-related changes occur in the body.
The onset and course of the menstrual cycle, and accordingly, ovulation, undergo some changes in the process of recovery of the body after certain female diseases, during a certain period after an abortion, and also for several months after childbirth.
The postpartum period is a special state of a woman, when the reproductive function resumes in the body. Since most of the organs functioned in a slightly different mode during pregnancy, undergoing hormonal and physiological changes, accordingly, they need some time after childbirth to regain their prenatal form. This applies to both the menstrual cycle and the onset of ovulation.
Since most of the organs functioned in a slightly different mode during pregnancy, undergoing hormonal and physiological changes, accordingly, they need some time after childbirth to regain their prenatal form. This applies to both the menstrual cycle and the onset of ovulation.
When ovulation occurs after childbirth
On average, the postpartum period lasts about 6 weeks, during which the female organs return to their normal mode. The process of maturation of the egg can occur in the period from 30 to 70 days after birth, regardless of whether breastfeeding is present or not. There is an opinion that during lactation the probability of getting pregnant is reduced to zero.
This is an erroneous opinion, since it has been proven that the first ovulation after childbirth occurs regardless of the presence of menstruation. This occurs approximately 40-45 days after discharge from the hospital.
Therefore, women in the postpartum period should be extremely careful in order to exclude the possibility of fertilization of the egg, since her body is exhausted and needs to be restored and complete psychological and physical rest after the birth of a child.
Ovulation during breastfeeding
The female body during lactation produces the hormonal substance prolactin, which not only stimulates the production of breast milk, but also reduces the development of the egg and its passage into the abdominal cavity.
Is it possible to ovulate while breastfeeding? Breastfeeding allows you to suspend the development of the egg for some time and reduce the likelihood of pregnancy, but does not exclude its onset.
Despite the fact that proclatin during breastfeeding somewhat suppresses the development of ovulation, nevertheless, the possibility of fertilization of the egg exists. Therefore, when ovulation occurs with HB, it often happens 6-7 weeks after childbirth, it is worth using the advice of a gynecologist, as a result of which it is recommended to choose the appropriate contraceptives.
Ovulation after childbirth without menstruation
The time of ovulation for any woman of childbearing period depends on the length of the menstrual cycle. By counting the number of calendar days, you can easily determine the most favorable day for conception - this is the middle of any cycle.
By counting the number of calendar days, you can easily determine the most favorable day for conception - this is the middle of any cycle.
As for the female body after childbirth, which is under the influence of hormonal substances, the absence of menstruation is a completely normal condition after the birth of a child. Failure to breastfeed for one reason or another can significantly accelerate the onset of the cycle, since the amount of hormones that are produced during lactation decreases, and as a result, the female body quickly restores its prenatal state.
Prolonged breastfeeding may delay the onset of menstruation, but this does not rule out the onset of ovulation. Of course, without a menstrual cycle, it is much more difficult to determine the right time to conceive, however, there are a number of ways to help determine the changes and production of sex hormones that promote conception.
Methods for determining ovulation:
- Conducting temperature tests by measuring basal body temperature.
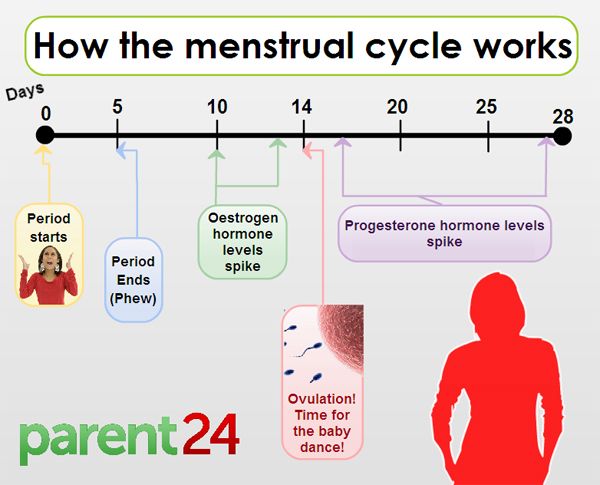
- Examination of blood plasma for the level of progesterone, which rises during the period of ovulation.
- The appearance of transparent discharge from the genitals.
- Ultrasound.
- Slight pain in the lower abdomen.
- Increased sexual desire.
Ovulation after childbirth is a purely individual process, and often depends on many factors in a woman's life, such as physical and psycho-emotional state, proper nutrition, proper rest and duration of breastfeeding.
The absence of a monthly cycle significantly increases the chance of pregnancy, as it becomes more difficult to determine the time of ovulation. If the monthly cycle after childbirth is restored, it is worth considering that the period of ovulation depends on the beginning of the next cycle, and not the end of the previous one. This will allow us to calculate a more accurate time of cell maturation and its further movement. Moreover, the probability of fertilization on the day of ovulation is about 33%, and in the next 2-3 days it is significantly reduced by 5-10%.