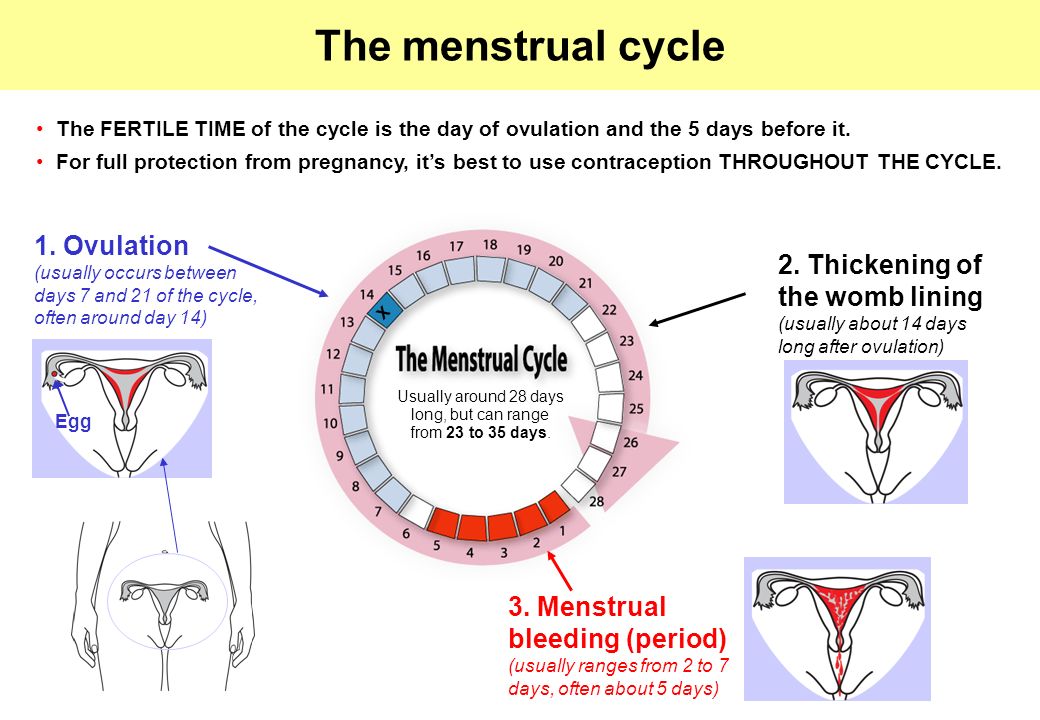
When are you supposed to ovulate
Right Time For Sex , When Do You Ovulate ?
When are you more likely to conceive?
We’re talking about the 'fertile window’ – the days in a woman’s menstrual cycle when pregnancy is possible. The ‘fertile window’ depends on the length of the menstrual cycle, which varies among women.
The ‘fertile window’ is the day an egg is released from the ovary (ovulation) and the five days beforehand. Having sex (intercourse) during this time gives you the best chance of getting pregnant.
Ovulation Calculator
What day did you your most recent period start?
Number of days in your cycle Please select20 Days21 Days22 Days23 Days24 Days25 Days26 Days27 Days28 Days29 Days30 Days31 Days32 Days33 Days34 Days35 Days36 Days37 Days38 Days39 Days40 Days41 Days42 Days43 Days44 Days45 Days
Your ovulation day
Most fertile time
-
What is an ovulation calculator and how does it help you get pregnant?
This ovulation calculator or ovulation calendar can help you work out your most fertile time.
These are the days you are most likely to get pregnant.
It can also estimate your due date if you do become pregnant during your next fertile days.
Others ways to help you work out when you're ovulating:
- Notice changes in vaginal mucus
A few days before ovulation, you may notice your vaginal mucus becomes clear, slick and slippery, and feels a bit like egg white.
This is a sign that ovulation is about to happen. It’s the best time to have sex, as sperm travel more easily in this kind of mucus.
- Use an ovulation predictor kit
You can use a predictor kit from a supermarket or pharmacy, to test your urine for signs of ovulation. If you start testing your urine a few days before the day you next expect to ovulate, a positive result means you are going to ovulate within the next 24 to 36 hours (one to two days).

-
Facts about timing
Ovulation is when a mature egg is released from the ovary. The egg then moves down the fallopian tube where it can be fertilised. If sperm are in the fallopian tube when the egg is released, there is a good chance that the egg will be fertilised, creating an embryo, which can grow into a baby.
Pregnancy is technically only possible if you have sex during the five days before ovulation or on the day of ovulation. But the most fertile days are the three days leading up to and including ovulation. Having sex during this time gives you the best chance of getting pregnant.
By 12-24 hours after ovulation, a woman is no longer able to get pregnant during that menstrual cycle because the egg is no longer in the fallopian tube.
There’s almost no chance of getting pregnant if you have sex before or after the fertile window (but if you’re not trying to get pregnant, don’t rely on this – contraception is your best option!).

-
How to know when you’re ovulating
Knowing when you ovulate can help you plan for sex at the right time and improve your chance of getting pregnant. You can keep track of your menstrual cycles on a chart, in a diary, or on a free period-tracker app on your smartphone.
To work out the length of your menstrual cycle, record the first day you start bleeding (first day of your period). This is day 1. The last day of your cycle is the day before your next period begins.
- What is a ‘menstrual cycle’ and a ‘period’?
Some people think the ‘menstrual cycle’ and a ‘period’ are the same thing.
A period is when you bleed (or menstruate).

A menstrual cycle starts on the day when a period starts (day 1) and ends the day before the next period. A cycle’s length is considered normal if it’s between 21 and 35 days. They can vary between women and from one cycle to the next.
- Working out your ‘average’ menstrual cycle length
If your menstrual cycles are different lengths (most women’s cycles are) you can work out your average cycle length.
The number of days in a woman’s menstrual cycle can vary month to month. Periods are not always regular. It can be useful to work out an ‘average’ cycle length, based on the length of three menstrual cycles, to estimate when you’re most likely to be ovulating.
If you add the number of days in three cycles and divide the total number by three, it gives you your average cycle length.
Example
Sarah tracked her last three menstrual cycles by counting the time from the first day of one period, to the day before the next period.

Cycle 1 was 28 days; Cycle 2 was 32 days; Cycle 3 was 27 days
28 + 32 + 27 = 87
87 divided by 3 = 29
So the average length of Sarah’s menstrual cycles is 29 days.
- Working out your most fertile days
When you know your average menstrual cycle length, you can work out when you ovulate.
Ovulation happens about 14 days before your period starts.
- If your average menstrual cycle is 28 days, you ovulate around day 14, and your most fertile days are days 12, 13 and 14.
- If your average menstrual cycle is 35 days ovulation happens around day 21 and your most fertile days are days 19,20 and 21.
- If you have shorter cycles, say 21 days, ovulation happens around day 7 and your most fertile days are days 5, 6 and 7.
Your most fertile days are the three days leading up to and including the day of ovulation.

Some women have very irregular cycles or find it difficult to work out an average cycle length. This can make it hard to work out when ovulation happens. If it’s all too hard, having sex every 2-3 days covers all bases and improves your chance of getting pregnant.
Myth busting
- MYTH
A woman can get pregnant any time of the month.
- FACT
A woman can only get pregnant on a few days during her menstrual cycle.
Why?
Because eggs and sperm only live for a short time:
- Sperm live for around five days.
- Eggs can only be fertilised for around 24 hours (one day) after being released from the ovary.
Eggs and sperm need to come together at the right time for fertilisation to happen to create an embryo.
Getting the timing right
If you're trying to get pregnant, timing is everything. Dr Karin Hammarberg explains how to work out when you are ovulating and the right time to have sex to improve your chance of pregnancy.
-
What are the chances?
Having sex as close as possible to the time of ovulation increases the chance of pregnancy.
If a woman has sex six or more days before she ovulates, the chance she will get pregnant is virtually zero.
If she has sex five days before she ovulates, her probability of pregnancy is about 10 percent.
If she has sex on the day of ovulation, or the two days before, the chance of getting pregnant is around 30 percent.
These are average figures and depend on a woman’s age.
When does preconception health begin?
Professor Sarah Robertson, Director of Robinson Research Institute, University of Adelaide, highlights the key time before pregnancy that your health is most important to ensure your child has the best start to life.
How to know you are ovulating
Kerry Hampton, a registered nurse and fertility specialist, discusses the importance of fertility awareness, and how to determine your fertile window to improve your chances of conceiving.
- References
- American Society for Reproductive Medicine, Optimizing natural fertility, https://www.reproductivefacts.org/news-and-publications/patient-fact-sheets-and-booklets/documents/fact-sheets-and-info-booklets/optimizing-natural-fertility/
- Berglund Scherwitzl, et al. (2015). Identification and prediction of the fertile window using Natural Cycles. The European Journal of Contraception and Reproductive Health Care, 20(5), 403-408. doi:10.3109/13625187.2014.988210
- Ecochard, R., et al. (2015). Self-identification of the clinical fertile window and the ovulation period.
 Fertility and Sterility, 103(5), 1319-1325.e1313. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.01.031
Fertility and Sterility, 103(5), 1319-1325.e1313. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.01.031 - Pfeifer, S., et al. (2017). Optimizing natural fertility: a committee opinion. Fertility and Sterility, 107(1), 52-58. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2016.09.029
- Stanford, J. B. (2015). Revisiting the fertile window. Fertility and Sterility, 103(5), 1152-1153. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.02.015
- Stanford, et al. (2002). Timing intercourse to achieve pregnancy: current evidence. Obstetrics and Gynecology, 100(6), 1333-1341.
- Stephenson, J., et al. (2018). Before the beginning: nutrition and lifestyle in the preconception period and its importance for future health. The Lancet, 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30311-8 doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30311-8
- Vélez, M. Pet al. (2015). Female exposure to phenols and phthalates and time to pregnancy: the Maternal-Infant Research on Environmental Chemicals (MIREC) Study. Fertility and Sterility.
 doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.01.005
doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.01.005 - Verón, G. L., et al. (2018). Impact of age, clinical conditions, and lifestyle on routine semen parameters and sperm kinematics. Fertility and Sterility, 110(1), 68-75.e64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2018.03.016
- Waylen, A. Let al. (2009). Effects of cigarette smoking upon clinical outcomes of assisted reproduction: a meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update, 15(1), 31-44.
- Zenzes, M. T. (2000). Smoking and reproduction: gene damage to human gametes and embryos. Hum Reprod Update, 6(2), 122-131.
Page created on: 28/08/2018 | Last updated: 17/10/2022
Calculating, Timeline, Pain & Other Symptoms
What is ovulation?
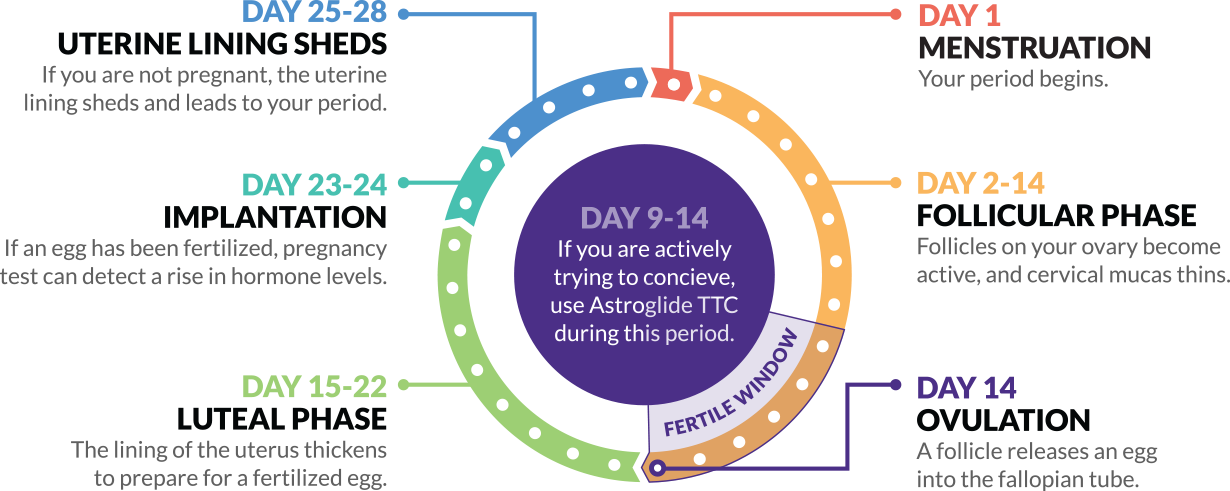
Ovulation is a phase in the menstrual cycle when your ovary releases an egg (ovum). Once an egg leaves your ovary, it travels down your fallopian tube where it waits to be fertilized by sperm. On average, it happens on day 14 of a 28-day menstrual cycle.
Ovulation and your menstrual cycle
The process of ovulation begins when your hypothalamus (a part of your brain) releases gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). GnRH causes your pituitary gland (a gland in your brain) to secrete follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH).
Between days six and 14 of your menstrual cycle, FSH causes follicles (small sacs of fluid in your ovaries that contain a developing egg) in one ovary to begin to mature. During days 10 to 14 of the cycle, only one of the developing follicles forms a fully mature egg. Around day 14 in the menstrual cycle, a sudden surge in LH causes the ovary to release this egg. This is ovulation. After ovulation, the hormone progesterone rises which helps prepare your uterus for pregnancy.
Ovulation, conception and pregnancy
Once ovulation occurs, your egg travels through your fallopian tube. It’s in your fallopian tube that your egg meets sperm for fertilization. If conception occurs (sperm fertilizes your egg), the fertilized egg travels down to your uterus. After about a week, the fertilized egg (now a blastocyst) attaches to the lining of your uterus. This is called implantation. Release of the hormones estrogen and progesterone causes the endometrium to thicken, which provides the nutrients the blastocyst needs to grow and eventually develop into a baby. As cells continue to divide — some developing into the fetus, others forming the placenta — hormones signal your body that a baby is growing inside your uterus. This also signals your uterus to keep its lining, which prevents you from getting your period. Not getting a period is usually the first sign you’re pregnant.
After about a week, the fertilized egg (now a blastocyst) attaches to the lining of your uterus. This is called implantation. Release of the hormones estrogen and progesterone causes the endometrium to thicken, which provides the nutrients the blastocyst needs to grow and eventually develop into a baby. As cells continue to divide — some developing into the fetus, others forming the placenta — hormones signal your body that a baby is growing inside your uterus. This also signals your uterus to keep its lining, which prevents you from getting your period. Not getting a period is usually the first sign you’re pregnant.
When does ovulation occur?
In an average 28-day menstrual cycle, ovulation occurs about 14 days before the beginning of your next menstrual period. The exact timing varies — your cycle length may be longer or shorter. You may find it helpful to track your menstrual cycle using an app on your phone or a calendar. This can help you determine when ovulation is most likely to occur. Most people will have a period 14 to 16 days after ovulation, regardless of the length of their overall cycle.
Most people will have a period 14 to 16 days after ovulation, regardless of the length of their overall cycle.
How many hours does ovulation last?
An egg only survives 12 to 24 hours after ovulation. If sperm doesn’t’ fertilize the egg, your body reabsorbs it. Unlike your egg, sperm can survive for several days in your body.
How do I know I’m ovulating?
Pinpointing ovulation can be tricky. There are several methods people use to track their menstrual cycle and estimate when ovulation occurs. Since each method has its drawbacks, it’s always best to use more than one for the most accurate answer.
Menstrual cycle
Ovulation happens at around the midpoint of your cycle if you have a 28-day cycle (day 14). However, a “normal” cycle is anything between 21 and 35 days, so this means ovulation is unique to your menstrual cycle. Keep track of your cycle on paper or on an app on your phone for several months. Take note of any unusual symptoms. Most people ovulate 14 days before their period begins, regardless of cycle length.
Calendar method
People using the calendar method to predict ovulation, analyze six months of menstrual cycles to determine when they’re fertile. To calculate when you may be ovulating, you find your shortest cycle and your longest cycle in a six month period. You subtract 18 days from your shortest cycle and 11 days from your longest cycle. These two numbers give you the days in your cycle you’re most fertile. For example, if your cycle lengths are 31 and 18, your fertile time is day 10 to 20 of your cycle.
Cervical mucus
Cervical mucus is a vaginal fluid produced by your cervix. Your cervical mucus goes through stages during your menstrual cycle. Your cervical mucus is thick, white and dry before ovulation. Just before ovulation, your cervical mucus turns clear and slippery (like egg whites). This consistency makes it easy for sperm to swim up to meet your egg.
Basal body temperature
Your body temperature increases slightly during ovulation (typically about 0. 5 to 1 degree). Take your temperature every morning using a digital thermometer meant specifically for measuring basal body temperature. This method only works if you take your temperature before you get out of bed and before you eat/drink. Record your results for several months and note what day of your cycle a temperature increase occurs.
5 to 1 degree). Take your temperature every morning using a digital thermometer meant specifically for measuring basal body temperature. This method only works if you take your temperature before you get out of bed and before you eat/drink. Record your results for several months and note what day of your cycle a temperature increase occurs.
Ovulation kits
Ovulation kits work similarly to at-home pregnancy tests because you pee on an indicator strip in the comfort of your own home. They work by detecting LH (luteinizing hormone) in your pee. LH is the hormone that surges before ovulation. A positive result means you’re about to ovulate (usually within 36 hours).
What are the symptoms of ovulation?
Every person is different and not everyone has signs of ovulation. In those that do, the most common symptoms are:
- Tender breasts.
- Bloating.
- Minor pelvic or abdominal pain.
- Light bleeding or spotting.
- Changes in the position and firmness of your cervix.

- Increased sex drive.
- Heightened sense of smell, taste or sight.
- Mood changes.
- Appetite changes.
How many days during ovulation can you get pregnant?
Even though your egg only lives for 24 hours, sperm can live in your uterus for between three and five days. This means you can get pregnant from having sex from about five days before ovulation to one day after ovulation. If pregnancy is your goal, it’s better to have sperm already in your body when you ovulate. The highest probability of conception occurs when intercourse takes place one to two days before ovulation and on the day of ovulation.
Is pain during ovulation normal?
Yes, many people experience ovulation pain. Ovulation pain (or mittelschmerz) is cramping or pelvic pain that happens around ovulation. You typically feel the pain in your lower abdomen and pelvis, in the middle or on one side. Ovulation pain may happen when an egg bursts from a follicle (the sacs in your ovaries that contain eggs). It can even cause light bleeding.
It can even cause light bleeding.
Pain during the time of ovulation may also be caused by a medical condition, so it’s best to contact your healthcare provider to be sure the pain isn’t something more serious.
What happens if I’m not ovulating?
Certain health conditions or life events may affect ovulation or cause you to stop ovulating. Some of these are:
- Breastfeeding (chestfeeding) or hyperprolactinemia.
- Menopause.
- PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome).
- Primary ovarian insufficiency.
- Amenorrhea from things like high or low body fat, excessive stress or fatigue or excessive exercise.
If your period is irregular or you go months without a period, you may have not be ovulating. Contact your healthcare provider if this is the case so they can rule out any serious conditions.
Do you still ovulate if you’re on birth control?
No, if you’re taking birth control pills or other hormonal contraception as directed, you shouldn’t ovulate. Keep in mind, this is only the case if you’re using pills, patches, IUDs or other devices exactly as prescribed. The hormones in birth control work by stopping ovulation and thickening cervical mucus (which makes it harder for sperm to swim).
Keep in mind, this is only the case if you’re using pills, patches, IUDs or other devices exactly as prescribed. The hormones in birth control work by stopping ovulation and thickening cervical mucus (which makes it harder for sperm to swim).
Can you ovulate but not get your period?
Yes. You can ovulate but not get your “period.” Technically, if you’re ovulating regularly, you should also get your period regularly. However, it’s possible to get your period without actually ovulating and to ovulate but not have a true period.
Can medicine help you ovulate?
Yes, there are fertility medications to induce ovulation. Talk to your healthcare provider about your symptoms and goals, such as if you wish to become pregnant. They can work with you on the best treatment based on your condition.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Ovulation is a process that occurs during your menstrual cycle. The exact timing of ovulation varies from person to person and even from cycle to cycle. Without ovulation, it’s hard for you to get pregnant or have regular menstrual periods. There are many methods available to help you predict ovulation. Knowing when you ovulate can help you either achieve a pregnancy or avoid a pregnancy. There are several health conditions that affect ovulation. Contact your healthcare provider if you’re concerned that you’re not ovulating.
Without ovulation, it’s hard for you to get pregnant or have regular menstrual periods. There are many methods available to help you predict ovulation. Knowing when you ovulate can help you either achieve a pregnancy or avoid a pregnancy. There are several health conditions that affect ovulation. Contact your healthcare provider if you’re concerned that you’re not ovulating.
| Author: http://www.jlady.ru/ |
| January 16, 2012 |
|
Everyone knows where babies come from, for this the sperm must meet with the egg. But for this meeting to take place, the most active sperm needs to “come” to the finish line first, and the egg must mature and leave the follicle. The word "ovulation" comes from the Latin "ovum", which means "egg". Ovulation is the release of a mature egg capable of fertilization from the ovarian follicle. The most important condition for pregnancy is the presence of a good mature egg, so doctors are interested in this issue in order to assess the general condition of the reproductive system. Ovulation TestsOvulation is characterized by individual signs, when a woman experiences discomfort in the lower abdomen around the middle of the menstrual cycle - this is the period of ovulation. On the same days, you can observe bloody discharge from the genital tract and an increase in sexual desire. However, for more accurate results, it is better to use one of the methods described below. Rectal (basal) temperature measurement This is one of the simplest methods that does not require any financial investments, except for the purchase of a thermometer. True, it is not perfectly accurate, since many conditions must be strictly observed here: normal and long sleep, temperature is measured in the morning at the same time, without getting out of bed. Temperature measurement takes place in the rectum. Information about the temperature is plotted on a graph, where the days of the menstrual cycle are indicated along the horizontal axis, and temperature is indicated along the vertical axis. Ovulation Test Strips This is a more accurate method for determining the level of LH (luteinizing hormone), which is one of the gonadotropins responsible for the normal functioning of the female reproductive system. Before ovulation, the level of this hormone increases significantly, thereby causing it. The pre-ovulatory peak point of LH can be guessed on certain days of the menstrual cycle in the urine, for this special test strips are used. With a constant cycle, tests should be started about 17 days before the next menstruation, since the corpus luteum phase lasts about 12-16 days. With a standard cycle of 28 days, the start of testing should be on the 11th day, and with a cycle of 35 days, it should be on the 18th day. Dynamic ultrasound and progesterone determination Ultrasound allows you to see the process of formation of a mature dominant follicle in the ovary. After the egg is released, a corpus luteum is formed in this place, which produces progesterone, which contributes to the normal development of pregnancy. By the level of this hormone, you can get effective information about ovulation. Age and ovulation If a young woman is of reproductive age, almost every menstrual cycle will be ovulatory. Moreover, the absence of ovulation in 10-15% of cycles during the year is considered the norm. The general trend can be described as follows: the older a woman becomes, the less often ovulation will occur. Over the age of 40, ovulation occurs no more than six times a year. However, it's not just the lack of ovulation. In women over 40, the likelihood of pregnancy is reduced not only due to a decrease in the number of ovulatory cycles, but also due to a decrease in egg quality. If you can't get pregnant1-1.5 years of regular sexual intercourse is considered a normal period. If, after its expiration, pregnancy does not occur in young women of reproductive age, the doctor makes a diagnosis of infertility in a married couple. After that, both spouses are recommended to be examined to clarify the possible reasons for the lack of pregnancy. Women over 35 are recommended to start examinations much earlier: if pregnancy has not occurred within six months of regular sexual activity. Such recommendations are given in order not to lose time, since with age, ovarian function and egg quality deteriorate. Factors that affect ovulation It can be any reason: environment, different diets, medications. All this can cause hormonal disruptions and, as a result, the lack of ovulation. Constant changes in time zones, long flights, changes in the usual climatic conditions - these factors are also a source of stress for the body, which can disrupt the usual rhythm of the reproductive system. Thoughtless use of drugs for weight loss, fasting often lead to persistent anovulation. A vivid example is patients with anorexia who voluntarily refuse food and bring themselves into a state of severe exhaustion. If the weight falls below the mark of 45 kg, the body clearly reacts to this and begins to inhibit the processes of the normal functioning of the reproductive system. These women stop menstruating and ovulating. Hormonal disorders can also cause disruption of the ovulation process, most of them due to genetic causes. Various conditions, such as polycystic ovary syndrome, hyperprolactinemia, thyroid dysfunction, syndromes that are accompanied by an increase in the level of male hormones, sexual differentiation disorders can cause the absence of normal ovulation. Some of these conditions are promising in terms of restoring ovulation and pregnancy, while others exclude the process of ovulation altogether. Therefore, the question of the treatment of hormonal disruptions and the choice of medicines should be decided by the doctor. Ovulation can be achieved by correcting hormonal disorders and prescribing drugs to stimulate the ovulation process. For this purpose, many means are intended: starting with tablets and ending with injectables. In the past few years, new means have appeared to stimulate the ovulation process. They contain gonadotropins, which are obtained using genetic engineering methods, this is guaranteed to exclude the presence of impurities. With the advent of such drugs, the effectiveness of the treatment of women with endocrine disorders has dramatically increased, both in order to restore the ovulation cycle, and in terms of pregnancy. How ovulation affects the sex of the baby American scientists from Harvard University David Rorvik and Lendran Shettles spent almost half a century developing a method based on planning sexual contacts relative to a known ovulation period. The method is as follows: empirically, it was found that spermatozoa with the male Y chromosome are more mobile than those that carry the X chromosome, so they can be the first to reach the egg. An interesting point is that there is a certain seasonality, which is proven by many observations.
Removal of the uterus (or hysterectomy) is a fairly common surgical operation. Indications for it can be different: uterine fibroids, various neoplasms and tumors (including postmenopausal ovarian cystomas), endometriosis. This volume of surgery is offered in the case when the preservation of the diseased organ is no longer possible, since it is accompanied by a high risk of complications (bleeding, malignancy, progression of the process) Similar operations began to be carried out about a hundred years ago, so a lot of experience has been accumulated in this field of gynecology. A large number of clinical studies have also been conducted, which allow drawing certain conclusions regarding the consequences of the operation and the quality of life of the operated patients. However, almost every woman whose doctors recommend hysterectomy is much more concerned about the consequences of the operation. Although, quite often, you need to worry more about the pathology that is an indication for surgery. How will life change? Will it be necessary to change something radically, to adapt to the work of the body, deprived of such an important organ as the uterus? How will the operation affect your sexual life, and how will you now need to build your relationship with your sexual partner? Will the operation entail changes in appearance: excess weight, rapid aging of the skin, the growth of dark hair on the face and body? If you try to answer all these questions briefly, the answer will be: "No radical changes will occur - neither in lifestyle, nor in appearance. And if you want more detailed explanations, then read on. Why do such questions arise?A stable stereotype works in the mind of a woman: No uterus - no menstruation - menopause. Climax = old age. Women are sure that the removal of the uterus will entail an artificially induced unnatural restructuring of the body, which will lead to premature aging, a decrease in libido, and the extinction of many functions. There will be problems with health and well-being, frequent mood swings, causeless fatigue - which, in turn, will affect relationships with others, especially with loved ones. Psychological problems will be superimposed on physiological problems, it will become difficult to achieve mutual understanding and trust in the family. The result is sad - early old age, loneliness, a sharp decline in the quality of life, a feeling of guilt and inferiority. In fact, this stereotype is quite easy to destroy if you understand the anatomical structure of the female body and understand the purpose of the uterus, the mechanism of menstruation and menopause. The uterus and its functions (briefly about the main things)The uterus is an organ of the female body that performs certain functions (for more details, see the section "Normal anatomy of the pelvic organs"). It is designed for the development of the embryo and the bearing of the fetus. In the process of childbirth, the uterus also takes a direct and very active part - it contracts, thereby contributing to the expulsion of the fetus. Inside the uterus, as it were, is “lined” with a mucous membrane, the endometrium. The endometrium is saturated with blood vessels, and the blood supply increases markedly by the middle of the menstrual cycle and in the second phase (medics say: "the endometrium thickens"). The body needs this so that the fertilized egg is safely fixed in the uterus and begins to develop. If fertilization does not occur, then the vessels do not receive nutrition, the upper layer of the endometrium is separated and rejected by the body. When the uterus is removed, there can be no menstruation, because there is no endometrium, the body simply has nothing to expel. However, such a state has a completely different nature than menopause. It's called "surgical menopause." What is menopauseMenopause is the extinction of ovarian function. They produce less and less sex hormones (estrogen, testosterone, progesterone), the egg does not mature in them. Estrogens (female sex hormones) are very important for the state of bone tissue and blood vessels, so their absence very often leads to problems with the musculoskeletal system and blood circulation. Reduced production of testosterone (male sex hormone) leads to a lack of sexual desire (libido). An active hormonal restructuring takes place in the body - it is this that can lead to such external changes as excess weight, skin aging, hair loss. Removal of the uterus cannot cause hormonal changes, because the ovaries will continue to function and produce sex hormones. Clinical studies prove that when the uterus is removed, the ovaries work in the same mode and during the same period that is planned, “programmed” by the body genetically. Estrogens are produced regardless of whether the uterus is removed or left, they continue to have a positive effect on bone tissue and the cardiovascular system. Testosterone is also produced, so libido does not decrease, and the quality of sexual life does not change in any way. Moreover, if you are familiar with such a condition as premenstrual syndrome (PMS), then it will continue. Because PMS is caused by the cyclic work of the ovaries. Approach to surgeryJust because the doctor thinks that it is necessary to remove the uterus, this does not mean that the adnexa (ovaries and fallopian tubes) should also be removed. The modern approach unequivocally says that the ovaries, as well as the cervix, can be left if they are healthy. The risk of developing ovarian cancer has also been shown to decrease after hysterectomy. Psychological consequences of hysterectomy
The right mental attitude is the key to your good health, quick recovery after surgery and return to your usual way of life. For a favorable psychological state, first of all, you need trust in the doctor and confidence that your body will function in the same way as it did before the operation (which is really true). A positive attitude and support from loved ones is very important. Many women attach some symbolism to the uterus, endow it with super-significance. In their minds, the uterus is, as it were, identified with the female essence. You can read above that the actual situation is different. If you attach great importance to the opinions of others and want to protect yourself from their negative psychological impact, then you do not have to dedicate them (including all close relatives, except for your husband) to the details of the operation. Sexual life after hysterectomy
Within 1-1.5 months, sexual intercourse after removal of the uterus (as well as after other operations) is prohibited. This is primarily due to the necessary time required for wound healing. When your body recovers and you realize that you can again lead a normal life, then there will be no obstacles to sexual intercourse. The sensitive zones that bring pleasure to a woman during intercourse are located not in the uterus, but in the vagina and external genitalia. Of course, the degree of trust in your relationship with your sexual partner plays a very important role here. It is possible that he will feel constrained and insecure, will try to adapt to your new state, be wary of sudden movements and experience banal fear. At the same time, his feelings will be determined solely by yours. Remember that your partner also needs reliable information. Feel free to discuss his questions and concerns with him. If necessary, contact a gynecologist for a joint consultation - perhaps your partner will treat his words with a greater degree of trust. He must be sure that your sexual desire and sensations will not undergo major changes, and you can still be a desirable and sensual woman for him. The way you were before. So you just have to weigh the pros and cons. The consequences of removing the uterus will not bring you discomfort. The choice between the state of health after the removal of a diseased organ, and your imaginary fears about changing your appearance and lifestyle, always remains with you. In the first phase of the menstrual cycle, the growth and maturation of the main follicle, which is called dominant, occurs. Ovulation is the rupture of the wall of the dominant follicle and the release of the egg.
The corpus luteum functions for 10–12 days. If conception does not occur, then the egg dies, the corpus luteum regresses, resulting in menstruation. Symptoms of ovulation
Most women ovulate completely asymptomatically, although some representatives of the weaker sex say that they can experience the onset of such days in advance. During ovulation, a woman may feel pain in the lower abdomen. They can be very pronounced. This disorder is called ovulatory syndrome. The discomfort lasts for several days. A woman's discharge may change, become more viscous.
Studies during one cycle are considered non-indicative. The duration of the menstrual cycle directly depends on the rate of maturation of the egg in its first phase, before the onset of ovulation. After the release of the egg, the second phase of the cycle (luteal) begins and in the same woman it is constant - from 12 to 16 days, but most often 14. In a long cycle, the period of egg maturation is longer than in the standard one, and ovulation occurs later. For example, if a woman has a cycle duration of 32-35 days, then the release of the egg is not in the middle of the cycle, as many people think, but on the 18-21st DC or two weeks before the start of the next menstruation. Ultrasonic folliculometrySeveral ultrasound procedures using a vaginal probe can calculate the day of ovulation or conception in a woman. A visit to the ultrasound room is carried out 3-4 times per cycle with an interval of every 2-3 days. If the cycle is irregular, the doctor will have to visit 3-4 times, starting from the 7th day after the end of menstruation - every 2-3 days. If the cycle is regular, it is worth doing an ultrasound 2-3 days before the expected day.
Ovulation TestsIf you can track the follicle using ultrasound, then ovulation tests can be done at home. They act like this: 24-36 hours before the release of the egg from the ovary in the urine, the amount of luteinizing hormone (LH) sharply increases. A day or two before that, he seems to “push out” the egg through the wall of the ovary. Ovulation tests determine if the amount of the hormone is elevated. They also allow you to calculate fertile days. 5-6 days before the expected ovulation, tests are carried out twice a day. Since we are interested in ovulation with a cycle of 30 days, measurements should be started from about day 13. If ovulation is not observed, then the second strip will be absent. But on the eve or on the 15th day, the test line will be as bright as the control line. A similar sign says that the upcoming ovulatory period is coming, which must be expected in the next 24 hours. It is necessary to lower the strip into a container with fresh urine for a few seconds, then put it on a dry surface and after about five minutes read the result.
Basal Temperature Method This method involves measuring the temperature in the rectum (rectal). It is measured immediately after sleep during the cycle. To do this, you need to use one thermometer. You need to shoot it down on the eve of sleep. Measurements are taken in the morning, immediately after waking up. The correct measurement of basal temperature will help determine whether the patient is normal, early or late ovulating. This is one of the easiest ways to determine favorable days for conception. This should be done after waking up in the morning, while you can’t get out of bed. Just woke up, and immediately for the thermometer. All results must be scrupulously noted on a special chart. At the end of the cycle, all points with measurement results are connected into a broken line. During monthly measurements are not carried out. On the first day of the cycle, the temperature reaches 36. Calendar methodThis method of determining ovulation is suitable for those who have a regular menstrual cycle. It is 14 days before the start of a new cycle that full ovulation occurs. In order to determine the calendar of days for conception, it is necessary to analyze the last 3 months. The first day of the menstrual cycle is the first day of menstruation. It is 12-14 days before the start of a new cycle that full-fledged ovulation occurs. The cycle changes under the influence of various factors - health, nervous strain, stress, physical activity, climate change when traveling, and so on. Cervical Mucus Assessment Method Before ovulation, a woman's ovaries experience a surge in estrogen production. This leads to an increase in the production of mucus by the cells of the vagina and cervix. Why doesn't ovulation occur?Ovulation may be absent for various reasons. They can be divided into 2 groups: physiological and pathological. Do not worry about the lack of ovulation in such cases:
Ovulation - reasons for absence
Early rupture of the follicle can also provoke
Not in all cases the female body works like a clock. The absence of ovulation during regular periods is called anovulation. If this phenomenon occurs no more than 2 times a year, there is no need to worry. The absence of ovulation with regular menstruation can only be judged after a long-term observation of the body (at least 3 months).
Warsaw
Krasnopresnenskaya
Annino
This question worries both those women who dream of a child and those who want to protect themselves from unwanted pregnancy. In this article, together with the Health clinic, we will analyze what ovulation is from a physiological point of view and how to detect its onset. Ovulation is the short period in a woman's menstrual cycle when conception is most possible. Ovulation lasts from 12 to 24 hours and traditionally falls in the middle of the cycle - 11-21 days - depending on its length. Only women with an impeccable menstrual cycle can calculate ovulation according to the calendar with high accuracy. It should be noted that there are few of them. Most women have to go to the gynecologist or try to determine ovulation by a set of symptoms characteristic of this period. Fortunately, we live in the 21st century, which offers us several methods for determining ovulation at once. Methods for determining ovulation1. Calendar method This method is very popular, but not very accurate. As we wrote above, using the calendar, only those women who do not have any disruptions in the menstrual cycle can determine ovulation. If, for example, your cycle from month to month is 29days, your period is right on time, and you don't have any reproductive health issues, then the calendar method might work for you. True, it is better to use it if you want to conceive a child. If not, it will be safer to use protection regardless of the day of the cycle. 2. Ovulation tests for determining ovulation are sold in any pharmacy and are now available to women in all developed countries. It is worth using such a test from the 11th day of the cycle, not earlier. 2 days before ovulation, both bands (test and control) will be bright, which indicates the onset of a favorable period for conception. However, the test shows only a peak of luteinizing hormone, which contributes to the rupture of the follicular capsule. 3. Folliculometry A modern and accurate method for determining ovulation, which is performed using . During the procedure, a special sensor is inserted into the vagina, with the help of which the doctor evaluates the condition of the follicles on each ovary. Among the follicles, at the time of ovulation, one dominant matures, and when it reaches 20 mm, the ideal moment for conception comes. It is necessary to carry out this procedure at least 3 times per cycle - on the first day after the end of menstruation, on days 11-12 and on days 24-25. During the first ultrasound, the doctor will assess the condition of the ovaries and the number of follicles, during the second ultrasound - the probability and date of ovulation, during the third ultrasound - the probability of pregnancy. In any case, a gynecologist should be consulted before the ultrasound procedure. The doctor will give precise instructions and recommendations. 4. Symptoms of ovulation Method with unspecified effectiveness, but also very popular among women. A few days before and during ovulation, a number of symptoms appear that indicate a convenient moment for conception. There are some nuances here: in some women, the symptoms appear brightly, in others - almost imperceptibly. But we will talk about them in the next part of the article. Symptoms of ovulationSo, what you should pay attention to: Basal body temperature (lowest body temperature after sleep). On the day of ovulation, it sharply decreases by about 0.5 * C, and the next day it rises sharply and continues to grow until the 23-27th day of the cycle. To calculate the exact day of ovulation, the temperature must be taken immediately after waking up daily on each day of the cycle and plotted with a curve of changes. Temperature is measured rectally, that is, by inserting a thermometer into the rectum. Changes in cervical mucus. In the period suitable for conceiving a child (4-6 days), the mucus becomes like egg white - almost transparent, watery, slippery, but at the same time dense and elastic. If you pay attention to such changes, then the probability of conception increases markedly. Swelling of the mammary glands. The breasts may become tighter and more painful, the nipples more sensitive. Increasing sexual desire. A few days before ovulation, a woman's attraction to a partner increases. Some women note that the condition of the skin and hair improves, there is greater self-confidence. Pain or unpleasant pulling sensations in the lower abdomen from the side of the ovary in which the maturation of the egg has occurred. It lasts no more than 5 days. To track all these symptoms, a woman has to make an effort and monitor the state of her body throughout the cycle for several months. Symptoms of the end of ovulationThere are also a number of symptoms that indicate that ovulation has ended:
How to accurately determine the days of ovulation?Today, only folliculometry can determine the day of ovulation and the possibility of conception with high accuracy. For the reason that ultrasound makes it possible to see and evaluate the condition of the follicles before and after ovulation. For example, in the second phase of the cycle, the follicle could degenerate into a functional cyst - this will immediately become clear on ultrasound. Sometimes ovulation simply does not occur due to various reasons - stress in a woman's life, sudden weight loss, climate change or hormonal disorders. Is it possible to get pregnant not on ovulation, but on other days of the cycle? Yes, you can. A woman's body is not a clockwork mechanism strictly in accordance with medical reference books. Sometimes ovulation occurs later than expected, sometimes earlier. You can calculate it yourself, but it is time-consuming and energy-consuming. If you are planning to conceive a baby or, conversely, want to protect yourself from an unwanted pregnancy, contact for advice. This increases the chances of success in both the first and second cases. Version of the site for the visually impaired |
When ovulation occurs after menstruation, on which day of the cycle
PreviousNext
- At what period does ovulation occur?
- Does ovulation occur every month?
- What day does ovulation occur?
- How many days does ovulation occur?
- How to know if ovulation is happening?
- When does fertilization occur after ovulation?
Contents:
Ovulation is the process of release of an egg from the follicle and normally happens regularly. Fertilization is possible exactly at the time when ovulation occurs. If a couple wants a baby and is looking forward to getting pregnant, the question of when a woman ovulates is very important.
Fertilization is possible exactly at the time when ovulation occurs. If a couple wants a baby and is looking forward to getting pregnant, the question of when a woman ovulates is very important.
When does ovulation occur?
If the reproductive system is working smoothly, a woman ovulates on average once a month. How often an egg matures depends on the characteristics of the menstrual cycle of a particular woman.
Does ovulation occur every month?
Normally, a woman can have several cycles a year without ovulating. With age, the number of anovulatory cycles increases, so after 30–35 years, the chances of a quick conception decrease. If a woman is about 40 years old, conception is possible, but to the question "how long does ovulation occur?" the likely answer would be: "In a few months." During menopause, ovulation in women stops altogether.
On what day does ovulation occur?
The menstrual cycle lasts an average of 28-32 days.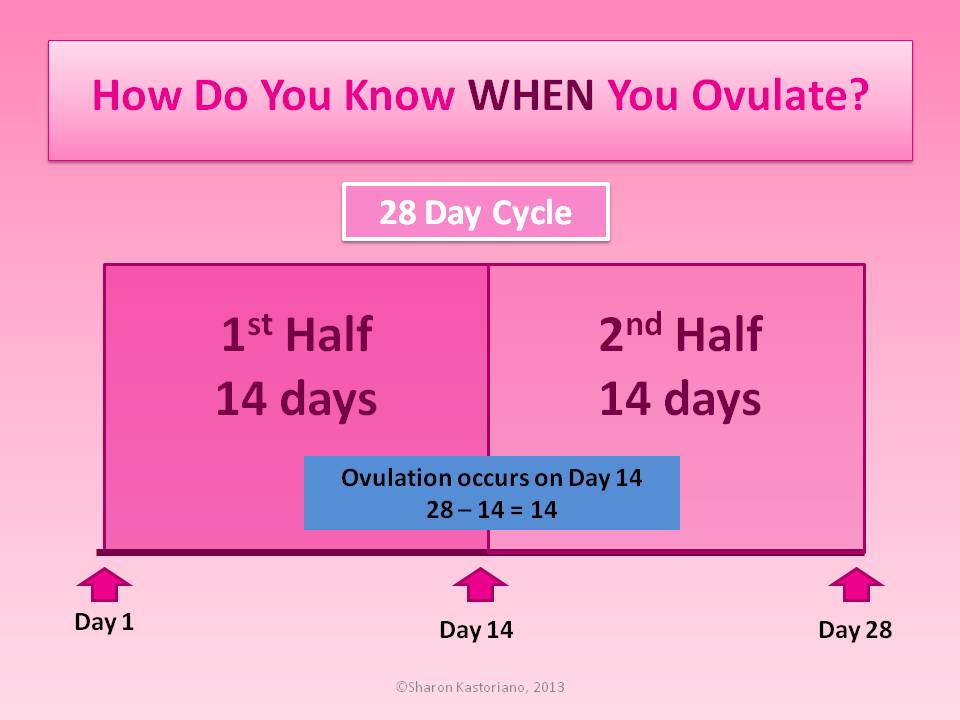 Without special studies, it is impossible to accurately answer the question of when a girl ovulates. Ovulation usually occurs in the middle of the menstrual cycle (day 12–15). For a more accurate calculation, it is necessary to plot the basal temperature over several months.
Without special studies, it is impossible to accurately answer the question of when a girl ovulates. Ovulation usually occurs in the middle of the menstrual cycle (day 12–15). For a more accurate calculation, it is necessary to plot the basal temperature over several months.
Another way to try to find out when ovulation occurs is with a calendar. To find out when ovulation occurs after menstruation, you need to count 14 days from the beginning of the last menstruation according to the calendar. With an ideal 28-day cycle, there will also be 14 days left until the next menstruation, that is, ovulation will occur exactly in the middle of the cycle. But does ovulation always occur on the 14th day?
Doctors say that the ideal classical version is not so common. Most women ovulate between day 11 and day 21 of their cycle, counting from the first day of their last period. At the same time, from 12 to 16 days remain until the next menstruation. After what time ovulation occurs, it depends on the hormonal background, and the emotional and physical state of the woman, and in different cycles ovulation may occur on different days.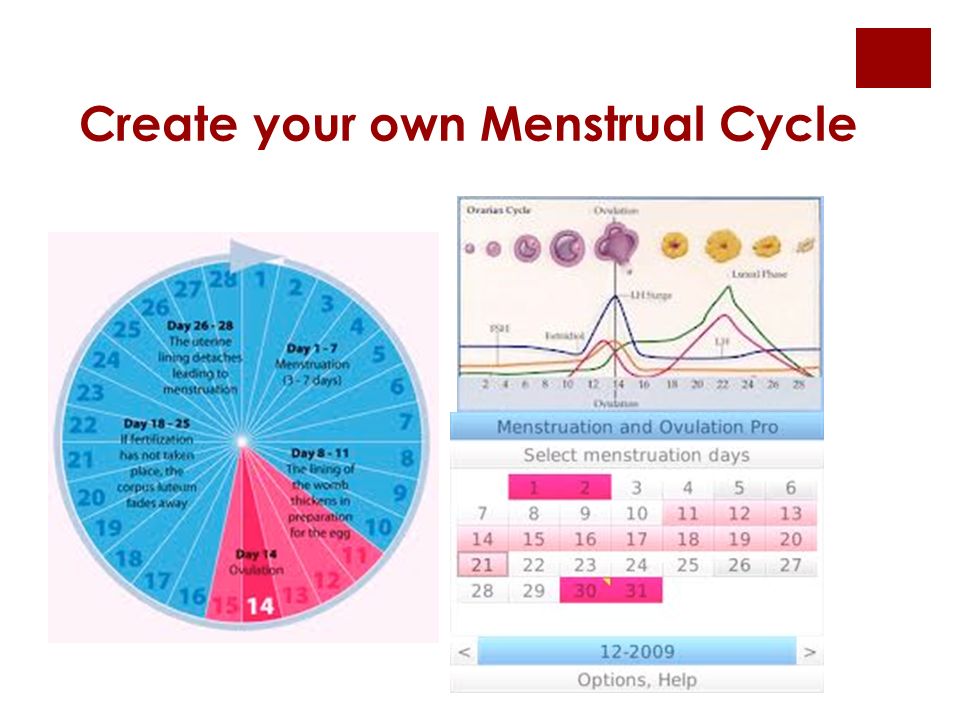 Doctors also know cases when a woman had two ovulations at once during one menstrual cycle.
Doctors also know cases when a woman had two ovulations at once during one menstrual cycle.
How many days does ovulation occur?
Ovulation is a short phase of the menstrual cycle, lasting only 48 hours. During this period of time, the egg, ready for fertilization, leaves the ovary, descends through the fallopian tube and moves towards the uterus, where it will wait for fertilization. If fertilization occurs, the egg will attach itself to the wall of the uterus.
Favorable days for pregnancy are two to three days before ovulation and one day after, and on the day of ovulation, the chances of conception are especially high. Therefore, in order to calculate favorable days, it is very important to keep an ovulation calendar and imagine how long ovulation occurs. More about this here.
A mature egg is viable for only 24 hours, so the so-called safe days come within a day after ovulation. The chance of conception after ovulation is extremely low.
How do you know if you are ovulating?
Many women think about how to find out when ovulation occurs - after all, the correct definition of this period will allow you to conceive a child faster. At home, without going to the doctor, it is convenient to use the following methods.
At home, without going to the doctor, it is convenient to use the following methods.
-
If you have regular periods, you can use the calendar method to calculate ovulation. According to him, ovulation should occur approximately in the middle of the cycle, but how to understand if ovulation occurred on the days you planned? Connect additional methods for determining ovulation!
-
To determine that ovulation has occurred, measurement of basal temperature will also help. An increase in temperature in the rectum indicates the release of an egg ready for fertilization. At what temperature ovulation occurs, you can find out by monthly charting your basal temperature. Usually, the basal temperature during ovulation differs from pre-ovulatory values by about half a degree.
-
An ovulation test is another way to determine if ovulation is occurring. Ovulation test strips are similar to pregnancy tests, only they show two strips not in case of successful fertilization, but when an egg is released from the ovary.

 Activity begins to show during puberty.
Activity begins to show during puberty. 

 Main reasons:
Main reasons: 
 Quite common causes of infertility in women are the lack of ovulation and various hormonal disruptions.
Quite common causes of infertility in women are the lack of ovulation and various hormonal disruptions.  The menstrual cycle can be considered ovulatory if the temperature difference in the first and second phases is at least 0.3 °C. The first phase is the period before ovulation, with a "classic" regular cycle of 28 days, its duration is 14 days. The second phase of the cycle is the remaining two weeks.
The menstrual cycle can be considered ovulatory if the temperature difference in the first and second phases is at least 0.3 °C. The first phase is the period before ovulation, with a "classic" regular cycle of 28 days, its duration is 14 days. The second phase of the cycle is the remaining two weeks.  Positive test results indicate that ovulation will begin in about 28-42 hours.
Positive test results indicate that ovulation will begin in about 28-42 hours.  This, in turn, affects the likelihood of pregnancy, its normal development and the quality of the embryos.
This, in turn, affects the likelihood of pregnancy, its normal development and the quality of the embryos.  However, these disturbances are usually transient.
However, these disturbances are usually transient. 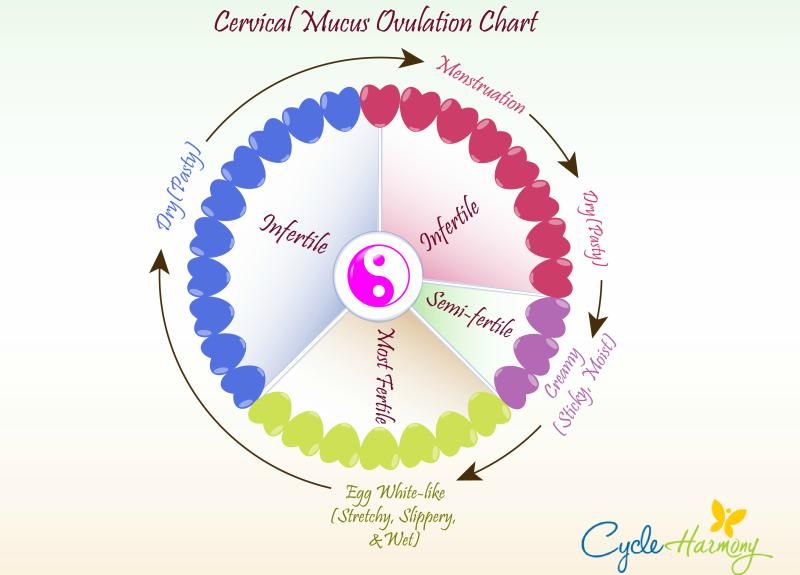
 When entering the acidic environment of the vagina, the activity of Y-spermatozoa decreases, since they quickly die there and, thereby, open the way for slower, but also more viable, X-spermatozoa. Scientists believed that X-spermatozoa can survive in the uterine environment for several days in anticipation of ovulation, unlike sperm with a Y-chromosome, which are not capable of this. As the day of ovulation approaches, the vaginal discharge becomes more alkaline, which increases the likelihood of survival of sperm with a Y chromosome. If you know exactly the day of ovulation, then you can try to increase the chances of certain spermatozoa to participate in the fertilization process, and, therefore, plan the sex of the unborn child.
When entering the acidic environment of the vagina, the activity of Y-spermatozoa decreases, since they quickly die there and, thereby, open the way for slower, but also more viable, X-spermatozoa. Scientists believed that X-spermatozoa can survive in the uterine environment for several days in anticipation of ovulation, unlike sperm with a Y-chromosome, which are not capable of this. As the day of ovulation approaches, the vaginal discharge becomes more alkaline, which increases the likelihood of survival of sperm with a Y chromosome. If you know exactly the day of ovulation, then you can try to increase the chances of certain spermatozoa to participate in the fertilization process, and, therefore, plan the sex of the unborn child.  Girls are most often born in early winter, spring, early summer, early and late autumn. Boys are most often born in the first two winter months, at the beginning and end of spring, late summer and mid-autumn. Based on these observations, you can plan the time of conception and increase the likelihood of having a child of a certain gender.
Girls are most often born in early winter, spring, early summer, early and late autumn. Boys are most often born in the first two winter months, at the beginning and end of spring, late summer and mid-autumn. Based on these observations, you can plan the time of conception and increase the likelihood of having a child of a certain gender.  The modern level of gynecology and medical equipment make it possible to perform hysterectomy using laparoscopy (in the case when the size of the uterus makes it possible), which guarantees high accuracy during the operation and a quick recovery after it.
The modern level of gynecology and medical equipment make it possible to perform hysterectomy using laparoscopy (in the case when the size of the uterus makes it possible), which guarantees high accuracy during the operation and a quick recovery after it.  "
"  We will try to help you do it!
We will try to help you do it!  Menstruation begins.
Menstruation begins. 
 Some sources cite the following statistics: the risk of developing ovarian cancer in women after a hysterectomy is 1/300, while in women with a preserved uterus - 1/80.
Some sources cite the following statistics: the risk of developing ovarian cancer in women after a hysterectomy is 1/300, while in women with a preserved uterus - 1/80.  This is the case when "a lie is for salvation." Remember that the most important thing in this case is your health. Both physical and psychological.
This is the case when "a lie is for salvation." Remember that the most important thing in this case is your health. Both physical and psychological.  He will perceive everything adequately with your positive attitude towards the situation.
He will perceive everything adequately with your positive attitude towards the situation.  It enters the fallopian tube. During the day, it can be fertilized. The dominant follicle in the 2nd phase of the cycle transforms into the corpus luteum, the main function of which is the synthesis of progesterone.
It enters the fallopian tube. During the day, it can be fertilized. The dominant follicle in the 2nd phase of the cycle transforms into the corpus luteum, the main function of which is the synthesis of progesterone.  During ovulation, her sexual desire increases. Egg maturation changes by day as follows:
During ovulation, her sexual desire increases. Egg maturation changes by day as follows:  The standard classic option is 14 days with a 28-day cycle.
The standard classic option is 14 days with a 28-day cycle.  With a 30-day cycle, ultrasound monitoring begins on the 10-11th day of the cycle, i.e., approximately 4-5 days before the middle of the monthly cycle. Subsequent sessions of ultrasonic monitoring of the egg are carried out every two days and last until the release of the egg. The onset of the ovulatory period is confirmed by ultrasound diagnostics, when the size of the follicle was 20-24 mm the day before, and now the growth of the corpus luteum has begun. The procedure can be performed through the vagina or through the abdominal wall. With an intravaginal examination, no preliminary preparation is required, the main thing is to empty the bladder. In an abdominal examination, a traditional examination is performed through the abdominal wall. In order for it to pass without difficulty, three days before the monitoring, it is necessary to exclude all products that can provoke flatulence or bloating, and on the day of the examination, you must not eat and drink at least a liter of water.
With a 30-day cycle, ultrasound monitoring begins on the 10-11th day of the cycle, i.e., approximately 4-5 days before the middle of the monthly cycle. Subsequent sessions of ultrasonic monitoring of the egg are carried out every two days and last until the release of the egg. The onset of the ovulatory period is confirmed by ultrasound diagnostics, when the size of the follicle was 20-24 mm the day before, and now the growth of the corpus luteum has begun. The procedure can be performed through the vagina or through the abdominal wall. With an intravaginal examination, no preliminary preparation is required, the main thing is to empty the bladder. In an abdominal examination, a traditional examination is performed through the abdominal wall. In order for it to pass without difficulty, three days before the monitoring, it is necessary to exclude all products that can provoke flatulence or bloating, and on the day of the examination, you must not eat and drink at least a liter of water.
 testing is carried out by analogy with tests to detect conception.
testing is carried out by analogy with tests to detect conception. 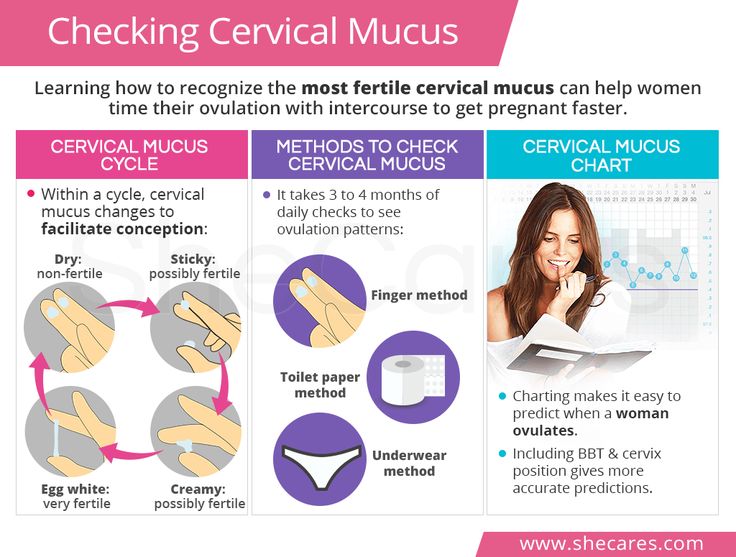 9°C A few days before ovulation, it can be 36.2 ° C - 36.4 ° C. An increase in temperature to 37°C - 37.4°C indicates that ovulation is occurring. If the temperature rises after ovulation, the woman is probably pregnant.
9°C A few days before ovulation, it can be 36.2 ° C - 36.4 ° C. An increase in temperature to 37°C - 37.4°C indicates that ovulation is occurring. If the temperature rises after ovulation, the woman is probably pregnant.  This mucus is viscous, which can be tested by stretching a small amount of it between the fingers about 2 cm.
This mucus is viscous, which can be tested by stretching a small amount of it between the fingers about 2 cm. 

 This does not guarantee 100% ovulation. Even in perfectly healthy women, the probability of conception on the day of ovulation rarely exceeds 40%. And if for some reason the dominant follicle has not matured, then the probability tends to zero.
This does not guarantee 100% ovulation. Even in perfectly healthy women, the probability of conception on the day of ovulation rarely exceeds 40%. And if for some reason the dominant follicle has not matured, then the probability tends to zero. 


 Six days before ovulation and two days after, there is a 16 to 30% chance that conception will occur. No one will give exact numbers, since each organism has its own biological rhythms. But it is worth remembering that on no single day of the menstrual cycle is the probability of conception equal to zero! Even during menstruation.
Six days before ovulation and two days after, there is a 16 to 30% chance that conception will occur. No one will give exact numbers, since each organism has its own biological rhythms. But it is worth remembering that on no single day of the menstrual cycle is the probability of conception equal to zero! Even during menstruation.